The yeast H+-ATPase Pma1 promotes Rag/Gtr-dependent TORC1 activation in response to H+-coupled nutrient uptake
Figures
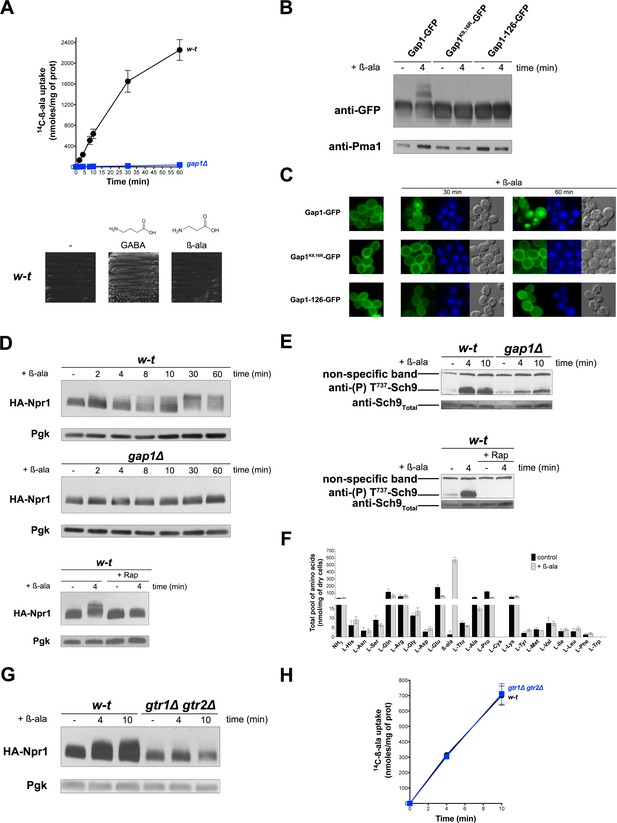
Uptake of β-alanine via the Gap1 permease causes Rag/Gtr-dependent TORC1 activation without increasing the internal pools of amino acids.
(A) Top. Wild-type (w–t) and gap1Δ cells were grown on Gluc Pro medium and [14C]-β-ala (0.5 mM) was added to the medium before measurement of the incorporated radioactivity at various times. Bottom. w-t cells were grown for 4 days on solid minimal medium without any N source or with GABA (0.5 mM) or β-ala (0.5 mM) as sole N source. (B) gap1Δ cells expressing, from plasmids, a gene encoding GFP-fused Gap1, Gap1(K9R-K16R), or Gap1-126 were grown on Gal Pro medium. Glucose was added for 30 min to stop Gap1 neosynthesis prior to addition of β-ala (0.5 mM) for 4 min. Crude cell extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-GFP and anti-Pma1 antibodies. (C) Fluorescence microscopy analysis of the cells in 1B. Cells were grown on Gal Pro medium. Glucose was added for 1.5 hr to stop Gap1 neosynthesis, and β-ala (0.5 mM) was added for 30 min or 1 hr. CMAC staining (blue) was used to highlight the vacuole. (D) Top. w-t and gap1Δ cells expressing HA-Npr1 from a plasmid were grown on Gluc Pro medium. Cells were collected before and at various times after addition of β-ala (0.5 mM). Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-HA and anti-Pgk antibodies. Bottom. Same as in the top panel, except that w-t cells were collected before and 4 min after addition of β-ala (0.5 mM). Rap was added to half of the culture for 30 min, before addition of β-ala (0.5 mM). (E) Top. w-t and gap1Δ cells were grown on Gluc Pro medium. Cells were collected before and 4 and 10 min after addition of β-ala (0.5 mM). Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-(P) T737-Sch9 and anti-Sch9Total antibodies. Bottom. Same as in panel G, except that w-t cells were collected before and 4 min after addition of β-ala (0.5 mM). Half of the culture was pretreated with Rap for 30 min. (F) w-t cells were grown on Gluc Pro medium. Cell extracts were prepared before and 30 min after addition of β-ala (0.5 mM) and used to measure amino acid pools as described under Materials and methods. The presented data are means ±SD of two independent experiments. (G) w-t and gtr1Δ gtr2Δ cells expressing HA-Npr1 from a plasmid were grown on Gluc Pro medium. Cells were collected before and 4 and 10 min after addition of β-ala (0.5 mM). Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-HA and anti-Pgk antibodies. (H) Cells as in G were grown on Gluc Pro medium. [14C]-β-ala (0.5 mM) was added to the medium before measuring the incorporated radioactivity at various times.
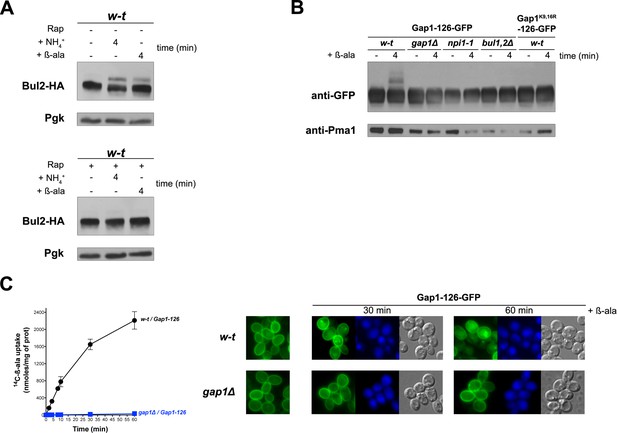
Uptake of β-alanine promotes ubiquitylation and downregulation of the inactive Gap1-126 permease via TORC1-dependent stimulation of the Bul arrestins.
(A) gap1Δ BUL2-HA cells expressing Gap1 from a plasmid were grown on Gluc Pro medium and NH4+ (20 mM) or β-ala (0.5 mM) was added to the culture for 4 min.
Rap was added to half of the culture for 30 min before addition of NH4+ or β-ala. Crude cell extracts were immunoblotted with anti-HA and anti-Pgk antibodies. The results show that the Rap-sensitive change in Bul2-HA migration upon addition of NH4+, previously shown to reflect its dephosphorylation and monoubiquitylation (Merhi and AndreAndré, 2012), also occurs upon addition of β-ala. Addition of β-ala thus activates TORC1. (B) w-t, gap1Δ, npi1-1/rsp5, and bul1Δ bul2Δ cells expressing the inactive Gap1-126-GFP from a plasmid, and w-t cells expressing Gap1-126(K9R-K16R)-GFP also from a plasmid, were grown on Gal Pro medium. Glucose was added for 30 min to stop Gap1-126 or Gap1-126(K9R,K16R) neosynthesis prior to β-ala addition (0.5 mM) for 4 min. Crude cell extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-GFP and anti-Pma1 antibodies. The results show that addition of β-ala induces the appearance of the typical two upper bands corresponding to ubiquitylated forms of Gap1. As expected, this ubiquitylation is impaired if the two Ub acceptor lysines (K9 and K16) of the permease are mutated. Ubiquitylation of Gap1-126 is impaired in the gap1Δ, bul1Δ bul2Δ and hypomorphic npi1/rsp5 mutants. Uptake of β-ala via the endogenous Gap1 permease thus promotes Ub-dependent downregulation of the inactive Gap1-126 protein (C) Left. w-t and gap1Δ cells expressing Gap1-126-GFP from a plasmid were grown on Gal Pro medium. Glucose was supplied for 30 min to stop Gap1 neosynthesis. [14C]-β-ala (0.5 mM) was added to the medium before measuring the incorporated radioactivity at various times. The result shows that [14C]-β-ala is incorporated into cells expressing the endogenous Gap1 permease. Right. Fluorescence microscopy analysis of cells in panel C. Cells were grown on Gal Pro medium. Glucose was added for 1.5 hr to stop Gap1 neosynthesis, and β-ala (0.5 mM) was added for 30 min or 1 hr before analysis by fluorescence microscopy. CMAC staining (blue) was used to highlight the vacuole. The result shows that uptake of β-ala by Gap1 elicits endocytosis of the inactive Gap1-126-GFP protein.
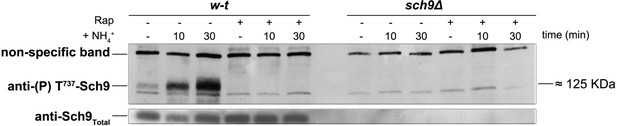
An anti-(P) T737-Sch9 antibody recognizes phosphorylated Sch9 after NH4+ addition.
w-t cells transformed with pFL38 (URA3) and +Δ cells (JW00035) co-transformed with pCJ366 (TRP1-LEU2-HIS3) and pFL38 (URA3) were grown on Gluc Pro medium (for JW00035 cells, the growth medium was supplemented with adenine to compensate for the ade2 auxotrophy). Cells pre-incubated or not with Rap for 30 min were collected before and 10 and 30 min after addition of NH4+ (20 mM). Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-(P) T737-Sch9 and anti-Sch9Total antibodies. The immunoblot shows that the anti-(P) T737-Sch9 antibody recognized a band corresponding to a molecular mass of ~125 KDa, whose intensity increased after NH4+ addition. This band was not detected in Rap-treated w-t cells or in cells of the sch9Δ mutant strain. The same antibody also revealed a nonspecific band corresponding to a higher molecular mass, which can be used as a loading control. As expected, the anti-Sch9Total antibody recognized Sch9 even in Rap-treated cells.
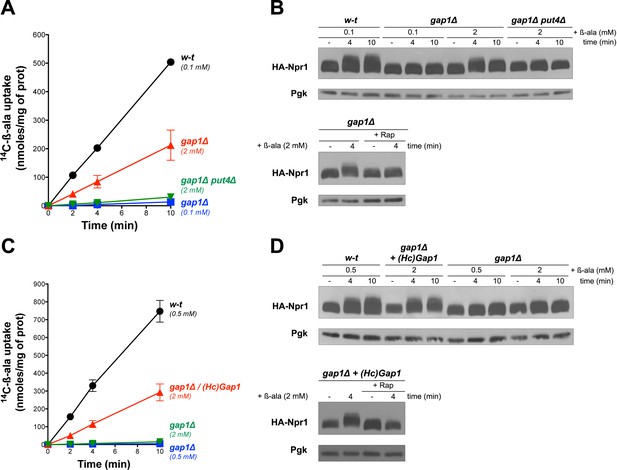
Uptake of β-ala via the endogenous Put4 or the heterologous HcGap1 permease also promotes TORC1 activation.
(A) w-t, gap1Δ, and gap1Δ put4Δ cells were grown on Gluc urea medium. [14C]-β-ala (0.1 or 2 mM) was added to the medium before measuring the incorporated radioactivity at various times. (B) Top. Cells as in A expressing HA-Npr1 from a plasmid were grown on Gluc urea medium. Cells were collected before and 4 and 10 min after addition of β-ala (0.1 or 2 mM). Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-HA and anti-Pgk antibodies. Bottom. Same as in panel B except that gap1Δ cells were also collected 30 min after Rap treatment. (C) w-t and gap1Δ cells expressing or not HcGap1 from a plasmid were grown on Gluc Pro medium. [14C]-β-ala (0.5 or 2 mM) was added to the medium before measuring the incorporated radioactivity at various times. (D) Top. w-t and gap1Δ cells expressing HA-Npr1 and gap1Δ cells co-expressing HcGap1 and HA-Npr1 from plasmids were grown on Gluc Pro medium. Cells were collected before and 4 and 10 min after addition of β-ala (0.5 or 2 mM). Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-HA and anti-Pgk antibodies. Bottom. Same as in top panel except that cells were also treated for 30 min with Rap before β-ala addition.
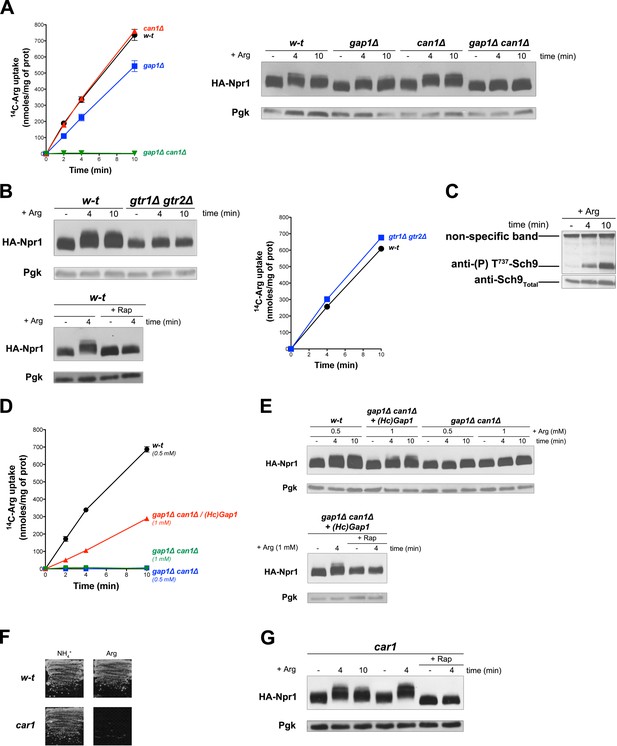
Uptake of arginine via an endogenous or a heterologous permease stimulates TORC1 even if arginine catabolism is impaired.
(A) Left. w-t, gap1Δ, can1Δ, and gap1Δ can1Δ cells were grown on Gluc Pro medium. [14C]-L-Arg (0.5 mM) was added to the medium before measuring the incorporated radioactivity at various times. Right. Cells as in A expressing HA-Npr1 from a plasmid were grown on Gluc Pro medium and collected before and 4 and 10 min after addition of Arg (0.5 mM). Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-HA and anti-Pgk antibodies. (B) Left top. w-t and gtr1Δ gtr2Δ cells expressing HA-Npr1 from a plasmid were grown on Gluc Pro medium. Cells were collected before and 4 and 10 min after addition of Arg (0.5 mM). Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-HA and anti-Pgk antibodies. Left bottom. Same as in panel left top except that half of the culture was treated for 30 min by Rap before addition of Arg. Right. Cells as in left panels although not expressing HA-Npr1 were grown on Gluc Pro medium. [14C]-L-Arg (0.5 mM) was added to the medium before measuring the incorporated radioactivity at various times. (C) w-t cells were grown on Gluc Pro medium. Cells were collected before and 4 and 10 min after addition of Arg (0.5 mM). Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-(P) T737-Sch9 and anti-Sch9Total antibodies. (D) w-t and gap1Δ can1Δ cells expressing or not HcGap1 from a plasmid were grown on Gluc Pro medium. [14C]-L-Arg (0.5 or 1 mM) was added to the medium before measurement of the incorporated radioactivity at various times. (E) Top. w-t and gap1Δ can1Δ cells expressing HA-Npr1 from plasmid, and gap1Δ can1Δ cells co-expressing HcGap1 and HA-Npr1 from plasmids, were grown on Gluc Pro medium. Cells were collected before and 4 and 10 min after addition of Arg (0.5 or 1 mM). Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-HA and anti-Pgk antibodies. Bottom. Same as in top panel except that half of the culture was treated for 30 min with Rap before addition of Arg. (F) Left. w-t and car1 mutant cells were grown on solid minimal medium with NH4+ or Arg at a concentration of 2 mM as sole N source. (G). car1 mutant cells expressing HA-Npr1 from a plasmid were grown on Gluc Pro medium. Cells were collected before and 4 and 10 min after addition of Arg (0.5 mM), and part of the culture was also treated for 30 min with Rap before Arg addition. Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-HA and anti-Pgk antibodies.
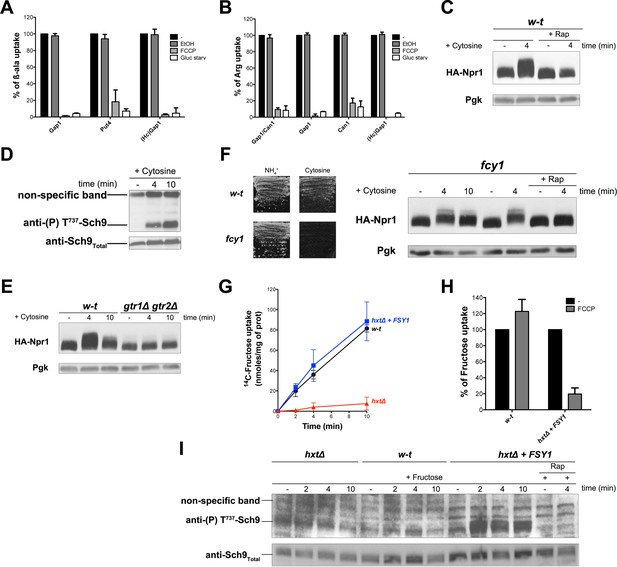
H+influx coupled to transport promotes Rag/Gtr-dependent stimulation of TORC1.
(A) The β-ala uptake activities of Gap1 (in w-t cells grown on Gluc Pro medium), Put4 (in gap1Δ cells grown on Gluc urea medium), and HcGap1 (in gap1Δ cells expressing HcGap1 and grown on Gluc Pro medium), were determined by measuring the initial rate of [14C]-β-ala incorporation (0.5 mM for Gap1, 2 mM for Put4 and HcGap1) before and after glucose starvation for 5 min or with or without prior incubation with FCCP (20 µM) or its solvent (0.2% EtOH) for 5 min. The presented data are means ± SD of two independent experiments. (B) The Arg uptake activities of Gap1 and Can1 (in w-t cells), of Gap1 alone (in can1Δ cells), of Can1 alone (in gap1Δ cells), and of HcGap1 (in gap1Δ can1Δ cells expressing HcGap1 from a plasmid) were determined by measuring the initial rate of [14C]-L-Arg incorporation (0.5 mM for Gap1 and Can1, 1 mM for HcGap1) as in A. The presented data are means ± SD of two independent experiments. (C) w-t cells expressing HA-Npr1 from a plasmid were grown on Gluc Pro medium. Cells were collected 4 min after addition of cytosine (1 mM). Half of the culture was treated with Rap for 30 min before addition of cytosine. Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-HA and anti-Pgk antibodies. (D) w-t cells were grown on Gluc Pro medium. Cells were collected before and 4 and 10 min after addition of cytosine (1 mM). Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-(P) T737-Sch9 and anti-Sch9Total antibodies. (E) w-t and gtr1 gtr2Δ cells expressing HA-Npr1 from a plasmid were grown on Gluc Pro medium. Cells were collected before and 4 and 10 min after addition of cytosine (1 mM). Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-HA and anti-Pgk antibodies. (F) Left. w-t and fcy1 cells were grown on solid medium with NH4+ or cytosine (2 mM) as sole N source. Right. fcy1 cells expressing HA-Npr1 were grown on Gluc Pro medium. Cells were collected before and 4 and 10 min after addition of cytosine (0.5 mM). Half of the culture was treated for 30 min with Rap before addition of cytosine. Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-HA and anti-Pgk antibodies. (G) w-t (CEN.PK2-1c), hxtΔ (EBY.VW4000), and hxtΔ+FSY1 (I3) cells were grown on maltose NH4+ medium, shifted for 6 hr on EtOH Pro, and [14C]-D-fructose (2 mM) was added to the medium before measuring the incorporated radioactivity at various times. (H) Cells of the w-t and hxtΔ+FSY1 srains (as in G) were grown on maltose NH4+ medium. The initial rate of [14C]-D-fructose incorporation (2 mM), with or without prior incubation with FCCP (20 µM) for 5 min, was then measured. The data are means ±SD of two independent experiments. (I) Strains and growth conditions as in G. Cells were collected before and 2, 4 and 10 min after addition of fructose (2 mM). For the I3 strain, half of the culture was treated for 30 min with Rap before addition of fructose. Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-(P) T737-Sch9 and anti-Sch9Total antibodies.
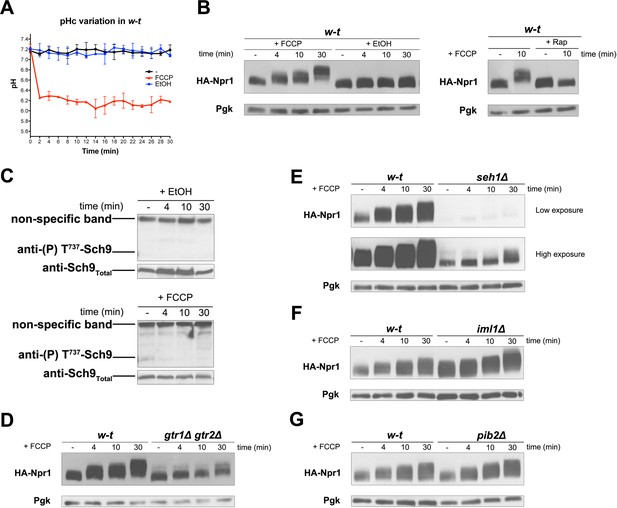
H+diffusion via a protonophore promotes Rag/Gtr-dependent stimulation of TORC1.
(A) w-t cells expressing pHluorin (strain ES075) were grown on Gluc Pro medium. The cytosolic pH was monitored for 30 min at regular intervals. FCCP (20 µM) or its solvent (0.2% EtOH) was added at 1 min. (B) w-t cells expressing HA-Npr1 from a plasmid were grown on Gluc Pro medium. Cells were collected before and at various times after addition of FCCP (20 µM) or its solvent (0.2% EtOH). Part of the culture was treated for 30 min with Rap before addition of FCCP. Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-HA and anti-Pgk antibodies. (C) w-t cells were grown on Gluc Pro medium. Cells were collected before and at various times after addition of FCCP (20 µM) or its solvent (0.2% EtOH). Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-(P) T737-Sch9 and anti-Sch9Total antibodies. (D–G) w-t and gtr1 gtr2Δ, seh1Δ, iml1Δ or pib2Δ cells expressing HA-Npr1 from a plasmid were grown on Gluc Pro medium. Cells were collected before and at various times after FCCP addition (20 µM). Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-HA and anti-Pgk antibodies.
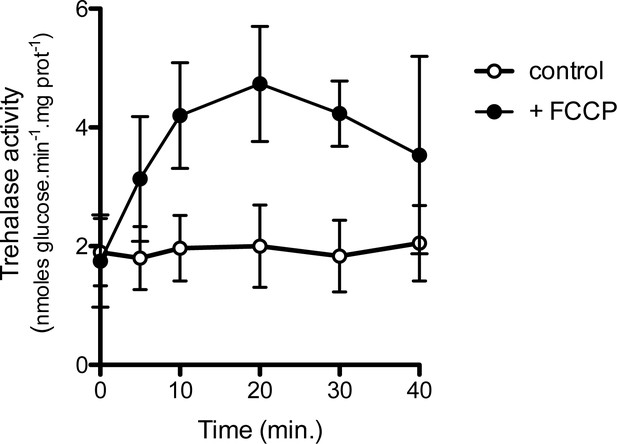
Addition of the FCCP uncoupler stimulates trehalase activity in N-deprived cells.
w-t cells were incubated for 16 hr in Gluc medium (pH 6.1) devoid of any N source. FCCP (20 μM) or its solvent (0.2% EtOH, control) was added to the cells and trehalase activity was measured in cell samples collected at various times. Plotted values represent means ±SD of three independent experiments.
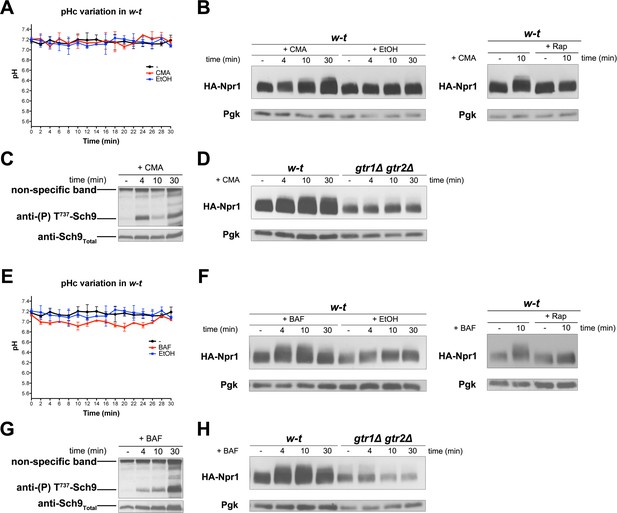
Inhibition of the vacuolar V-ATPase activates TORC1.
(A) w-t cells expressing pHluorin (strain ES075) were grown on Gluc Pro medium. The cytosolic pH was monitored for 30 min at regular intervals. Concanamycin A (CMA) (1 µM) or its solvent (0.2% EtOH) was added at 1 min. (B) Left. w-t cells expressing HA-Npr1 from a plasmid were grown on Gluc Pro medium. Cells were collected before and at various times after addition of CMA (1 µM) or its solvent (0.2% EtOH). Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-HA and anti-Pgk antibodies. Right. Same except that half of the culture was treated with Rap for 30 min before CMA addition. (C) Same as in B except that crude extracts from w-t cells were immunoblotted with anti-(P) T737-Sch9 and anti-Sch9Total antibodies. (D) Same as in B except that w-t and gtr1Δ gtr2Δ cells were analyzed. (E, F, G, H) Same as in A, B, C and D, respectively, except that cells were treated with bafilomycin A (BAF) (1 µM). The data of Figure 6A and E and those of Figure 5A were obtained in the same experiments but are presented in separate graphs for clarity.
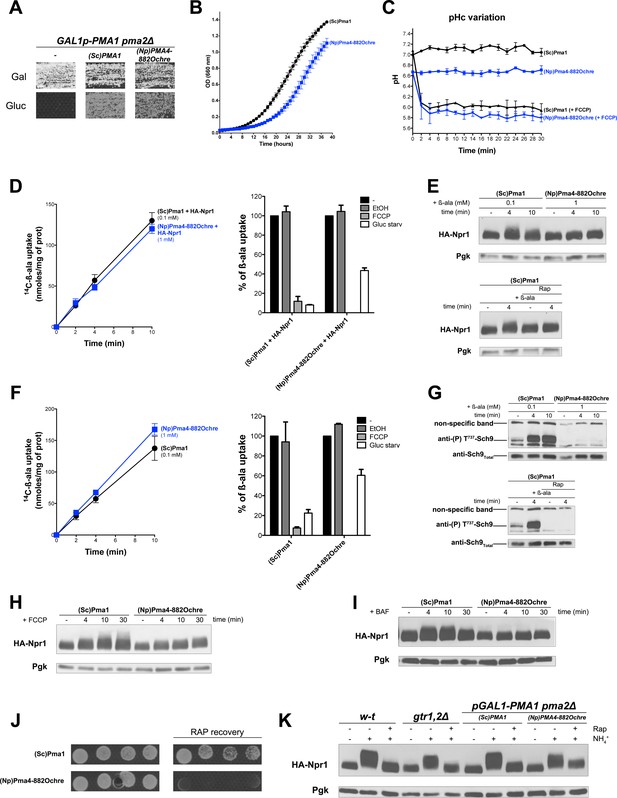
TORC1 activation in response to increased cytosolic H+involves the Pma1 H+-ATPase.
(A) GAL1p-PMA1 pma2Δ cells transformed with the YCp(Sc)PMA1, YEp(Np)PMA4882Ochre, or pFL36 (empty) plasmid (-) were grown for 3 days on solid medium with Pro as sole N source and Gal or Gluc as carbon source. (B) GAL1p-PMA1 pma2Δ cells expressing (Sc)Pma1 or (Np)Pma4882Ochre from a plasmid (as in A) were grown on Gluc Pro medium in a microplate reader for 40 hr. Data points represent averages of the OD at 660 nm of two biological replicates; error bars represent SD. (C) Strains and growth conditions as in B, except that the strains were also transformed with a plasmid (pHl-U) expressing pHluorin. The cytosolic pH was monitored during growth with or without addition, starting at 1 min, of FCCP (20 µM) for various times. (D) Left. Cells as in B but also expressing HA-Npr1 from a plasmid were grown on Gluc NH4+ medium. After a shift to Gluc Pro medium for 3 hr, [14C]-β-ala (0.1 or 1 mM) was added to the medium before measuring the incorporated radioactivity at various times. Right. Strains and growth conditions as in left. Uptake via Gap1 of [14C]-β-ala (provided at 0.1 mM to (Sc)PMA1-expressing cells and at 1 mM to (Np)PMA4882Ochre-expressing cells) was measured before and after glucose starvation for 5 min or after addition of FCCP (20 µM) or its solvent alone (0.2% EtOH) for 5 min. Plotted values represent percentages of initial Gap1 activity, and correspond to means ± SD of two independent experiments. (E) Top. Strains and growth conditions as in D, except that the cells were collected before and 4 and 10 min after addition of β-ala (0.1 or 1 mM). Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-HA and anti-Pgk antibodies. Bottom. Same as in top panel, except that only (Sc)PMA1-expressing cells were collected and half of the culture was treated for 30 min with Rap. (F) Experiments similar to those in D, except that the cells harbored an empty URA3 plasmid instead of the HA-Npr1 plasmid and were grown on Gluc Pro medium. (G) Top. Strains and growth conditions were as in F, and cells were treated as in E. Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-(P) T737-Sch9 and anti-Sch9Total antibodies. Bottom. Same as in top panel except that (Sc)PMA1-expressing cells were collected and half of the culture was treated for 30 min with Rap. (H–I) Strains, growth conditions, and immuno-detection as in E except that cells were collected before and at various times after addition of FCCP (20 µM) or BAF (1 µM). (J) Rapamycin recovery assay for GAL1p-PMA1 pma2Δ cells expressing (Sc)Pma1 or (Np)Pma4882Ochre from plasmids. Cells were treated or not with Rap (200 ng/ml) for 6 hr, washed twice, plotted in two-fold serial dilutions on solid Gluc Pro medium, and incubated for 4 days. (K) w-t and gtr1Δ gtr2Δ cells expressing HA-Npr1 from a plasmid and GAL1p-PMA1 pma2Δ cells co-expressing (Sc)Pma1 or (Np)Pma4882Ochre and HA-Npr1 from plasmids were grown on Gluc NH4+ medium. After a shift to Gluc Pro medium for 3 hr, cells were collected before and 30 min after addition of NH4+ (5 mM). Cells were also collected after addition of Rap for 30 min, followed by addition of NH4+ (5 mM) for 30 min. Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-HA and anti-Pgk antibodies.

Pma4882Ochre from tobacco fails to compensate for the lack of Pma1 as regards TORC1 activation in a pma1Δ pma2Δ mutant
(A) Left. The pma1Δ pma2Δ strain co-transformed with the YCp(Sc)PMA1 or YEp(Np)PMA4882Ochre plasmid and a LEU2-HIS3-LYS2 (pCJ315) plasmid were grown on Gluc Pro medium (pH = 6.5) containing 0.00225% adenine to compensate for the ade2 auxotrophy. [14C]-β-ala was added (at 0.1 mM to (Sc)PMA1-expressing cells, at 1 mM to (Np)PMA4882Ochre-expressing cells) before measuring the incorporated radioactivity at various times. Right. Strains and growth conditions as in the left panel. Percentages of initial Gap1 activity were calculated after glucose starvation for 5 min, or after addition of FCCP (20 µM) or EtOH (0.2%) for 5 min. Plotted values represent means ±SD of two independent experiments. (B) Top. Strains and growth conditions as in A. Cells were collected before and 4 and 10 min after addition of β-ala (as in A). Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-(P) T737-Sch9 and anti-Sch9Total antibodies. Bottom. Same as in the previous experiment, except that (Sc)PMA1-expressing cells were treated or not with Rap for 30 min before addition of β-ala (0.1 mM).
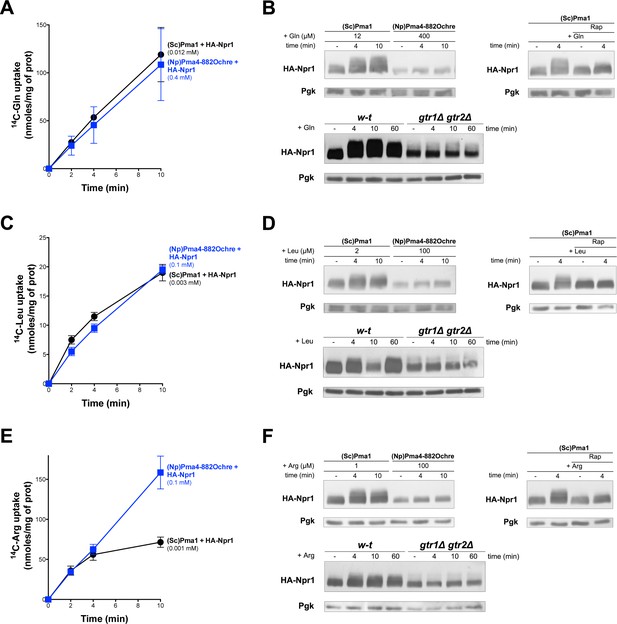
TORC1 is not stimulated by Gln, Leu, or Arg, transported into Pma4882Ochre expressing cells
(A) GAL1p-PMA1 pma2Δ cells co-expressing (Sc)Pma1 or (Np)Pma4882Ochre and HA-Npr1 from plasmids were grown on Gluc NH4+ medium. After a shift to Gluc Pro medium for 3 hr, [14C]-L-Gln (0.012 mM to (Sc)PMA1-expressing cells, 0.4 mM to (Np)PMA4882Ochre cells) was added to the medium before measuring the incorporated radioactivity at various times. (B) Top left. Strains and growth conditions as in A, except that the cells were collected before and 4 and 10 min after addition of Gln. Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-HA and anti-Pgk antibodies. Top right. Same as in top left, except that only (Sc)PMA1-expressing cells were collected and half of the culture was treated for 30 min with Rap. Bottom. w-t and gtr1Δ gtr2Δ cells expressing HA-Npr1 from a plasmid were grown on Gluc Pro medium. Cells were collected before and 4 and 10 min after addition of Gln (0.5 mM). Crude extracts were prepared and immunoblotted with anti-HA and anti-Pgk antibodies. (C and D) and (E and F) Same as in A and B except that Leu and Arg were added instead of Gln, respectively. The concentrations used for Leu and Arg are indicated in the figure. In the experiment comparing the w-t and gtr1Δ gtr2Δ strains, Leu and Arg were added at a final concentration of 0.5 mM.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody | anti-GFP (mouse monoclonal) | Roche (Belgium) | 11814460001 ; RRID : AB_390913 | (1:10000) | |
| Antibody | anti-Pma1 (rabbit polyclonal) | (De Craene et al., 2001) | RRID : AB_2722567 | (1:5000) | |
| Antibody | anti-HA (12CA5) (mouse monoclonal) | Roche (Belgium) | 11583816001 ; RRID : AB_514506 | (1:5000) | |
| Antibody | anti-Pgk (mouse monoclonal) | Invitrogen/Life technologies (Belgium) | 459250 ; RRID : AB_221541 | (1:10000) | |
| Antibody | anti-(P)T737-Sch9 (rabbit purified polyclonal antibody) | This paper | RRID : AB_2722566 | GeneCust compagny; rabbit purified polyclonal antibody; against CKFAGF(pT)FVDESAIDE; (1:2500) | |
| Antibody | anti-Sch9Total (rabbit polyclonal) | (Prouteau et al., 2017) | (1:20000) | ||
| Antibody | anti-mouse IgG (whole Ab), HRP conjugate (polyclonal) | GE Healthcare/Fisher Scientific (Belgium) | NA931 ; RRID : AB_772210 | (1:10000) | |
| Antibody | anti-rabbit IgG (whole Ab), HRP conjugate (polyclonal) | GE Healthcare/Fisher Scientific (Belgium) | NA934 ; RRID : AB_772206 | (1:10000) | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Glucose Assay Kit | Sigma-Aldrich (Germany) | GAGO20 | Manufacture instructions | |
| Chemical compound, drug | R-5000 Rapamycin | LC Laboratories (U.S.A.) | 53123-88-9 | 200 ng/ml | |
| Chemical compound, drug | CellTracker Blue CMAC Dye | Life technologies (Belgium) | C2110 | ||
| Chemical compound, drug | Lumi-LightPlus Western blotting substrate | Roche (Belgium) | 12015196001 | Manufacture instructions | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Digitonin | Sigma-Aldrich (Germany) | D141 | ||
| Chemical compound, drug | Carbonyl cyanide 4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenylhydrazone (FCCP) | Sigma-Aldrich (Germany) | C2920 | 20 µM | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Concanamycin A (Folimycin) | Abcam (U.K.) | ab144227 | 1 µM | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Bafilomycin A1 | Cell Signaling Technology (France) | 54645S | 1 µM | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Alanine, β-[1–14C] | Hartmann analytic (Germany) | ARC0183 | ||
| Chemical compound, drug | Arginine, L-[14C(U)] | Perkin-Elmer (Belgium) | NEC267E2 | ||
| Chemical compound, drug | Leucine, L-[14C(U)] | Perkin-Elmer (Belgium) | NEC279E0 | ||
| Chemical compound, drug | Glutamine, L-[14C(U)] | Perkin-Elmer (Belgium) | NEC4510 | ||
| Chemical compound, drug | Fructose, D-[14C(U)] | Hartmann analytic (Germany) | ARC0116 | ||
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism 5 | RRID:SCR_015807 | Statistical analysis and graphs representation | ||
Yeast strains used in this study
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.31981.015| Strain | Genotype | Reference or source |
|---|---|---|
| 23344 c | ura3 | Laboratory collection |
| EK008 | gap1Δ ura3 | Lab collection |
| ES032 | can1Δ ura3 | (Gournas et al., 2017) |
| ES029 | gap1Δ can1Δ ura3 | (Gournas et al., 2017) |
| MA032 | gap1Δ BUL2-HA ura3 | (Merhi and AndreAndré, 2012) |
| 27038a | npi1-1rsp5 ura3 | (Hein et al., 1995) |
| OS27-1 | bul1Δ bul2Δ ura3 | Lab collection |
| 34210 c | gap1Δ put4Δ ura3 | Lab collection |
| 33007 c | gap1Δ ura3 leu2 | Lab collection |
| 30911b | car1 ura3 | Lab collection |
| CG059 | gap1Δ can1Δ ura3 leu2 | (Gournas et al., 2017) |
| OS26-1 | gtr1Δ gtr2Δ ura3 | Lab collection |
| CEN.PK2-1c | leu2-3,112 ura3-52 trp1-289 his3-Δ1 MAL2-8c SUC2 hxt17Δ | (Wieczorke et al., 1999) |
| EBY.VW4000 | hxt1-17Δ gal2Δ stl1Δ agt1Δ mph2Δ mph3Δ leu2-3,112 ura3-52 trp1-289 his3-Δ1 MAL2-8c SUC2 | (Wieczorke et al., 1999) |
| I3 | EBY.VW4000 URA3::FSY1 | (Rodrigues de Sousa et al., 2004) |
| CG146 | seh1Δ ura3 | This study |
| CG148 | pib2Δ ura3 | This study |
| CG150 | iml1Δ ura3 | This study |
| 35652d | fcy1 ura3 | This study |
| ES075 | uga1::loxP-kanMX-loxP-GPD1p-pHluorin ura3 | This study |
| YPS14-4 | ade 2–101, leu2Δ1, his3-Δ200, ura3–52, trp1Δ63, lys2–801 pma1Δ::HIS3, pma2Δ::TRP1 + YCp-(Sc)PMA1 (LEU2) | (Supply et al., 1993) |
| PMA4–882Oc hre | ade 2–101, leu2Δ1, his3-Δ200, ura3–52, trp1Δ63, lys2–801 pma1Δ::HIS3, pma2Δ::TRP1 + YEp-PMA1p-(Np)PMA4882ochre (LEU2) | (Luo et al., 1999) |
| JW00035 | leu2-3-112 ura3-1 trp1-1 his3-11-15 ade2-1 can1-100 sch9Δ::TRP1 | (Wilms et al., 2017) |
| JX023 | GAL1p-PMA1 pma2Δ ura3 leu2 | This study |
Plasmids used in this study
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.31981.016| Plasmid | Description | Reference or source |
|---|---|---|
| pFL38 | CEN-ARS (URA3) | (Bonneaud et al., 1991) |
| pFL36 | CEN-ARS (LEU2) | (Bonneaud et al., 1991) |
| p416 GAL1 | CEN-ARS GAL1p (URA3) | (Mumberg et al., 1994) |
| pJOD10 | p416 GAL1p-GAP1-GFP (URA3) | (Nikko et al., 2003) |
| pCJ038 | p416 GAL1p -GAP1(K9R,K16R)-GFP (URA3) | (Lauwers and André, 2006) |
| pMA065 | p416 GAL1p -GAP1-126-GFP (URA3) | (Merhi et al., 2011) |
| pMA091 | p416 GAL1p -GAP1-126-K9R,K16R-GFP (URA3) | (Merhi et al., 2011) |
| pCH500 | CEN-ARS-GAP1 (URA3) | (Hein and André, 1997) |
| pHcGAP1 | YEp-HcGAP1 (URA3) | (Wipf et al., 2002) |
| pES103 | YEp-HA-NPR1 (LEU2) | This study |
| pAS103 | YEp-HA-NPR1 (URA3) | (Schmidt et al., 1998) |
| pCJ315 | CEN-ARS (LEU2-HIS3-LYS2) | Lab collection |
| pMYC008 | YCp-AGP1p-LACZ (HIS3 TRP1 LEU2) | Lab collection |
| pES154 | YCp-AGP1p-LACZ (HIS3 TRP1) | This study |
| pHl-U | YEp-ADH1p-pHluorin (URA3) | (Orij et al., 2009; Zimmermannova et al., 2015) |
| pHl-I | YCp-loxP-kanMX-loxP-GPD1p-pHluorin (URA3) | (Orij et al., 2009; Zimmermannova et al., 2015) |
| pCJ366 | YEp (TRP1-LEU2-HIS3) | Lab collection |
| pPS15-P1 | YCp-(Sc)PMA1 (LEU2) | (Supply et al., 1993) |
| pPMA4882ochre | YEp-PMA1p-(Np)PMA4882ochre (LEU2) | (Luo et al., 1999) |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.31981.017





