Highly efficient 5' capping of mitochondrial RNA with NAD+ and NADH by yeast and human mitochondrial RNA polymerase
Figures
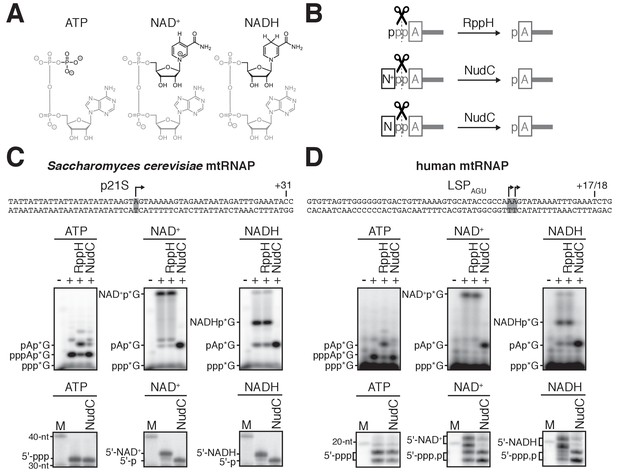
S. cerevisiae and human mtRNAPs cap RNA with NAD+ and NADH in vitro.
(A) Structures of ATP, NAD+, and NADH. Grey, identical atoms; black, distinct atoms. (B) Processing of RNA 5' ends by RppH and NudC. A, adenosine; N+, NAD+ nicotinamide; N, NADH nicotinamide; p, phosphate. (C and D) NCIN capping with NAD+ and NADH by S. cerevisiae mtRNAP (C) and human mtRNAP (D). Top, promoter derivatives. Middle, initial RNA products of in vitro transcription reactions with ATP, NAD+, or NADH as initiating nucleotide and [α32P]-GTP as extending nucleotide. Bottom, full-length RNA products of in vitro transcription reactions with ATP, NAD+, or NADH as initiating nucleotide and [α32P]-GTP, ATP, UTP, and 3'-deoxy-CTP (C), or [α32P]-GTP, ATP, and UTP (D) as extending nucleotides. Products were treated with RppH or NudC as indicated. Grey box and arrow, transcription start site (TSS);+31 and+17/18, position of last NTP incorporated into full-length RNA products; M, 10-nt marker.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Source data for Figure 1C,D.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42179.004
-
Figure 1—source data 2
Data for Figure 1—figure supplement 1.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42179.005
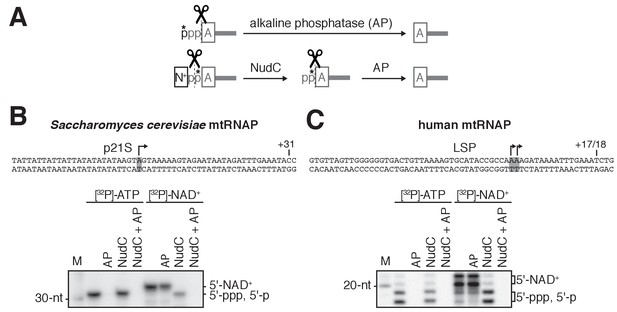
S. cerevisiae and human mtRNAPs cap RNA with NAD+ in vitro: additional data.
(A) Processing of radiolabeled RNA 5'-ends by alkaline phosphatase (AP) and NudC. A, adenosine; N+, NAD+ nicotinamide; p, phosphate. *, radiolabeled phosphate. (B and C). NCIN capping with NAD+ by S. cerevisiae mtRNAP (B) and human mtRNAP (C). Top, promoter derivatives. Bottom, full-length RNA products of in vitro transcription reactions with [γ32P]-ATP or [α32P]-NAD+ as initiating nucleotide and GTP, ATP, UTP, and 3'-deoxy-CTP (C), or GTP, ATP, and UTP (D) as extending nucleotides. Products were treated with NudC alone, AP alone, or NudC and AP, as indicated. Grey box and arrow, TSS; +31 and +17/18, position of last NTP incorporated into RNA; M, 10-nt marker.
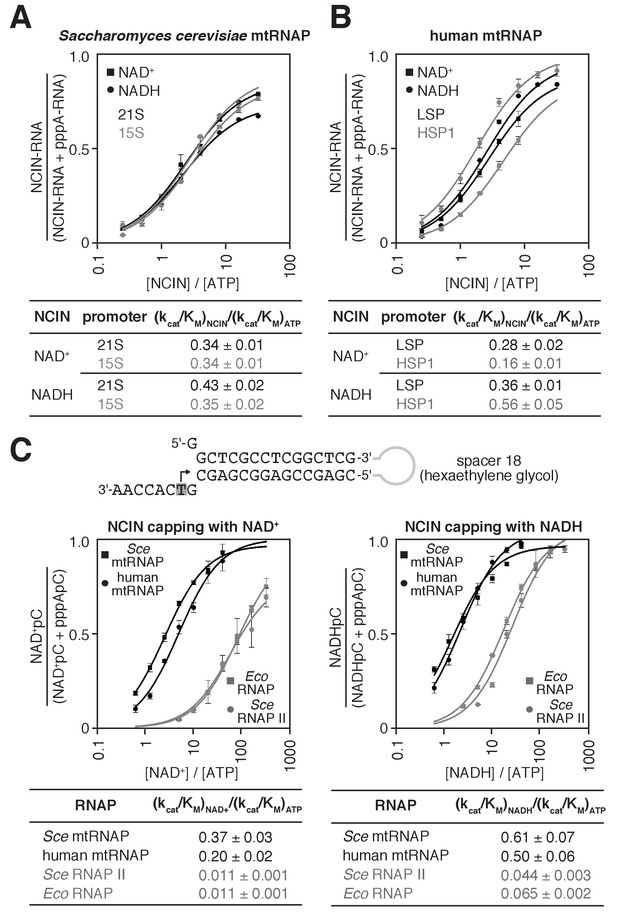
S. cerevisiae and human mtRNAPs cap RNA with NAD+ and NADH more efficiently than bacterial and nuclear RNAPs.
(A and B) Dependence of NCIN-mediated capping with NAD+ and NADH on [NCIN] / [ATP] ratio for S. cerevisiae mtRNAP (A) and human mtRNAP (B) (mean ± SD; n = 3). DNA templates and representative data are shown in Figure 2—figure supplement 1. (C) Dependence of NCIN-mediated capping with NAD+ and NADH on [NCIN] / [ATP] ratio for mtRNAPs vs. E. coli RNAP and S. cerevisiae RNAP II. Top, tailed template. Grey box and arrow indicate TSS. Bottom, dependence of NCIN-mediated capping with NAD+ and NADH on [NCIN] / [ATP] ratio for S. cerevisiae mtRNAP (Sce mtRNAP), human mtRNAP, E. coli RNAP (Eco RNAP) and S. cerevisiae RNAP II (Sce RNAP II) (mean ± SD; n = 3).
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Data for Figure 2A,B.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42179.009
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Data for Figure 2C,D, and Figure 2—figure supplement 1.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42179.010
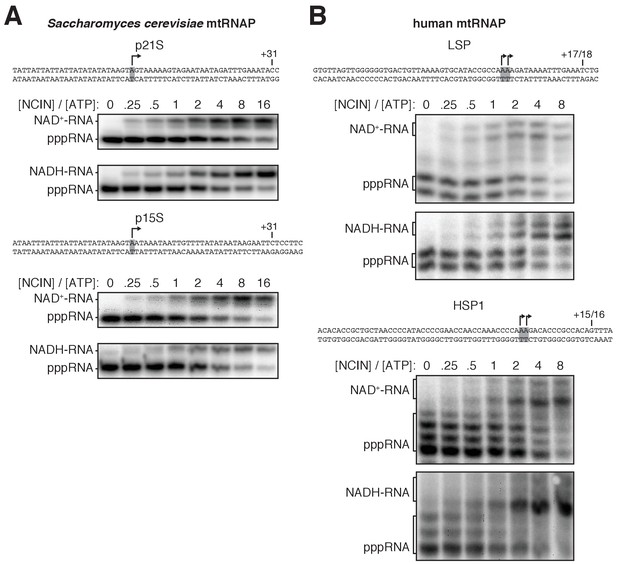
Dependence of NCIN-mediated capping with NAD+ and NADH on [NCIN] / [ATP] ratio for mtRNAPs: representative data.
(A and B) Panels show DNA templates and full-length RNA products of in vitro transcription reactions performed with S. cerevisiae mtRNAP (A) and human mtRNAP (B) with the indicated [NCIN] / [ATP] ratio. Grey box and arrow, TSS; +31, +17/18, +15/16, position of last NTP incorporated into RNA; M, 10-nt marker.
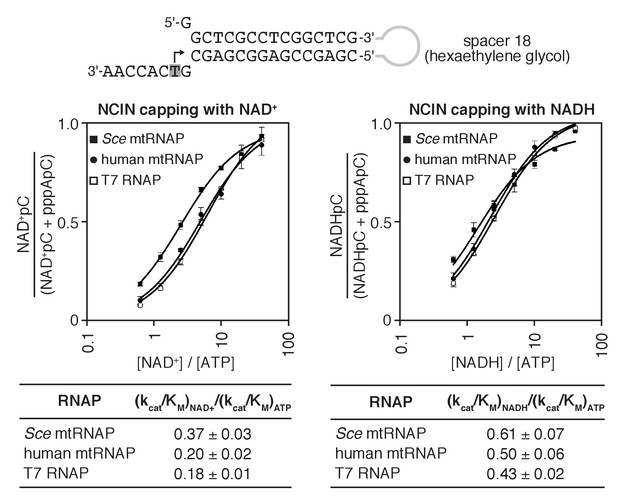
S. cerevisiae and human mtRNAPs cap RNA with NAD+ and NADH at least as efficiently as bacteriophage T7 RNAP.
Dependence of NCIN-mediated capping with NAD+ and NADH on [NCIN] / [ATP] ratio for mtRNAPs vs. T7 RNAP. Top, tailed template. Grey box and arrow indicate TSS. Bottom, Dependence of NCIN-mediated capping with NAD+ and NADH on [NCIN] / [ATP] ratio for S. cerevisiae mtRNAP (Sce mtRNAP), human mtRNAP, and T7 RNAP (mean ± SD; n = 3).
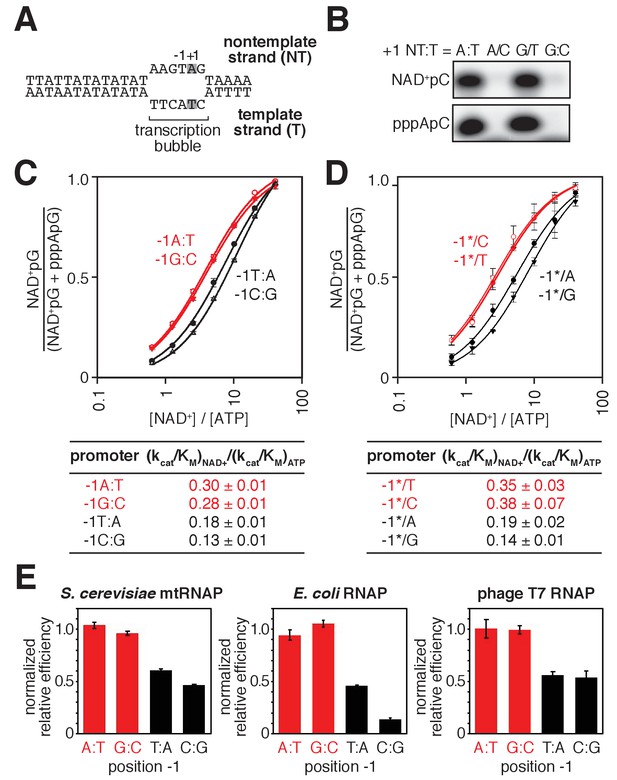
Promoter sequence determines efficiency of RNA capping with NAD+ by mtRNAP.
(A) S. cerevisiae mitochondrial 21S promoter DNA depicted in the context of the mtRNAP-promoter open complex. DNA nontemplate strand (NT) on top; DNA template strand (T) on bottom; Unwound, non-base-paired DNA region, ‘transcription bubble,’ indicated by raised and lowered nucleotides; +1 and grey boxes, bases at the TSS; −1, bases immediately upstream of the TSS (the 21S promoter is a −1Y promoter). (B) Products of transcription reactions with NAD+ as initiating nucleotide and [α32P]-CTP as extending nucleotide for templates having complementary or non-complementary nucleotides at position +1. (C) Dependence of NAD+ capping on [NAD+] / [ATP] ratio for homoduplex templates having A:T, G:C, T:A, or C:G at position −1 relative to TSS (mean ± SD; n = 3). Red, −1R promoters; black, −1Y promoters. (D) Dependence of NAD+ capping on [ATP] / [NAD+] ratio for heteroduplex templates having an abasic site (*) on the DNA nontemplate strand (mean ± SD; n = 3). Red, promoters with a template-strand Y; black, promoters with a template-strand R. (E) Sequence preferences at position −1 for S. cerevisiae mtRNAP, E. coli RNAP, and T7 RNAP. Graphs show normalized values of (kcat/KM)NAD+ / (kcat/KM)ATP determined for homoduplex templates having A:T, G:C, T:A, or C:G at position −1 (mean ± SD; n = 3). Normalized values were calculated by dividing the value for each individual promoter by the average value measured for −1R promoters. Data for S. cerevisiae mtRNAP are from panel C, data for E. coli RNAP are from (Vvedenskaya et al., 2018), and data for T7 RNAP are from Figure 3—figure supplement 1.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Data for Figure 3B.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42179.013
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Data for Figure 3C,D,E, and Figure 3—figure supplement 1.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42179.014
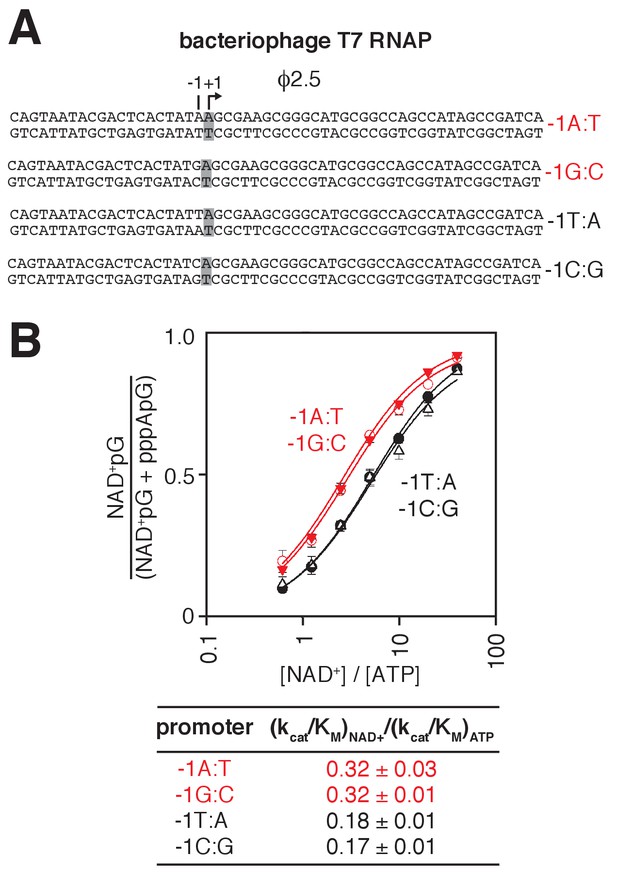
Promoter sequence determines efficiency of RNA capping with NAD+: bacteriophage T7 RNAP.
(A) Bacteriophage T7 RNAP-dependent promoter derivatives analyzed. Red, −1R promoters; black, −1Y promoters; +1 and grey box, bases at the TSS; −1, bases immediately upstream of the TSS. (B) Dependence of NAD+ capping on [NAD+] / [ATP] ratio for homoduplex templates having A:T, G:C, T:A, or C:G at position −1 relative to TSS (mean ± SD; n = 3).
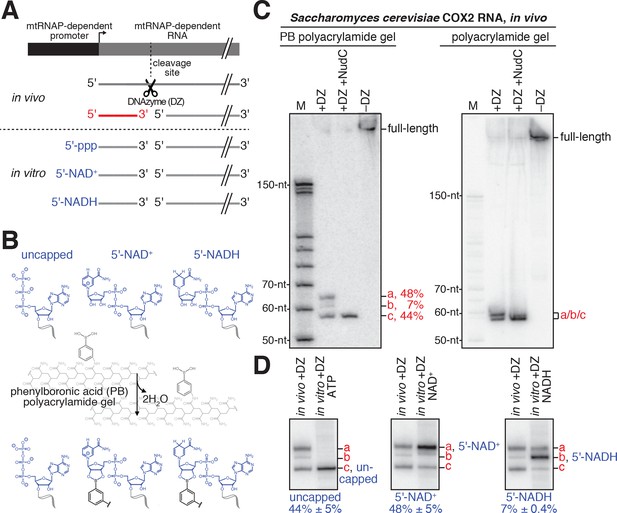
Detection and quantitation of NAD+- and NADH-capped mitochondrial RNA in vivo: boronate affinity electrophoresis with DNAzyme-cleaved cellular RNA and DNAzyme-cleaved synthetic NCIN-capped RNA standards.
(A) Use of DNAzyme (DZ) to process RNA to yield a defined, short 5'-end-containing subfragment, in parallel in vivo (red) and in vitro (blue). Uncapped, 5'-triphosphate (ppp) end generated using ATP-mediated initiation; 5'-NAD+, NAD+-capped end generated using NAD+-mediated initiation; 5'-NADH, NADH-capped end generated using NADH-mediated initiation. (B) Use of boronate affinity electrophoresis to resolve 5'-uncapped, 5'-NAD+, and 5'-NADH containing RNAs. Grey, structure of phenylboronic acid (PB) polyacrylamide gel. (C) PB-polyacrylamide gel (left) and polyacrylamide gel (right) analysis of DNAzyme-generated 5'-end-containing subfragments of S. cerevisiae mitochondrial RNA COX2. Red, observed 5'-end-containing RNA subfragments resolved by PB-polyacylamide-gel (left) or not resolved by polyacrylamide gel (right); identities of these subfragments are defined in Panel D. (D) Comparison of electrophoretic mobilities of observed 5'-end-containing subfragments of COX2 RNA generated in vivo to 5'-end-containing subfragments of synthetic RNA standards generated in vitro. a, NAD+-capped RNA; b, NADH-capped RNA; c, uncapped RNA (mean ± SD; n = 3).
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Data for Figure 4D.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42179.016
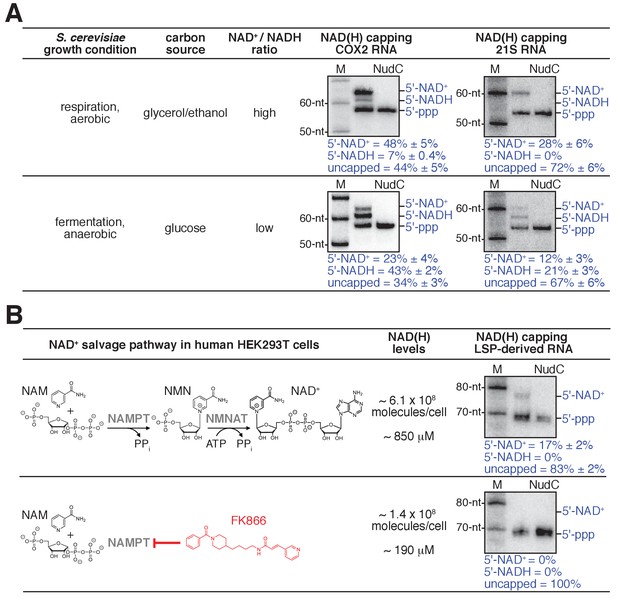
Detection and quantitation of NAD+- and NADH-capped mitochondrial RNA in vivo: effects of intracellular NAD+ and NADH levels in S. cerevisiae and human cells.
(A) Changes in intracellular NAD+/NADH ratios result in changes in levels of NAD+- and NADH-capped mitochondrial RNA (mean ± SD; n = 3). Gel images show representative data for S. cerevisiae COX2 RNA (left) and 21S RNA (right). Blue annotations as in Figure 4. (B) Changes in intracellular NAD(H) levels result in changes in levels of NAD+- and NADH-capped mitochondrial RNA (mean ± SD; n = 3). Gel images show representative data for LSP-derived RNAs. Red, NAD(H) biosynthesis inhibitor FK866; NAMPT, Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase; NMNAT, Nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Data for Figure 5 (gels).
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42179.018
-
Figure 5—source data 2
Data for Figure 5 (values of NCIN capping).
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42179.019
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | BL21(DE3) bacteria | NEB | C2527H | |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | NiCo21(DE3) bacteria | NEB | C2529H | |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | Artic Express (DE3) bacteria | Fisher Scientific | NC9444283 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. cerevisiae) | 246.1.1 (MATa ura3 trp1 leu2 his4) | Gift of A. Vershon | ||
| Cell line (human) | HEK293T (human embryonic kidney cells) | ATCC | CRL-3216 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pIA900 | Gift of I. Artsimovitch | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pET NudC-His | (Bird et al., 2016) | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pJJ1399 | gift of J. Jaehning | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pTrcHisC-Mtf1 | gift of J. Jaehning | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPROEXHTb-POLRMT (43–1230)−6xHis | (Ramachandran et al., 2017) | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPROEXHTb-TFAM (43-245)−6xHis | (Ramachandran et al., 2017) | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pT7TEV-HMBP4 | (Yakubovskaya et al., 2014) | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAR1219 | (Jia et al., 1996) | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | DK64 | Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT) | tailed template with PEG6 linker | GGCTCGCCTCGGCTCG/iSp18/ CGAGCCGAGGCGAGCGTCACCAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | JB459 | IDT | human LSP DNA template + 1 AGU variant nontemplate strand | GTGTTAGTTGGGGGGTGACTGTT AAAAGTGCATACCGCCAAAGTATA AAATTTGTGGGCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | JB460 | IDT | human LSP DNA template + 1 AGU variant template strand | GGCCCACAAATTTTATACTTTGGC GGTATGCACTTTTAACAGTCACCC CCCAACTAACAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | JB469 | IDT | T7φ2.5–35 n nontemplate strand (−1T) | CAGTAATACGACTCACTATTAGCGAA GCGGGCATGCGGCCAGCCATAGC CGATCA |
| Sequence-based reagent | JB470 | IDT | T7φ2.5–35 n template strand (−1A) | TGATCGGCTATGGCTGGCCGCATGCC CGCTTCGCTAATAGTGAGTCGTA TTACTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | JB471 | IDT | T7φ2.5–35 n nontemplate strand (−1A) | CAGTAATACGACTCACTATAAGCGAAGC GGGCATGCGGCCAGCCATAG CCGATCA |
| Sequence-based reagent | JB472 | IDT | T7φ2.5–35 n template strand (−1T) | TGATCGGCTATGGCTGGCCGCATGCCC GCTTCGCTTATAGTGAGTCGTATTACTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | JB473 | IDT | T7φ2.5–35 n nontemplate strand (−1G) | CAGTAATACGACTCACTATGAGCGAAG CGGGCATGCGGCCAGCCATAG CCGATCA |
| Sequence based reagent | JB474 | IDT | T7φ2.5 35 n template strand (−1C) | TGATCGGCTATGGCTGGCCGCATGCC CGCTTCGCTCATAGTGAGTCGTATTACTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | JB475 | IDT | T7φ2.5–35 n nontemplate strand (−1C) | CAGTAATACGACTCACTATCAGCGAA GCGGGCATGCGGCCAGCCA TAGCCGATCA |
| Sequence-based reagent | JB476 | IDT | T7φ2.5–35 n template strand (−1G) | TGATCGGCTATGGCTGGCCGCATGC CCGCTTCGCTGATAGTG AGTCGTATTACTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | JB515 | IDT | probe for human LSP-generated RNA (complementary to positions + 2 to+31) | CACCAGCCTAACCAGATTTCAA ATTTTATC |
| Sequence-based reagent | JB525 | IDT | probe for S. cerevisiae 21S RNA (complementary to positions + 9 to+42) | CTATATAATAAATATTTCAAATC TATTATTCTAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | JB526 | IDT | S. cerevisiae 21S RNA DNAzyme; cleaves transcript at position + 53 | ACTCCATGATTAGGCTAGCTACAA CGACTCTTTAAATCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | JB555 | IDT | probe for S. cerevisiae COX2 RNA (complementary to positions + 8 to+46) | ATCTTAACCTTTAGACTCTTTTGTC TATTTATAATATGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | JB557 | IDT | S. cerevisiae COX2 DNAzyme; cleaves at position + 57 | TCTTAATAAATCTAAGGCTAGCTACA ACGAATTTTAATAAATCTT |
| Sequence-based reagent | JB559 | IDT | human LSP-generated RNA DNAzyme; cleaves at position + 67 | GCACTTAAACAGGCTAGCTACAA CGAATCTCTGCCA |
| Sequence-based reagent | JB560 | IDT | S. cerevisiae COX2 −40 to + 125 nontemplate strand oligo (for generation of in vitro transcription template) | TATATAATAATAAATTATAAATAAATTTT AATTAAAAGTAGTATTAACATATTATAAA TAGACAAAAGAGTCTAAAGGTTAAGATT TATTAAAATGTTAGATTTATTAAGATTAC AATTAACAAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | JB561 | IDT | S. cerevisiae COX2 −40 to + 3 forward primer (for generation of in vitro transcription template) | TATATAATAATAAATTATAAATAAATTTT AATTAAAAGTAGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | JB562 | IDT | S. cerevisiae COX2 + 83 to+125 reverse primer (for generation of in vitro transcription template) | GTTGTTAATTGTAATCTTAATAAATCTAA CATTTTAATAAATC |
| Sequence-based reagent | UB1 | IDT | human LSP DNA template (−43 to + 19) nontemplate strand | ATGTGTTAGTTGGGGGGTGACTGTTAA AAGTGCATACCGCCAAAAGATAAAATT TGAAATCTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | UB2 | IDT | human LSP DNA template (−43 to + 19) template strand | CAGATTTCAAATTTTATCTTTTGGCGGT ATGCACTTTTAACAGTCACCCCCCAAC TAACACAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | UB3 | IDT | human HSP1 DNA template (−43 to + 20) nontemplate strand | ACACACCGCTGCTAACCCCATACCCCGA ACCAACCAAACCCCAAAGACACCCGCC ACAGTTTA |
| Sequence-based reagent | UB4 | IDT | human HSP1 DNA template (−43 to + 20) template strand | TAAACTGTGGCGGGTGTCTTTGGGGT TTGGTTGGTTCGGGGTATGGGGTTA GCAGCGGTGTGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | UB5 | IDT | S. cerevisiae 15S DNA template (−25 to + 1; C-less cassette) nontemplate strand | ATAATTTATTTATTATTATATAAGTAAT AAATAATTGTTTTATATAATAAGAA TTCTCCTTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | UB6 | IDT | S. cerevisiae 15S DNA template (−25 to + 1; C-less cassette) template strand | GAAGGAGAATTCTTATTATATAAAACA ATTATTTATTACTTATATAATAATAA ATAAATTAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | UB7 | IDT | S. cerevisiae 21S DNA template (−25 to + 1; C-less cassette) nontemplate strand | TATTATTATTATTATATATATAAGTAG TAAAAAGTAGAATAATAGATTT GAAATACC |
| Sequence-based reagent | UB8 | IDT | S. cerevisiae 21S DNA template (−25 to + 1; C-less cassette) template strand | GAAGGAGACCAACCACAAACACACA ACAACCACCAACTACTTATATAATAA TAAATAAATTAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | UB9 | IDT | S. cerevisiae 21S DNA template (−25 to + 1; C-less and A-less cassette) nontemplate strand | ATAATTTATTTATTATTATATAAGTAG TTGGTGGTTGTTGTGTGTTTGTG GTTGGTCTCCTTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | UB10 | IDT | S. cerevisiae 21S DNA template (−25to + 1; C-less and A-less cassette) template strand | GAAGGAGACCAACCACAAACACAC AACAACCACCAACTACTTATATAA TAATAAATAAATTAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | UB11 | IDT | S. cerevisiae 21S nontemplate strand (−1A) | ATAATTTATTTATTATTATATAAGAA GTTGGTGGTTGTTGTGTGTTTGTG GTTGGTCTCCTTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | UB12 | IDT | S. cerevisiae 21S template strand (−1T) | GAAGGAGACCAACCACAAACACA CAACAACCACCAACTTCTTATATA ATAATAAATAAATTAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | UB13 | IDT | S. cerevisiae 21S nontemplate strand (−1G) | ATAATTTATTTATTATTATATAAGG AGTTGGTGGTTGTTGTGTGTTTG TGGTTGGTCTCCTTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | UB14 | IDT | S. cerevisiae 21S template strand (−1C) | GAAGGAGACCAACCACAAACACA CAACAACCACCAACTCCTTATAT AATAATAAATAAATTAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | UB15 | IDT | S. cerevisiae 21S nontemplate strand (−1C) | ATAATTTATTTATTATTATATAAG CAGTTGGTGGTTGTTGTGTGT TTGTGGTTGGTCTCCTTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | UB16 | IDT | S. cerevisiae 21S template strand (−1G) | GAAGGAGACCAACCACAAACACA CAACAACCACCAACTGCTTATATA ATAATAAATAAATTAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | UB17 | IDT | S. cerevisiae 21S nontemplate strand (+1C) | ATAATTTATTTATTATTATATAAGTC GTTGGTGGTTGTTGTGTGTTTGT GGTTGGTCTCCTTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | UB18 | IDT | S. cerevisiae 21S template strand (+1G) | GAAGGAGACCAACCACAAACACAC AACAACCACCAACGACTTATATAA TAATAAATAAATTAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | JB527 | IDT | S. cerevisiae 21S nontemplate strand (−1 abasic) | ATAATTTATTTATTATTATATAAG/ idSp/AGTTGGTGGTTGTTGTGTGT TTGTGGTTGGTCTCCTTC |
| Peptide, recombinant protein (S. cerevisiae) | Rpo41 (mtRNAP) | (Tang et al., 2009) | ||
| Peptide, recombinant protein (S. cerevisiae) | Mtf1 | (Paratkar and Patel, 2010) | ||
| Peptide, recombinant protein (Human) | POLRMT (mtRNAP) | (Ramachandran et al., 2017) | ||
| Peptide, recombinant protein (Human) | TFAM | (Ramachandran et al., 2017) | ||
| Peptide, recombinant protein (Human) | TFB2 | (Yakubovskaya et al., 2014) | ||
| Peptide, recombinant protein (S. cerevisiae) | RNA polymerase II | Gift of C. Kaplan | ||
| Peptide, recombinant protein (E. coli) | RNA polymerase core (β'−6xHis) | (Artsimovitch et al., 2003) | ||
| Peptide, recombinant protein | T7 RNA polymerase | (Jia et al., 1996) | ||
| Peptide, recombinant protein (E. coli) | NudC | (Cahová et al., 2015) | ||
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Phusion Flash HF master mix | ThermoFisher | F-548L | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | T4 Polynucleotide Kinase | NEB | M0201L | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | RNA 5' pyrophosphohydrolase (RppH) | NEB | M0356S | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | FastAP Alkaline Phosphatase | Thermo Fisher | EF0651 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Monarch PCR and DNA clean up kit | NEB | T1030S | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Nuclease-free water (not DEPC-treated) | ThermoFisher | AM9932 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Bacto agar | VWR | 90000–760 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Bacto tryptone | VWR | 90000–286 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Bacto yeast extract | VWR | 90000–726 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | D-Glucose monhydrate | Amresco | 0643–1 kg | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Glycerol | EMD Millipore | 55069521 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DMEM medium | Thermo Fisher | 11965–092 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Fetal Bovine Serum | Atlanta Biological | S11150H | |
| Chemical compound, drug | dNTP solution mix, 10 mM of each NTP | NEB | N0447S | |
| Chemical compound, drug | NTP set (ultra-pure), 100 mM solutions | GE Healthcare | 27-2025-01 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | NAD+ | Roche (Sigma-Aldrich) | 10127965001 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | NADH | Roche (Sigma-Aldrich) | 10107735001 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tris base (Amresco) | VWR | 97061–800 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Boric Acid (ACS grade) | VWR | 97061–980 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | EDTA disodium salt dyhydrate | VWR | 97061–018 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 0.5 M EDTA pH 8 | ThermoFisher | AM9260G | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dibasic Sodium phosphate | EMD Millipore | SX0715-1 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Sodium Chloride | EMD Millipore | SX0420-3 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Potassium Chloride | EMD Millipore | 7300–500 GM | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Sodium Citrate | EMD Millipore | 7810–1 KG | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Sodium Acetate, trihydrate | VWR | MK736406 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Ficoll 400 | VWR | AAB22095-18 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Polyvinylpyrrolidone | EMD Millipore | 7220–1 KG | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Diethyl Pyrocarbonate (DEPC) | VWR | AAB22753-14 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Formamide, deionized | VWR | EM-4610 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Sodium dodecylsulfate (SDS) | VWR | 97064–470 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Magnesium chloride hexahydrate | VWR | EM-5980 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate | VWR | EM-MX0070-1 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Glycerol (ACS grade) | VWR | EMGX0185-5 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) fraction V | VWR | 101174–932 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Bromophenol Blue | VWR | EM-BX1410-7 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Xylene Cyanol | Sigma-Aldrich | X4126-10G | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Amaranth Dye | VWR | 200030–400 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Temed (JT Baker) | VWR | JT4098-1 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Ammonium Persulfate | VWR | 97064–594 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dithiothreitol (DTT) | Gold Bio | DTT50 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Glycogen from Oyster (type II) | Sigma-Aldrich | G8751 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Hydrochloric Acid (ACS plus) | Fisher Scientific | A144-212 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Ethyl Alcohol | Pharmco-AAPER | 111000200 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | GeneMate LE Quick Dissolve agarose | BioExpress | E-3119–500 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | SequaGel sequencing system | National Diagnostics | EC833 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Nytran SuPerCharge Nylon Membrane | VWR | 10416296 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | SigmaSpin G25 cleanup columns | Sigma-Aldrich | S5059 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 32P NAD+ 250 uCi | Perkin Elmer | BLU023X250UC | |
| Chemical compound, drug | γ-32P ATP Easy Tide 1 mCi | Perkin Elmer | BLU502Z001MC | |
| Chemical compound, drug | α-32P CTP Easy Tide 250 uCi | Perkin Elmer | BLU508H250UC | |
| Chemical compound, drug | α-32P GTP Easy Tide 250 uCi | Perkin Elmer | BLU506H250UC | |
| Chemical compound, drug | α-32P UTP Easy Tide 250 uCi | Perkin Elmer | BLU507H250UC | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Decade Marker | Thermo Fisher | AM7778 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | TRI Reagent | Molecular Research Center | TR118 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Acid phenol:chloroform (CHCl3) pH 4.5 | ThermoFisher | AM9720 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | FK866 hydrochloride hyrate | Sigma-Aldrich | F8557 | |
| Software, algorithm | Excel | Microsoft | 365 | |
| Software, algorithm | ImageQuant | GE Healthcare | TL 5.1, TL v8.2 | |
| Software, algorithm | SigmaPlot | Systat Software Inc. | Version 10 | |
| Software, algorithm | Pymol | Schrodinger, LLC | http://www.pymol.org | |
| Software, algorithm | Illustrator | Adobe | Version CS6 | |
| Other | Typhoon RBG Imager | GE Healthcare | ||
| Other | NanoDrop 2000C spectrophotometer | Thermo Fisher | ||
| Other | UV Crosslinker | Fisher Scientific | FB-UVXL-1000 | |
| Other | Hybridization oven 5420 | VWR | 97005–252 | |
| Other | Sequi-Gen GT sequencing systems (21 × 50) (38 × 30) | Bio-Rad | 1653871 and 1653873 |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42179.020





