The ion channel ppk301 controls freshwater egg-laying in the mosquito Aedes aegypti
Figures
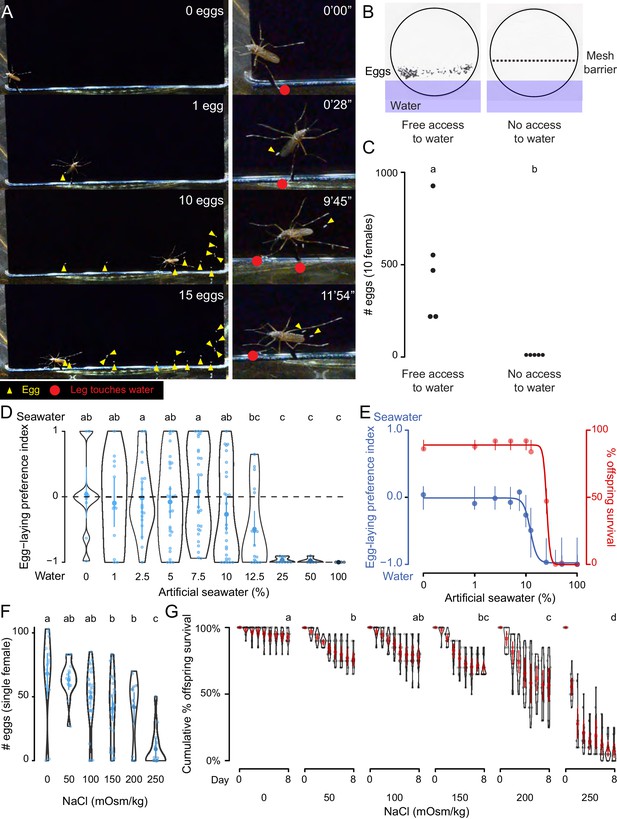
Ae. aegypti mosquitoes use freshwater contact to guide egg-laying, ensuring offspring survival.
(A) Still video frames of Ae. aegypti female with newly laid eggs (yellow triangles) and contact between sensory appendages and liquid water (red circles) indicated. Right panels are magnification of animal in left panels. (B) Egg-papers (black circles) from 10 females allowed to lay eggs for 18 hr with access to water (left) or access blocked by metal mesh (right). (C) Eggs laid after 18 hr under conditions in b. n = 5; each dot represents data from a group of 10 females. (D) Egg-laying preference of single females between water and increasing concentrations of artificial seawater. Mean ±95% confidence interval. n = 4–29/concentration. (E) Four-parameter log-logistic curve fit to egg-laying preference in D (blue, n = 4–29/concentration) or offspring surviving (red, n = 5/ concentration) in indicated concentrations of artificial seawater. Mean of the data is presented along with 95% confidence intervals of the model fit. (F) Eggs laid by single females given access to liquid of the indicated NaCl concentration. Mean ±95% confidence interval. n = 14–28/concentration. (G) Cumulative survival of larvae in indicated concentration of NaCl. Mean ±95% confidence interval. n = 9 groups/concentration. In a given panel, data labeled with different letters are significantly different from each other; p<0.05, two-way paired t-test (C), ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD (D, F) or ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD of survival at day 8 (G).
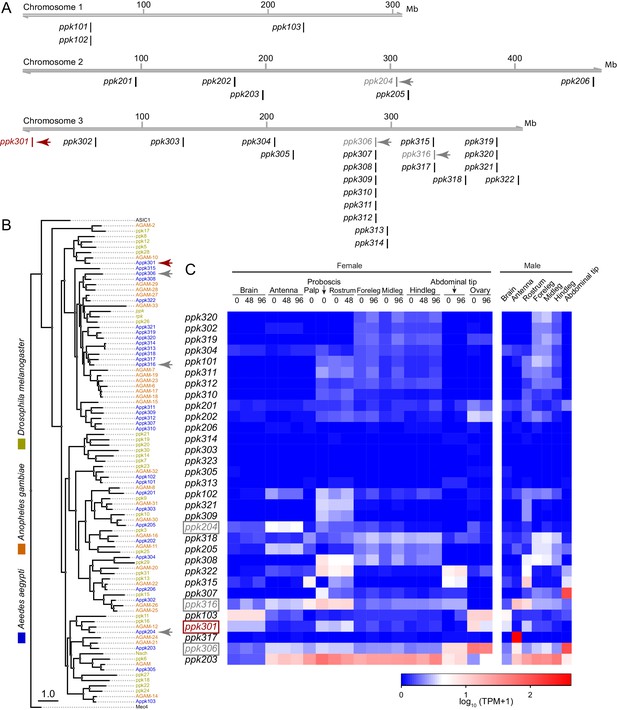
Genomic organization and tissue-specific expression of Ae. aegypti ppk ion channels.
(A) Genomic organization of ppk ion channels on the three chromosomes of Ae. aegypti. (B) Phylogenetic tree of ppk ion channel proteins from Ae. aegypti, Anopheles gambiae, and Drosophila melanogaster. Scale bar = 1.0 substitution/site. (C) Gene expression of ppk ion channels across tissues. Data originally generated in a survey of gene expression across neural tissues (Matthews et al., 2016) were aligned to the AaegL5 genome (Matthews et al., 2018). Values represent mean of multiple replicates for each tissue. Genes studied in this paper are marked with arrowheads in A-C.
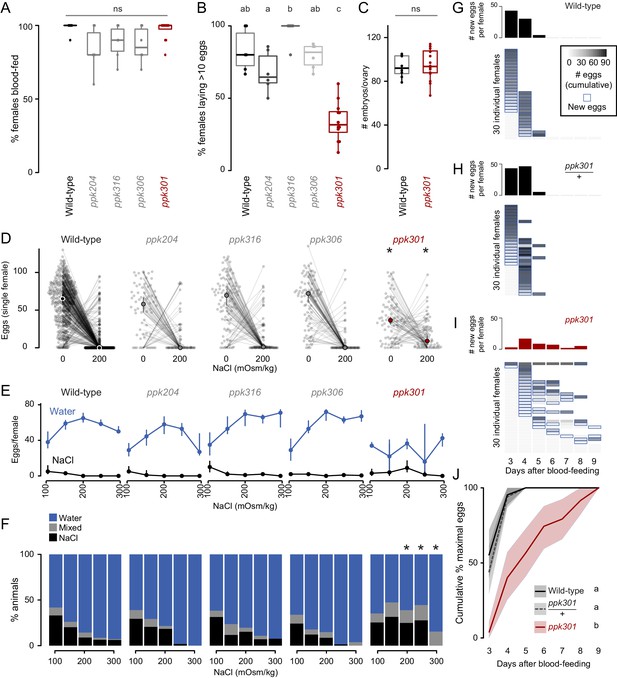
Mutations in the ppk301 ion channel disrupt egg-laying preference and timing.
(A, B) Females of indicated genotype who blood-fed (A) or laid >10 eggs given 18 hr to lay (B). n = 6–12 groups/genotype. (C) Embryos/ovary 72 hr post-blood-meal. n = 8–16/genotype. (D–F) Eggs laid by single females of the indicated genotype in the indicated NaCl concentration. Only females laying >10 eggs are presented. In D, lines connect data from individual animals (dots). Median (points) ± 95% confidence interval (bars). n = 65–314 animals/genotype (D) or n = 3–314 animals/genotype (E) per concentration. In F, proportion of animals are binned into three behavioral groups by eggs laid on each substrate. (G–I) Eggs laid in 0 mOsm/kg NaCl by single females of the indicated genotype. n = 30 females/genotype. Blue outline indicates days on which new eggs were laid and histograms indicate mean new eggs (per female). (J) Summary of data in G-I. Mean (line) ±95% confidence interval (shaded bars). In B, data labeled with different letters are significantly different from each other p<0.05, in D,F * indicate difference from wild-type p<0.05 (D) p<0.01 (F); ns = not significant, ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD (A, B, E, H), unpaired t-test (C), and chi-squared test corrected for FDR (F). Boxplots in A-C indicate median and 1st and 3rd quartiles, whiskers extend to 1.5x interquartile range.
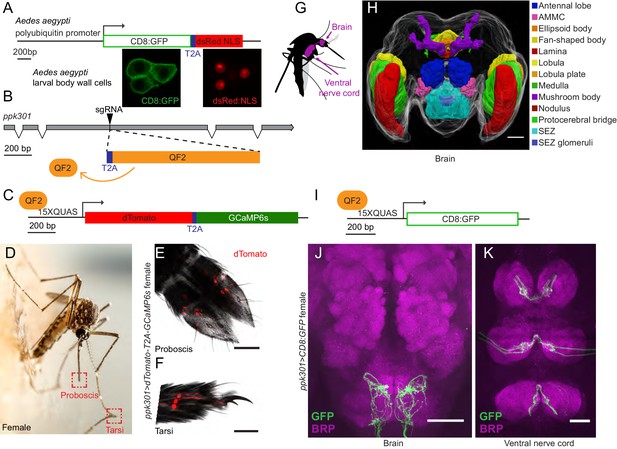
In-frame insertion of T2A-QF2 into the ppk301 locus labels sensory neurons that project to central taste centers.
(A) Top, construct used to test the efficacy of T2A in Ae. aegypti. Bottom, confocal images of three Ae. aegypti body wall cells expressing both mCD8:GFP (green) and dsRed:NLS (red). (B) Diagram of coding region of ppk301 locus with exons (gray boxes), introns (connecting lines), and CRISPR-Cas9 gRNA site used to insert T2A (blue) and QF2 (orange). (C) Map of 15x-QUAS-dTomato-T2A-GCaMP6s transgene. (D) Female mosquito laying an egg on a moist substrate, highlighting proboscis and tarsal appendages that contact water (red boxes). Photo: Alex Wild. (E, F) Confocal image dTomato expression in ppk301>dTomato-T2A-GCaMP6s proboscis (E) and tarsi (F) with transmitted light overlay. (G) Cartoon of mosquito adult neural tissues. (H) 3D-reconstruction of female Ae. aegypti brain. Different regions of the brain are identified by Bruchpilot (Brp) immunostaining and homology to other insects. AMMC = Antennal Mechanosensory and Motor Center, SEZ = subesophageal zone. (I) Map of 15x-QUAS-mCD8:GFP transgene (J, K) Expression of ppk301>mCD8:GFP in female brain (J) and ventral nerve cord (K) Scale bars: 50 µm.
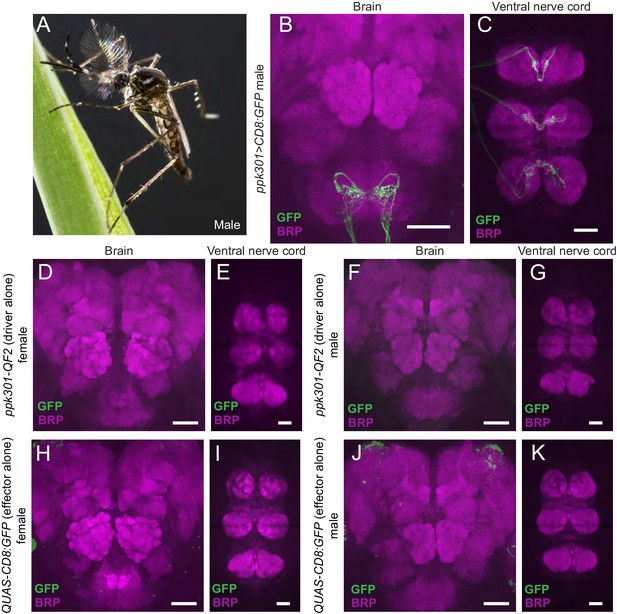
Male expression of ppk301>mCD8:GFP and QF2/QUAS controls for ppk301-QF2 reagent.
Expression of ppk301>mCD8:GFP in males and controls for QF2/QUAS expression. (A) Male Ae. aegypti mosquito. Photo: Alex Wild. (B, C) Expression of ppk301>CD8:GFP in male brain (B) or ventral nerve cord (C). (D–G) Female brain (D) or ventral nerve cord (E) and male brain (F) or ventral nerve cord (G) in driver-only ppk301-QF2 control animals. (H–K) Female brain (H) or ventral nerve cord (I) and male brain (J) or ventral nerve cord (K) in responder-only 15x-QUAS-mCD8:GFP control animals. In all panels, Brp is in magenta and mCD8:GFP in green. Scale bars: 50 µm.
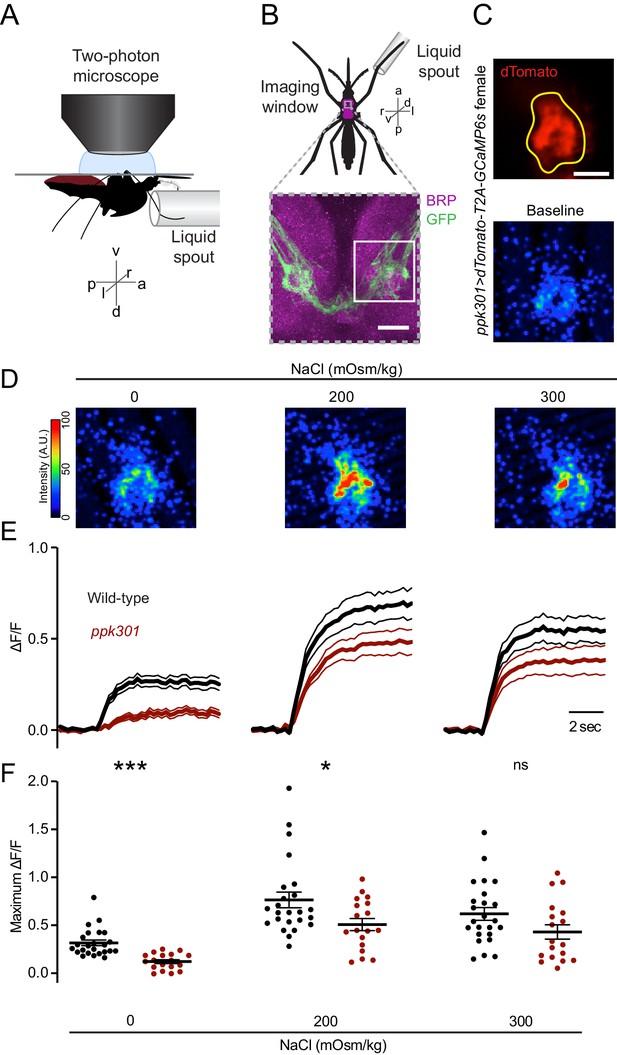
ppk301 neurons respond to water and salt.
(A) Side view schematic of ventral nerve cord imaging setup. (B) Top, ventral view schematic of mosquito during imaging showing ventral nerve cord (magenta) and imaging window (gray box). Bottom, confocal image of the approximate area contained in the imaging window. White box highlights the approximate area in C. Image from ppk301>mCD8:GFP animal. Scale bar 10 µm. (C) Top, two-photon image of dTomato (red) and region of interest (yellow). Scale bar 20 µm. Bottom: Representative GCaMP6s fluorescence at baseline (scale: arbitrary units). (D) Representative GCaMP6s fluorescence increase to indicated NaCl concentrations compared to baseline (scale: arbitrary units). (E) Average GCaMP6s traces from all wild-type and ppk301 mutant animals presented with three concentrations of NaCl until end of the trial, n = 24 sweeps from eight animals each. Mean (thick lines) ± S.E.M. (thin lines). (F) Summary of data in E comparing the maximum ΔF/F (arbitrary units) for each individual stimulus presentation in wild-type and ppk301 mutant animals. Lines denote mean and SEM. *p<0.05 ***p<0.001, t-test between genotypes at each concentration with Bonferroni correction.
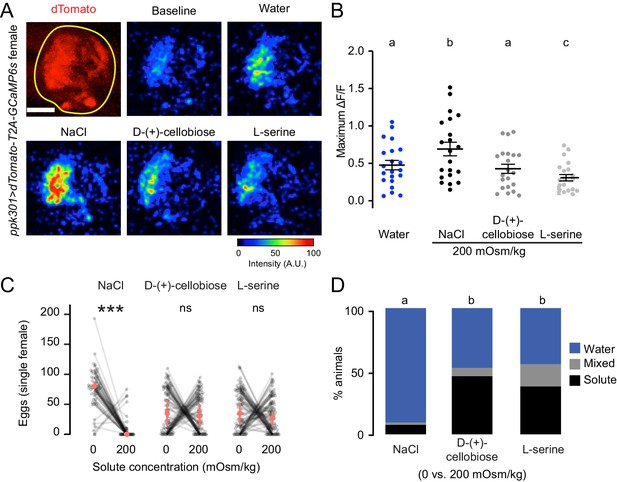
ppk301 neurons are not tuned to osmotic pressure.
(A) Top left, two-photon image of dTomato (red) and region of interest (yellow). All other panels show representative GCaMP6s fluorescence increase to indicated solutions at 200mOsm/kg compared to baseline (scale: arbitrary units). (B) Maximum ΔF/F (arbitrary units) for individual sweeps in wild-type animals. n = 21 sweeps/condition from n = 7 animals. (C) Eggs laid by single females of the indicated genotype in the indicated solute concentration. Only females laying >10 eggs are presented, and lines connect data from individual animals. n = 53–79 animals/genotype. (D) Proportion of animals are binned into three behavioral groups by eggs laid on each substrate. Scale bar: 10 µm (B). In B, data labeled with different letters are significantly different from each other (two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD p<0.05). In (C) stars denote that the number of eggs laid on water are significantly different than the number of eggs laid on each solute (Paired Wilcoxon rank-sum test corrected for multiple comparisons by the Bonferroni method, ***=p < 0.001). In (D), different letters indicate that conditions are different from one another (p<0.05) by a chi-squared test corrected for FDR.
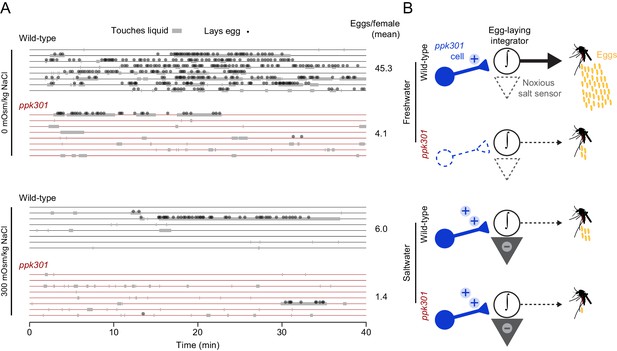
ppk301 gates egg laying, pointing to integration of water and salt cues that drive preference.
(A) Raster plot of eggs laid (circles) and physical contact with liquid (gray boxes) by eight individual females of the indicated genotype over 40-min observation period in the indicated NaCl solution. (B) Model for ppk301 control of freshwater egg-laying.
Videos
Ae. aegypti mosquitoes use contact with freshwater to guide egg-laying (related to Figure 1).
This video shows a single female mosquito, 4 days after a blood-meal, in a small chamber with deionized water and a vertically oriented piece of black paper partially submerged in the water. The mosquito directly contacts the liquid with sensory appendages including all legs and proboscis, followed by egg-laying on the moist black paper substrate above the water line. Freshly laid Ae. aegypti eggs are initially un-melanized and therefore appear white in this video and in Figure 1A.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody | anti-Brp (mouse monoclonal) | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | DSHB:NC82 RRID:AB_2314866 | (1:50) |
| Antibody | anti-GFP (rabbit polyclonal) | Life Technologies | Molecular Probes: A11122 RRID:AB_221569 | (1:10,000) |
| Chemical compound, drug | L-serine | Sigma | Sigma:s4500 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | D-(+)-cellobiose | Sigma | Sigma:22150 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | NaCl | Sigma | Sigma:s7653 | |
| Gene (Aedes aegypti) | ppk301 | NA | NCBI:LOC5564307 | previously known as AAEL000582, ppk582 |
| Gene (Ae. aegypti) | ppk204 | NA | NCBI:LOC5573846 | previously known as AAEL010779, ppk10779 |
| Gene (Ae. aegypti) | ppk316 | NA | NCBI:LOC5567201 | previously known as AAEL000926, ppk00926 |
| Gene (Ae. aegypti) | ppk306 | NA | NCBI:LOC5563925 | previously known as AAEL014228, ppk14228 |
| Genetic reagent (Ae. aegypti) | ppk301 -/- | PMID:25818303 | NA | previously generated and referred to asAAEL00582 ECFP in Kistler et al., 2015 (PMID:25818303). Contains an insertion of a poly-ubiquitin promoter-driven ECFP into the coding sequence of ppk301 |
| Genetic reagent (Ae. aegypti) | ppk204 -/- | PMID:25818303 | NA | previously generated and referred to asAAEL010779 -/- in Kistler et al., 2015 (PMID:25818303). Contains a 150 bp deletion in the coding sequence ofppk301 with a corresponding integration of a cassette with triple-stop codons. |
| Genetic reagent (Ae. aegypti) | ppk316 -/- | PMID:25818303 | NA | previously generated and referred to asAAEL00926-/- in Kistler et al., 2015 (PMID:25818303). Contains an 86 bp deletion in the coding sequence of ppk316 with a corresponding integration of a cassette with triple-stop codons and several downstream SNPs. |
| Genetic reagent (Ae. aegypti) | ppk306 -/- | PMID:25818303 | NA | previously generated and referred to asAAEL014228-/- in Kistler et al., 2015 (PMID:25818303). Contains a 106 bp deletion in the coding sequence of ppk306 with a corresponding integration of a cassette with triple-stop codons. |
| Genetic reagent (Ae. aegypti) | ppk301-T2A-QF2 | this paper | NA | T2A-QF2 knockin into the ppk301 locus, described in Materials and methods. |
| Genetic reagent (Ae. aegypti) | Pub-mCD8:GFP-T2A-dsRed:NLS-SV40 | this paper | NA | Ae. aegypti poly-ubiquitin promoter driving expression of membrane tethered GFP and nuclear dsRed separated by a T2A peptide. Described inMaterials and methods |
| Genetic reagent (Ae. aegypti) | 15x-QUAS-mCD8-GFP | this paper | NA | QUAS reporter strain driving expression of membrane-targeted GFP. Produced by transforming wild-type Ae. aegypti with plasmid RRID:Addgene_104878 |
| Genetic reagent (Ae. aegypti) | 15x-QUAS-dTomato-T2A-GCaMP6s | this paper | NA | QUAS reporter strain driving expression of cytosolic dTomato and GCaMP6s separated by a T2A peptide. Described in Materials and methods |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.43963.012
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.43963.013





