Sequestration and activation of plant toxins protect the western corn rootworm from enemies at multiple trophic levels
Figures
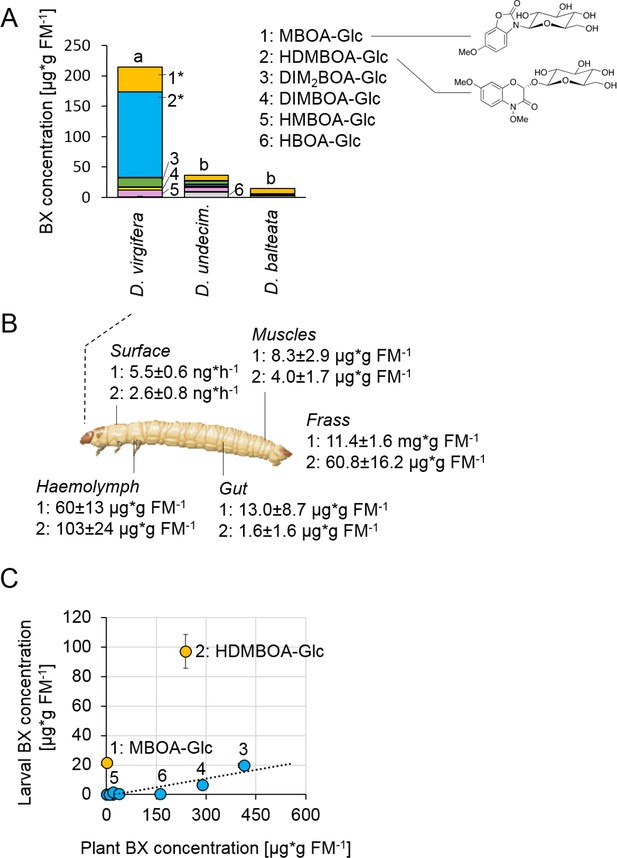
Diabrotica virgifera specifically and actively sequesters maize benzoxazinoids (BXs) (Figure 1—figure supplements 1–3).
(A) BX concentration in larvae of the specialist D. virgifera, and the generalists D. undecimpunctata (D.undecim.) and D. balteata. Numbers denote the six most abundant BXs. Stars indicate significant differences between species (one-way ANOVA on transformed data (rank and square root transformations), *p<0.05). (B) BX concentrations in the haemolymph, gut, muscles, exudates (surface), and frass of D. virgifera larvae fed on wild-type B73 plants. (C) Correlation between BX concentrations in maize B73 plants and in third instar D. virgifera larvae that fed on those plants since hatching. Unlabeled blue dots correspond to other types of BXs. A linear regression between plant and larval concentrations is shown (R2 = 0.8141, p=0.004, excl. MBOA-Glc and HDMBOA-Glc). Means ± SE are shown. Raw data are available in Figure 1—source data 1.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Diabrotica virgifera sequesters maize benzoxazinoids.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29307.007
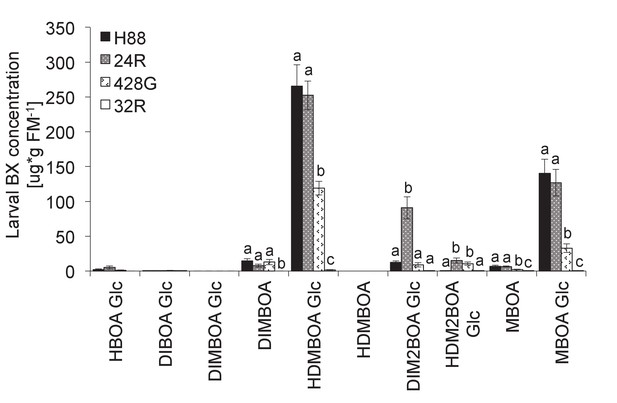
Benzoxazinoid levels in Diabrotica virgifera larvae fed on different maize lines.
H88 corresponds to the wild type, 428G to the original bx1 mutant, 24R to an igl mutant and 32R to a 100% BX-deficient bx1.igl double mutant (see [29]). Means ± SE are shown. Letters indicate significant differences between genotypes (one-way ANOVAs, p<0.05). No BXs were detected in larvae fed on 32R.
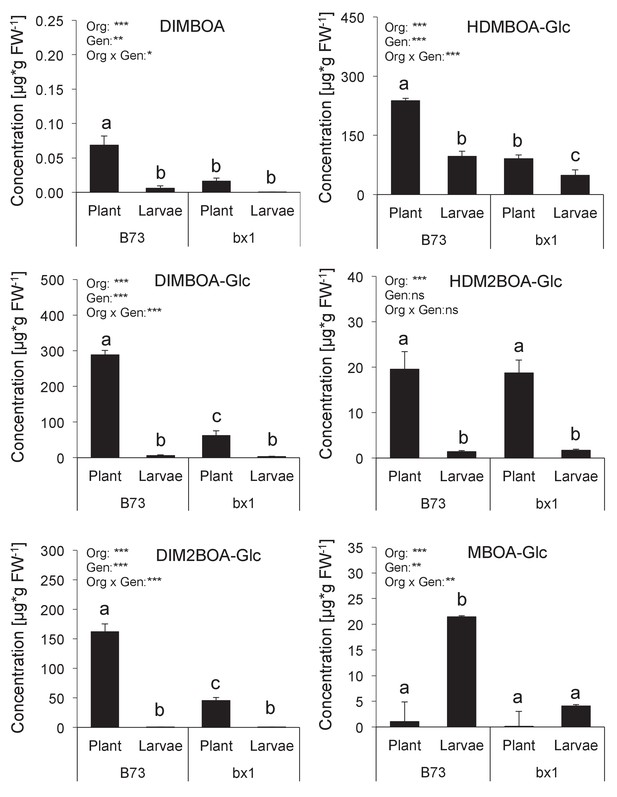
Benzoxazinoid levels in Diabrotica virgifera larvae fed wild-type (B73) and bx1 (bx1:B73) mutant plants.
Means ± SE are shown. Results of two-way ANOVAs are shown (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001). Letters indicate significant differences between genotypes (post-hoc test, p<0.05).
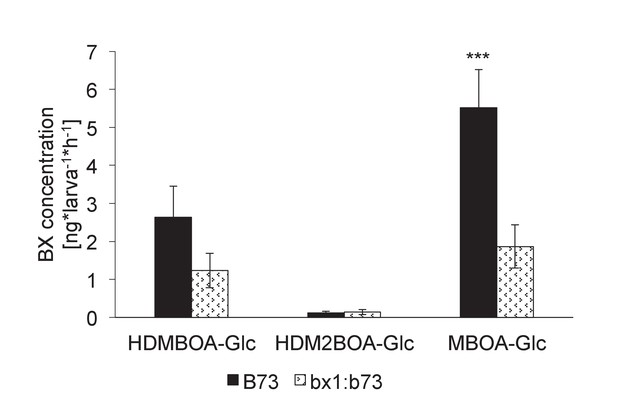
Benzoxazinoid levels in aqueous surface extracts of Diabrotica virgifera larvae fed on wild-type (B73) and bx1 (bx1:B73) mutant plants.
Means ± SE are shown. Stars indicate significant differences between genotypes (Student t-test, p<0.001).
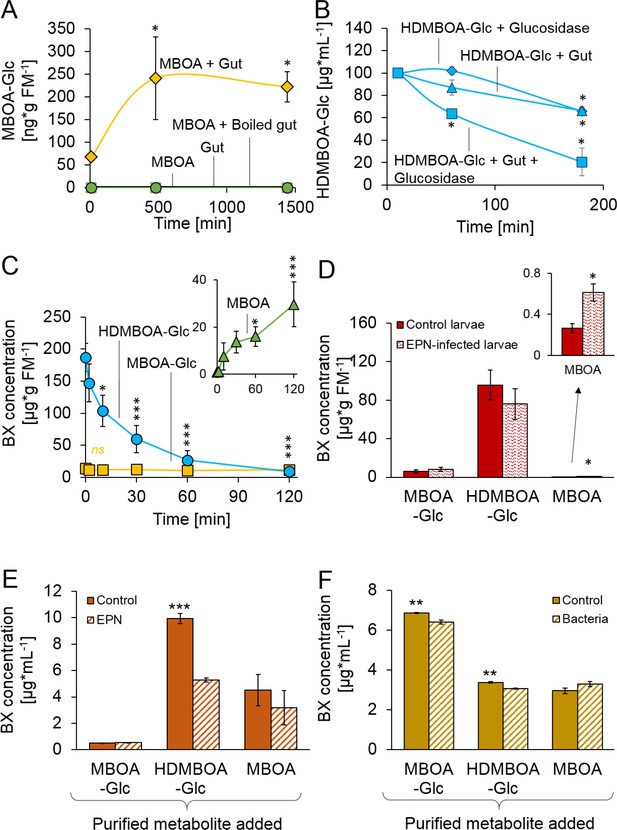
Stabilization and reactivation of stored benzoxazinoids (BXs) by Diabrotica virgifera and its natural enemies (Figure 2—figure supplement 1).
(A) Stabilization of MBOA by conversion to MBOA-Glc in D. virgifera gut extracts. (B) HDMBOA-Glc deglucosylation in D. virgifera gut extracts. (C) BX reactivation in D. virgifera larvae upon mechanical tissue disruption. (D) BX reactivation in D. virgifera larvae upon exposure to the entomopathogenic nematode (EPN) Heterorhabditis bacteriophora. (E) BX reactivation by H. bacteriophora 24 hr after addition of purified metabolites. (F) BX reactivation by the EPN endosymbiotic bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens 24 hr after addition of purified metabolites. Means ± SE are shown. Stars indicate significant differences between time points (repeated measures ANOVAs, A–C) or between treatments (Student’s t-tests, D-F; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001). Raw data are available in Figure 2—source data 1.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Diabrotica virgifera stabilizes and reactivates stored benzoxazinoids.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29307.010
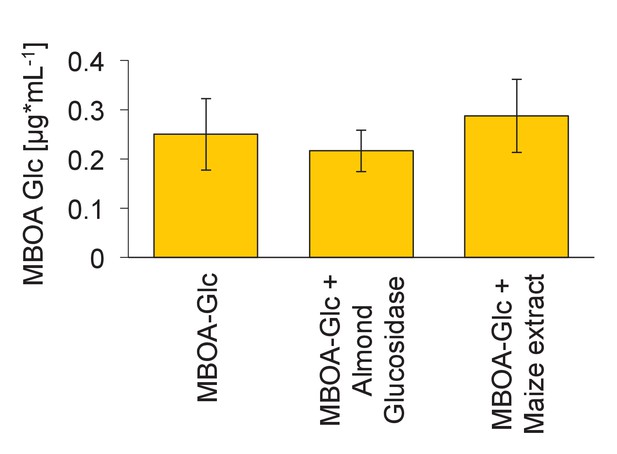
Degradation of MBOA-Glc by plant-derived hydrolases.
MBOA-Glc concentrations upon incubation with a broad-spectrum almond glucosidase (CAS Nr. 9001-22-3) and with root extracts of a benzoxazinoid-free maize seedling (32R). Means ± SE are shown. No significant change in MBOA-Glc was observed (one-way ANOVA).
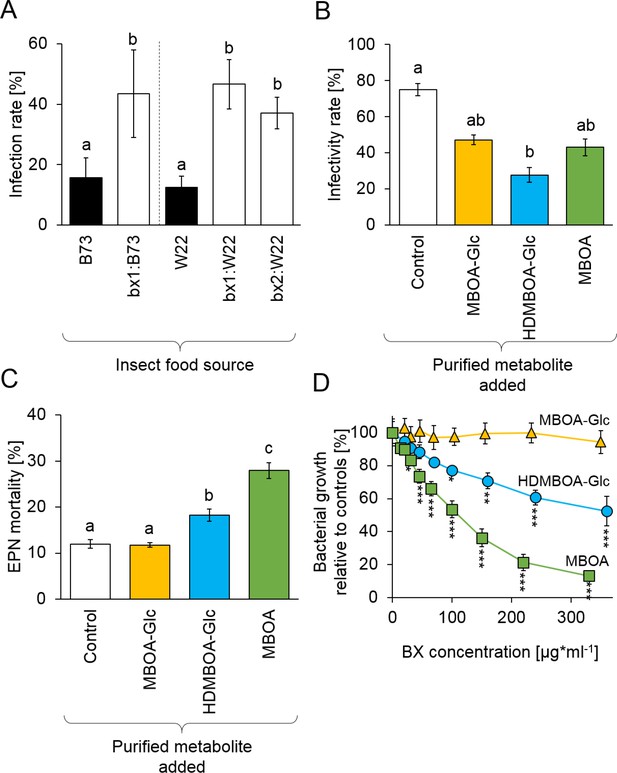
Benzoxazinoids (BXs) protect Diabrotica virgifera from its natural enemies (Figure 3—figure supplement 1).
(A) Infection success by the entomopathogenic nematode (EPN) Heterorhabditis bacteriophora on D. virgifera larvae fed on WT (B73 and W22) or BX-deficient (bx1:B73, bx1:W22, bx2:W22) plants. (B) Effect of 7 days exposure to BXs on H. bacteriophora infectivity. (C) Effect of 7 days exposure to BXs on H. bacteriophora mortality. (D) Effect of BXs on the growth of the symbiotic entomopathogenic bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens. Different letters indicate significant differences between plant genotypes. Means ± SE are shown. Stars indicate significant differences between concentrations (A-C: one-way ANOVA, D: repeated measures ANOVA, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001). Raw data are available in Figure 3—source data 1.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Benzoxazinoids protect Diabrotica virgifera from its natural enemies.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29307.013
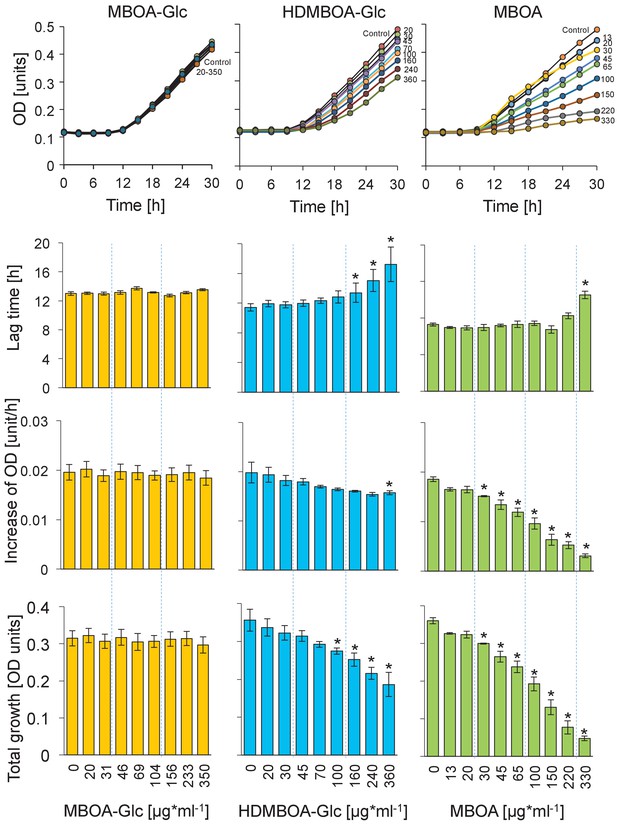
Growth curves and growth characteristics of Photorhabdus luminescens EN01 upon exposure to MBOA-Glc, HDMBOA-Glc and MBOA at different concentrations.
Means ± SE are shown. Stars indicate significant differences between genotypes (repeated measures ANOVAs, p<0.05).
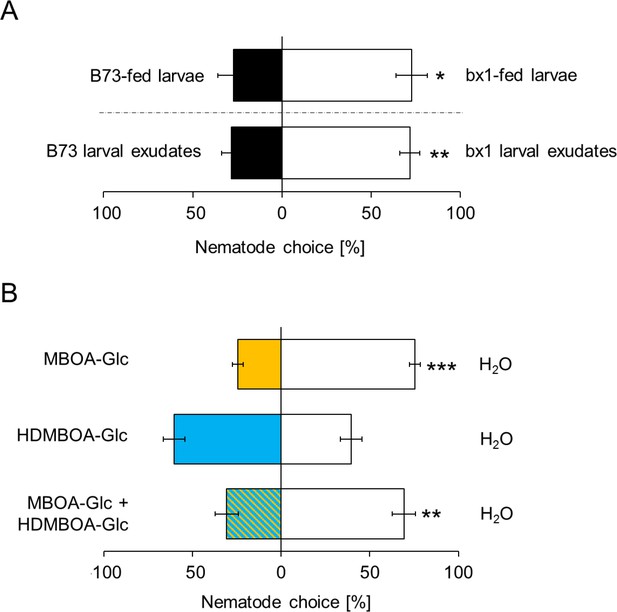
MBOA-Glc decreases the attractiveness of Diabrotica virgifera larvae.
(A) Attraction of the entomopathogenic nematode (EPN) Heterorhabditis bacteriophora to D. virgifera larvae fed on wild-type (B73) and bx1-mutant (bx1:B73) (top) and aqueous surface extracts of larvae fed on wild type and bx1-mutant (bottom). (B) H. bacteriophora attraction to pure MBOA-Glc and HDMBOA-Glc at physiological concentrations. Means ± SE are shown. Letters indicate significant differences between treatments (one sample t-tests, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001). Raw data are available in Figure 4—source data 1.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
MBOA-Glc decreases the attractiveness of Diabrotica virgifera larvae.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29307.015
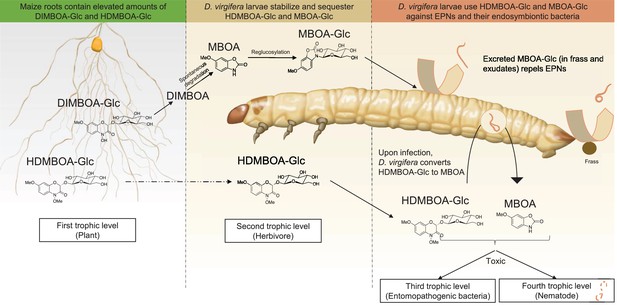
A model illustrating how BX sequestration and activation of plant toxins protects Diabrotica virgifera larvae from their enemies at multiple levels.
MBOA-Glc, released in the frass and on the exoskeleton, repels infective juvenile entomopathogenic nematodes. Upon infection by nematodes and their symbiontic entomopathogenic bacteria, HDMBOA-Glc is activated to produce MBOA. Both HDMBOA-Glc and the activated MBOA reduce the growth of the symbiotic bacteria and kill EPNs.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
List of BX abbreviations.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29307.017
-
Supplementary file 2
Summary statistics.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29307.018
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29307.019





