Two receptor tyrosine phosphatases dictate the depth of axonal stabilizing layer in the visual system
Figures
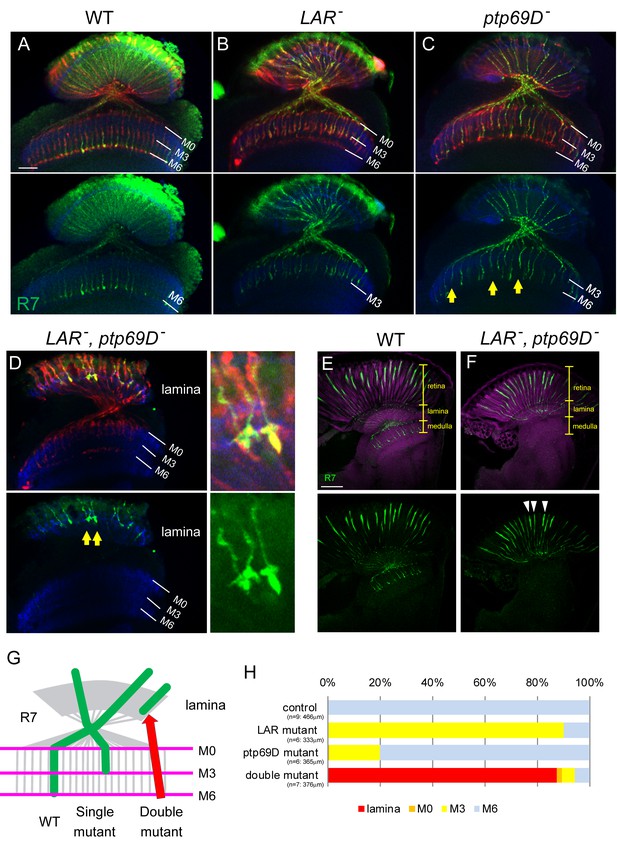
Defects of R7 axons in the Lar, Ptp69D double mutant.
(A–D) Horizontal image of the adult medulla; WT (A), LAR mutant (B), Ptp69D mutant (C) and LAR, Ptp69D double mutant (D). Photoreceptor axons were labeled with mAb24B10 (red), R7 photoreceptor axons with Rh4-mCD8GFP (green), and medulla layers with an antibody to N-Cadherin (blue). Medulla layers are indicated with white lines. In WT, all R7 axons terminated at layer M6 (A). 90% of R7 axons in LAR mutant (B), and 20% of R7 axons in Ptp69D mutant (C, arrows) terminated improperly in layer M3. In Lar, Ptp69D double mutants, R7 axons did not innervate the medulla and instead terminated inside the lamina (D: arrows). The magnified images of R7 terminals are shown on the right side. (E, F) Horizontal agar section of WT (E) and Lar, Ptp69D double mutant (F), labeled with Rh4-mCD8GFP (green) and N-Cadherin (magenta). R7 axons extending from their cell bodies (arrowheads) can be observed in the retina of the double mutant (F). (G) A schematic drawing of the phenotype of R7 axons in single mutants and double mutant of LAR and Ptp69D. (H) Quantification of the R7 axons terminating in each layer for each genotype. The number of axons terminating inside the lamina was estimated. See Methods for quantification details. Scale bars: (A) 20 μm (E) 50 μm.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Excel file compiling source data for the Figure 1H.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.31812.003
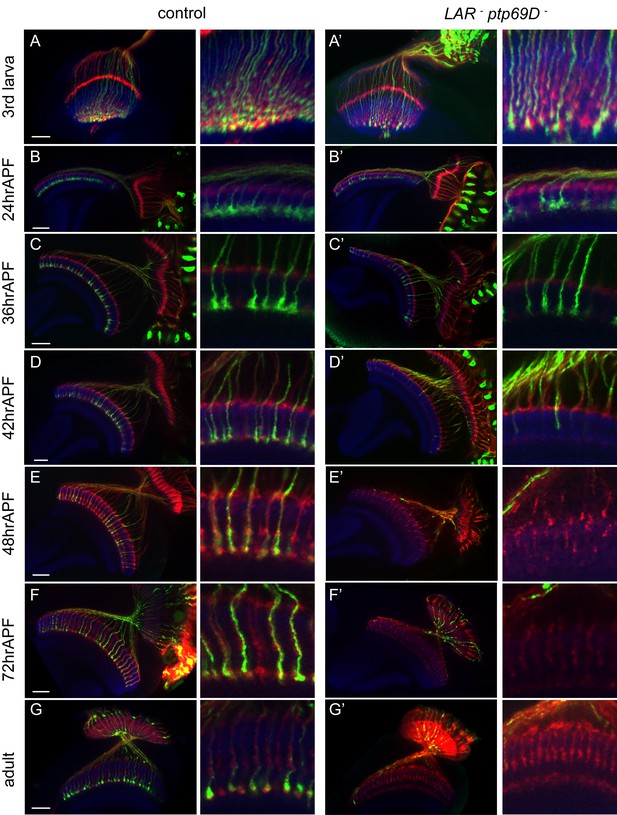
Retraction of R7 axons in the LAR, Ptp69D double mutant.
(A–G’) The R7 axons of control (A–G) and LAR, Ptp69D double heterozygote with double RNAi (A’–G’) during the pupal stage were visualized with mCD8GFP (green) and counterstained with mAb24B10 (red) and N-Cadherin (blue). More than two samples were analyzed for each stage. Higher magnification images are shown on the right side of each panel. In late third instar larvae (A, A’) and pupae at 24hrAPF (B, B’), R7 axons of double mutant reached the R7 temporary layer correctly. At 36hrAPF (C, C’), R7 axon terminals started to get thinner. At 42hrAPF (D, D’), growth cones had collapsed and retraction of R7 axons was observed. At 48hrAPF (E, E’), almost all the R7 axons retracted out of medulla and remained in that location into adulthood (F–G’). Scale bars: 20 μm.
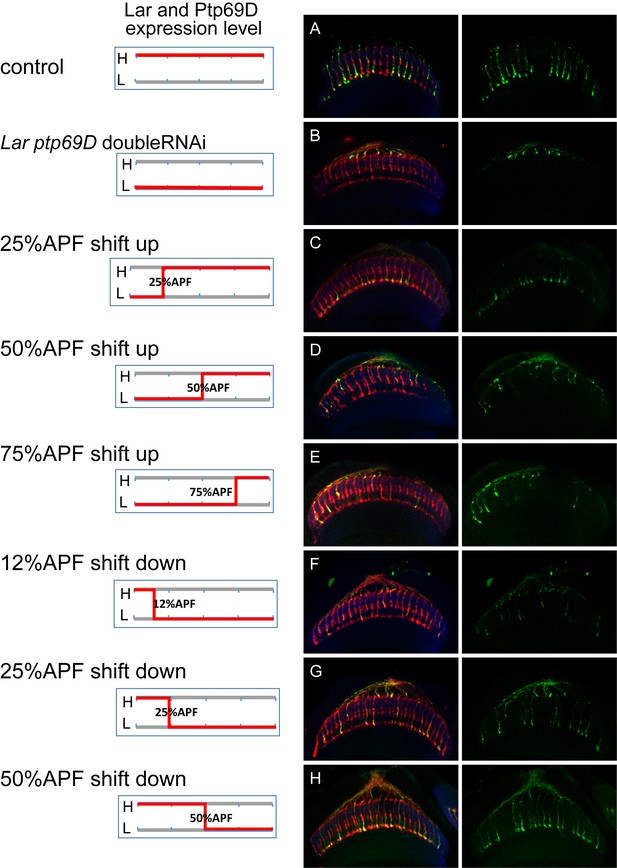
Temporal requirement of LAR and Ptp69D.
(A–H) The expression level of LAR and Ptp69D was manipulated temporally using LAR Ptp69D double RNAi. When LAR and Ptp69D RNAi was expressed simultaneously by GMR-Gal4 together with tub-Gal80[ts], most of the R7 axons terminate at M0 at 27°C (B). (C–E) The temperature was changed from 27°C to 18°C at 25% (C), 50% (D) and 75% APF (E) to shift up the expression in the later stages. (F–H) The temperature was changed from18°C to 27°C at 12% (F), 25% (G) and 50%APF (H) to shift down the expression in the later stages. The phenotype of double RNAi was observed when the expression level was reduced between 25% to 50% APF, indicating two phosphatases are functioning during this period.
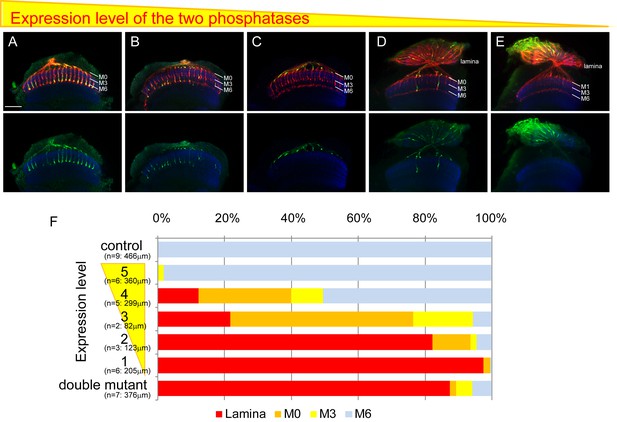
Final stabilizing layer determinations by LAR and Ptp69D.
(A–E) Genetic manipulation using a temperature sensitive Gal80ts system driving RNAi expression was employed to manipulate the cumulative expression level of LAR and Ptp69D. (A–C) LAR, Ptp69D RNAi transcripts were expressed using the eye specific GMR-Gal4 line and RNAi expression level was controlled using Gal80ts (A: 23°C, B: 25°C, C: 27°C). (D, E) LAR, Ptp69D RNAi was simultaneously expressed using eye specific GMR-Gal4 in the Lar−/+, Ptp69D−/+ background (D: 18°C E: 25°C). Photoreceptor axons are labeled with mAb24B10 (red), R7 photoreceptor axons with Rh4-mCD8GFP (green), and the medulla layers with an antibody to N-Cadherin (blue). The medulla layers are indicated with white lines. (F) Quantification of the R7 axons terminated in each layer. The depths of the R7 axons depicted in A-E were quantified and defined according to expression levels of 5 to 1 (A=5, B=4, C=3, D=2, E=1). The number of axons terminating inside the lamina was estimated as in Figure 1. Scale bar: 20 μm.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Excel file compiling source data for the Figure 3F.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.31812.008
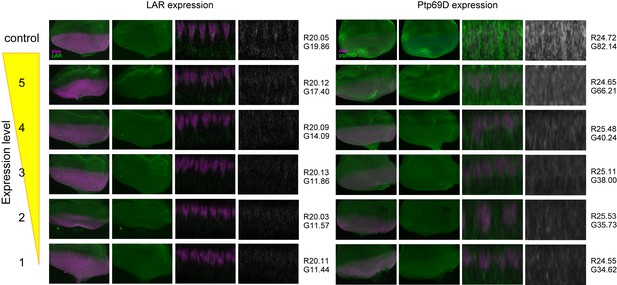
The expression level of LAR and Ptp69D in the fly strain used in Figure 3.
Genetic manipulation using a temperature sensitive Gal80ts system driving RNAi expression was employed to manipulate the cumulative expression level of LAR and Ptp69D. The expression level of LAR and Ptp69D in the fly strain used in Figure 3 was assessed by the antibody staining against third instar larval eye-discs (green). The nuclei of photoreceptors were labeled with anti-Elav antibody (magenta). Maximum intensity projection and cross section images of eye-discs are shown. The intensity of the images of cross section was measured using Photoshop. First, the intensity of the images was normalized with red anti-Elav staining (mean average intensity value was set to around 20 for LAR and 25 for Ptp69D. The exact values are shown on the right side of the each panel after R). Then, the average intensity value for green channel (LAR or Ptp69D protein) was measured and indicated after G. The intensities of both LAR and Ptp69D staining decreased as expected from the genotype.
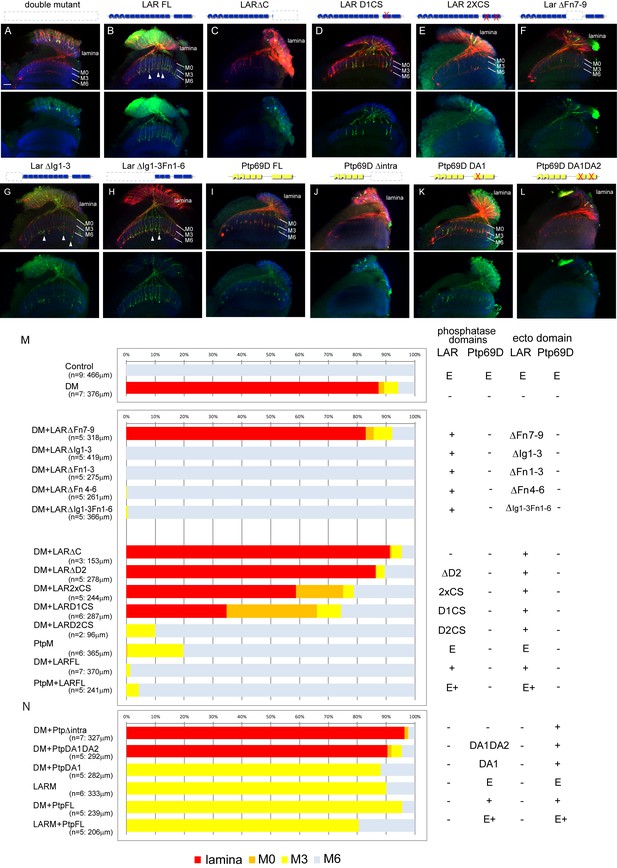
Specificity of RPTP signaling in R7 stabilization.
(A–L) Horizontal images of the medulla of LAR, Ptp69D adult double mutant that also harbored the indicated transgene expressed using the GMR-Gal4 driver. Photoreceptor axons are labeled with mAb24B10 (red), R7 photoreceptor axons with Rh4-mCD8GFP (green), and the medulla layer with an antibody to N-Cadherin (blue). Medulla layers are indicated with white lines. R7 axon retraction in the Lar, Ptp69D double mutant eye (A) is almost completely rescued with full length Lar (LARFL), (B) but this is not the case if the intracellular domain (LARΔC) (C) or the extracellular FNIII 7–9 domains are deleted (LARΔFn7-9) (F). Lar constructs without activity from either the first phosphatase domain (LARD1CS) (D) or both phosphatase domains (LAR2XCS) (E) conveyed partial rescue. LAR constructs without extracellular Ig1-3 domains fully rescued R7 phenotype (G), and presence of extracellular FNIII 7–9 (LARΔIg1-3ΔFn1-6) was sufficient to rescue the double mutant phenotype (H). Notably, the constructs without Ig domains caused some R7 axons to overextend beyond M6 layer (arrowheads in G and H). Expressing either full length Ptp69D (PTP69D FL) (I) and Ptp69D lacking the first phosphatase domain (Ptp69D DA1) (K) rescued R7 retraction in Lar, Ptp69D double mutant axons to the Lar single mutant levels, but with termination in layer M3. Expression of Ptp69D lacking the intracellular domain (Ptp69DΔintra) (J) or both phosphatase activity (Ptp69D DA1DA2) (L) did not rescue the double mutant phenotype at all. (M, N) Quantification of R7 terminations in each layer for each of the indicated LAR (M) or Ptp69D (N) rescue transgenes. Abbreviations: DM stands for Lar, Ptp69D double mutant, PtpM for Ptp69D mutant, and LARM for Lar mutant. The transgenes of Ptp69D are abbreviated as ‘Ptp’. On the right side of the graph, composition of the intracellular phosphatase domains and ectodomain are indicated. ‘E’ stands for endogenous protein and ‘+' represents overexpression by GMR-Gal4. The number of axons terminating inside the lamina was estimated as in Figure 1. Scale bar: 20 μm.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Excel file compiling source data for the Figure 4M and N.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.31812.012
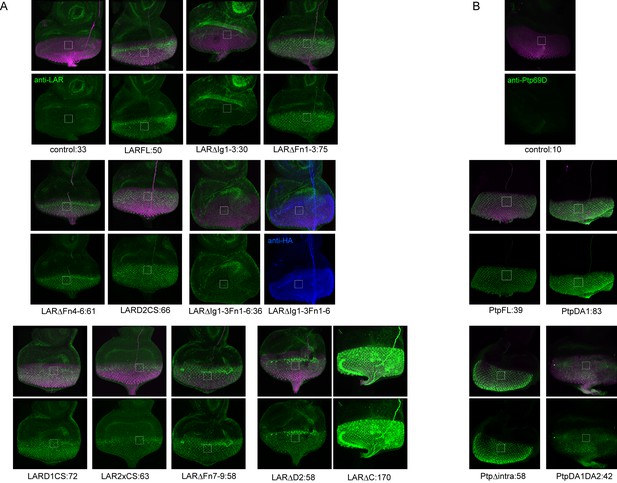
The expression level of LAR and Ptp69D transgenes used in Figure 4.
The expression level of transgenes used for rescue experiments in Figure 4 was evaluated. Each UAS-transgene was crossed to GMR-Gal4 and larval eye-discs were stained with anti-LAR antibody (green in A) or anti-Ptp69D antibody (green in B). The flies also carry GMR-myrRFP to label the photoreceptor cells (magenta). The intensity of the staining was normalized by the intensity of the antennal-disc where GMR-Gal4 is not expressed (around 35 for LAR and 3 for Ptp69D). The mean average intensity value of green channel inside the white square is shown below each panel after the transgene name, indicating the expression level of each transgene. (A) The staining with LAR antibody revealed that the intensity of endogenous LAR level is around 30. All transgenes had higher intensity than 50 except for the ones lacking Ig domains (ΔIg1-3 and ΔIg1-3ΔFn1-6). Since LARFL which had a full rescue showed 50, such expression level was probably sufficient for the rescue. We speculate that the lack of detection against transgenes without Ig domains is because the LAR antibody was raised against the Ig domains. In fact, LARΔIg1-3ΔFn1-6 which also has HA tag was strongly detected by HA antibody (shown in blue). Genetically, both LARΔIg1-3 and LARΔIg1-3ΔFn1-6 fully rescued the double mutant phenotype (Figure 4G, H and M) supporting the idea that they were expressed sufficiently. We also noticed that the antibody against LAR has different sensitivity in staining against UAS-LARΔC used in (Maurel-Zaffran et al., 2001) and others made in (Krueger et al., 2003) probably due to polymorphism. Overall data suggest that the expression level does not correlate with the rescuing ability of the transgenes. (B) The staining with Ptp69D antibody revealed that all four Ptp69D transgenes had high expression levels compared to the control without transgene.
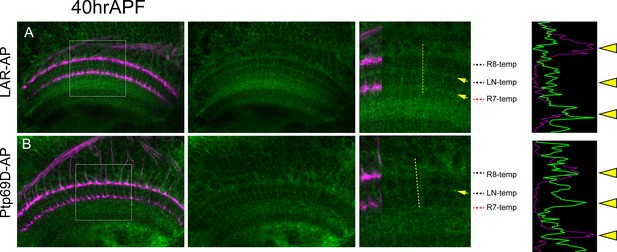
Layer-specific binding of LAR and Ptp69D extracellular domain.
(A) The extracellular domain of LAR fused to PLAP sequence was applied to the agarose section of 40hrAPF wild type pupae. LAR-AP staining was detected in R7 temporary layer and the layer between R7 and R8 temporary layer (arrows). The histogram of the intensity along the dotted yellow line is shown on the right side, supporting the high detection at R7 temporary layer. (B) The extracellular domain of Ptp69D fused to PLAP sequence was applied to the agarose section of 40APF wild type pupae. Ptp69D-AP staining was detected in the layer between R7 and R8 temporary layer but staining was weak at R7 temporary layer. The histogram of the intensity also indicates the low detection at R7 temporary layer.
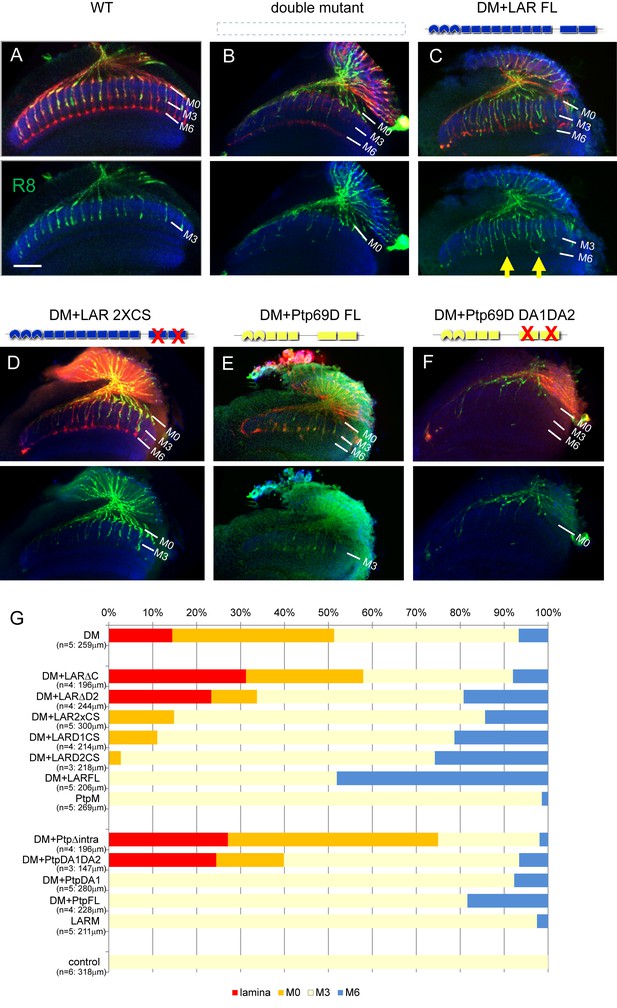
Specificity of RPTP signaling in R8 axons.
(A–F) Horizontal images of adult medulla of LAR, Ptp69D double mutants also harboring the indicated transgene expressed under the GMR-Gal4 driver. Photoreceptor axons were labeled with mAb24B10 (red), R8 photoreceptor axons with Rh6-mCD8GFP (green), and the medulla layer with antibodies to N-Cadherin (blue). Medulla layers are indicated with white lines. The R8 axons in control flies terminated in M3 layer (A). In Lar, Ptp69D double mutant, more than half of the R8 axons terminated at the surface of the medulla M0 or the lamina (B). The R8 axon defects in double mutant were rescued with full length Lar (LARFL) with some axons overextending to layer M6 (arrows) (C). Lar constructs lacking phosphatase activity (LAR2XCS) rescued the double mutant phenotype, but do not cause axon overextension as the LARFL construct did (D). Full length Ptp69D (PTP69DFL) almost completely rescues the double mutant phenotype (E), but Ptp69D lacking phosphatase activity (Ptp69D DA1DA2) was incapable of rescue (F). (G) Quantification of R8 termination in each layer for the indicated LAR or Ptp69D rescue transgenes. Genotype descriptions are the same as in Figure 4. The number of axons terminating inside the lamina was estimated. Scale bar: 20 μm.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Excel file compiling source data for the Figure 5G.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.31812.015
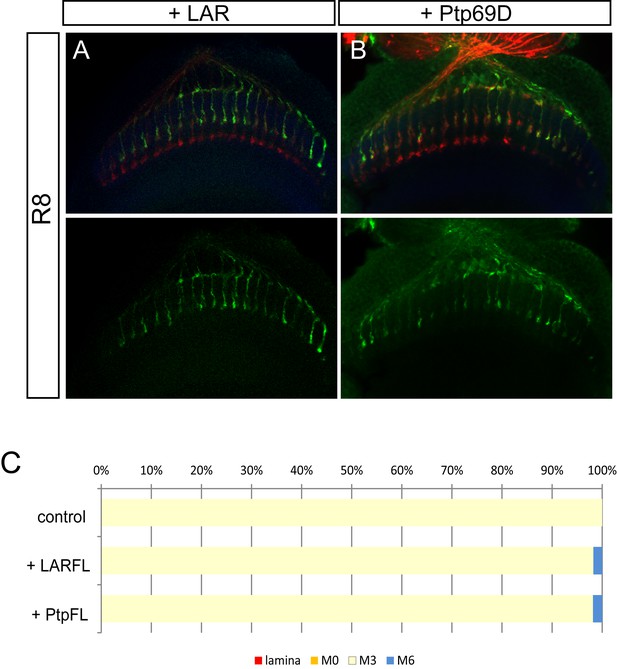
Overexpression of LAR and Ptp69D has no effect on R8 axons.
(A–C) Overexpression of LAR (A) as well as Ptp69D (B) did not cause any dominant effect on R8 axons. The quantifications are shown in (C).
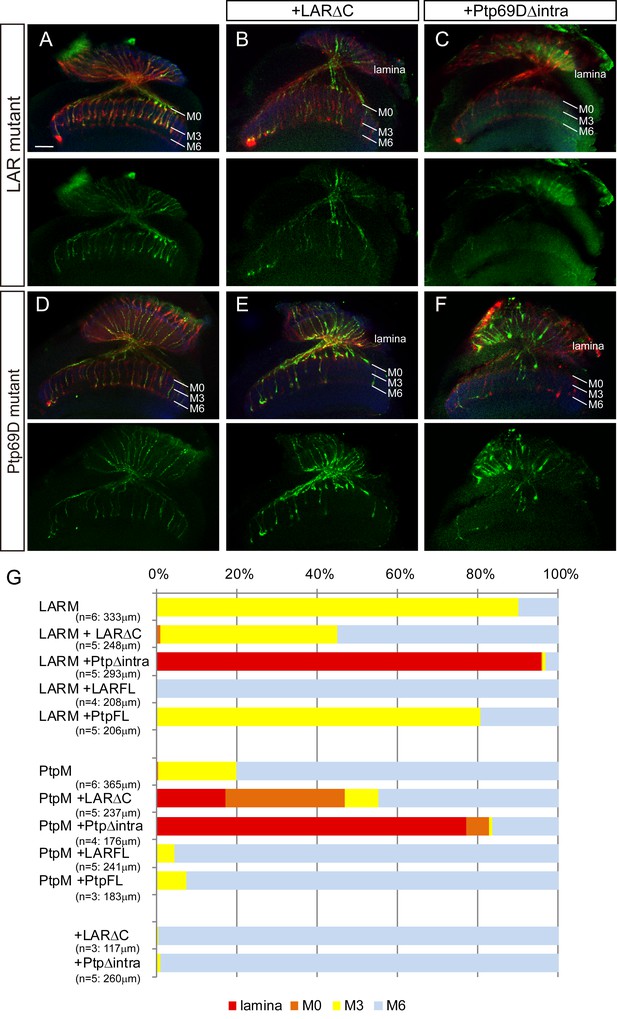
Specificity of RPTP ectodomains in R7 axons.
(A–F) Horizontal images of adult medulla of LAR (A–C) or Ptp69D (D–F) single mutants carrying the indicated transgene expressed by the GMR-Gal4. Photoreceptor axons are labeled with mAb24B10 (red), R7 photoreceptor axons with Rh4-mCD8GFP (green), and the medulla layer with an antibody to N-Cadherin (blue). Medulla layers are indicated with white lines. A total of 90% of the R7 axons terminated in layer M3 in the LAR mutant eye (A). Half of the R7 axons terminated at proper M6 layer when the LAR mutant was rescued with LAR transgene lacking intracellular domain (LARΔC) (B), while Ptp69D transgene lacking intracellular domain (Ptp69DΔintra) enhances the phenotype and almost all the R7 axons terminated in the lamina (C). A total of 20% of the R7 axons terminated in layer M3 in the Ptp69D mutant eye (D). Both LAR transgene lacking intracellular domain (LARΔC) (E) and Ptp69D transgene lacking intracellular domain (Ptp69DΔintra) (F) enhanced the phenotype of Ptp69D mutant. (G) Quantification of R7 terminations in each in the indicated mutants rescued with LAR or Ptp69D transgenes. Note that neither LARΔC nor Ptp69DΔintra had a dominant effect. Genotype descriptions are the same as in Figure 4. The number of axons terminating inside lamina was estimated as in Figure 1. Scale bar: 20 μm.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Excel file compiling source data for the Figure 6G.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.31812.018
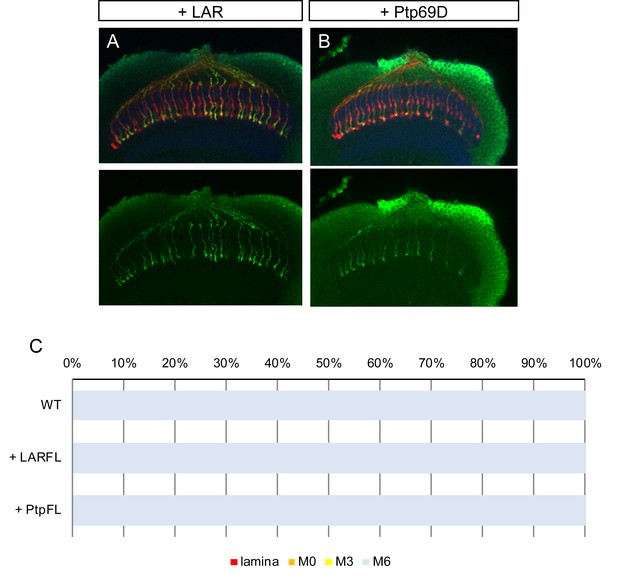
Overexpression of LAR and Ptp69D.
(A–C) Overexpression of LAR (A) as well as Ptp69D (B) did not cause any dominant effect on R7 axons. The quantifications are shown in (C).
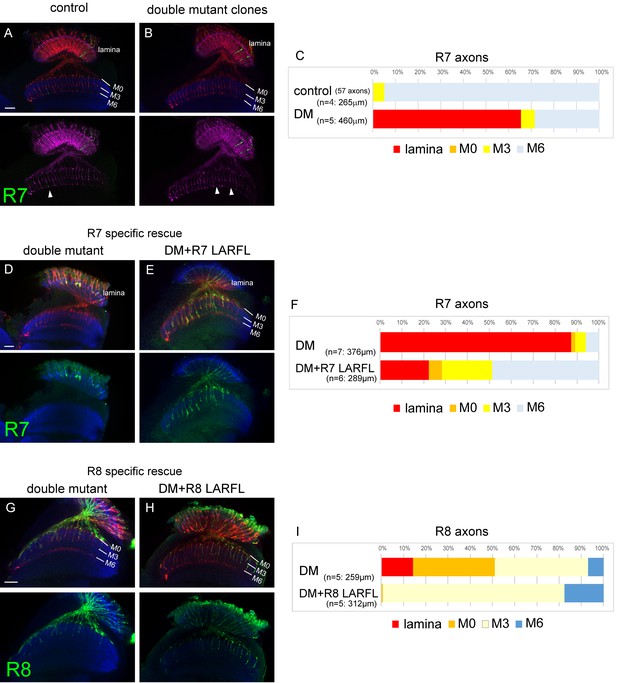
Cell-autonomous function of LAR and Ptp69D.
(A–C) Single R7 clones of LAR, Ptp69D double mutant. Ptp69D mutation was introduced by creating the clone with MARCM system using GMR-FLP, whereas LAR expression was down-regulated by combining LAR heterozygous mutation with LAR-RNAi expressed only in the clones by GMR-Gal4. The detailed genotypes are the following: (A: control) GMR-FLP, UAS-mCD8GFP/+; GMR-Gal4/+; FRT80/tub-Gal80, GMR-mCD8KO, FRT80, (B: double mutant) GMR-FLP, UAS-mCD8GFP/+; LAR[2127], GMR-Gal4/UAS-LARRNAi; Ptp69D[D1689] FRT80/ tub-Gal80, GMR-mCD8KO, FRT80. (A, B) Horizontal images of adult medulla; mCD8GFP was used to label mutant R7 axons (green), whereas mCD8-Kusabira Orange (red) to complementarily label wild type photoreceptor cells. The medulla layer was visualized with an antibody to N-Cadherin (blue). In the control animals, single R7 axons labeled in green extending to M6 layer were observed (arrowhead in A). However, when double mutant clones were generated, some axon terminals in M6 layer were absent (arrowheads in B) indicating that double mutant R7 axons failed to innervate the medulla. (C) Quantification of R7 termination in each layer. The estimation of total number of R7 axons was made from the control medulla. 65% of the double mutant R7 axons terminated inside the lamina. (D, E) Horizontal images of the adult medulla of LAR, ptp69D double mutants carrying the LARFL transgene expressed by the R7-specific PM181-Gal4. Photoreceptor axons were labeled with mAb24B10 (red), R7 photoreceptor axons with Rh4-mCD8GFP (green), and the medulla layer with an antibody to N-Cadherin (blue). With R7-specific LAR expression in LAR, ptp69D double mutants, about half of the R7 axons terminated at the proper layer (M6) and 77% innervated the medulla (E). (F) Quantification of the R7 axons terminating in each layer. (G, H) Horizontal images of the adult medulla of LAR, ptp69D double mutants carrying the LARFL transgene expressed by the R8-specific 2–80–Gal4. Photoreceptor axons were labeled with mAb24B10 (red), R8 photoreceptor axons with Rh6-mCD8GFP (green), and the medulla layer with an antibody to N-Cadherin (blue). With R8-specific LAR expression in LAR, ptp69D double mutants, about 80% of the R8 axons terminated at the proper layer (M3) and 17% overextended to the M6 layer. (I) Quantification of the R8 axons terminating in each layer. The number of axons terminating inside the lamina was estimated. Scale bars: 20 μm.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Excel file compiling source data for the Figure 7C and F and 7I.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.31812.021
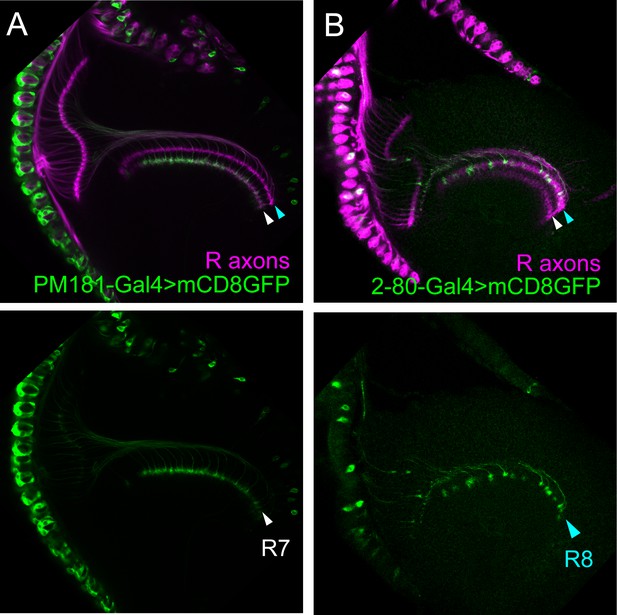
Specificity of the PM181-Gal4 and 2–80 Gal4.
(A–B) The expression pattern of R7-specific PM181-Gal4 (A) and R8-specific 2–80-Ga4 (B) was assessed at 24 hr after puparium formation (APF) by crossing to UAS-mCD8GFP (Green). Photoreceptor axons are labeled with mAb24B10 (magenta). At this stage, R7 and R8 axons target to distinct medulla layers. The layer of R7 terminals is indicated by white arrowheads and the layer of R8 terminals by light blue arrowheads. PM181-Gal4 is specifically expressed in R7 (A), whereas 2–80-Ga4 is specifically expressed in R8 (B).
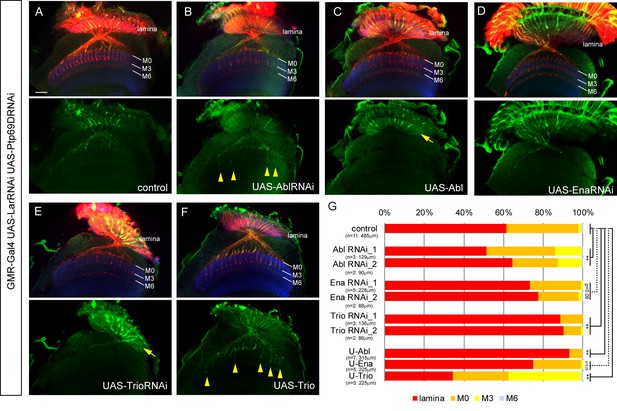
Genetic interactions between LAR, Ptp69D and Abl, Ena, and Trio in R7 targeting.
(A–F) The expression of Abl, Ena, and Trio was downregulated using RNAi or upregulated by overexpression of transgenes in LAR, Ptp69D double RNAi background. All the RNAi and transgenes were expressed under the GMR-Gal4 driver. Photoreceptor axons are labeled with mAb24B10 (red), R7 photoreceptor axons with Rh4-mCD8GFP (green), and the medulla layers with an antibody to N-Cadherin (blue). The medulla layers are indicated with white lines. Around 60% of R7 axons expressing the LAR, Ptp69D double RNAi terminated inside the lamina. The phenotype is suppressed by downregulation of Abl (B) or upregulation of Trio (F) with some R7 axons terminating in layer M3 (arrowheads). By contrast, upregulation of Abl (C) or downregulation of Trio (E) enhanced the phenotype with most R7 axons terminating in the lamina (arrows). Ena had no significant effect on the phenotype (p=0.06) upon both downregulation (D) and upregulation (not shown). (G) Quantification of R7 terminations in each layer in the control LAR, Ptp69D double RNAi line with and without each indicated RNAi or overexpression transgene of Abl, Ena, and Trio. RNAi_1 and RNAi_2 refer to the two different RNAi lines used for each gene. '**' indicates statistical significance at the p<0.01 level using chi-square test. The number of axons terminating inside the lamina was estimated. Scale bar: 20 μm.
-
Figure 8—source data 1
Excel file compiling source data for the Figure 8G.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.31812.024
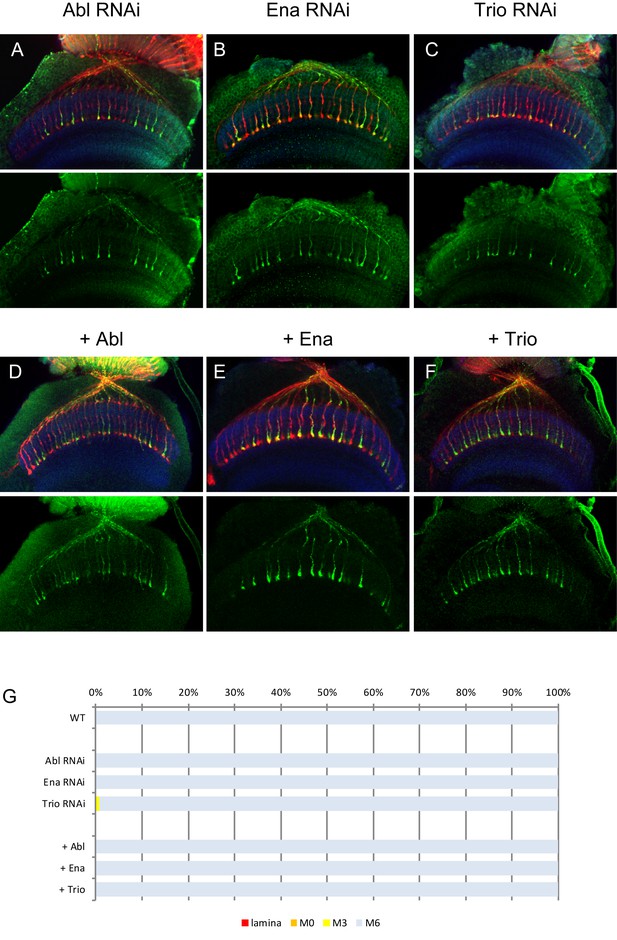
RNAi and overexpression of Abl, Ena and Trio.
(A–C) Downregulation of Abl (A), Ena (B) and Trio (C) using RNAi driven by GMR-Gal4 did not show any defects on R7 axons. (D–F) Overexpression of Abl (D), Ena (E) and Trio (F) did not cause any dominant effect on R7 axons. The quantifications are shown in (G).
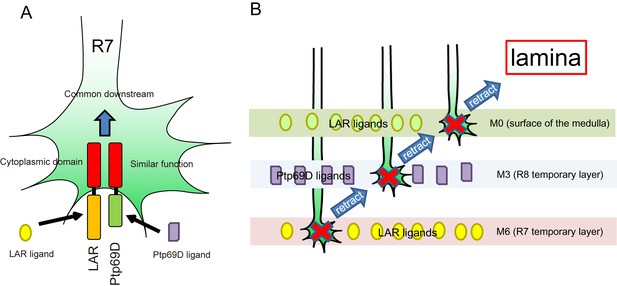
A model for common and distinct functions of LAR and Ptp69D in R7Axons.
(A) Both LAR and Ptp69D are expressed in R7 axon terminals. Their ectodomains bind to distinct ligands whereas intracellular domains share a common downstream pathway. (B) Around 24hrAPF, R7 axons reach the R7 temporary layer, which becomes M6. When they fail to detect Lar ligands, however, they start to retract. While retracting, the terminals of R7 axons pass by the M3 layer. If they detect Ptp69D ligands, they stabilize at M3, but if unbound by ligands they keep retracting. The next layer is M0 where LAR ligands appear to also be present. Here, lower signaling levels, even without phosphatase activity, can stabilize axons. If axon stabilization fails across M0, M3, and M6, R7 axons retract to the lamina.
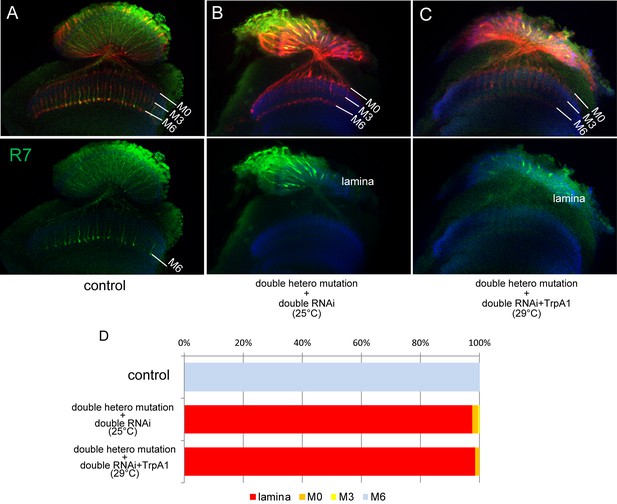
R7 axon stabilization is not dependent on neuronal activity.
(A–D) R7 axons normally project to M6 layer (A) but they do not innervate medulla and terminate inside lamina in LAR and Ptp69D double knock-out created by combining heterozygous double mutant and double RNAi (B). The activation of R7 axons using TrpA1 (Transient Receptor Potential Cation Channel A1) did not induce stabilization at any layers (C). The quantifications are shown in (D).
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers |
|---|---|---|---|
| gene (Drosophila) | LAR | NA | |
| Ptp69D | NA | ||
| strain, strain background (Drosophila) | D. melanogaster: ey-FLP2 | (Newsome et al., 2000a) | BDRC5580 |
| D. melanogaster: Ptp69D[D1689] | (Newsome et al., 2000a) | DGRC109897 | |
| D. melanogaster: LAR[2127] | (Maurel-Zaffran et al., 2001) | BDRC63796 | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-LAR | (Maurel-Zaffran et al., 2001) | N/A | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-LARΔC | (Maurel-Zaffran et al., 2001) | N/A | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-LARΔIg1-3ΔFn1-6 | (Hofmeyer and Treisman, 2009) | N/A | |
| D. melanogaster: Rh4-mCD8GFP | (Berger et al., 2001) | N/A | |
| D. melanogaster: Rh6-mCD8GFP | (Berger et al., 2001) | N/A | |
| D. melanogaster: 20C11-FLP | (Chen et al., 2014) | BDRC63796 | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-Trio | (Newsome et al., 2000b) | N/A | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-Abl | (Fogerty et al., 1999) | N/A | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-Ena | (Wills et al., 1999) | N/A | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-FRT-stop-FRT-mcd8GFP | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDRC30032 | |
| D. melanogaster: tub-Gal80[ts] | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDRC7108 | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-Lar.ΔIg123 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDRC8586 | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-Lar.ΔFn123 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDRC8587 | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-Lar.ΔFn456 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDRC8588 | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-Lar.ΔFn789 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDRC8589 | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-Lar.ΔPTP-D2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDRC8590 | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-Lar.C1638S | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDRC8591 | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-Lar.C1929S | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDRC8592 | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-Lar.CSX2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDRC8593 | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-Ptp69D Δintra | KYOTO Stock Center | DGRC109088 | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-Ptp69D DA1 | KYOTO Stock Center | DGRC109089 | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS- Ptp69D DA3(DA1DA2) | KYOTO Stock Center | DGRC109090 | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-Ptp69D | KYOTO Stock Center | DGRC109091 | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-LAR RNAi | Vienna Drosophila Resource Center | VDRC36269 | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-ptp69D RNAi | Vienna Drosophila Resource Center | VDRC27090 | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-abl RNAi | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDRC28325, 35327 | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-ena RNAi | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDRC31582, 39034 | |
| D. melanogaster: UAS-trio RNAi | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDRC27732, 43549 | |
| D. melanogaster:<LAR < | This paper | Harvard Exelixis collection; e04149, e00822 | |
| D. melanogaster:<Ptp69D< | This paper | Harvard Exelixis collection; f03442, e00274 | |
| antibody | mAb24B10 | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | 24B10 |
| rat antibody to CadN(N-Cad) | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | DN-Ex #8 | |
| rat antibody to elav | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | 7E8A10 | |
| mouse antibody to LAR | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | 9D8 | |
| mouse antibody to Ptp69D | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | 3 F11 | |
| GFP Tag Polyclonal Antibody, Alexa Fluor 488 | Life technologies | Cat #A-21311 | |
| Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H + L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 568 | Life technologies | Cat #A-11011 | |
| Goat anti-Rat IgG (H + L) Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 633 | Life technologies | Cat #A-21094 | |
| Anti-Placental alkaline phosphatase (PLAP) | Abcam | Cat #ab118856 | |
| Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG H&L (Alexa Fluor 488) preabsorbed | Abcam | Cat #ab150085 | |
| rabbit antibody to HA | Abcam | Cat #ab9110 | |
| chemical compound, drug | Paraformaldehyde 16% | Nisshin EM | Cat#15710 |
| Agar powder (gelling temperature 30–31°C) | Nacalai tesque | Cat#01059–85 | |
| Vectashield mouting medium | Vector Laboratories | Funakoshi #H-1000 | |
| software, algorithm | NIS-Elements AR | Nikon | |
| Adobe Photoshop CS6 | Adobe |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Table showing the list of all full genotypes used.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.31812.027
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.31812.028





