Differential requirements of androgen receptor in luminal progenitors during prostate regeneration and tumor initiation
Figures
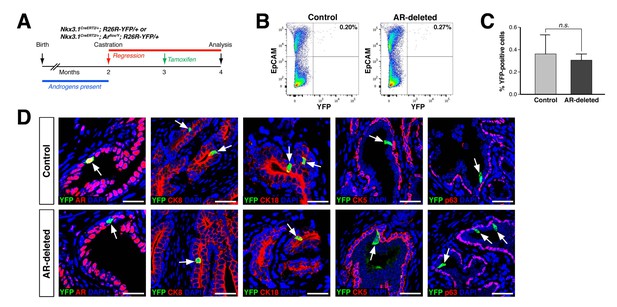
CARNs remain luminal after AR deletion.
(A) Time course for lineage-marking of CARNs and inducible AR deletion using castrated and tamoxifen-treated control Nkx3.1CreERT2/+; R26R-YFP/+ mice and Nkx3.1CreERT2/+; Arflox/Y; R26R-YFP/+ mice. (B) FACS analyses of lineage-marked YFP+ cells in total EpCAM+ epithelial cells. (C) Percentage of YFP+ cells among total epithelial cells in castrated and tamoxifen-induced Nkx3.1CreERT2/+; R26R-YFP/+ controls and Nkx3.1CreERT2/+; Arflox/Y; R26R-YFP/+ mice. Error bars represent one standard deviation; the difference between groups is not significant (p=0.51, independent t-test). (D) Expression of AR, luminal markers (CK8 and CK18), and basal markers (CK5 and p63) in lineage-marked CARNs (top) and AR-deleted CARNs (bottom). Note that all lineage-marked cells express luminal but not basal markers (arrows). Scale bars in D) correspond to 50 μm.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Quantitation of CARNs and AR-deleted CARNs in vivo.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28768.004
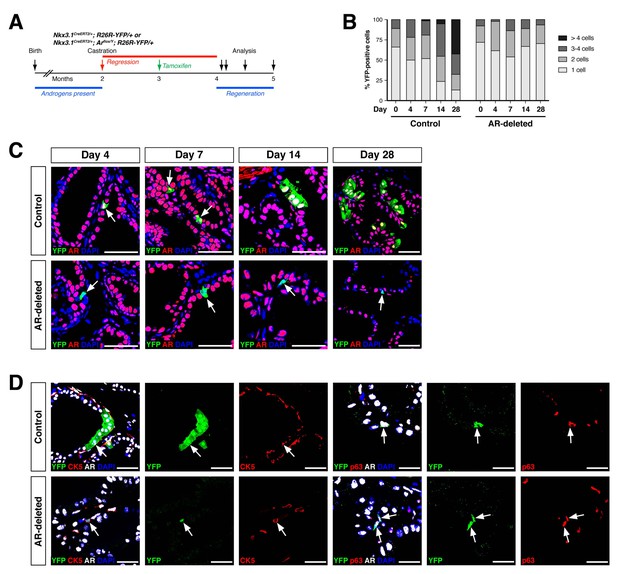
AR-deleted CARNs fail to generate lineage-marked cell clusters but remain bipotential during androgen-mediated regeneration.
(A) Time course for lineage-marking and androgen-mediated regeneration. (B) Percentage of single YFP+ cells or YFP+ clusters of 2 cells, 3–4 cells, and >4 cells at 4, 7, 14, and 28 days of androgen-mediated regeneration. This analysis does not include YFP+AR+ cells that fail to undergo AR deletion in the experimental mice; full quantitation of all cell populations is provided in Figure 2—source data 1. (C) YFP+ cells (arrows) in prostates of mice with lineage-marked CARNs (top) and AR-deleted CARNs (bottom) at days 4, 7, 14 and 28 days during androgen-mediated regeneration. (D) Identification of basal YFP+ cells (arrows) as progeny of CARNs (top) or AR-deleted CARNs (bottom). Scale bars in C) and D) correspond to 50 μm.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Quantitation of YFP+ cells during regeneration.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28768.006
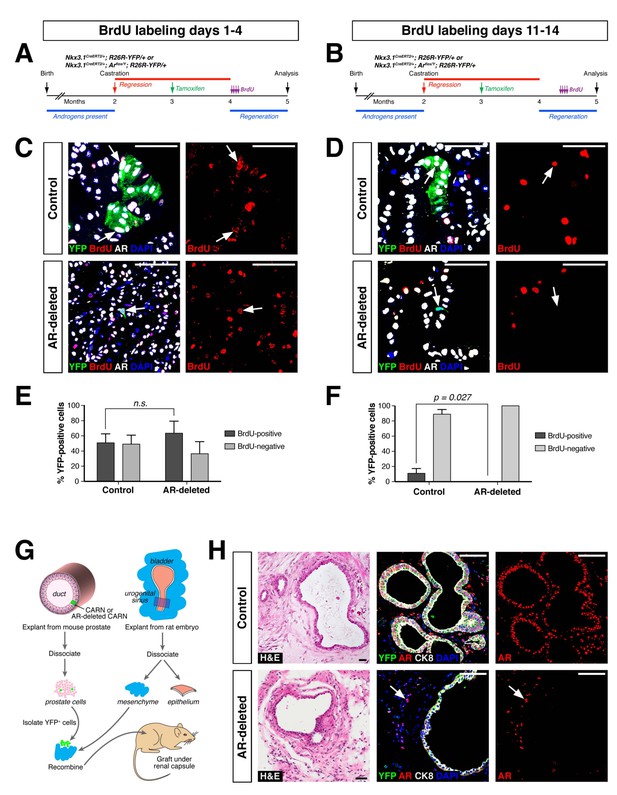
AR-deleted CARNs and/or their progeny have defects in proliferation during regeneration and in renal grafts.
(A,B) Time course of BrdU incorporation during androgen-mediated regeneration of castrated and tamoxifen-treated control Nkx3.1CreERT2/+; R26R-YFP/+ mice and Nkx3.1CreERT2/+; Arflox/Y; R26R-YFP/+ mice. BrdU injections were performed during either days 1 through 4 (A) or days 11 through 14 (B), followed by analysis at 28 days. (C) Identification of BrdU+YFP+ cells (arrows) in control (top) and AR-deleted (bottom) prostate tissue after administration of BrdU during early stages of regeneration. (D) YFP-positive cells in control prostate tumors (top) can incorporate BrdU (arrow) but not in AR-deleted prostate tumors (bottom), after administration of BrdU during later stages of regeneration. (E,F) Percentage of BrdU+ and BrdU– cells among total YFP+ cells after injection of BrdU from days 1 through 4 (E) or days 11 through 14 (F) of regeneration. Error bars represent one standard deviation; the difference in (E) is not statistically significant (p=0.34, independent t-test), but is significant in (F) (p=0.027, independent t-test). This analysis excludes YFP+AR+ cells that fail to undergo AR deletion in the experimental mice; full quantitation of all cell populations is provided in Figure 3—source data 1. (G) Schematic depiction of tissue recombination of lineage-marked CARNs with rat urogenital mesenchyme followed by renal grafting. (H) Analysis of grafts generated from lineage-marked CARNs (top) and AR-deleted CARNs (bottom); arrows in bottom panels indicate AR-expressing stromal cells surrounding the AR-negative prostate duct. Scale bars in C), D) and H) correspond to 50 μm.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Quantitation of BrdU incorporation and renal grafting data.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28768.008
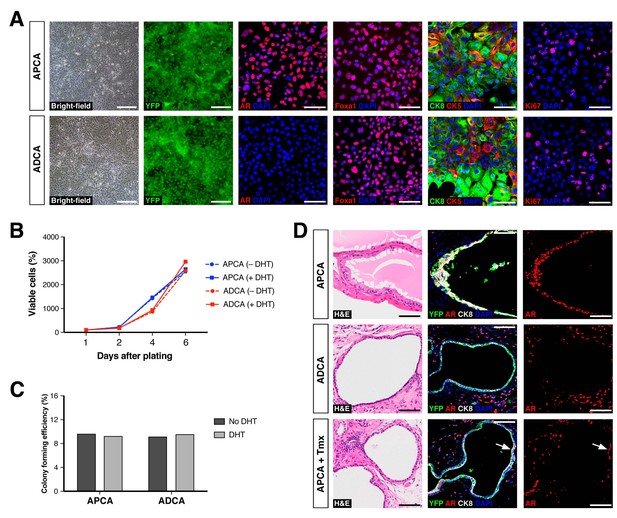
Properties of cell lines established from CARNs and AR-deleted CARNs.
(A) Morphology and marker expression of cell lines derived from single YFP+ cells from castrated and tamoxifen-treated control Nkx3.1CreERT2/+; R26R-YFP/+ mice and Nkx3.1CreERT2/+; Arflox/Y; R26R-YFP/+ mice. The APCA lines (top) and ADCA lines (bottom) show similar bright-field morphology, expression of YFP, Foxa1, and Ki67, as well as co-expression of CK8 and CK5, but differ in expression of AR. (B) APCA and ADCA cell lines display similar cell growth at days 1, 2, 4, and 6 after plating in the absence or presence of DHT, as assessed by CellTiter-Glo assay. Results shown are from a single experiment with five technical replicates and are representative of two biological replicates after normalization with day 0 luminescent signal. (C) Colony formation by APCA and ADCA cell lines in the absence or presence of DHT. Results are from a single experiment with three technical replicates and are representative of two biological replicates. (D) Renal grafts generated from tissue recombinants of 100,000 APCA or ADCA cells with rat urogenital mesenchyme, and analyzed at 12 weeks. Bottom row shows APCA grafts treated with tamoxifen for 4 days at 7 weeks of growth to induce Ar deletion (bottom); arrows indicate cells that did not undergo Ar deletion after tamoxifen treatment. Scale bars in A) and D) correspond to 50 μm.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Epithelial cell lines established from mouse and human prostate tissue.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28768.011
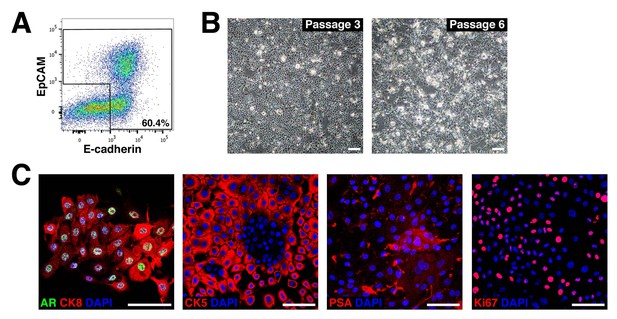
Establishment of novel human prostate epithelial cell lines.
(A) Flow-sorting strategy to eliminate EpCAM–E-cadherin– cells from dissociated benign human prostate epithelial cells obtained from radical prostatectomies. (B) Bright-field images of a human prostate epithelial cell line at passages 3 and 6. (C) HPE cells broadly express AR and both luminal (CK8) and basal (CK5) markers, and have more limited expression of PSA and Ki67. Scale bars in B) correspond to 100 μm, and in C) to 50 μm.
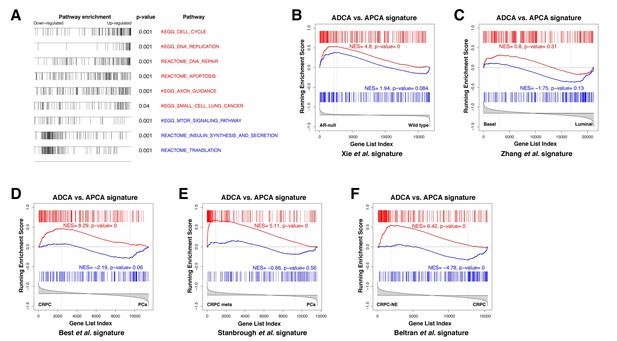
Gene set enrichment analysis of the ADCA signature.
(A) Selected biological pathways that are enriched in the ADCA versus APCA signature. (B) GSEA plot showing enrichment in the positive tail for a signature of AR-null mouse prostate epithelial cells. (C) Cross-species GSEA showing lack of enrichment with a signature based on isolated human prostate basal and luminal epithelial populations. (D–F) Cross-species GSEA comparing the ADCA expression signature with three independent expression signatures based on tumor samples from human patients. NES: normalized enrichment score; p-value is calculated using 1000 gene permutations.
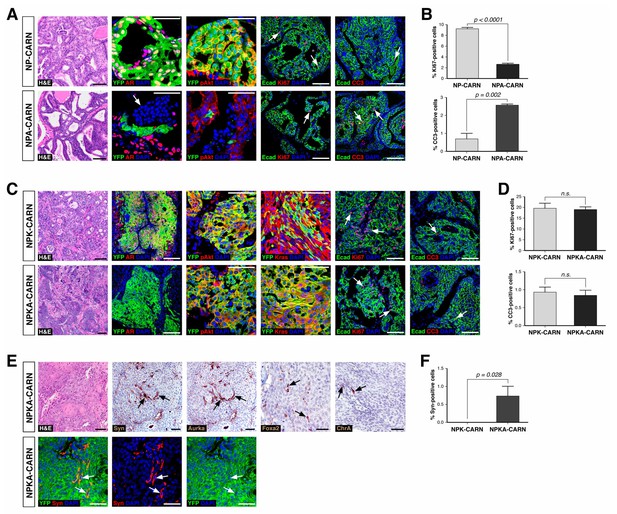
Deletion of AR alters the ability of CARNs to serve as a cell of origin for prostate cancer.
(A) Prostate histology and marker expression in Nkx3.1CreERT2/+; Ptenflox/flox; R26R-YFP/+ (NP-CARN) and Nkx3.1CreERT2/+; Ptenflox/flox; Arflox/Y; R26R-YFP/+ (NPA-CARN) mice that have been castrated and tamoxifen-treated, followed by androgen-mediated regeneration for 1 month. Shown are representative images for hematoxylin-eosin staining (H and E) and immunofluorescence for YFP, AR, phospho-Akt (pAkt), E-cadherin (Ecad), Ki67, and cleaved caspase-3 (CC3). Arrows indicate occurrence of cell death (YFP/AR in NPA-CARN), proliferation (Ecad/Ki67), and apoptosis (Ecad/CC3). (B) Quantitation of Ki67+ and CC3+-positive cells in total Ecad+ epithelial cells in NP-CARN and NPA-CARN prostates. Error bars represent one standard deviation; differences between groups are statistically significant as determined by independent t-test. (C) Prostate tumor histology and marker expression in Nkx3.1CreERT2/+; Ptenflox/flox; KrasLSL-G12D/+; R26R-YFP/+ (NPK-CARN) and Nkx3.1CreERT2/+; Ptenflox/flox; KrasLSL-G12D/+; Arflox/Y; R26R-YFP/+ (NPKA-CARN) mice that have been castrated and tamoxifen-treated, followed by androgen-mediated regeneration for 1 month. Arrows indicate cells undergoing proliferation (Ecad/Ki67) and apoptosis (Ecad/CC3). (D) Quantitation of Ki67+ and CC3+-positive cells in total Ecad+ epithelial cells in NPK-CARN and NPKA-CARN prostates. Differences between groups are not statistically significant as determined by independent t-test (Ki67, p=0.724; CC3, p=0.507). (E) Focal neuroendocrine differentiation in NPKA-CARN tumors. Shown are H and E and immunohistochemical staining (IHC) of serial sections for Synaptophysin (Syn) and Aurora kinase A (Aurka), IHC for Foxa2 and Chromogranin A (ChrA), as well as immunofluorescence for YFP and Syn shown as an overlay and as individual channels; arrows indicate positive cells. (F) Quantitation of Syn+ cells in total epithelial cells in NPK-CARN and NPKA-CARN tumors. Scale bars for H and E and IHC in A, C,) and E) correspond to 100 μm, and in other panels to 50 μm.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Tumor phenotypes and marker quantitation.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28768.014
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain (M. musculus) | NOG | PMID: 15879151 | NOD.Cg-Prkdcscid Il2rgtm1Sug/JicTac | Taconic (Hudson, NY) |
| Strain (M. musculus) | Nkx3.1CreERT2 | PMID: 19741607 | Nkx3-1tm4(CreERT2)Mms | established by Shen lab |
| Strain (M. musculus) | Ptenflox | PMID: 11691952 | C;129S4-Ptentm1Hwu/J | JAX #004597 (Bar Harbor, ME) |
| Strain (M. musculus) | KrasLSL-G12D | PMID: 11751630 | B6.129-Krastm4Tyj/Nci | MMHCC #01XJ6 |
| Strain (M. musculus) | ARflox | PMID: 14745012 | B6N.129-Artm1Verh/Cnrm | EMMA #02579 |
| Strain (M. musculus) | R26R-YFP | PMID: 11299042 | B6.129 × 1-Gt(ROSA) 26Sortm1(EYFP)Cos/J | JAX #006148 |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HPE-1 | this work | Adherent cell line established from radical prostatectomy 23 tissue, sorted for EpCAM+Ecad+ cells | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | HPE-2 | this work | Adherent cell line established from radical prostatectomy 23 tissue, sorted for EpCAM+Ecad+ cells | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | HPE-3 | this work | Adherent cell line established from radical prostatectomy 24 tissue, sorted for EpCAM+Ecad+ cells | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | HPE-4 | this work | Adherent cell line established from radical prostatectomy 25 tissue | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | HPE-5 | this work | Adherent cell line established from radical prostatectomy 25 tissue, sorted for EpCAM+Ecad+ cells | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | HPE-6 | this work | Adherent cell line established from radical prostatectomy 25 tissue, sorted for EpCAM+Ecad+Ngfr+ cells | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | HPE-7 | this work | Adherent cell line established from radical prostatectomy 25 tissue, sorted for EpCAM+Ecad+Cd24+ cells | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | HPE-8 | this work | Adherent cell line established from radical prostatectomy 26 tissue | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | HPE-9 | this work | Adherent cell line established from radical prostatectomy 26 tissue, sorted for EpCAM+Ecad+ cells | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | HPE-10 | this work | Adherent cell line established from radical prostatectomy 26 tissue, sorted for EpCAM+Ecad+Cd24+ cells | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | HPE-11 | this work | Adherent cell line established from radical prostatectomy 26 tissue, sorted for EpCAM+Ecad+Agr2+ cells | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | HPE-12 | this work | Adherent cell line established from radical prostatectomy 27 tissue | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | HPE-13 | this work | Adherent cell line established from radical prostatectomy 27 tissue; sorted for EpCAM+Ecad+cells | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | HPE-14 | this work | Adherent cell line established from radical prostatectomy 27 tissue, sorted for EpCAM+Ecad+Cd24+ cells | |
| Cell line (M. musculus) | ADCA-1 | this work | Adherent cell line established from single YFP+ cell isolated from castrated and tamoxifen-treated Nkx3.1CreERT2/+; Arflox/Y; R262R-YFP/+ mouse with deletedAr (recombined) allele | |
| Cell line (M. musculus) | ADCA-2 | this work | Adherent cell line established from single YFP+ cell isolated from castrated and tamoxifen-treated Nkx3.1CreERT2/+; Arflox/Y; R262R-YFP/+ mouse with deletedAr (recombined) allele | |
| Cell line (M. musculus) | APCA-1 | this work | Adherent cell line established from single YFP+ cell isolated from castrated and tamoxifen-treated Nkx3.1CreERT2/+; Arflox/Y; R262R-YFP/+ mouse with intact Ar (non-recombined) allele | |
| Cell line (M. musculus) | APCA-2 | this work | Adherent cell line established from single YFP+ cell isolated from castrated and tamoxifen-treated Nkx3.1CreERT2/+; Arflox/Y; R262R-YFP/+ mouse with intact Ar (non-recombined) allele | |
| Antibody | Androgen receptor (AR) | Sigma (St. Louis, MO) | A9853 | |
| Antibody | Cytokeratin 8 (CK8) | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank (Iowa City, IA) | TROMA-1 | |
| Antibody | Cytokeratin 18 (CK18) | Abcam (Cambridge, MA) | ab668 | |
| Antibody | Cytokeratin 5 (CK5) | Covance (San Diego, CA) | SIG3475 | |
| Antibody | Cytokeratin 5 (CK5) | Covance | PRB-160P | |
| Antibody | p63 | Santa Cruz (Dallas, TX) | sc-8431 | |
| Antibody | GFP | Abcam | ab13970 | |
| Antibody | GFP | Roche (St. Louis, MO) | 11814460001 | |
| Antibody | BrdU | AbD Serotec MCA (Hercules, CA) | 2060 | |
| Antibody | Foxa1 | Abcam | ab55178 | |
| Antibody | Ki67 | eBiosciences (San Diego, CA) | 14–5698, clone SolA15 | |
| Antibody | Cleaved-caspase-3 (CC3) | BD Pharmingen (San Jose, CA) | 559565 | |
| Antibody | Prostate specific antigen (PSA) | Dako (Santa Clara, CA) | M0750, clone ER-PR8 | |
| Antibody | Kras | Abcam | ab84573 | |
| Antibody | Synaptophysin (Syn) | BD Transduction Laboratories (San Jose, CA) | 611880 | |
| Antibody | Aurora A (Aurka) | Abcam | ab13824 | |
| Antibody | Chromogranin A (ChrA) | Abcam | ab15160 | |
| Antibody | Foxa2 | Abnova (Taiwan) | H00003170-M12 | |
| Antibody | AMACR | Zeta Corp (Arcadia, CA) | Z2001 | |
| Antibody | EpCAM | BioLegend | 118214 | |
| Antibody | E-cadherin | eBiosciences | 46-3249-82 | |
| Antibody | Nerve growth factor receptor (Ngfr) | BioLegend | 345108 | |
| Antibody | Cd24 | BioLegend | 311008 | |
| Antibody | Anterior gradient 2 (Agr2) | Abcam | ab1139894 | |
| Antibody | EpCAM | BioLegend | 324208 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Nkx3.1 wild-type primers | PMID: 19741607 | DOI 10.1038/nature08361 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Nkx3.1CreERT2 primers | PMID: 19741607 | DOI 10.1038/nature08361 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | CreERT2 primers | PMID: 19741607 | DOI 10.1038/nature08361 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | R262R-YFP primers | PMID: 11299042 | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | Ptenflox primers | PMID: 11691952 | DOI: 10.1126/science.1065518 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Pten wild-type primers | PMID: 11691952 | DOI: 10.1126/science.1065518 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | KrasLSL-G12D primers | PMID: 11751630 | DOI:10.1101/gad.943001 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Kras wild-type primers | PMID: 11751630 | DOI:10.1101/gad.943001 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Arflox primers | PMID: 14676301 | DOI: 10.1084/jem.20031233 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Ar wild-type primers | PMID: 14676301 | DOI: 10.1084/jem.20031233 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Arflox (recombined) primers | PMID: 14676301 | DOI: 10.1084/jem.20031233 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Arflox (not recombined) primers | PMID: 14676301 | DOI: 10.1084/jem.20031233 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Tyramide amplification | ThermoFisher Scientific (Waltham, MA) | T20922 | |
| Ccommercial assay or kit | Tyramide amplification | ThermoFisher Scientific | T30953 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Tyramide amplification | ThermoFisher Scientific | T30954 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Tyramide amplification | ThermoFisher Scientific | T20926 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Tyramide amplification | ThermoFisher Scientific | T20912 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | ABC Elite | Vector Labs (Burlingame, CA) | pk6101 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Citrate-based antigen unmasking solution | Vector Labs | H3300 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Tris-based antigen unmasking solution | Vector Labs | H3301 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | NovaRED | Vector Labs | SK3800 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | CellTiter-Glo 3D | Promega (Madison, Wi) | G9681 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | MagMAX−96forMicroarrays Total RNA Isolation Kit | Ambion (Waltham, MA) | Am1839 | Used the ‘no spin’ protocol for RNA purification |
| Commercial assay or kit | TruSeq Stranded mRNA library prep kit | Illumina (San Diego, CA) | 20020595 | Library preparation was performed by the Columbia Genome Center using Illumina kits |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tissue Tek OCT compound | VWR Scientific (Radnor, PA) | 25608–930 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Glutamax | Invitrogen (Waltham, MA) | 35050061 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tamoxifen; TM | Sigma | T5648-5G | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Gentamicin | Invitrogen | 15750–060 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Collagenase/hyaluronidase | STEMCELL Technologies (Cambridge, MA) | 07912 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Modified Hank's Balanced Salt Solution; HBSS | STEMCELL Technologies | 37150 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dnase I | STEMCELL Technologies | 07900 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Y-27632 ROCK inhibitor | STEMCELL Technologies | 72307 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 10x Earle's Balanced Salt Solution | ThermoFisher Scientific | 14155063 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Hepatocyte medium supplemented withepidermal growth factor (EGF) | Corning (Corning, NY) | 355056 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Matrigel | ThermoFisher Scientific | 354234 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 0.25% trypsin-EDTA | STEMCELL Technologies | 07901 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | FBS | ThermoFisher Scientific | 12676029 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DMEM/F12 | ThermoFisher Scientific | 11320033 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | BrdU | Sigma | B5002 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dispase | STEMCELL Technologies | 07913 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dihydrotestosterone; DHT | Sigma | A8380 | |
| Software, algorithm | Real time analysis; RTA | Illumina | https://support.illumina.com/sequencing/sequencing_software/real-time_analysis_rta.html | Base calling using this software was performed by the Columbia Genome Center |
| Software, algorithm | bcl2fastq2 | Illumina | Ilumina: version 2.17 | The sequencing data was trimmed and converted to fastq format by the Columbia Genome Center |
| Software, algorithm | Spliced Transcripts Alignment to a Reference (STAR) | PMID: 23104886 | Github: version 2.5.2b | Sequencing reads mapping to mouse genome (USCS/mm10) was performed by the Columbia Genome Center |
| Software, algorithm | FeatureCounts | PMID: 24227677 | subread.sourceforge.net version: v1.5.0-p3 | Sequencing reads mapping to mouse genome (USCS/mm10) was performed by the Columbia Genome Center |
| Software, algorithm | R-studio 0.99.902, R v3.3.0 | The R Foundation for Statistical Computing, ISBN 3-900051-07-0 | v3.3.0 | R language for statistical computing was used for data analysis and visualization |
| Software, algorithm | homoloGene | NCBI | ||
| Software, algorithm | Gene Set Enrichment Analysis | PMID: 16199517 | DOI 10.1073/pnas.0506580102 | GSEA was used to compares differential gene expression signatures |
| Software, algorithm | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences; SPSS, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, Arcsine transformation, Welch t-test, Fisher's Exact Test | IBM SPSS Statistics | ||
| Software, algorithm | Histological grading of mouse prostate phenotypes | PMID: 12163397 | DOI 10.1016/S0002-9440 (10)64228-9 | |
| Other | Mini-osmotic pump | Alzet (Cupertino, CA) | 0000298 | |
| Other | 40 µm cell strainer | Falcon (Corning, NY) | Fisher Scientific 352340 | |
| Other | 96-well Primaria plate | Corning | Fisher Scientific 353872 | |
| Other | 6-well Primaria plate | Corning | Fisher Scientific 353846 | |
| Other | 96-well CELLSTAR plate | Greiner Bio-One (Monroe, NC) | 655090 | |
| Other | Lab-Tek Chamber Slide | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 154534 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Primers and antibodies used in this study.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28768.015
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28768.016





