Cellular acidosis triggers human MondoA transcriptional activity by driving mitochondrial ATP production
Figures
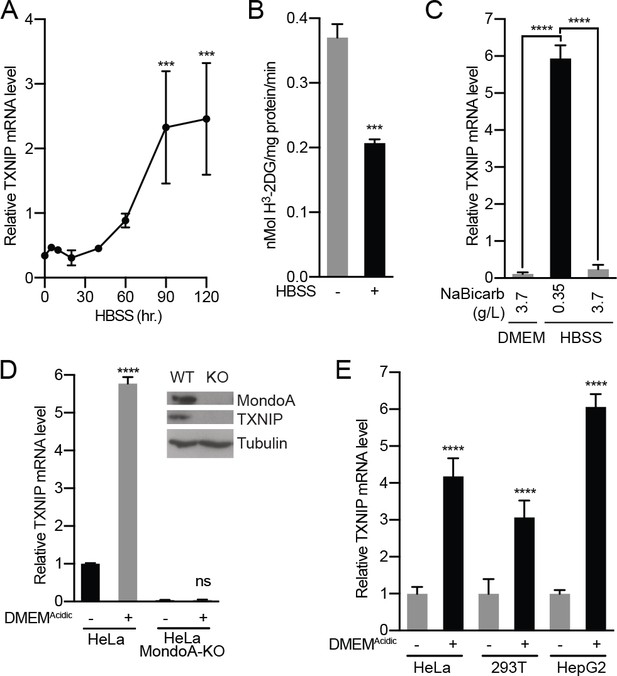
Acidosis drives MondoA transcriptional activity.
(A) TXNIP mRNA levels in murine embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) following treatment with HBSS for the indicated times. (B) Glucose uptake was determined by quantifying the rate of 3H-2-deoxyglucose uptake in MEFs following a 4 hr treatment with HBSS. (C) TXNIP mRNA levels from MEFs treated for 4 hr with DMEM, HBSS and HBSS supplemented with sodium bicarbonate to the amount in DMEM (3.7 g/L). (D) CRISPR/Cas9 was used to disrupt expression of MondoA in HeLa cells. Amounts of the indicated proteins in HeLa and HeLa:MondoA-KO cells were determined using immunoblotting. Consistent with our previous findings TXNIP expression was highly dependent on MondoA. TXNIP mRNA levels from HeLa and HeLa:MondoA-KO cells following a 4 hr treatment with DMEMAcidic. (E) TXNIP mRNA levels in HEK-293T, HeLa and HepG2 cells following 4 hr treatments with DMEMAcidic. In A, C, D and E, TXNIP mRNA levels were determined by reverse transcriptase-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR). ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001; ns – not significant.
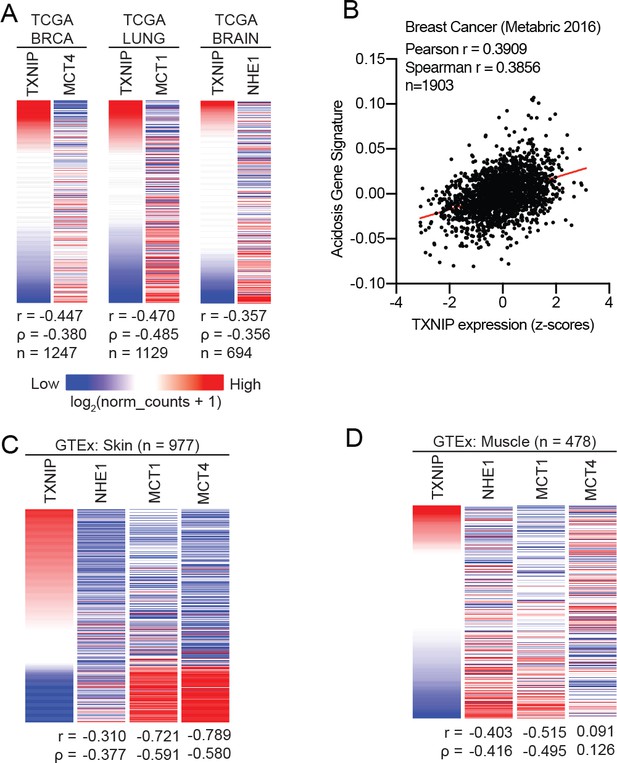
TXNIP expression correlates with genes that regulate intracellular pH.
(A) Heatmaps showing the expression of TXNIP mRNA compared to MCT4 (breast cancer), MCT1 (lung cancer) and NHE1 (brain cancer). All expression data was collected from TCGA. Spearman and Pearson correlation statistics are reported as r and ρ, respectively. (B) An acidosis gene signature was determined for the 2016 METABRIC breast cancer dataset. These scores were compared to TXNIP expression from the dataset and correlation statistics were performed. Heatmaps depicting the expression of TXNIP mRNA compared to MCT4, MCT1 and NHE1 for normal (C) skin and (D) muscle tissues. All expression data was collected from GTEx. Spearman and Pearson correlation statistics are reported as r and ρ, respectively.
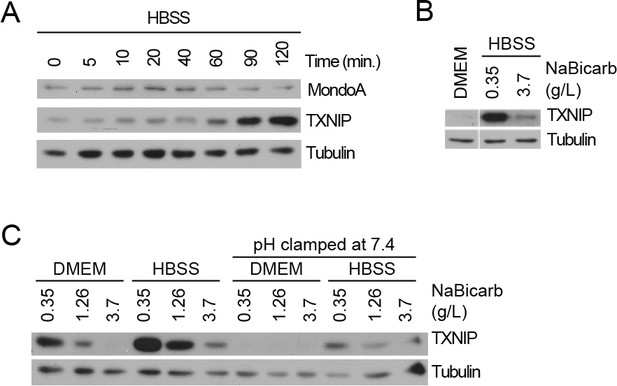
Acidosis drives MondoA transcriptional activity.
(A) TXNIP and MondoA protein levels in MEFs treated with HBSS for the indicated times was determined by immunoblotting. (B) TXNIP protein levels of MEFs following 4 hr treatments with DMEM, HBSS and HBSS supplemented with sodium bicarbonate to the amount in DMEM (3.7 g/L). (C) TXNIP protein levels in MEFs following 4 hr treatments with DMEM or HBSS containing the indicated amounts of sodium bicarbonate. Cells were also treated were with the identical medias with their pH clamped to pH 7.4 with 25 mM HEPES.
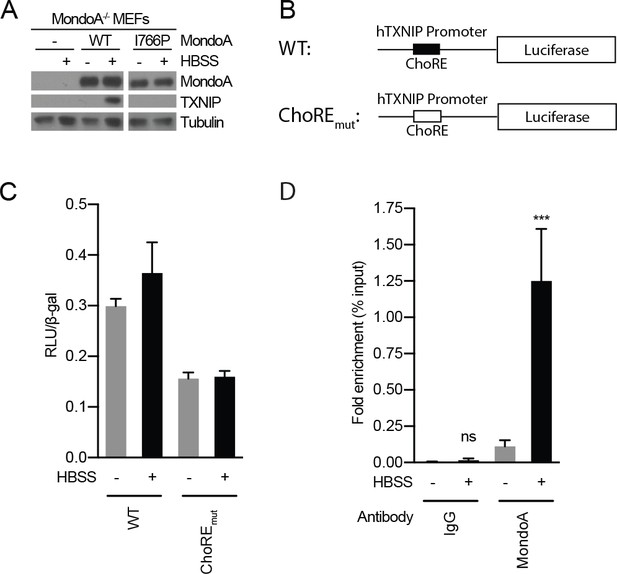
Acidosis drives MondoA transcriptional activity.
(A) TXNIP and MondoA protein levels were determined from MondoA-knockout MEFs complemented with empty vector, wild-type MondoA or MondoA(I766P) following 4 hr HBSS treatments. (B) Schematic showing TXNIP-promoter luciferase reporter constructs. ChoREmut contains mutations in each half of the double E-box carbohydrate-responsive element ChoRE that are predicted to reduce or eliminate MondoA:Mlx binding. Luciferase activity was measured in MEFs transfected with each reporter construct following a 4 hr HBSS treatment. Luciferase activity and transfection efficiency was normalized to β-galactosidase (β-gal) activity encoded by a co-transfected plasmid expressing LacZ (C) Chromatin-immunoprecipitation using antibodies specific for MondoA or IgG was performed on chromatin preparations from MEFs treated for 4 hr with HBSS. ***p<0.001; ns – not significant.
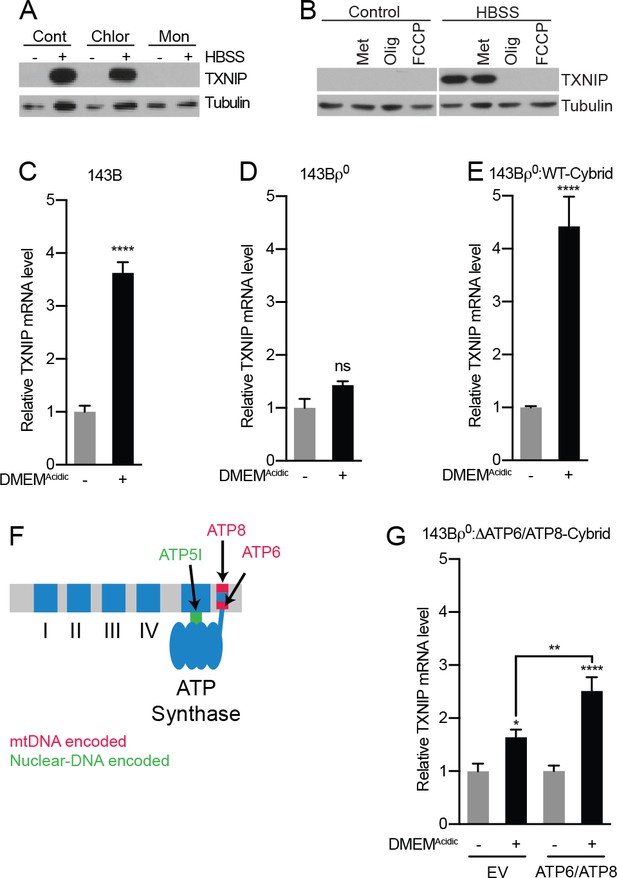
Acidosis-driven MondoA transcriptional activity depends on electron transport.
(A and B) TXNIP protein levels were determine by immunoblotting following a 4 hr HBSS treatment of MEFs in the presence of the indicated inhibitors. Cont; control, Chlor; Chloroquine (25 μM), Mon; monensin (5 μM), Met; metformin (1 mM), FCCP; carbonilcyanide p-triflouromethoxyphenylhydrazone (1 µM), Oligo; oligomycin (1 μM). (C–E), TXNIP mRNA levels were determine using RT-qPCR following 4 hr treatments with DMEMAcidic: (C) 143B osteosarcoma cells, (D) 143Bρ0 cells, and (E) 143Bρ0:WT-Cybrid cells complemented with wild type mitochondria. (F) Schematic depicting nuclear- and mitochondrial-DNA encoded components of the ETC. (G) TXNIP mRNA levels following 4 hr DMEMAcidic treatments of 143Bρ0:ΔATP6/ATP8-Cybrid cells expressing empty vector or nuclear encoded, mitochondrial-targeted ATP6 and ATP8. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ****p<0.0001; ns – not significant.
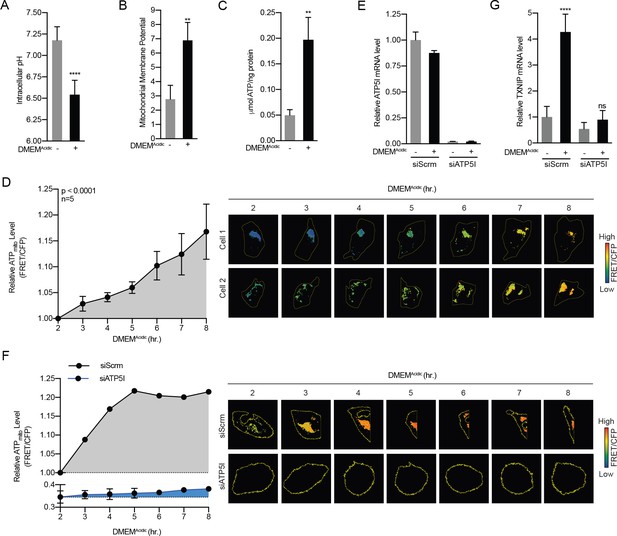
Acidosis drives the synthesis of mitochondrial ATP.
(A) Intracellular pH of HeLa cells was determined using BCECF-AM staining after a 4 hr treatment with DMEMAcidic. (B) Mitochondrial membrane potential of HeLa cells was determined by JC1 staining after a 1 hr treatment with DMEMAcidic. (C) Total cellular ATP levels in a lysate prepared from HeLa cells was determined using a luciferase-based assay after a 4 hr treatment with DMEMAcidic. (D) Mit-ATEAM, which is a mitochondrial-targeted ATP-biosensor, was used to determine the relative level of mtATP in HeLa cells treated with DMEMAcidic for the indicated times. Widefield microscopy was used to capture images in the FRET and CFP channels. Images were then used to analyze FRET and CFP signals in mitochondria in individual cells. FRET signal was normalized using CFP. (E) ATP5I mRNA levels in HeLa cells that expressed scrambled (siScrm, n = 1) or ATP5I-specific siRNA (siATP5I, n = 2) following a 4 hr DMEMAcidic treatment. (F) Mit-ATEAM was used to determine relative mtATP levels in HeLa cells transfected with siScrm or siATP5I and treated with DMEMAcidic for the indicated times. (G) TXNIP mRNA levels following a 4 hr DMEMAcidic treatment of HeLa cells that had been transfected siScrm or siATP5I. In (E and G), ATP5I and TXNIP mRNA levels were measured using RT-qPCR. **p<0.01; ****p<0.0001; ns – not significant.
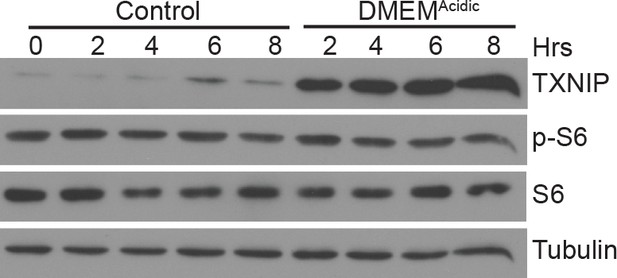
DMEMAcidic does not inhibit mTORC1 activity Immunoblotting was used to measure the levels of the indicated proteins following DMEMAcidic treatment of HeLa cells for the indicated times.
Levels of phosphorylated S6 (p–S6), which is a mTORC1 substrate, reflect mTORC1 activity.
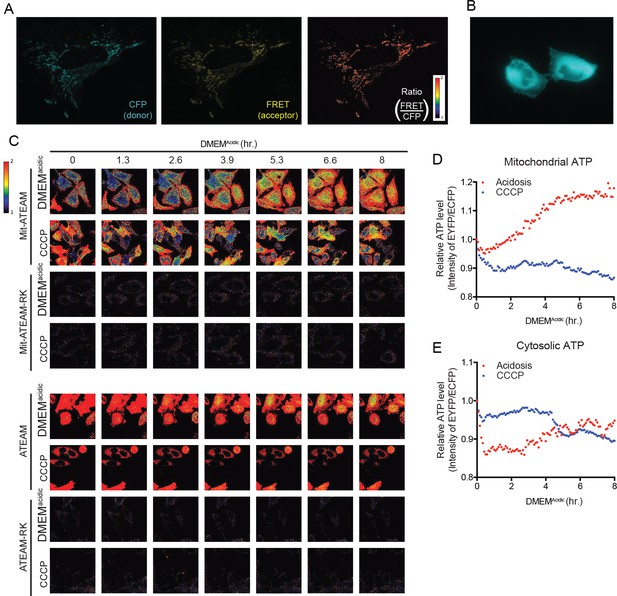
Acidosis drives synthesis of mitochondrial ATP.
(A) Confocal images at 60X of Mit-ATEAM expressed in HeLa cells. Shown are the CFP and FRET channels as well as the ratio of FRET to CFP (indicating mtATP). (B) Widefield image at 60X of ATEAM. CFP channel only is shown. (C) Confocal images of Mit-ATEAM, Mit-ATEAM(R122K/R126K), ATEAM and ATEAM(R122K/R126K) in HeLa cells. The R122K/R126K mutations block ATP binding providing a negative control for this experimental system. HeLa cells were treated with DMEMAcidic or CCCP (1 μM) for up to 8 hr and images captured at the indicated times. Images are pseudo-colored according to the FRET/CFP ratio. Notably, the FRET/CFP ratios for Mit-ATEAM(R122K/R126K) and ATEAM(R122K/R126K) was negligible compared to non-mutated constructs. Quantification of relative mitochondrial (D) and cytosolic (E) ATP.
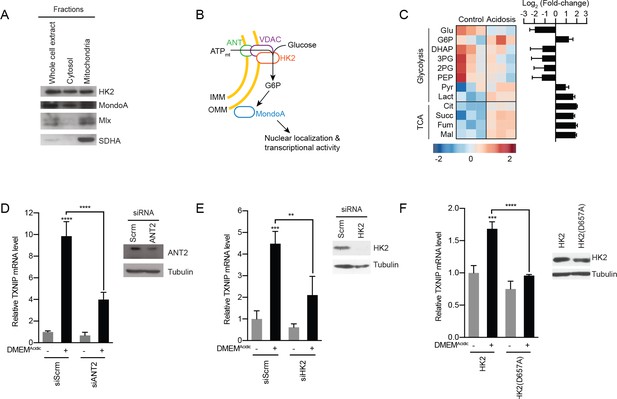
MondoA is activated by G6P produced by hexokinase utilization of mtATP.
(A) Cellular fractionation of BJ-Tert cells indicating mitochondrial localization of HK2, MondoA and Mlx. Succinate dehydrogenase A (SDHA) serves as a control for the mitochondria fraction. (B) Schematic illustrating how mtATP could contribute to MondoA transcriptional activity. As mtATP is exported from the mitochondria, it is used by as a substrate by mitochondria-bound HK2 to produce G6P, resulting in MondoA activation. (C) Heatmap and log2 fold-changes of glycolytic and TCA metabolites measured using GC-MS following a 4 hr treatment of HeLa cells with DMEMAcidic. TXNIP mRNA levels, as measured by RT-qPCR, following 4 hr DMEMAcidic treatments of HeLa cells and expressing pools of four siRNAs against (D) ANT2 and (E) HK2, or (F) expressing HK2 and HK2(D657A). Immunoblots validate knockdown of the indicated proteins. **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001; ns – not significant.
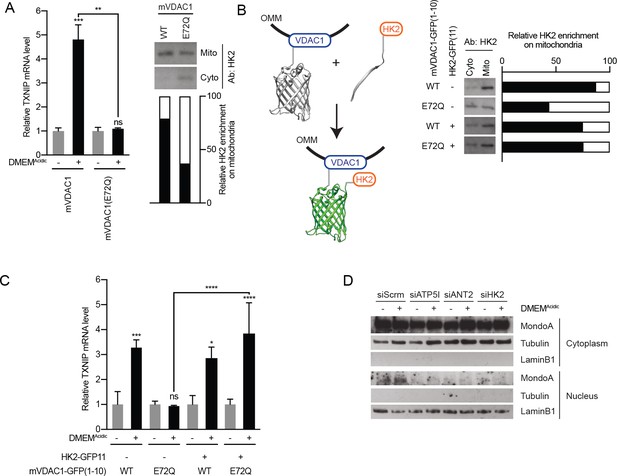
MondoA senses G6P produced by mitochondrial-bound hexokinase.
(A) TXNIP mRNA levels in BJ-Tert cells expressing mVDAC1-GFP and mVDAC1(E72Q)-GFP and treated for 4 hr with DMEMAcidic. HK2 localization was also analyzed by cellular fractionation and densitometry was used to quantify the relative amount of HK2 localized to the mitochondria. HK2 was increasingly enriched in the cytoplasmic fraction in cells expressing mVDAC1(E72Q), suggesting that it had been displaced from mitochondria. (B) Schematic depicting the use of GFP(1-10) and GFP(11) to artificially tether mVDAC1 and HK2. HK2 localization was also analyzed by cellular fractionation and densitometry was used to quantify the relative amount of HK2 present in the mitochondrial fraction. (C) TXNIP mRNA levels in BJ-Tert cells treated for 4 hr with DMEMAcidic and expressing mVDAC1-GFP, mVDAC1(E72Q)-GFP and HK2-GFP(11) in the indicated combinations. (D) MondoA nuclear localization was determined by cellular fractionation of HeLa cells treated for 4 hr with DMEMAcidic and transfected with siScrm (siRNA control), siATP5I, siANT2 or siHK2. Tubulin and LaminB1 served as controls for cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions, respectively. In (A and C), TXNIP mRNA levels were determined by RT-qPCR. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001; ns – not significant.
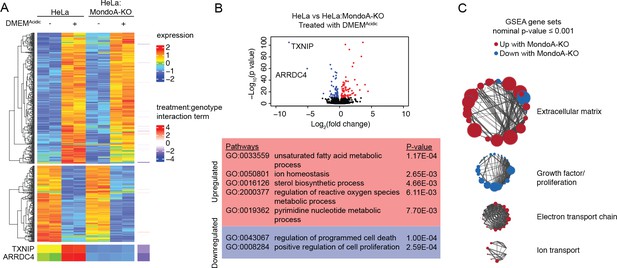
The MondoA-dependent acidosis response.
RNA-sequencing was used to determine differentially regulated genes for HeLa and HeLa:MondoA-knockout cells treated with DMEMAcidic for 4 hr. Differentially regulated genes from duplicate biological samples were determined. (A) Heatmaps depicting TXNIP, ARRDC4 and the top 500 differentially regulated genes in HeLa cells following DMEMAcidic. The genotype:treatment interaction term was calculated using DESeq2 and indicates the influence of both genotype and treatment on differential expression. (B) Volcano plot of log2(fold-change) of HeLa cells treated with DMEMAcidic compared to HeLa:MondoA-KO cells treated with DMEMAcidic. Genes with an adjusted p-value≤1E-10 that are upregulated or downregulated in HeLa:MondoA-KO cells treated with DMEMAcidic are indicated in red and blue, respectively. Overrepresentation analysis was performed for upregulated and downregulated genes. Enriched pathways and their respective p-values are given in the red and blue boxes for upregulated and downregulated genes, respectively. (C) GSEA and leading edge analysis was conducted for HeLa cells treated with DMEMAcidic compared to HeLa:MondoA-KO cells treated with DMEMAcidic. Depicted are networks of gene sets with a nominal p-value≤0.001. Node colors are representative of whether the gene set was positively (red) or negatively (blue) enriched. Node size represents gene set size. Connecting line thickness represents similarity between two nodes.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Acidosis regulated genes and pathways.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40199.013
-
Figure 6—source data 2
Pathways enriched in acidosis treated MondoA knockout HeLa cells.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40199.014
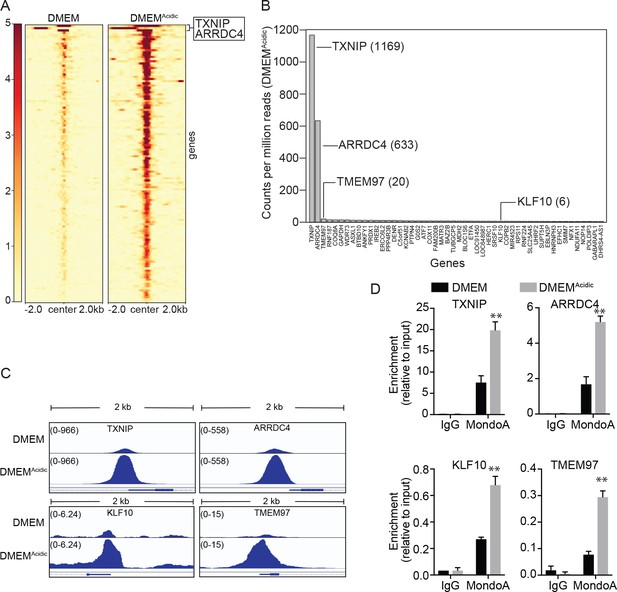
MondoA preferentially occupies the promoters of TXNIP and ARRDC4.
ChIP sequencing was performed on single biological samples and used to identify MondoA’s genomic binding sites in HeLa cells grown in DMEM or treated with DMEMAcidic for 4 hr. (A) Heatmaps showing ~100 MondoA binding sites located within the promoters of potentially regulated genes. We defined the promoter region as being 2 kb upstream or downstream of the transcriptional start site (TSS). (B) Histogram of counts per million reads (CPM) values for the top 50 promoter-localized MondoA genomic binding sites following a 4 hr DMEMAcidic treatment of HeLa cells. (C) Genome browser views derived from ChIP-seq experiment of the MondoA binding sites in the promoters of the indicated genes. (D) Independent biological triplicates were grown in DMEM or treated for 4 hr with DMEMAcidic. ChIP-PCR was used to validate MondoA occupancy on the promoters of the indicated genes under the two experimental conditions. **p<0.01.
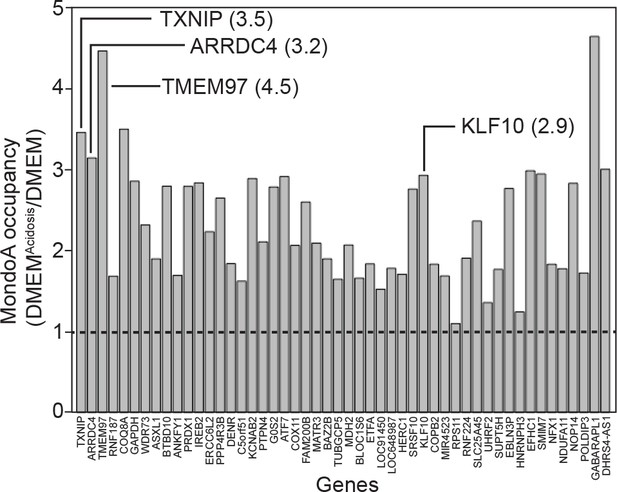
DMEMAcidic increases MondoA genomic occupancy.
We analyzed the occupancy of MondoA at the 50 most highly bound promoters identified in our ChIP-seq experiment. The ratio of binding in DMEMAcidic/DMEM is presented and shows the fold increase in occupancy following DMEMAcidic treatment.
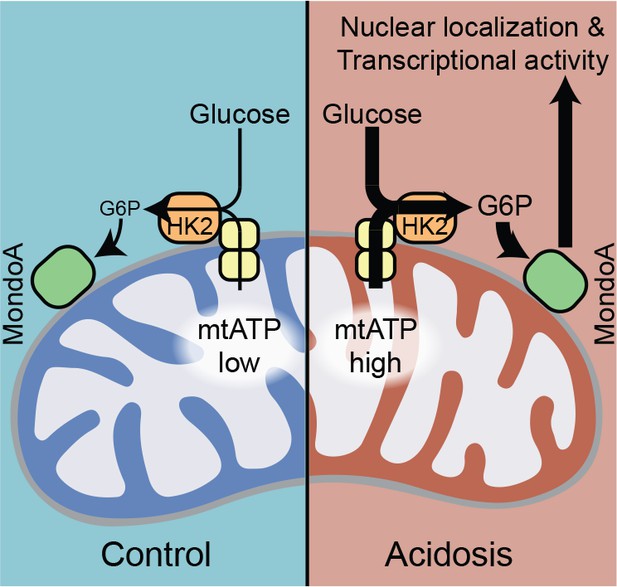
MondoA coordinates the transcriptional response to cytoplasmic glucose and mitochondrial ATP.
Schematic depicting how acidosis drives MondoA transcriptional activity through the generation of mitochondrial ATP and utilization by mitochondria-bound hexokinase to produce G6P, which drives MondoA nuclear localization and transcriptional activity.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody | Anti-HK2 (goat polyclonal) | Santa Cruz | sc6521 | (1:1,000) |
| Antibody | Anti-MLX (rabbit monoclonal (D8G6W) | Cell Signaling | 85570S | (1:1,000) |
| Antibody | Anti-MlxIP (MondoA) (rabbit polyclonal) | Proteintech | 13614–1-AP | (1:2,000) |
| Antibody | Anti-SDHA (2E3GC12FB2AE2) (mouse monoclonal | Abcam | AB147 | (1:15,000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Tubulin (mouse monoclonal) | Molecular Probes | 236–10501 | (1:50,000) |
| Antibody | Anti-TXNIP (rabbit monoclonal) | Abcam | ab188865 | (1:2,000) |
| Antibody | Anti-LaminB1 (rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | ab16048 | (1:1,000) |
| Antibody | anti-goat IgG-HRP (donkey polyclonal) | Santa Cruz | sc-2056 | (1:2,000) |
| Antibody | Mouse IgG, HRP-linked whole Ab (sheep polyclonal) | GE Life Science | NA-931 | (1:5,000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit IgG, HRP-linked whole Ab (donkey polyclonal) | GE Life Science | NA-934 | (1:15,000) |
| Chemical compound, drug | BCECF-AM | Thermo Fisher | B1170 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Blotting Grade Blocker Non-fat Dry Milk | Bio-Rad | 1706404XTU | |
| Chemical compound, drug | CCCP | Sigma Aldrich | C2759 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Chloroquine | Sigma Aldrich | 415480 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Deoxy-D-Glucose, 2-[1,2-3H(N)] | American Radiolabeled Chemicals, Inc. | 0103–250 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DMEM | Gibco | 11995–065 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DMEM Powder without sodium bicarbonate, glucose, L-glutamine, sodium pyruvate and phenol red | Cellgro | 90–113-PB | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DMSO | Fisher | BP231 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | FCCP | Sigma Aldrich | C2920 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Fetal bovine serum (FBS) | Gibco | 26140–079 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Glucose | Fisher | D16-1 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Glutamine | Cellgro | 25–005 Cl | |
| Chemical compound, drug | HBSS | Gibco | 24020–117 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | HEPES | Sigma Aldrich | H3375 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | JC1 | Thermo Fisher | T3168 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Metformin | Sigma Aldrich | D150959 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Monensin | Sigma Aldrich | M5273 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Non-essential amino acids | Gibco | 11140–050 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Oligomycin A | Sigma Aldrich | 75351 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Pennicillin/Streptomycin | Gibco | 15140–112 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Phenol Red | Sigma Aldrich | P-0290 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Sodium bicarbonate | Fisher | L-23200 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Sodium pyruvate | Gibco | 11360–070 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Trypsin-EDTA (0.25%) | Gibco | 25200–056 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tween-20 | Fisher | BP-337 | |
| Commercial assay, or kit | Quick RNA miniprep kit | Genesee Scientific | R1055 | |
| Commercial assay, or kit | ATP determination kit | Thermo Fisher | A22066 | |
| Commercial assay, or kit | Mitochondria isolation kit for cultured cells | Thermo Fisher | 89874 | |
| Commercial assay, or kit | Stranded mRNA-Seq kit with mRNA capture beads | Kapa Biosystems | KK8421 | |
| Commercial assay, or kit | Galacto-Light Reaction Buffer Diluent with Galacton-Plus | Thermo Fisher | T1055 | |
| Commercial assay, or kit | Luciferase Assay System | Promega | E4550 | |
| Commercial assay, or kit | ProSignal Pico ECL | Genesee Scientific | 20-300B | |
| Commercial assay, or kit | Reporter 5X Lysis Buffer | Promega | E4030 | |
| Commercial assay, or kit | SuperSignal West Femto | Thermo Fisher | 34094 | |
| Cell line (M. musculus) | MondoA +/+mouse embryonic fibroblasts | Peterson et al. (2010), PMID: 20385767 | ||
| Cell line (M. musculus) | MondoA Δ/Δmouse embryonic fibroblasts | Peterson et al. (2010), PMID: 20385767 | ||
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | 143B | Weinberg et al. 2010, PMID: 20421486 | ||
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | 143Bρ0 | Weinberg et al. 2010, PMID: 20421486 | ||
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | 143Bρ0:Wild type cybrid | Weinberg et al. 2010, PMID: 20421486 | ||
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | 143Bρ0:ΔATP6/ΔATP8 cybrid | Boominathan et al. (2016), PMID: 27596602 | ||
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | 143Bρ0:ΔATP6/ΔATP8 cybrid + ATP6nuc+ATP8nuc | Boominathan et al. (2016), PMID: 27596602 | ||
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | HeLa | ATCC | CCL-2 | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | BJ-Tert | ATCC | CRL-4001 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | TXNIP_forward (human): TGACTTTGGCCTACAGTGGG | Peterson et al. (2010), PMID: 20385767 | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | TXNIP_reverse (human): TTGCGCTTCTCCAGATACTGC | Peterson et al. (2010), PMID: 20385767 | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | TXNIP_forward (mouse): CCTGACCTAATGGCACC | Peterson et al. (2010), PMID: 20385767 | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | TXNIP_reverse (mouse): GAGATGTCATCACCTTCAC | Peterson et al. (2010), PMID: 20385767 | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | ATP5I_forward: CAGGTCTCTCCGCTCATCAAG | This paper | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | ATP5I_reverse: GCCCGAGGTTTTAGGTAATTGT | This paper | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | Actin_forward: TCCATCATGAAGTGTGACGT | Peterson et al. (2010), PMID: 20385767 | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | Actin_reverse: TACTCCTGCTTGCTGATCCAC | Peterson et al. (2010), PMID: 20385767 | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | TXNIP_forward ChIP primer: CAGCGATCTCACTGATTG | This paper | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | TXNIP_reverse ChIP primer: AGTTTCAAGCAGGAGGCG | This paper | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | ARRDC4_forward ChIP primer: TGCTTTAGCGAGAACCCAGT | This paper | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | ARRDC4_reverse ChIP primer: TGGACAGACAGTGGGAAACA | This paper | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | TMEM97_forward ChIP primer: CTTACTGCAGAAGGCCCAAG | This paper | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | TMEM97_reverse ChIP primer: TGTAGATTGCGGTTGTGAGC | This paper | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | KLF10_forward ChIP primer: AATCAACGGCAAAGGTGTGT | This paper | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | KLF10_reverse ChIP primer: CACTCAATCAGGTGGCCTCT | This paper | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | siRNA: Dharmacon ON-TARGETplus control siRNA | GE Life Sciences | D00-1810-10-20 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | siRNA: siATP5I SmartPool | GE Life Sciences | M-019688–01 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | siRNA: siSLC25A5 SmartPool (siANT2) | GE Life Sciences | M-007486 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | siRNA: siHK2 SmartPool | GE Life Sciences | L-006735-00-0005 | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | LXSH (plasmid) | Stoltzman et al. (2008), PMID: 18458340 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | LXSH-MondoA (plasmid) | Stoltzman et al. (2008), PMID: 18458340 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | LXSH-MondoA(I766P) (plasmid) | Stoltzman et al. (2008), PMID: 18458340 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pcDNA3-AT1.03 (ATEAM) (plasmid) | Imamura et al. (2009), PMCID: PMC2735558 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pcDNA3-mitAT1.03 (Mit-ATEAM) (plasmid) | Imamura et al. (2009), PMID: 19720993 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pcDNA3-AT1.03 R122K/R126K (plasmid) | Imamura et al. (2009), PMID: 19720993 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pcDNA3-mitAT1.03 R122K/R126K (plasmid) | Imamura et al. (2009), PMID: 19720993 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pEGFP-N1-mVDAC1 (plasmid) | Zaid et al. (2005), PMID: 15818409 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pEGFP-N1-mVDAC1 (E72Q) (plasmid) | Zaid et al. (2005), PMID: 15818409 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCDV-SPORT6-HK2 (plasmid) | Stoltzman et al. (2008), PMID: 18458340 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCDV-SPORT6-HK2 (D657A) (plasmid) | Stoltzman et al. (2008), PMID: 18458340 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pcDNA3.1-mVDAC1- GFP(1-10) (plasmid) | This paper | Progenitors: PCR, pcDNAGFP(1-10) | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pcDNA3.1-mVDAC1 (E72Q)-GFP(1-10) (plasmid) | This paper | Progenitors: PCR, pcDNAGFP(1-10) | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pcDNA3.1-HK2-GFP(11) (plasmid) | This paper | Progenitors: PCR, pcDNAGFP(11) | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pGL3Basic-TXNIP_Promoter (plasmid) | Peterson et al. (2010), PMID: 20385767 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pGL3Basic-TXNIP_Promoter(ChoREmut) (plasmid) | Peterson et al. (2010), PMID: 20385767 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pcDNAGFP(1-10) | Kamiyama et al. (2016), PMID: 26988139 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pcDNAGFP(11) | Kamiyama et al. (2016), PMID: 26988139 | ||
| Software, algorithm | Prism | Graphpad Software | ||
| Software, algorithm | ImageJ | https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ | ||
| Software, algorithm | CFX Manager 3.1 | Bio-Rad | ||
| Software, algorithm | R | https://www.r-project.org | ||
| Software, algorithm | javaGSEA | Broad Institute | ||
| Software, algorithm | Cytoscape 3.6.1 | https://cytoscape.org | ||
| Software, algorithm | NIS Elements | Nikon | ||
| Other | Nunc Lab-Tek II Chambered Coverglass, 8-well | Thermo Fisher | 155409PK | |
| Other | 3.5 mm glass bottom culture dishes | MatTek Corporation | P35G-.15–14 C | |
| Other | Hybond P PVDF Membrane; 0.45 μm | Genesee Scientific | 83–646R | |
| Other | 2 ml PTFE tissue grinder | VWR | 89026–398 | |
| Other | Bioruptor Plus sonication devise | Diagenode | B01020001 |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40199.018





