Multiple neurons encode CrebB dependent appetitive long-term memory in the mushroom body circuit
Figures
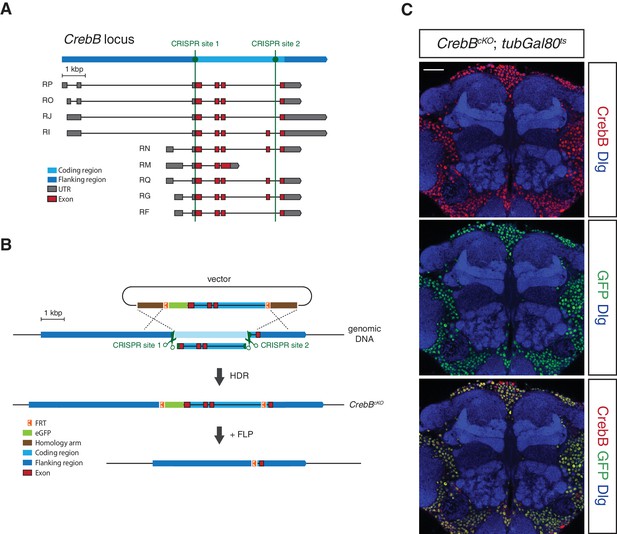
Generation of a conditional knockout allele for CrebB.
(A) Schematic representation of the CrebB gene locus with nine different transcript isoforms. The location of the two used CRISPR sites are highlighted in green. (B) The CrebB conditional knockout allele (CrebBcKO) was generated using the CRISPR/Cas9 technique. The donor vector contained the coding region of CrebB with eGFP in front and two FRT sites flanking this sequence. The endogenous CrebB coding region was replaced by the donor DNA through CRISPR/Cas9 mediated homology-directed repair (HDR). In the resulting CrebBcKO allele the inserted eGFP and CrebB coding sequence can be removed by flippase (FLP) recombinase. (C) CrebB::GFP expression in a frontal brain confocal section of CrebBcKO; tubGal80ts flies was visualized using anti-GFP (green) and anti-CrebB (red) antibodies. Brain structures were labeled with anti-Discs large (Dlg, blue) antibodies. Scale bar: 30 μm.
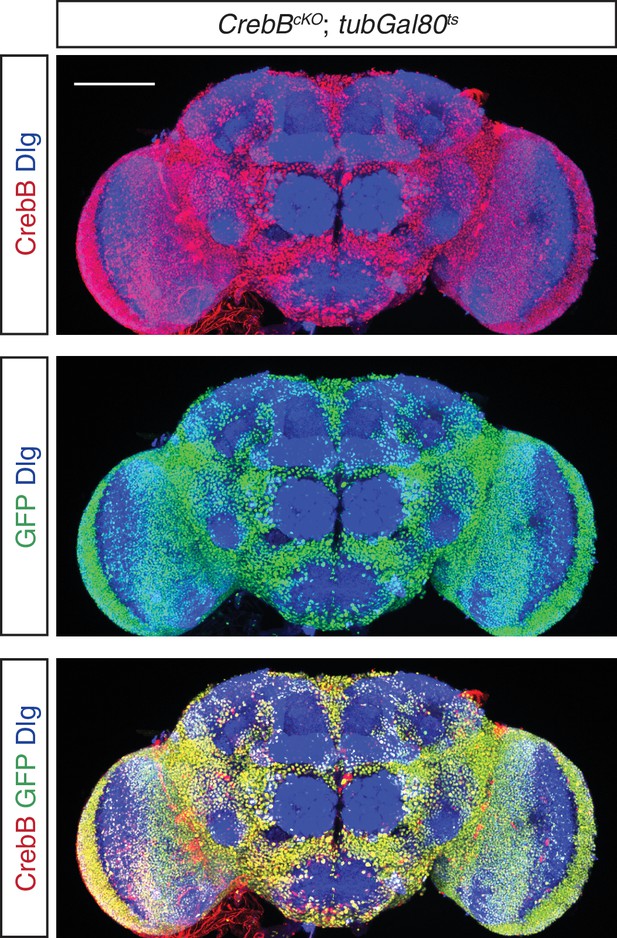
Expression pattern of CrebB::GFP.
A whole-mount Drosophila adult brain stained for GFP (green), CrebB (red) and Discs large (blue). Scale bar: 100 μm.
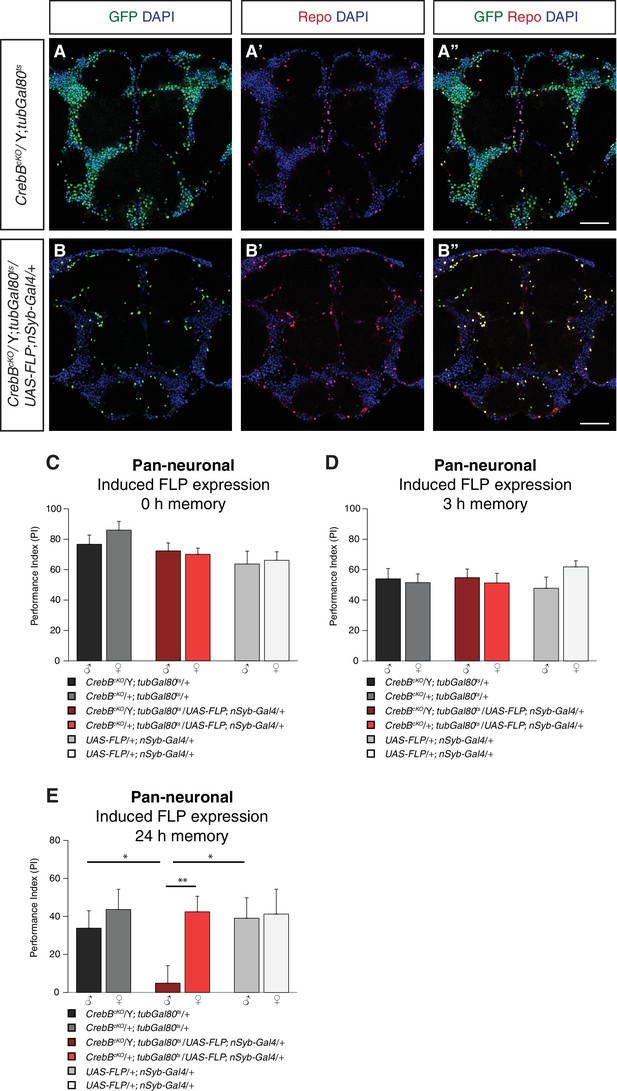
CrebB is dispensable for STM and MTM, but required for LTM.
CrebB::GFP was removed from neurons and antibody stainings were conducted along with appetitive olfactory conditioning experiments. (A, B) Brains were stained with anti-GFP antibodies (green), anti-Repo antibodies (red) and DAPI (blue). (A, A’, A’) In CrebBcKO, tubGal80ts brains, CrebB::GFP was detected in most of the cells. (B, B’, B’’) After pan-neuronal induction of CrebB::GFP knockout, GFP was only expressed in Repo-positive glia cells. Scale bars: 50 μm. (C–E) Short-term, middle-term and long-term memory performance was assessed. (C,D) Pan-neuronal CrebB knockout did not affect STM (N ≥ 10) and MTM (N = 8). (E) LTM, tested 24 h after conditioning, was severely impaired in flies with induced CrebB knockout in all neurons. Memory performance of male CrebBcKO/Y; tubGal80ts/UAS-FLP; nSyb-Gal4/+ flies was significantly lower than in female flies (CrebBcKO/+; tubGal80ts/UAS-FLP; nSyb-Gal4/+), and in male flies of the parental control flies. N ≥ 9. Bar graphs represent the mean and error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM). Asterisks denote significant differences between groups; *p<0.05, **p<0.01 (Welch two sample t-test).
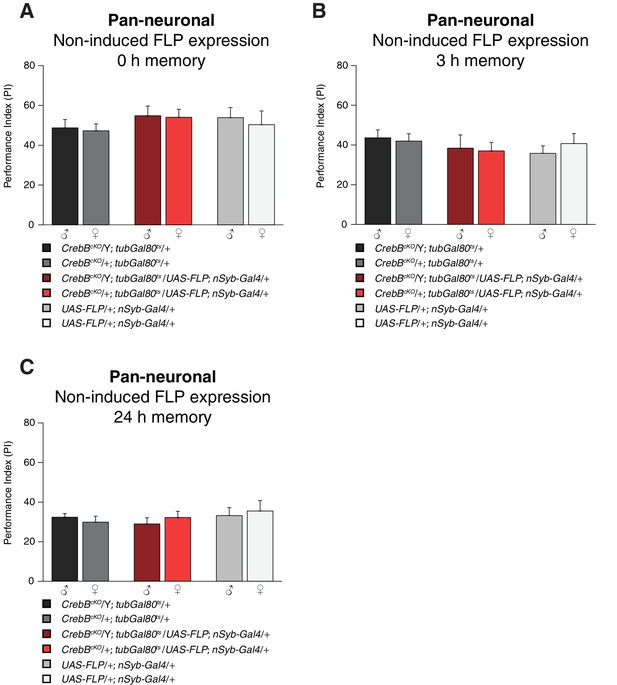
LTM is not impaired in non-induced CrebB knockout flies.
Non-induced control flies for the pan-neuronal CrebB knockout experiment, that were kept at 18°C, were tested for 0 h (A; N ≥ 8), 3 h (B; N ≥ 8) and 24 h memory (C; N ≥ 8). No significant memory performance differences were observed between the genotypes at the tested memory phases (Welch two sample t-test). Bar graphs represent the mean and error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM).
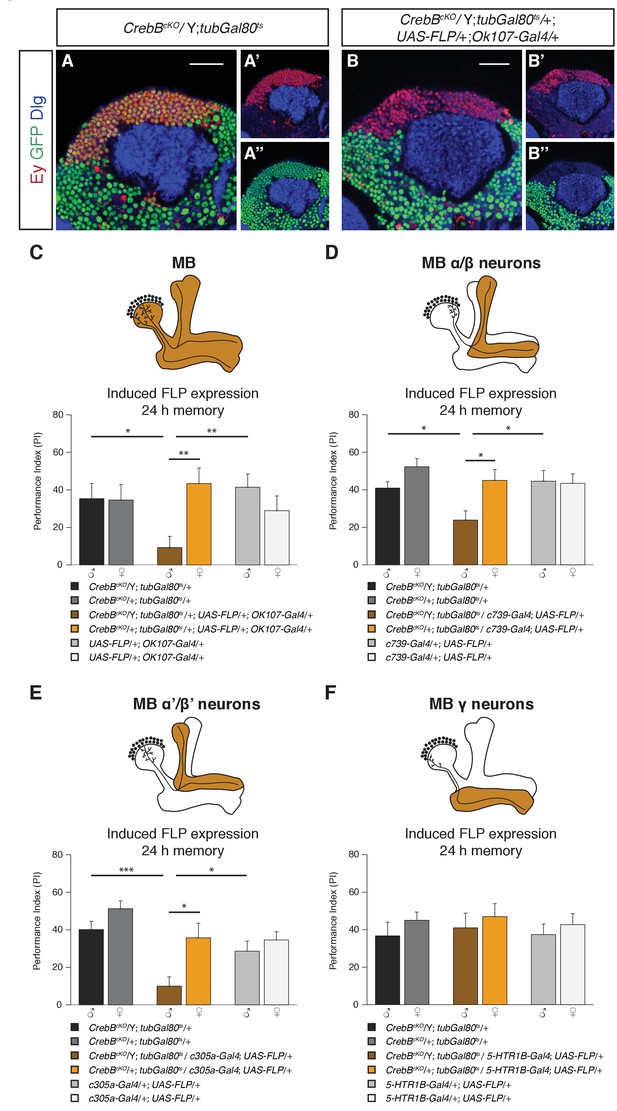
CrebB is required in MB α/β and MB α’/β’ neurons for LTM formation.
(A, B) Brains were stained using anti-GFP (green), anti-Discs large (Dlg, blue) and anti-Eyeless (Ey, red) antibodies, which labels Kenyon cells. (A–A’’) CrebB::GFP is expressed in Kenyon cells of CrebBcKO; tubGal80ts male flies. (B–B’’) After induction of mushroom body-specific CrebB::GFP knockout, Ey-expressing Kenyon cells lost GFP expression. Scale bars: 25 μm. (C–F) Different MB-Gal4 driver lines were used to induce deletion of CrebB in Kenyon cells and to test for the requirement of CrebB for 24 h memory. (C) Induction of CrebB knockout in the entire MB using OK107-Gal4 severely impaired LTM. N ≥ 10. (D, E) The 24 h memory scores were significantly reduced by the knockout of CrebB in MB α/β neurons with c739-Gal4 (N ≥ 9) and in MB α’/β’ neurons with c305a-Gal4 (N ≥ 8). (F) CrebB knockout in MB γ neurons with 5-HTR1B-Gal4 did not impair LTM formation. No significant difference was observed between the tested groups. N ≥ 8. Bar graphs represent the mean and error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM). Asterisks denote significant differences between groups; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 (Welch two sample t-test).
STM is not affected by CrebB knockout in Kenyon cells.
(A) Induced knockout of CrebB in MB neurons did not impair STM. Memory scores of the tested genotypes did not differ from each other (Welch two sample t-test). N = 8. (B) Non-induced CrebB knockout flies kept at low temperature showed no difference in STM performance compared to genetic control flies (Welch two sample t-test). N ≥ 8. Bar graphs represent the mean and error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM).
Non-induced controls display normal 24 h memory.
Flies that were used for CrebB knockout experiments in Kenyon cells were tested for LTM under non-induction conditions. 24 h memory performance of non-induced experimental flies was similar to the genetic control flies. Memory scores were not significantly different from each other for the MB knockout experiment (A; N = 8), the MB α/β neurons knockout experiment (B; N = 8), the MB α’/β’ neurons knockout experiment (C; N ≥ 8) and the MB γ neurons knockout experiment (D; N = 8; Welch two sample t-test). Bar graphs represent the mean and error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM).
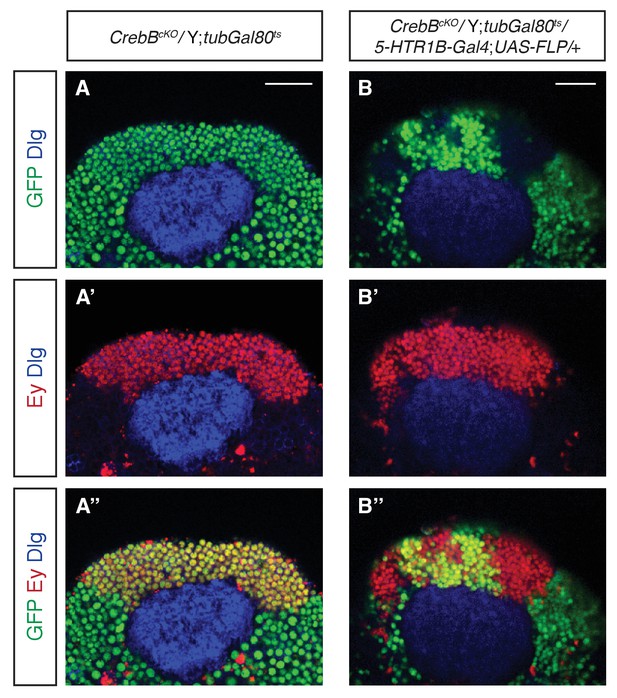
Successful removal of CrebB::GFP from MB γ neurons.
Confocal sections of adult brains showing the Kenyon cell (KC) region stained for GFP (green), the KC marker Eyeless (Ey, red) and Dlg to outline the neuropile (blue). (A, A’, A’’) In control flies, CrebB::GFP is expressed in all KCs. (B, B’, B’’) In flies with induced CrebB::GFP knockout in MB γ neurons, some KCs do not express CrebB::GFP anymore. Scale bars: 25 μm.
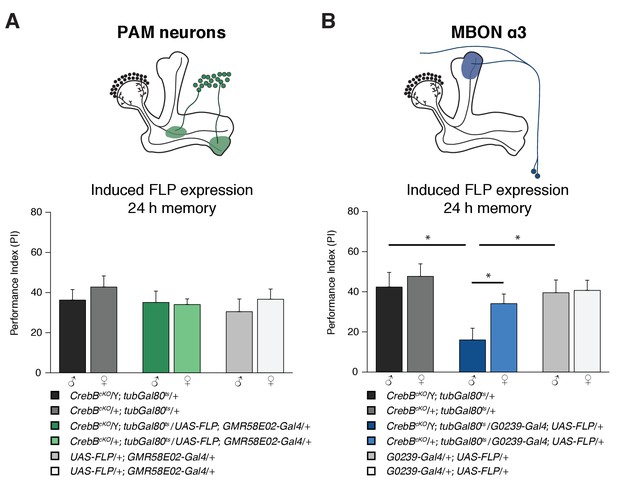
The CrebB gene is required for LTM in MBON α3.
(A) Deleting CrebB in PAM neurons using the driver GMR58E02-Gal4 did not affect LTM formation. Performance indices did not differ between the groups. N ≥ 9. (B) CrebB knockout in MBON α3 with G0239-Gal4 impaired LTM. N ≥ 9. Bar graphs represent the mean and error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM). Asterisks denote significant differences between groups; *p<0.05 (Welch two sample t-test).
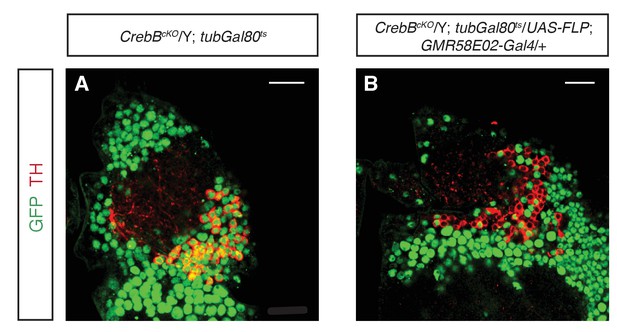
Effective CrebB::GFP knockout in PAM neurons.
Brains were stained with anti-GFP (green) and anti-TH antibodies (red). Central brain regions, where TH-positive dopaminergic PAM neurons are located, are shown. Control flies displayed GFP-positive dopaminergic neurons (A), while in PAM neuron CrebB::GFP knockout flies, GFP could not be detected in most of the TH-positive cells in this region (B). Scale bars: 15 μm.
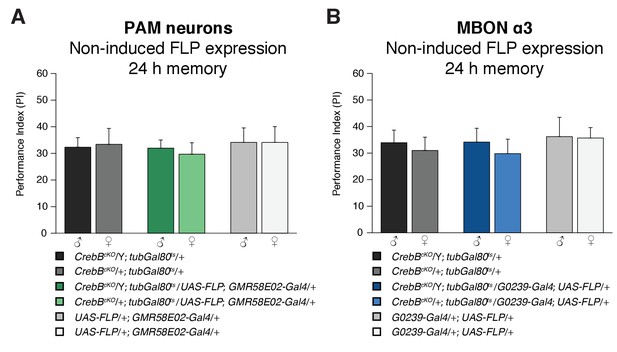
Non-induced controls for the CrebB knockout experiment in PAM neurons and MBON α3 show normal LTM.
Memory performance measured 24 h after conditioning was assessed in flies with non-induced FLP expression. Control flies were not significantly different from experimental flies for the PAM neurons experiment (A; N = 8) or the MBON α3 experiment (B; N ≥ 8; Welch two sample t-test). Bar graphs represent the mean and error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM).
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | CrebBcKO | this paper | See Materials and Methods section: Creation of CrebBcKO | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | c739-Gal4 | Hiromu Tanimoto (Tohoku University) | RRID:BDSC_7362 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | OK107-Gal4 | Kyoto stock center | RRID:DGGR_106098 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | nSyb-Gal4 | Bloomington stock center | RRID:BDSC_51635 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | c305a-Gal4 | Bloomington stock center | RRID:BDSC_30829 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | 5-HTR1B-Gal4 | Bloomington stock center | RRID:BDSC_27636 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | GMR58E02-Gal4 | Bloomington stock center | RRID:BDSC_41347 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | G0239-Gal4 | Bloomington stock center | RRID:BDSC_12639 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | tubGal80ts | Bloomington stock center | RRID:BDSC_7019 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | nos-Cas9 | Bloomington stock center | RRID:BDSC_54591 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-FLP (Chr 2) | Bloomington stock center | RRID:BDSC_55806 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-FLP (Chr 3) | Bloomington stock center | RRID:BDSC_55804 | |
| Antibody | guinea pig anti-CrebB | this paper | polyclonal anti-CrebB antibody raised against the CrebB full-length protein sequence of isoform F; 1:400 | |
| Antibody | rabbit anti-Eyeless | Uwe Waldorf (Saarland University) | 1:400 | |
| Antibody | chicken anti-GFP | Abcam | Cat. #: ab13970 RRID:AB_300798 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | rabbit anti-GFP | Invitrogen | Cat. #: A-6455 RRID:AB_221570 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | rabbit anti-Tyrosine hydroxylase | Merck | Cat. #: AB152 RRID:AB_390204 | 1:100 |
| Antibody | mouse anti-Repo | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | Cat. #: 8D12 RRID:AB_528448 | 1:20 |
| Antibody | mouse anti- Discs large | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | Cat. #: 4F3 RRID:AB_528203 | 1:50 |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.39196.014





