The glycosphingolipid MacCer promotes synaptic bouton formation in Drosophila by interacting with Wnt
Figures
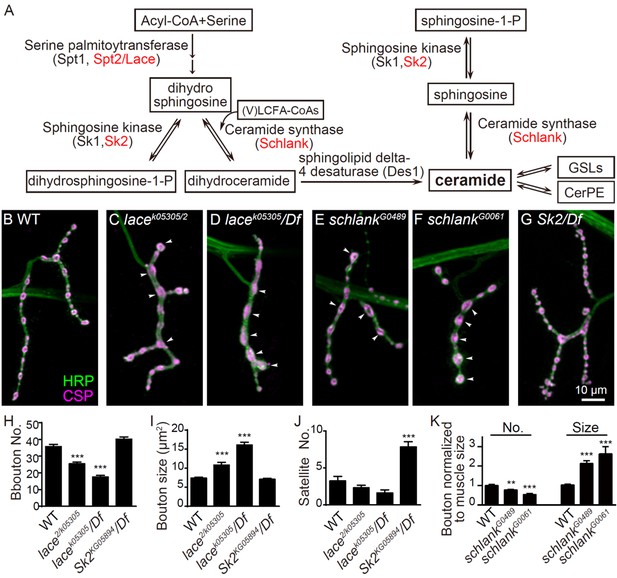
NMJ growth depends on de novo synthesis of ceramides
(A) Simplified de novo biosynthesis pathway of sphingolipid in Drosophila is shown.(B–G) Representative images of NMJ4 co-stained with anti-HRP (green) and anti-CSP (magenta) in wild type (B), lace k05305/lace2 (C), lacek05305/Df(2L)Exel7063 (D), schlankG0489/Y (E), schlankG0061/Y (F) and Sk2KG05894/Df(3L)BSC671 (G). Scale bar: 10 μm; Arrowheads indicate large boutons in different mutants. (H–J) Quantifications of bouton number (H), bouton size (I) and satellite bouton number (J) of NMJs in abdominal segments A3 or A4 of different genotypes. (K) Bouton number and size in schlank mutants were normalized to muscle surface area as schlank mutants showed decreased body size (Bauer et al., 2009). *p<0.05; **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001 by student’s t test between a test genotype and the wild-type control; n ≥ 10 larvae; error bars: s.e.m. Source data 1. Numerical data for the statistical graphs. The following figure supplement is available for Figure 1.
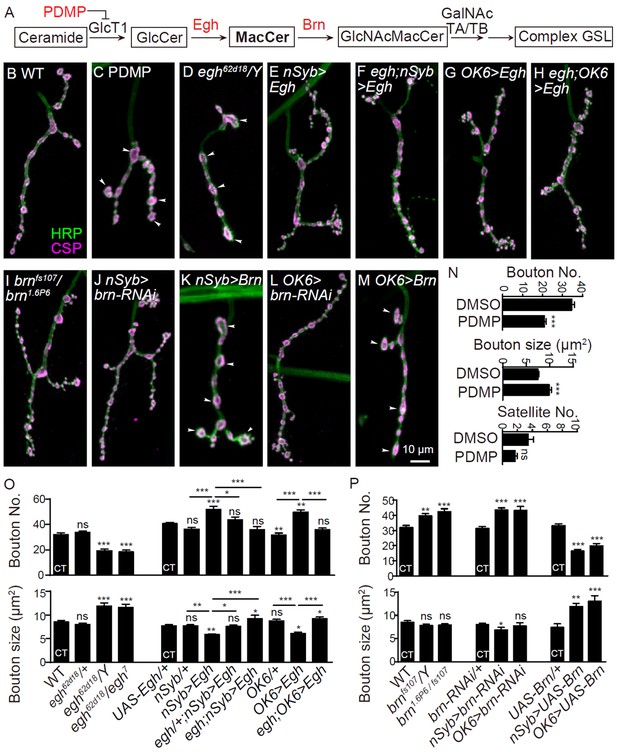
GSL synthases Egh and Brn bi-directionally regulates NMJ growth presynaptically
(A) GSL synthesis pathway in Drosophila.(B–M) Images of NMJ4 co-stained with anti-HRP (green) and anti-CSP (magenta) in wild type (B), larvae treated with 0.5 mg/ml D, L-threo-PDMP (C), egh62d18/Y (D), UAS-Egh/+; nSyb-Gal4/+ (E), egh62d18/Y; UAS-Egh/+; nSyb-Gal4/+ (F), UAS-Egh/OK6-Gal4 (G), egh62d18/Y; UAS-Egh/OK6-Gal4 (H) brn fs107/brn1.6P6 (I), UAS-brn-RNAi/+; nSyb-Gal4/+ (J) nSyb-Gal4/UAS-brn (K), UAS-brn-RNAi/OK6 Gal4 (L), and OK6-Gal4/+; UAS-brn/+ (M). Scale bar: 10 μm; Arrowheads point at large boutons. (N–P) Quantifications of total bouton number, bouton size, and satellite bouton number of NMJs in different genotypes or treated with PDMP. ‘CT’ denotes corresponding control in each multiple comparison.*p<0.05; **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc tests; n ≥ 12 larvae; error bars: s.e.m.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Numerical data for the statistical graphs.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38183.006
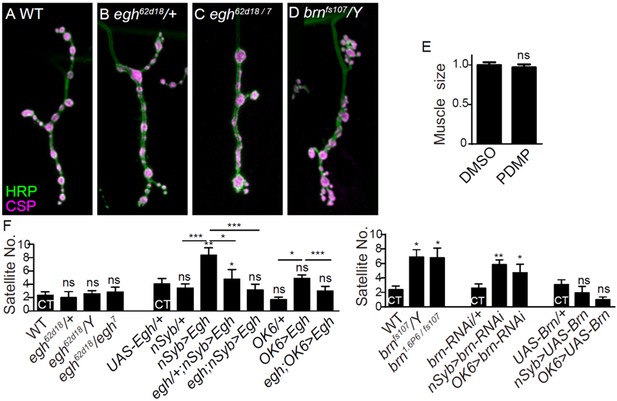
Additional NMJ images and quantifications.
(A–D) Images of NMJ4 co-stained with anti-HRP (green) and anti-CSP (magenta) in wild type (A), egh62d18/+ (B), egh62d18/egh7 (C), brnfs107/Y (D). Scale bar: 10 μm. (E) Quantifications of muscle four surface area from wild type with or without D, L-threo-PDMP treatment at 0.5 mg/ml. ns, no significance, one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc tests; n ≥ 8 larvae; error bars: s.e.m. (F) Quantifications of satellite bouton number of NMJ4 from different genotypes. ns, no significance, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc tests; n ≥ 12; error bars: s.e.m.
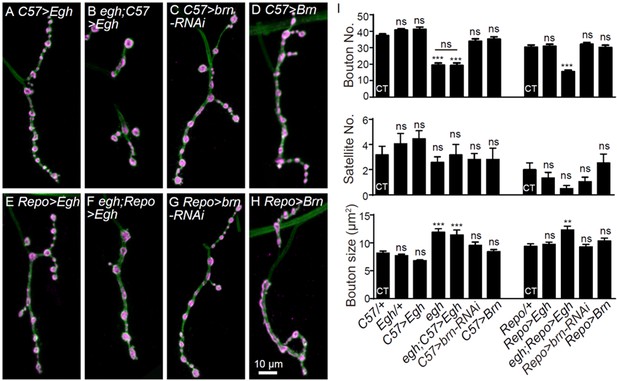
Alteration of egh and brn level in glia or muscle does not affect NMJ growth.
(A–H) Images of NMJ4 co-stained with anti-HRP (green) and anti-CSP (magenta) in UAS-Egh/+; C57-Gal4/+ (A), egh62d18/Y; UAS-Egh/+; C57-Gal4/+ (B), UAS-brn-RNAi/+; C57-Gal4/+ (C), UAS-brn/C57-Gal4 (D), UAS-Egh/+; Repo-Gal4/+ (E), egh62d18/Y; UAS-Egh/+; Repo-Gal4/+ (F), UAS-brn-RNAi/+; Repo-Gal4/+ (G) and UAS-brn/Repo Gal4 (H). Scale bar: 10 μm. (I) Quantifications of bouton number, satellite bouton number, and bouton size of NMJ4 from different genotypes. ‘CT’ denotes corresponding control in each multiple comparison. ns, no significance, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc tests; n ≥ 12 larvae; error bars: s.e.m.
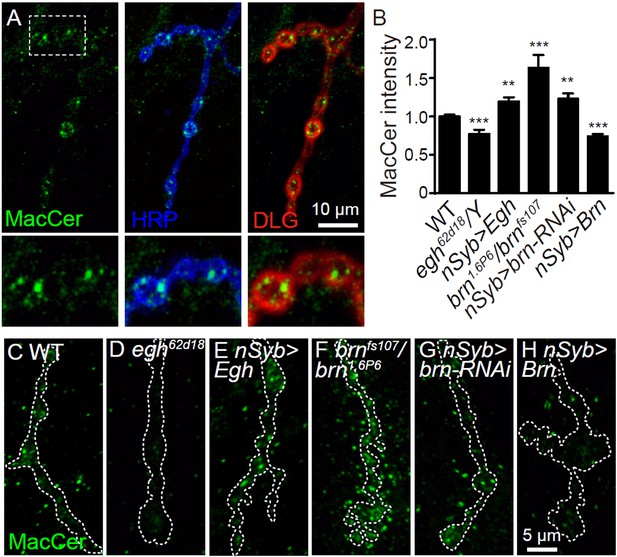
MacCer staining intensity at NMJs is bi-directionally regulated by Egh and Brn.
(A) Images of wild-type NMJ4 co-stained with anti-MacCer (green), anti-HRP (blue) and anti-DLG (red).MacCer puncta were apparent in presynaptic boutons. Scale bar: 10 μm. (B) Statistical results of normalized intensities of MacCer against anti-HRP staining within presynaptic boutons in different genotypes. **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 by student’s t test between a test genotype and wild type; n ≥ 16 larvae; error bars: s.e.m. (C–H) Representative images of NMJ4 stained with anti-MacCer in wild type (C), egh62d18/Y (D), UAS-Egh/+; nSyb-Gal4/+ (E), brn1.6P6/brnfs107 (F), UAS-brn-RNAi/+; nSyb-Gal4/+ (G) and nSyb-Gal4/UAS-Brn (H). Scale bar: 5 μm.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Numerical data for the statistical graphs.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38183.009
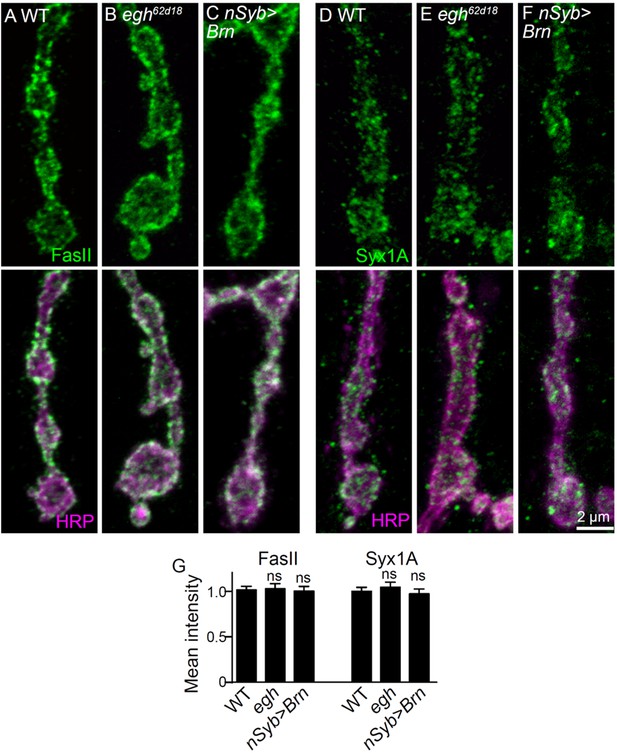
Images and quantifications of Fas II and Syx1A staining at NMJs of different genotypes.
(A–C) Images of NMJ4 co-stained with anti-Fas II (green) and anti-HRP (magenta) in wild type, egh62d18/Y, and nSyb-Gal4/UAS-brn. (D–F) Images of NMJ4 co-stained with anti-Syx1A (green) and anti-HRP (magenta) in wild type, egh62d18/Y, and nSyb-Gal4/UAS-brn. Scale bar: 2 μm. (G) Quantification of intensities of indicated markers normalized to HRP intensities in different genotypes. n ≥ 10 larvae; ns, no significance by student’s t test; error bars: s.e.m.
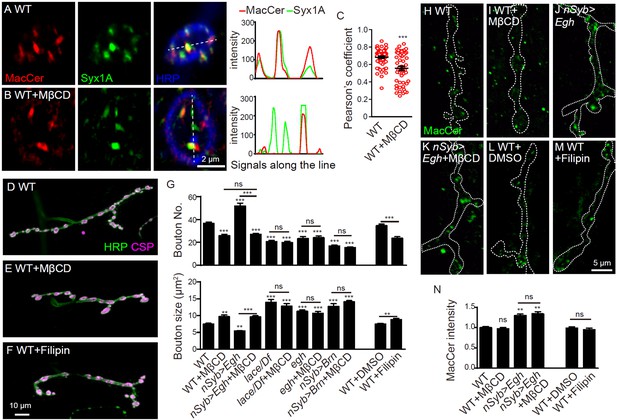
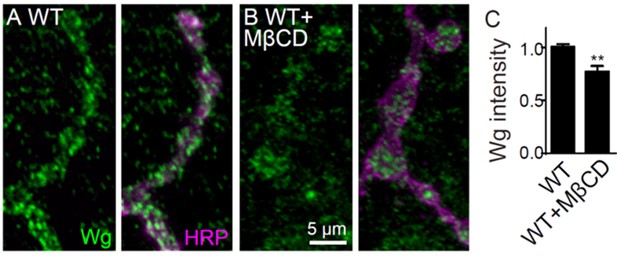
Sterol-depletion inhibits NMJ growth in a common genetic pathway with MacCer.
(A and B) Confocal images of single slice of NMJ4 boutons triple-labeled with anti-MacCer (red), anti-Syx1A (green) and anti-HRP (blue) in wild type with or without 20 mM MβCD treatment. Plot profiles of the relative intensity along the dashed lines are shown. (C) Pearson’s coefficients of colocalization between MacCer and Syx1A. n = 63 and 52 boutons from eight wild-type larvae each with or without MβCD treatment. (D–F) Images of NMJ4 co-labeled for anti-HRP (green) and anti-CSP (magenta) in untreated wild type (D), wild type treated with 20 mM MβCD (E), wild type treated with 50 μg/ml filipin III (F), Scale bar: 10 μm. (G) Quantification of bouton number and bouton size of NMJs. ns, no significance, ***p<0.001 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc tests, error bars: s.e.m. (H–M) Images of NMJs from larvae stained with anti-MacCer of wild type (H), wild type treated with 20 mM MβCD (I), UAS-Egh/+; nSyb-Gal4/+ (J), and UAS-Egh/+; nSyb-Gal4/+ treated with 20 mM MβCD (K), wild-type larvae treated with vehicle DMSO (L) or 50 μg/ml filipin III (M). Scale bar: 5 μm. (N) Quantification of MacCer intensities normalized to HRP intensities in different genotypes. ns, no significance; **p<0.01 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc tests; n ≥ 12 larvae; error bars: s.e.m.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Numerical data for the statistical graphs.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38183.012
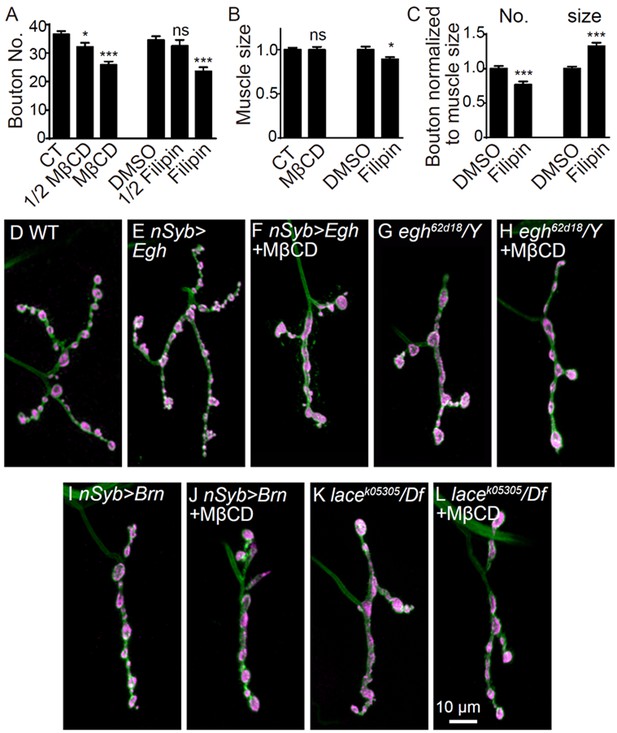
Additional NMJ images and quantifications of bouton number and bouton size.
(A) Quantification of bouton number of NMJ4 from wild-type larvae fed with 0 mM (CT), 10 mM, 20 mM MβCD and 0 μg/ml (DMSO vehicle only), 25 μg/ml, 50 μg/ml filipin III. (B and C) Quantifications of muscle four surface area (B), relative bouton number and size normalized to muscle surface area (C) upon indicated treatments. n ≥ 8 larvae; ns, no significance, *p<0.05, ***p<0.001 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc tests; error bars: s.e.m. (D–L) Images of NMJ4 co-labeled for anti-HRP (green) and anti-CSP (magenta) in untreated wild type (D), UAS-Egh/+; nSyb-Gal4/+ (E), UAS-Egh/+; nSyb-Gal4/+treated with 20 mM MβCD (F), egh62d18/Y (G), MβCD treated egh62d18/Y (H), nSyb-Gal4/UAS-brn (I), MβCD treated nSyb-Gal4/UAS-brn (J), lacek05305/Df(2L)Exel7063 (K), and MβCD treated lacek05305/Df(2L)Exel7063 (L). Scale bar: 10 μm.
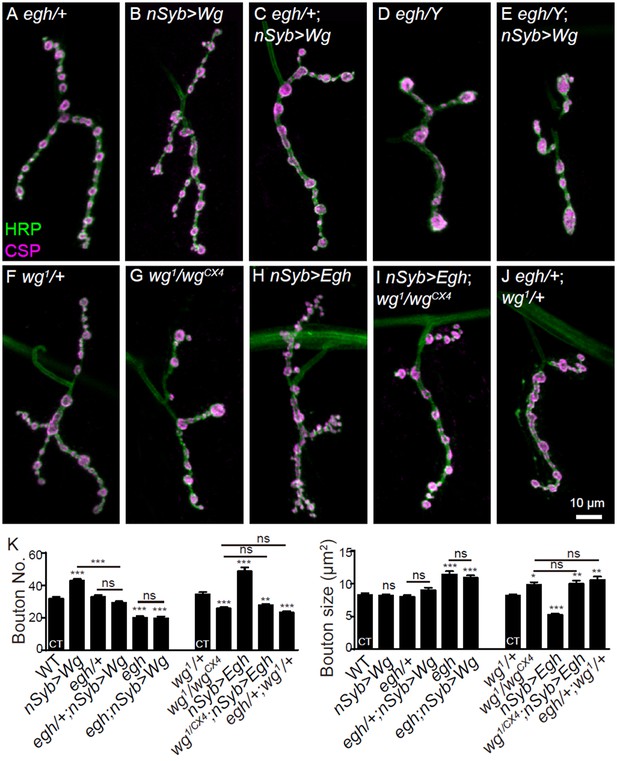
MacCer is required for the NMJ growth-promoting effect of Wg signaling.
(A–J) Representative images of NMJ4 co-stained with anti-HRP (green) and anti-CSP (magenta) in egh62d18/+ (control, (A), UAS-Wg-HA/+; nSyb-Gal4/+ (B), egh62d18/+; UAS-Wg-HA/+; nSyb-Gal4/+ (C), egh62d18 (D), egh62d18; UAS-Wg-HA/+; nSyb-Gal4/+ (E), wg1/+ (F), wg1/wgCX4 (G), nSyb-Gal4/UAS-Egh (H), wgCX4,UAS-Egh/wg1; nSyb-Gal4/+ (I), and egh62d18/+; wg1/+ (J).Scale bar: 10 μm. (K) Quantifications of bouton number and bouton size of NMJs in different genotypes. ‘CT’ denotes corresponding control in each multiple comparison. n ≥ 12 larvae; ns, no significance, *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc tests, error bars: s.e.m.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Numerical data for the statistical graphs.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38183.016
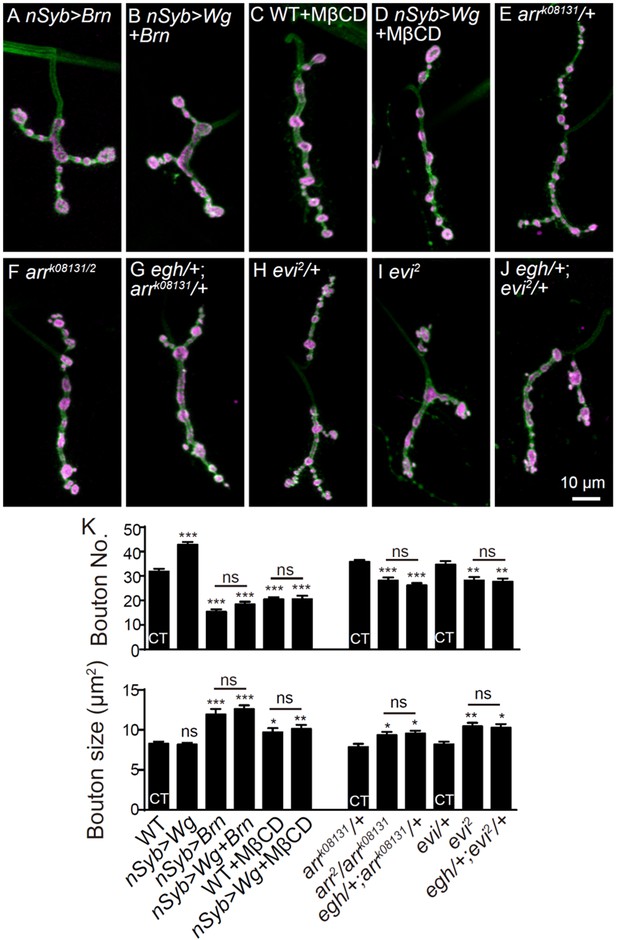
Additional NMJ images and quantifications.
Images of NMJ4 co-labeled for anti-HRP (green) and anti-CSP (magenta) in nSyb-Gal4/UAS-brn (A), UAS-Wg-HA/+; nSyb-Gal4/UAS-brn (B), wild type treated with 20 mM MβCD (C), UAS-Wg-HA/+; nSyb-Gal4/+ treated with 20 mM MβCD (D), arrk0813/+ (E), arrk0813/arr2 (F), egh62d18/+; arrk0813/+ (G), evi2/+ (H), evi2 (I), and egh62d18/+; evi2/+ (J). Scale bar: 10 μm. (K) Quantification of bouton number and bouton size of NMJs. n ≥ 12 larvae; ns, no significance, *p<0.05; **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc tests, error bars: s.e.m. (L and M) Representative images of NMJ4 co-labeled with anti-Wg (green) and anti-HRP (magenta) in wild type (L) and wild type treated with 20 mM MβCD (M). Scale bar: 5 μm. (N) Quantification of Wg intensity normalized to HRP intensity. n ≥ 15 larvae; ns, no significance; **p<0.01 by student’s t test; error bars: s.e.m.
Additional NMJ images and quantifications.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38183.015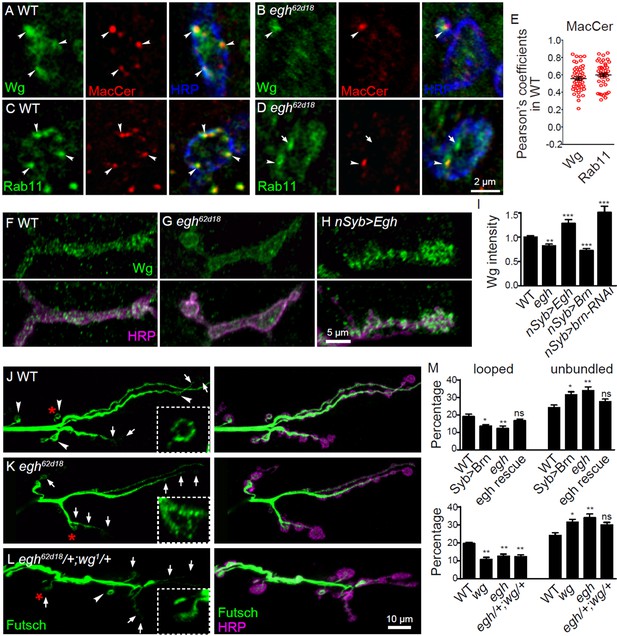
MacCer is required for the local presynaptic Wg signaling at NMJs.
(A–D) Confocal images of single slice of NMJ4 boutons triple-labeled with anti-MacCer (red), anti-HRP (blue) and anti-Wg (green; A–B) or anti-Rab11 (green; C–D) in wild type and egh62d18 mutants. MacCer puncta showed substantial colocalization (arrowheads) with Wg and Rab11 in boutons. Arrows indicate Rab11-positive puncta without MacCer staining in the egh62d18 mutants. Images were processed by deconvolution. Scale bar: 2 μm. (E) Pearson’s coefficients of colocalization between MacCer and indicated proteins. n = 51 and 44 boutons (from ten wild-type larvae each) for colocalization of MacCer with Wg and Rab11, respectively. (F–H) Representative images of NMJ4 co-labeled with anti-Wg (green) and anti-HRP (magenta) in wild type (F), egh62d18 mutants (G) and UAS-Egh/+; nSyb-Gal4/+(H). Scale bar: 5 μm. (I) Quantification of intensities of endogenous Wg normalized to HRP intensities in different genotypes. n ≥ 15 larvae; ns, no significance; **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 by student’s t test; error bars: s.e.m. (J–L) Representative images of NMJ6/7 labeled with anti-Futsch (green) and anti-HRP (magenta) in wild type (J), egh62d18 mutants (K) and egh62d18/+; wg1/+transheterozygotes (L). Insets show higher magnification images of Futsch staining of a single bouton (asterisk). Arrows indicate boutons displaying unbundled Futsch; arrowheads denote boutons with Futsch loops. Scale bar: 10 μm. (M) Quantifications of percentage of Futsch loops and unbundled Futsch staining in different genotypes. The genotype of egh rescue was egh62d18; UAS-Egh/+; nSyb-Gal4/+; the genotype of wg was wg1/wgCX4. n ≥ 12 larvae; ns, no significance, *p<0.05; **p<0.01 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc tests, error bars: s.e.m.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Numerical data for the statistical graphs.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38183.022
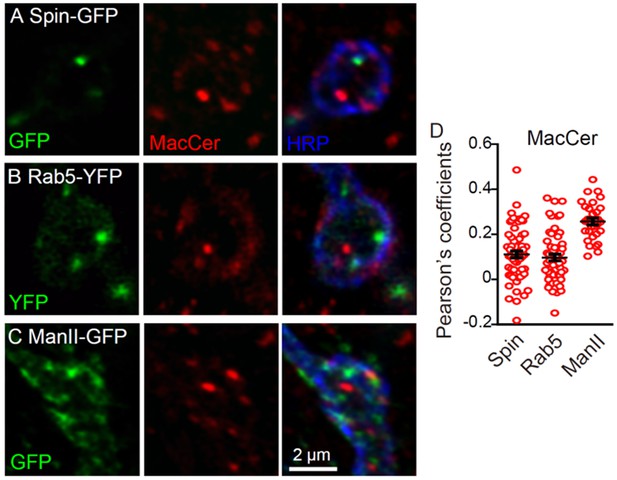
MacCer puncta showed few overlap with Rab5-YFP, Spinster-GFP and Mannose II-GFP.
Single sections of NMJ4 boutons triple-labeled with anti-MacCer (red), anti-HRP (blue), and specific organelle markers (green) in nSyb-Gal4/UAS-Spin-GFP (A), UAS-YFP-Rab5/+; nSyb-Gal4/+ (B), and nSyb-Gal4/UAS-ManII-GFP (C) larvae. MacCer puncta showed few overlaps with these organelles in NMJ boutons. Images were processed by deconvolution. Scale bar: 2 μm. (D) Pearson’s coefficients of colocalization between MacCer and indicated proteins. n = 61/9, 57/8, and 30/5 (from left to right, boutons/animals).
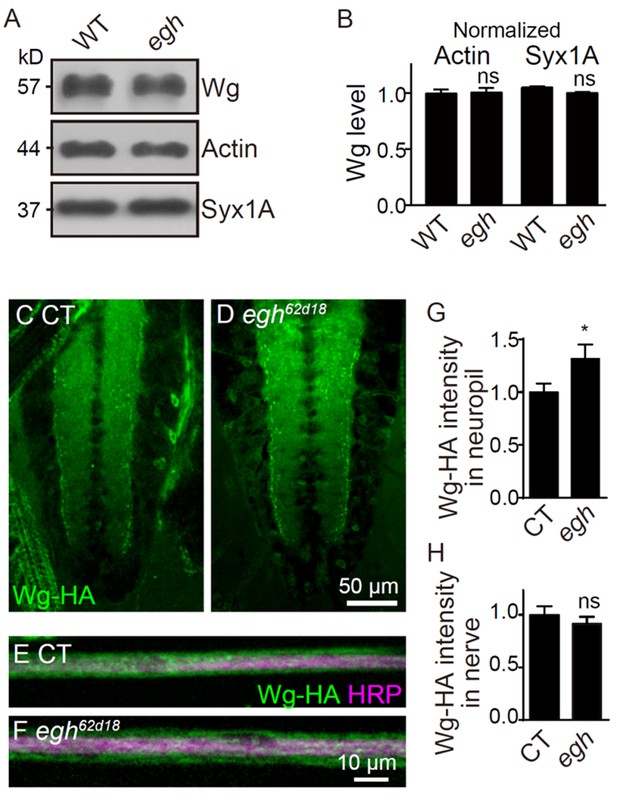
The Wg level in egh brains by immunochemical analysis.
(A and B) Western blotting and quantification of Wg from 3rd instar larval brains of wild type and egh62d18 mutants, normalized to the level of Actin and Syntaxin 1A (Syx1A). n = 3; ns, no significance by one-way ANOVA test; error bars: s.e.m. (C and D) Images of ventral nerve cord stained with anti-HA in UAS-Wg-HA/+; nSyb-Gal4/+ (control, C) and egh62d18/Y; UAS-Wg-HA/+; nSyb-Gal4/+ (D). Scale bar: 50 μm. (E and F) Images of segmental nerve stained with anti-HA (green) and anti-HRP (magenta) in UAS-Wg-HA/+; nSyb-Gal4/+ (control, E) and egh62d18/Y; UAS-Wg-HA/+; nSyb-Gal4/+ (F). Scale bar: 10 μm. (G and H) Quantifications of HA intensity in neuropils and segmental nerves of control and egh mutants. n ≥ 8 larvae; ns, no significance, *p<0.05 by student’s t test; error bars: s.e.m.
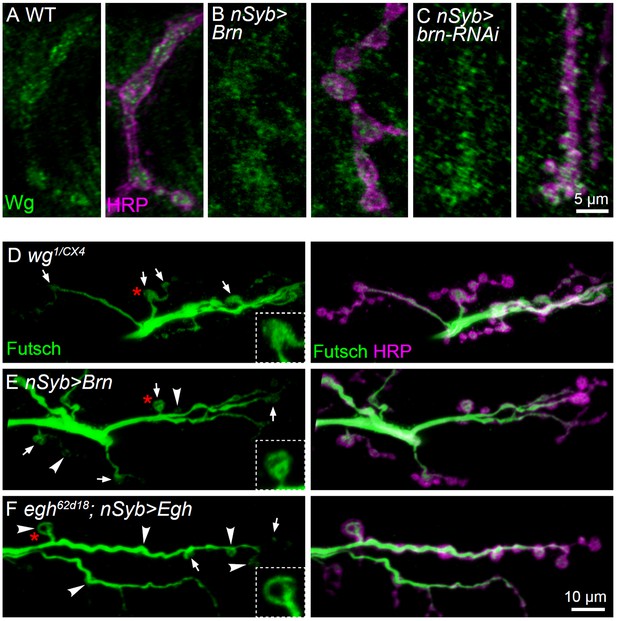
Additional images showing Wg and Futsch staining at NMJ of different genotypes.
(A–C) Representative images of NMJ4 co-labeled with anti-Wg (green) and anti-HRP (magenta) in wild type (A), nSyb-Gal4/UAS-brn (B) and UAS-brn-RNAi/+; nSyb-Gal4/+ (C). Scale bar: 5 μm. (D–F) Representative images of NMJ6/7 co-labeled with anti-Futsch (green) and anti-HRP (magenta) in wg1/wgCX4 (D), nSyb-Gal4/UAS-Brn (E), and egh62d18/Y; UAS-Egh/+; nSyb-Gal4/+ (F). Insets show higher magnification images of Futsch staining of a single bouton (asterisk in red). Arrows indicate boutons displaying unbundled Futsch; arrowheads denote boutons with Futsch loops. Scale bar: 10 μm..
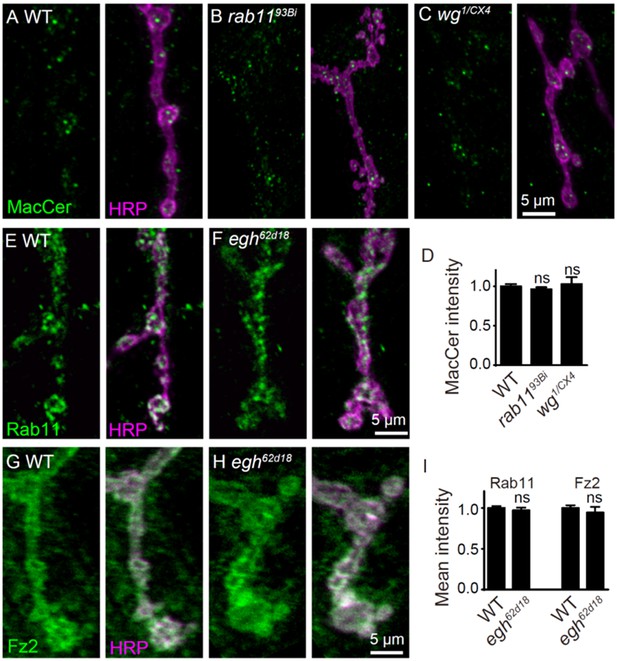
Images and quantifications of MacCer, Rab11, and Fz2 staining at NMJ of different genotypes.
(A–C) Images of NMJ4 co-stained with anti-MacCer (green) and anti-HRP (magenta) in wild type (A), rab1193Bi (B) and wg1/wgCX4 (C). (D) Quantification of MacCer intensity normalized to HRP intensity in different genotypes. n ≥ 12 larvae; ns, no significance by student’s t test; error bars: s.e.m. (E–H) Images of NMJ4 co-stained with anti-Rab11 or anti-Fz2 (green) and anti-HRP (magenta) in wild type and egh62d18 mutants. (I) Quantification of synaptic intensities of Rab11 and Fz2 normalized to HRP intensities in different genotypes. n ≥ 12 larvae; p>0.05 by student’s t test; error bars: s.e.m.
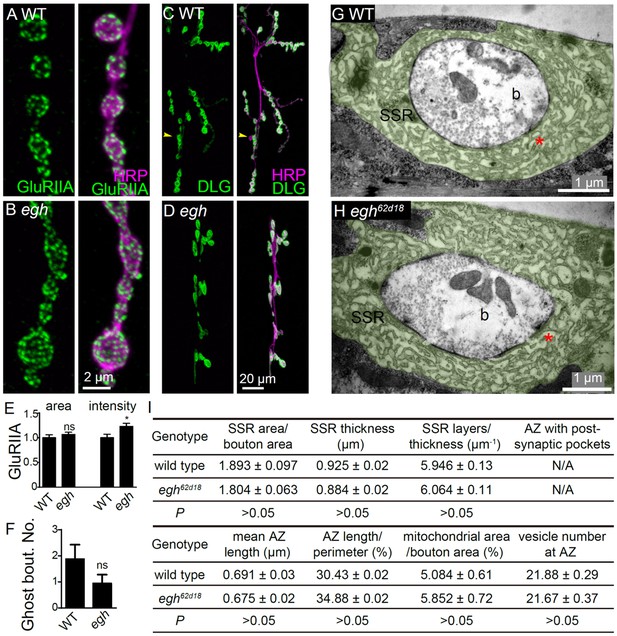
Postsynaptic differentiation is normal in egh mutants.
(A and B) Representative images of NMJ4 from wild type and egh62d18 mutants co-stained with anti-HRP (magenta) and anti-GluRIIA (green). Scale bar: 2 μm. (C and D) Images of NMJ6/7 from wild type and egh62d18 mutants co-stained with anti-HRP (magenta) and anti-DLG (green). An arrowhead points at a ghost bouton. Scale bar: 20 μm. (E and F) Quantification of normalized intensities and area of GluRIIA against anti-HRP staining of NMJ4 (E) and ghost bouton number of NMJ6/7 (F) in wild type and egh62d18 mutants. ns, no significance, *p<0.05 by student’s t test; n ≥ 12 larvae; error bars: s.e.m. (G and H) Ultrastructure images of NMJ6/7 boutons from wild type and egh62d18 mutants. The subsynaptic reticulum (SSR; green) is folded membrane network that surrounds the presynaptic bouton (b); The SSR region juxtaposed to the active zone (AZ) is indicated by asterisks in red. Scale bar: 1 μm. (I) Quantification of various bouton parameters of NMJ 6/7 synapses in wild type and egh62d18 mutants. n = 50 boutons from five wild-type animals, and n = 37 boutons from three egh62d18 larvae. Statistical analysis was performed by student’s t test.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Numerical data for the statistical graphs.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38183.024
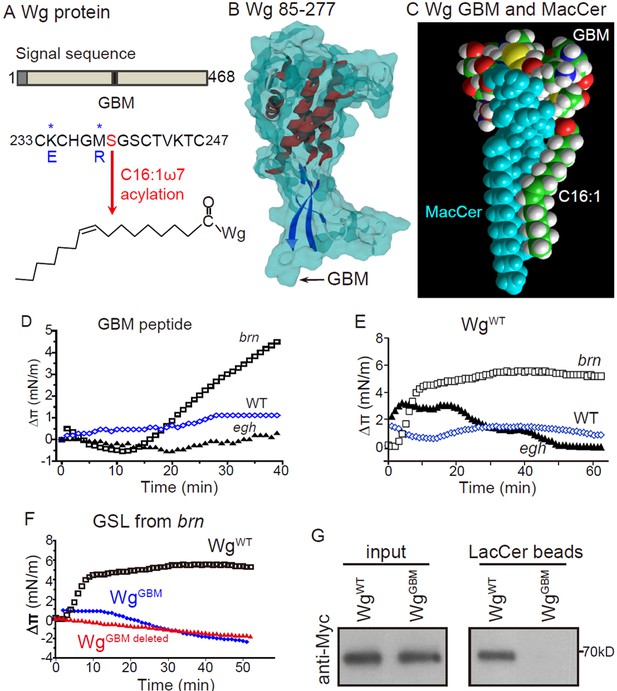
Wg has a functional MacCer-binding domain
(A) Schematic representation of Wg protein and amino acid sequence of a putative GSL-binding motif (GBM) and mutated GBM with asterisks denoting the mutated amino acids.(B) A 3D model of Wg residues 85–277 with the location of the GBM, which exposes on the protein surface. (C) Energy-minimized model of the acylated (C16:1 ω7) GBM in Wg binding with MacCer. (D and E) Surface pressure change (Δπ) by the addition of Wg233-247 peptide (GBM peptide; D) and full-length Wg produced by in vitro translation system (E) on a monolayer of GSLs purified from wild type, egh62d18 and brn1.6P6 larvae. GBM peptide and full-length Wg showed specific high affinity to MacCer enriched GSLs. (F) Surface pressure change (Δπ) by the addition of Myc-tagged wild-type Wg (WgWT) and Wg with GBM deleted (WgGBM deleted) or mutated (WgGBM) on a monolayer of GSLs purified from brn1.6P6 larvae. All surface pressure measurements were performed in triplicate and a representative curve is shown. (G) Wild-type Wg (WgWT) but not Wg with mutated GBM (WgGBM) was pulled-down by LacCer-beads. Five biological repeats were carried out for the pull-down assay and a representative blot is shown.
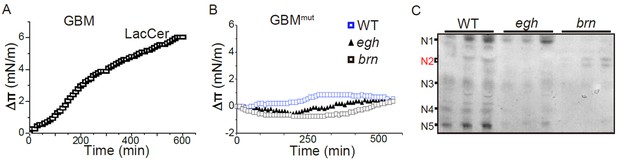
Additional monolayer data and GSL profiles of egh and brn mutants.
(A) Surface pressure increase (Δπ) by the addition of the Wg233-247 (GBM) peptide on a monolayer of LacCer. A maximal value was reached after 1 hr of incubation. (B) Surface pressure change (Δπ) by the addition of mutated GBM at Lys and Met (GBMmut) on a monolayer of GSLs purified from wild type, egh62d18 and brn1.6P6 larvae. All surface pressure measurements were performed in triplicate and a representative curve is shown. (C) GSL profile of wild type, egh62d18 and brn1.6P6 extracts (Ceramide mono-, di-, tri-, tetra- and penta-hexoside are denoted as N1, N2, N3, N4 and N5, respectively). Wild-type larvae express a broad range of GSLs including tetra- and penta-hexosylceramides, while egh62d18 mutants lacked MacCer and brn1.6P6 mutants contained almost exclusively MacCer (N2).
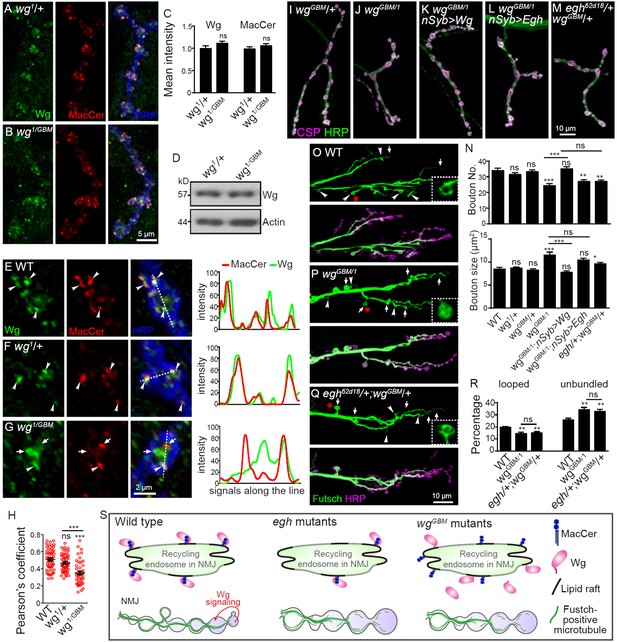
Wg GBM is required for Wg-MacCer colocalization and NMJ growth.
(A and B) Representative images of NMJ4 co-labeled with anti-Wg (green), anti-MacCer (red) and anti-HRP (blue) in wg1/+ (A) and wgGBM/wg1 mutants (B). (C) Quantification of Wg and MacCer intensities normalized to HRP intensities in different genotypes. n ≥ 15 larvae; ns, no significance by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc tests; error bars: s.e.m. (D) Western results of Wg and Actin from 3rd instar larvae of wg1/+and wgGBM/wg1 mutants. Actin was used as a loading control. Western blots were performed in triplicate and a representative image is shown. (E–G) Representative images of NMJ4 boutons triple-labeled with anti-Wg (green), anti-MacCer (red) and anti-HRP (blue) in wild type (E), wg1/+ (F) and wgGBM/wg1 mutants (G). Arrowheads indicate puncta positive for both MacCer and Wg signals; arrows indicate puncta without obvious overlap of MacCer and Wg. Images were processed by deconvolution. Scale bar: 2 μm. Plot profiles of relative intensity of MacCer and Wg along the dashed lines were shown. (H) Pearson’s coefficients of colocalization between MacCer and Wg. n = 58/10, 57/8, and 46/8 (from left to right, boutons/animals). ns, no significance, ***p<0.001 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc tests; error bars: s.e.m. (I–M) Representative images of NMJ4 co-stained with anti-HRP (green) and anti-CSP (magenta) in wgGBM/+ (I), wgGBM/wg1 (J), UAS-Wg-HA, wgGBM/wg1; nSyb-Gal4/+ (K), UAS-Egh, wgGBM/wg1; nSyb-Gal4/+ (L), and egh62d18/+; wgGBM/+ (M). Scale bar: 10 μm. (N) Quantifications of bouton number and bouton size of NMJs in different genotypes. n ≥ 12 larvae; ns, no significance, *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc tests, error bars: s.e.m. (O–Q) Representative images of NMJ6/7 labeled with anti-Futsch (green) and anti-HRP (magenta) in wild type (O), wgGBM/wg1 (P), and egh62d18/+; wgGBM/+ transheterozygotes (Q). Insets show higher magnification images of Futsch staining of a single bouton (asterisk). Arrows indicate boutons displaying unbundled Futsch; arrowheads denote boutons with Futsch loops. Scale bar: 10 μm. (R) Quantifications of percentage of Futsch loops and unbundled Futsch staining in different genotypes. n ≥ 12 larvae; ns, no significance, **p<0.01 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc tests, error bars: s.e.m. (S) A schematic presentation of the role for MacCer in promoting synapse growth via interacting with Wg in lipid rafts. The presynaptic Wg signaling is denoted by a curved arrow.
-
Figure 9—source data 1
Numerical data for the statistical graphs.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38183.028
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | wgGBM | this paper | NA | This allele carries the point mutation of K234E and M238R in Wg |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | wg1 | doi: 10.1523/Jneurosci.3714–13.2014 | RRID: BDSC_2978 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | wgCX4,wgl-17 | doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674 (02)01047–4 | RRID: BDSC_2980 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Wg-HA(6C) | doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674 (02)01047–4 | RRID: BDSC_5918 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Wg-HA(3C) | doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674 (02)01047–4 | RRID: DGGR_108488 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | egh7 | PMID: 9012507 | RRID: BDSC_3902 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | egh62d18 | PMID: 9012507 | NA | Dr. Stephen M. Cohen (National University of Singapore) |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Egh-Myc | doi: 10.1074/jbc.C400571200 | NA | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | brnfs107 | PMID: 1483386 | RRID: BDSC_4303 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | brn1.6P6 | PMID: 1483386 | RRID: BDSC_50762 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Brn | doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.04.013 | NA | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-brn-RNAi | doi: 10.1038/nmeth | RRID: BDSC_55386 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | arrk08131 | doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.026427 | RRID: BDSC_665 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | arr2 | doi: 10.1038/35035110 | RRID: BDSC_3087 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | evi2 | doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.342667 | NA | Dr. Vivian Budnik (University Massachusetts Medical School) |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | lace2 | doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.10.7276 | RRID: BDSC_3159 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | lacek05305 | doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.10.7276 | RRID: BDSC_12176 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Df(2L)Exel7063 | NA | RRID:BDSC_7831 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | schlankG0489 | doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.305 | RRID: DGGR_111936 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | schlankG0061 | doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.305 | RRID: BDSC_11665 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Sk2KG05894 | doi: 10.1194/jlr.M300005-JLR200 | RRID: BDSC_14133 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Df(3L)BSC671 | NA | RRID: BDSC_26523 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-ManII-GFP | doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.06.032 | RRID: BDSC_65248 | Dr. Yuh Nung Jan (University of California, San Francisco) |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Spin-GFP | doi: S0896627302010140 | RRID:BDSC_39668 | Dr. Graeme Davis (University of California, San Francisco) |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-YFP-Rab5 | doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.066761 | RRID: BDSC_24616 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | nSyb-Gal4 | NA | RRID: BDSC_51635 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | OK6-Gal4 | NA | RRID: BDSC_64199 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | C57-Gal4 | NA | RRID: BDSC_32556 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Repo-Gal4 | NA | RRID: BDSC_7415 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | act-Cas9 | NA | RRID: BDSC_54590 | |
| Antibody | Mouse IgM anti-MacCer | doi: 10.1074/jbc.C400571200 | NA | IHC (1:1) |
| Antibody | Mouse anti-CSP | DSHB Cat. #: 6D6 | RRID:AB_528183 | IHC (1:300) |
| Antibody | Mouse anti-Wg | DSHB Cat. #: 4D4 | RRID:AB_528512 | IHC (1:10), WB (1:50) |
| Antibody | Mouse anti-Futsch | DSHB Cat. #: 22C10 | RRID:AB_528403 | IHC (1:50) |
| Antibody | Mouse anti-DLG | DSHB Cat. #: 4F3 | RRID:AB_528203 | IHC (1:500) |
| Antibody | Mouse anti-GluRIIA | DSHB Cat. #: 8B4D2 | RRID:AB_528269 | IHC (1:200) |
| Antibody | Mouse anti-Fas II | DSHB Cat. #: 1D4 | RRID:AB_528235 | IHC (1:50) |
| Antibody | Mouse anti-Syx1A | DSHB Cat. #: 8C3 | RRID:AB_528484 | IHC (1:20), WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Mouse anti-dFz2 | DSHB Cat. #:12A7 | RRID:AB_528257 | IHC (1:5) |
| Antibody | Mouse anti-Rab11 | BD Biosciences Cat. #: 610656 | RRID:AB_397983 | IHC (1:50) |
| Antibody | Mouse anti-HA | MBL International Cat. #: M180 | RRID:AB_10951811 | IHC (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Mouse anti-Myc | CWBIO Cat. #: CW0259 | IHC (1:300), WB (1:1000) | |
| Antibody | Mouse anti-Myc | MBL International Cat. #: M192 | RRID:AB_11160947 | IHC (1:300), WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Rat anti-GFP | MBL International Cat. #: D153 | RRID:AB_591820 | IHC (1:200) |
| Antibody | fluorescence-conjugated anti-HRP | Jackson ImmunoResearch | RRID:AB_2314647 | IHC (1:200) |
| Antibody | Mouse anti-β-actin | Millipore Bioscience Research | RRID:AB_2223041 | WB (1:50000) |
| Chemical compound, drug | D,L-threo-PDMP | Matreya | Cat.#: 1719 | 0.5 mg/ml |
| Chemical compound, drug | filipin III | Cayman | 70440 | 50 μg/ml |
| Chemical compound, drug | MβCD | Sigma-Aldrich | C4555 | 20 mM |
| Chemical compound, drug | Lactosylceramide | Matreya | Cat.#: 1500 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | GBM | this paper | CKCHGMSGSCTVKTC | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | GBMmut | this paper | CECHGRSGSCTVKTC | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pcDNA3.1-Myc-Wg | Invitrogen | V790-20 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | U6b-sgRNA | Addgene | 65956 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pBluescript SK (-) | Stratagene | 212206 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | TNT T6 Quick Coupled Transcription/Translation System | Promega | Cat.#: L1171 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | LacCer-coated beads | Echelon | Cat.#: P-B0LC | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Control beads | Echelon | Cat.#: P-B000 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | HPTLC Silica Gel (aluminium plates) | Merck-Millipore | Cat.#: 105547 | |
| Software, algorithm | Hyperchem software | Hypercube |
Additional files
-
Supplementary File 1
Genetic screen for NMJ morphology by manipulating selected genes involved in synthesis and turnover of membrane lipids.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38183.029
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38183.030





