Calcium-mediated shaping of naive CD4 T-cell phenotype and function
Figures
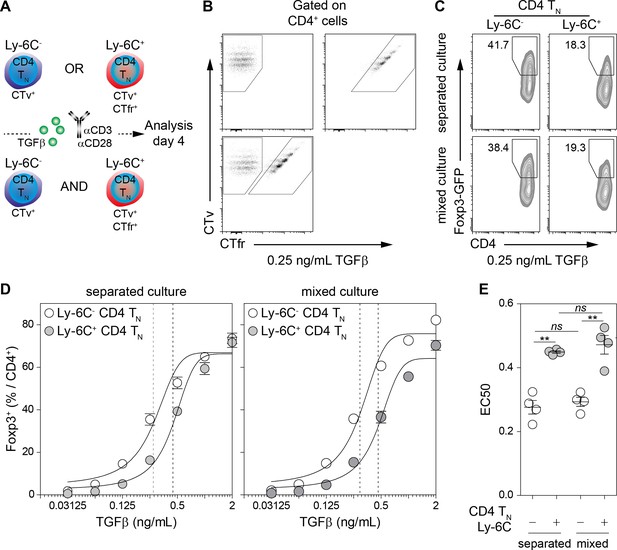
Cell-intrinsic enhanced ability of Ly-6C- CD4 TN cells to commit into iTreg cells.
(A–E) Flow-cytometry sorted Ly-6C- and Ly-6C+ CD4 TN cells from C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP mice were stained with CTv (Ly-6C-) or CTv and CTfr (Ly-6C+) and stimulated separately or together for 4 days with coated αCD3 and αCD28 Abs (4 µg/mL), in the presence of graded doses of TGFβ1. (A) Diagram illustrating the experimental protocol. (B) Representative CTv/CTfr dot-plots for gated CD4+ cells recovered after 4 days of culture. Ly-6C- and Ly-6C+ CD4 TN cells were either cultured separately (top left and right panels, respectively) or together (bottom panel) (C) Representative Foxp3/CD4 contour-plots and proportions of Foxp3+ cells for gated CD4+ cells are shown at a dose of 0.25 ng/mL TGFβ1. (D) Proportions of Foxp3+ cells among CD4+ cells are shown as a function of TGFβ1 concentration. Mean ± s.e.m of four independent experiments are shown. (E) Concentrations of TGFβ1 needed to obtain 50% of the maximal percentages of iTreg-cell polarization (EC50) were calculated for each CD4 TN cell subset in separated or mixed cultures. Each dot represents an independent experiment. Significance of differences were assessed using a two-tailed paired Student’s t-test. Values of p<0.05 were considered as statistically significant (**p<0.01; ns, not significant).
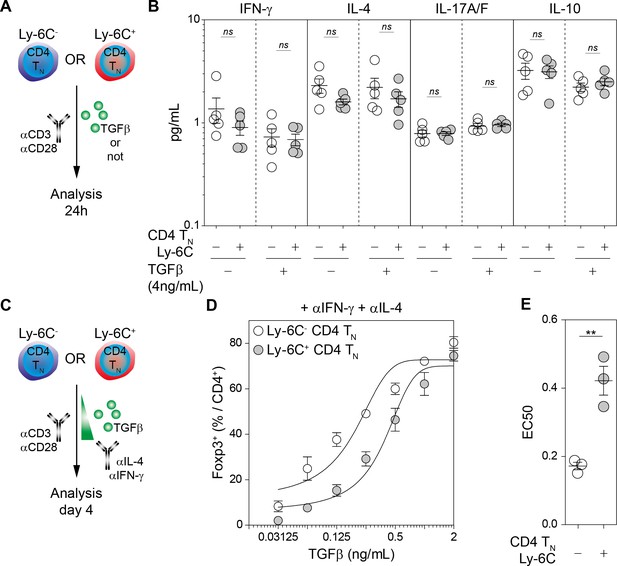
Cytokine-independent enhanced ability of Ly-6C- CD4 TN cells to commit into iTreg cells.
(A–B) Flow-cytometry sorted Ly-6C- and Ly-6C+ CD4 TN cells from C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP mice were stimulated separately with coated αCD3 and αCD28 Abs (4 µg/mL), in the presence of TGFβ1 (4 ng/mL) or not. 24 hr later, culture supernatants were collected and analyzed for the presence of interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and interleukins (IL) −4, −17A/F and −10. (A) Diagram illustrating the experimental protocol. (B) IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-17A/F and IL-10 concentrations in the culture supernatants of both Ly-6C- and Ly-6C+ CD4 TN cells after 24 hr culture are shown. (C–E) Flow-cytometry sorted Ly-6C- and Ly-6C+ CD4 TN cells from C57BL/6 mice were stimulated separately with coated αCD3 and αCD28 Abs (4 µg/mL), in the presence of αIFN-γ and αIL-4 blocking antibodies and graded doses of TGFβ1. (C) Diagram illustrating the experimental protocol. (D) Proportions of Foxp3+ cells among CD4+ cells are shown as a function of TGFβ1 concentration. Mean ± s.e.m of two independent experiments are shown. (E) Concentrations of TGFβ1 needed to obtain 50% of the maximal percentages of iTreg-cell polarization (EC50) were calculated for each CD4 TN-cell subset in separated or mixed cultures. Each dot represents an independent experiment. Significance of differences were assessed using a two-tailed paired Student’s t-test. Values of p<0.05 were considered as statistically significant (**p<0.01; ns, not significant).
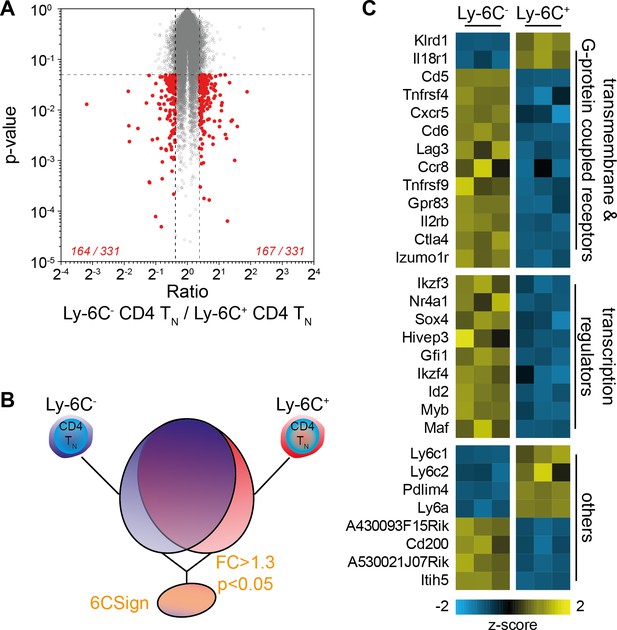
Transcriptional profiling identifies a set of differentially regulated genes between Ly-6C- and Ly-6C+ CD4 TN-cell subsets.
(A–E) Microarray analysis was performed on Ly-6C- and Ly-6C+ CD4 TN cells sorted from LNs of C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP mice. (A) ‘Volcano plot’ representation (Log2 (ratio) versus Log10 (t test p-value)). Genes expressed >1.3 fold higher or lower in Ly-6C- CD4 TN cells compared to Ly-6C+ CD4 TN cells with a p-value of <0.05 are highlighted in red. The number of genes up- or down-regulated (1.3-fold cut-off) for each comparison is indicated. (B) Scheme depicting the selection of genes that were included in the 6CSign (list of the genes differentially expressed between Ly-6C- and Ly-6C+ CD4 TN cells, at a 1.3-fold cut-off). (C) Heat map of selected differentially expressed genes between Ly-6C- and Ly-6C+ CD4 TN cells. The scaled expression of each replicate, denoted as the row z-score, is plotted in yellow-blue color scale with yellow indicating high expression and blue indicating low expression.
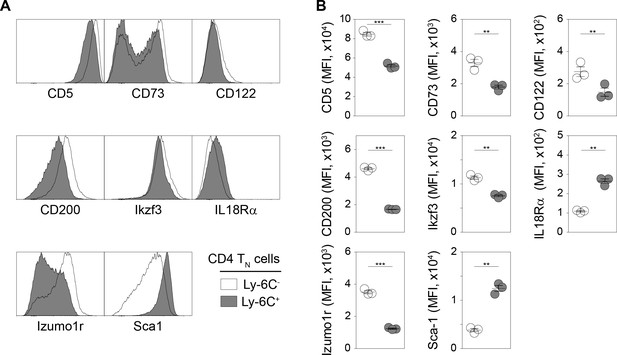
Validation of the 6CSign at the protein level.
(A–B) CD5, CD73, CD122, CD200, Ikzf3, IL18Rα, Izumo1r and Sca-1 expression at the cell surface of Ly-6C- and Ly-6C+ CD4 TN cells was analysed by FACS. (A) Fluorescence histograms of gated Ly-6C- and Ly-6C+ CD4 TN (CD4+ CD8α- TCRβ+ CD44lo CD25lo Foxp3-GFP-) cells recovered from pLNs are shown for a representative C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP mouse. (B) Mean fluorescence intensities (MFIs) are shown as means ± s.e.m. for a representative experiment. Each dot represents an individual mouse.
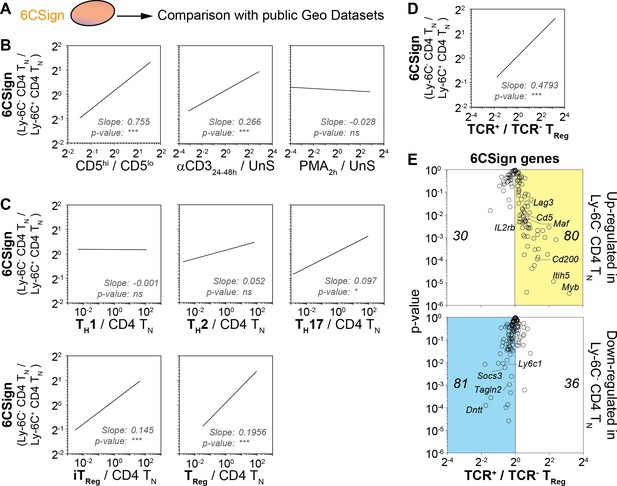
Transcriptomic signature of Ly-6C- CD4 TN cells reveals both their active TCR signaling and their bias toward iTreg-cell polarization.
(A–E) 6CSign was compared to several public Geo Datasets. (A) Diagram illustrating the analysis protocol. (B) Ratio vs ratio representation comparing gene expression ratio between Ly-6C- CD4 TN cells and Ly-6C+ CD4 TN cells (6CSign) with either CD5hivslo cell signature (Richards et al., 2015) (ratio of CD5hi CD4 TN cells to CD5lo CD4 TN cells, left panel), anti-CD3 activated CD4 TN-cell signature (Wakamatsu et al., 2013) (ratio of CD4 TN cells stimulated for 24–48 hr with anti-CD3 coated Ab to unstimulated CD4 TN cells, middle panel) and PMA-activated CD4 TN-cell signature (Bevington et al., 2016) (ratio of CD4 TN cells stimulated for 2 hr with PMA to unstimulated CD4 TN cells, right panel). (C) Ratio vs ratio representation comparing gene expression ratio between Ly-6C- CD4 TN cells and Ly-6C+ CD4 TN cells (6CSign) with in-vitro-induced TH1, TH2, TH17, iTreg and ex vivo purified Treg cell signatures that have been identified by Wei et al. (2009) (ratio of CD4 TH-cell subsets to CD4 TN cells). (D) Ratio vs ratio representation comparing gene expression ratio between Ly-6C- CD4 TN cells and Ly-6C+ CD4 TN cells (6CSign) with TCR-signaling-dependent CD4-Treg-specific signature (Vahl et al., 2014) (ratio between TCR+ Treg cells and TCR-ablated (TCR-) Treg cells). (B–D) Correlation analyses were performed using Pearson’s correlation test. (E) ‘Volcano plot’ representation (Log2 (ratio) versus Log10 (t-test p-value)) between TCR+ Treg cells and TCR-ablated (TCR-) Treg cells (Vahl et al., 2014), for 6CSign genes upregulated (upper panel) or downregulated (lower panel) in Ly-6C- CD4 TN cells. (B–E) Datasets were filtered to common probes between the two arrays.
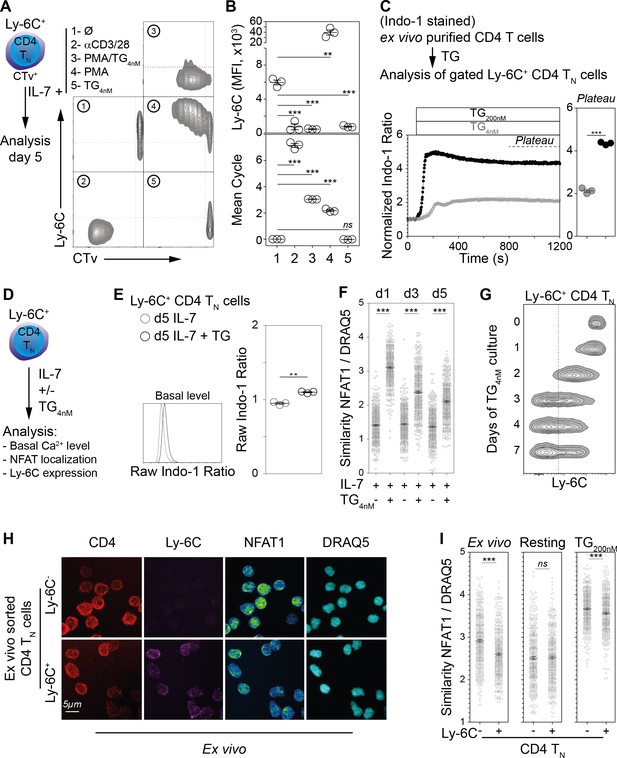
Ly-6C- CD4 TN-cell phenotype relies upon calcium signaling pathway in vitro.
(A–B) Flow-cytometry sorted Ly-6C+ CD4 TN cells from C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP mice were labelled with CTv and cultured in IL-7 (10 ng/ml) in the presence of either coated αCD3/28 (4µg/ml), PMA and TG (1.25 ng/ml and 4 nM, respectively), PMA alone (1.25 ng/ml) or TG (4 nM). Cells were recovered and analyzed after 5 days of culture. (A) Representative Ly-6C/CTv contour-plots are shown. (B) Ly-6C Mean fluorescence intensities (MFIs), for gated CD4+ TCR+ cells, are shown as means ± s.e.m. for a representative experiment with three mice per group (upper panel). Mean cell cycle numbers were calculated (lower panel). (C) Ex-vivo-purified CD4 T cells from C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP mice were stained with Indo-1 and cell surface molecules CD44, Ly-6C and lineage markers (CD11c, CD11b, CD8β, CD25, TCRγδ and NK1.1). Intracellular calcium concentration was assessed before and after stimulation with 4 or 200 nM TG to the extracellular medium and monitored by flow cytometry for 20 min; results are presented as normalized ratio of Indo-1 emission at 405 nm to that at 510 nm (405/510) for gated Ly-6C+ CD4 TN cells (Lineage- Foxp3-GFP- CD44lo Ly-6C+ cells). Normalized Indo-1 ratio at the Plateau are shown as means ± s.e.m. for a representative experiment (out of two independent experiments) with three mice per group (Each dot represents an individual mouse). (D–G) Flow-cytometry sorted Ly-6C+ CD4 TN cells from C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP mice were cultured in the presence of IL-7 (10 ng/mL) with TG (4 nM) or not. (D) Diagram illustrating the experimental protocol. (E) Basal intracellular calcium concentration was assessed, as in C, after 5 days of culture. Raw Indo-1 ratio are shown as means ± s.e.m. for a representative experiment (out of two independent experiments) with three mice per group (each dot represents an individual mouse). (F) After 1, 3 and 5 days of culture, cells were analyzed by imaging flow cytometry. NFAT1 nuclear localization was calculated as similarity score between NFAT1 and DRAQ5 intensities. Data are representative of one of two independent experiments. (G) Cells were analyzed after 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 and 7 days of culture. Representative Ly-6C contour plots are shown for gated CD4 TN cells (CD4+ CD44lo CD25lo Foxp3-GFP-) are shown. (H, I) LN cells were isolated from C57BL/6 mice and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde immediately (Ex vivo) or after 30 min of culture in the presence of 200 nM of TG (TG) or not (Resting). Ly-6C- and Ly-6C+ CD4 TN cells (CD4+ CD44lo CD25lo Foxp3-) were sorted by flow cytometry and stained for NFAT1, and DNA (DRAQ5). (H) Cells were analyzed by confocal microscopy; CD4 (Red), Ly-6C (Magenta), NFAT1 (pseudocolor) and DNA (DRAQ5, cyan) fluorescence are shown for ‘ex vivo’ purified Ly-6C- (upper panel) and Ly-6C+ (lower panel) CD4 TN cells. Original magnification ×63. (I) Cells were analyzed by imaging flow cytometry and NFAT1 nuclear localization assessed as in F. Data are representative of one of three independent experiments. (B, C, E, F, I) Significance of differences were assessed using a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. Values of p<0.05 were considered as statistically significant (**p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ns, not significant).
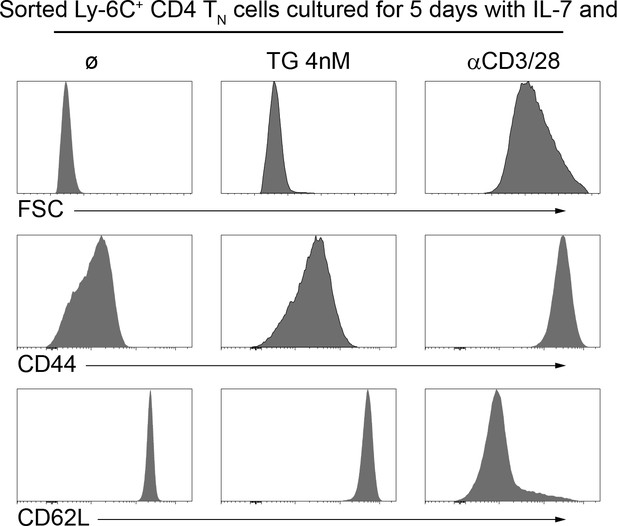
‘Ca2+-converted’ Ly-6C+CD4 TN cells keep a naive phenotype.
Flow-cytometry sorted Ly-6C+ CD4 TN cells from C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP mice were cultured in IL-7 (10 ng/mL) alone or in the presence of TG (4 nM) or αCD3 and αCD28 coated antibodies (4 µg/mL). After 5 days, cells were analyzed for their forward scatter profile (FSC) and their expression of CD44 and CD62L.
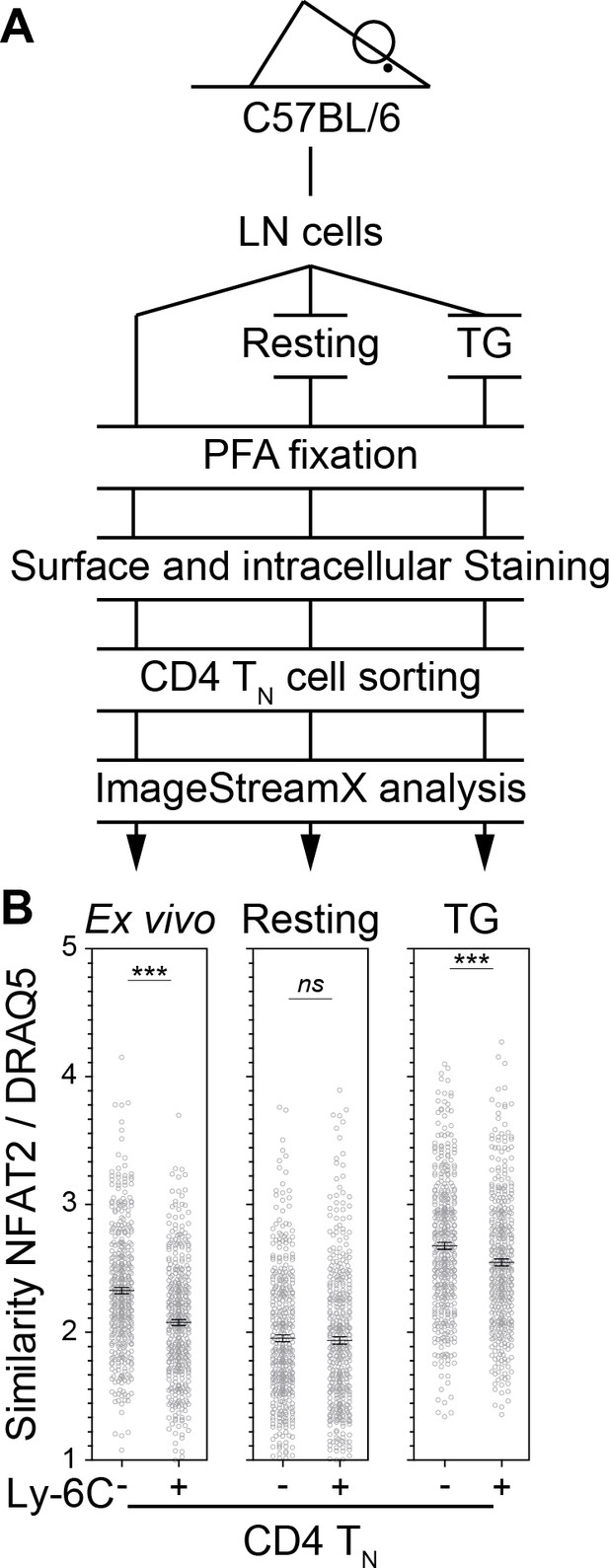
NFAT2 localization is more nuclear in Ly-6C- CD4 TN cells than in their Ly-6C+-cell counterparts.
LN cells were isolated from C57BL/6 mice and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde immediately (Ex vivo) or after 30 min of culture alone (Resting) or in the presence of 200 nM of TG (TG). Ly-6C- and Ly-6C+ CD4 TN cells (CD4+ CD44lo CD25lo Foxp3-) were sorted by flow cytometry and stained for NFAT2, and DNA (DRAQ5). Cells were then analyzed by imaging flow cytometry. (A) Scheme depicting the experimental procedure. (B) NFAT2 nuclear localization was calculated as similarity score between NFAT2 and DRAQ5 intensities. Data are representative of one of three independent experiments.
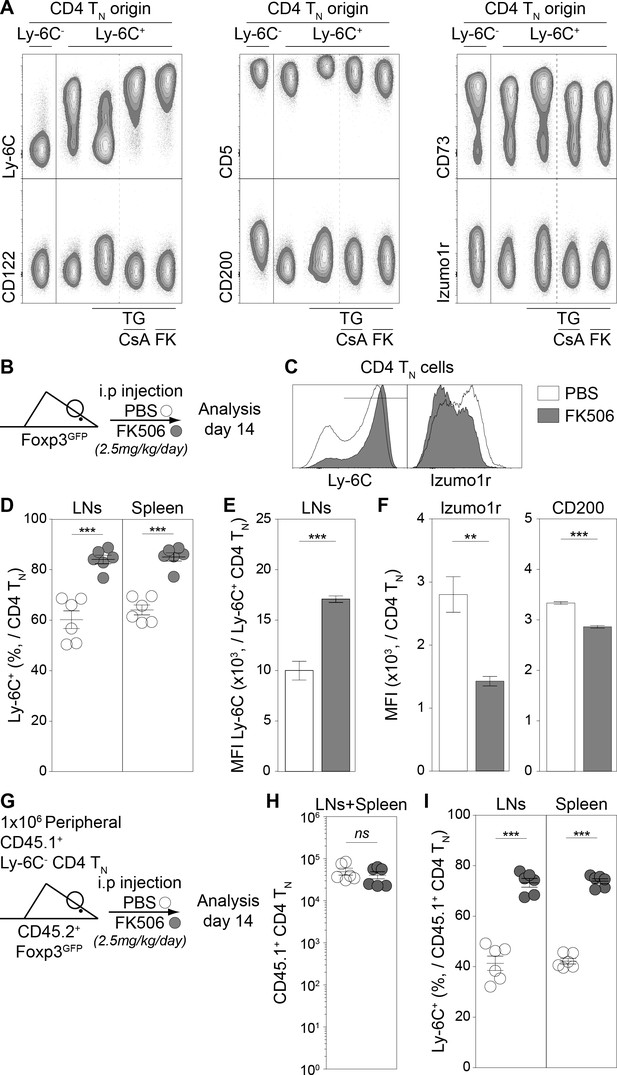
The calcium-calcineurin pathway shapes the phenotype of the CD4 TN-cell compartment in vivo.
(A) Flow-cytometry sorted Ly-6C+ CD4 TN cells from C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP mice were cultured in IL-7 (10 ng/mL) alone or in the presence of either TG (4 nM), TG and Cyclosporin A (CsA; 50 nM) or TG and FK506 (FK; 200 nM). Flow-cytometry sorted Ly-6C- CD4 TN cells rested in IL-7 were used as control. After 5 days, cells were analyzed for their expression of Ly-6C, CD5, CD73, CD122, CD200 and Izumo1r. Representative contour-plots of cell surface markers are shown for gated CD4 TN cells (CD4+ TCRβ+ CD44lo CD25lo Foxp3-GFP-) as a function of culture condition. (B–F) C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP mice were daily injected intraperitoneally with Prograf (FK506; 2.5 mg/kg) or diluent (PBS). Two weeks after treatment LNs (pooled pLNs and mLNs) and spleen were recovered and CD4 T cells were analyzed. (B) Diagram illustrating the experimental procedure. (C) Ly-6C and Izumo1r fluorescence histograms for gated CD4 TN cells (CD4+ TCRβ+ CD44lo CD25lo Foxp3-GFP-) recovered from LNs of PBS (white) and FK506 (grey) treated mice. (D) Percentage of Ly-6C+ cells among CD4 TN (CD4+ TCRβ+ CD44lo CD25lo Foxp3-GFP-) cells are shown for LNs and spleens of PBS (white) and FK506 (grey) treated mice. (E) Ly-6C Mean fluorescence intensities (MFIs), for gated Ly-6C+ CD4 TN (Ly-6C+ CD4+ TCRβ+ CD44lo CD25lo Foxp3-GFP-) cells recovered from LNs of PBS (white) and FK506 (grey) treated mice, are shown as means ± s.e.m. for two independent experiments with three mice per group. (F) Izumo1r and CD200 mean fluorescence intensities (MFIs), for gated Ly-6C+ CD4 TN (Ly-6C+ CD4+ TCRβ+ CD44lo CD25lo Foxp3-GFP-) cells recovered from LNs of PBS (white) and FK506 (grey) treated mice, are shown as means ± s.e.m. for a representative experiment with three mice per group. (G–I) 1 × 106 flow-cytometry sorted Ly-6C- CD4 TN cells from CD45.1+ C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP mice were adoptively transferred into sex-matched CD45.2+ C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP recipient mice daily injected intraperitoneally with Prograf (FK506; 2.5 mg/kg) or diluent (PBS). Two weeks after transfer and treatment, LNs (pooled pLNs and mLNs) and spleen were recovered and donor-derived CD45.1+ CD4 T cells were analyzed. (G) Diagram illustrating the experimental model. (H) Absolute numbers of donor-derived CD4 TN (CD45.1+ CD45.2- CD4+ TCRβ+ CD44lo CD25lo Foxp3-GFP-) cells recovered from LNs and spleen of recipient mice are shown as means ± s.e.m. for two independent experiments with three mice per group. (I) Percentage of Ly-6C+ among donor-derived CD4 TN (CD45.1+ CD45.2- CD4+ TCRβ+ CD44lo CD25lo Foxp3-GFP-) cells recovered from LNs and spleen of recipient mice are shown as means ± s.e.m. for two independent experiments with three mice per group. (D, H, I) Each dot represents an individual mouse. (D-F; H, I) Significance of differences were assessed using a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. Values of p<0.05 were considered as statistically significant (**p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ns, not significant).
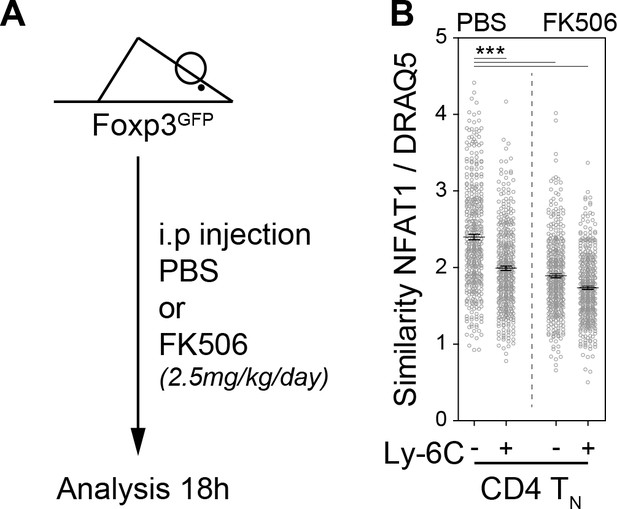
The calcium-calcineurin cascade drives NFAT nuclear translocation in CD4 TN cells in vivo.
(A) C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP mice were injected intraperitoneally with Prograf (FK506; 2.5 mg/kg; two times) or diluent (PBS). 18 hr later LN cells were isolated from C57BL/6 mice and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde immediately. CD4 TN cells (CD4+ CD44lo CD25lo Foxp3-) were sorted by flow cytometry and stained for Ly-6C, NFAT1, and DNA (DRAQ5). Cells were then analyzed by imaging flow cytometry. (A) Scheme depicting the experimental procedure. (B) NFAT1 nuclear localization was calculated as similarity score between NFAT1 and DRAQ5 intensities. Data are representative of one of two independent experiments.
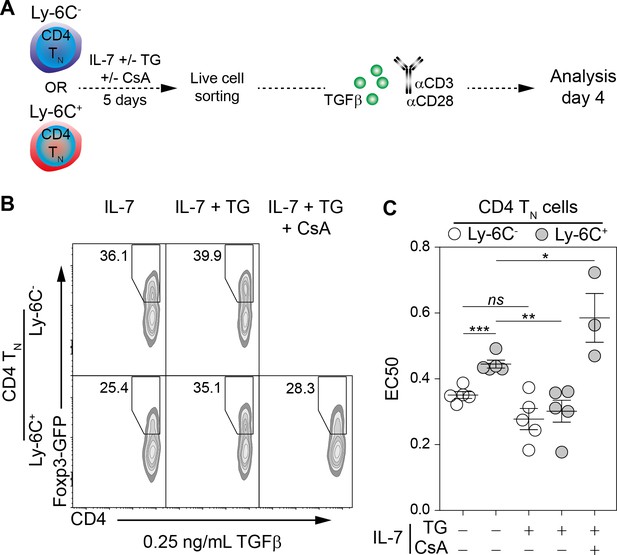
Ly-6C- CD4 TN-cell sensitization to iTreg-cell polarization signals relies upon calcium signaling pathway in vitro.
Flow-cytometry sorted Ly-6C- and Ly-6C+ CD4 TN cells from C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP mice were cultured in IL-7 (10 ng/mL) with or without TG (4 nM) and CsA (50 nM). After 5 days, live cells were flow-cytometry sorted and stimulated with coated αCD3 and αCD28 Abs (4 µg/ml) in the presence of graded doses of TGFβ1. Cells were analyzed after 4 days of stimulation. (A) Diagram illustrating the experimental procedure. (B) Representative Foxp3/CD4 contour-plots and proportions of Foxp3+ cells for gated CD4+ cells are shown at a dose of 0.25 ng/mL TGFβ1, as a function of pre-culture condition. (C) Concentrations of TGFβ1 needed to obtain 50% of the maximal percentage of iTreg-cell polarization (EC50) were calculated for each CD4 TN-cell subset and each pre-culture condition. Each dot represents an independent experiment. Significance of differences were assessed using a two-tailed paired Student’s t-test. Values of p<0.05 were considered as statistically significant (*p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ns, not significant).
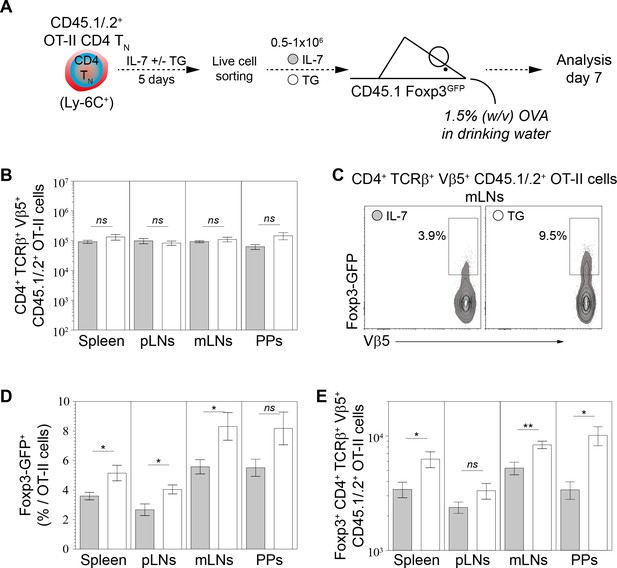
Calcium-mediated shaping of the CD4 TN-cell pTreg-cell differentiation potential in vivo.
Purified CD4 T cells from CD45.1/.2+ C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP OT-II mice were cultured in IL-7 (10 ng/ml) with or without TG (4 nM). After 5 days live CD4 TN (CD44lo CD25lo CD8β- CD11b- CD11c- NK1.1- TCRγδ- Foxp3-GFP-) cells were flow-cytometry sorted and injected intravenously (0.5−1 × 106 cells) into sex-matched CD45.1+ C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP recipient mice fed with Ovalbumin (OVA; 1.5% w/v) in the drinking water. One week after transfer, peripheral and mesenteric LNs (pLNs and mLNs, respectively), Peyer’s Patches (PPs) and spleen were recovered separately and donor-derived CD4 T cells were analyzed. (A) Diagram illustrating the experimental model. (B) Absolute numbers of donor-derived OT-II CD4 T (CD45.1+ CD45.2+ CD4+ TCRβ+ Vβ5+) cells recovered from pLNs, mLNs, PPs and spleen of recipient mice are shown as means ± s.e.m. for three independent experiments with two or three mice per group. (C) Representative Foxp3/Vβ5 contour-plots and proportions of Foxp3-GFP+ cells for gated donor-derived OT-II CD4 T (CD45.1+ CD45.2+ CD4+ TCRβ+ Vβ5+) cells recovered from mLNs are shown. (D–E) Percentages (D) and absolute numbers (E) of Foxp3-GFP+ among donor-derived OT-II CD4 T (CD45.1+ CD45.2+ CD4+ TCRβ+ Vβ5+) cells recovered from pLNs, mLNs, PPs and spleen of recipient mice are shown as means ± s.e.m. for three independent experiments with two or three mice per group. (B, D, E) Significance of differences were assessed using a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. Values of p<0.05 were considered as statistically significant (*p<0.05; ns, not significant). figure supplement legends.
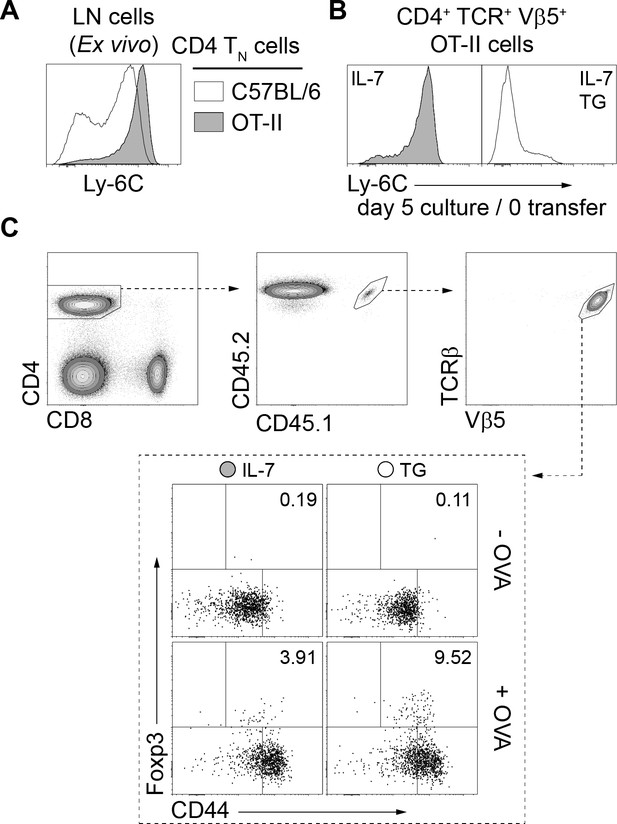
OT-II CD4 TN cells are Ly-6C+and can be Ca2+-converted and tested for their ability to convert into pTreg cells in vivo.
(A) Ly-6C fluorescence histograms of gated CD4 TN (CD4+ CD8α- TCRβ+ CD44lo CD25lo Foxp3-GFP-) cells recovered from LNs of C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP and C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP OT-II mice are shown. (B, C) Purified CD4 T cells from CD45.1/.2+ C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP OT-II mice were cultured in IL-7 (10 ng/ml) with or without TG (4 nM). After 5 days, live CD4 TN (CD44lo CD25lo CD8β- CD11b- CD11c- NK1.1- TCRγδ- Foxp3-GFP-) cells were flow-cytometry sorted, analyzed for their cell surface expression of Ly-6C (B) and injected intravenously (0.5−1 × 106 cells) into sex-matched CD45.2+ C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP recipient mice fed with Ovalbumin (+OVA; 1.5% w/v) or not (-OVA) in the drinking water (C). One week after transfer, mesenteric LNs (mLNs) were recovered and donor-derived CD4 T cells were analyzed. (C) Gating strategy and representative CD44/Foxp3 dot-plots for gated donor-derived OT-II CD4 T (CD45.1+ CD45.2+ CD4+ TCRβ+ Vβ5+) cells recovered from mLNs are shown. Percentages of Foxp3-GFP+ cells are indicated.
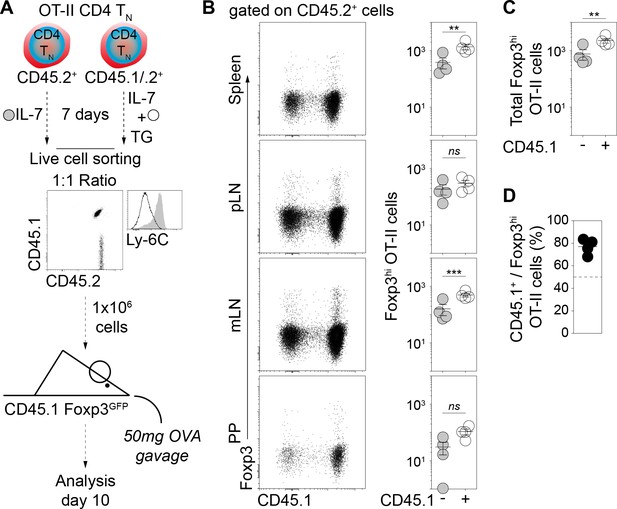
Calcium-mediated shaping of the CD4 TN-cell phenotype increases the pTreg-cell differentiation potential of OT-II CD4 TN cells in vivo.
Purified CD4 T cells from CD45. 2+ and CD45.1/.2+ C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP OT-II mice were cultured in IL-7 (10 ng/ml) without or with TG (4 nM), respectively. After 5 days live CD4 TN (CD44lo CD25lo CD8β- CD11b- CD11c- NK1.1- TCRγδ- Foxp3-GFP-) cells were flow-cytometry sorted, mixed at a 1:1 ratio and injected intravenously (0.5−1 × 106 cells) into sex-matched CD45.1+ C57BL/6 Foxp3-GFP-recipient mice gavaged with Ovalbumin (OVA; 50 mg) 4 and 24 hr later. 10 days after transfer, peripheral and mesenteric LNs (pLNs and mLNs, respectively), Peyer’s Patches (PPs) and spleen were recovered separately and donor-derived CD4 T cells were analyzed. (A) Diagram illustrating the experimental model and Ly-6C surface expression of transferred cells. (B) Representative CD45.1/Foxp3 dot-plots for gated donor-derived OT-II CD4 T (CD45.2+ CD4+ TCRβ+) cells recovered from Spleen, pLNs, mLNs and PP of recipient mice are shown. Absolute numbers of donor-derived Foxp3-GFP+ OT-II CD4 T cells recovered from pLNs, mLNs, PPs and spleen of recipient mice are shown as means ± s.e.m. for a representative experiment with four mice per group. (C) Total (pool of Spleen, pLNs, mLNs and PPs cells) absolute numbers of Foxp3-GFP+ OT-II CD4 T cells recovered from recipient mice are shown as means ± s.e.m. (D) Percentages of CD45.1+ cells among donor-derived Foxp3-GFP+ OT-II CD4 T (CD45.2+ CD4+ TCRβ+) cells recovered from pLNs, mLNs, PPs and spleen of recipient mice are shown as means ± s.e.m. (B, C) Significance of differences were assessed using a two-tailed paired Student’s t-test. Values of p<0.05 were considered as statistically significant (**p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ns, not significant).
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus) | B6.Cg-Foxp3tm1Mal/J | Wang et al. (2008) (PMID: 18209052) | IMSR Cat# JAX:018628, RRID:IMSR_JAX:018628 |
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus) | B6.Cg-Tg(TcraTcrb)425Cbn/J | Barnden et al., 1998(PMID: 9553774) | IMSR Cat# JAX:004194, RRID:IMSR_JAX:004194 |
| Antibody | Alexa Fluor 700-conjugated anti CD45.2 (104) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 560693 |
| Antibody | Allophycocyanin (APC)-conjugated anti-CD25 (PC61) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 561048 |
| Antibody | Allophycocyanin (APC)-conjugated anti-CD44 (IM7) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 561862 |
| Antibody | Brilliant Violet (BV) 421-conjugated anti Ly-6C (AL-21) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 562727 |
| Antibody | BV 510-conjugated anti-CD4 (RM4-5) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 563106 |
| Antibody | BV 786-conjugated anti-CD25 (PC61) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 564023 |
| Antibody | Phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated anti-CD25 (PC61) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 561065 |
| Antibody | Phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated anti-CD69 (H1.2F3) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 553237 |
| Antibody | Phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated anti-Izumo1r (TH6) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 560320 |
| Antibody | Phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated anti-TCRgd (GL3) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 553178 |
| Antibody | Phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated anti-Vb5.1/5.2 (MR9-4) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 553190 |
| Antibody | PE-Cy7-conjugated anti-CD44 (IM7) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 560569 |
| Antibody | PE-Cy7-conjugated anti-CD45.1 (A20) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 560578 |
| Antibody | Biotinylated anti-CD5 (53–7,3) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 553019 |
| Antibody | Biotinylated anti-CD62L (MEL14) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 553149 |
| Antibody | Biotinylated anti-Ly-6C (AL-21) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 557359 |
| Antibody | Biotinylated anti-Sca1 (E13-161.7) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 553334 |
| Antibody | Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated anti-IL18ra (BG/IL18ra) | BioLegend | Cat# 132903 |
| Antibody | APC-conjugated streptavidin | BioLegend | Cat# 405207 |
| Antibody | BV 421-conjugated anti-Ly-6C (HK1.4) | BioLegend | Cat# 128032 |
| Antibody | PE-conjugated anti-Ly-6C (HK1.4) | BioLegend | Cat# 128008 |
| Antibody | Alexa 448-conjugated anti-NFAT2 (7A6) | BioLegend | Cat# 649603 |
| Antibody | Alexa 448-conjugated anti-NFAT1 (D43B1) | Cell Signaling | Cat# 14324 |
| Antibody | PE-conjugated anti-CD200 (OX-90) | eBioscience | Cat# 12-5200-82 |
| Antibody | PE-conjugated anti-Ikzf3 (8B2) | eBioscience | Cat# 12-5789-80 |
| Antibody | PE-conjugated anti-Nur77 (12.14) | eBioscience | Cat# 12-5965-82 |
| Antibody | PerCP-Cy5.5-conjugated anti-TCRb (H57-597) | eBioscience | Cat# 45-5961-82 |
| Antibody | Biotinylated anti-CD73 (eBioTY/11.8) | eBioscience | Cat# 14-0731-82 |
| Antibody | APC-conjugated anti-Foxp3 (FJK-165) | eBioscience | Cat# 12-5773-82 |
| Antibody | PE-conjugated anti-Foxp3 (FJK-165) | eBioscience | Cat# 17-5773-82 |
| Antibody | Pacific Blue-conjugated streptavidin | Invitrogen | Cat# S11222 |
| Antibody | APC-Vio770-conjugated anti-CD8a (53–6.7) | Miltenyi Biotec | Cat# 130-102-305 |
| Antibody | PE-conjugated anti-CD122 (TM-b1) | Miltenyi Biotec | Cat# 130-102-569 |
| Chemical compound, drug | Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) | Calbiochem | CAS 16561-29-8 |
| Chemical compound, drug | FK506 (tacrolimus) | Sigma Aldrich | CAS 109581-93-3 |
| Chemical compound, drug | CellTrace Violet | Invitrogen | Cat# C34557 |
| Chemical compound, drug | CellTrace Far Red | Invitrogen | Cat# C34564 |
| Chemical compound, drug | Recombinant Mouse IL-7 | R and D Systems | Cat# 407 ML-025 |
| Chemical compound, drug | Thapsigargin | Calbiochem | CAS 67526-95-8 |
| Chemical compound, drug | TGFβ1 | Invitrogen | Cat# PHG9204 |
| Chemical compound, drug | DRAQ5 | Cell Signaling | Cat# 4084 |
| Chemical compound, drug | Indo-1, AM | Invitrogen | Cat# I1223 |
| Software, algorithm | Illustrator CS5 | Adobe Systems Inc. | http://www.graphpad.com |
| Software, algorithm | GeneChip Scanner 3000 7G | Affymetrix | N/A |
| Software, algorithm | Expression Console | Affymetrix | https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ |
| Software, algorithm | DIVA8.0.1 | BD Biosciences | N/A |
| Software, algorithm | R | Bioconductor | N/A |
| Software, algorithm | Prism 7 | GraphPad | N/A |
| Software, algorithm | ImageJ | NIH | https://www.bioconductor.org/ |
| Software, algorithm | Partek Genomics Suite | Partek | N/A |
| Deposited data | GSE14308 | Wei et al. (2009), PMID: 19144320 | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE14308 |
| Deposited data | GSE42276 | Wakamatsu et al. (2013), PMID: 23277554 | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE42276 |
| Deposited data | GSE67464 | Bevington et al., 2016, PMID: 26796577 | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE67464 |
| Deposited data | GSE70154 | Richards et al. (2015), PMID: 26195815 | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE70154 |
| Deposited data | GSE62532 | Vahl et al. (2014), PMID: 25464853 | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE62532 |
| Deposited data | GSE97477 | This paper | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE97477 |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.27215.017





