SET-9 and SET-26 are H3K4me3 readers and play critical roles in germline development and longevity
Figures
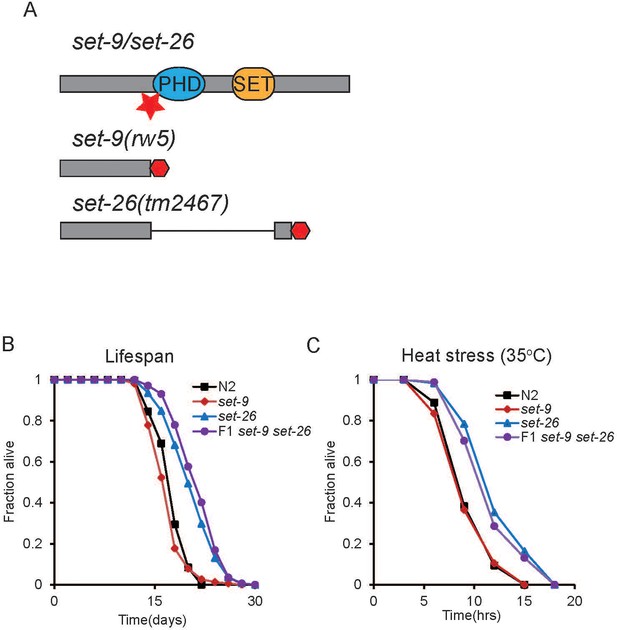
set-26 but not set-9 is important for longevity.
(A) Schematic of the set-9(rw5) and set-26(tm2467) mutants. Red star indicates the position of the sgRNA (single guide RNA) targeting the set-9 gene. Premature stop codons caused by deletions of 38 nucleotides in the set-9 gene and 1090 nucleotides in the set-26 gene are depicted as red hexagons. Loss of set-26 gene but not set-9 gene extended lifespan (B), and increased resistance to heat stress (C). Survival curves for N2, set-26(tm2467), set-9(rw5), and set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) strains from representative experiments are shown. Quantitative data for all replicates are shown in Supplementary file 1 Table S1.
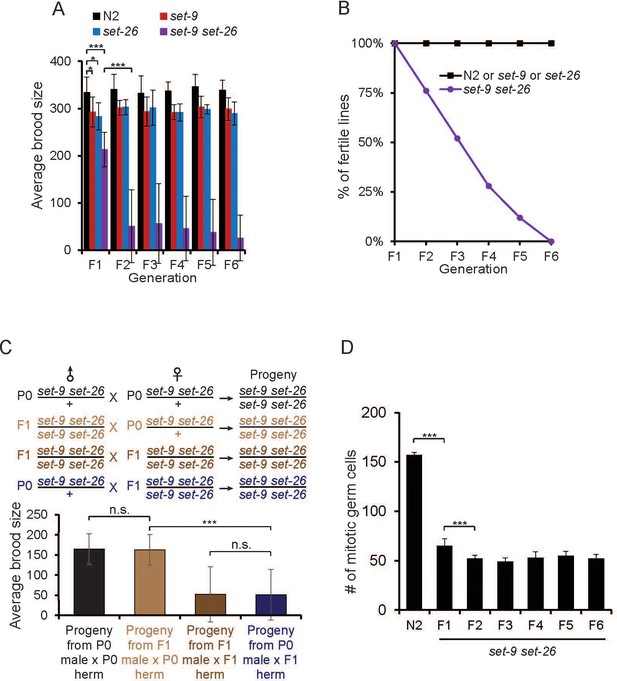
set-9 and set-26 act redundantly to maintain fertility.
(A) The set-9(rw5) set26(tm2467) double mutant worms derived from heterozygous parents (F1) displayed a mild fertility defect. The double mutant worms displayed a much more severe fertility defect at later generations (F2–F6). Average brood size of N2, set-26(tm2467), set-9(rw5), and set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) strains at the indicated generation were shown (*p<0.05, ***p<0.001). The error bars represent standard errors. n = 9 ~10 for N2, set-9 mutant, set-26 mutant, and F1 set-9 set-26 double mutant worms; n = ~50 for F2-F6 set-9 set-26 double mutants. (B) The set-9(rw5) set26(tm2467) double mutant exhibited a mortal germline phenotype. At each generation, 6 L1s for N2, set-26(tm2467), set-9(rw5) and set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) strains were transferred to a new plate. Plates were scored as not fertile when no progeny were found. % of fertile lines indicated percentage of plates that were fertile. n = 6 for N2, set-9 and set-26 mutants; n = 25 for set-9 set-26 double mutants. (C) Maternal contribution of set-9 and set-26 appeared important for alleviating the fertility defect in the double mutant. Average brood size of the set-9(rw5) set26(tm2467) double mutants derived from four different crosses were shown (***p<0.001, n.s. no significant). n = 11 ~ 12 for assessing the brood size of the set-9(rw5) set26(tm2467) homozygous progeny from heterozygous male(P0) X heterozygous hermaphrodite(P0) and homozygous male(F1) X heterozygous hermaphrodite(P0); n = 30 ~34 for progeny from homozygous male (F1) X heterozygous hermaphrodite(P0) and heterozygous male(P0) X homozygous hermaphrodite(F1). (D) The set-9(rw5) set26(tm2467) double mutant worms that remained fertile nevertheless exhibited reduced number of mitotic germ cells. Whole worms or dissected gonads of fertile set-9(rw5) set26(tm2467) mutants were stained by DAPI and the mitotic cells were counted. D2 adults were scored. n = 18 ~ 27, ***p<0.001. Analyses of sterile set-9(rw5) set26(tm2467) double mutant worms are shown in Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Quantitative data are shown in Supplementary file 1 Table S2.
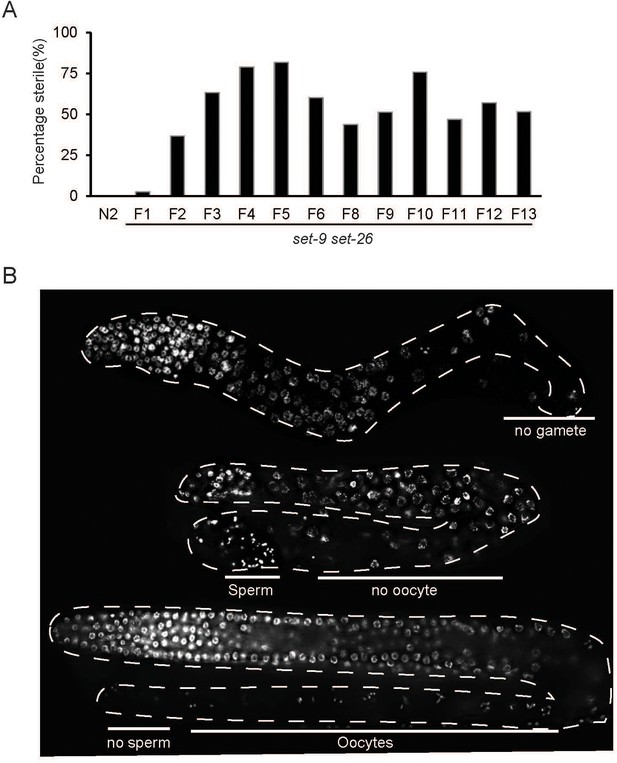
Fertility defects of the set-9 set-26 double mutant.
(A) The set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant exhibited variable percentage of sterility at the different generations. N = 155–517. (B) Representative DAPI staining images showing the germline of three different sterile F3-F4 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant worms. The germline of these sterile worms showed variable phenotypes, including no differentiated germ cells, no oocytes, or no sperms. D1-D2 adults were scored.
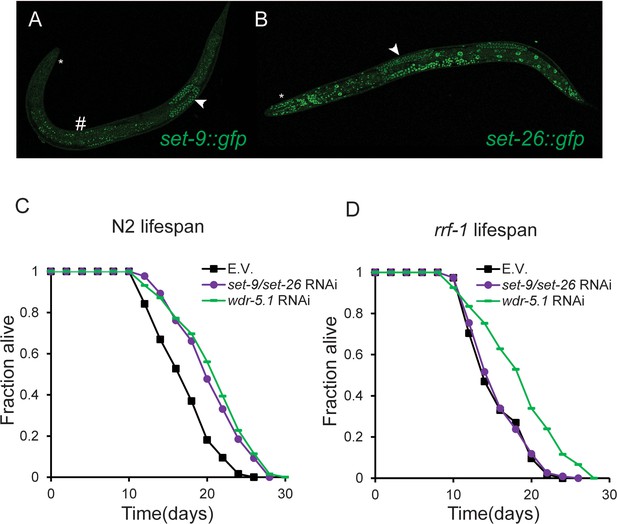
SET-26 is broadly expressed and SET-9 is only detectable in the germline.
(A, B) Fluorescent micrographs of worms carrying gfp knock-in at the C-terminus of set-9 or set-26 gene (set-9::gfp and set-26::gfp). GFP-fused SET-26 was detected in all cells and GFP-fused SET-9 was only detected in the germline. Star indicates head, arrow indicates germline in the images. The signal outside of the germline detected in the set-9::gfp strain represented autofluorescence (marked by hashtag), which appeared yellow under the microscope. (C, D) Germline-specific knockdown of set-9 and set-26 was not sufficient to extend lifespan. RNAi Knockdown of set-9 and set-26 or wdr-5.1 extended lifespan in N2 worms (C). RNAi knockdown of wdr-5.1, but not set-9 and set-26, extended lifespan in the rrf-1(pk1417) mutant worms. Quantitative data are shown in Supplementary file 1 Table S3.
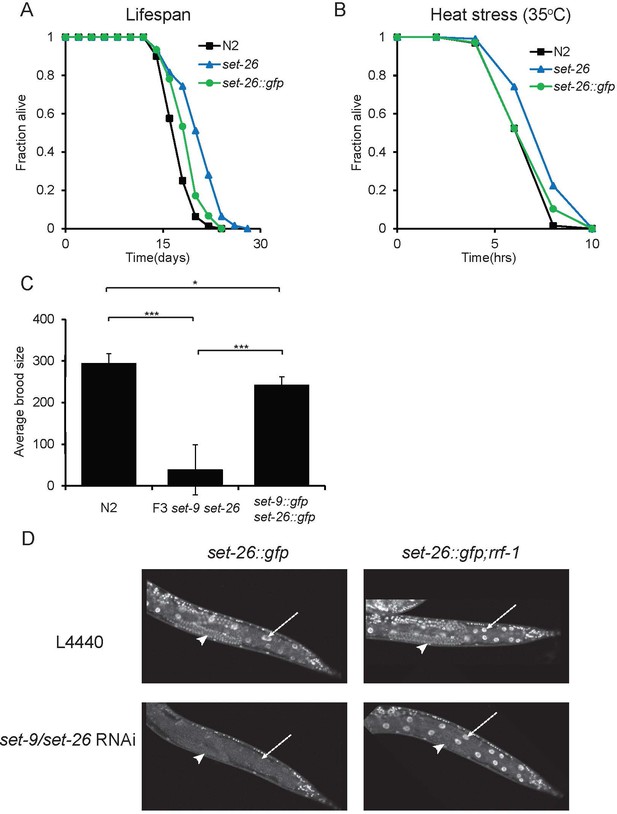
GFP-tagged SET-9 and SET-26 are largely functional.
(A–B) Worms carrying a gfp knock-in at the C-terminus of set-26 exhibited mild lifespan extension and heat resistance phenotypes, but the phenotypes were much weaker than those of the loss-of-function set-26(tm2467) mutant. (C) Worms carrying gfp knock-ins at the C-termini of set-9 and set-26 genes exhibited a mild fertility defect, which was significantly different from the severe fertility defect observed in the set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant (*p<0.05, ***p<0.001). n = 8–10 for set-9::gfp set-26::gfp and N2; n = 28 for F3 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467). Quantitative data are shown in Supplementary file 1 Table S4. (D) SET-26::GFP expression upon RNAi knockdown of set-9 and set-26 and L4440. set-26::gfp; rrf-1(pk1417) and set-26::gfp strains are shown. Arrow heads indicate germline, arrows indicate intestine nuclei in the images.
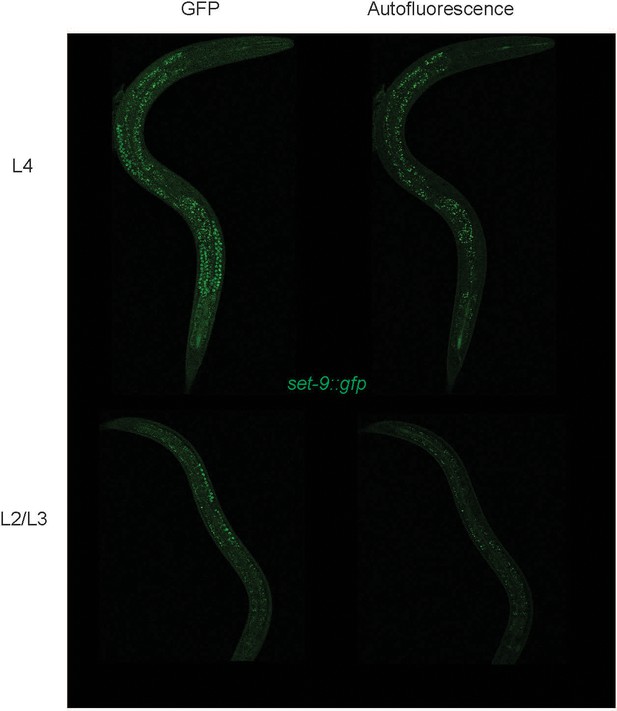
GFP-tagged SET-9 is only detectable in the germline.
Fluorescent micrographs of worms carrying gfp knock-in at the C-terminus of set-9 gene (set-9::gfp) is shown. ‘GFP’ indicates signals under GFP channel and ‘Autofluorescence’ indicates signals under YFP channel. Top panel shows L4 stage worm whereas bottom panel shows L2/L3 stage.
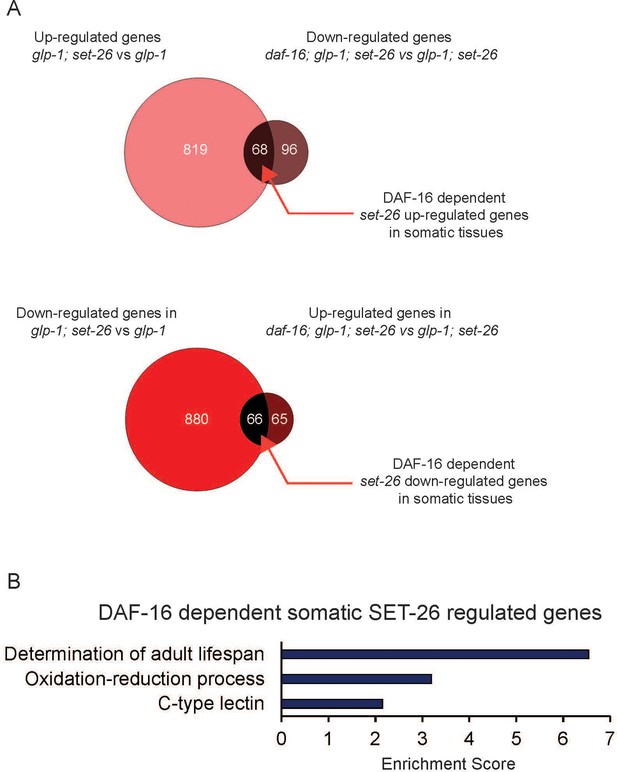
DAF-16-dependent somatic SET-26 regulated genes are enriched for lifespan determinant genes.
(A) Venn diagrams show the overlap between up-regulated genes in glp-1(e2141); set-26(tm2467) (comparing with glp-1(e2141)) and down-regulated genes in daf-16(mgDf47); glp-1(e2141); set-26(tm2467) (comparing with glp-1(e2141); set-26(tm2467)); and the overlap between down-regulated genes in glp-1(e2141); set-26(tm2467) (comparing with glp-1(e2141)) and up-regulated genes in daf-16(mgDf47); glp-1(e2141); set-26(tm2467) (comparing with glp-1(e2141); set-26(tm2467)). (B) GO term analysis of DAF-16-dependent somatic SET-26 regulated genes. Gene lists can be found in Supplementary file 2.
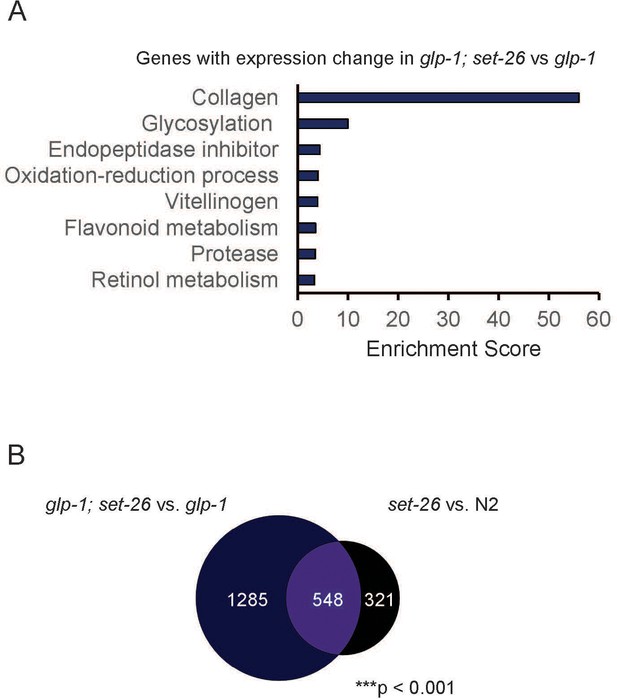
Transcriptional profile of glp-1(e2141); set-26(tm2467) mutant.
(A) GO term analysis of genes with expression change in glp-1(e2141); set-26(tm2467) (comparing with glp-1(e2141)). (B) Venn diagram shows the overlap between set-26 regulated genes in glp-1(e2141); set-26(tm2467) (comparing with glp-1(e2141)) and set-26 regulated genes in set-26(tm2467) (comparing with N2). Gene lists can be found in Supplementary file 2.
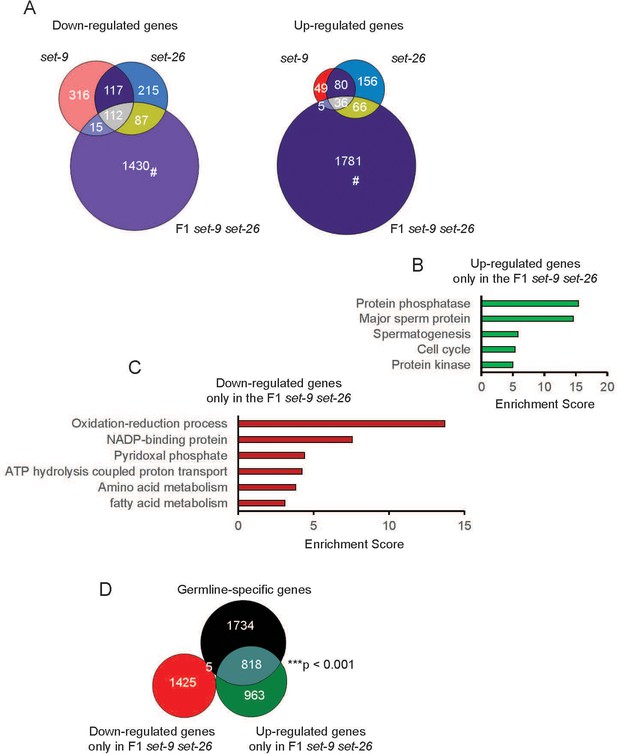
Transcriptional profiles of set-9(rw5), set-26(tm2467), and F1 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) mutants.
(A) Venn diagrams show the overlap among set-9(rw5), set-26(tm2467), and set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) down-regulated (left) and up-regulated (right) gene sets. Hashtag indicates genes that only show expression change in the F1 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant. GO term analysis of up-regulated (B) and down-regulated (C) genes that only show expression change in the F1 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant. (D) Venn diagram shows the overlaps between genes that only show expression change in the F1 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant identified in our RNA-seq data with the previously reported germline-specific gene lists (Reinke et al., 2004). Gene lists can be found in Supplementary file 2.
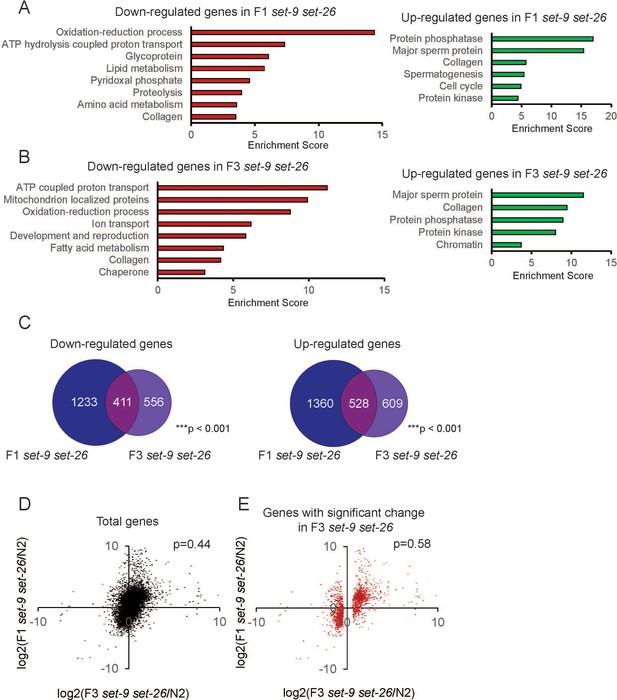
Transcriptional profile comparison between F1 and F3 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutants.
(A) GO term analysis of down-regulated and up-regulated genes in F1 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant. (B) GO term analysis of down-regulated and up-regulated genes in F3 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant. (C) Venn diagrams show the overlaps between down-regulated and up-regulated genes in the F1 and F3 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutants. (D) Scatter plot of log2 fold change of all mRNAs in F3 and F1 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant. (E) Scatter plot of log2 fold change of genes in F3 and F1 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutants. Only genes that show significant expression change in set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutants are shown. Gene lists can be found in Supplementary file 2.
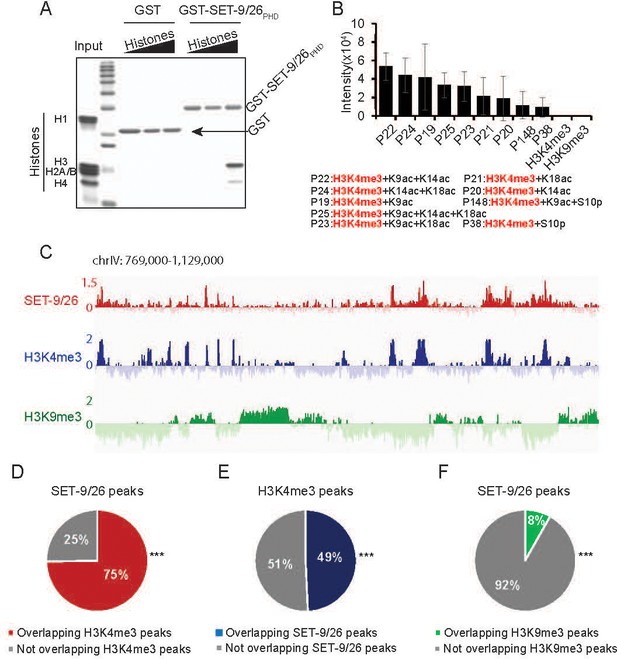
SET-9 and SET-26 bind to H3K4me3.
(A) PHD domain of SET-9 and SET-26 specifically pulled down H3 in vitro. Coomassie-blue stained gel showing pulldown results using GST–SET-9/26PHD and GST control. (B) Binding intensity of GST-SET-9/26PHD to the significant hits from histone peptide arrays. Quantitative data are shown in Supplementary file 1 Table S5. (C) Genome browser view showing ChIP z-scores (standardized log2 ratios of ChIP/Input or ChIP/H3ChIP signals) for SET-9/26, H3K4me3 and H3K9me3 at a representative region. (D) 75% of the SET-9 and SET-26 peaks overlapped with H3K4me3 peaks. (***p<0.001 indicates overlapping more than expected) (E) 49% of the H3K4me3 peaks overlapped with SET-9 and SET-26 peaks. (***p<0.001 indicates overlapping more than expected) (F) 8% of the SET-9/26 peaks overlapped with H3K9me3 peaks. (***p<0.001 indicates overlapping less than expected).
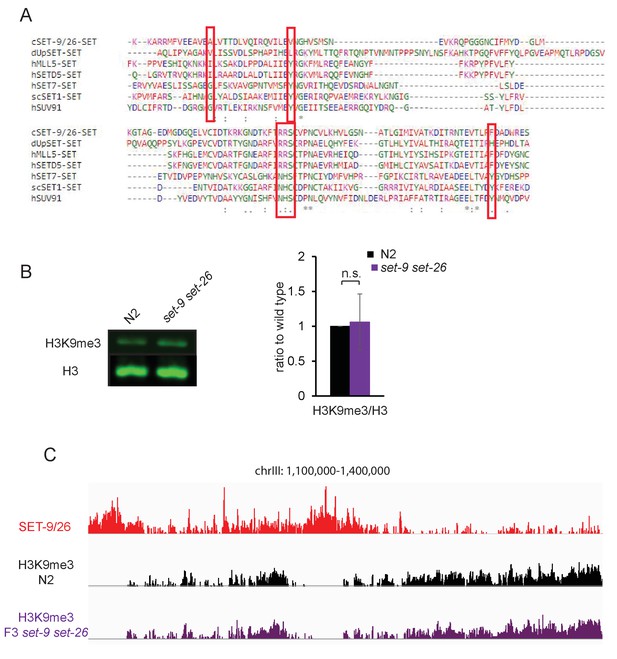
SET-9 and SET-26 are not the major enzymes for H3K9me3 in vivo.
(A) Clustal Omega alignment of the SET domains of SET-9 and SET-26 from C. elegans, SETD5, MLL5, SET7 and SUV91 from human, UpSET from Drosophila melanogaster and SET1 from Saccharomyces. Red boxes indicate the proposed key residues. The online tool used is: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/. (B) Western blotting showing H3K9me3 levels in N2 and the set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant (left). Synchronized L4 worms for N2 and the set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant were used. Quantification of three independent Western experiments (right). (C) Representative genome browser views of H3K9me3 profiles in N2 (black) and the F3 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant (purple). z-scores for normalized H3K9me3 and SET-9 and SET-26 ChIP signals in N2 and the set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) are shown.
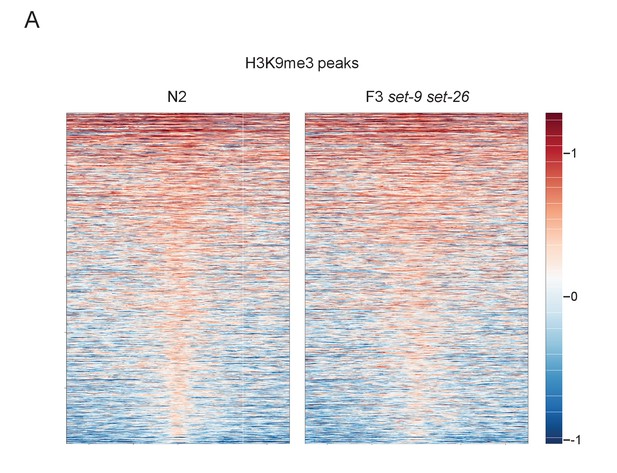
SET-9 and SET-26 are not the major enzymes for H3K9me3 in vivo (part 2).
(A) Heatmaps showing the H3K9me3 profiles in wild-type and the F3 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant for all H3K9me3 peaks.
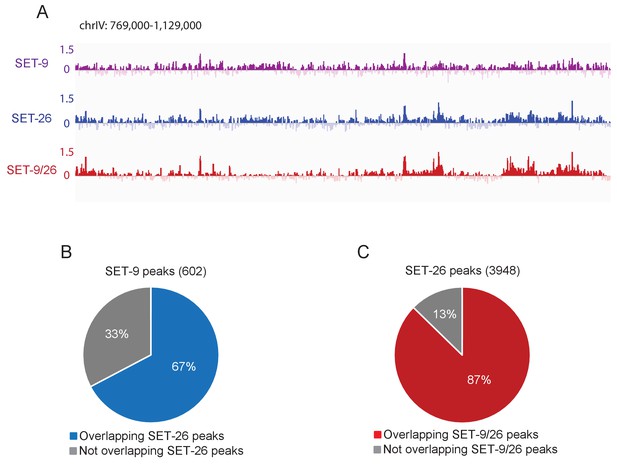
SET-9 and SET-26 share similar genomic binding profiles in vivo.
(A) Genome browser view showing ChIP z-scores (standardized log2 ratios of ChIP/Input or ChIP/H3ChIP signals) for SET-9, SET-26 and SET-9/26 at a representative region. (B) A large proportion of SET-9 peaks overlapped with SET-26 peaks. (C) A large proportion of SET-26 peaks overlapped with SET-9 and SET-26 peaks.
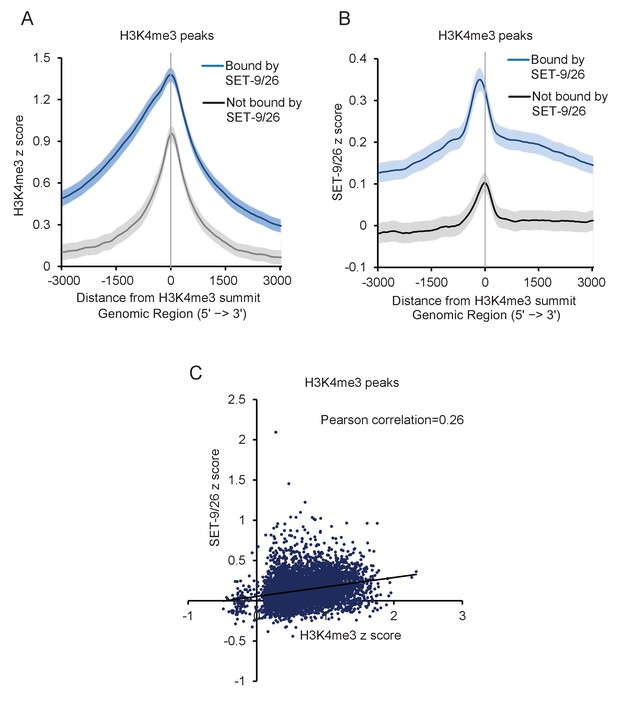
SET-9 and SET-26 bind to H3K4me3 in vivo.
(A) Metagene plots showing the average H3K4me3 z-score (standardized log2 ratios of H3K4me3ChIP/H3ChIP signals) for the H3K4me3 peaks bound (shown in blue) and not bound by SET-9 and SET-26 (shown in grey) in N2 worms. Regions 3000 bp upstream and downstream of the peak summits are shown. The light blue and light grey indicate 95% confidence intervals. (B) Metagene plots showed the average SET-9 and SET-26 z-score (standardized log2 ratios of SET-9 and SET-26 ChIP/input signals) for the H3K4me3 peaks bound (shown in blue) and not bound by SET-9 and SET-26 peaks (shown in grey). The light blue and light grey indicate 95% confidence intervals. (C) Scatter plot of H3K4me3 z-score and SET-9 and SET-26 z-score for H3K4me3 peak regions.
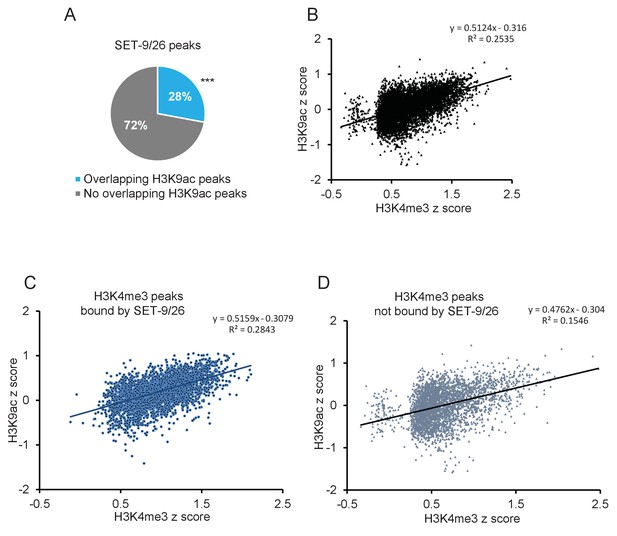
SET-9 and SET-26 bind to H3K4me3 in vivo (part 2).
(A) 28% of the SET-9 and SET-26 peaks overlapped with H3K9ac peaks. (***p<0.001 indicates overlapping more than expected) (B) Scatter plot of H3K4me3 z-score and H3K9ac z-score for all H3K4me3 peak regions. (C) Scatter plot of H3K4me3 z-score and H3K9ac z-score for H3K4me3 peak regions bound by SET-9 and SET-26. (D) Scatter plot of H3K4me3 z-score and H3K9ac z-score for H3K4me3 peak regions not bound by SET-9 and SET-26.
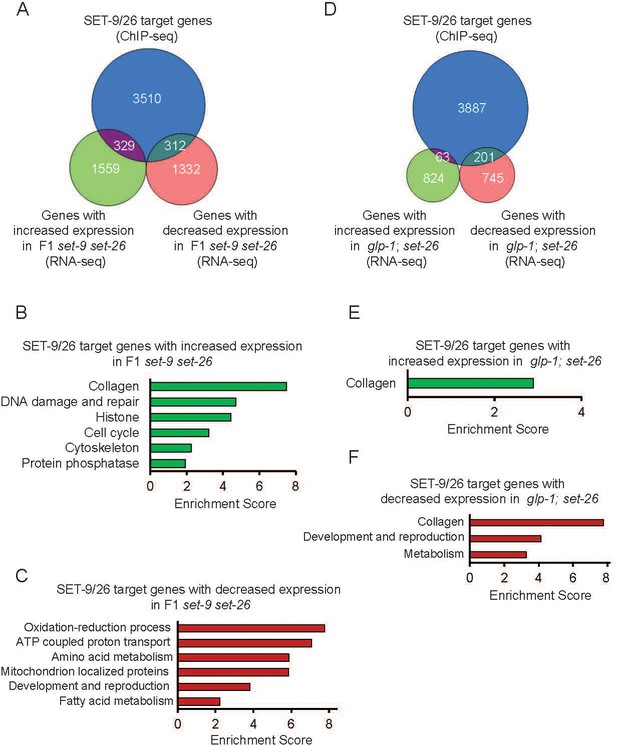
Binding of SET-9 and SET-26 regulate the RNA expression of specific target genes.
(A) Venn diagram showing comparisons of the genes with increased and decreased expression changes in the F1 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant and the SET-9 and SET-26 target genes. (B) GO term analyses of the up-regulated genes in the F1 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant that were bound by SET-9 and SET-26. (C) GO term analyses of the down-regulated genes in the F1 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant that were bound by SET-9 and SET-26. (D) Venn diagram showing comparisons of the up-regulated and down-regulated somatic SET-26 regulated genes and the SET-9 and SET-26 target genes. (E) GO term analyses of the up-regulated somatic SET-26 regulated genes bound by SET-9 and SET-26. (F) GO term analyses of the down-regulated somatic SET-26 regulated genes bound by SET-9 and SET-26. Gene lists can be found in Supplementary file 2.
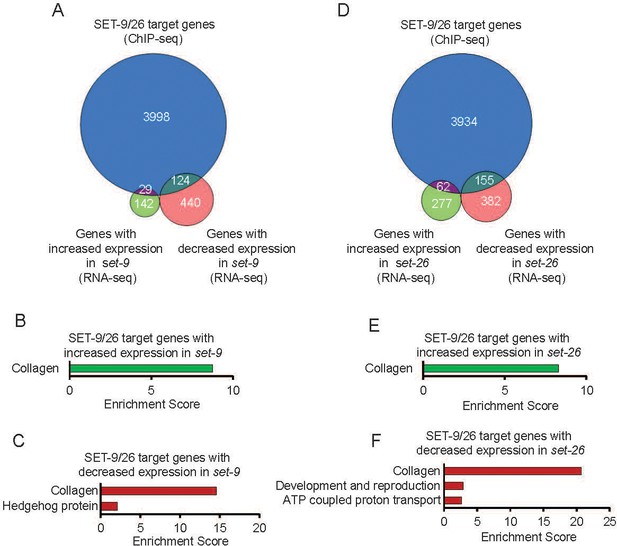
SET-9 and SET-26 target genes.
(A) Venn diagrams showing comparisons of the genes with increased and decreased expression changes in the set-9(rw5) mutant. (B) GO term analyses of the up-regulated genes in set-9(rw5) bound by SET-9 and SET-26. (C) GO term analyses of the down-regulated genes in set-9(rw5) bound by SET-9 and SET-26. (D) Venn diagrams showing comparisons of the genes with increased and decreased expression changes in the set-26(tm2467) mutant. (E) GO term analyses of the up-regulated genes in set-26(tm2467) bound by SET-9 and SET-26. (F) GO term analyses of the down-regulated genes in set-26(tm2467) bound by SET-9 and SET-26. Gene lists can be found in Supplementary file 2.
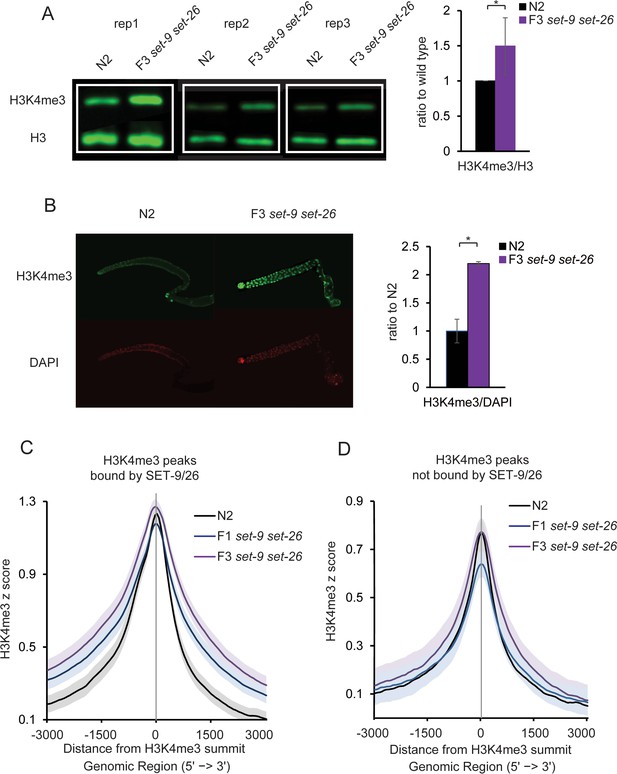
SET-9 and SET-26 restrict the spreading of H3K4me3.
(A) Western blotting of H3K4me3 levels in three independent replicates of wild type and F3 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant (left). Synchronized L4 worms for N2 and the F3 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant were used. Quantification of normalized H3K4me3 levels from three independent Western experiments (right). (*p<0.05) (B) Elevated H3K4me3 levels were observed in the dissected gonads of the F3 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant. Synchronized D1-D2 adults for N2 and the F3 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant were used. Representative immunostaining images are shown. Right panel shows quantification of images shown on left. (*p<0.05) (C) Metagene plots showing the average H3K4me3 z-score (standardized log2 ratios of ChIP/H3ChIP signals) for the peaks bound by SET-9 and SET-26 in N2 (black) and the F1 (blue) and F3 (purple) set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutants. Regions 3000 bp upstream and downstream of the peak summits are shown. The grey areas indicate 95% confidence intervals. (D) Metagene plots showing the average H3K4me3 z-score for the peaks not bound by SET-9 and SET-26 in N2 (black) and the F1 (blue) and F3 (purple) set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant. The grey areas indicate 95% confidence intervals.
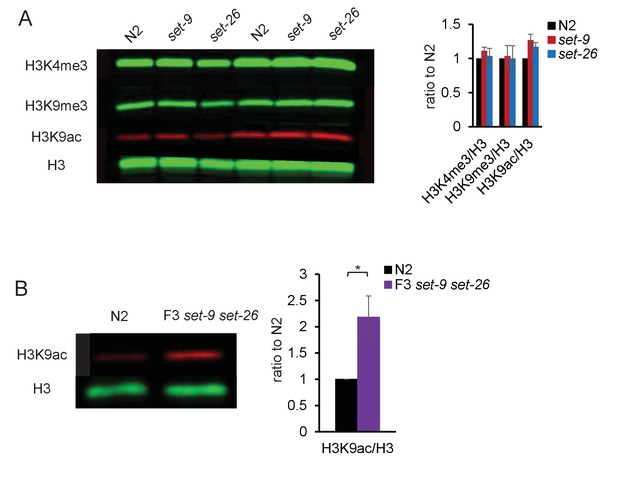
SET-9 and SET-26 restrict the spreading of H3K4me3.
(A) H3K4me3 and H3K9me3 levels in N2, set-9(rw5) and set-26(tm2467) mutants. Synchronized L4 worms were used. Quantification showed results from three independent experiments. (B) Western blotting showing elevated H3K9ac levels in the set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant (left). Synchronized L4 worms for N2 and the set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant were used. Quantification of normalized H3K9ac levels from three independent Western experiments (right). (*p<0.05).
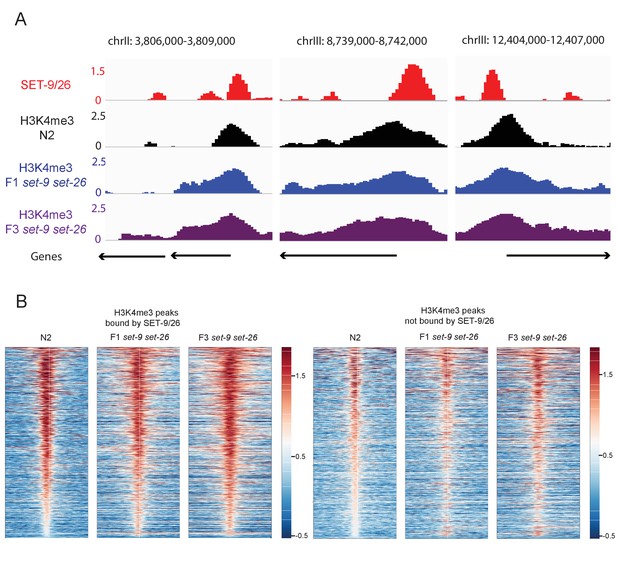
SET-9 and SET-26 restrict the spreading of H3K4me3 (part 2).
(A) Representative genome browser views of H3K4me3 profiles in N2 (black) and the F1 (blue) and F3 (purple) set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant surrounding SET-9 and SET-26 binding sites (red). z-scores for normalized H3K4me3 and SET-9 and SET-26 ChIP signals in N2 and the F1 and F3 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) are shown. (B) Heatmaps showing the H3K4me3 profiles in wild-type and the F1 and F3 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant for H3K4me3 peaks bound and not bound by SET-9/26.
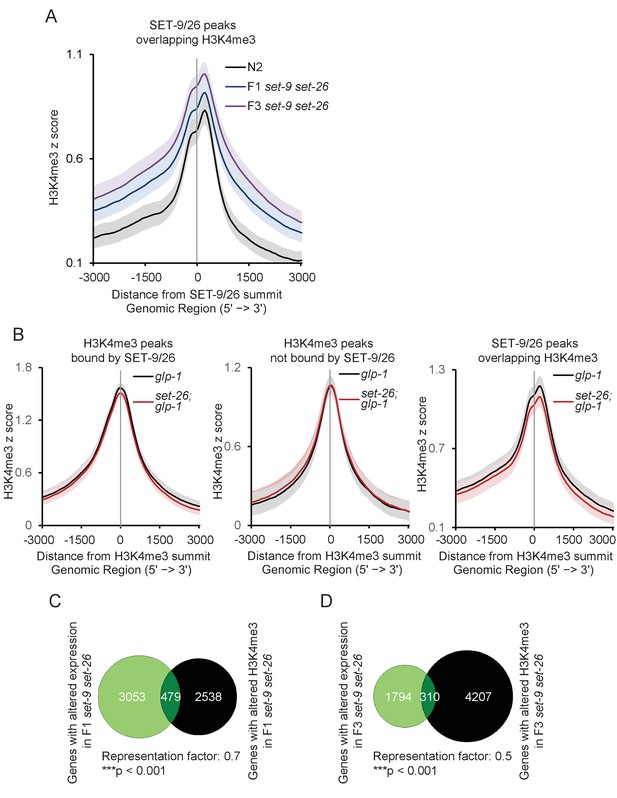
SET-9 and SET-26 restrict the spreading of H3K4me3 (part 3).
(A) Metagene plots showing the average H3K4me3 z-score (standardized log2 ratios of ChIP/H3ChIP signals) in N2 (black) and the F1 (blue) and F3 (purple) set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutants. Regions 3000 bp upstream and downstream of the peak summits of SET-9 and SET-26 binding are shown. The light grey and light purple areas indicate 95% confidence intervals. (B) Metagene plots showing the average H3K4me3 z-score (standardized log2 ratios of ChIP/H3ChIP signals) in glp-1(e2141) (black) and glp-1(e2141); set-26(tm2467) (orange) for H3K4me3 peaks bound by SET-9 and SET-26 (left), not bound by SET-9 and SET-26 (middle) and SET-9 and SET-26 peaks overlapping H3K4me3 (right). The light grey and light purple areas indicate 95% confidence intervals. (C, D) Venn diagrams showing genes with altered expression in the F1 and F3 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant identified by RNA-seq and genes with altered H3K4me3 in the F1 and F3 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant identified by ChIP-seq. (***p<0.001 indicate less than expected). Gene lists can be found in Supplementary file 2.
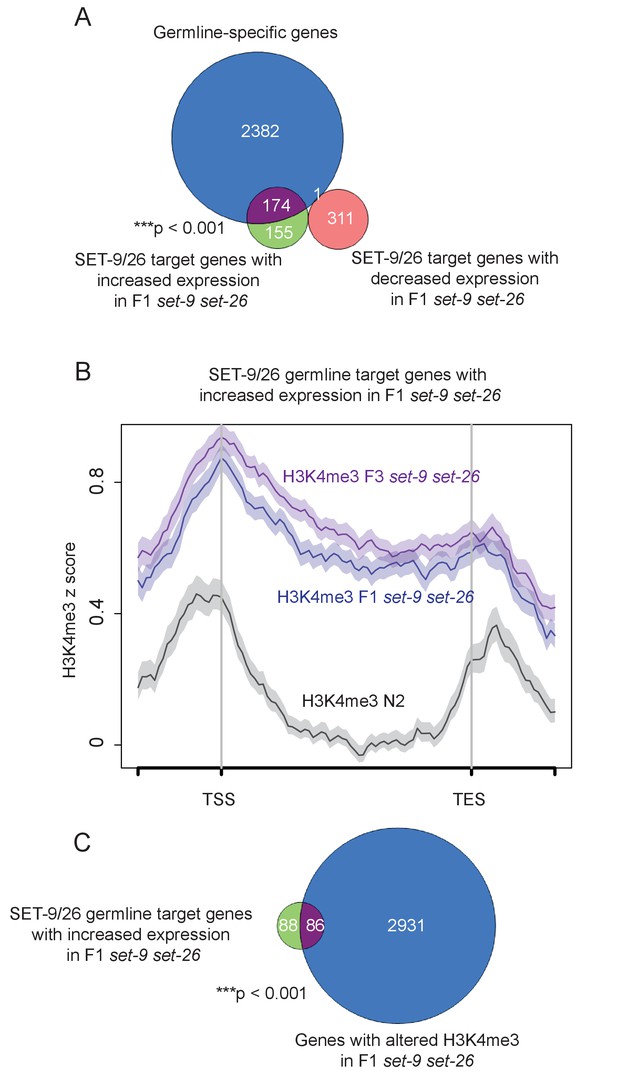
Germline-specific genes show correlated changes in H3K4me3 and RNA expression.
(A) Venn diagram shows the overlaps between SET-9/26 target genes with expression change in F1 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) and germline-specific genes. (B) Average H3K4me3 z-score in N2 (black) and the F1 (blue) and F3 (purple) set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutants for the SET-9/26 germline target genes that showed elevated expression in F1 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) (compared to N2). (C) Venn diagram shows the overlap between SET-9/26 germline target genes with increased RNA expression in F1 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant and genes with expanded H3K4me3 marking in F1 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant. Gene lists can be found in Supplementary file 2.
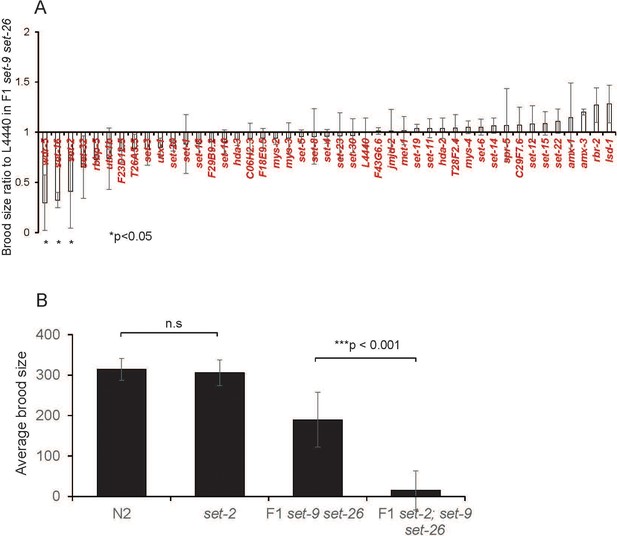
SET-9 and SET-26 and SET-2 act synergistically to regulate fertility.
(A) Ratio of eggs laid by F1 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant worms fed dsRNA of C. elegans potential histone modifiers (mainly methyltransferases and demethylases) or empty vector (L4440) for one generation. (B) Average brood size in N2, set-2(ok952), F1 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) double mutant and F1 set-2(ok952); set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) triple mutant.
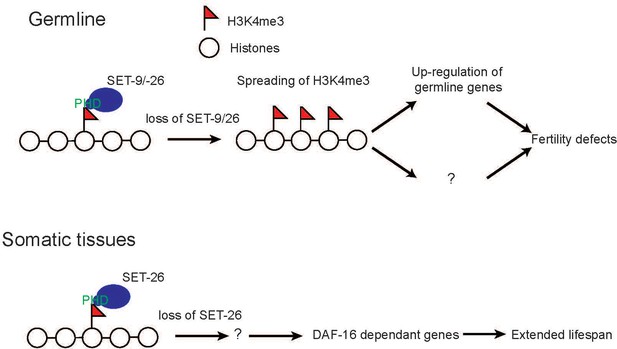
SET-9 and SET-26 regulate H3K4me3 and target gene expression.
In the germline, loss of set-9 and set-26 results in the broadening of H3K4me3 domains surrounding most SET-9 and SET-26 binding regions and up-regulation of germline genes. In the soma, loss of set-26 modulates lifespan by indirectly regulating DAF-16-dependent genes. We propose that SET-9 and SET-26 are critical for organizing local chromatin environment and regulating the expression of specific target genes, and these activities together contribute to their roles in germline development and longevity.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Quantitative data for experiments reported.
Table S1 (A) Lifespan data for Figure 1B were shown. (B) Heat stress resistance data for Figure 1C were shown. Table S2 (A) Brood size data for Figure 2A were shown. (B) Mortal germline assay data for Figure 2B were show. (C) Maternal and paternal effect on brood size for Figure 2C were shown. (D) Mitotic germ cell number for Figure 2D were shown. Table S3 (A) Wild type lifespan data with RNAi treatment for Figure 3B were shown. (B) rrf-1(pk1417) mutant lifespan data with RNAi treatment for Figure 3C were shown. Table S4 (A) Lifespan data for Figure 3—figure supplement 1A were shown. (B) Heat stress resistance data for Figure 3—figure supplement 1B were shown. (C) Brood size data for Figure 3—figure supplement 1C were shown. Table S5 (A) Histone peptide array binding assay for Figure 6B were shown. Table S6 (A) qPCR RNA-seq validation for set-26(tm2467) compare with wild type data were shown. (B) qPCR RNA-seq validation for F3 set-9(rw5) set-26(tm2467) compare with wild type data were shown.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34970.028
-
Supplementary file 2
Gene lists for comparison indicated gene list comparisons were shown.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34970.029
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34970.030





