Transcription-factor-dependent enhancer transcription defines a gene regulatory network for cardiac rhythm
Figures
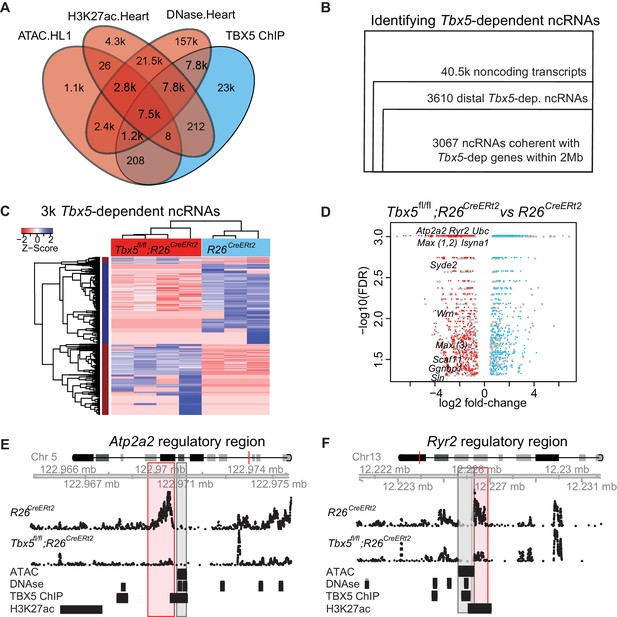
TF-dependent noncoding transcription defines regulatory elements.
(A) Venn-diagram of peak call overlaps for HL-1 ATAC-sequencing (ATAC.HL1), histone 3 lysine 27 acetylation in mouse heart (H3K27ac.Heart, GSE52123), DNase hypersensitivity in mouse heart (DNase.heart, ENCODE) and TBX5 ChIP-seq (TBX5.HL1, GSE21529). (B) Workflow for identifying TF-dependent ncRNAs. Total noncoding transcripts from mouse left atrium were narrowed to Tbx5-dependent distal intergenic ncRNAs, defined as >1 kbp away from the known transcriptional start sites of known coding genes (GENCODE mm10), and narrowed again to coherent changes with nearby Tbx5-dependent genes within a 2-Mbp window. (C). Heatmap of identified Tbx5-dependent ncRNAs in Tbx5fl/fl;R26CreERt2 (red, left) and corresponding R26CreERt2 control (blue, right) in left atrial tissue. The hierarchical cluster analysis is based on the Euclidean distances of normalized sequencing counts. 1577 Tbx5-activated ncRNAs were downregulated after Tbx5 deletion and 1490 Tbx5-repressed ncRNAs were upregulated after Tbx5 deletion across n = 5 and n = 3 resp. (D) Volcano-plot of significantly misregulated TF-dependent ncRNAs, select identifications were labeled by nearest TBX5-dependent gene. Plot of log2 fold-change of ncRNAs in Tbx5fl/fl;R26CreERt2 compared to R26CreERt2 vs –log10 false discovery rate (FDR) for the same comparison (FDR < 0.05, |FC| > 2). The ncRNAs within 2 Mb of coherently mis-expressed TBX5-dependent genes are red or blue for activated and repressed, respectively. Gray dots represent those ncRNAs without coherently mis-expressed coding genes in the 2-Mb window. (E, F) Example genomic views of two of the most significantly TF-dependent ncRNAs, adjacent to the Atp2a2 (E) and Ryr2 (F) genes, respectively. Top track is chromosomal location, followed by the ncRNA read density from R26CreErt2control and Tbx5fl/fl;R26CreERt2. Below is ATAC-Seq peak call in HL-1 cells, cardiac DNase hypersensitivity (ENCODE), TBX5 ChIP-seq (GSE21529) and cardiac H3k27 acetylation (GSE52123). The identified differential ncRNA is marked in the red box, and the putative regulatory element, as defined by the enhancer marks above, is marked in the gray box.
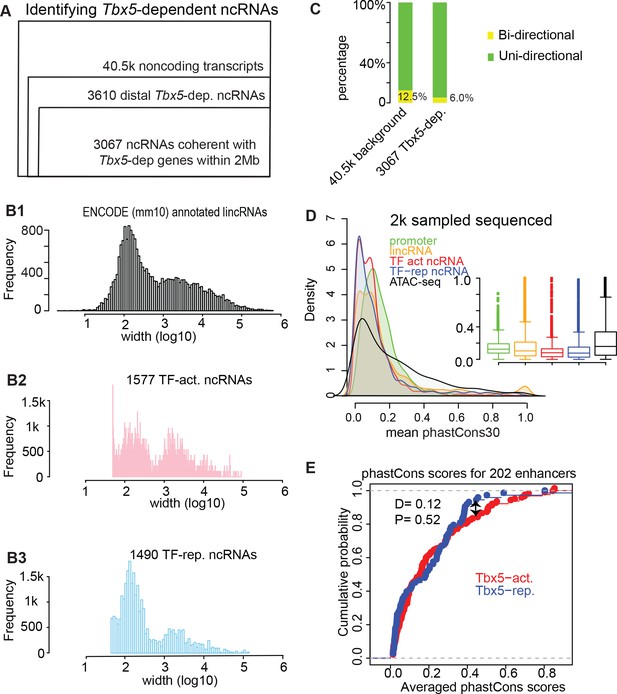
Genomic features of the identified TF-dependent ncRNAs recapitulate known features of annotated lincRNAs.
(A) Pie chart showing the composition for the identified TBX5-dependent ncRNAs using de novo assembly (Cufflinks). The 3067 ncRNAs were categorized into six groups. GENCODE (mm10)-annotated ncRNAs with relatively few instances were grouped together as ‘predicted ncRNAs’. De novo indicates a previously unannotated noncoding transcript. (B) Histogram distribution of the ncRNA width on log10 scale. The distribution of GENCODE annotated lincRNAs (B1), the identified TF-activated ncRNAs (B2), and the TF-repressed ncRNAs (B3) are shown. (C) Stacked bar-graphs showing percentage of unidirectional (green) and bi-directional (yellow) noncoding transcripts among the total noncoding transcript calls, the Tbx5-activated ncRNAs, and the Tbx5-repressed ncRNAs. (D) Histograms and boxplots of average phastCons30 sequence conservation scores for promoter regions (green), GENCODE annotated lincRNAs (yellow), TBX5-activated and TBX5-repressed ncRNAS (red and blue, respectively), and ATAC-Seq (black). (E) Two-sample Kolmogorov–Smirnov statistics. The cumulative probabilities exhibit no difference in conservation between Tbx5-activated and Tbx5-repressed cis-regulatory elements (red and blue lines, respectively).
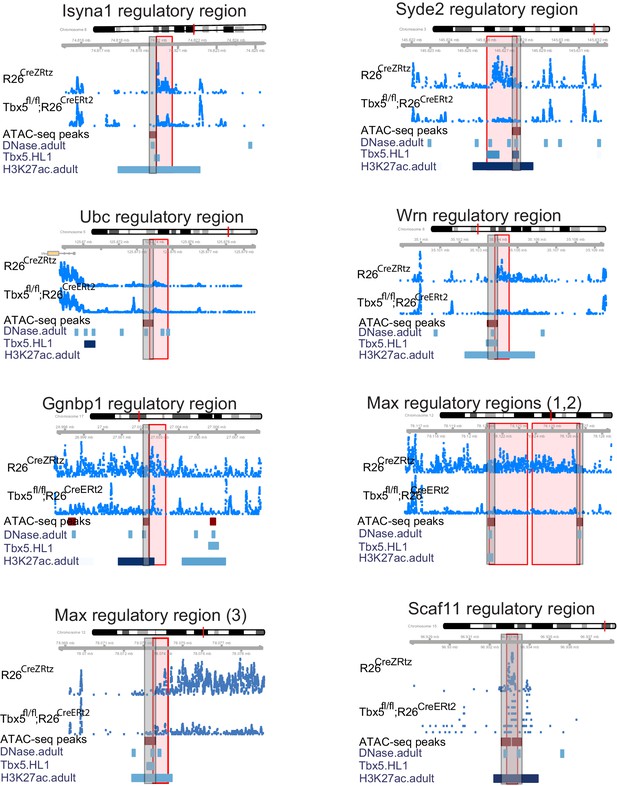
Genomic view of nine TF-dependent ncRNAs (mm9).
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are labeled by nearest TBX5-dependent coding gene. Top track is chromosomal location, followed by the ncRNA read density from R26CreErt2 control and Tbx5fl/fl;R26CreERt2. Below is ATAC-Seq peak call in HL-1 cells, cardiac DNase hypersensitivity (ENCODE), TBX5 ChIP-seq (GSE21529) and cardiac H3k27 aAcetylation (GSE52123). The identified differential ncRNA is marked in the red box, the putative regulatory element as defined by the enhancer marks above is in the gray box.
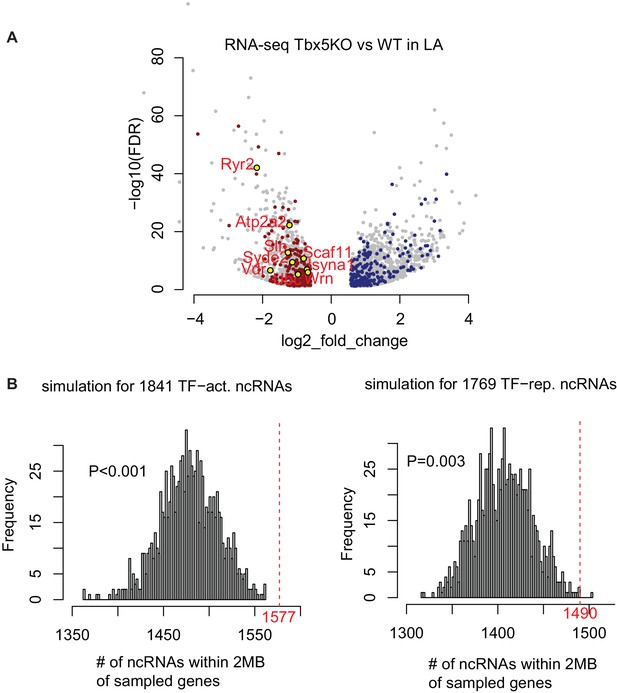
Identifying TF-dependent ncRNA targets from TF-dependent expressed genes.
(A) TF-dependent genes are coherent with TF-dependent ncRNAs. Volcano-plot of TF-dependent genes (FDR < 0.05, |FC| > 1.5). Genes residing within 2 Mb of coherently TBX5-dependent ncRNAs are colored red for Tbx5-activated, blue for Tbx5-repressed ncRNAs. (B) Simulation study shows the empirical significance of Tbx5-dependent ncRNAs within a 2-Mb window of Tbx5-dependent coding-genes. The histograms show the distribution of randomly sampled ncRNAs within 2 Mb window of randomly sampled genes. The red dashed line showing the observed number iof Tbx5-activated or Tbx5-repressed ncRNAs, respectively. An empirical P-value was calculated.
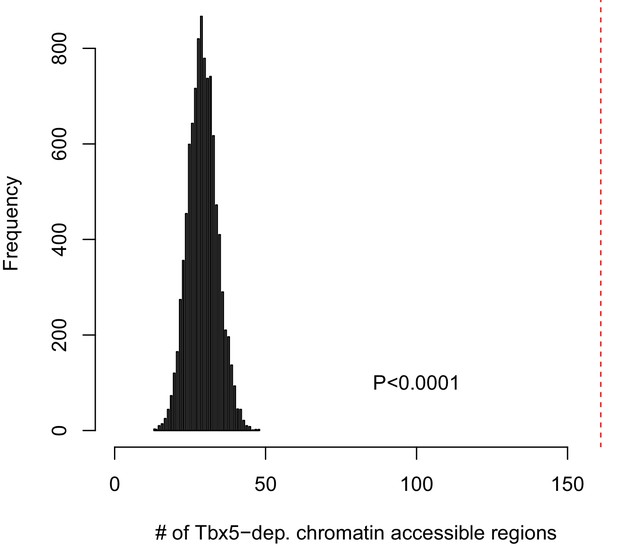
Identifying TF-dependent ncRNA targets from open chromatin regions.
161 Tbx5-dependent ncRNAs at open chromatin regions were determined by the overlap between ncRNAs and ATAC peaks (allowing up to 500-bp edge-to-edge distance). The empirical significance of Tbx5-dependent ncRNAs at open chromatin regions was determined by comparing the observed overlap (161 ncRNAs) with that estimated by simulation using randomly sampled noncoding transcripts within this distance to total open chromatin regions. The histogram shows the distribution of the number of regions with overlap from each simulation, performed 10,000 times. In contrast, the red dashed line shows the observed number for the identified Tbx5-dependent transcripts. In every case, the simulation estimated a lower number, resulting in an empirical P-value (p<0.0001).
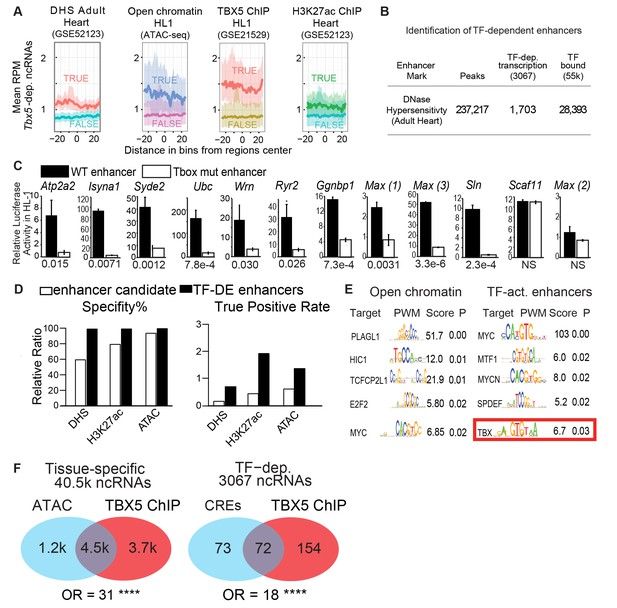
TF-dependent ncRNAs predict functional enhancers.
(A) Meta-gene plot showing reads per million (RPM) of Tbx5-dependent ncRNAs, being divided by enhancer makers DNase Hypersensitivity (DHS), ATAC Sequencing in HL-1 cells, TBX5 ChIP-Seq, and H3K27Ac, respectively. Each subpanel is centered around all Tbx5-dependent ncRNAs, the averaged RPM of the ncRNAs hold an enhancer mark (top line, TRUE) vs those ncRNAs that do not (bottom line, FALSE). (B) Identification TF-dependent ncRNAs associated with cis-regulatory elements (CREs) by overlap with accessible chromatin defined by DNase hypersensitivity. Overlap of ncRNAs ("TF-dep transcription") and TF ChIP ("TF bound"), respectively. (C) Relative luciferase activity of select enhancers identified in HL-1 cardiomyocytes, labeled by nearest TBX5-dependent gene. Activity of wildtype enhancers (black) and T-box mutant enhancers (white) are shown. P-values for statistical comparisons of wildtype vs mutant enhancers are given below each graph. n = 3 each, activity normalized to co-transfected Renilla vector, and to vector with scrambled insert. (D) Predictive specificity and True Positive Rate of enhancer marks alone (white) and when combined with Tbx5-dependent ncRNA (black). Defined enhancers were identified and compared against 240 cardiac and 1162 non-cardiac enhancers reported in the VISTA database. The enhancers were defined by DNase hypersensitivity (DHS), H3K27 acetylation, and open chromatin by ATAC-seq. (E) Motif analysis showing enriched motifs in HL-1 open chromatin (ATAC, left) and ncRNA-defined TBX5-dependent enhancers (right). Motif patterns are presented as position weight matrix (PWM) with enrichment statistics. Enrichment scores >1.5 and p-value <0.05 were considered significant, and the top five most-significant motifs are reported here. (F) Venn diagram of ATAC-seq and TBX5 ChIP-seq in background of ncRNAs (left) and TF-dependent elements overlapped with open chromatin in a background of TF-dep ncRNAs (right). Odds ratios (OR) are given for each background. **** indicates p<1e-10.
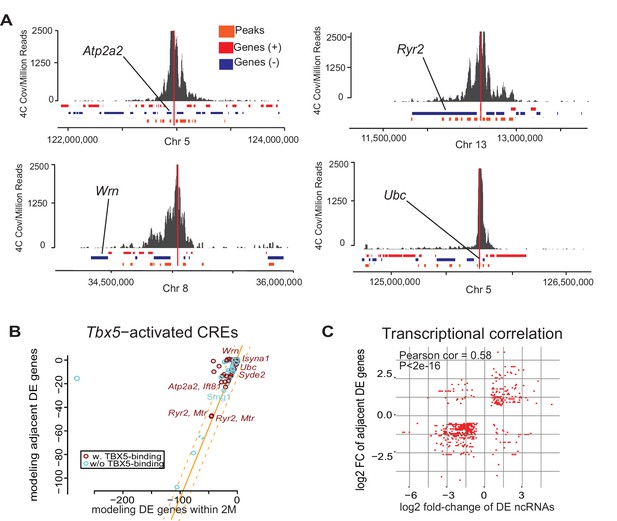
Enhancer transcription mediates target gene expression.
(A) Genomic loci showing circularized chromatin conformation capture (4C) from the viewpoint of four identified regulatory elements (near Atp2a2, Wrn, Ryr2, and Ubc). Total reads (top) and significant contacts (bottom, orange) are plotted. Annotated genes are shown in blue and red (sense and antisense, respectively). The viewpoint is with a dashed red line and the nearest TBX5-dependent target is labeled. (B) Sparse scatterplot for combined Pi-scores calculated from Tbx5-activated enhancers and Tbx5-activated genes. The X-axis is the pi-score using the ‘nearest’ Tbx5-dependent gene, and the Y-axis is the pi-score using all potential TF-dependent gene targets within a 2-Mbp window. The orange line indicates y = x. The dashed lines mark the standard deviations. Example enhancers were labeled with the names of their nearest Tbx5-dependent gene. Red indicates enhancers with TBX5 occupancy, and blue indicates enhancers without TBX5 occupancy as determined by ChIP-seq. (C) Scatterplot in hexagonal binning for the 3067 identified TF-dependent ncRNAs. The X-axis is the differential expression fold change on a log2 scale of these ncRNAs, and the Y-axis is the differential expression fold change on log2 scale of any nearest gene targets. The fold change with the maximum absolute value is used when both neighbor genes are TF-dependent.
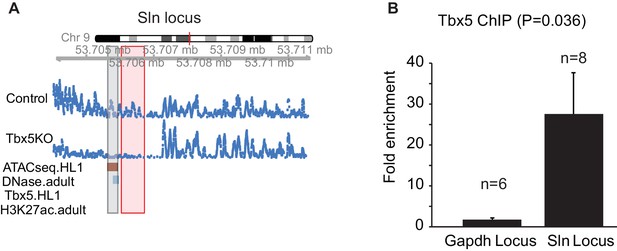
A TBX5-dependent enhancer at Sln that was not identified by TF ChIP-seq.
(A) Genomic view of a Tbx5-activated ncRNA region adjacent to gene Sln. This locus shows significant Tbx5-dependence as determined by transcription expression in mouse atrium, open chromatin detected by ATAC-seq in HL1 cells, DHS signature in adult mice, but not by TBX5 occupancy or H3K27Ac in HL1 cells (GSE21529). (B) ChIP-qPCR of TBX5 comparing this Sln locus with the Gapdh locus. The Sln locus shows enrichment for TBX5 occupancy (n = 8, p=0.036). Two-sided t-test assuming unequal variances was performed.
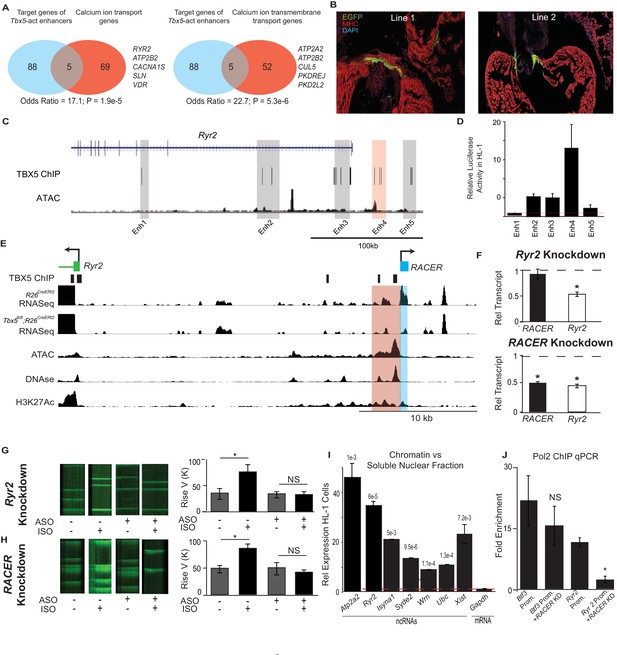
Enhancer-associated ncRNAs at Ryr2 and Atp2a2 are necessary for calcium-handling gene expression and cellular phenotype.
(A) Gene Ontology functional enrichment for gene targets within a 2-Mb window of the TBX5-activated enhancers. Odds Ratio (OR) and P-value of overlap with GO terms ‘Calcium Ion Transport Genes’ and ‘Calcium Ion Transmembrane Transport Genes’. (B) Representative 3 days post fertilization (Dpf) zebrafish embryos injected with a reporter construct containing the wildtype Ryr2 enhancer reporter, showing cardiac EGFP expression. One Representative embryos from two stable lines are also shown (Line 1 and Line 2, one embryo each). Stable lines display EGFP fluorescence in the heart in addition to other tissues (see Supplement). (C) Genomic view of the Ryr2 locus showing four candidate TBX5-dependent regulatory elements identified by TBX5 ChIP-seq (gray) and by RACER expression (Enh 4, red). (D) Relative luciferase activity in HL-1 cardiomyocytes of candidate Ryr2 enhancers, normalized to co-transfected Renilla vector and to a vector with a scrambled insert (n > 3 replicates). (E) Genomic view of the Ryr2 locus, showing identified noncoding RNA Ryr2 Associated Cis- Element RNA (RACER) in blue. A putative regulatory element associated with ncRNA is marked in red. Tracks show TBX5 ChIP (GSE21529), RNASeq from R26CreERt2 and Tbx5fl/fl;R26CreERt2, ATAC-Seq in HL-1 cardiomyocytes, DNASe hypersensitivity (ENCODE), and H3K27 acetylation (GSE52123). (F) Gene expression of Ryr2 mRNA and the RACER transcript after knockdown of Ryr2 mRNA (top) and knockdown of RACER (below). Relative transcript expression (RTE) after mRNA knockdown: 0.52 ± 0.03, p = 5.3E-5, for mRNA; RTE 0.92 ± 0.09, p = 0.43, and 0.82 for RACER. For ncRNA knockdown: RTE 0.44 ± 0.03 for mRNA and 0.45 ± 0.02 for RACER, p = 5.64E-6 and 0.04, respectively. (G, H) Representative calcium transient line scans from control (left) and ASO knockdown (right) HL-1 cardiomyocytes in the presence or absence of isopropteranol (+ISO, –ISO resp) after knockdown of Ryr2 mRNA (top) or RACER (bottom) with antisense oligonucleotides (ASO). Quantification of rise velocity under control and isoproterenol treatments (right). (I) Relative transcript expression of chromatin enriched vs soluble nuclear fractions in HL1 cardiomyocyte cells of several ncRNAs and (as controls) Xist and the Gapdh-coding mRNA transcript. Expression was normalized to 18S ribosomal RNA. P values compared the relative expression in soluble vs nuclear fractions of the ncRNAs and Xist to that of GAPDH mRNA, and were less than Bonferroni corrected p<6e-3 for all ncRNAs. (J) Fold-enrichment of RNA Polymerase 2 (Pol2) occupancy by ChIP at housekeeping gene Btf3 promoter (prom.) and at the Ryr2 promoter in the control (left) and after antisense oligonucleotide knockdown of Ryr2 enhancer ncRNA (ASO, right). Normalized to a control locus near the Gapdh gene.
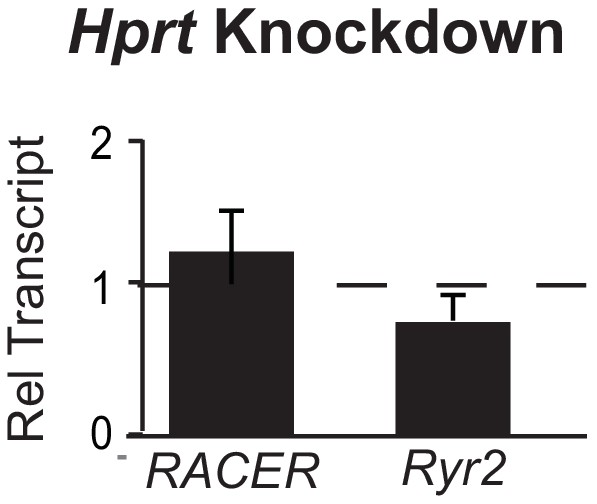
Knockdown of control Hprt locus does not change Ryr2 or RACER expression.
Gene expression of Ryr2 mRNA and RACER transcript after knockdown of Hprt mRNA. Relative transcript expression (RTE) after mRNA knockdown for RACER 1.23 ± 0.25, p = 0.77; for Ryr2 RTE 0.84 ± 0.09, p = 0. 21.
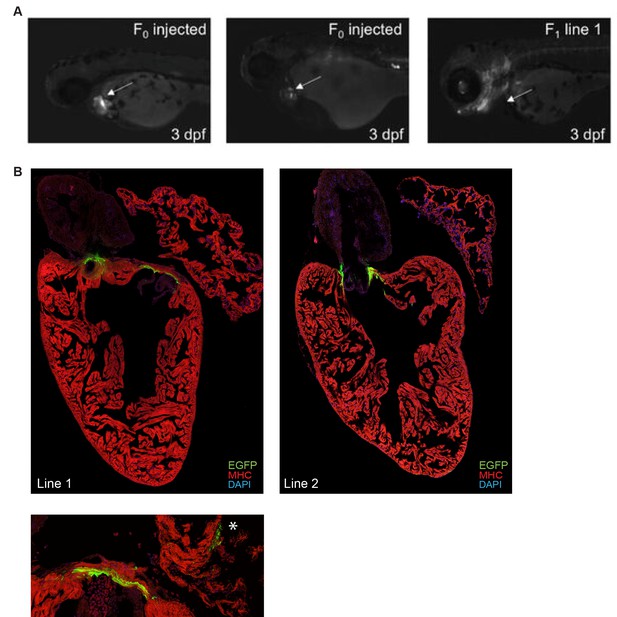
Ryr2 enhancer shows cardiac expression in 3 days post fertilization (dpf) zebrafish.
(A) Representative F0 (left) and F1 (right) 3 dpf zebrafish embryos surviving injection with a reporter construct containing the wildtype Ryr2 enhancer reporter, showing cardiac EGFP expression. Fluorescence was assessed at 3 dpf, after injection of constructs with either wildtype or T-box mutant enhancers. F0 and F1 transgenic zebrafish show cardiac expression of the reporter construct. (B) High-resolution images of stable transgenic zebrafish from two independent lines showing myocardial expression of the wildtype Ryr2 enhancer reporter at 3 dpf. * indicates atrial expression pattern in high-resolution image of line 1 (bottom).

TF-dependent transcription of regulatory elements.
mRNA and enhancer transcription occur in the presence of transcription factor (TBX5) through the Transcription Preinitiation Complex (PIC) (left). Loss of the TBX5 results in decreased PIC complex, leading to decreased enhancer ncRNA (RACER) and mRNA (Ryr2) transcription (right).
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.31683.014





