Molecular organization and dynamics of the fusion protein Gc at the hantavirus surface
Figures
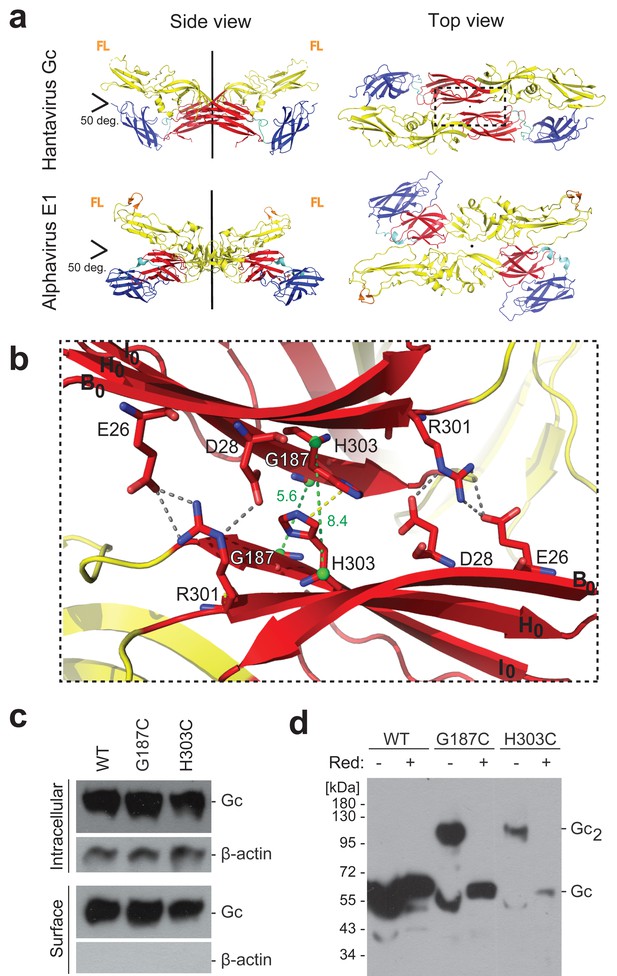
A cysteine residue engineered at the crystallographic Gc dimer interface cross-links spikes on viral particles.
(a) X-ray structure of the crystallographic Hantaan virus Gc dimer (upper panel, PDB: 5LJY, Guardado-Calvo et al., 2016), displayed alongside the crystallographic alphavirus E1 dimer (PDB:2ALA, Roussel et al., 2006) also observed in the contact between spikes on the alphavirus particles (PDB:3J2W, Sun et al., 2013) (lower panel). The two-fold axis is drawn in black. The three domains are labeled; domain I, red; domain II, yellow; domain III, blue. The fusion loops are indicated in orange (FL). Domain III of Hantaan virus Gc appears to have adopted an orientation different than would be expected in the spike, but as it is not part of the dimer interface, it does not affect the contacts made by domain I examined here. (b) Closeup of the crystallographic Gc dimer interface, view slightly titled with respect to the 2-fold axes to show the selected residues for cysteine substitution as well as other residues at the interface, shown in sticks color-coded according to atom type (nitrogen blue, oxygen red, carbon same as the domain color). The Cα of Gly187 and H303 are as green spheres and the Cα-Cα distances across the interface for Gly187-Gly187 and His303-His303 are drawn as green dotted lines. Salt bridges and hydrogen bonds between the carboxyl groups of Glu26 and Asp28 with the guanidinium group of Arg301 are drawn as gray dotted lines. The imidazole rings of His303 interact by π-stacking, indicated with a yellow dotted line. The domain I β-strands B0, H0 and I0 from each protomer are labeled. (c) Expression yields and cell localization of ANDV Gc mutants G187C and H303C representative for two biological replicates. Western blot of fractions obtained from 293FT cells expressing Gn and wild type (WT) or mutant Gc after surface biotinylation using anti-Gc or anti-β-actin antibodies. (d) SDS Page and western blot under reducing and non-reducing conditions of VLPs obtained from supernatants of cells expressing wild type Gn together with wild type, G187C or H303C Gc, representative for four biological replicates. The absence or presence of the reducing agent β-mercaptoethanol is indicated by Red: - and +, respectively.
Conservation of Gc:Gc dimer interface contacts.
Multiple sequence alignment of Gc from seven representative hantaviruses. Strictly conserved and highly similar residues are highlighted in red or brown background, respectively. Each host is noted in accordance to its rodent subfamily as MUR (Murinae), SIG (Sigmodontinae), ARV (Arvicolinae) or as INS (Insectivores) and BAT (Chiroptera). The white arrow displayed above the sequences indicate beta strands with its respective nomenclature, on a background colored according to the domain, as in indicated in Figure 3A. The red stars highlight mutated residues.
The covalent Gc:Gc dimer disulfide bond G187C increases Gn/Gc spike stability.
(a–b) Representative BN-PAGE and western blotting of ANDV wild type (a) and G187C mutant spikes (b). The spikes were extracted from VLPs by Triton X-100 and treated at the indicated temperatures of 20–60°C at neutral pH. The presence of Gn or Gc in each lane was detected by western blot analysis by splitting the transferred gel in two parts and revealing with anti-Gn (left panel) and anti-Gc (right panel) antibodies. As internal control for Gc species migration, Gc wild type homotrimers were examined in each gel by treatment of VLPs at pH 5.5. No signal for Gn was detected when treated at low pH, suggesting that either the mAb may not react with Gn in native gels when forming a more compact tetramer (Rissanen et al., 2017), or that Gn may not enter the native gels. To further estimate the oligomerization species of Gn and Gc (indicated on the left side of the blot), the migration of their monomeric and multimeric forms was compared with a native protein standard (indicated on the right side of the blot). (c) Graph of the temperature-induced Gn/Gc dissociation of detergent solubilized spikes from wild type or G187C mutant VLPs and quantified by densitometry. Averages ± s.d. from three biological replicates are shown. The curves were fitted using a sigmoidal equation (Equation 1) and are indicated as a line.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Original blots and data points for Figure 2c.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46028.006
The inter-spike Gc:Gc dimer interface affect VLP release and hantavirus Gn/Gc spike stability.
a) VLP assembly and release of ANDV Gc mutants including Ala-substitutions, chemically similar mutations and opposed charge substitutions quantified from western blot analysis using anti-Gc antibody of concentrated supernatant (VLP) obtained from 293FT cells expressing Gn and wild type or mutant Gc. Averages ± s.d. representative for two biological replicates are shown relative to VLP wild type (WT) release. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni adjustment for multiple comparisons, p<0.001 (***), p<0.01 (**), p<0.05 (*). b) Graph of the temperature-induced Gn/Gc dissociation of the different Gc mutants compared to wild type quantified by densitometry. Averages ± s.d. from two biological replicates are shown. All dissociation curves were fitted using a sigmoidal equation (Equation 1) and are indicated as a continuous or dotted line.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Data points for graphs of Figure 3a and b.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46028.008
Characterization of the expression yields, trafficking and VLP assembly of ANDV Gc mutants.
Mutants include Ala-substitutions (a, d), chemically similar mutations (b), and opposed charge substitutions (c). Western blot analysis using anti-Gc or anti-β-actin antibodies of different fractions obtained from 293FT cells expressing Gn and wild type or mutant Gc after surface biotinylation. The fractions correspond to the non-biotinylated fraction (intracellular proteins), the biotinylated fraction (surface proteins), or the concentrated supernatant (VLPs). Equal amounts of total proteins in cellular fractions were loaded of in each lane. Anti-β-actin antibody was used only as cytoplasmic protein control to corroborate membrane integrity during manipulation of cells. Shown are representative blots of two biological replicates. Mutants shown in brackets were not further analyzed in this manuscript. (d) To reach equal amounts of properly folded GPC for VLP release, the amount of cell surface accumulation equivalent to wild type GPC was adjusted by the amount of GPC encoding plasmid used for transfection. In the case of the D28A mutant, in panel a) equal amount of plasmid was used for D28A and wild type, while in d) the amount of plasmid encoding D28A was twice as much as plasmid coding for wild type. (e) Truncated expression products of Gc mutants R301A and H303A. SDS PAGE and western blot of Vero E6 cells expressing Gn/Gc wild type construct or having either the Gc R301A or H303A mutation. The Gc expression products were labeled with anti-Gc antibody; the full length Gc product is indicated.
Thermal stability of the Gn/Gc spike complex from Gc:Gc interface mutants.
(a–d) Native western blot of spikes including Gc mutants E26Q (a), D28A (b), R301Q (c) and H303F (d) treated at the indicated temperatures and extracted from mutant VLPs by Triton X-100. To detect the presence of Gn or Gc, each blot was splitted in two parts and was revealed with anti-Gn (left panels) and anti-Gc (right panels) antibodies. The Gn and Gc oligomerization species (indicated on the left side of each blot) were estimated by comparison with their monomeric forms, low pH induced Gc trimer species and a native protein standard (indicated on the right side of the anti-Gc blot). Representative western blots are shown from at least two biological replicates.
The Gc:Gc dimer contacts modulate low pH fusion activation.
(a-b) Fusion activity of cells expressing ANDV wild type Gn/Gc (WT) or wild type Gn/mutant Gc at different pHs. Syncytia formation was induced by lowering the pH to 5.5 or 4.5 and was quantified by counting cells and nuclei using three color fluorescence microscopy. Averages ± s.d. from three biological replicates are shown. In (b) the maximal fusion activity of WT or mutant Gn/Gc was normalized by its setting to 100% in each case. (c) Liposome coflotation assay to visualize acid-induced activation and membrane interaction of WT and mutant VLPs. VLPs were incubated with DPH-labeled liposomes at different pHs at 37°C. Fractions of the step gradient sedimentation were examined for the presence of Gc by western blot and liposomes by fluorescence. Western blots were quantified by densitometry and averages ± s.d. from two (D28A) and three (WT and H303F) biological replicates are shown.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Data points for graphs of Figure 4a, b and c.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46028.013
Acid-induced activation and membrane interaction of WT and mutant VLPs assessed by a VLP-liposome coflotation assay.
VLPs including wt spikes (a) or Gc mutants D28A (b) or H303F (c) were incubated with DPH-labeled liposomes at different pHs at 37°C. Fractions of the step gradient sedimentation were examined for the presence of Gc by western blot and liposomes by fluorescence. Representative western blots are shown from two (D28A) and three biological replicates.
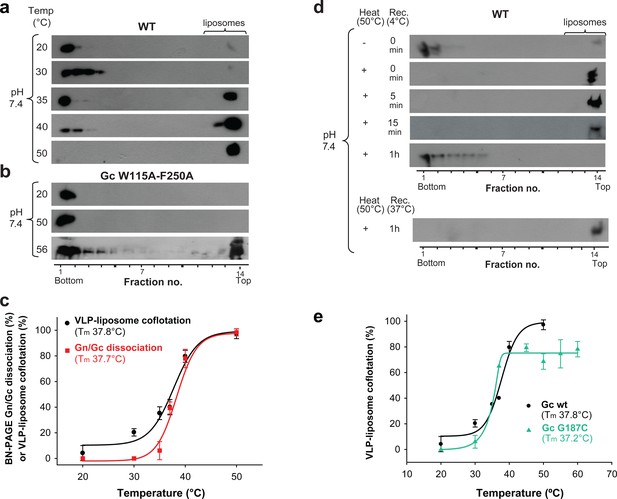
Temperature-induced Gc fusion loop exposure.
(a-b) Liposome coflotation assay to visualize temperature-induced membrane interaction of ANDV wild type (WT) VLPs (a) or ANDV VLPs bearing the Gc fusion loop mutant W115A/F250A (b). VLPs were incubated with DPH-labeled liposomes at pH 7.4 at the indicated temperatures. After flotation in a step gradient, fractions were examined for the presence of liposomes by fluorescence and Gc by western blot. (c) Graph indicating temperature-induced Gn/Gc spike dissociation by BN-PAGE (from Figure 2a) and temperature-induced wild type VLP-liposome coflotation (from Figure 5a) quantified by densitometry. Averages ± s.d. from three biological replicates are shown. Both curves (indicated as a line) were fitted using sigmoidal Equations 1 and 2, respectively, and show a 50% response at approximately ~37°C. Tm indicates either the 50% Gn/Gc dissociation temperature of Triton X-100 solubilized spikes or the temperature at which 50% of the spikes expose the fusion loops allowing for liposome coflotation. (d) Liposome coflotation assay showing the reversibility of the fusion loop exposure. VLPs were incubated at 50°C for 15 min. Then the heat-treated VLPs were allowed to recover at the indicated temperature and time, and next incubated for 5 min with liposomes at RT. Flotation and detection was performed as in (a-b). Rec., recovery. Result representative for three biological replicates. (e) Graph of the temperature-induced flotation of liposome with VLPs bearing the Gc disulfide mutant G187C compared to wild type (WT) quantified by densitometry. Averages ± s.d. from three biological replicates are indicated. The fitting of the curves was performed by using a sigmoidal equation (Equation 2). Tm indicates the temperature at which 50% of the spikes expose the fusion loops inducing membrane interaction.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Data points for graphs of Figure 5c and d.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46028.016
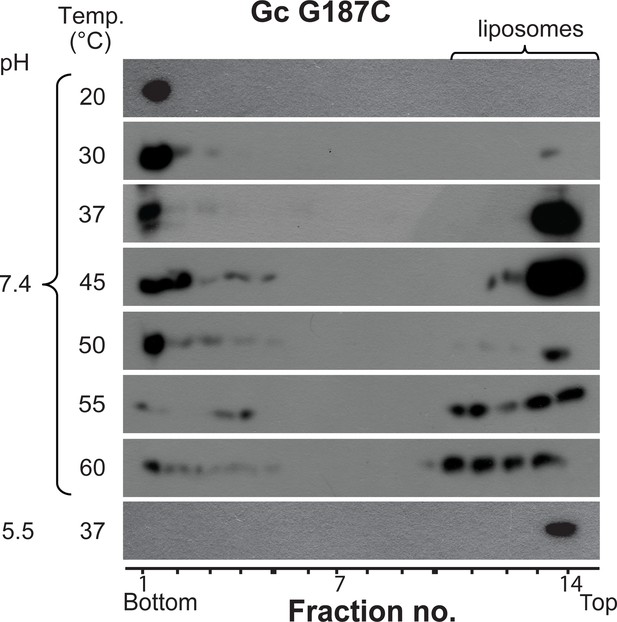
Temperature-induced Gc fusion loop exposure of VLPs bearing the Gc 187C mutant measured by a VLP-liposome coflotation assay.
The mutant VLPs were incubated with DPH-labeled liposomes at pH 7.4 at different temperatures and subsequently subjected to flotation in a step gradient. The different fractions were examined for the presence of Gc by western blot and liposomes by fluorescence. Representative experiment of three biological replicates.
The open spike conformation does not induce viral infection and membrane fusion.
(a-b) Infectivity of ANDV after temperature treatment and recovery at 37°C (a) or 4°C (b) during adsorption to cells for 1 h. Infection was quantified by flow cytometry 16 h later using anti-ANDV nucleoprotein antibody. Averages ± standard derivation from three biological replicates; ANDV treated at 20˚C versus temperature-treated ANDV were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni adjustment for multiple comparisons, p<0.001 (***), p<0.01 (**), p<0.05 (*) and non-significant (ns). (c-e) Lipid mixing of R18-labeled Andes VLPs (c), Hantaan virus VLPs (d) or Sin Nombre virus VLPs (e) with liposomes at pH 5.5. Before the VLPs were incubated with liposomes, they were either untreated, or incubated for 15 min at 50˚C. Alternatively, the VLPs treated at 50˚C were allowed to recover for 1 h at 4˚C, before being subject to the lipid mixing assay. ‘Rec’ indicates recovery. R18 dequenching was continuously measured at 37°C and constant stirring. (f) Effect of heat-treatment of VLPs on acid-induced Gc trimerization. VLPs were either untreated, or incubated for 15 min at 50˚C. Subsequently, they were incubated for 30 min at 37°C at the indicated pH. The Gc multimerization species were separated by sucrose gradient sedimentation and the fractions subjected to western blot using anti-Gc antibody. A molecular standard was used to estimate their molecular mass. Results of (c) to (f) are representative for three biological replicates.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Data points for graphs and statistics of Figure 6a–e.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46028.018
Hantavirus Gn/Gc spike dynamics and Gc conformational changes.
Diagrammatic representation of ‘breathing’ spikes. (a) The Gn ectodomain is represented in gray and Gc in colors: red for domain I; yellow domain II; blue domain III; stem and transmembrane (TM) segment magenta. The Gc fusion loops are labeled FL. Gn-masked Gc FLs are in orange, while the exposed FLs are highlighted in red. (b-d) Top view of two (Gn/Gc)4 hetero-octameric spikes on the viral surface. The spike 4-fold symmetry axis and the 2-fold axis relating the spikes are perpendicular to the plane of the Figure (radial in the particle). For clarity, only the Gn ectodomain is represented, and in the top views the Gc stem and TM segments are not drawn either. At the Tm of 37°C (d), the Andes virus spikes are in equilibrium between closed (b) and open (c) forms, with Gc exposing the fusion loops in the latter. At lower temperatures, the equilibrium is shifted towards the closed conformation (b) and at higher temperatures toward the open conformation (c). The latter conformation is unstable, and leads to aggregates and inactivation at even higher temperatures (e). A side view closeup of two Gn/Gc heterodimers from the two spikes and related by Gc contacts at the inter-spike 2-fold symmetry axis is shown at the center, in between panels b) and c), corresponding to the area marked by dotted rectangles in the tops views. (f) Side view of a Gc homotrimer in the post-fusion conformation, bound to a fused membrane resulting from the low-pH triggered fusogenic conformational change of Gc. (g) Diagram represents an open spike interacting with membranes at neutral pH. Incubation at acidic pH in this conformation does not result in productive fusion, and no Gc homotrimer is formed.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Add. inform. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Andes virus) | Andes virus isolate CHI-7913 | Galeno et al., 2002 | ||
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | 293FT | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat.:R700-07; RRID:CVCL_6911 | |
| Cell line (Cercopithecus aethiops) | Vero 76 (Vero E6) | American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) | CRL 1587; RRID:CVCL_0603 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pI.18/GPC from ANDV | Cifuentes-Muñoz et al., 2010 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pWRG/PUU-M(s2) | Hooper et al., 2006 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pcDNA/Sin Nombre virus-GP | Kleinfelter et al., 2015 | ||
| Biological sample | L-α-phosphatidylcholine (egg, chicken) | Avanti Polar Lipids | Cat.:840051C | |
| Biological sample | L-α-phosphatidyl-ethanolamine (egg, chicken) | Avanti Polar Lipids | Cat.:840021C | |
| Biological sample | Sphingomyelin (Brain, Porcine) | Avanti Polar Lipids | Cat.:860062C | |
| Biological sample | Cholesterol (ovine wool) | Avanti Polar Lipids | Cat.:700000P | |
| Biological sample | Gel Filtration Standard | Biorad | Cat.:1511901 | |
| Biological sample | NativeMark Unstained Protein Standard | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat.:LC0725 | |
| Biological sample | PageRuler Prestained Protein Ladder | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat.:26616 | |
| Antibody (monoclonal) | Mouse anti-ANDV nucleoprotein clone 7B3/F6 | Tischler et al., 2008 | 1:2000 dilution | |
| Antibody (monoclonal) | Mouse anti-Gc clone 2H4/F6 | Godoy et al., 2009 | 1:2500 dilution | |
| Antibody (monoclonal) | Mouse anti-Gn clone 6B9/F5 | Cifuentes-Muñoz et al., 2010 | 1:2500 dilution | |
| Antibody (monoclonal) | Mouse anti-β-actin | Sigma | Cat:A2228; RRID:AB_476697 | 1:2500 dilution |
| Antibody (oligoclonal) | Goat anti-mouse immunoglobulin Alexa 555 conjugate | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat:A28180; RRID:AB_2536164 | 1:500 dilution |
| Antibody (polyclonal) | Goat anti-mouse IgG (H + L) horseradish peroxidase conjugate | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat:31430; RRID:AB_228307 | 1:5000 dilution |
| Antibody (oligoclonal) | Goat anti-mouse IgG (H + L) Alexa555 conjugate | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat:A28175; RRID:AB_2536161 | 1:500 dilution |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Mutant constructs of pI.18/GPC | This paper, produced by GenScript, Piscataway, NJ. | ||
| Commercial assay or kit | Cell surface protein isolation kit | Pierce | Cat:89881 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | 1,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-hexatriene (DPH) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat.:D208000 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Octadecyl Rhodamine B Chloride (R18) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat.:O246 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | 5-chloromethyl-fluorescein diacetate (Cell Tracker green CMFDA) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat.:C7025 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Lipofectamine 2000 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat.:11668019 | |
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism, version 6, and SPSS software (SPSS, Inc) | GraphPad Software | ||
| Software, algorithm | SigmaPlot 12.0 | Systat Software | ||
| Other (Hantaan virus) | Gc ectodomain structure from Hantaan virus | Guardado-Calvo et al., 2016 | PDB: 5LJY | |
| Other (Semliki Forest virus) | E1 ectodomain structure from Semliki Forest virus | Roussel et al., 2006 | PDB: 2ALA |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46028.020





