Endoplasmic reticulum-associated SKN-1A/Nrf1 mediates a cytoplasmic unfolded protein response and promotes longevity
Figures
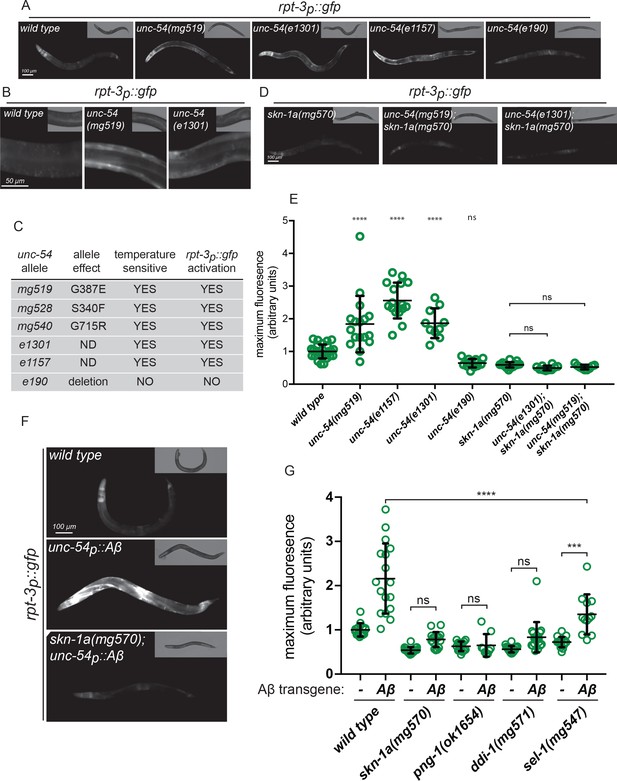
Misfolded proteins activate SKN-1A.
(a, b) Fluorescence images showing rpt-3p::gfp expression in various unc-54 mutants. (c) Temperature dependent paralysis and rpt-3p::gfp effects of unc-54 alleles. (d) Fluorescence images showing rpt-3p::gfp induction in unc-54(mg519) and unc-54(e1301) requires skn-1a. (e) Quantification of rpt-3p::gfp expression in various unc-54 mutants. (f) Fluorescence images showing Aβ expression in muscle increases rpt-3p::gfp fluorescence in wild type but not in skn-1a mutant animals. (g) Quantification of Aβ-induced activation of rpt-3p::gfp in various mutant backgrounds. Panels e and g: ****p<0.0001; ***p<0.001; ns p>0.05. (one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test), P-value compared to wild type unless otherwise indicated.
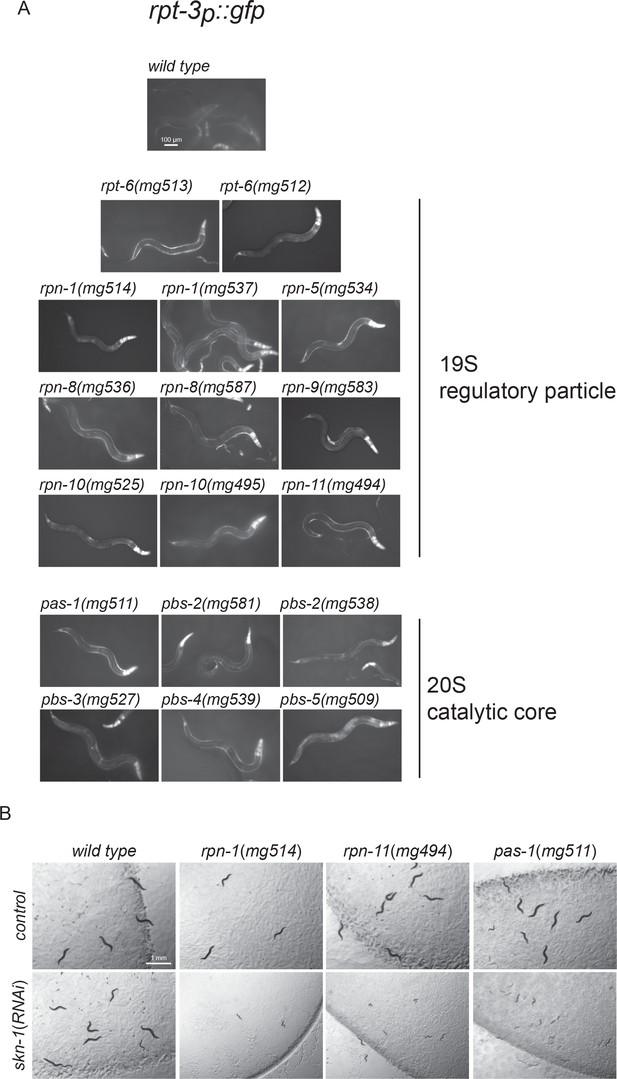
Proteasome subunit mutations that activate SKN-1A.
(a) Fluorescence images showing rpt-3p::gfp activation in proteasome subunit mutant strains. Scale bar shows 100 μm. (c) Images showing larval lethality of proteasome subunit mutants on skn-1(RNAi) but not control RNAi. Scale bar shows 1 mm.
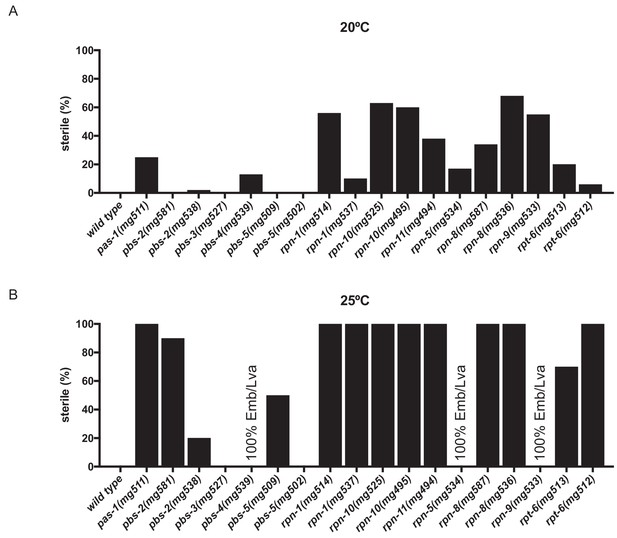
Fertility defects of proteasome subunit mutant strains.
Sterility of proteasome subunit mutants raised at (a) 20°C and (b) 25°C. At 20°C n = 20–60; at 25°C n = 10. All animals contain the mgIs72 rpt-3p::gfp integrated transgene.
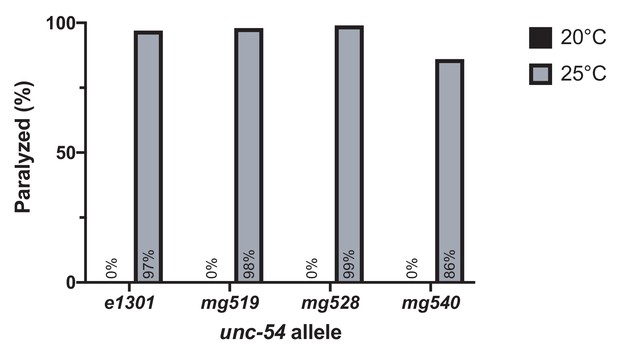
Temperature sensitive paralysis of unc-54 mutants.
Percentage of adult animals paralyzed at 20°C and 25°C. n > 100 for each strain and condition.
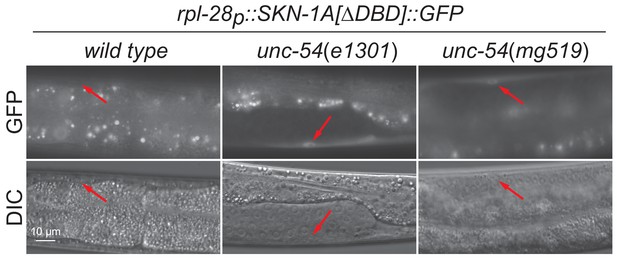
unc-54ts mutants activate SKN-1A.
Fluorescence images showing accumulation of SKN-1A[∆DBD]::GFP in muscle cells of unc-54(e1301) and unc-54(mg519) animals. Scale bar shows 10 μm.
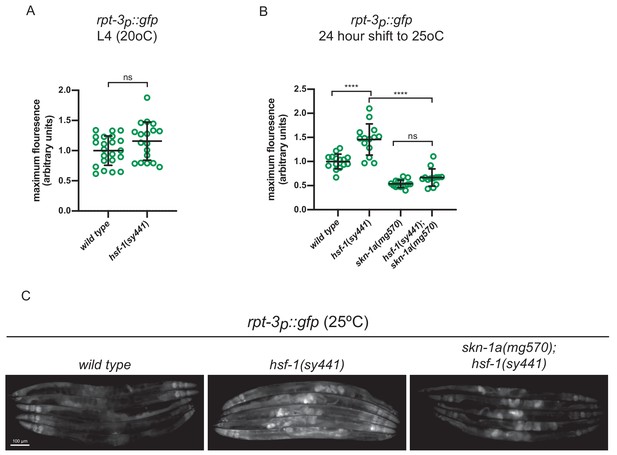
Increased expression of rpt-3p::gfp in hsf-1 mutants.
(a) Quantification of rpt-3p::gfp expression in hsf-1(sy441) and wild type animals at (a) 20°C. ns p>0.05 (Welch’s t-test) (b) Quantification of rpt-3p::gfp expression 24 hr after upshift to 25°C. rpt-3p::gfp expression is increased in hsf-1(sy441) mutants in a skn-1a-dependent manner. ****p<0.0001; ns p>0.05 (one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). (c) Fluorescence images showing increased rpt-3p::gfp expression in wild type, hsf-1(sy441) and hsf-1(sy441); skn-1a(mg570) double mutant animals 24 hr after upshift to 25°C. Scale bar shows 100 μm.
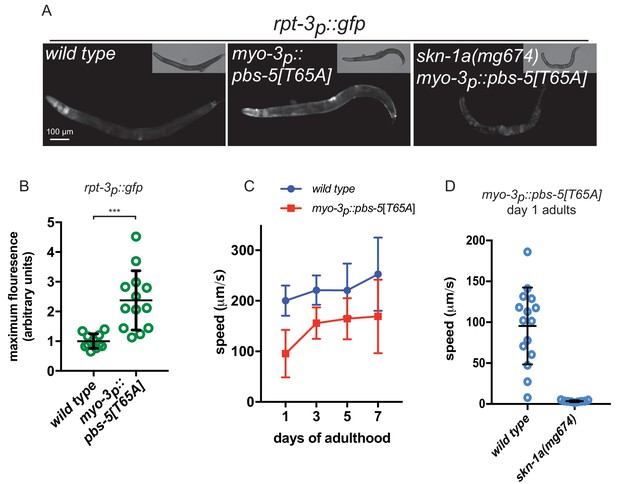
Proteasome impairment in muscle causes cell autonomous activation of SKN-1A.
(a) Fluorescence images showing rpt-3p::gfp expression in animals expressing a dominant negative proteasome subunit in the muscle (myo-3p::pbs-5[T65A]). (b) Quantification of rpt-3p::gfp expression in animals expressing a mutant proteasome subunit in the muscle. ***p<0.001 (Welch’s t-test). (c) Comparison of locomotor rate between wild type and myo-3p::pbs-5[T65A] transgenic animals. (d) Comparison of locomotor rate between wild type and skn-1a mutant animals carrying the myo-3p::pbs-5[T65A] transgene on day 1 of adulthood.
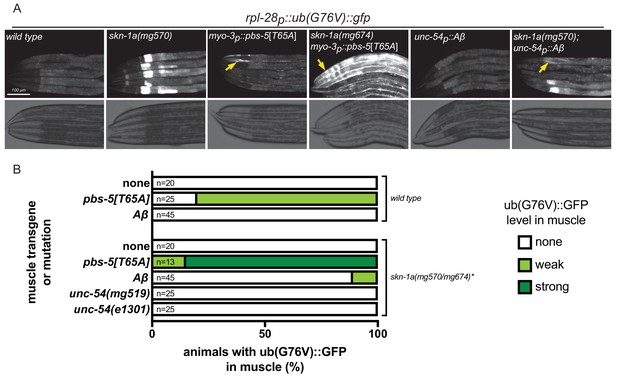
Proteasome function is not impaired in animals expressing misfolded proteins.
(a) Fluorescence micrographs showing impairment of UB(G76V)::GFP degradation in various genotypes. Arrows indicate UB(G76V)::GFP accumulation in muscle cells. (b) Comparison of UB(G76V)::GFP stabilization in muscles of animals carrying various SKN-1A-activating transgenes or mutations. *The skn-1a mutation used in the pbs-5[T65A] strain is mg674, which is an identical CRISPR-induced lesion to mg570. All animals were examined for UB(G76V)::GFP stabilization in the muscle at the L4 stage. We note that animals lacking SKN-1A show a defect in basal proteasome function, causing accumulation of UB(G76V)::GFP. This basal effect is limited to the intestine, and so we were still able to detect muscle-specific effects.
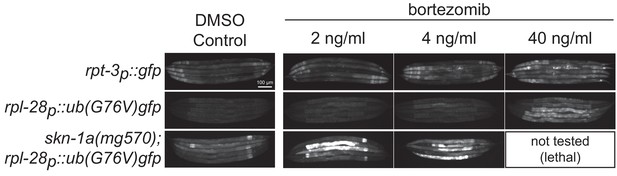
Comparison of rpt-3p::gfp activation and UB(G76V)::GFP accumulation in animals exposed to low doses of bortezomib.
Fluorescence images showing rpt-3p::gfp and rpl-28p::ub(G76V)::gfp transgenic animals raised on plates supplemented with different concentrations of bortezomib, or DMSO control. rpt-3p::gfp is not induced by 2 ng/ml bortezomib, is weakly induced by 4 ng/ml bortezomib, and more strongly induced by 40 ng/ml bortezomib. In wild type animals, only exposure to 40 ng/ml bortezomib causes increased levels of UB(G76V)::GFP accumulation. In skn-1a(mg570) mutant animals, exposure to 2 or 4 ng/ml causes increased accumulation of UB(G76V)::GFP. Scale bar shows 100 μm.
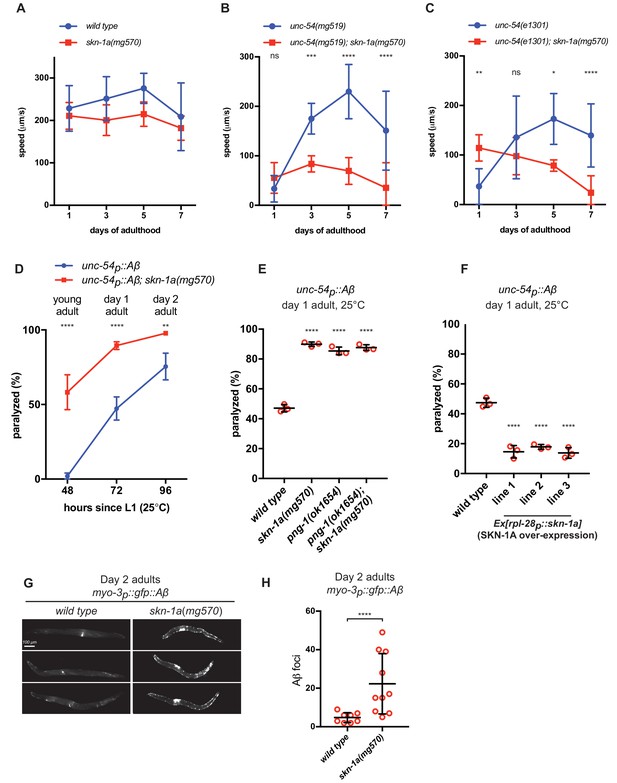
SKN-1A ameliorates age-dependent toxicity of misfolded proteins.
Analysis of locomotion of (a) wild type and skn-1a(mg570) mutant animals, (b) unc-54(mg519) and unc-54(mg519); skn-1a(mg570) double mutant animals and (c) unc-54(e1301) and unc-54(e1301); skn-1a(mg570) double mutant animals during aging. (d) Age-dependent paralysis of wild type and skn-1a(mg570) mutant Aβ expressing animals. Panels b, c, d: ****p<0.0001; ***p<0.001; **p<0.01; *p<0.05; ns p>0.05 indicates P-value compared to the skn-1a(+) control at each time point (two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test). (e) increased paralysis of Aβ expressing with defective SKN-1A activation. (f) reduced paralysis of Aβ expressing animals with increased SKN-1A levels. Panels e and f: ****p<0.0001 compared to wild type (one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). (g) Fluorescence images showing increased accumulation of Aβ::GFP in day two adults in skn-1a(mg570) as compared to wild type. (h) Quantification of Aβ::GFP puncta in wild type and skn-1a(mg570). ****p<0.0001 (Welch’s t-test).
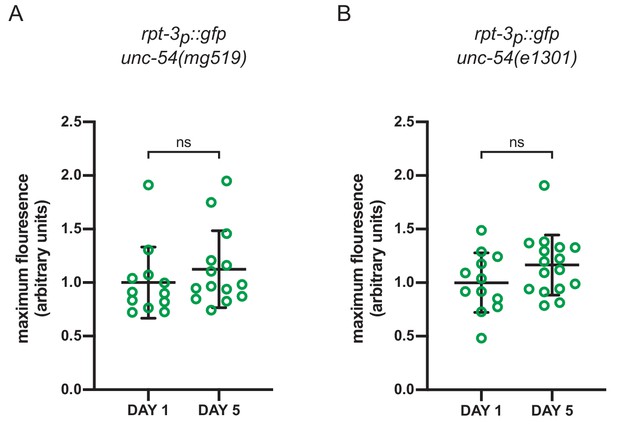
Activation of rpt-3p::gfp in unc-54ts mutants is not increased during aging.
Quantification of rpt-3p::gfp expression in (a) unc-54(mg519) and (b) unc-54(e1301) animals on day 1 and day 5 of adulthood. ns p>0.05 (Welch’s t-test).
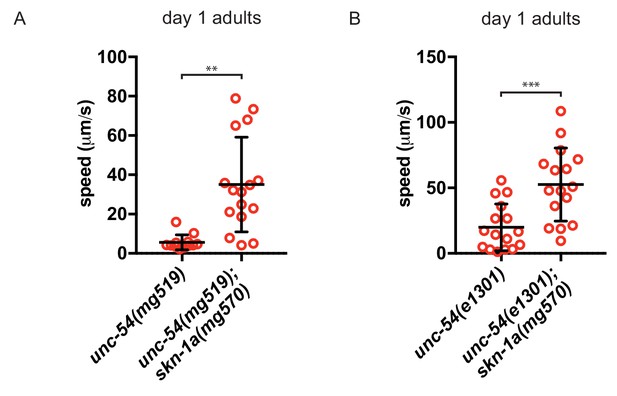
The effect of SKN-1A on locomotion of unc-54ts mutants on day 1 of adulthood.
(a) Analysis of locomotion of (a) unc-54(mg519) and unc-54(mg519); skn-1a(mg570) double mutant animals and (b) unc-54(e1301) and unc-54(e1301); skn-1a(mg570) double mutant animals on day 1 of adulthood. ***p<0.001, **p<0.01 (Welch’s t-test).
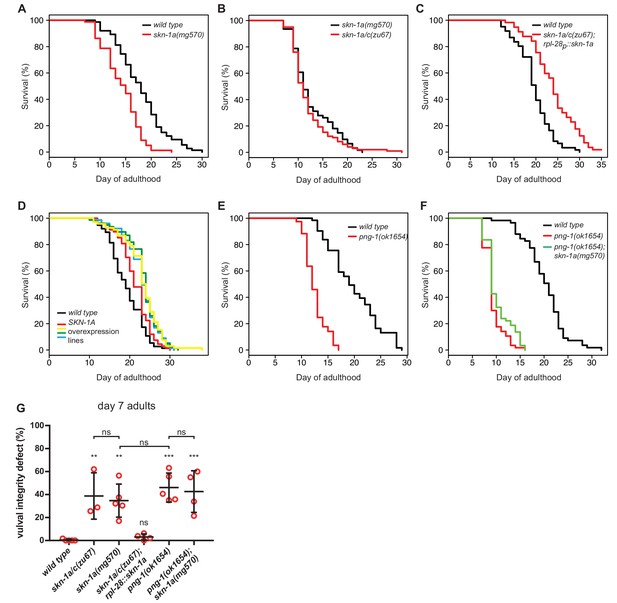
SKN-1A and PNG-1 control lifespan.
(a–f) Experiments showing that SKN-1A and PNG-1 control lifespan, and that SKN-1A accounts for the effect of skn-1a/c mutations on normal lifespan: (a) The lifespan of skn-1a(mg570) mutant animals is reduced compared to the wild type. (b) The lifespan of skn-1a/c(zu67) mutant animals is not further reduced compared to skn-1a(mg570). (c) The reduced lifespan of skn-1a/c(zu67) mutant animals is rescued by a transgene expressing SKN-1A under control of the rpl-28 promoter. (d) Overexpression of SKN-1A increases lifespan. In five independent rpl-28p::skn-1a::gfp lines we found a 10–20% increase in lifespan compared to the wild type. (e) The lifespan of png-1(ok1654) mutant animals is reduced compared to wild type. (f) Removal of SKN-1A does not further reduce the lifespan of png-1(ok1654) mutant animals. For summary of lifespan statistics see Supplementary file 1 (g) Analysis of vulval degeneration in day 7 adults. ***p<0.001; **p<0.01; ns p>0.05; P-value compared to wild type control is shown unless otherwise indicated (one-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test).
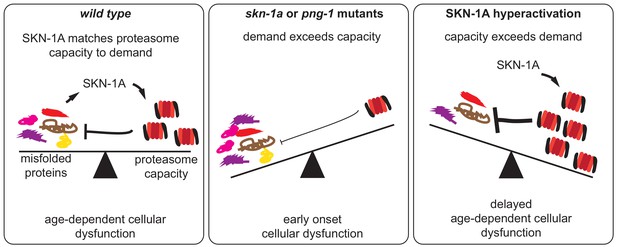
SKN-1A modulates functional decline during aging by adjusting proteasome capacity to meet demand for degradation of misfolded proteins.
During aging, misfolded proteins eventually accumulate to levels that disrupt cellular function. SKN-1A adjusts proteasome capacity to meet demand for degradation of damaged and misfolded proteins. This modulates the age-dependent accumulation and toxicity of misfolded proteins, thereby altering the rate of functional decline during aging. In animals lacking this pathway (i.e. skn-1a or png-1 mutants), insufficient proteasome capacity leads to a rapid decline and reduced lifespan. Conversely, enhancement of this pathway (by increasing SKN-1A levels or activity) delays the cellular dysfunction caused by misfolded proteins and extends lifespan.
Tables
Protesome subunit mutants.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.44425.002| genotype | allele effect | Viability at 20ºC | Viability at 25ºC | rpt-3p::gfp induction on skn-1(RNAi) | growth on skn-1(RNAi) |
| wild type | + | Yes | Yes | + | |
| pas-1(mg511) | G82R | Yes | No (Ste) | lost | Lva |
| pbs-2(mg581) | C90Y | Yes | Yes | lost | Lva |
| pbs-2(mg538) | G93E | Yes | Yes | lost | Lva |
| pbs-2(mg530) | D97N | Yes | ND | lost | Lva |
| pbs-3(mg527) | S180L | Yes | Yes | lost | Lva |
| pbs-4(mg539) | M48K | Yes | No (Emb/Lva) | lost | Lva |
| pbs-5(mg509) | 3'UTR | Yes | Yes | lost | Lva |
| pbs-5(mg502) | promoter* | Yes | Yes | lost* | +* |
| rpt-6(mg513) | I302N, P328S | Yes | Yes | lost | Lva |
| rpt-6(mg512) | E278K | Yes | No (Ste) | lost | Lva |
| rpn-1(mg514) | S519F | Yes | No (Ste) | lost | Lva |
| rpn-1(mg537) | G431E | Yes | No (Ste) | lost | Lva |
| rpn-5(mg534) | T76I | Yes | No (Emb/Lva) | lost | Lva |
| rpn-8(mg587) | G73R | Yes | No (Ste) | lost | Lva |
| rpn-8(mg536) | A88V | Yes | No (Ste) | lost | Lva |
| rpn-9(mg533) | G357STOP | Yes | No (Emb/Lva) | lost | Lva |
| rpn-10(mg525) | G114E | Yes | No (Ste) | lost | Lva |
| rpn-10(mg495) | K130STOP | Yes | No (Ste) | lost | Lva |
| rpn-10(mg531) | Frameshift | Yes | ND | lost | Lva |
| rpn-10(mg529) | Q298STOP | Yes | ND | lost | Lva |
| rpn-11(mg494) | E108K | Yes | No (Ste) | lost | Lva |
-
ND: Not determined
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | E. coli OP50 | CGC | OP50 | |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | E. coli HT115 | CGC | HT115 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | unc-54(e1301) I. | CGC | CB1301 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | dvIs2 | CGC | CL2006 | unc-54::Aβ |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | dvIs37 | CGC | CL2331 | myo-3::gfp::Aβ |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | mgIs72 II | Lehrbach and Ruvkun, 2016 | GR2183 | rpt-3::gfp integrated array |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | pbs-5(mg502) I; mgIs72 II | Lehrbach and Ruvkun, 2016 | GR2184 | proteasome mutant |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | mgIs72 II; skn-1(mg570) IV | Lehrbach and Ruvkun, 2016 | GR2197 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | mgIs72 II; ddi-1(mg571) IV | Lehrbach and Ruvkun, 2016 | GR2211 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | unc-119(ed3) III; mgTi4 | Lehrbach and Ruvkun, 2016 | GR2212 | rpl-28::ha::skn-1a::gfp::tbb-2 |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | unc-119(ed3) III; mgTi5 | Lehrbach and Ruvkun, 2016 | GR2213 | rpl-28::ha::skn-1a::gfp::tbb-2 |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | mgIs72 II; sel-1(mg547) V | Lehrbach and Ruvkun, 2016 | GR2215 | Strain, strain |
| background (C. elegans) | unc-119(ed3) III; skn-1(zu67) IV; mgTi1 | Lehrbach and Ruvkun, 2016 | GR2221 | rpl-28::skn-1a::GFP::tbb-2 rescues skn-1(zu67) |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | png-1(ok1654) I; mgIs72 II | Lehrbach and Ruvkun, 2016 | GR2236 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | skn-1(mg570) IV | Lehrbach and Ruvkun, 2016 | GR2245 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | png-1(ok1654) I | CGC | GR2246 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | png-1(ok1654) I; skn-1(mg570) IV | this study | GR3089 | Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | mgIs77 V | this study | GR3090 | rpl-28::ub(G76V)::gfp::tbb-2, myo-3::mcherry marker. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | unc-119(ed3) III; mgTi15 | this study | GR3091 | rpl-28::skn-1a::GFP::tbb-2. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | unc-119(ed3) III; mgTi17 | this study | GR3092 | rpl-28::HA::skn-1a::GFP::tbb-2. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | skn-1(mg570) IV; mgIs77 V | this study | GR3094 | rpl-28::ub(G76V)::gfp::tbb-2. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | mgIs72 II; pas-1(mg511) V | this study | GR3141 | proteasome mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | rpn-10(mg525) I; mgIs72 II | this study | GR3142 | proteasome mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | mgIs72 II; rpn-1(mg514) IV | this study | GR3143 | proteasome mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | pbs-5(mg509) I; mgIs72 II | this study | GR3144 | proteasome mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | mgIs72 II; rpt-6(mg513) III | this study | GR3145 | proteasome mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | rpn-10(mg495) I; mgIs72 II | this study | GR3146 | proteasome mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | mgIs72 II; rpt-6(mg512) III | this study | GR3147 | proteasome mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | mgIs78 IV | this study | GR3148 | myo-3::H2B::mcherry::SL2::pbs-5[T65A] (pNL47). Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | mgIs72 II; mgIs78 IV | this study | GR3149 | Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | rpn-10(mg529) I; mgIs72 II | this study | GR3150 | proteasome mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | pbs-2(mg530) I; mgIs72 II | this study | GR3151 | proteasome mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | rpn-10(mg531) I; mgIs72 II | this study | GR3152 | proteasome mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | unc-54(e190) I; mgIs72 II | this study | GR3153 | Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | mgIs78 IV; mgIs77 V | this study | GR3154 | myo-3::H2B::mcherry::SL2::pbs-5[T65A] and Ub(G76V)::gfp. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | rpn-11(mg494) mgIs72 II | this study | GR3155 | proteasome mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | unc-54(mg519) I; mgIs72 II | this study | GR3156 | unc-54ts. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | unc-54(mg519) I | this study | GR3157 | unc-54ts. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | mgIs72 II; skn-1 (mg674) mgIs78 IV | this study | GR3158 | mg674 causes G2STOP in SKN-1A. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | unc-54(e1157) I; mgIs72 II | this study | GR3159 | unc-54ts. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | unc-54(e1301) I; mgIs72 II | this study | GR3160 | unc-54ts. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | unc-54(mg528) I; mgIs72 II | this study | GR3161 | unc-54ts. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | unc-54(mg540) I; mgIs72 II | this study | GR3162 | unc-54ts. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | skn-1(mg674) mgIs78 IV | this study | GR3163 | mg674 causes G2STOP in SKN-1A. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | unc-54(e1301) I; mgIs72 II; skn-1(mg570) IV | this study | GR3164 | Reagent requests: see Materials and methods. |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | unc-54(e1301) I; skn-1(mg570) IV | this study | GR3165 | Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | unc-54(mg519) I; mgIs72 II; skn-1(mg570) IV | this study | GR3166 | Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | unc-54(mg519) I; skn-1(mg570) IV | this study | GR3167 | Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | skn-1(mg674) mgIs78/nT1[qIs51] IV; mgIs77/nT1[qIs51] V | this study | GR3168 | skn-1(mg674) mgIs78; mgIs77 animals are very sick, use balancer to maintain. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | unc-54(e1301) I; skn-1 (mg570) IV; mgIs77 V | this study | GR3169 | Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | unc-54(mg519) I; skn-1 (mg570) IV; mgIs77 V | this study | GR3170 | Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | pbs-3(mg527) mgIs72 II | this study | GR3171 | proteasome mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | pbs-2(mg581) I; mgIs72 II | this study | GR3172 | proteasome mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | rpn-9(mg533) mgIs72 II | this study | GR3173 | proteasome mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | rpn-8(mg587) I; mgIs72 II | this study | GR3174 | proteasome mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | rpn-5(mg534) mgIs72 II | this study | GR3175 | proteasome mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | rpn-8(mg536) I; mgIs72 II | this study | GR3176 | proteasome mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | mgIs72 Il; rpn-1(mg537) IV | this study | GR3177 | proteasome mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | pbs-2(mg538) I; mgIs72 II | this study | GR3178 | proteasome mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | pbs-4(mg539) I; mgIs72 II | this study | GR3179 | proteasome mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | mgIs72 II; dvIs2 | this study | GR3180 | Amyloid beta + rpt-3::gfp. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | mgIs72 II; dvIs2; skn-1(mg570) IV | this study | GR3181 | Amyloid beta + rpt-3::gfp in skn-1a mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | skn-1(mg570) IV; mgIs77 V; dvIs2 | this study | GR3182 | unc-54::Aβ+Ub(G76V):: gfp in skn-1a mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | mgIs77 V; dvIs2 | this study | GR3183 | unc-54::Aβ+Ub(G76V)::gfp. Reagent requests: s ee Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | skn-1(mg570) IV; dvIs2 | this study | GR3184 | unc-54::Aβ in skn-1a mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | skn-1(mg570) IV; dvIs37 | this study | GR3185 | myo-3::gfp::Aβ in skn-1a mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | png-1(ok1654) I; dvIs2 | this study | GR3186 | unc-54::Aβ in a png-1 mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | png-1(ok1654) I; skn-1(mg570) IV; dvIs2 | this study | GR3187 | unc-54::Aβ in png-1 skn-1a double mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | mgIs72 II; ddi-1(mg571) IV; dvIs2 | this study | GR3188 | unc-54::Aβ in ddi-1 mutant + rpt-3::gfp. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | png-1(ok1645) I; mgIs72 II; dvIs2 | this study | GR3189 | unc-54::Aβ in png-1 mutant + rpt-3::gfp. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | dvIs2; mgEx813 | this study | GR3190 | skn-1a overexpression (pNL214), array marked by myo-2::mcherry. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | dvIs2; mgEx814 | this study | GR3191 | skn-1a overexpression (pNL214), array marked by myo-2::mcherry. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | dvIs2; mgEx815 | this study | GR3192 | skn-1a overexpression (pNL214), array marked by myo-2::mcherry. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | mgIs72 II; sel-1(mg547) V; dvIs2 | this study | GR3193 | unc-54::Aβ in sel-1 mutant + rpt-3::gfp. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | hsf-1(sy441) I; mgIs72 | this study | GR3291 | rpt-3::gfp, hif-1 mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | unc-119(ed3) III; mgEx831 | this study | GR3292 | rpl-28p::skn-1a[∆DBD]:: gfp marked by myo-2::mcherry and unc-119(+). Reagent requests: s ee Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | unc-54(e1301) I; mgEx831 | this study | GR3293 | rpl-28p::skn-1a[∆DBD]::gfp, unc-54ts mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | unc-54(mg519) I; mgEx831 | this study | GR3294 | rpl-28p::skn-1a[∆DBD]::gfp, unc-54ts mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | hsf-1(sy441) I; mgIs72; skn-1a(mg570) | this study | GR3295 | rpt-3::gfp, hif-1, skn-1a double mutant. Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | skn-1(zu67) IV/nT1 [unc-?(n754) let-?](IV;V) | CGC | EU1 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | wild type | CGC | N2 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent (plasmid) | rpl-28::skn-1a::tbb-2 | Lehrbach and Ruvkun, 2016. | pNL214 | Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Recombinant DNA reagent (plasmid) | myo-3::mcherry::his-58:: SL2::pbs-5[T65A] | this study | pNL47 | Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Recombinant DNA reagent (plasmid) | rpl-28::ub(G76V)::gfp::tbb-2 | this study | pNL121 | Reagent requests: see Materials and methods |
| Chemical compound, drug | Bortezomib | L C Laboratories | Cat#B1408 | |
| Software, algorithm | ImageJ | NIH | https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ | |
| Software, algorithm | Zen | Zeiss | https://www.zeiss.com/microscopy/us/products/microscope-software/zen.html | |
| Software, algorithm | Ape (A plasmid editor) | M Wayne Davis | http://jorgensen.biology.utah.edu/wayned/ape/ | |
| Software, algorithm | Graphpad Prism | Graphpad | https://www.graphpad.com/scientific-software/prism/ |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Lifespan data and statistics.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.44425.017





