The antimicrobial peptide defensin cooperates with tumour necrosis factor to drive tumour cell death in Drosophila
Figures
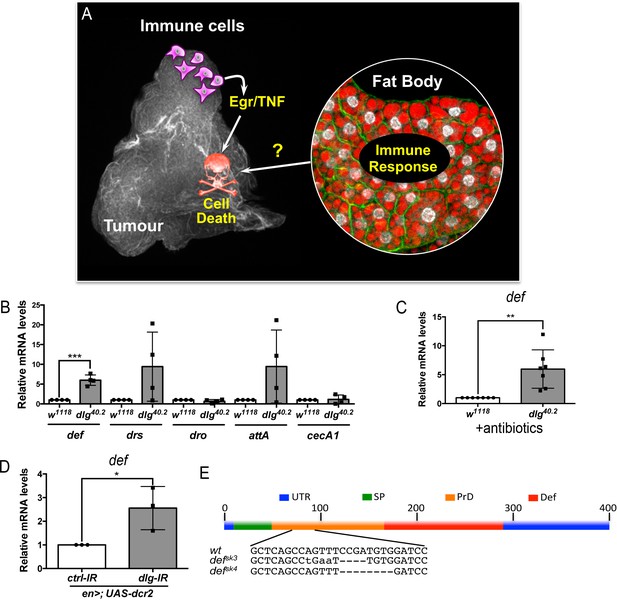
def is induced in dlg mutant tumour bearing animals.
(A) Working model showing the cooperation between haemocyte-derived TNF and the immune response in the fat body in tumour cell death (Parisi et al., 2014). (B) RT-qPCR analyses showing expression of several AMPs in the fat body of dlg40.2 mutant tumour bearing larvae compared to wild-type (w1118) larvae (n = 4). (C) RT-qPCR analysis of def expression in w1118 and dlg40.2 whole larvae reared on antibiotics (n = 7). (D) RT-qPCR analysis showing def expression in larvae expressing a ctrl-IR or a dlg-IR in the posterior part of the wing disc (en>;UAS-dcr2) (n = 3). (E) Schematic representation of the def gene locus showing mutant alleles generated (UTR: Untranslated Regions, SP: Signal Peptide, PrD: Pro-Domain, Def: Mature Defensin). Statistical analysis: B-D, Student t-test, B, ***p=0.0003, C, **p=0.0074, D, *p=0.042.
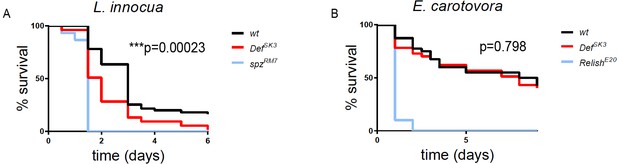
def mediates animal survival to infection by Gram-positive bacteria.
(A) Survival of defsk3 mutant flies (n = 53), upon Gram-positive, Listeria innocua infection, is compared to wild-type (wt) (n = 55) and spatzle (spzM7) (n = 30) (the Toll ligand) mutant flies. (B) Survival of defsk3 mutant flies (n = 37), upon Gram-negative, Erwinia carotovora carotovora infection, is compared to wild-type (wt) (n = 40) and relish (relE20) (n = 10) (an Imd-pathway downstream effector) mutant flies. Statistical analysis: A, B, Log-rank test, A, ***p=0.00023, B, p=0.798.
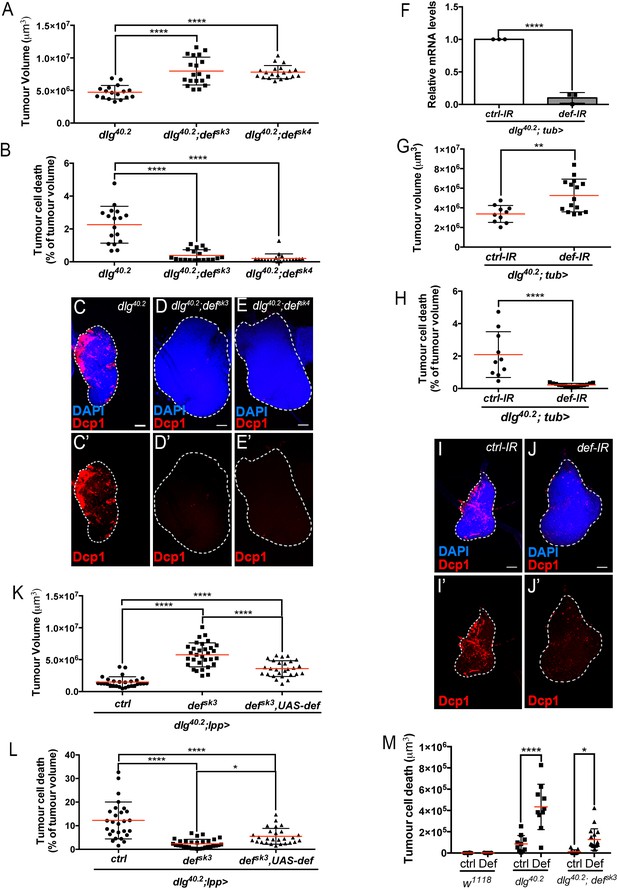
Def restricts tumour growth and promotes tumour cell death.
(A-E’) Quantification of tumour volume (TV) (A) and tumour cell death (TCD) (B) in wing imaginal discs from dlg40.2 (n = 17), dlg40.2;defsk3 (n = 19) and dlg40.2;defsk4 (n = 20) mutant larvae and representative immunofluorescence images of tissues quantified (C–E’). F, RT-qPCR analysis showing def expression upon ubiquitous knockdown (dlg40.2; tub>) (n = 3). G-J’, Quantification of TV (G) and TCD (H) in wing imaginal discs from larvae ubiquitously expressing a control-IR (ctrl-IR: n = 10) or a def-IR (n = 15) and representative immunofluorescence images of tissues quantified (I–J’). K-L, Quantification of TV (K) and TCD (L) in wing imaginal discs from dlg mutant controls (dlg40.2;lpp>: n = 28), dlg;defsk3 mutants controls (dlg40.2;defsk3;lpp>: n = 31) or dlg;defsk3 mutants expressing def in the fat body (dlg40.2;defsk3,UAS-def;lpp>: n = 27). M, Effect of PBS (ctrl) or synthetic Def injection on TCD from wild-type larvae (w1118, ctrl: n = 10, Def: n = 9), dlg40.2 (ctrl: n = 10, Def: n = 10) and dlg40.2;defsk3 (ctrl: n = 11, Def: n = 18) mutant larvae. Tissues were stained with 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, blue) for nuclei visualisation and with anti-cleaved Decapping protein 1 (Dcp1) antibody (red) to detect apoptotic cell death. Scale bars = 50 μm. Statistical analysis: A, B, K, L, One way ANOVA, *p<0.05, ****p<0.0001; F, Student t-test, ****p<0.0001, G-H, Mann-Whitney test, G, **p=0.0054, H, ****p<0.0001; M, Two way ANOVA (only relevant significant statistics are indicated), *p<0.05, ****p<0.0001.
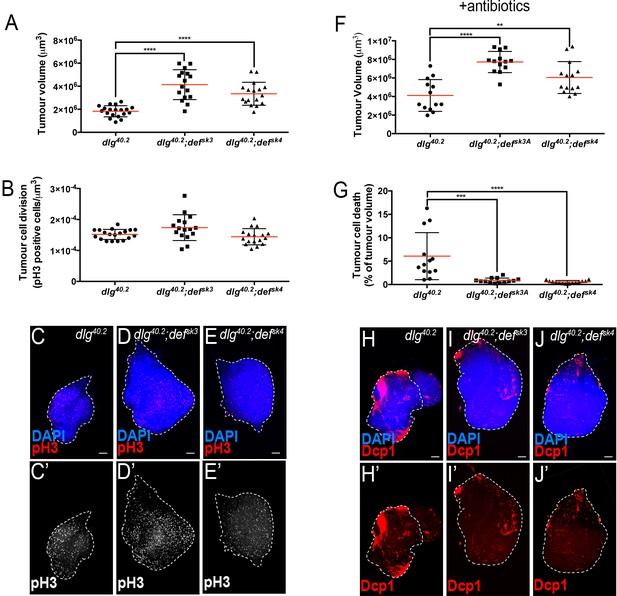
Tumour suppression by Def is independent of infection and tumour cell proliferation.
(A-E’) Quantification of TV (A) and tumour proliferation (B) from dlg40.2 (n = 19), dlg40.2;defsk3 (n = 16) and dlg40.2;defsk4 (n = 17) mutant larvae and representative pictures of the corresponding tumours stained with DAPI (blue) or anti-phosphoHistone H3 (pH3) antibody to determine cell proliferation (red, C-E or white, C’–E’). F-J’, Quantification of TV (F) and TCD (G) from dlg40.2 (n = 13), dlg40.2;defsk3 (n = 13) and dlg40.2;defsk4 (n = 14) mutant larvae reared on antibiotics and representative pictures of the corresponding tumours stained with DAPI (blue) and anti-Dcp1 antibody (red) (H–J’). Scale bars = 50 μm. Statistical analysis: A, B, F, G, One way ANOVA, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
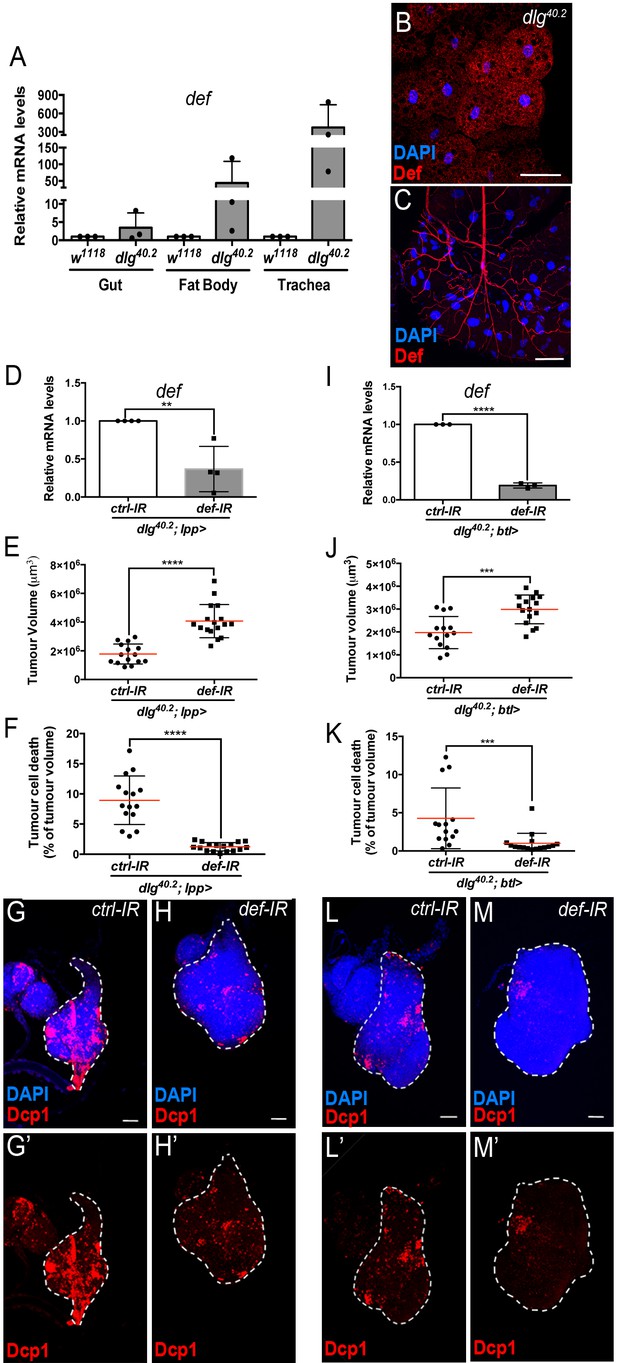
Def from the trachea and the fat body mediates tumour cell death.
(A) RT-qPCR analysis of def expression in gut, fat body and trachea dissected from w1118 or dlg40.2 mutant larvae (n = 3). B-C, Fat body (B) and trachea (C) from dlg40.2 mutant larvae stained with DAPI (blue) and anti-Def antibody (red). D, RT-qPCR analysis of def expression in dlg40.2 mutant larvae (dlg40.2;lpp>) expressing a ctrl-IR or def-IR in the fat body (n = 4). E-H’, Quantification of TV (E) and TCD (F) in wing imaginal discs from dlg40.2 mutant larvae (dlg40.2;lpp>) expressing a ctrl-IR (n = 15) or def-IR (n = 17) in the fat body and representative immunofluorescence images of tissues quantified (G–H’). I, RT-qPCR analysis of def expression in dissected trachea from dlg40.2 mutant larvae (dlg40.2;btl>) expressing a ctrl-IR or def-IR in the trachea (n = 3). J-M’, Quantification of TV (J) and TCD (K) in wing imaginal discs from dlg40.2 mutant larvae (dlg40.2;btl>) expressing a ctrl-IR (n = 14) or def-IR (n = 16) in the trachea and representative immunofluorescence images of tissues quantified (L–M’). Tumours were stained with DAPI (blue) and anti-Dcp1 antibody (red). Scale bars = 50 μm. Statistical analysis: A, D, I, Student t-test, D, **p=0.0054, I, ****p<0.0001; E, F, J, K, Mann-Whitney test, E, F, ****p<0.0001, J, ***p=0.0009, K, ***p=0.0004.
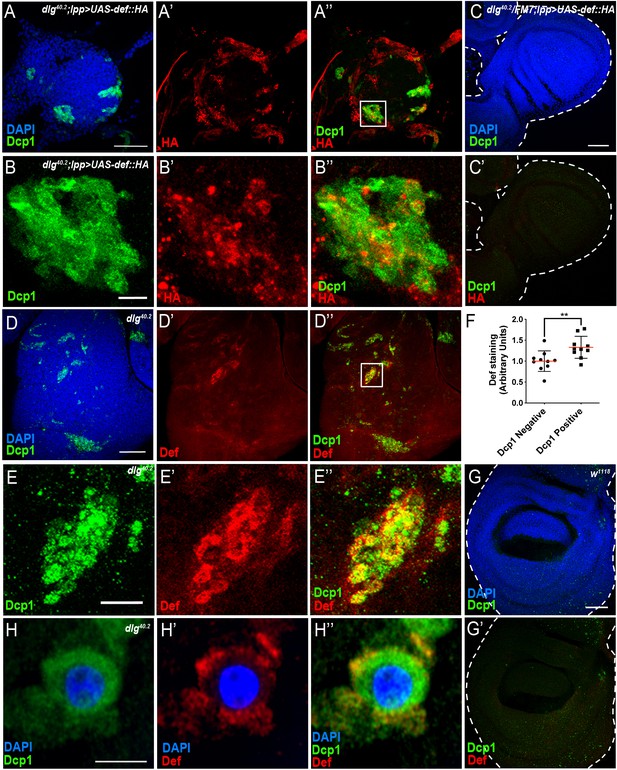
Def produced by immune tissues specifically targets tumour cells.
(A-A’’) DAPI (blue), anti-Dcp1 (green) and anti-HA antibody (red) staining of dlg40.2 mutant tumour from larvae overexpressing a def-HA construct in the fat body and the trachea (dlg40.2;lpp >UAS-def-HA). B-B’’, Enlargement of inset from A’’ (white outline) showing Dcp1 (B), Def-HA (B’) and merged channels (B’’). C-C’, DAPI (blue), anti-Dcp1 (green) and anti-HA antibody (red) staining of dlg40.2 heterozygous wing disc from larvae overexpressing def-HA (dlg40.2/FM7;lpp >UAS-def-HA). D-D’’, dlg40.2 mutant tumour stained with DAPI (blue), anti-Def (red) and anti-Dcp1 (green) antibodies. E-E’’, Enlargement of inset from D’’ (white outline) showing Dcp1 (E), Def (E’) and merged channels (E’’). F, Quantification of colocalization between Def and Dcp1 staining (n = 10). G-G’, wild type (w1118) wing imaginal disc stained with DAPI (blue), anti-Def (red) and anti-Dcp1 (green) antibodies. H-H’’, High-resolution imaging of a single dying tumour cell stained with DAPI (blue), anti-Def (red) and anti-Dcp1 (green) antibodies. A, C, D, G, Scale bars = 50 μm; B, E, Scale bars = 10 μm; H, Scale bar = 2.5 μm. Statistical analysis: F, Student t-test, **p=0.0093.
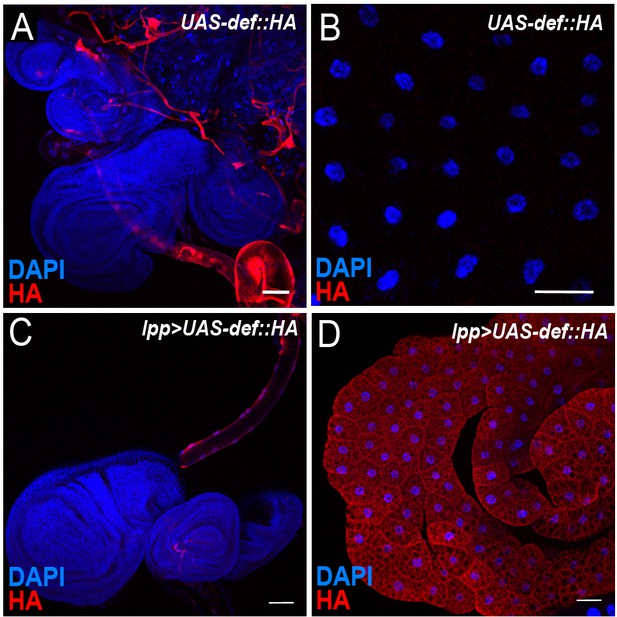
Characterisation of UAS-def-HA expression.
(A-B) DAPI (blue) and anti-HA antibody (red) staining showing basal expression of Def-HA in trachea (A) but not in fat body (B) of UAS-def-HA larvae. C-D, DAPI (blue) and anti-HA antibody (red) staining showing expression of Def-HA in the fat body and the trachea when overexpressed with a fat body specific driver (lpp >UAS-def-HA). Scale bars = 50 μm.
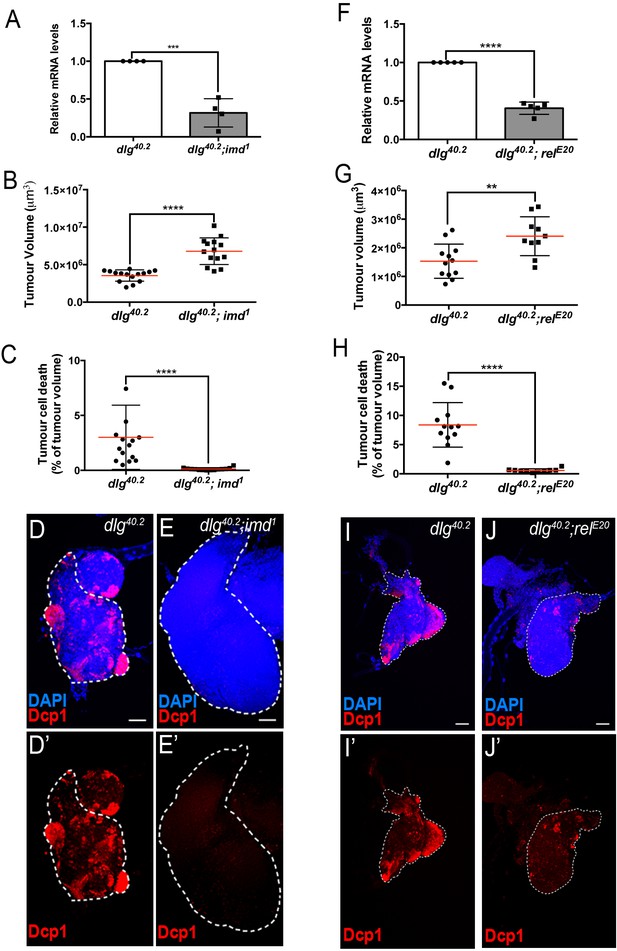
Imd pathway activation is required for def expression and Def-mediated tumour cell death.
(A) RT-qPCR analysis of def expression from dlg40.2 and dlg40.2;imd1 mutant larvae (n = 4). B-E’, Quantification of TV (B) and TCD (C) in wing imaginal discs from dlg40.2 (n = 15) and dlg40.2;imd1 (n = 14) mutants larvae and representative immunofluorescence images of tissues quantified stained with DAPI (blue) and anti-Dcp1 antibody (red) (D–E’). F, RT-qPCR analysis showing def expression in dlg40.2 and dlg40.2; relE20 mutant animals (n = 5). G-J’, Quantification of TV (G) and TCD (H) from dlg40.2 (n = 12) and dlg40.2;relE20 (n = 10) mutant larvae and representative pictures of the corresponding tumours (I–J’). Scale bars = 50 μm. Statistical analysis: A, F, Student t-test, A, ***p<0.0003, F, ****p<0.0001; B, C, G, H, Mann-Whitney test, B, C, H, ****p<0.0001, G, **p=0.009.
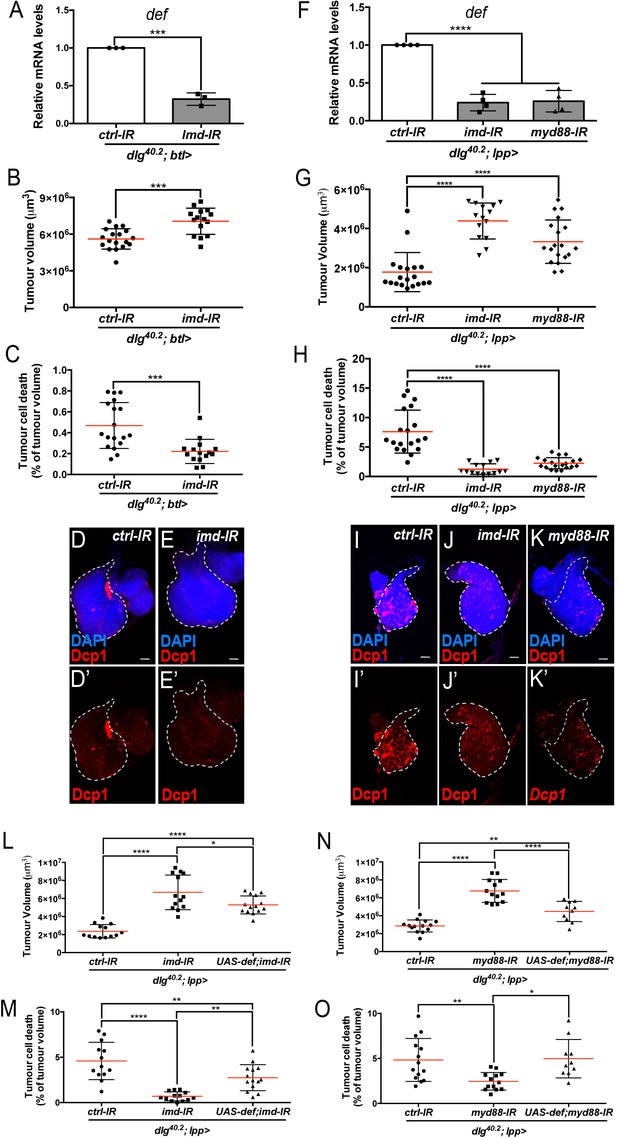
Imd and Toll pathway activation are required in the trachea and the fat body to promote Defensin-dependent tumour cell death.
(A) RT-qPCR analysis of def expression from dlg40.2 mutant larvae (dlg40.2;btl>) expressing a ctrl-IR or imd-IR in the trachea (n = 3). B-E’, Quantification of TV (B) and TCD (C) from dlg40.2 mutant larvae (dlg40.2;btl>) expressing a ctrl-IR (n = 18) or imd-IR (n = 15) in the trachea and representative immunofluorescence images of tissues quantified stained with DAPI (blue) and anti-Dcp1 antibody (red) (D–E’). F, RT-qPCR analysis of def expression from dlg40.2 mutant larvae (dlg40.2;lpp>) expressing a ctrl-IR, an imd-IR or a myd88-IR in the fat body. G-K’, Quantification of TV (G) and TCD (H) from dlg40.2 mutant larvae (dlg40.2;lpp>) expressing a ctrl-IR, an imd-IR or a myd88-IR in the fat body and representative immunofluorescence images of tissues quantified (I–K’). L-O, Quantification of TV (L, N) and TCD (M, O) from dlg40.2 mutant larvae (dlg40.2;lpp>) expressing a ctrl-IR, an imd-IR alone or in combination with a UAS-def in the fat body (L, M) and from dlg40.2 mutant larvae (dlg40.2;lpp>) expressing a ctrl-IR, a myd88-IR alone or in combination with a UAS-def in the fat body (N, O). Scale bars = 50 μm. Statistical analysis: A, Student t-test, A, ***p=0.0001; B, C, Mann-Whitney test, B, ***p=0.0003, C, ***p=0.0002; F, G, H, L-O, One way ANOVA, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001.
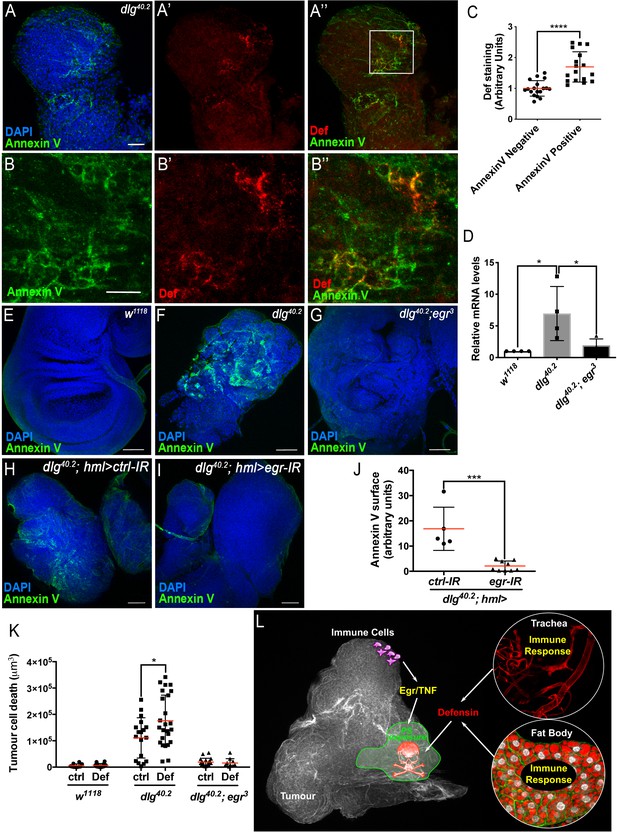
TNF is required for PS exposure and Defensin-driven tumour cell death.
(A-A’’) DAPI (blue), Annexin V (green) and anti-Def (red) staining of dlg40.2 mutant tumours. (B-B’’) Enlargement of inset from A’’ (white outline) showing Annexin V (B), Def (B’) and merged channels (B’’). (C) Quantification of colocalisation between Def and Annexin V staining (n = 18). (D) RT-qPCR analysis showing def expression in wild-type, dlg40.2 or dlg40.2;egr3 mutants. (E- G) Annexin V (green) and DAPI (blue) staining of wing imaginal discs from larvae of the indicated genotypes. (H, I) Annexin V (green) and DAPI (blue) staining of wing imaginal discs from dlg mutant larvae (dlg40.2,hml>) expressing a ctrl-IR (n = 5) or an egr-IR (n = 9) in the haemocytes. (J) Quantification of Annexin V signal on tumours from the corresponding genotypes. (K) Quantification of TCD upon PBS (ctrl) or Def injection in wild-type (w1118, ctrl: n = 10, Def: n = 14), dlg40.2 (ctrl/Def: n = 18) or dlg40.2;egr3 (ctrl: n = 20, Def: n = 13) mutant larvae. (L) A model for Def antitumoural activity. A, E-I, Scale bars = 50 μm; B, Scale bars = 20 μm. Statistical analysis: C, Student t-test, ****p<0.0001; D, One way ANOVA, *p<0.05; J, Mann-Whitney test, ***p=0.001; K, Two way ANOVA (only relevant significant statistics are indicated), *p<0.05.
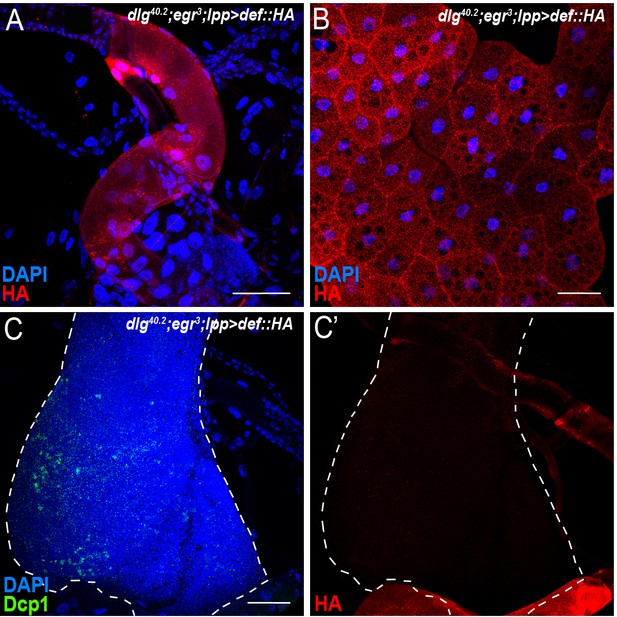
Def-HA does not associate to PS-negative egr-mutant tumours.
(A-B) DAPI (blue) and anti-HA antibody (red) staining showing expression of Def-HA in trachea (A) and fat body (B) of dlg40.2;egr3;lpp-gal4 >UAS def-HA larvae. C-C’, DAPI (blue), anti-Dcp1 (green) and anti-HA antibody (red) staining showing absence of Def-HA on tumours of dlg40.2;egr3;lpp-gal4 >UAS def-HA larvae. Scale bars = 50 μm.
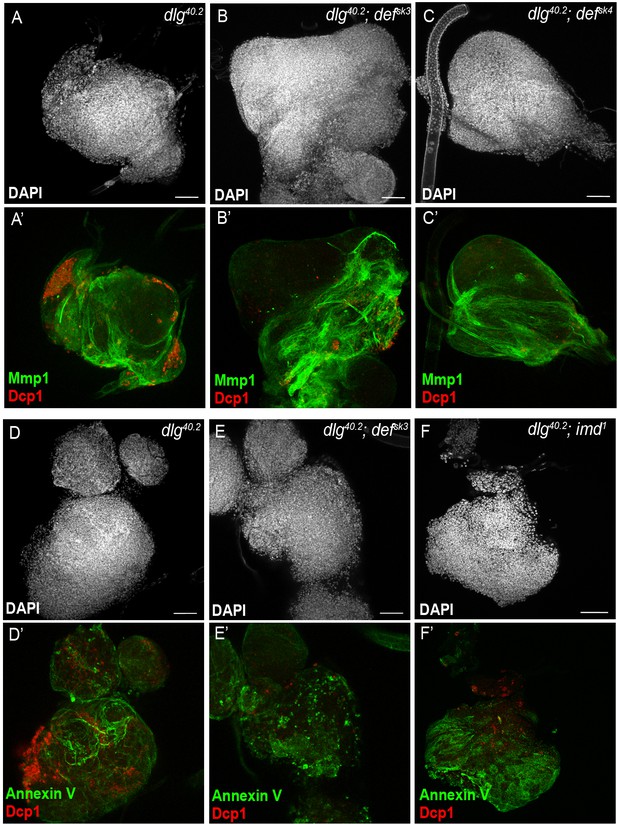
TNF signalling activation does not require functional def.
(A-C’) DAPI (white), anti-Dcp1 (red) and anti-Matrix metalloproteinase 1 (Mmp1, a reporter of JNK pathway activation, green) antibody staining of wing disc from dlg40.2, dlg40.2;defsk3 and dlg40.2;defsk4 mutant larvae. D-F’, DAPI (white), Annexin V (green) and anti-Dcp1 (red) staining of tumours from dlg40.2, dlg40.2;defsk3 and dlg40.2,imd1 mutant larvae. Scale bars = 50 μm.
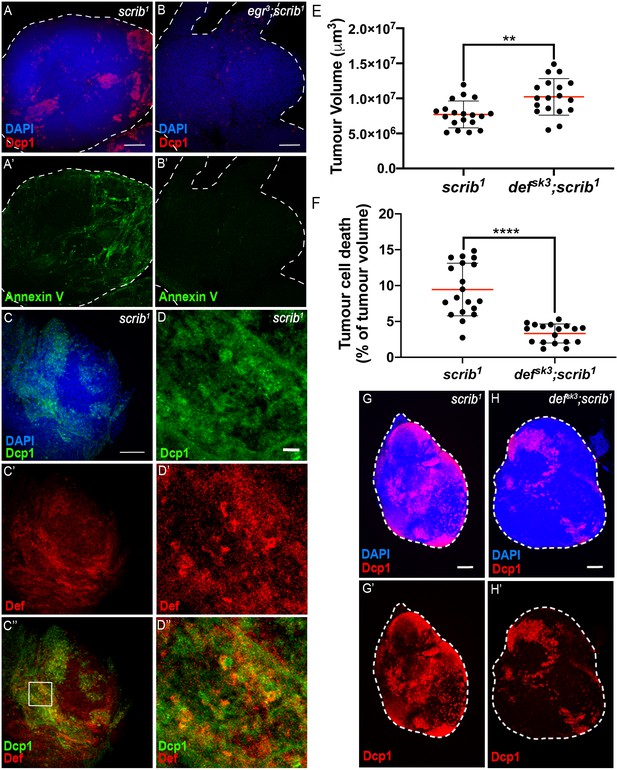
scrib mutant tumours expose PS in a TNF-dependent manner and are sensitive to Def action.
(A-A’) DAPI (blue), anti-Dcp1 (red) and Annexin V (green) staining of scrib1 mutant tumours. (B-B’) DAPI (blue), anti-Dcp1 (red) and Annexin V (green) staining of egr3;scrib1 double mutant tumours. (C-C’’) scrib1 mutant tumour stained with DAPI (blue), anti-Dcp1 (green) and anti-Def (red) antibodies. D-D’’, Enlargement of inset from C’’ (white outline) showing anti-Dcp1 (D), anti-Def (D’) and merged (D’’) channels. E, F, Quantification of tumour volume (E) and tumour cell death (F) in wing imaginal discs from scrib1 (n = 19) and defsk3;scrib1 (n = 18) mutant larvae. G-H’, representative immunofluorescence images of tissues quantified in E, F. A, B, C, G, H, Scale bars = 50 μm; D, Scale bar = 10 μm. Statistical analysis: E, F, Mann-Whitney test, E, **p=0.0015, F, ***p<0.0001.
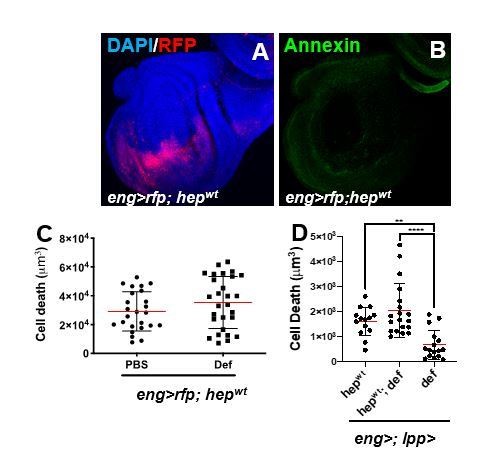
Anti-tumoural immunity in flies: the key players.
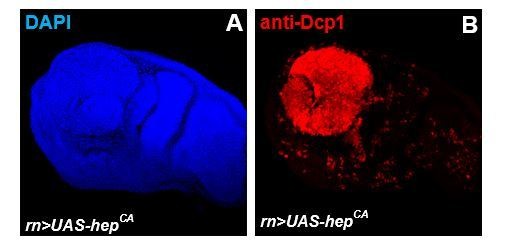
(A, B) Third instar larval imaginal wing disc overexpressing of hepwt using engrailed-gal4, UAS-rfp (eng>rfp; hepwt) (A; red). Discs where stained with AnnexinV to visualize PS exposure (B; green). (C) Assessment of apoptotic cell death in wing discs from eng>rfp; hepwtanimals injected with PBS (control) or recombinant Defensin. (D) Assessment of apoptotic cell death in wing discs from animal following overexpression of hepwt only, def only, or co-expression of both transgenes using combined eng-gal4 and lpp-gal4 drivers.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | w1118 | (Dewey et al., 2004) | BDSC: 3605; RRID:BDSC_3605 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | w1118 iso | (Ferreira et al., 2014) | N/A | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | dlg40.2/FM7 | (Mendoza-Topaz et al., 2008) | Flybase_FBal0240608 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | FRT82B,scrib1/TM6 | (Bilder et al., 2000) | Flybase_FBal0103577 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | egr3 | (Igaki et al., 2002) | Flybase_FBal0147163 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | imd1 | (Leulier et al., 2000) | Flybase_ FBal0045906 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | relE20 | (Leulier et al., 2000) | DGGR: 109927; RRID:DGGR_109927 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | defsk3 | (Hanson et al., 2019) | N/A | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | defsk4 | (Hanson et al., 2019) | N/A | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | btl-gal4,UAS-RFP/CyO | Irene Miguel-Aliaga | N/A | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | lpp-gal4/TM6B | (Brankatschk and Eaton, 2010) | N/A | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | tub-gal4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 5138; RRID:BDSC_5138 | y(1) w[*]; P{w[+mC]=tubP-GAL4}LL7/TM3, Sb(4) Ser(1) |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | hmlΔ-gal4,UAS-gfp | Bruno Lemaitre | N/A | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | en-gal4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 30564; RRID:BDSC_30564 | y1 w*; P{w + mW.hs=en2.4 GAL4}e16E |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-def IR | Vienna Drosophila Resource Centre | VDRC: 102437; RRID:Flybase_FBst0474306 | P{KK111656}VIE-260B |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-imd IR | Vienna Drosophila Resource Centre | VDRC: 101834; RRID:Flybase_FBst0473707 | P{KK109863}VIE-260B |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-myd88 IR | Vienna Drosophila Resource Centre | VDRC: 25402; RRID:Flybase_FBst0455868 | w1118; P{GD9716}v25402 |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-dlg IR | Vienna Drosophila Resource Centre | VDRC: 41136; RRID:Flybase_FBst0463952 | w1118; P{GD4689}v41136/TM3 |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-egr IR | Vienna Drosophila Resource Centre | VDRC: 108814; RRID:Flybase_FBst0480608 | P{KK103432}VIE-260B |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-w IR | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 25785; RRID:BDSC_25785 | y(1) v(1); P{y[+t7.7] v[+t1.8]=TRiP.JF01786}attP2 |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-def | (Tzou et al., 2000) | Flybase_FBal0145092 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-def-3xHA | FlyORF | FlyORF: F002467; RRID:Flybase_FBal0298643 | M{UAS-Def.ORF.3xHA.GW}ZH-86Fb |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-dcr2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 24650; RRID:BDSC_24650 | w[1118]; P{w[+mC]=UAS-Dcr-2.D}2 |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | spzM7 | (Neyen et al., 2014) | N/A | |
| Antibody | Anti-GFP (Chicken polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat# ab13970; RRID:AB_300798 | IF(1:4000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Def (Mouse polyclonal) | Dahua Chen (Ji et al., 2014) | N/A | IF(1:100) |
| Antibody | Anti-HA (Mouse monoclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 2367, RRID:AB_10691311 | IF(1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-dcp1 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 9578, RRID:AB_2721060 | IF(1:100) |
| Antibody | Anti-phospho-Histone H3 (Ser10) (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 9701, RRID:AB_331535 | IF(1:100) |
| Antibody | Anti-phospho-Histone H3 (Ser28) (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 9713, RRID:AB_823532 | IF(1:100) |
| Antibody | Anti-Mmp1 (Mouse clonality unknown) | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | Cat# 3B8D12, RRID:AB_579781 | IF(1:10) |
| Antibody | Anti-Chicken IgY Alexa 488 (Goat polyclonal) | Molecular Probes | Cat# A-11039, RRID:AB_142924 | IF(1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-Mouse IgG Alexa 488 (Goat polyclonal) | Molecular Probes | Cat# A-11029, RRID:AB_138404 | IF(1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-Mouse IgG Alexa 594 (Goat polyclonal) | Molecular Probes | Cat# A-11032, RRID:AB_141672 | IF(1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-Rabbit IgG Alexa 488 (Goat polyclonal) | Molecular Probes | Cat# A-11008, RRID:AB_143165 | IF(1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-Rabbit IgG Alexa 594 (Goat polyclonal) | Thermo Fischer Scientific | Cat# A-11037, RRID:AB_2534095 | IF(1:500) |
| Sequence-based reagent | rpl32-fwd | This paper | PCR primers | AGGCCCAAGATCGTGAAGAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | rpl32-rev | This paper | PCR primers | TGTGCACCAGGAACTTCTTGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | def-fwd | This paper | PCR primers | CTTCGTTCTCGTGGCTATCG |
| Sequence-based reagent | def-rev | This paper | PCR primers | ATCCTCATGCACCAGGACAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | def-PCR-fwd | This paper | PCR primers | TTATTGCAGAAACGGGCTCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | def-PCR-rev | This paper | PCR primers | ATGGTAAGTCGCTAACGCTAATG |
| Sequence-based reagent | def-seq | This paper | Sequencing primers | CGTGTCTTCCTGCACAGAAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | attA-fwd | This paper | PCR primers | ATGCTCGTTTGGATCTGACC |
| Sequence-based reagent | attA-rev | This paper | PCR primers | TCAAAGAGGCACCATGACCAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | cecA1-fwd | This paper | PCR primers | CTCAGACCTCACTGCAATAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | cecA1-rev | This paper | PCR primers | CCAACGCGTTCGATTTTCTT |
| Sequence-based reagent | dro-fwd | This paper | PCR primers | CGTTTTCCTGCTGCTTGCTT |
| Sequence-based reagent | dro-rev | This paper | PCR primers | GGCAGCTTGAGTCAGGTGAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | drs-fwd | This paper | PCR primers | CTCTTCGCTGTCCTGATGCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | drs-rev | This paper | PCR primers | ACAGGTCTCGTTGTCCCAGA |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Drosophila endogenous Defensin | Bulet EIRL | N/A | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Drosophila Synthetic Defensin | Genepep | N/A | ATCDLLSKWNWNHTACAGHCIAKGFKGGYCNDKAVCVCRN |
| Commercial assay or kit | High Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit | Applied Biosystems | Cat# 4368813 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | PerfeCTa SYBR Green FastMix (Low ROX) | Quanta Bio | Cat# 95074–012 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | TRIzol Reagent | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 15596018 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Turbo DNA free Kit | Life Technologies LTD | Cat# AM1907 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | High Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit | Applied Biosystems | Cat# 4368813 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 4′,6-Diamidine-2′-phenylindole dihydrochloride (DAPI) | Sigma | Cat# D9542 | 1 μg/mL |
| Software, algorithm | Fiji | NIH | https://fiji.sc/ | |
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism 6 | GraphPad | RRID:SCR_002798 | |
| Software, algorithm | 7500 Real-Time PCR Software | Applied Biosystems | RRID:SCR_014596 | |
| Software, algorithm | BatchQuantify | (Johansson et al., 2019) | https://github.com/emltwc/2018-Cell-Stem-Cell | |
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism 6 | GraphPad | RRID:SCR_002798 | |
| Software, algorithm | Volocity 3D Image Analysis Software | Perkin Elmer | RRID:SCR_002668 | |
| Software, algorithm | ZEN two lite | Zeiss | RRID:SCR_013672 | |
| Other | RNasine Plus RNase Inhibitor | Promega | Cat# N261 | |
| Other | Vectashield mounting media | Vector Laboratories, Inc. | Cat# H-1000–10 | |
| Other | Annexin V, Alexa Fluor 568 conjugate | Life Technologies LTD | Cat# A13202 | 1:20 |
| Other | Annexin V, Alexa Fluor 488 conjugate | Life Technologies LTD | Cat# A13201 | 1:20 |
| Other | Penicillin-Streptomycin (10,000 U/mL) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 15140122 | Pen: 100 IU/mL Strep: 100 mg/mL |
| Other | PfuUltra II Fusion HS DNA Polymerase | Agilent | Cat# 600670 | |
| Other | AnnexinV binding buffer | Fisher Scientific | Cat# BDB556454 |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45061.016