Insights into the molecular architecture and histone H3-H4 deposition mechanism of yeast Chromatin assembly factor 1
Figures
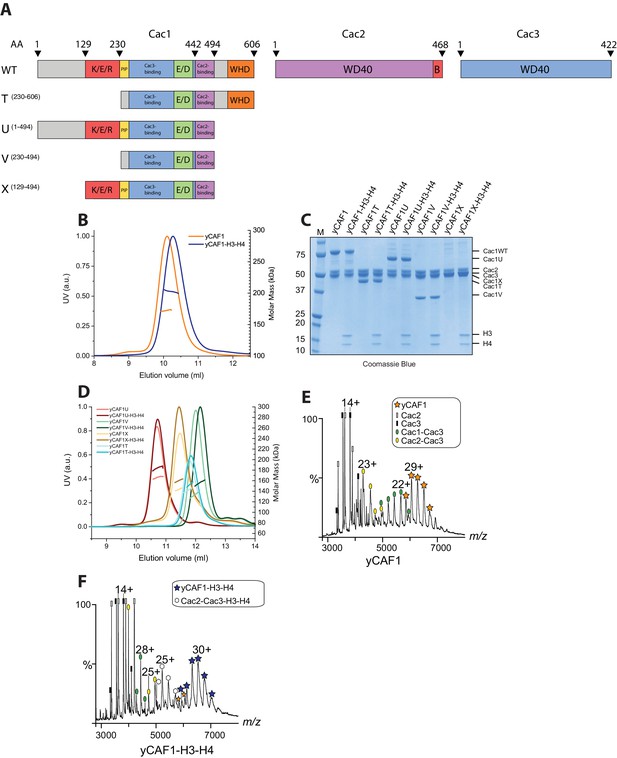
Domain architecture and purification of yCAF1.
(A) Domain architecture of Cac1, Cac2 and Cac3 with K/E/R domain containing a predicted coiled-coil segment; PIP, PCNA interacting peptide; E/D, acidic domain; WHD, winged helix domain; WD40-repeat β-propeller domain; B, Asf1 interaction domain. Constructs used are shown below. yCAF1T and yCAF1V are missing the first two residues of the PIP motif (227-Q-x-x-I-x-x-F-F-234) in Cac1 (B) Determination of the apparent molecular mass of yCAF1 ± H3-H4 using SEC-MALLS. Lines correspond to the UV280nm traces of yCAF1 (red) or yCAF1–H3-H4 (blue) eluting from the SEC column. Dots correspond to the molar mass determined for yCAF1 or yCAF1 –H3-H4. (C) SDS-PAGE analysis of purified yCAF1 constructs ± H3-H4. (D) Determination of the apparent molecular mass of yCAF1 mutants ± H3-H4 using SEC-MALLS. The UV280nm traces are shown as lines and the molar mass measurements as dots. (E) Native mass spectra of yCAF1 in (E) the absence or (F) the presence of H3-H4. The yCAF1 (★), yCAF1-H3-H4 (★) and the subcomplexes are labeled.
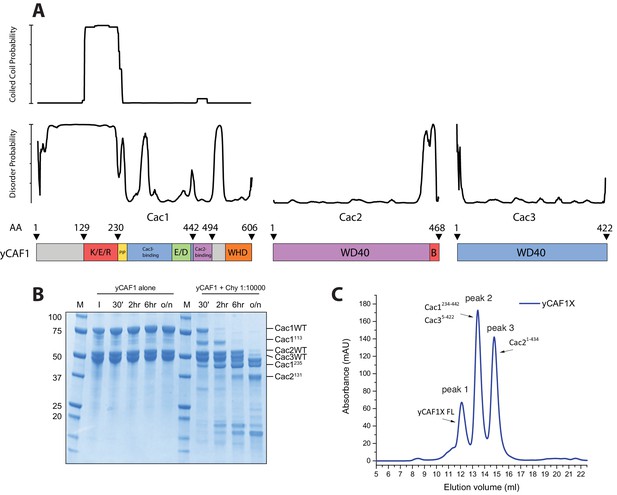
Structural and biochemical characterization of yCAF1 complexes.
(A) Coiled-coil and disorder probability as determined by COILS and Disopred3, respectively. Domain arrangements of Cac1, Cac2 and Cac3 are shown below. (B) Limited proteolysis using chymotrypsin digestion revealed stable yCAF1 fragments. Left half of gel: yCAF1 control without protease; I, input. Identity of these fragments was determined by LC/MS. (C) Limited proteolysis of yCAF1X followed by SEC analysis. The resulting peaks were analyzed by LC/MS. Peak two contained a complex of Cac1234-442 and Cac35-422 indicating that these fragments interact directly. Peak three contained Cac21-434. (D) Tandem MS spectrum of the 32+ ion of yCAF1-H3-H4. The 32+ ion population of yCAF1-H3-H4 was subjected to collision-induced dissociation (CID). This experiment broke the complex into subcomplexes (yCAF1-H3, yCAF1-H4, Cac1-Cac3-H3-H4, Cac1-Cac2-H3-H4) and monomers (H3, H4, Cac2 and Cac3) and confirms the 1:1:1:1:1 stoichiometry of the yCAF1-H3-H4 complex. (E) Native MS analysis of yCAF1-H3-H4 complexes with an excess of H3-H4. The yCAF1 (at a concentration of 4.6 μM) was incubated with 1.5 time molar excess of H3-H4 for 30 min at 4°C and then analyzed by native MS. The peaks at high m/z range showed that the yCAF1 was bound to a single copy of H3-H4 (201 kDa). At low m/z range, signal for the tetrameric (H3–H4)2 was detected (53 kDa) in close proximity to the peaks belonging to Cac2 (53 kDa). (F) Native MS analysis of H3-H4 preparations.
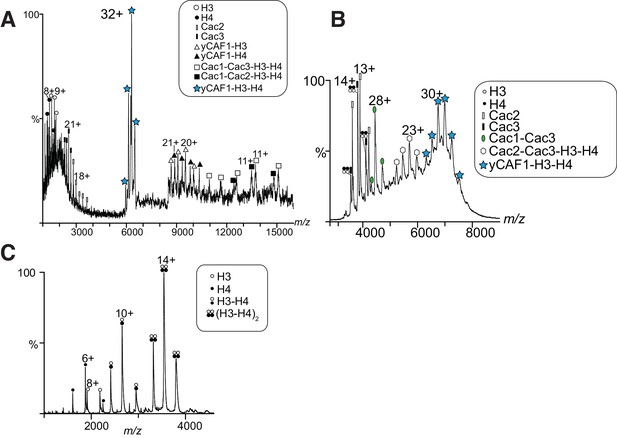
MS analysis of yCAF1-H3-H4 and H3-H4.
(A) Tandem MS spectrum of the 32+ ion of yCAF1-H3-H4. The 32+ ion population of yCAF1-H3-H4 was subjected to collision-induced dissociation (CID). This experiment broke the complex into subcomplexes (yCAF1-H3, yCAF1-H4, Cac1-Cac3-H3-H4, Cac1-Cac2-H3-H4) and monomers (H3, H4, Cac2 and Cac3) and confirms the 1:1:1:1:1 stoichiometry of the yCAF1-H3-H4 complex. (B) Native MS analysis of yCAF1-H3-H4 complexes with an excess of H3-H4. The yCAF1 (at a concentration of 4.6 μM) was incubated with 1.5 time molar excess of H3-H4 for 30 min at 4°C and then analyzed by native MS. The peaks at high m/z range showed that the yCAF1 was bound to a single copy of H3-H4 (201 kDa). At low m/z range, signal for the tetrameric (H3–H4)2 was detected (53 kDa) in close proximity to the peaks belonging to Cac2 (53 kDa). (C) Native MS analysis of H3-H4 preparations.
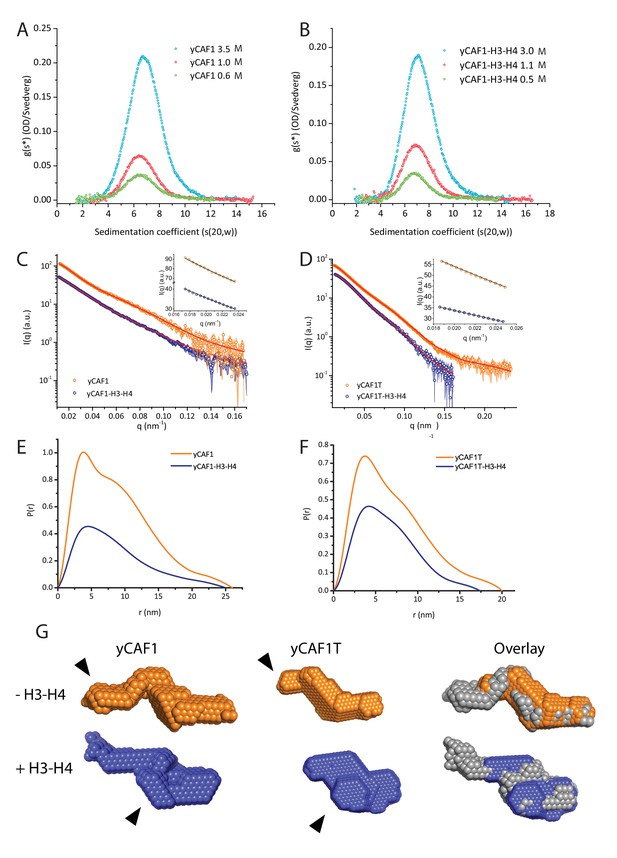
yCAF1 binds a single H3-H4 heterodimer.
(A) Sedimentation velocity analytical ultracentrifugation of the yCAF1 complex. (B) yCAF1-H3-H4. Shown is the plot of the sedimentation coefficient distribution at different protein concentrations. (C) The experimental SAXS profile (log intensity (I) as a function of the momentum transfer (q)). Dots with error bars are the experimental scattering data. yCAF1 ± H3-H4 (blue or orange respectively). The normalized fit to the experimental data is superimposed as a black line. Inset: Guinier plot (log I vs. (q2) of the low q region of the X-ray scattering data (D) yCAF1T ± H3-H4 (blue or orange, respectively). Bottom panels: Normalized interatomic distance distribution functions. (E) The p(r) distribution plot for yCAF1 alone (blue) and bound to H3-H4 (orange). (F) The p(r) distribution plot for yCAF1T alone (blue) and bound to H3-H4 (orange). (G) Average DAMMIN bead models. Left: yCAF1 (orange) and yCAF1-H3-H4 (blue). Middle: yCAF1T (orange) and yCAF1T-H3-H4 (blue). Right: Superposition of yCAF1 (grey) onto yCAF1T (orange) and yCAF1-H3-H4 (grey) onto yCAF1T-H3-H4 (blue). Arrows indicate the N-terminal extension of Cac1 and the possible positioning of H3-H4.
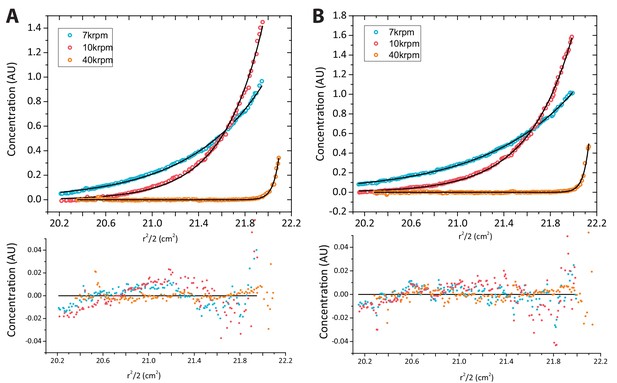
Analytical ultracentrifugation of yCAF1 complexes.
(A) Sedimentation equilibrium analytical ultracentrifugation of yCAF1. Shown is the plot of the concentration of 3.2 μM yCAF1 as a function of the radial distance after reaching equilibrium at 7.000 (blue), 10.000 (red) and 40.000 (orange) rpm. Solid black lines are derived from a global fit of all datasets to a model describing an ideal non-interacting single-component system. Bottom panel: Random scatter in the residuals indicates that this model describes the data well. (B) Plot as described above for yCAF1-H3-H4 at a concentration of 3.1 μM.
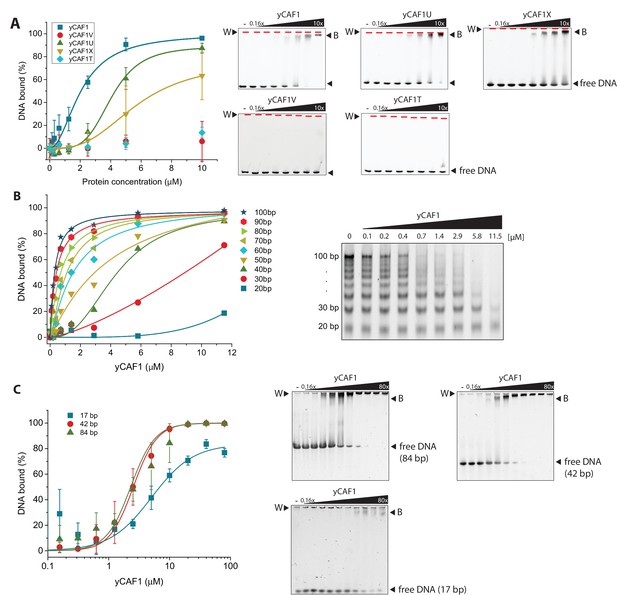
yCAF1 binding to DNA.
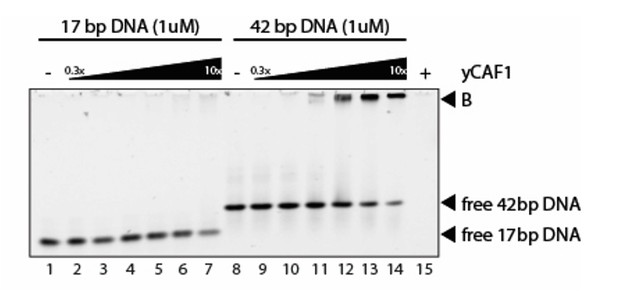
(A) Left panel: Binding curves of yCAF1 variants to 147 bp DNA. Right panels: EMSA showing binding of yCAF1 variants to 147 bp DNA. Free DNA and yCAF1-bound (B) DNA are indicated. Wells (W) are indicated additionally with red horizontal bars. Increasing amounts of yCAF1 (0.15, 0.3, 0.61, 1.25, 2.5, 5 or 10 μM) were mixed with 1 μM DNA. Error bars represent SEM values of three technical replicates (B) Left panel: binding curves of yCAF1 binding to DNA fragments of 20–100 bp (Sequence information in Table 5). Right panel: EMSA showing yCAF1 binding to free DNA fragments of 20–100 bp. Concentration of the DNA 10–100 bp ladder was 275 nM overall nucleotide base pairs present in the binding reaction. yCAF1- DNA binding was quantified by measuring DNA substrate depletion. (C) Left panel: Binding curves of yCAF1 to 17 bp, 42 bp and 84 bp DNA. Right panels: EMSA showing binding of yCAF1 to 17 bp, 42 bp and 84 bp DNA. Wells (W), free DNA and yCAF1-bound (B) DNA are indicated. Increasing amounts of yCAF1 (0.15, 0.3, 0.61, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10, 20, 40 or 80 μM) were mixed with 1 μM DNA. Error bars represent SEM values of three technical replicates.
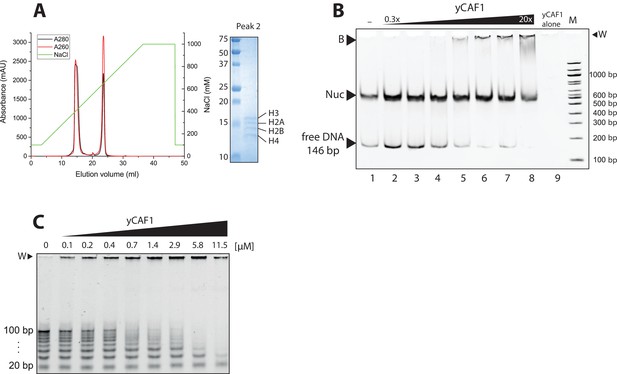
Analysis of nucleosome binding by yCAF1.
(A) Anion exchange chromatography of yCAF1 (first peak) revealing a histone-DNA contaminant in the yCAF1 preparation from Trichoplusia ni insect cells (second peak). The identity of all four Trichoplusia ni histones was confirmed by SDS-PAGE and LC-MS. (B) EMSA showing that yCAF1 does not bind to nucleosomes but to free DNA. Increasing amounts of yCAF1 (0.3 μM to 20 μM in two fold steps) were mixed with 2 μM nucleosome. Free DNA, nucleosomes (Nuc), and DNA-bound yCAF1 (B) are indicated. Lane one contained no yCAF1 (-) and lane nine contained yCAF1 but no nucleosome. (C) Uncropped gel image of Figure 3B - EMSA showing yCAF1 binding to free DNA fragments of 20–100 bp.
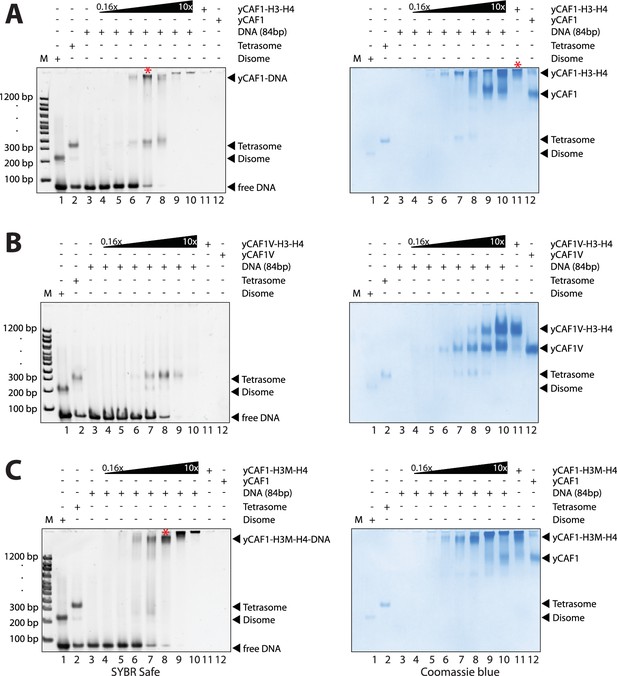
yCAF1 deposition of H3-H4.
(A) EMSA showing tetrasome deposition on 84 bp DNA. Increasing amounts of yCAF1-H3-H4 (0.15, 0.3, 0.61, 1.25, 2.5, 5 or 10 μM) were mixed with 1 μM 84 bp DNA and the bands resolved by native PAGE. Gels were stained for DNA with SYBR Safe (left panel) and for protein with Coomassie (right panel). (B) As above but for yCAF1V-H3-H4. (C) As above but for yCAF1-H3M-H4 (H3M contains the L126R/I130R mutation). * indicates extracted gel bands that we analyzed by SDS-PAGE (Figure 4—figure supplement 2D). All EMSA experiments were repeated at least two times with consistency.
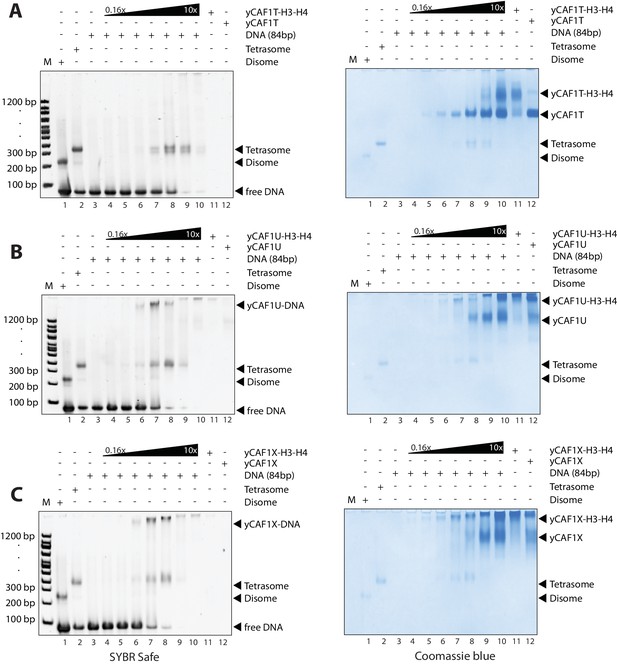
EMSA analysis of H3-H4 deposition.
(A) EMSA showing H3-H4 deposition by yCAF1T. (B) yCAF1U. (C) yCAF1X.
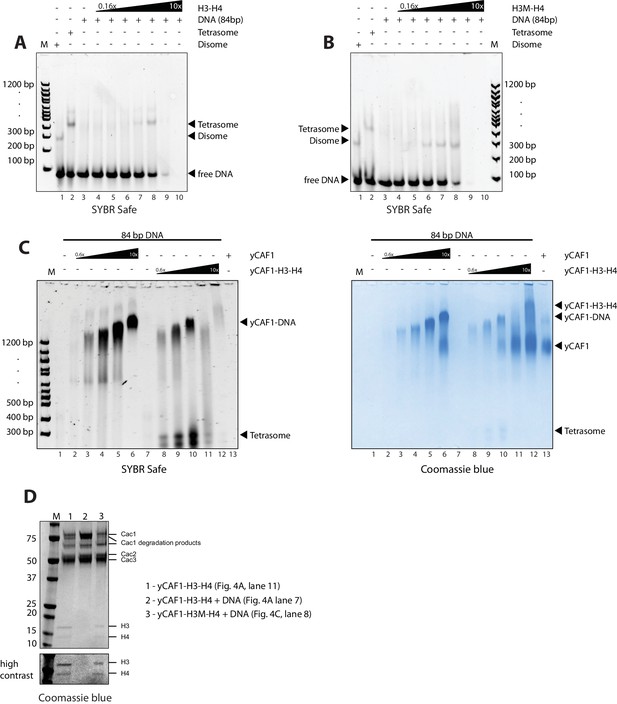
EMSA analysis of H3-H4 deposition.
(A) EMSA showing tetrasome and (B) disome assembly controls. The position of migration of the dimsome, tetrasome and free DNA are indicated. The gels were stained with SYBR Safe or Coomassie stain as indicated. Increasing amounts of yCAF1-H3-H4 (0.2 μM to 10 μM in two fold steps) were mixed with 1 μM 84 bp DNA. (C) EMSA showing that yCAF1 binding to the 84 base pair DNA substrate migrates at the same position as yCAF1 that has released its H3-H4 cargo and subsequently bound to excess free DNA. All EMSA experiments were repeated at least two times with consistency. (D) Bands indicated by * in Figure 4A,C were extracted from the native PAGE gel and analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie blue staining. The bottom panel shows a high contrast rendering of the bottom part of the SDS-PAGE gel.
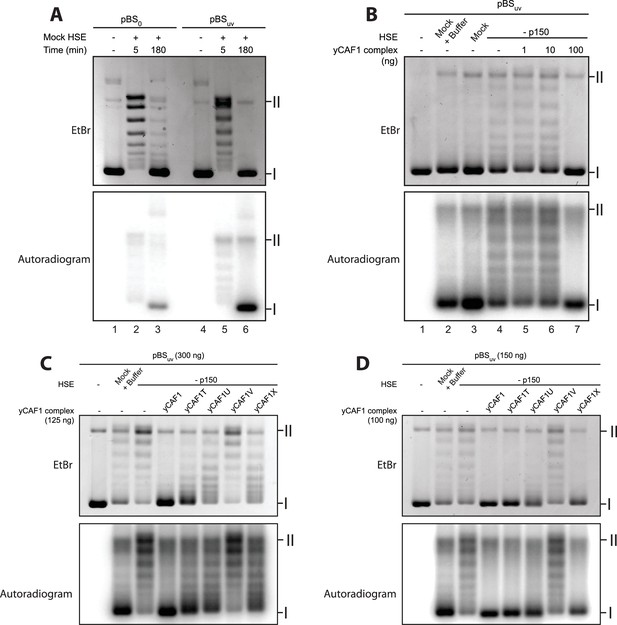
DNA-binding of yCAF1 is required for DNA synthesis-coupled nucleosome assembly.
(A) Nucleosome assembly reactions with either non-UV-treated plasmid (pBS0) or plasmid irradiated with UV (pBSuv) in presence of [α−32P]. After an incubation time of 5 or 180 min, DNA was extracted, resolved on an agarose gel and visualized by ethidium bromide staining (EtBr) or by autoradiography (Autradiogram). (B) 150 ng of pBSuv plasmid was incubated with p150-depleted HSE extracts and complemented with the indicated amounts of yCAF1. After 3 hr incubation, DNA was extracted, resolved on and agarose gel and visualized as above. (C) As in (B) but reactions were complemented with 125 ng of the different yCAF1 variants and the amount of pBSuv plasmid was increased to 300 ng (D) As in (B) but reactions were complemented with 100 ng of the different yCAF1 variants. (I) Supercoiled and (II) relaxed plasmid. All reactions were repeated two times with consistency.
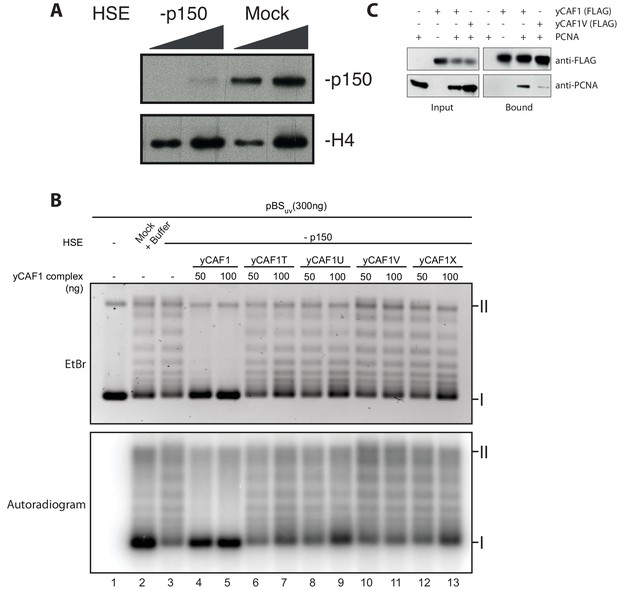
Depletion of Xenopus p150 from HSE.
(A) p150- or mock-depleted HSEs were analyzed by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. (B) Nucleosome assembly reactions with 300 ng of pBSuv plasmid and 50 or 100 ng of yCAF1 variants showing that none of the yCAF1 mutants reach wild-type level activity. (C) Western blot of a FLAG pulldown of yeast PCNA with FLAG tagged yCAF1 WT or yCAF1V to investigate the effect of the N-terminal mutant on PCNA binding.
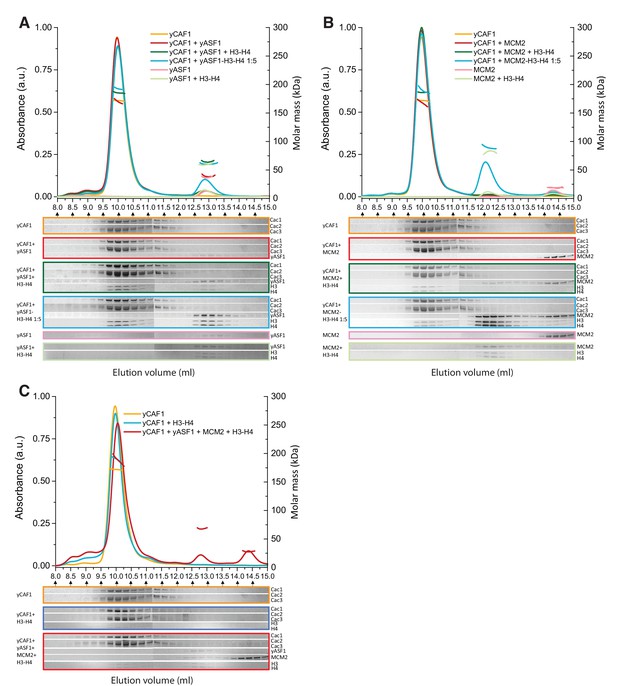
Competition of yCAF1 with yAsf1 or Mcm2 for H3-H4 binding.
SEC-MALLS analysis of complexes formed upon mixing of up to three histone chaperones with H3-H4. In all experiments, lines correspond to the UV280nm traces of the eluting complex. Dots correspond to the molar mass measurements. Eluting fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and the relevant areas of the gels are displayed below each chromatogram using the corresponding color code. When there are two or more proteins in the mixture, the ‘+' in the labeling indicates the order in which the samples were mixed together (eg. yCAF1 + yAsf1 +H3-H4 indicates that yAsf1 was added to yCAF1 followed by addition of H3-H4). The final protein concentration used was 20 µM for all proteins except where preformed yAsf1-H3-H4 and Mcm2-H3-H4 were supplied in 5-fold molar excess to yCAF1 (blue lines in A and B). (A) H3-H4 competition experiments of yCAF1 with yAsf1. (B) H3-H4 competition experiments of yCAF1 with Mcm2. (C) H3-H4 competition experiments of yCAF1 in the presence of yAsf1 and Mcm2.
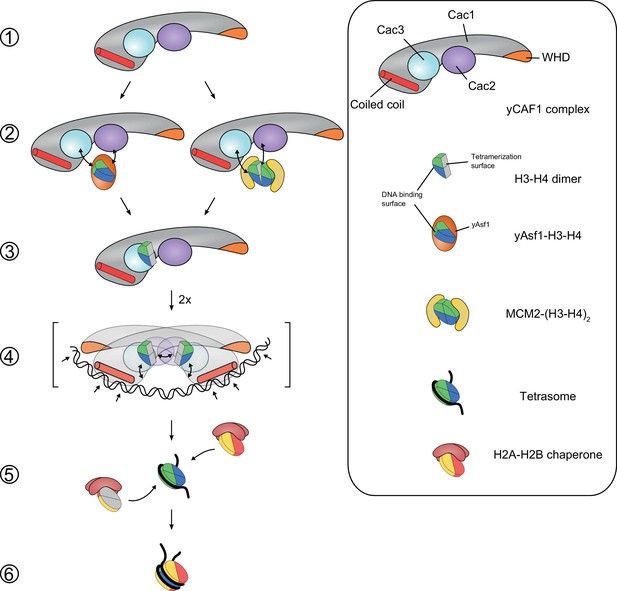
Model for yCAF1 recruitment and H3-H4 deposition.
Free monomeric yCAF1 (step 1) is loaded with dimeric H3-H4 through association of yAsf1 with the Cac2 subunit. Alternatively, loading can occur through hand over of H3-H4 from Mcm2 (step 2). yCAF1 binds the histones via their DNA binding and oligomerization surfaces (step 3). During DNA synthesis, two yCAF1-H3-H4 complexes bind cooperatively to an extended DNA element >50 bp (step 4) to deposit H3-H4 dimers and form tetrasomes. The WHD (orange) and coiled-coil (red) DNA-binding domains of yCAF1 are required for deposition of H3-H4 tetramers. The requirement of an extended free DNA region together with PCNA interaction may direct yCAF1 activity to replication forks. H2A-H2B chaperones like NAP1 or FACT recognize the tetrasome intermediate and deposit two copies of H2A-H2B (step 5) to form a complete nucleosome (step 6).
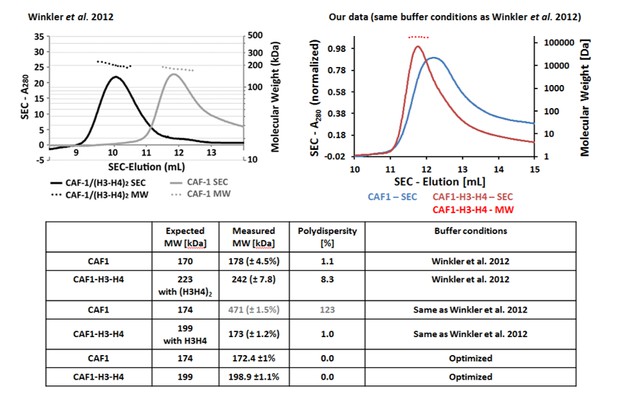
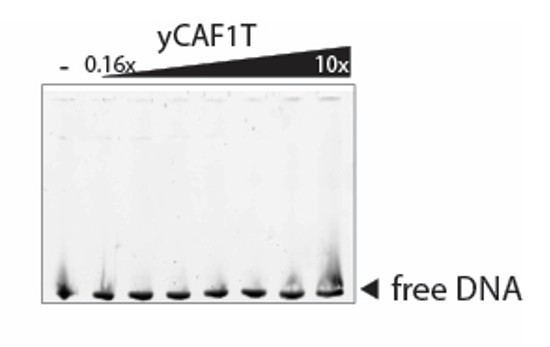
Tables
Overall biophysical parameters of yCAF1. Column labeling: SEC-MALLS (Size-exclusion chromatography - multi-angle laser light scattering); EQ-AUC (equilibrium analytical ultracentrifugation); SV-AUC (sedimentation velocity analytical ultracentrifugation); SAXS (small angle X-ray scattering); Native MS (native mass spectrometry); MMSLS (Molar masses determined by SEC-MALLS); MMAUC (Molar masses determined by equilibrium analytical ultracentrifugation); s020,w (Sedimentation coefficient determined by velocity analytical ultracentrifugation); sth (computed sedimentation coefficient derived from SAXS envelopes); Rg (radius of gyration); MMSAXS (molar masses determined by SAXS); Dmax (maximum dimension); Vp (excluded particle Volume); MMMS (molar masses determined by native MS; MMth (theoretical molar mass calculated).
The errors reported for SEC-MALLS are the residual standard deviations of the observed data from the fitted values calculated using Astra. The errors of the AUC experiments are derived from the standard deviations of linear fits of the obtained data points to extrapolate the respective values (MMAUC and s020,w) to zero protein concentration. The errors reported for the parameters derived from SAXS are based on the observed range of results is it possible to obtain, adjusting (within acceptable theoretical limits) the data points used for the calculation and as such represent the confidence range of the parameter. Resolution of the ab inito SAXS models was calculated according to (Tuukkanen et al., 2016). Errors in native MS were determined according to (McKay et al., 2006). CSLS, CSAXS, CMS are the concentrations of samples used for SEC-MALLS, SAXS and native MS respectively. N.D. (not determined)
| Sec-malls | Eq-auc | Sv-auc | SAXS | SAXS | SAXS | SAXS | SAXS | Native MS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | MMSLS kDa (CSLS, µM) | MMAUC kDa | sth Svedberg | s020,w Svedberg | Rg nm (CSAXS mg·ml−1) | MMSAXS kDa | Dmax nm | Vp nm3 | Resolution Å | MMMS kDa (CMS µM) | MMth kDa |
| yCAF1 | 172.4 ± 1% (67) | 180 ± 10 | 6.2 | 6.41 ± 0.03 | 6.39 ± 0.22 (11.4) | 175 ± 3 | 26 ± 2 | 307 ± 5 | 57 ± 4 | 174.49 ± 0.30 (2.5) | 174.0 |
| yCAF1-H3-H4 | 198.9 ± 1.1% (50) | 200 ± 11 | 7.1 | 6.84 ± 0.06 | 6.02 ± 0.35 (10) | 203 ± 13 | 25 ± 2 | 355 ± 23 | 54 ± 4 | 201.00 ± 0.01 (7) | 200.7 |
| yCAF1T | 142 ± 1% (15) | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | 5.66 ± 0.03 (30.0) | 127 ± 1 | 20 ± 1.2 | 222 ± 2 | 49 ± 4 | N.D. | 146.8 |
| yCAF1T-H3-H4 | 153 ± 1% (15) | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | 5.10 ± 0.03 (13.2) | 163 ± 1 | 17.3 ± 1.3 | 285 ± 2 | 52 ± 4 | N.D. | 173.6 |
Summary of SEC-MALLS data for yCAF1 variants. Column labeling: SEC-MALLS (Size-exclusion chromatography - multi-angle laser light scattering); MMSLS (Molar masses determined by SEC-MALLS); MMth (theoretical molar mass calculated). CSLS is the concentration used for SEC-MALLS. Errors reported are the residual standard deviations of the observed data from the fitted values calculated using Astra.
| Sample | MMSLS kDa (CSLS, µM) | MMth kDa |
|---|---|---|
| yCAF1U | 166 ± 1.1% (20) | 161.4 |
| yCAF1U-H3-H4 | 184 ± 1% (20) | 188.2 |
| yCAF1V | 133 ± 1.2% (20) | 134.4 |
| yCAF1V-H3-H4 | 156 ± 1.1% (20) | 161.2 |
| yCAF1X | 143 ± 1% (15) | 147.2 |
| yCAF1X-H3-H4 | 160 ± 1% (15) | 174.0 |
Summary of native mass spectrometry.
| Protein sample | Concentration (μM) | Oligomerization state | Measured mass ± error (Da)* | Calculated mass (Da) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| yCAF1 | 2.5 | Cac1:Cac2:Cac3 | 174 492 ± 3 | 173965.1 |
| yCAF1 | 2.5 | Cac1:Cac3 | 123 927 ± 5 | 120735 |
| yCAF1 | 2.5 | Cac2:Cac3 | 103 840 ± 4 | 103755.1 |
| yCAF1 | 2.5 | Cac2 | 53 273 ± 6 | 53230.1 |
| yCAF1 | 2.5 | Cac3 | 50 568 ± 7 | 50525 |
| yCAF1-H3-H4 | 7 | Cac1:Cac2:Cac3:H3:H4 | 201 002 ± 5 | 200 720.3 |
| yCAF1-H3-H4 | 7 | Cac2:Cac3:H3:H4 | 130 343 ± 7 | 130510.4 |
| H3-H4 | 10† | (H3-H4)2 | 53 015 ± 4 | 53510.6 |
| H3-H4 | 10† | H3-H4 | 26 508 ± 2 | 26755.3 |
| H3-H4 | 10† | H3 | 15 271 ± 2 | 15388 |
| H3-H4 | 10† | H4 | 11236 ± 3 | 11367.3 |
-
*Values reported represent the mean value ± standard deviation according to (McKay et al., 2006). Combinations of neighboring m/z values were used to determine distinct M values of a macromolecule. Using these values, a mean value of M and its standard deviation were calculated.
-
†Values reported assume that H3-H4 are tetrameric in solution.
DNA binding by yCAF1.
| Protein sample | DNA substrate | KD [μM] * | Hill coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|
| yCAF1 | 147 bp | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 2.0 ± 0.4 |
| 84 bp | 2.3 ± 0.3 | 2.2 ± 0.3 | |
| 42 bp | 2.5 ± 0.5 | 2.2 ± 0.4 | |
| 17 bp | 5.1 ± 1.0 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | |
| yCAF1U | 147 bp | 4.1 ± 1.9 | 4.3 ± 5.8 |
| yCAF1V | 147 bp | >10 | N.D. |
| yCAF1X | 147 bp | 5.7 ± 1. 7 | 2.9 ± 0.6 |
| yCAF1T | 147 bp | >10 | N.D. |
-
*Values determined from experiments using the 147, 84, 42 or 17 bp DNA fragment. Errors, where reported, correspond to the SEM value of three technical replicates.
Sequence information on 10 bp DNA ladder (Promega). AT content (%) for all DNA fragments is 60%.
| Length (bp) | Sequence |
|---|---|
| 10 | GGACTATACT |
| 20 | GGACTATACTAGACATTGAC |
| 30 | GGACTATACTAGACATTGACGTGGTTGTAA |
| 40 | GGACTATACTAGACATTGACGTGGTTGTAAGATGATCATG |
| 50 | GGACTATACTAGACATTGACGTGGTTGTAAGATGATCATGTGTTAATGGC |
| 60 | GGACTATACTAGACATTGACGTGGTTGTAAGATGATCATGTGTTAATGGCAAGGTGAGTT |
| 70 | CATGATCATCTTACAACCACGTCAATGTCTAGTATAGTCCTACTCTGTGATATGGTTCTCTGTCGATGTA |
| 80 | GCCATTAACACATGATCATCTTACAACCACGTCAATGTCTAGTATAGTCCTACTCTGTGATATGGTTCTCTGTCGATGTA |
| 90 | AACTCACCTTGCCATTAACACATGATCATCTTACAACCACGTCAATGTCTAGTATAGTCCTACTCTGTGATATGGTTCTCTGTCGATGTA |
| 100 | ATGATCATCTAACTCACCTTGCCATTAACACATGATCATCTTACAACCACGTCAATGTCTAGTATAGTCCTACTCTGTGATATGGTTCTCTGTCGATGTA |
Summary of SEC-MALLS data. Column labeling: Ve (elution Volume); MMSLS (Molar masses determined by SEC-MALLS); MMth (theoretical molar mass calculated). When there are more than two proteins in the injected sample, ‘+' indicates the mixing order. In sample 4, a five-fold molar excess of a preformed yAsf1-H3-H4 complex was incubated with yCAF1 before injection. In sample 9, a five-fold molar excess of a preformed MCM2-H3-H4 complex was incubated with yCAF1. The errors reported are the residual standard deviations of the observed data from the fitted values calculated using Astra.
| Peak 1 | Peak 2 | Peak 3 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Ve (ml) | MMsls (kDa) | MMth (kDa) | Ve (ml) | MMsls (kDa) | MMth (kDa) | Ve (ml) | MMsls (kDa) | MMth (kDa) |
| yCAF1 | 9.96 | 172.1 ± 0.1 | 174.0 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| yCAF1 + yAsf1 | 9.96 | 171.1 ± 0.6 | 174.0 | 12.91 | 38.6 ± 0.2 | 31.6 | – | – | – |
| yCAF1 + yAsf1 + H3 H4 | 10.00 | 185.3 ± 0.1 | 200.7 | 12.85 | 64.3 ± 0.2 | 58.3 | – | – | – |
| yCAF1 + yAsf1-H3-H4 1 :5 | 9.98 | 192.9 ± 0.2 | 200.7 | 12.88 | 60.1 ± 0.1 | 58.3 | – | – | – |
| yAsf1 | – | – | – | 12.96 | 36.3 ± 0.1 | 31.6 | – | – | – |
| yAsf1 + H3 H4 | – | – | – | 12.86 | 58.7 ± 0.2 | 58.3 | – | – | – |
| yCAF1 + MCM2 | 9.95 | 174.1 ± 0.7 | 174.0 | – | – | – | 14.32 | 19.1 ± 0.5 | 17.6 |
| yCAF1 + MCM2 + H3 H4 | 9.97 | 185.9 ± 0.1 | 200.7 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| yCAF1 + MCM2-H3-H4 1 :5 | 9.98 | 190.5 ± 0.7 | 200.7 | 12.09 | 90.8 ± 0.4 | 71.0 | – | – | – |
| MCM2 | – | – | – | – | – | – | 14.32 | 18.8 ± 0.1 | 17.6 |
| MCM2 + H3 H4 | – | – | – | 12.16 | 82.6 ± 0.4 | 71.0 | – | - | – |
| yCAF1 + H3 H4 | 9.97 | 191.3 ± 0.4 | 200.7 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| yCAF1 + yAsf1+Mmc2 + H3 H4 | 10.05 | 188.8 ± 0.9 | 200.7 | 12.79 | 67.5 ± 0.1 | 75.9 | 14.38 | 27.4 ± 0.1 | 17.6 |





