Data-driven identification of potential Zika virus vectors
Figures
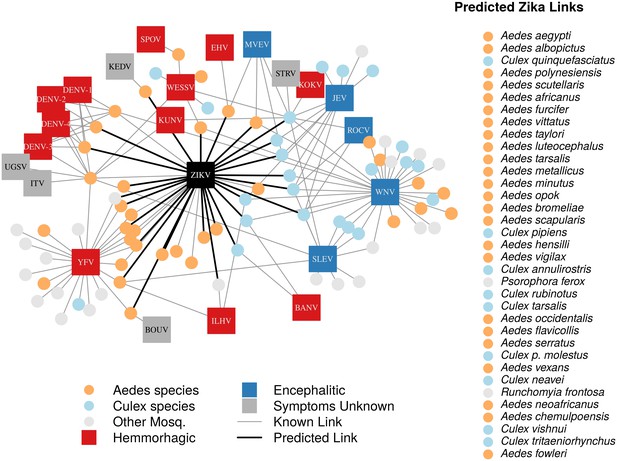
A network diagram of mosquito vectors (circles) and their flavivirus pairs (rectangles).
The Culex mosquitoes (light blue) and primarily encephalitic viruses (blue) are more clustered than the Aedes (orange) and hemmorhagic viruses (red). Notably, West Nile Virus is vectored by both Aedes and Culex species. Predicted vectors of Zika are shown by bolded links in black. The inset shows predicted vectors of Zika and species names, ordered by the model’s propensity scores. Included flaviviruses are Banzi virus (BANV), Bouboui virus (BOUV), dengue virus strains 1, 2, 3 and 4 (DENV-1,2,3,4), Edge Hill virus (EHV), Ilheus virus (ILHV), Israel turkey meningoencephalomyelitis virus (ITV), Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV), Kedougou virus (KEDV), Kokobera virus (KOKV), Kunjin virus (KUNV), Murray Valley encephalitis virus (MVEV), Rocio virus (ROCV), St. Louis encephalitis virus (SLEV), Spondwendi virus (SPOV), Stratford virus (STRV), Uganda S virus (UGSV), Wesselsbron virus (WESSV), West Nile Virus (WNV), yellow fever virus (YFV), and Zika virus (ZIKV).
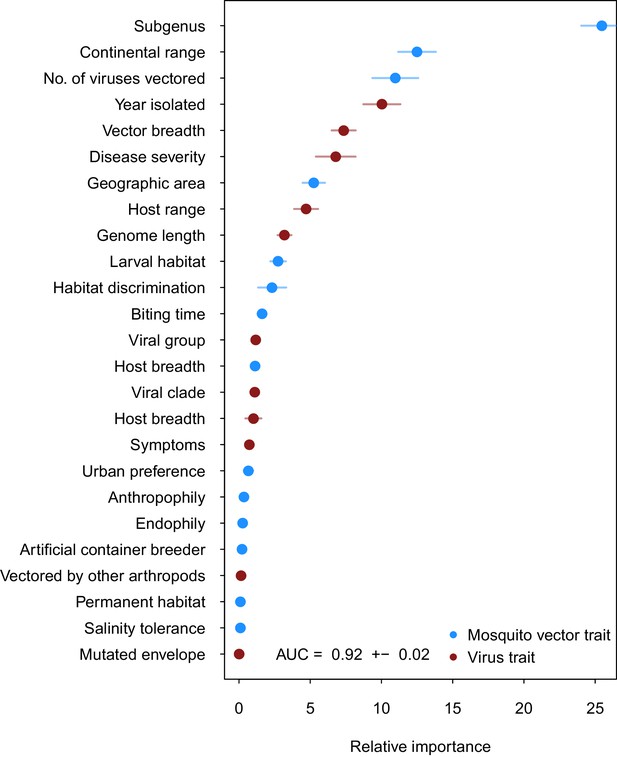
Variable importance by permutation, averaged over 25 models.
Because some categorical variables were treated as binary by our model (i.e. continental range), the relative importance of each binary variable was summed to result in the overall importance of the categorical variable. Mosquito and virus traits are shown in blue and maroon, respectively. Error bars represent the standard error from 25 models.
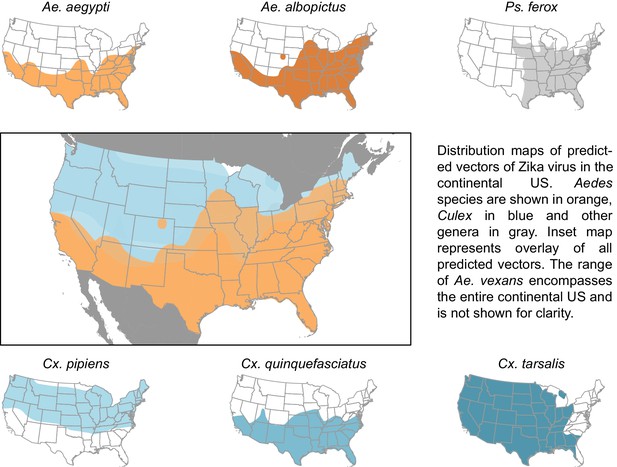
Distribution maps of predicted vectors of Zika virus in the continental US.
Maps of Aedes species are based on Centers for disease control and prevention (2016). All other species’ distributions are georectified maps from Darsie and Ward (2005).
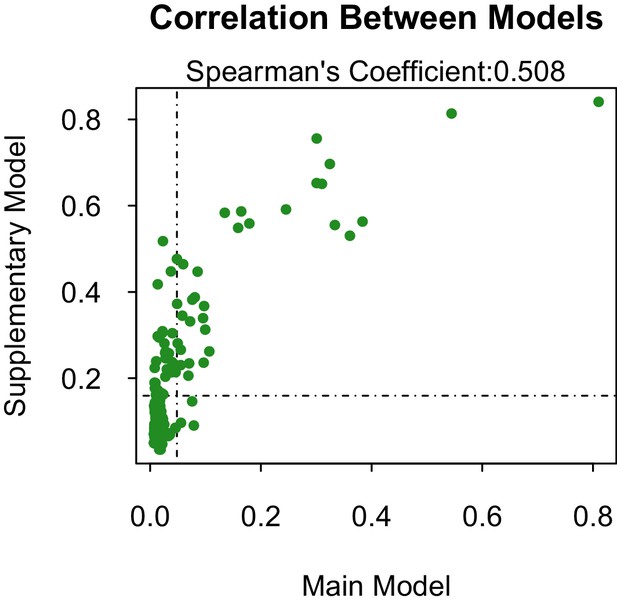
Propensity values of the main and supplementary models.
Dashed lines represent corresponding threshold values for each model based on lowest ranked known vector propensities.
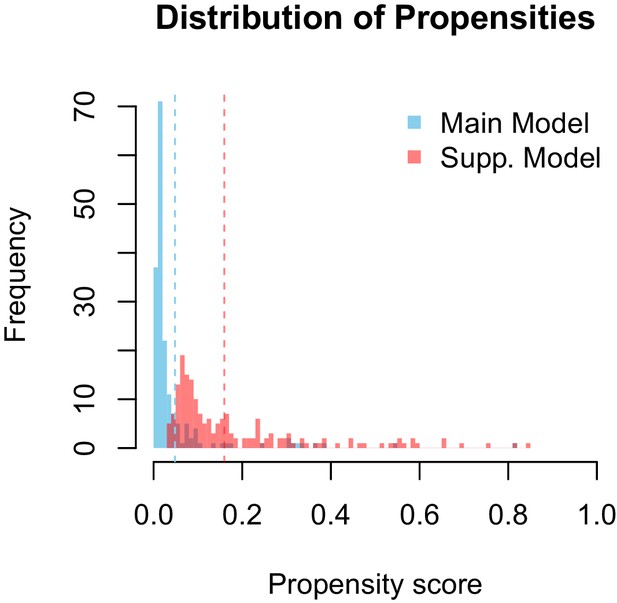
Distribution of propensity values for the main and supplementary models.
Dashed lines represent corresponding threshold values for each model based on lowest ranked known vector propensities.
Tables
Predicted vectors of Zika virus, as reported by our model. Mosquito species endemic to the continental United States are bolded. A species is defined as a known vector of Zika virus if a full transmission cycle (see main text) has been observed.
| Species | GBM prediction SD | Known vector? |
|---|---|---|
| Aedes aegypti | 0.81 ± 0.12 | Yes |
| Ae. albopictus | 0.54 ± 0.14 | Yes |
| Culex quinquefasciatus | 0.38 ± 0.14 | No |
| Ae. polynesiensis | 0.36 ± 0.13 | No |
| Ae. scutellaris | 0.33 ± 0.13 | No |
| Ae. africanus | 0.32 ± 0.11 | No |
| Ae. furcifer | 0.31 ± 0.16 | Yes |
| Ae. vittatus | 0.30 ± 0.20 | Yes |
| Ae. taylori | 0.30 ± 0.16 | Yes |
| Ae. luteocephalus | 0.25 ± 0.12 | Yes |
| Ae. tarsalis | 0.18 ± 0.11 | Yes |
| Ae. metallicus | 0.16 ± 0.08 | No |
| Ae. minutus | 0.16 ±0.09 | No |
| Ae. opok | 0.14 ± 0.06 | No |
| Ae. bromeliae | 0.11 ± 0.06 | No |
| Ae. scapularis | 0.10 ± 0.04 | No |
| Cx. pipiens | 0.10 ± 0.04 | No |
| Ae. hensilli | 0.10 ± 0.06 | Yes |
| Ae. vigilax | 0.10 ± 0.05 | No |
| Cx. annulirostrix | 0.08 ± 0.03 | No |
| Psorophora ferox | 0.08 ± 0.05 | No |
| Cx. rubinotus | 0.08 ± 0.07 | No |
| Cx. tarsalis | 0.08 ± 0.03 | No |
| Ae. occidentalis | 0.08 ± 0.05 | No |
| Ae. flavicolis | 0.07 ± 0.04 | No |
| Ae. serratus | 0.07 ± 0.04 | No |
| Cx. p. molestus | 0.07 ± 0.04 | No |
| Ae. vexans | 0.06 ± 0.04 | No |
| Cx. neavei | 0.06 ± 0.02 | No |
| Runchomyia frontosa | 0.06 ± 0.04 | No |
| Ae. neoafricanus | 0.06 ± 0.03 | No |
| Ae. chemulpoensis | 0.06 ± 0.03 | No |
| Cx. vishnui | 0.05 ± 0.01 | No |
| Cx. tritaeniorhynchus | 0.05 ± 0.01 | No |
| Ae. fowleri | 0.04 ± 0.03 | Yes |
Vector predictions by the supplementary model.
| Vector | GBM Prediction | SD |
|---|---|---|
| Aedes aegypti | 0.84 | 0.06 |
| Aedes albopictus | 0.81 | 0.07 |
| Aedes vittatus | 0.76 | 0.10 |
| Aedes africanus | 0.70 | 0.11 |
| Aedes taylori | 0.65 | 0.14 |
| Aedes furcifer | 0.65 | 0.14 |
| Aedes luteocephalus | 0.59 | 0.12 |
| Aedes metallicus | 0.59 | 0.13 |
| Aedes opok | 0.58 | 0.13 |
| Culex quinquefasciatus | 0.56 | 0.13 |
| Aedes tarsalis | 0.56 | 0.12 |
| Aedes scutellaris | 0.56 | 0.11 |
| Aedes minutus | 0.55 | 0.12 |
| Aedes polynesiensis | 0.53 | 0.11 |
| Mansonia uniformis | 0.52 | 0.12 |
| Aedes fowleri | 0.48 | 0.14 |
| Aedes vexans | 0.46 | 0.11 |
| Aedes dalzieli | 0.45 | 0.13 |
| Culex annulirostris | 0.45 | 0.08 |
| Mansonia africana | 0.42 | 0.12 |
| Psorophora ferox | 0.39 | 0.14 |
| Culex tarsalis | 0.38 | 0.09 |
| Culex tritaeniorhynchus | 0.37 | 0.08 |
| Culex pipiens | 0.37 | 0.13 |
| Culex neavei | 0.34 | 0.06 |
| Aedes vigilax | 0.34 | 0.07 |
| Aedes flavicollis | 0.33 | 0.14 |
| Aedes scapularis | 0.31 | 0.07 |
| Aedes taeniarostris | 0.31 | 0.13 |
| Aedes jamoti | 0.31 | 0.13 |
| Aedes circumluteolus | 0.30 | 0.13 |
| Eretmapodites inornatus | 0.30 | 0.15 |
| Aedes cumminsii | 0.29 | 0.11 |
| Culex vishnui | 0.28 | 0.05 |
| Aedes lineatopennis | 0.28 | 0.11 |
| Aedes neoafricanus | 0.27 | 0.11 |
| Aedes bromeliae | 0.26 | 0.10 |
| Culex guiarti | 0.26 | 0.06 |
| Culex perfuscus | 0.26 | 0.06 |
| Aedes stokesi | 0.26 | 0.12 |
| Culex telesilla | 0.25 | 0.06 |
| Anopheles gambiae | 0.24 | 0.11 |
| Sabethes chloropterus | 0.24 | 0.11 |
| Aedes hensilli | 0.24 | 0.09 |
| Aedes serratus | 0.23 | 0.06 |
| Aedes chemulpoensis | 0.23 | 0.08 |
| Aedes normanensis | 0.23 | 0.06 |
| Culex bitaeniorhynchus | 0.22 | 0.09 |
| Culex pseudovishnui | 0.22 | 0.05 |
| Aedes argenteopunctatus | 0.21 | 0.06 |
| Wyeomyia vanduzeei | 0.21 | 0.15 |
| Culex p. molestus | 0.21 | 0.06 |
| Culex salinarius | 0.20 | 0.04 |
| Aedes grahami | 0.19 | 0.15 |
| Anopheles coustani | 0.19 | 0.08 |
| Aedes longipalpis | 0.18 | 0.18 |
| Uranotaenia sapphirina | 0.17 | 0.08 |
| Aedes domesticus | 0.17 | 0.06 |
| Aedes abnormalis | 0.17 | 0.06 |
| Aedes natronius | 0.17 | 0.06 |
| Eretmapodites chrysogaster | 0.17 | 0.08 |
| Aedes mcintoshi | 0.17 | 0.06 |
| Aedes ochraceus | 0.16 | 0.06 |
| Culex fatigans | 0.16 | 0.07 |
| Anopheles amictus | 0.16 | 0.06 |
| Eretmapodites quinquevittatus | 0.16 | 0.08 |
Table of mosquito traits used in model.
| Trait | Type | Subcategories |
|---|---|---|
| Anthropophily | binary | NA |
| Subgenus | factor | NA |
| Host breadth | numeric | NA |
| Host range | binary (x4) | Primate, Non-Primate Mammal, Bird, Cold-Blooded Vertebrate |
| Geographic area | numeric | NA |
| Continental range | binary (x8) | Africa, Middle East, Australia, Pacific, Asia, Europe, North America, South America |
| Biting time | binary (x4) | Dawn, Day, Dusk, Night |
| Artificia container breeder | binary | NA |
| Oviposition site | binary (x8) | Treehole, Natural Container, Permanent Fresh Water, Rockhole, Marsh, Swamp, Temporary Ground Pools, Rice Paddy |
| Habitat discrimination | numeric | NA |
| Salinity tolerance | binary | NA |
| Habitat permanence | binary | NA |
| Urban preference | binary | NA |
| Endophily | binary | NA |
| No. of flaviviruses vectored | numeric | NA |
Table of virus traits used in model.
| Trait | Type | Subcategories |
|---|---|---|
| Group | factor | Japanese Encephalitis, Ntaya, Yellow Fever, Aroa, Dengue, Kokobera, Spondweni |
| Continental range | binary(x8) | Africa, Middle East, Australia, Pacific, Asia, Europe, North America, South America |
| Clade | factor | VI, VII, IX, X, XI, XII, XIV, |
| Year isolated | numeric | NA |
| Mutated envelope | binary | NA |
| Host breadth | numeric | NA |
| Host Range | binary(x6) | Human, Non-Human Primate, Rodent, Other Mammal, Bird, Marsupial |
| Mosquito vector breadth | numeric | NA |
| Vectored by other arthropods | binary | NA |
| Disease symptoms | binary (x2) | Encephalitis, Fever |
| Disease severity | numeric | NA |
| Genome length | numeric | NA |
Primary sources for mosquito traits.
Primary sources for virus traits.





