A novel twelve class fluctuation test reveals higher than expected mutation rates for influenza A viruses
Figures
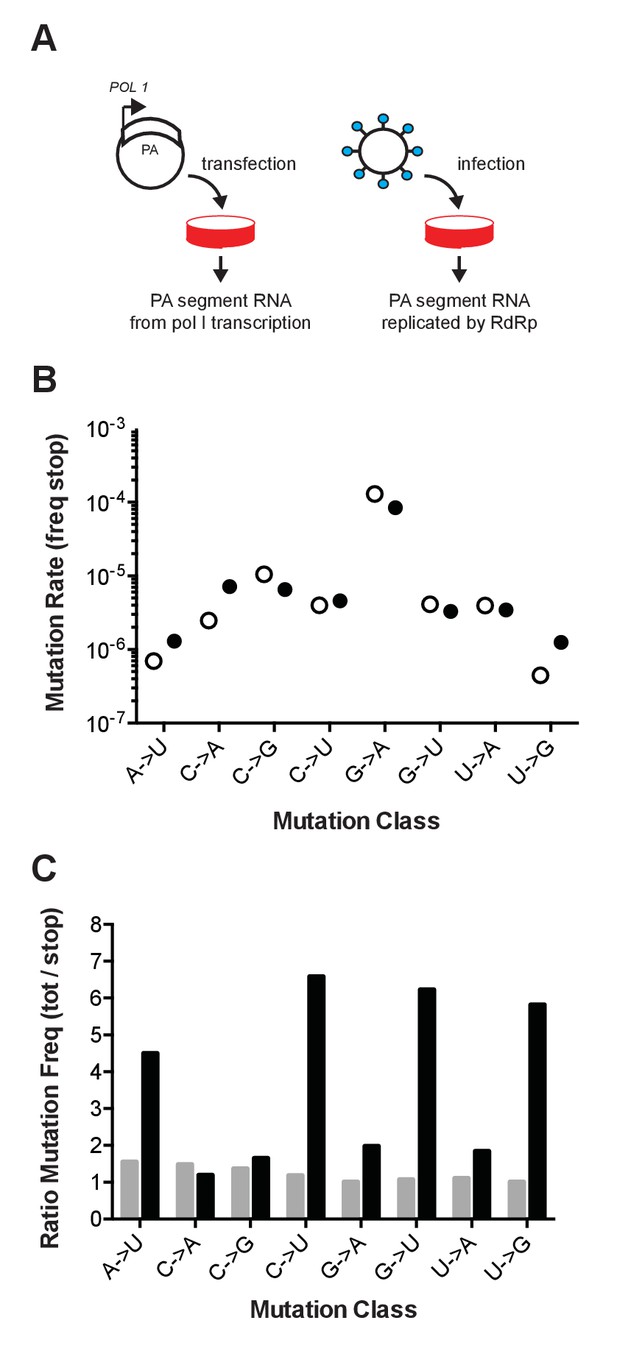
Influenza mutation rates by PrimerID next generation sequencing.
(A) Segment 3 (PA) RNA was isolated from either cells transfected with pol I expression plasmids or cell-free supernatants of cells infected with influenza virus. These RNA were reverse transcribed with barcoded PrimerID primers and amplified by PCR for sequencing as described in the methods. We obtained 449,655 PrimerID consensus sequences for the plasmid-derived RNA sample and 481,286 consensus sequences for the virus-derived RNA sample. (B) The frequencies of mutations to stop codons in pol I transcribed RNA (open circles) and virus-derived RNA (filled circles) were determined by dividing the number of stop codon mutations across the consensus sequences by the total number of nonsense mutation target (NSMT) sites analyzed. Plotted data are in Figure 1—source data 1. See also Supplementary file 1. (C) Total mutation frequencies were calculated as the number of observed mutations for a particular mutation class divided by the number of sequenced sites that could mutate by that same class. Shown is the ratio of total mutation frequency to stop codon mutation frequency by mutation class for sequences derived from plasmid-derived RNA (grey bars) and virus-derived RNA (black bars). Plotted data are in Figure 1—source data 2.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Spreadsheet with frequencies of mutations to stop codons in plasmid- and virus-derived RNA.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26437.003
-
Figure 1—source data 2
Spreadsheet with mutation frequency by class for plasmid- and virus-derived RNA.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26437.004
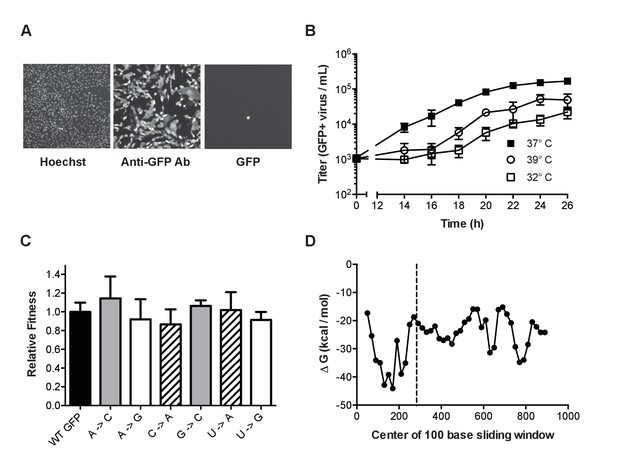
Characterization of mutant ΔHA-GFP influenza viruses.
(A) Fluorescent images of cells infected with mutant ΔHA-GFP (shown are data for the A to C virus, see Table 1) and stained with Hoechst and anti-GFP Alexa 647 conjugate. Cells were imaged at 4x magnification and the resulting images were digitally magnified to an equal extent for this figure. (B) Growth kinetics of mutant ΔHA-GFP viruses. MDCK-HA cells were infected at an MOI of 0.01 in 96-well plates and incubated at 32°C (open squares), 37°C (filled squares), or 39°C (open circles). At each time point, the supernatants from 4 wells were transferred to a new 96-well plate containing MDCK cells. After 14 hr the cells were fixed and stained using an anti-GFP antibody. The number of cells stained were determined by fluorescence microscopy and used to calculate the titer of GFP expressing virus. Data shown are the cumulative mean and standard deviations for 4 measurements at each time point for each of two mutant ΔHA-GFP viruses (C to U and U to A viruses). Each point is the therefore the mean ± standard deviation for 8 values. Plotted data are in Figure 2—source data 1. (C) The fitness of 6 of the mutant ΔHA-GFP viruses (x-axis) were compared to wild type ΔHA-GFP through direct competition with a genetically barcoded competitor over 4 serial passages. Quantitative PCR was used to determine the relative changes in the frequency of the two competitors and fitness values were calculated as described in the Methods. Mutant viruses are classified by the GFP amino acid mutated, with wild type (black), T65 (gray), Y66 (striped), G67 (white). Shown are the mean and standard deviation for three competitions and fitness measurements for each virus. Plotted data are in Figure 2—source data 2. (D) The minimum free energy of RNA folding for 100 base sliding windows (80 base overlaps) were determined for the ΔHA-GFP construct. The location of the three mutated sites (bases 280–288) are indicated by the dashed line. Plotted data are in Figure 2—source data 3.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Spreadsheet with virus titer (GFP+ virus per ml) in imaging plate at the indicated time points and temperatures.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26437.007
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Spreadsheet with replicate fitness values for wild type and ΔHA-GFP viruses as shown in Figure 2C.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26437.008
-
Figure 2—source data 3
Spreadsheet with minimum free energy of RNA folding by window start position as shown in Figure 2D.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26437.009
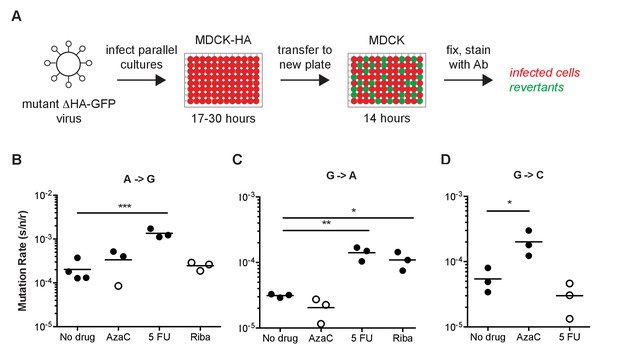
Fluorescent Luria-Delbruck fluctuation test.
(A) General workflow for measuring the mutation rate using mutant ΔHA-GFP viruses. Parallel cultures of MDCK-HA cells were infected with passage one stocks of mutant ΔHA-GFP viruses at low multiplicity. The time for initial replication was varied to allow for a number of replicated viruses and revertants adequate to measure the mutation rate for a given class. Supernatants were transferred to 96-well plates of MDCK cells and incubated for 14 hr to allow for infection and GFP expression in target cells. The mutation rate for each mutant ΔHA-GFP virus and class was calculated as described in the methods and text based on the initial and final titer (Ni and Nf, anti-GFP positive infected cells) and proportion of cultures with no revertants (P0, wells without green fluorescence). (B–D) Specificity of the reversion to fluorescence assay. The (B) A to G, (C) G to A, and (D) G to C mutation rates for A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 H1N1 were measured at 37°C in cells pretreated with 0.625 μM 5-azacytidine (AzaC), 15 μM 5-fluorouracil (5 FU), or 2.5 μM ribavirin (Riba). No data are shown for G to C with 2.5 μM ribavirin because large titer decreases upon drug treatment prohibited measurements. Filled symbols represent measurements in which P0 is between 0.1 and 0.69, where the assay is most precise. Open circles represent data with P0 between 0.7 and 0.9. Arithmetic means are indicated. A one-way ANOVA with a Dunnett’s correction for multiple comparisons was used for each mutation class to compare each drug treatment to no drug treatment. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.005. Plotted data are in Figure 3—source data 1.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Mutation rates for A to G, G to A, and G to C viruses in the presence and absence of AzaC, 5FU and Riba as measured by fluctuation test.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26437.011
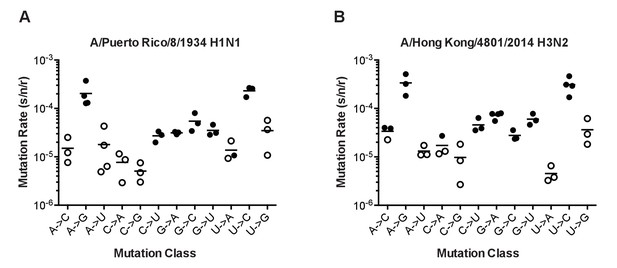
The mutation rates of influenza viruses replicated at 37°C.
(A) Measurements of A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 H1N1 viruses encoding the 12 different mutant ΔHA-GFP constructs. (B) Measurements of viruses encoding the replication complex (PB2, PB1, PA, and NP) from A/Hong Kong/4801/2014 H3N2 and the remaining genes coming from A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 H1N1. Filled symbols represent measurements in which P0 is between 0.1 and 0.69. Open circles represent data with P0 between 0.7 and 0.95. Plotted data are in Figure 4—source data 1. Raw counts of green cells in positive wells for Hong Kong viruses are in Figure 4—source data 2. The arithmetic means are indicated on the graphs and the means and standard deviations reported in Supplementary file 2.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Mutation rates for all twelve mutational classes for PR8 and Hong Kong viruses as measured by fluctuation test.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26437.013
-
Figure 4—source data 2
Raw data for all experiments with Hong Kong viruses showing number of wells with n green cells (n = 0–10).
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26437.014
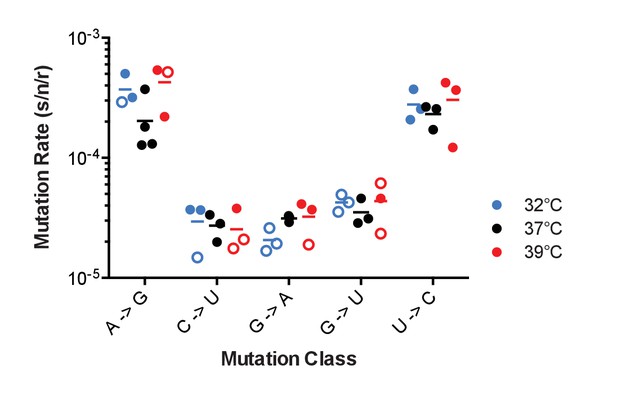
The effect of temperature on influenza A virus mutation rates.
Mutation rates were determined for A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 H1N1 viruses encoding the indicated mutant ΔHA-GFP constructs replicated at 32°C (blue), 37°C (black) and 39°C (red). Filled symbols represent measurements in which P0 is between 0.1 and 0.69. Open circles represent data with P0 between 0.7 and 0.90. The arithmetic means are indicated. A two-way ANOVA revealed no significant differences in mutation rates based upon temperature. Plotted data are in Figure 5—source data 1.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Mutation rates for all twelve mutational classes for PR8 at the indicated temperatures as measured by fluctuation test.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26437.016
Tables
Non-fluorescent ΔHA-GFP constructs.
| Mutation Probed* | Nucleotide Sequece† | Amino acid Sequence‡ |
|---|---|---|
| WT eGFP | acc uac ggc | T Y G |
| A -> C | aAa uac ggc | K Y G |
| A -> G | acc uac gAc | T Y D |
| A -> U | acc Aac ggc | T N G |
| C -> A | acc uCc ggc | T S G |
| C -> G | acc uac gCc | T Y A |
| C -> U | acc Cac ggc | T H G |
| G -> A | acc uGc ggc | T C G |
| G -> C | uGg uac ggc§ | W Y G |
| G -> U | acc Gac ggc | T D G |
| U -> A | acc uUc ggc | T F G |
| U -> C | aUa uac ggc | I Y G |
| U -> G | acc uac gUc | T Y V |
-
*Mutations are in the mRNA coding sense.
-
†Nucleotides 193–201 of the eGFP reading frame are shown. Changes from wild type are in bold and italics. Site that allows reversion to fluorescence is capitalized.
-
‡Amino acids 65–67 of eGFP are shown. Changes from wild type are in bold and italics.
-
§This construct is able to revert to wild type GFP (S65).
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Nonsense mutation counts from PrimerID sequencing of the influenza PA gene.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26437.017
-
Supplementary file 2
Influenza A virus mutation rates for PR8 and Hong Kong viruses.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26437.018





