Two mechanisms regulate directional cell growth in Arabidopsis lateral roots
Figures
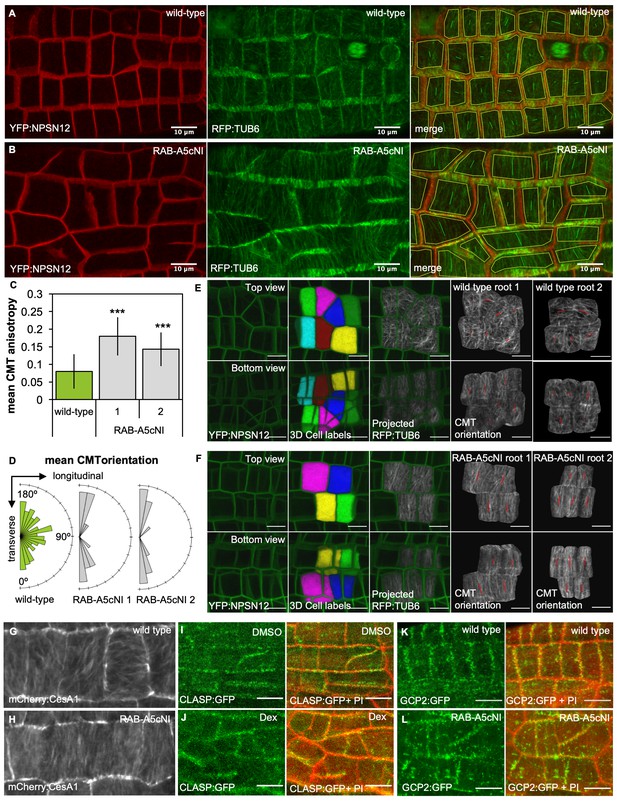
Inhibition of RAB-A5c function caused increased anisotropy of the CMT array in meristematic cells.
(A,B) Maximum intensity projections of confocal stacks of lateral roots co-expressing YFP:NPSN12 (top) and RFP:TUB6 (middle) either in wild-type (A) or in a RPS5a > Dex > RAB-A5c[N125I] line (B) three days after seedlings were transferred to agar plates containing 20 µM Dex. Bottom image shows merge of both channels as well as manually drawn cell outlines (yellow) and vectors indicating mean orientation and degree of anisotropy of the CMT array in each cell as measured with FibrilTool (Boudaoud et al., 2014). (C) Plot showing anisotropy of CMTs in meristematic cells from lateral roots like those shown in (A) for wild-type (n = 114 cells) and RPS5a > Dex > RAB-A5c[N125I] line 1 (n = 43 cells) and line 2 (n = 41 cells). Note 0 corresponds to a fully isotropic array, one to a completely parallel (anisotropic) array. Mean CMT array anisotropy was significantly increased in the presence of RAB-A5c[N125I] (Welch’s t-test: p<0.001 (***)). Error bars are SD. (D) Rose diagrams showing mean orientation of the CMT array in cells used in (C) relative to the longitudinal and transverse axes of the lateral root. (E,F) CMT orientation at inner vs. outer periclinal cell walls in wild-type (E) and RPS5a > Dex > RAB-A5c[N125I] (F) roots. Epidermal meristematic cells expressing YFP:NPSN12 were segmented in 3D using MorphoGraphX (Barbier de Reuille et al., 2015), co-expressed RFP:TUB6 was projected onto the 3D cell mesh, and mean CMT orientation at inner and outer periclinal faces was quantified using with FibrilTool (Boudaoud et al., 2014). Seedlings were imaged 24 hr after transfer to agar plates containing 20 µm Dex. (G,H) Average time projections of maximum intensity projections of confocal stacks of lateral roots expressing mCherry:CESA1 in a wild-type (G) or RPS5a > Dex > RAB-A5c[N125I] background (H). Seedlings were imaged 24 hr after transfer to agar plates containing 20 µm Dex. Stacks were acquired in 10 s intervals, each time average projection is based on 60 stacks (corresponding to 10 min total imaging time). (I,J) Maximum intensity projections of confocal stacks expressing CLASP:GFP in the RPS5a > Dex > RAB-A5c[N125I] background showing lateral roots 3 days after transfer to agar plates containing 0.1% DMSO (I) or 20 µM Dex (J). Cell walls were stained with Propidium Iodide (PI). (K,L) Maximum intensity projections of confocal stacks expressing GCP2:3xGFP in a wild-type (K) and RPS5a > Dex > RAB-A5c[N125I] (L) background showing lateral roots 3 days after transfer to agar plates containing 20 µM Dex. Scale bars 10 µm. Cell walls were stained with Propidium Iodide (PI). All scale bars 10 µm.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Quantification of CMT anisotropy and mean orientation in the absence and presence of RAB-A5c[N125I].
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.47988.008
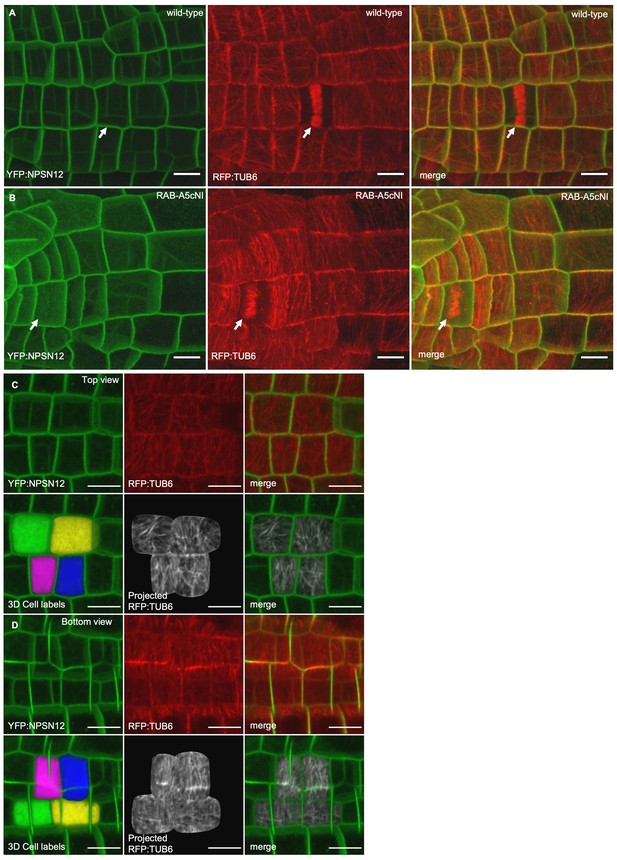
CMTs in the absence and presence of RAB-A5cNI.
(A,B) Confocal stacks of lateral roots co-expressing YFP:NPSN12 and RFP:TUB6 either in wild-type (A) or in a RPS5a > Dex > RAB-A5c[N125I] line (B) three days after seedlings were transferred to agar plates containing 20 µM Dex. Note the phragmoplasts in dividing cells (arrows). (C,D) Visualising microtubule orientation at inner versus outer periclinal cell walls using MorphoGraphX (as shown in Figure 1E,F). Epidermal meristematic cells expressing YFP:NPSN12 were segmented in 3D and co-expressed RFP:TUB6 was projected onto the 3D cell mesh to visualise CMT orientation at the outer (C) and inner (D) periclinal cell face. All scale bars 10 µm.
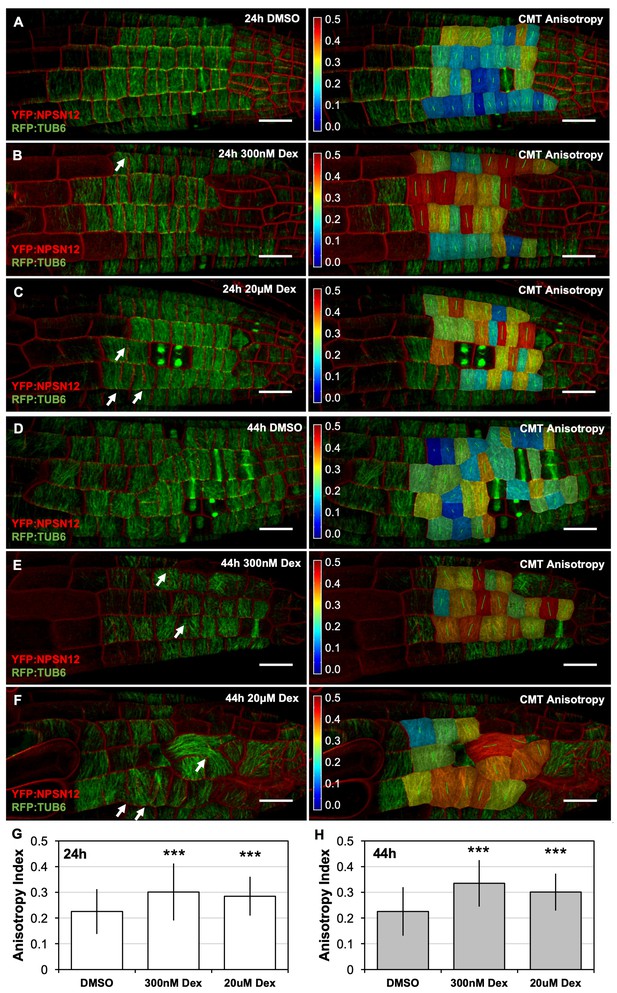
CMT rearrangement occurs during early stages of RAB-A5c[N125I] induction.
(A–F) Confocal stacks of seedlings expressing YFP:NPSN12 (red), RFP:TUB6 (green), and the Dex-inducible RAB-A5c[N125I]. Images were acquired 24 hr (A–C) and 44 hr (D–F) after seedlings were transferred to agar plates containing 0.1% DMSO (A,D), 300 nM Dex (B,E), or 20 µM Dex (C,F). Left: confocal stack as snap shots from MorphoGraphX, right: the same confocal stack with a heat map and vector (green) overlay displaying CMTanisotropy quantified using the fibril orientation plugin in MorphoGraphX (0 corresponds to a fully isotropic array, one to a completely parallel (anisotropic) array). Note the incomplete cell divisions (arrows). Scale bars 20 µm. (G,H) Mean anisotropy of cortical microtubules in meristematic cells from lateral roots shown in (A–C) (G) and (D–F) (H). n ≥ 88 cells (G) and n ≥ 53 cells (H). Anisotropy is significantly increased in the presence of RAB-A5c[N125I] (two-way ANOVA and post hoc Tukey’s test: p<0.001 (***)).
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Quantification of CMT anisotropy in epidermal lateral root cells during early stages of RAB-A5c[N125I] induction.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.47988.006
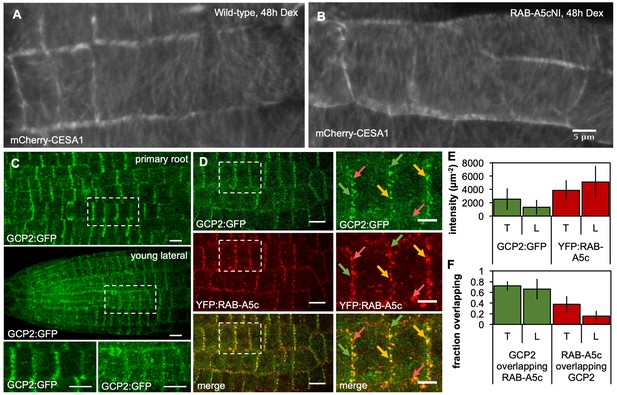
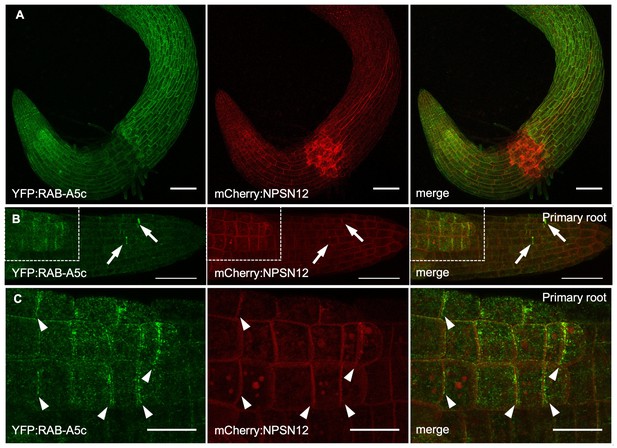
GCP2 and RAB-A5c localisation in lateral roots.
(A,B) Average time projections of maximum intensity projections of confocal stacks of lateral roots expressing mCherry:CESA1 in a wild-type (A) or RPS5a > Dex > RAB-A5c[N125I] background (B). Seedlings were imaged 48 hr after transfer to agar plates containing 20 µM Dex. Stacks were acquired in 10 s intervals, each time average projection is based on 60 stacks (corresponding to 10 min total imaging time). Scale bar 5 µm. (C) Maximum intensity projections of confocal stacks of a primary root (top and bottom left insert) and a lateral root (middle and bottom right insert) expressing GCP2:3xGFP (Nakamura et al., 2010). Scale bars 10 µm. (D) Maximum intensity projection of a confocal stack of a lateral root co-expressing GCP2:3xGFP (top) and YFP:RAB-A5c (middle). Scale bars 10 µm and 5 µm (insets). (E,F) Plots showing mean intensity and reciprocal colocalisation of GCP2:3xGFP and YFP:RAB-A5c at transverse and longitudinal edges (n ≥ 23, edge width 2 µm). Error bars are SD.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 3—source data 1
Quantification of colocalisation between YFP:RAB-A5c and GCP2:GFP at cell edges.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.47988.012
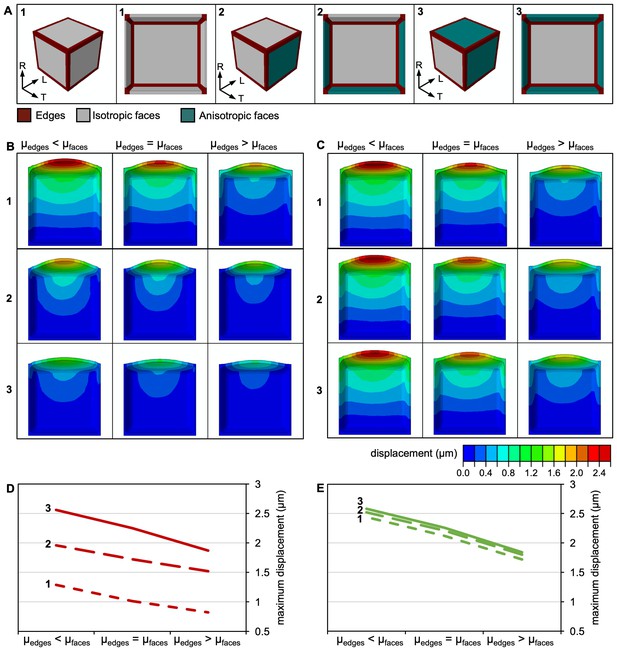
A 3D FE model of a meristematic root cell.
(A) Morphology of the uninflated model from the outside (left) and in section (right) of a cell with isotropic CMFs at all faces (left, 1), isotropic CMFs at transverse anticlinal and the outer periclinal face, and anisotropic CMFs at longitudinal anticlinal and the inner periclinal face (middle, 2), and isotropic CMFs at transverse anticlinal, and anisotropic CMFs at longitudinal anticlinal and periclinal faces (right, 3). Edges are colour-coded in red, isotropic faces in grey, and anisotropic faces in teal. R: radial, L: longitudinal, T: transverse. (B,C) Effect of selective increase or reduction by factor 10 of shear moduli shear moduli , , and at cell edges (µedges) compared to shear moduli at faces (µfaces) on cell morphology for cells in which CMFs were oriented as described in 1,2, and 3 in (A). Cells are colour coded for displacement. (B) idealised cases with FA of 0 (fully isotropic) and 1 (fully anisotropic); (C) cases with FA corresponding to experimentally determined CMT orientation, with FA = 0.08 corresponding to the isotropic and FA = 0.2 corresponding to the anisotropic case. At faces, = 10 GPa, = 18 MPa, = 1.2 GPa, = 18 MPa and = 0.5 in all cases. (D,E) Plots showing maximum displacement of cell models as those shown in (B,C).
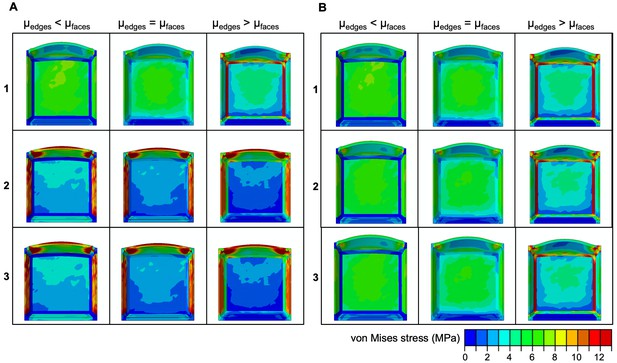
Stress distribution in in silico meristematic cells.
(A,B) Effect of selective increase or reduction of the shear moduli at cell edges (µedges) compared to shear moduli at faces (µfaces) on stress distribution for simulations shown in Figure 2B,C.
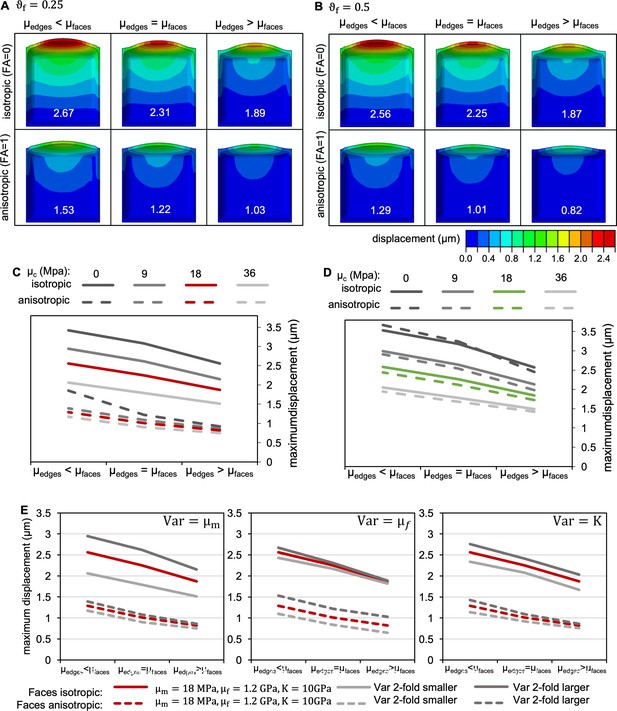
Effect of varying model parameters.
(A,B) Effect of variation in fibre fraction on cell morphology when shear moduli at cell edges (µedges) were selectively increased or decreased compared to shear moduli at faces (µfaces) for cells in which CMFs at all faces were oriented isotropically (top), and cells in which CMFs at longitudinal anticlinal and periclinal faces were anisotropic in transverse orientation (bottom). Cells are colour coded for displacement, maximum displacement for each simulation is displayed in white for each cell. was either 0.25 (A) or 0.5 (B); at faces, = 10 GPa, = 18 MPa, = 1.2 GPa, = 18 MPa in all cases. (C,D) Effect of variations in the cross-linking shear modulus . (C) idealised cases with FA of 0 (fully isotropic) and 1 (fully anisotropic) as shown in (B); (D) cases with FA corresponding to experimentally determined CMT orientation, with FA = 0.08 corresponding to the isotropic and FA = 0.2 corresponding to the anisotropic case. At faces, = 10 GPa, = 18 MPa, = 1.2 GPa, and = 0.5 in all cases. (E) Effect of variations in , , and for idealised cases with FA of 0 (fully isotropic) and 1 (fully anisotropic) as shown in (B).
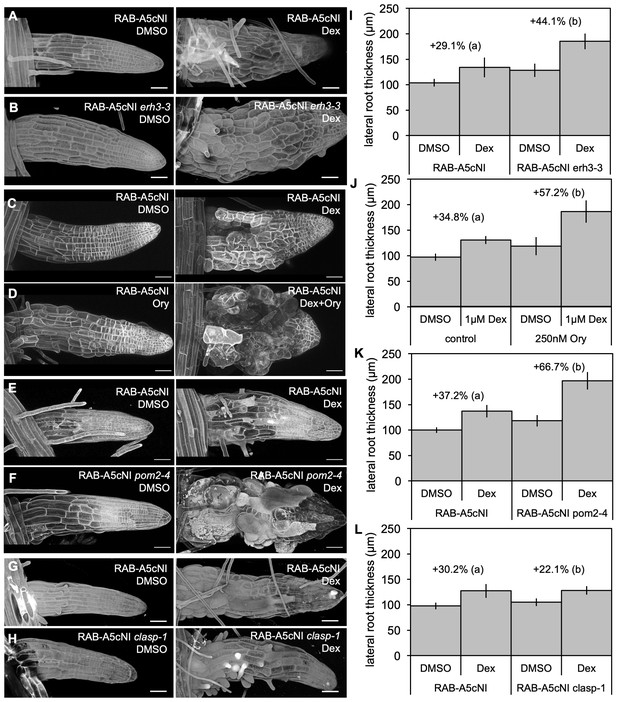
Phenotypic interactions between microtubule mutants and RAB-A5c[N125I].
(A–H) Confocal stacks of lateral roots expressing RPS5a > Dex > RAB-A5c[N125I] in wild-type (A,C,D,E,G), erh3-3 (B), pom2-4 (F), or clasp-1 (H) backgrounds; 3 days after transfer to 0.1% DMSO (left) or 1 µM Dex (right), in (D), plates additionally contained 250 nM Ory. Cell walls were stained with Propidium Iodide (A,B,E–H), or cell outlines were visualised using the plasma membrane marker YFP:NPSN12 (C,D). Images are snapshots from MorphoGraphX or maximum intensity projetions of confocal stacks. Scale bars 50 µm. (I–L) Mean diameter of lateral roots such as those shown in (A–H) (n ≥ 21). Difference in diameter (%) between DMSO and 1 µM Dex treatments for each genotype noted above respective columns. Two-way ANOVA and post hoc Tukey’s test: same letter indicates no significant difference in relative diameter increase (p≥0.05), different letters indicate significant difference (p<0.05).
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Quantification of lateral root thickness in microtubule mutants in the absence or prasence of RAB-A5c[N125I].
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.47988.016
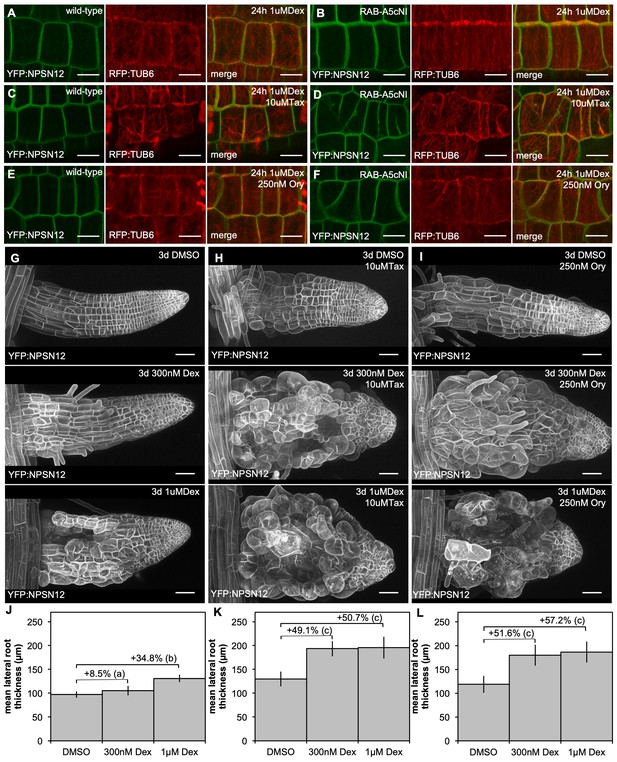
Synergistic effect of microtubule inhibitors and RAB-A5c[N125I] expression on lateral root morphology.
(A,B) Maximum intensity projections of confocal stacks of lateral root meristematic cells expressing YFP:NPSN12 (green) and RFP:TUB6 (red) in a wild-type (A,C,E) and RPS5a > Dex > RAB-A5c[N125I] (B,D,F) background after 24 hr induction with Dex in the absence (A,B) or presence of taxol (C,D) or oryzalin (E,F). Scale bars 5 µm. (C,H,I) Maximum intensity projections of confocal stacks from lateral roots expressing YFP:NPSN12 in a RPS5a > Dex > RAB-A5c[N125I] background grown for 3d in in the absence (G) or presence of taxol (H) or oryzalin (I) and the presence of subsaturating (middle) or saturating (bottom) concentrations of Dex. Scale bars 50 µm. (J–L) Mean diameter of lateral roots as those shown in (G–I) (n ≥ 21). Differences in diameter (%) between treatments noted above respective columns. Two-way ANOVA and post hoc Tukey’s test: same letter indicates no significant difference in relative diameter increase (p≥0.05), different letters indicate significant difference (p<0.01).
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Quantification of lateral root thickness in response to treatment with oryzalin and taxol in the absence or presence of RAB-A5c[N125I].
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.47988.015
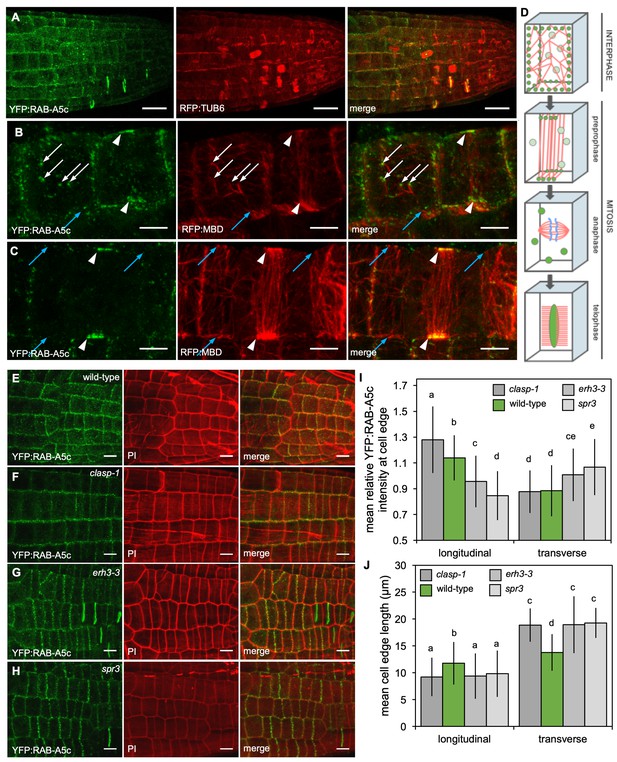
YFP:RAB-A5c localisation and CMT organisation.
(A) Maximum intensity projections of 3D confocal stacks from lateral roots expressing YFP:RAB-A5c (left) and RFP:TUB6 (middle). Scale bar 20 µm. (B,C) Maximum intensity projections of 3D confocal stacks from lateral roots expressing YFP:RAB-A5c (left) and RFP:MBD (middle). Scale bars 5 µm. White arrows indicate YFP:RAB-A5c compartments at cell faces co-localising with RFP:MBD, blue arrows indicate CMTs at cell edges not labelled with YFP:RAB-A5c, white arrowheads indicate preprophase bands. (D) Schematic summary of RAB-A5c localisation in relation to microtubule localisation at different stages of the cell cycle based on images such as those shown in (A–C) and S6. (E–H) Maximum intensity projections of confocal stacks of lateral roots expressing YFP:RAB-A5c either in wild-type (E), clasp-1 (F), erh3-3 (G), and spr3 (H) backgrounds. Cell walls were stained with propidium iodide (PI). Scale bars 10 µm. (I,J) Plots showing relative enrichment of YFP:RAB-A5c intensity at an edge normalised against mean edge intensity in the respective cell (I) and mean transverse and longitudinal edge length in those cells (J) for lateral roots like those shown in (E–H). (n ≥ 103 cells for each genotype; two-way ANOVA and post hoc Tukey’s test: same letter indicates no significant difference (p≥0.05), different letters indicate significant difference (p<0.01).
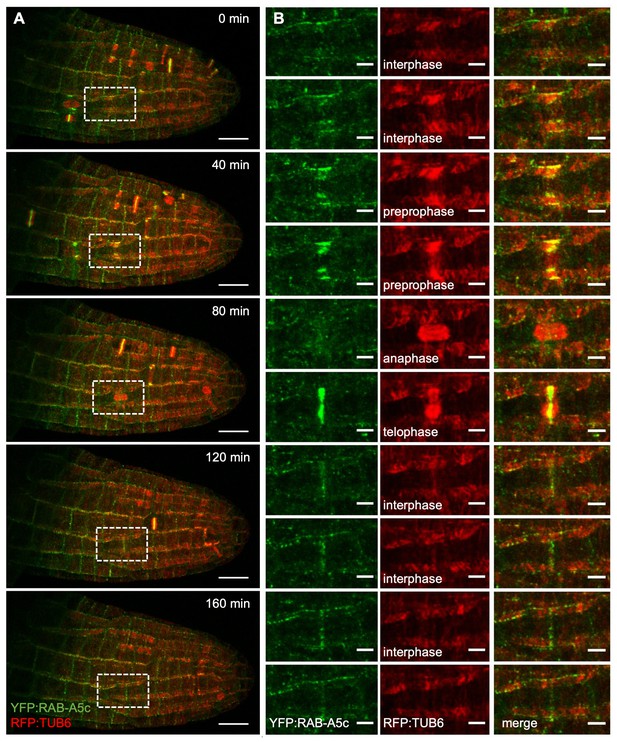
YFP:RAB-A5c and RFP:TUB6 dynamics during lateral root development.
(A) Maximum intensity projections of a 4D confocal stack from a lateral root expressing YFP:RAB-A5c (green) and RFP:TUB6 (red) at consecutive 40 min time intervals. (B) Close-up of the box shown in (A), as well as intermediate time-points (20 min, 60 min, 100 min, 140 min) following one cell’s progression through the cell cycle. Scale bars 20 µm (A) and 5 µm (B).
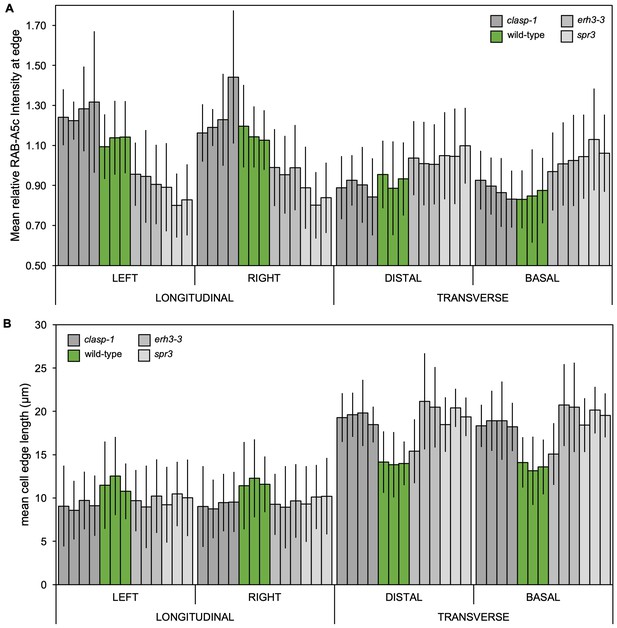
YFP:RAB-A5c localisation in microtubule mutants.
(A,B) Plots as those shown in Figure 4 showing relative enrichment of YFP:RAB-A5c intensity at an edge normalised against mean edge intensity in the respective cell (Figure 4I) and mean transverse and longitudinal edge length in those cells (Figure 4J). Plots differentiate between cells of different roots (n ≥ 3) and left and right longitudinal and apical and basal transverse walls, respectively.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Quantification of YFP:RAB-A5c intensity at cell edges in microtubule mutant backgrounds.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.47988.020
3D maximum intensity projections of 3D confocal stacks from lateral roots expressing YFP:RAB-A5c (top, green) and RFP:MBD (middle, red).
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.47988.0213D maximum intensity projections of 3D confocal stacks from lateral roots expressing YFP:RAB-A5c (top, green) and RFP:MBD (middle, red).
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.47988.022Maximum intensity projections of a 4D confocal stack from a lateral root expressing YFP:RAB-A5c (green) and RFP:TUB6 (red) at consecutive 40 min time intervals.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.47988.023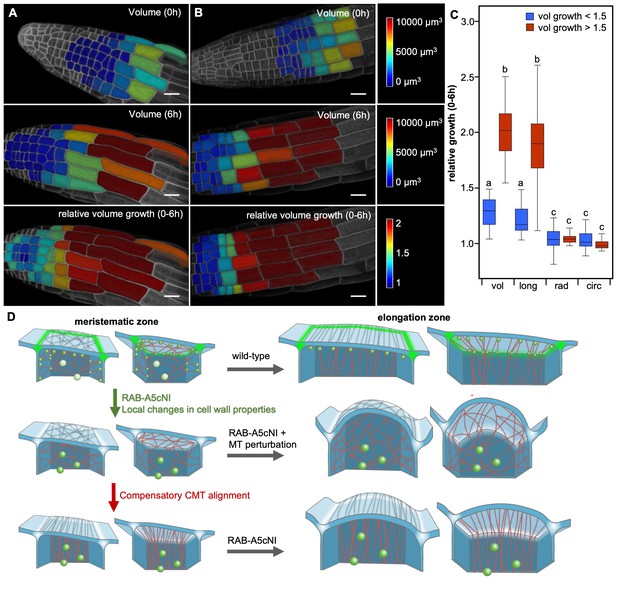
Two mechanisms drive growth anisotropy in meristematic lateral root cells.
(A,B) Snapshots from time-lapse confocal series of two lateral roots expressing YFP:NPSN12 at 0 hr (top) and 6 hr (middle, bottom). Epidermal cells were segmented in 3D using MorphoGraphX (Barbier de Reuille et al., 2015) and are colour-coded for absolute volume (top, middle) or relative volume growth (bottom). (C) boxplot showing relative volume (vol), longitudinal (long), radial (rad), and circumferential (circ) growth for cells shown in (A,B). Cells were split up in two populations based on volume growth to separate slow-growing meristematic cells (growth <1.5, n = 51) from more rapidly growing elongation zone cells (growth >1.5, n = 31). Two-way ANOVA and post hoc Tukey’s test: same letter indicates no significant difference (p≥0.05), different letters indicate significant difference (p<0.01). Note that while cells grow substantially faster once they have entered the elongation zone, growth is predominantly longitudinal in both meristematic and elongation zone cells, and there is no significant difference in radial or circumferential growth between both cell populations. (D) Proposed model of growth anisotropy regulation in epidermal lateral root cells. Top: in wild-type meristematic cells, CMTs (red) and consequently CMFs (grey) are largely isotropic. Growth anisotropy is predominantly conferred through local modification of cell wall properties at edges (green) through a RAB-A5c-dependent trafficking pathway. In elongation zone cells, CMTs and CMFs are aligned transverse anisotropic, further contributing to anisotropic growth. Middle/Bottom: inhibition of RAB-A5c function through RAB-A5c[N125I] abolishes local modification of cell wall properties at edges, leading to the lack of a mechanism promoting anisotropic growth in meristematic cells. This can be partially compensated through premature transverse alignment of CMTs, leading to moderate swelling of cells. If compensatory CMT alignment is prevented through genetic or pharmacological means, cells lack both mechanisms promoting growth anisotropy, and cells swell dramatically.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Quantification of directional growth in epidermal cells of lateral roots.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.47988.027
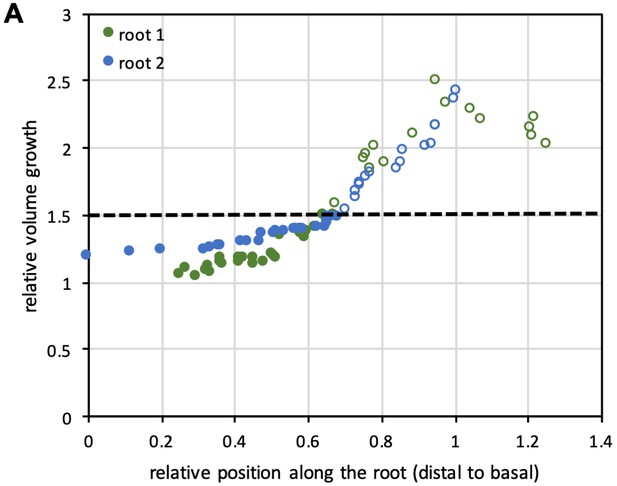
Cell growth rates in lateral roots.
(A) Plot showing relative volume growth for roots shown in Figure 5A along the longitudinal axis of the roots. The dotted line corresponds to 1.5-fold volume growth, which was identified manually as the point where cells entered into rapid elongation.
YFP:RAB-A5c localisation in young primary roots.
(A–C) Maximum intensity projections of confocal stacks from 2d old seedlings expressing YFP:RAB-A5c (left) and mCHerry:NPSN12 (middle). (B) Arrows indicate cell plates. Note that edge label is most prominent in epidermal cells not covered by the lateral root cap. (C) Boxed area in (B). Arrowheads, YFP:RAB-A5c labelled edges. Scale bars 50 µm (A,B) or 20 µm (C).
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (Arabidopsis thaliana) | RAB-A5c/ARA4 | PMID: 1748311 PMID: 26906735 | AT2G43130 | |
| Gene (Arabidopsis thaliana) | KTN | PMID: 11283338 | AT1G80350 | |
| Gene (Arabidopsis thaliana) | CLASP | PMID: 17873093 | AT2G20190 | |
| Gene (Arabidopsis thaliana) | CSI1/POM2 | PMID: 20616083 | AT2G22125 | |
| Gene (Arabidopsis thaliana) | TUB6 | PMID: 1498609 | AT5G12250 | |
| Gene (Arabidopsis thaliana) | GCP2 | PMID: 17714428 | AT5G05620 | |
| Gene (Arabidopsis thaliana) | CESA1/RSW1 | PMID: 9445479 | AT4G32410 | |
| Strain, strain background (Arabidopsis thaliana) | WT; Wild- Type; Col0 | NASC | Nasc stock number: N1093 | |
| Genetic reagent (Arabidopsis thaliana) | erh3-3 | PMID: 11782406 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Arabidopsis thaliana) | spr3 | PMID: 19509058 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Arabidopsis thaliana) | clasp-1 | PMID: 17873093 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Arabidopsis thaliana) | pom2-4 | PMID: 22294619 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Arabidopsis thaliana) | RPS5a > Dex > RAB-A5c[N125I] | PMID: 26906735 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Arabidopsis thaliana) | RAB-A5c::YFP:RAB-A5c | PMID: 26906735 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Arabidopsis thaliana) | UBQ10:: YFP:NPSN12 | PMID: 19309456 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Arabidopsis thaliana) | UBQ10:: mCherry:NPSN12 | PMID: 19309456 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Arabidopsis thaliana) | CLASP::GFP:CLASP | PMID: 17873093 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Arabidopsis thaliana) | UBQ1::RFP:TUB:6 | PMID: 21847104 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Arabidopsis thaliana) | GCP2::GCP2:3xGFP | PMID: 20935636 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Arabidopsis thaliana) | p35S::RFP:MBD | This paper | ||
| Chemical compound, drug | Oryzalin | Sigma-Aldrich | CAS: 19044-88-3 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Taxol | Sigma-Aldrich | CAS: 33069-62-4 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dexamethasone | Sigma-Aldrich | CAS: 50-02-2 | |
| Software, algorithm | Fiji (Fiji is just ImageJ) | PMID: 22743772 | https://imagej.net/Fiji | |
| Software, algorithm | MorphoGraphX | PMID: 25946108 | https://www.mpipz.mpg.de/MorphoGraphX |
Additional files
-
Source code 1
Computational model, abaqus subroutine.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.47988.028
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.47988.029





