Feedback contribution to surface motion perception in the human early visual cortex
Figures
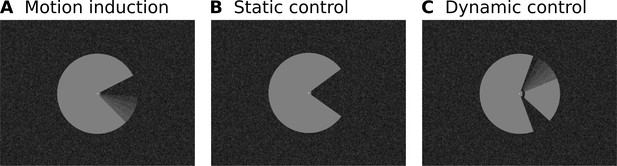
Stimulus Design.
(A) A ‘Pac-Man’ figure rotating about its centre served as the main experimental stimulus. This experimental condition is referred to as ‘motion induction stimulus’. (B) In the first of two control conditions, the same Pac-Man figure as in (A) was presented statically, that is without rotating about its centre. This condition is referred to as ‘static control’. (C) In the second control condition, a figure consisting of a stationary wedge on its left side, and a smaller, rotating wedge on its right side was presented. In (A) and (C), the angular position of the ‘mouth’ and the wedge were modulated sinusoidally, in order to create the impression of a smooth, natural, back and forth movement. Importantly, the motion induction stimulus is perceived to rotate as a whole, whereas the dynamic control stimulus creates the impression of a rotating wedge on the right, and a stationary wedge on the left. At the same time, the retinal image of all three stimuli is identical in the left visual field. All stimuli were presented on a textured random noise background in order to enhance figure-ground segmentation. The stimuli, including the texture background, were adapted from Akin et al., 2014. See Figure 1—figure supplement 1 for a higher-resolution image of the Pac-Man stimulus and the texture background. Videos of the stimuli are available online (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.2583017).
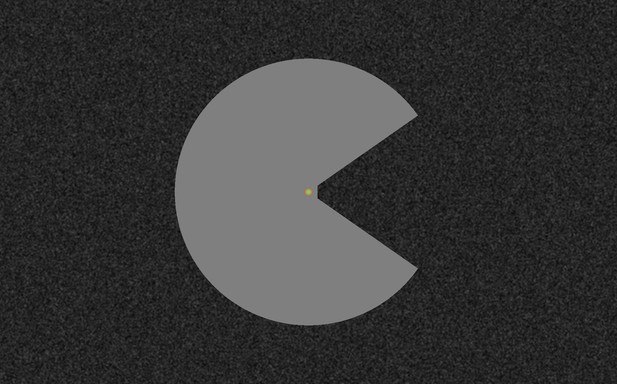
High-resolution image of the ‘Pac-Man’ stimulus and the texture background.
When this figure is rendered such that the radius of the disk is 3.75 cm, and viewed from a distance of approximately 57 cm, it gives an impression of what the stimuli looked like to the participants in the scanner. Videos of the stimuli are available online (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.2583017).
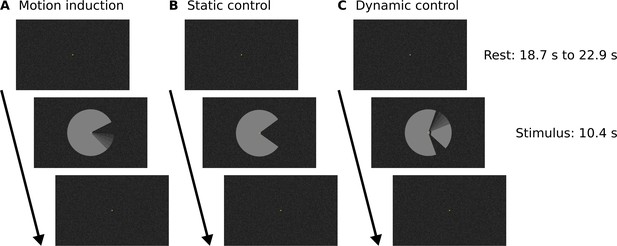
Experimental design.
Stimuli were presented in a block design with rest blocks of variable duration. The three stimulus conditions were presented in separate runs (A, B, C). A central fixation dot and the random texture background pattern were present throughout the duration of each run. See Figure 1—figure supplement 1 for a higher-resolution image of the ‘Pac-Man’ stimulus and the texture background.
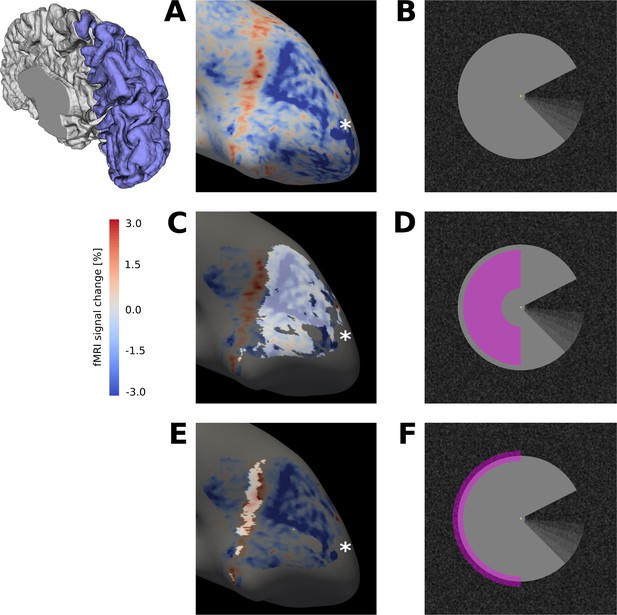
Surface activation maps.
(A) Activation map for motion induction condition (stimulus shown in (B)), projected on the inflated cortical surface, for a representative subject (GLM parameter estimates for sustained response). An extended region of negative signal change (blue) is surrounded by a band of positive signal change (red). (C) The activation map from (A) is masked for V1, and the cortical area that retinotopically corresponds to the centre of the Pac-Man stimulus (D) is highlighted. (E) Same as (C), but the cortical area that contains the retinotopic representation of the edge of the Pac-Man stimulus (F) is highlighted. The band of positive signal change corresponds to the retinotopic representation of the edge of the Pac-Man stimulus. The areas highlighted in (C) and (E) were selected as ROIs for the stimulus centre and edge, respectively. Discontinuities in the ROIs are due to thresholding of the retinotopic map (R2 >0.15). The asterisk marks the approximate location of the cortical representation of the fovea (A, B, C). The schematic of a right hemisphere next to (A) indicates the approximate location of the inflated surface in (A, C, E), highlighted in blue.
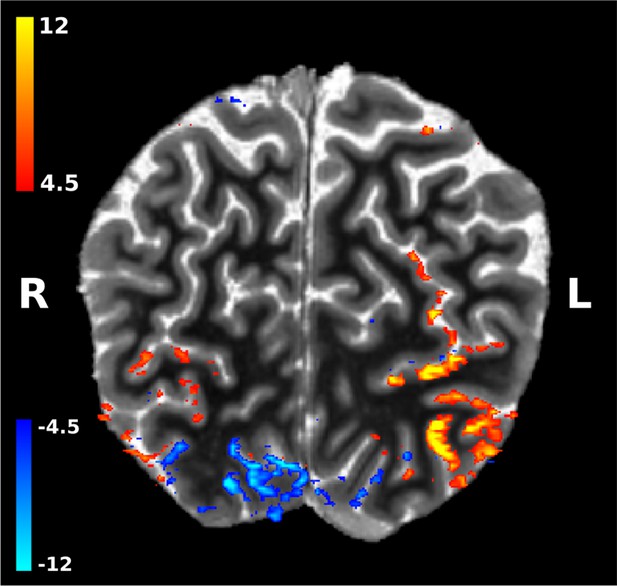
The Pac-Man stimulus caused positive and negative fMRI signal changes across visual cortex.
Shown are the z-scores for the GLM contrast Pac-Man dynamic (sustained response) against rest, overlaid on a brain-masked T1 image, for a representative subject. Negative signal changes are particularly pronounced in early visual cortex of the right hemisphere, that is the hemisphere that ‘sees’ the left side of the Pac-Man. (Image is in radiological convention.).
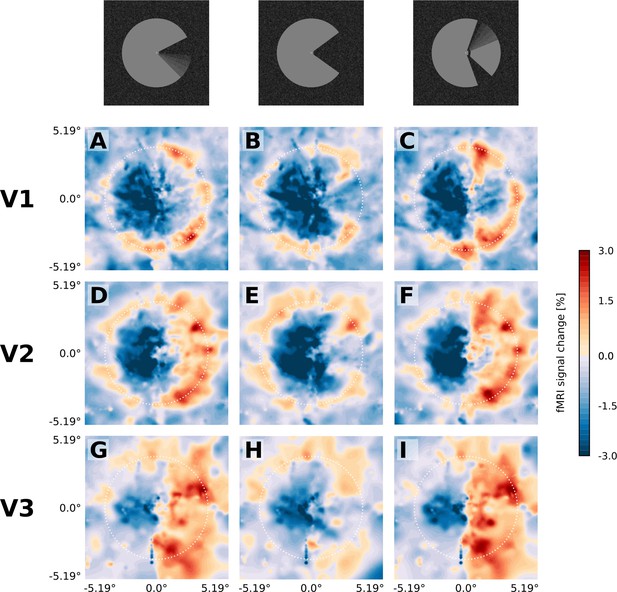
Projection of GLM parameters into visual space.
The parameter estimates for the three stimulus conditions (motion induction stimulus (A, D, G), static control stimulus (B, E, H), and dynamic control stimulus (C, F, I)) were projected into a model of the visual space based on their retinotopic location, and the size of their respective population receptive fields. The dashed white circles correspond to an eccentricity of 3.75°, that is the radius of the Pac-Man stimulus. In all three stimulus conditions, there is a negative response to the left half of the stimulus. Visual field projections are averaged over depth levels (mean).
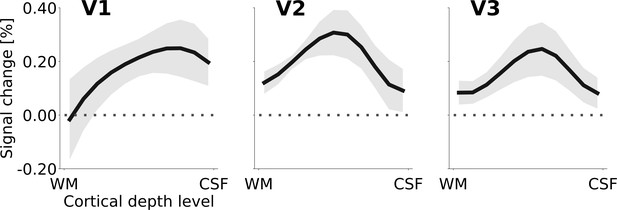
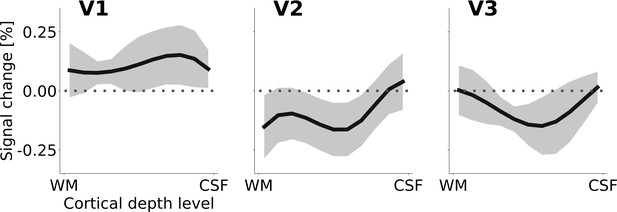
Cortical depth profiles of the apparent motion effect for the cortical representation of the stimulus centre (see Figure 2C & D).
The apparent motion effect was defined as the relative signal change associated with the condition contrast ‘motion induction’ (Figure 1A) minus ‘dynamic control’ (Figure 1C). Shading represents the standard error of the mean (across subjects). See Figure 4—figure supplement 1 for the same results for all experimental conditions, Figure 4—figure supplement 3 for single subject data, and Figure 4—figure supplement 2 for the cortical depth profile of the apparent motion effect at the representation of the stimulus edge.
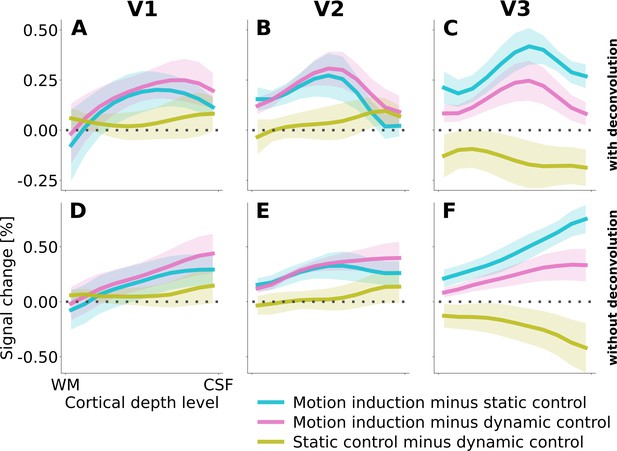
Cortical depth profiles of all three condition contrasts, with (A, B, C) and without (D, E, F) spatial deconvolution for removal of signal spread due to draining veins.
There are three possible condition contrasts: motion induction vs. static control (blue line), motion induction vs. dynamic control (magenta line), and static control vs. dynamic control (yellow line). Shading represents the standard error of the mean (across subjects).
Cortical depth profiles of the apparent motion effect for the cortical representation of the stimulus edge (see Figure 2C and F).
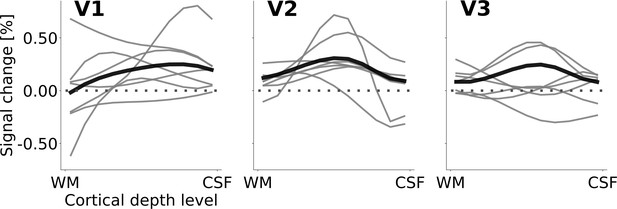
Cortical depth profiles of the apparent motion effect for the cortical representation of the stimulus centre.
Same as Figure 4 in the main text, but showing single-subject profiles (light grey) in addition to group level profiles. Please note that the group level profiles are a weighted average, reflecting the number of sampling points comprised within the respective region of interest (ROI) for each subject. (ROIs were defined in a quantitative, observer-independent way, and the number of sampling points differed between subjects. The size of the ROI dependent mostly on the quality of each subject’s retinotopic map.).
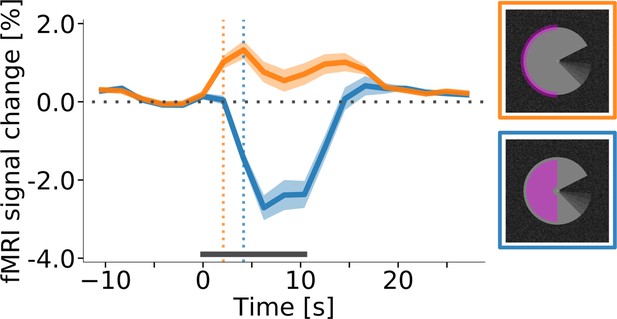
Response onset times in V1.
(A) Event-related fMRI timecourses for regions of interest corresponding to the stimulus centre (blue line) and the edge of the stimulus (orange line). The dotted vertical lines indicate the response onset, defined as the first time point at which the signal was significantly different from zero (one-sample t-test, p<0.05, Bonferroni corrected). The positive response at the stimulus edge precedes the negative response at the stimulus centre by one volume (i.e. by about 2 s), suggesting that the negative response is not caused by the onset of the stimulus, but by its prolonged presentation. The response is shown for area V1 of the right hemisphere, averaged (mean) over subjects, stimulus conditions, and cortical depth levels. The horizontal grey bar marks the duration of the stimulus block. Error shading represents the standard error of the mean (across subjects). (See Figure 5—figure supplement 1 for same results separately for all areas and conditions, and Figure 5—figure supplement 2 for single-subject data.).
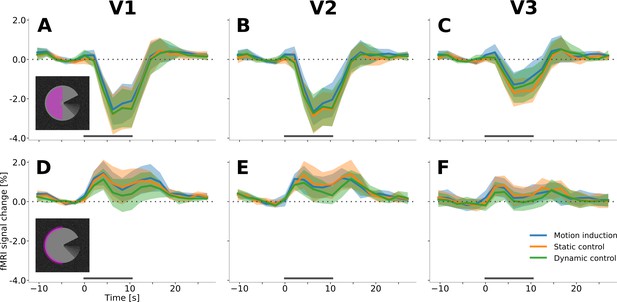
Event-related fMRI timecourses for region of interest corresponding to the stimulus centre (A, B, C) and the edge of the stimulus (D, E, F) in the right hemisphere.
The horizontal grey bar marks the duration of the stimulus block. All three stimulus conditions (represented by separate lines) evoked a sustained negative response in V1, V2, and V3 in cortex that retinotopically represents the stimulus centre. In contrast, the cortex that represents the stimulus edge exhibits a transient, positive response at stimulus onset and stimulus offset. Interestingly, the positive response at the stimulus edge precedes the negative response at the stimulus centre (see also Figure 5 in the main text). Error shading represents the standard error of the mean (across subjects). The scale of the axes is identical in all subplots.
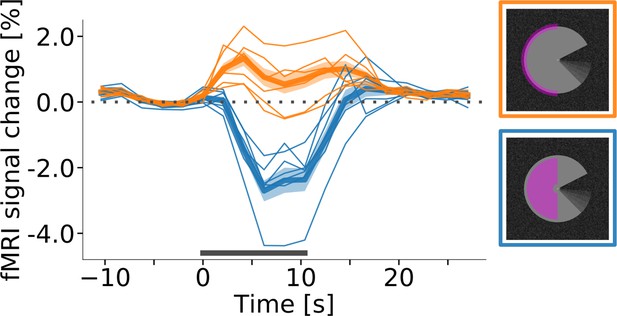
Single-subject response onset times in V1.
Event-related fMRI timecourses for regions of interest corresponding to the stimulus centre (blue line) and the edge of the stimulus (orange line). Same as Figure 5, but with single-subject timecourses (thin lines) overlaid on group average (thick lines).
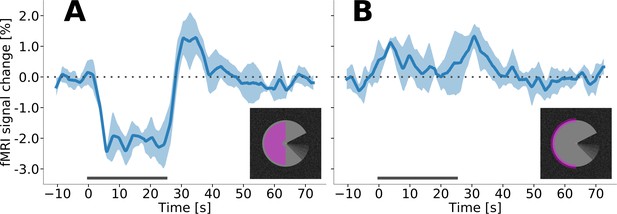
Event-related fMRI timecourses from an additional run with longer stimulus blocks, for V1 in the right hemisphere.
In order to further investigate the temporal dynamics of the stimulus-evoked response, we acquired and additional run during which the motion induction stimulus was presented with longer block durations (in a subset of subjects, n = 5). Stimulus duration was 25 s, with rest blocks of 50 s. (A) The region of interest that corresponds to the stimulus centre shows a sustained, negative response that resembles the ‘canonical’ haemodynamic response function. (B) The response to the stimulus edge is transient and positive.
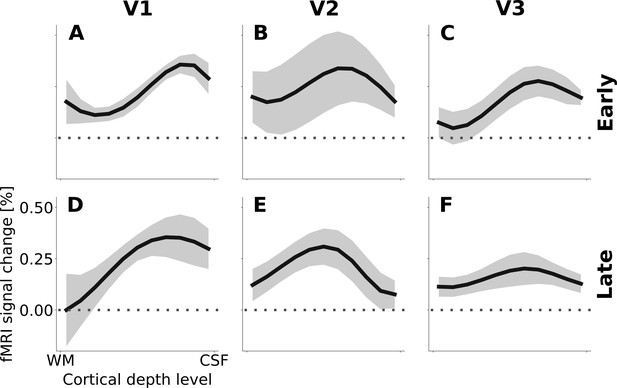
Cortical depth profiles of the apparent motion effect for the cortical representation of the stimulus centre.
Similar to Figure 4, but separately for the early and late phases of the response. (A, B, C) The early response includes the second and third fMRI volumes after stimulus onset (i.e. ~2 to~6 s after stimulus onset). (D, E, F) The late phase comprises the last two fMRI volumes during which the stimulus was presented (~8 to~12 s after stimulus onset). The apparent motion effect was defined as the relative signal change associated with the condition contrast ‘motion induction’ (Figure 1A) minus ‘dymanic control’ (Figure 1C). Shading represents the standard error of the mean (across subjects).
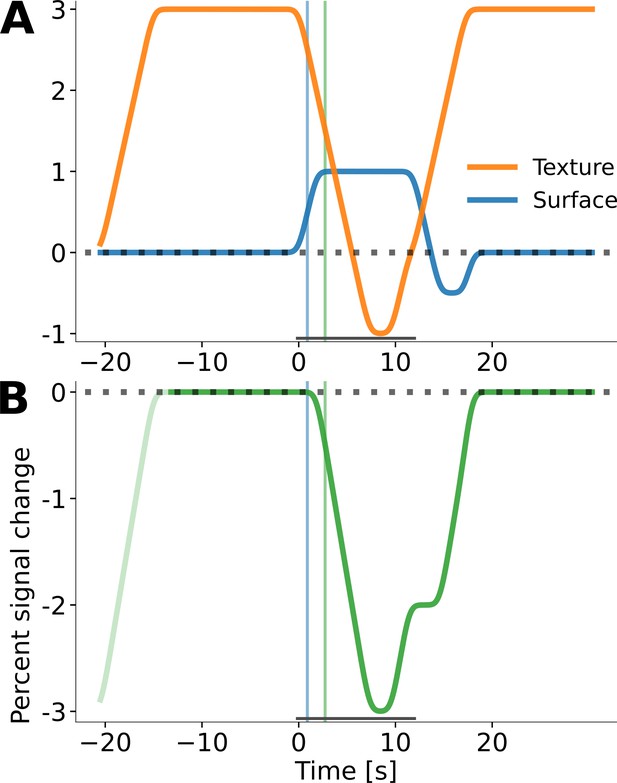
Simulation of negative fMRI response at the cortical representation of the stimulus centre.
The observed negative response (Figures 5,6) might be the result of an elevated baseline. A control experiment showed that the full screen texture background causes a strong positive response, relative to a uniform background (response amplitude circa 3%; Figure 7—figure supplement 1). The horizontal grey bar indicates the duration of the surface stimulus in the simulation. The orange line in (A) represents this positive texture response (corresponding to Figure 7—figure supplement 1C). Another control experiment demonstrated that a uniform grey surface stimulus results in a positive response, relative to a dark uniform background (response amplitude circa 1%, Figure 6A, orange and red lines therein). This positive surface response is represented by the blue timecourse in (A). In the main experiment (Figures 5,6), a positive response to the texture background and a positive response to the grey surface stimulus might have had the same onset time. This is illustrated in (B), where the texture and surface responses from (A) are added, and the pre-stimulus interval is taken as a baseline with amplitude zero. The time point at which the composite negative response in (B) reaches –0.5% is indicated by the thin, vertical green lines. For comparison, the timepoint at which the surface response has reached its peak amplitude of 0.5% is indicated by the thin, vertical, blue lines. The simulated composite response resembles the empirically observed negative response in Figure 6A (green and blue lines therein).
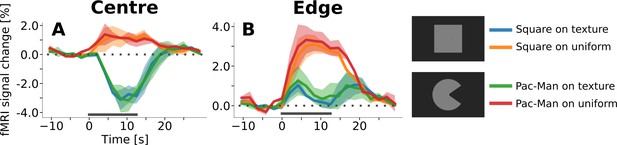
Event-related time courses from control experiment with texture background and uniform background, separately for regions of interest corresponding to the retinotopic representation of the centre of the stimulus (A) and to its edges (B).
Irrespective of the shape of the stimulus (square or ‘Pac-Man’), there is a positive response to the centre of the stimulus when the background is uniform (A, red and orange lines), and a negative response when the stimuli are presented on a random texture pattern (A, green and blue lines). Interestingly, the positive response has a shorter latency than the negative response. The response to the edges of the stimuli is positive under all conditions (B). However, the response amplitude is much stronger when the stimuli are presented on a uniform background. Moreover, the temporal dynamics changes as a function of the background; the response is sustained when the background is uniform (B, orange and red lines), but transient for the texture background (B, green and blue lines). The horizontal grey bar marks the duration of the stimulus.
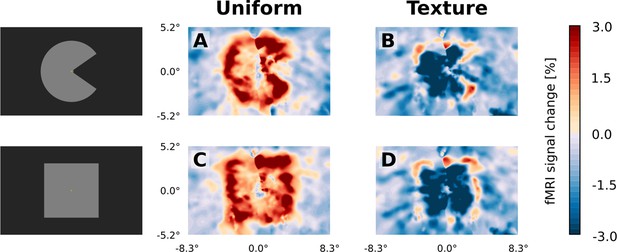
Visual field projections of GLM parameter estimates from control experiment with texture background and uniform background, for V1.
A ‘Pac-Man’ figure and a square were presented either on a uniform background (A and C) or on a random texture background (B and D). When presented on a uniform background, the stimuli caused a positive response, especially at the retinotopic representation of the edges (A and C). In stark contrast, the response to the interior of the stimuli was negative when presented on a random texture background (B and D). At the edges of the stimuli, a small band of positive activity can still be observed (B and D).
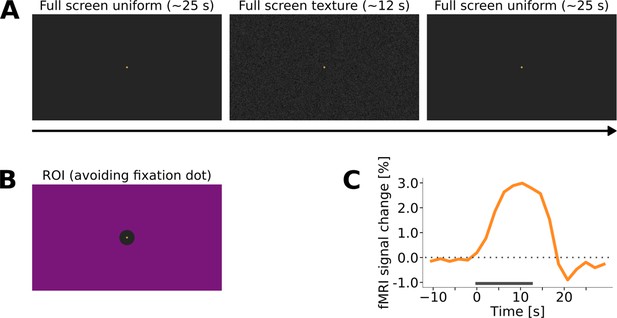
Control experiment to investigate the response to the texture pattern, in the absence of any additional stimulus.
(A) A full-screen texture (same as the background in the main experiment; see Figure 1 and Figure 1—figure supplement 1 and Figure 1—figure supplement 2) was presented in a block design. The rest blocks consisted of a uniform grey background, with the same mean luminance as the texture. (B) The region of interest (ROI) comprised almost the entire visual field covered by the projector screen, only excluding the central area around the fixation dot. (C) Event-related time course of the stimulus induced response in V1 (grey bar represents the duration of the stimulus, n = 1).
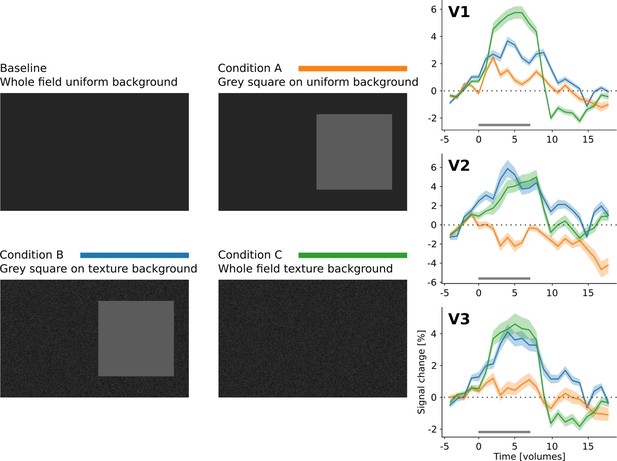
Additional control experiment, investigating the effect of a texture background on stimulus-induced responses relative to a uniform baseline (n = 1).
The grey bar underneath the signal timecourses indicates the duration of the stimulus. Time is given in volumes; the duration of one volume was 2.604 s.
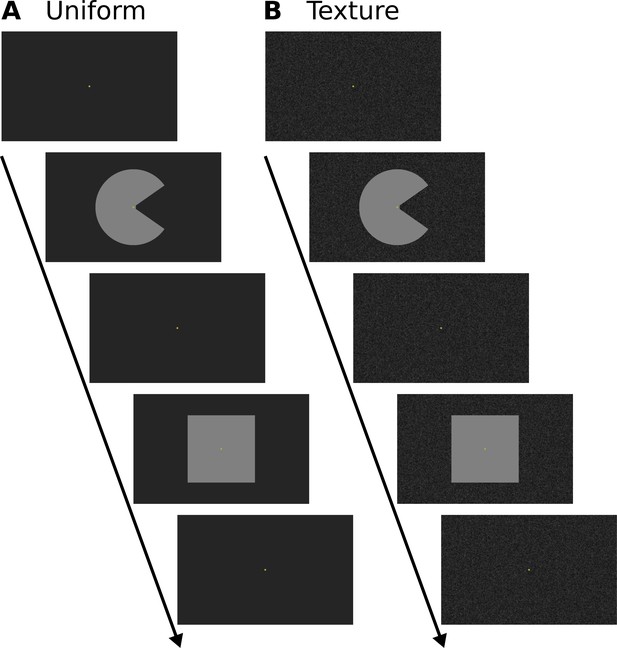
Stimulus design of the control experiment.
The purpose of the control experiment was to investigate the role of the background and the stimulus shape. Participants were presented with a static ‘Pac-Man’ stimulus (same as in the main experiment, static control condition), and a square with the same area as the ‘Pac-Man’. Stimuli were presented in a block design. In separate runs, these stimuli were presented on a uniform background (A) and a texture background (B, same as in the main experiment). The order of stimulus conditions was randomised. Participants performed a central fixation task (as in the main experiment). See Figure 1—figure supplement 1 for a higher-resolution image of the texture background. Videos of the stimuli are available online (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.2583017).
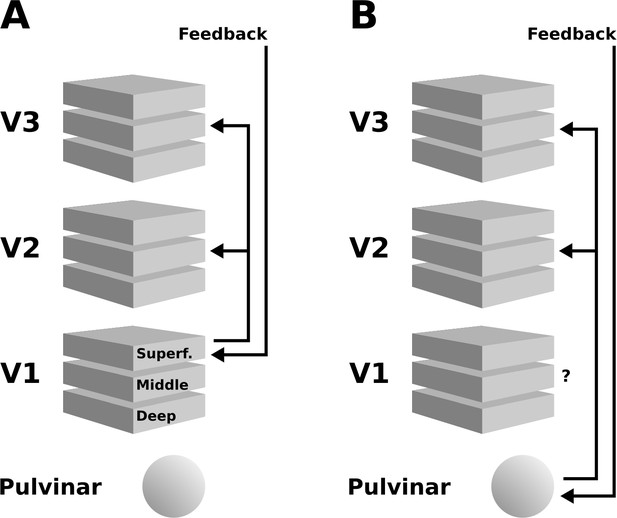
Schematic illustration of two possible interpretations of the present results.
(A) Higher cortical areas may integrate the global motion percept across hemispheres, and send feedback projections to superficial layers of V1. Subsequently, this re-entrant feedback would be sent to V2 and V3 via feedforward connections. (B) Alternatively, the pulvinar may act as a ‘higher-order relay’, and send feedback from higher cortical areas to V2 and V3. These scenarios are not mutually exclusive, and other possibilities exist, such as an involvement of the LGN – see discussion section for details.
Tables
Comparison of stimulus parameters in Akin et al., 2014 and in the present study.
| Akin et al., 2014 | Present study | |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter of stimulus | 15° visual angle | 7.5° visual angle |
| Viewing mode | Central fixation task & passive viewing | Central fixation task |
| Rest block duration | 12 s | 18.7 s, 20.8 s, or 22.9 s |
| Stimulus block duration | 12 s | 10.4 s |
| Stimulus luminance | 503 cd/m2 | 163 cd/m2 |
| Mean background luminance | 189 cd/m2 | 8 cd/m2 |
| Oscillation rate of stimulus | 1.04 Hz | 0.85 Hz |





