Apolipoprotein L-1 renal risk variants form active channels at the plasma membrane driving cytotoxicity
Figures
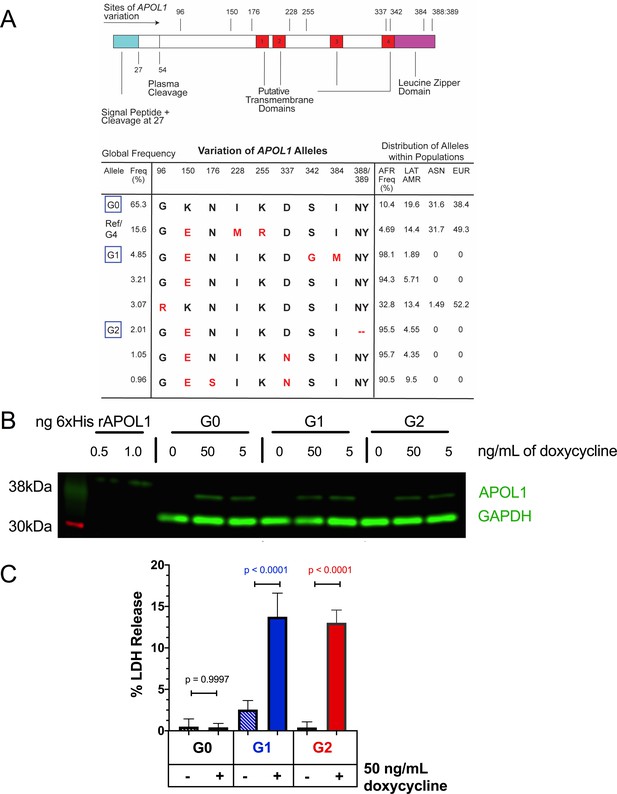
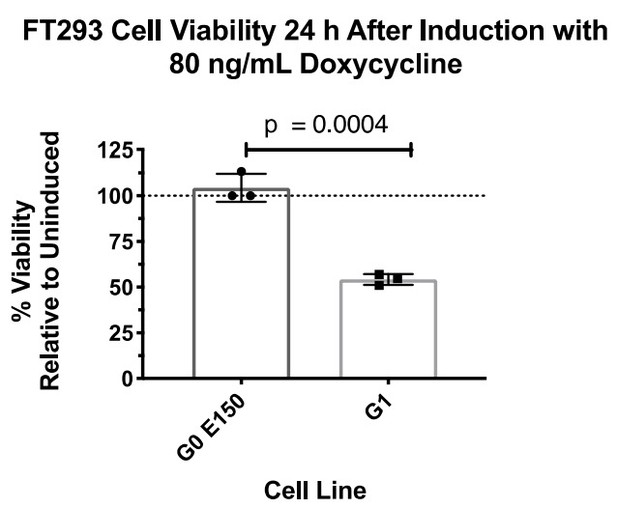
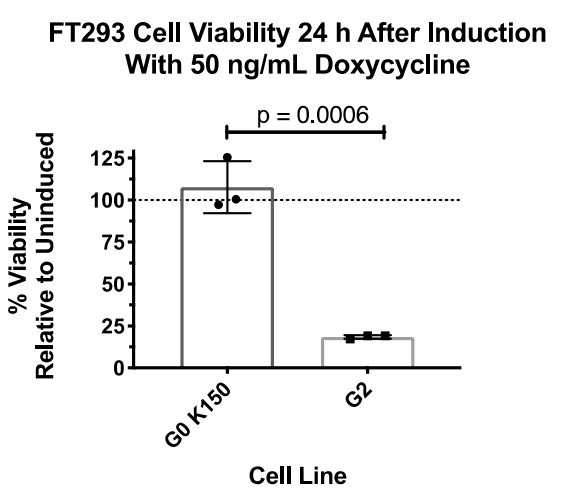
Expression of APOL1-G1 and G2 cDNA leads to cytotoxicity in FT293 cells.
(a) Predicted linear structure of APOL1, using JPred, with major sites of amino acid variation highlighted in red (a deletion is represented as a dash). Haplotypes are organized by frequency in the human population, which is depicted in the left-hand column as Freq (%). The right-hand column represents the distribution of each allele within populations. AFR = African, LAT AMR = Latin America, ASN = Asian, EUR = European. Haplotypes in blue boxes were those used in this study. Data retrieved from 1000 Genomes Project. (b) Western blot of whole cell lysates displaying similar levels of protein production between FT293 cell lines. Cells were treated with doxycycline for 4 hr. 6x-His tagged APOL1 was expressed and purified from E. coli and used as a positive control. (c) Cell death assay displaying the cytotoxicity caused by doxycycline-induced expression of APOL1-G1 and G2, but not G0, in FT293 cells. Cells were induced with 50 ng/mL doxycycline for 24 hr, and cytotoxicity was measured via cellular release of lactate dehydrogenase. A two-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was performed to compare induced and un-induced cells (n = 14).
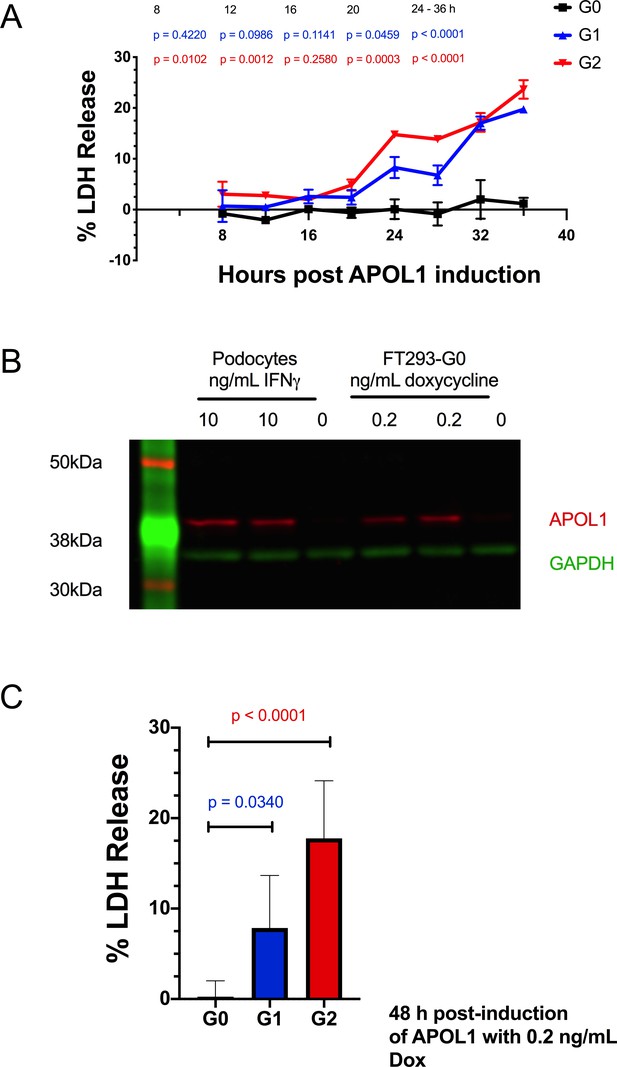
Expressing APOL1 protein at levels found in podocytes leads to RRV cytotoxicity in FT293 cells.
(a) A time-course of APOL1 expression in FT293 cells treated with 50 ng/mL doxycycline reveals that RRV cytotoxicity occurs 24 hr post-induction (n = 3). Data are represented as mean ± s.d. (b) Western blot of whole cell lysates displaying similar levels of APOL1 protein production between differentiated, conditionally-immortalized human podocytes and FT293-G0 cells. Podocytes were treated with 10 ng/mL interferon- γ and FT293 cells with 0.2 ng/mL doxycycline for 24 hr. (c) Expression of APOL1 protein at comparable levels to a podocyte leads to cytotoxicity with G1 and G2. Cells were induced with 0.2 ng/mL doxycycline (n = 7). (a) A two-way ANOVA or (b) one-way ANOVA were performed with multiple comparisons to compare G0 vs G1 and G2.
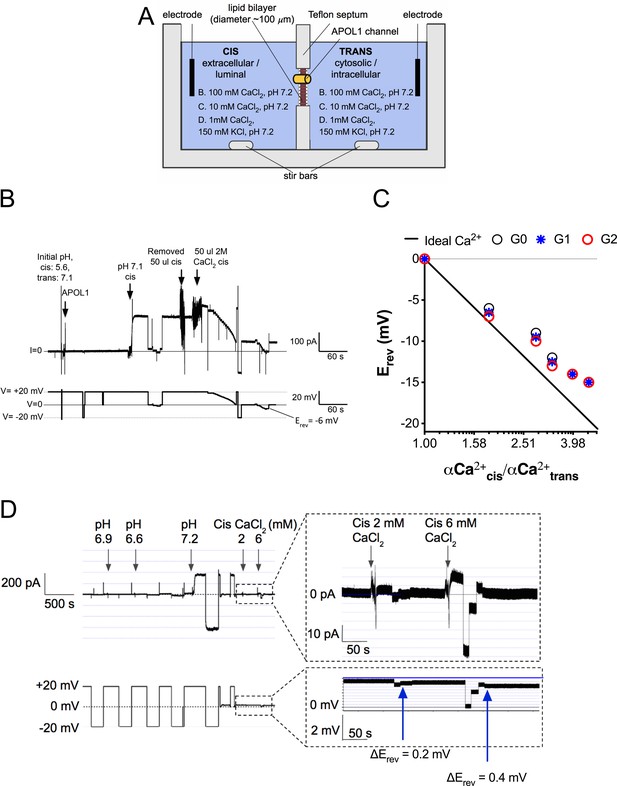
The APOL1 channel is permeable to Ca2+.
(a) Planar lipid bilayer setup. The starting buffer composition for (b–d) are shown. During each experiment the composition of the cis side is altered by the experimenter, whereas the trans side is left unaltered. After APOL1 channel formation (typically many thousands per bilayer) a current (pA, upper trace) can be measured in response to a voltage (V, lower trace). In each case the voltage is set by the experimenter. (b) Planar lipid bilayer demonstrating that the rAPOL1-G0 channel is selective for Ca2+ over Cl-. rAPOL1 was added to the cis side at pH 5.6 to drive insertion, which caused a minor increase in conductance that was amplified approximately 450-fold upon cis neutralization (pH 7.1). The voltage required to zero the current (reversal potential, Erev) with a 1.95-fold CaCl2 gradient was −6 mV, indicating Ca2+ selectivity. (c) Ca2+ versus Cl- permeability did not differ between APOL1 G0, G1 and G2. A conductance was obtained as in b, except that the chambers contained symmetrical 10 mM CaCl2. The Erev was determined as CaCl2 was titrated into the cis side. Plotted are cis/trans Ca2+ activity gradients (Robinson and Stokes, 2002) versus Erev. Also plotted is the Nernst equation for calcium, which represents ideal selectivity for Ca2+ over Cl- (d) Ca2+ permeability in the presence of excess KCl. Before recording, the cis side was adjusted to pH 6.9 and then 1 µg APOL1 G0 was added to the cis side. APOL1 was allowed to associate with the bilayer for 1 hr and then the cis side was perfused with chamber buffer (150 mM KCl, 1 mM CaCl2, pH 7.2). Once recording began, the cis side was adjusted to pH 6.6, allowing for APOL1 insertion and channel formation. A large increase in the conductance upon re-neutralization of the cis side (pH 7.2) indicates pH-dependent channel opening. Erev (+1.75 mV) was determined by adjusting the voltage until the current read zero. CaCl2 was then titrated into the cis compartment to the indicated concentrations. Upon each addition there was an upward shift in the current and the Erev became more negative, indicating Ca2+ permeability of the APOL1 channel. The pCa/pK permeability ratio at 2 mM calcium was calculated as 0.6 (See Materials and methods).
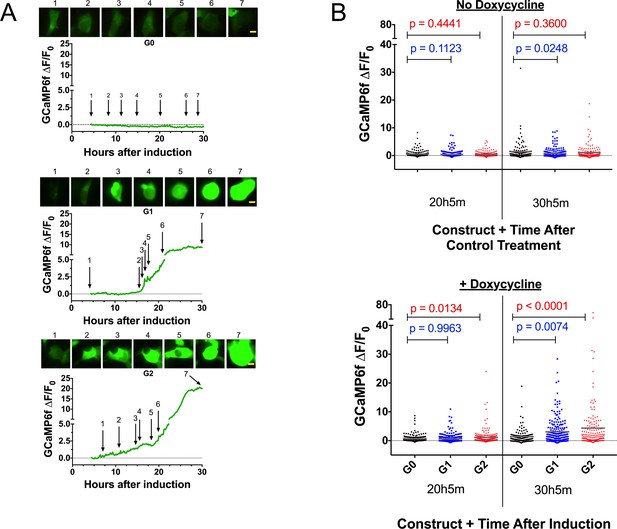
Expression of the RRVs leads to a Ca2+ influx that precedes cell swelling and death.
(a) Fluorescence traces of representative GCaMP6f-positive cells demonstrating that G1 and G2 cause a Ca2+ influx prior to cell swelling. GCaMP6f-transfected FT293 cells were incubated with DRAQ7 followed by 50 ng/mL doxycycline to induce APOL1 expression and then imaged via widefield every 10 min for 4.5–30 hr post induction. Traces represent levels of cytoplasmic Ca2+ over time as measured by GCaMP6f fluorescence (no DRAQ7 was observed in depicted cells). Cells are from Video 1. Scale bars = 20 μm. (b) High-throughput analysis revealed a significant increase of cytoplasmic Ca2+ levels driven by G1 and G2 compared to G0. Each point is the ∆F/F0 for an individually tracked cell and bars represent the cell population mean of GCaMP6f fluorescence. Cells were analyzed from 4 fields of view per condition, n = 1748. A one-way ANOVA multiple comparisons test was performed to compare the RRVs with G0 at the indicated timepoints.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
FT283 cells GCaMP6f microscopy, 30 hours after induction one way ANOVA.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/51185/elife-51185-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx
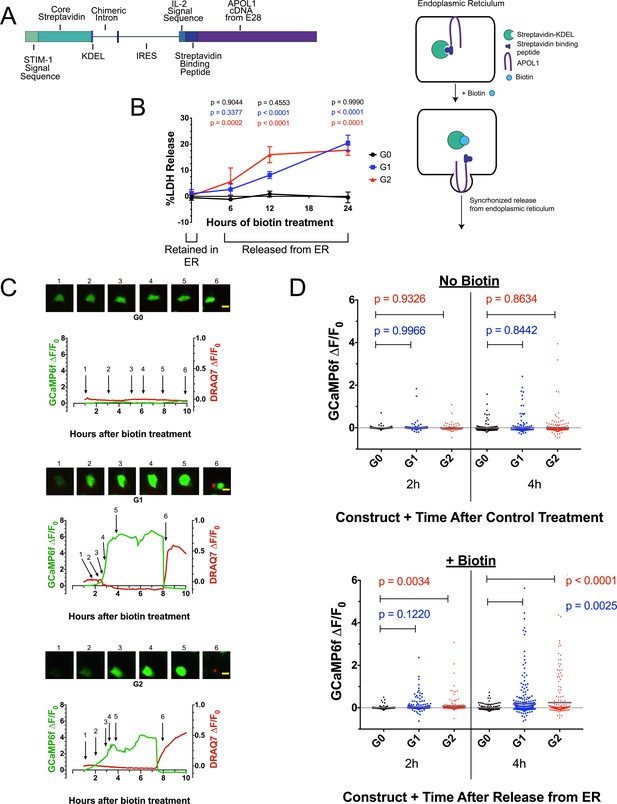
Ca2+ influx and cytotoxicity of G1 and G2 requires trafficking from the ER.
(a) Schematic of the RUSH system. Streptavidin was expressed with a signal peptide and KDEL allowing for localization and retention in the ER lumen along with streptavidin-binding protein (SBP) tagged APOL1. SBP binds to streptavidin causing APOL1 to be retained in the ER until synchronous release is initiated by the addition of biotin. (b) Time course showing that RRV cytotoxicity requires trafficking from the ER. 24 hr after transfection, HEK293 cells were treated with or without (0 hr) 80 µM biotin at the indicated times. 48 hr post-transfection, cytotoxicity was measured via release of lactate dehydrogenase. To compare cytotoxicity between biotin treated and untreated (0 hr) for respective genotypes, a two-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was performed (n = 6). (c) Fluorescence traces of GCaMP6f-positive HEK293 cells showing that the G1 and G2-mediated Ca2+ influx occurs after trafficking from the ER. GCaMP6f-transfected cells were incubated with DRAQ7 followed by 80 µM biotin to release APOL1 and were then imaged via widefield every 5 min for 1–18 hr post treatment. Cells are from Video 2. Scale bars = 20 μm. (d) High-throughput imaging and analysis was performed as in Figure 3b, demonstrating that the G1 and G2-mediated Ca2+ influx requires trafficking from the ER. Each point is the ∆F/F0 for an individually tracked cell and bars represent the cell population mean of GCaMP6f fluorescence. Cells were analyzed from 3 fields of view per condition, n = 1657. A one-way ANOVA multiple comparisons test was performed to compare the RRVs with G0 at the indicated timepoints.
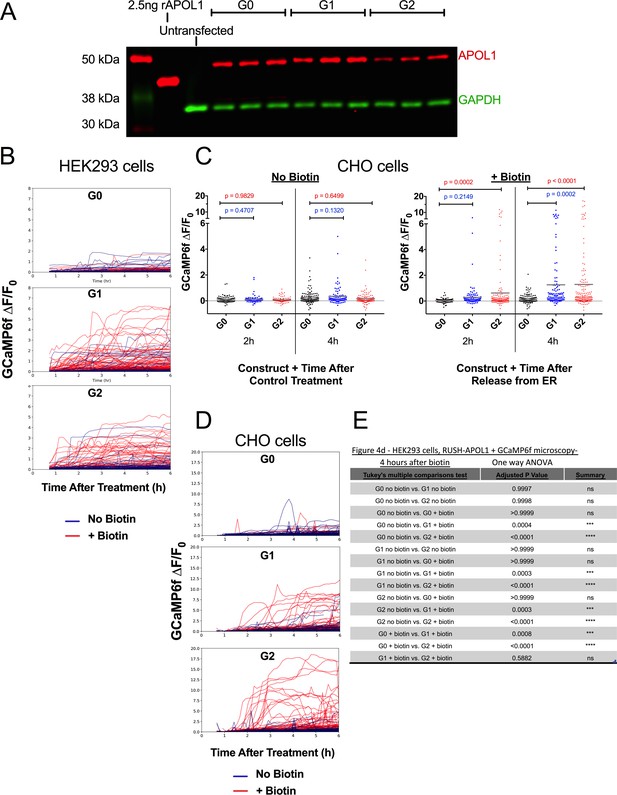
Validation of protein expression and Ca2+-driven cytotoxicity of APOL1 in the RUSH system.
(a) Western blot of whole cell lysates displaying protein expression of RUSH-APOL1 in HEK293 cells 24 hr after transfection. Cells were not treated with biotin. (b) Fluorescent traces of all GCaMP6f-positive HEK293 cells in Video 2 and Figure 4d (c) High throughput microscopy and analysis was performed as in Figures 3b and 4d, validating in CHO cells the requirement of G1 and G2 trafficking from the ER to mediate a Ca2+ influx and cell swelling. RUSH-APOL1 transfected CHO cells were treated with or without 80 µM biotin and imaged via widefield every 5 min for 1–12 hr post treatment. Each point is the ∆F/F0 for an individually tracked cell and bars represent the cell population mean of GCaMP6f fluorescence. Representative cells from this analysis can be viewed in Video 3. Cells were analyzed from 3 different fields of view per condition, n = 882. A one-way ANOVA multiple comparisons test was performed to compare G1 and G2 with G0 at the indicated timepoints. (d) Fluorescent traces of all GCaMP6f-positive CHO cells from Video 3. (e) All cells from 4 hr after +/- biotin treatment in Figure 4d were directly compared via one-way ANOVA.
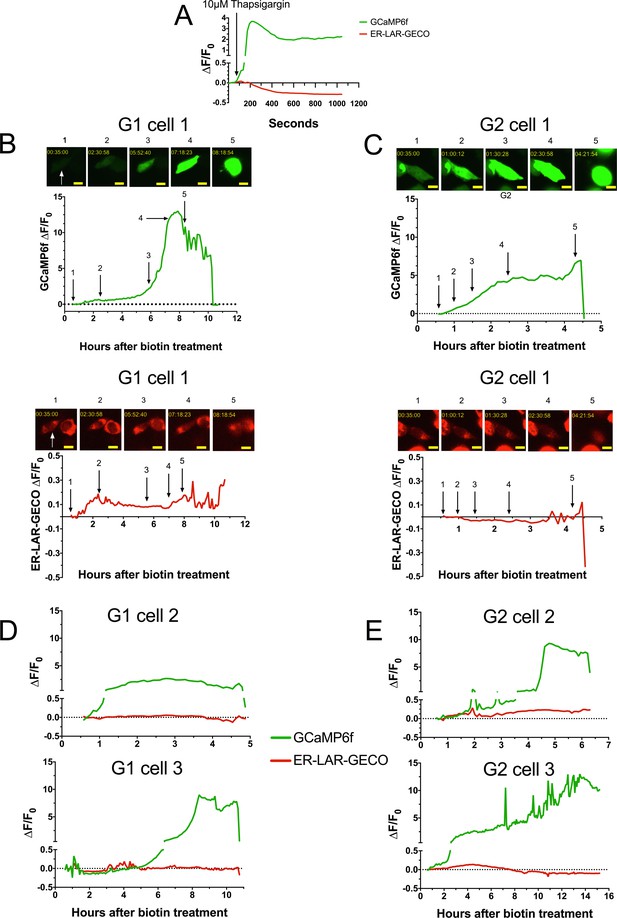
The G1 and G2-mediated cytoplasmic Ca2+ influx is not due to ER Ca2+ release.
(a) Validation for the simultaneous use of Ca2+ sensors GCaMP6f and ER-LAR-GECO from a representative cell. Co-transfected cells were treated with 10 µM thapsigargin to prevent Ca2+ reuptake in the ER, which increases cytoplasmic Ca2+ levels (GCaMP6f) while concurrently depleting ER Ca2+ (ER-LAR-GECO). Cells were imaged via widefield. (b–e) Fluorescence traces revealing that there is no ER Ca2+ release during G1 and G2 mediated cytotoxicity. CHO cells were co-transfected with RUSH-APOL1, GCaMP6f, and ER-LAR-GECO, then treated with 80 µM biotin and imaged via widefield every 5 min for 0.5–12 hr post treatment. Cells that displayed the established phenotype of Ca2+ influx followed by cell swelling were selected for analysis. Representative cells are from Video 4. A minimum of 5 cells were analyzed per genotype. Scale bars = 10 µm.
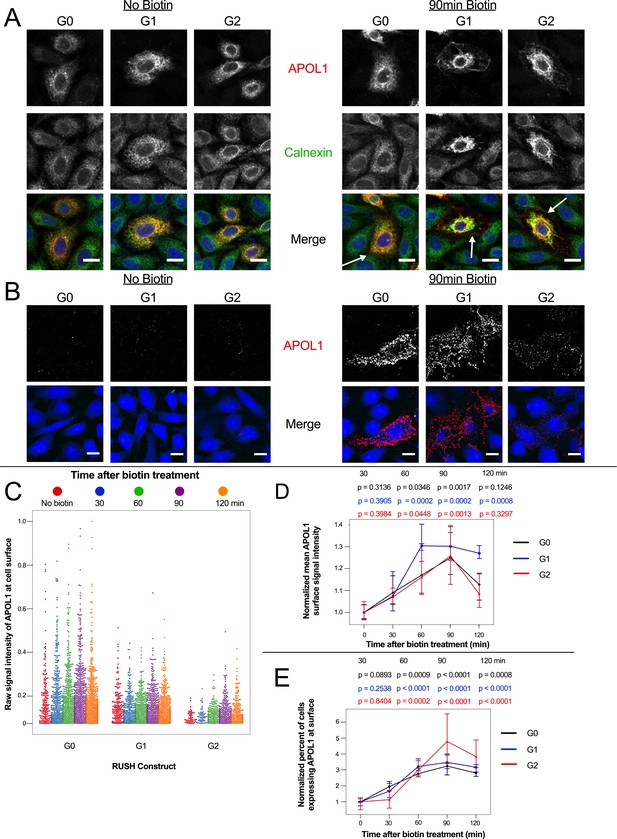
APOL1 traffics to the PM prior to Ca2+ influx.
(a) Confocal images of transfected and permeabilized CHO cells depict RUSH-APOL1 (red) localized to the ER (stained via calnexin, green) without biotin followed by partial PM localization after 90 min of biotin treatment. Representative cells from n = 3 independent experiments. (b) RUSH-APOL1 localizes to and forms punctae at the PM within 90 min of biotin treatment. CHO cells were treated and imaged as in (a) except without permeabilization. Here anti-calnexin (green) was used as a control for cell permeabilization (depicted in the merged images, no permeabilization was detected). Representative cells from n = 4 independent experiments. (c) High-throughput confocal microscopy reveals that RUSH-APOL1 begins localizing to the PM within 60–90 min. Cells were randomly imaged at 20x, capturing ≥10 fields of view per well from 3 replicate wells for each condition. Calnexin signal was used to filter out permeabilized cells. Each dot represents a single cell (n = 462,918 cells analyzed). (d–e) RUSH-APOL1 localization to the PM steadily increases until 90 min post release from the ER. (d) The mean intensity of all cells in (c) was normalized to the respective no biotin controls. (e) The percentage of cells expressing RUSH-APOL1 at the PM was determined using a threshold set by untransfected wells, and then normalized to the respective no biotin controls. For analysis of (d) and (e), a generalized linear model was used to make pairwise comparisons between all samples. Comparisons were performed between biotin treated and untreated cells within each respective genotype. All data are represented as mean ± s.d. (a–b) Scale bars = 10 µm.
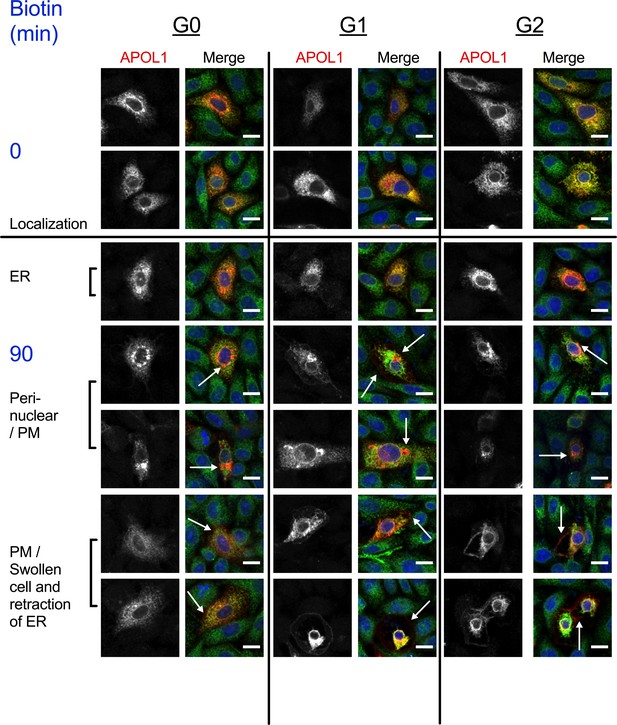
RUSH-APOL1 traffics to the peri-nuclear region and PM post-biotin treatment.
Additional confocal images of immunostained CHO cells from Figure 5a. All three APOL1 variants are found in the ER prior to biotin treatment, and then traffic to the peri-nuclear region or PM within 90 min of release (white arrows indicating the plasma membrane and perinuclear compartments). Some G1 and G2 expressing cells start to swell within 90 min, which leads to retraction of the ER. Scale bars = 10 µm.
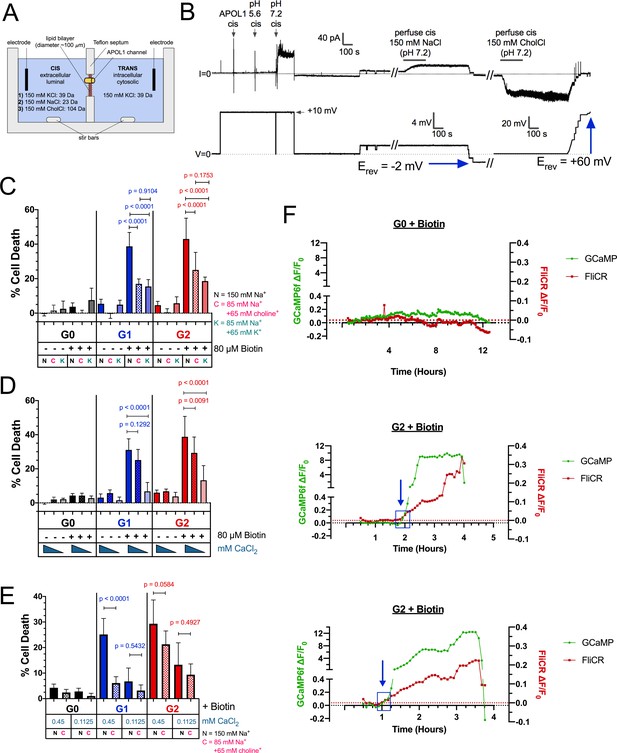
RRV cytotoxicity is driven by the influx of both Na+ and Ca2+.
(a) Schematic of the planar lipid bilayer setup showing the sequence of cis buffer perfusions. (b) The APOL1 channel is readily permeable to Na+, but not choline+. In symmetrical KCl solutions Erev was determined as + 1 mV. Then, after cis perfusion with equimolar NaCl buffer (pH 7.2, horizontal bar) there was only a slight change in Erev (Erev = −2 mV; 4 mV scale). In contrast, Erev increased to + 60 mV after exchanging the cis solution for chamber buffer containing equimolar choline chloride. Substituting into the Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equation (assuming zero permeability to chloride) gives K:Na and K:choline permeability ratios of 1.0:1.1 and 1.0:0.1 respectively. There are two breaks in the record (indicated by //), during which the perfuser was recharged with the appropriate solution. (c) The cytotoxicity of the RRVs in RUSH transfected HEK293 cells is significantly reduced by lowering extracellular Na+ from 150 mM to 85 mM. The rescue from cytotoxicity was indistinguishable between replacement with either K+ or choline+ (n = 9). (d) RRV cytotoxicity was reduced by lowering extracellular Ca2+ from 1.8 mM to 0.45 or 0.1125 mM (n = 12). (e) Reduction of both extracellular Ca2+ and Na+ (replaced by choline+) has an additive effect in lowering RRV cytotoxicity, as seen by further rescue from cell death with 0.45 mM Ca2+ combined with 85 mM Na+ (n = 13). (c–e) Cell death was assayed 12 hr post-biotin treatment with the Promega MultiTox fluorescent assay. Two-way ANOVAs with multiple comparisons were performed. (f) RRV mediated cytotoxicity is driven by the concurrent influx of both Ca2+ and Na+. CHO cells were co-transfected with either RUSH-G0 or G2, GCaMP6f, and the membrane voltage sensor FliCR. G2 cells exhibiting the established phenotype of Ca2+ influx followed by cell swelling were analyzed for changes in membrane voltage (used as a surrogate for the influx of Na+) (n = 21). G0 cells treated with biotin were analyzed for comparison (n = 7). Blue boxes and arrows indicate when the sustained increase in Ca2+ initiates. The representative cells from this figure can be viewed in Figure 6—video 1.
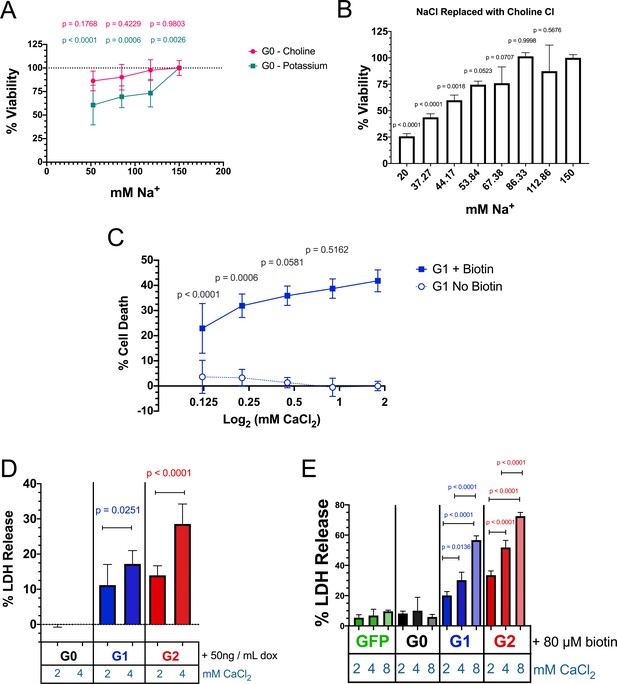
Replacement of Na+ with K+ significantly reduces cell viability.
RRV cytotoxicity is exacerbated with increased extracellular Ca2+. (a) Replacement of extracellular NaCl with KCl for 12 hr significantly reduces cell viability in RUSH-G0 transfected HEK293 cells (no biotin was added) (n = 6). (b) Further replacement of NaCl with choline Cl for 12 hr also reduces cell viability, but only below 86.33 mM Na+ (n = 3). (c) Reduction of extracellular CaCl2 lowers the cytotoxicity of RUSH-G1. (a–c) Cell viability and death were measured 12 hr post-biotin treatment using the Promega MultiTox fluorescent assay. (d–e) Increasing the levels of CaCl2 in the media exacerbates RRV cytotoxicity in both FT293 (d), n = 10) and RUSH-transfected HEK 293 cells (e), n = 3). Cytotoxicity was assayed 24 hr post induction/biotin treatment via release of lactate dehydrogenase. (a, c–e) Analysis was performed with two-way ANOVAs using multiple comparisons. In (a and c), cells incubated with the indicated salt reductions/replacements were compared with the controls in each treatment group. (b) A one-way ANOVA multiple comparisons test was performed.
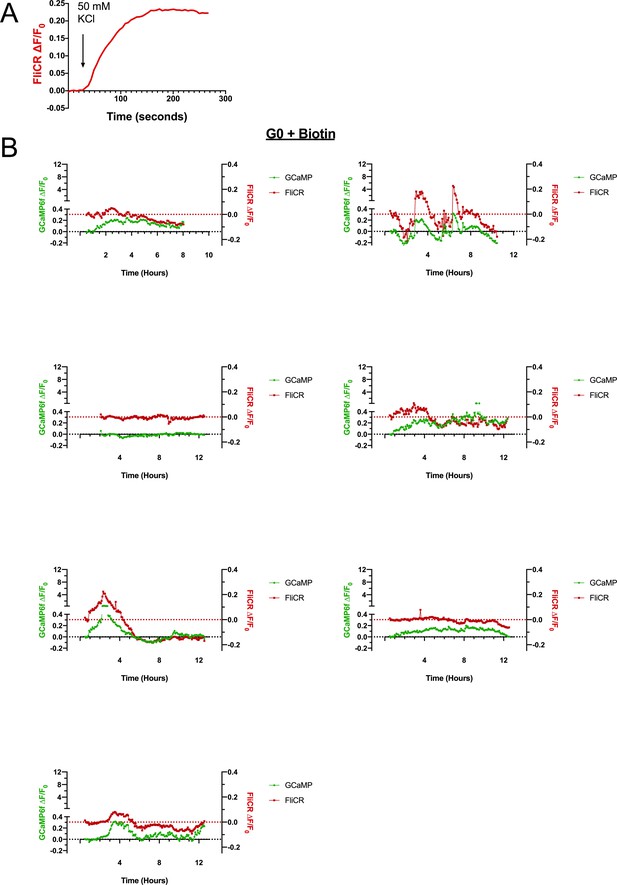
Validation of the FliCR sensor.
Release of RUSH-G0 from the ER does not elicit a sustained increase in cytoplasmic Ca2+ or membrane depolarization. (a) Fluorescent trace of a representative CHO cell transfected with the plasma membrane voltage sensor FliCR. Cells were depolarized by adding 50 mM KCl to the media while imaging. (b) RUSH-G0 does not lead to a sustained increase in GCaMP6f or FliCR fluorescence after biotin treatment (n = 7). Some cells elicit temporary increases in cytoplasmic Ca2+ and membrane voltage, which may be due to signaling events or passage through the cell cycle.
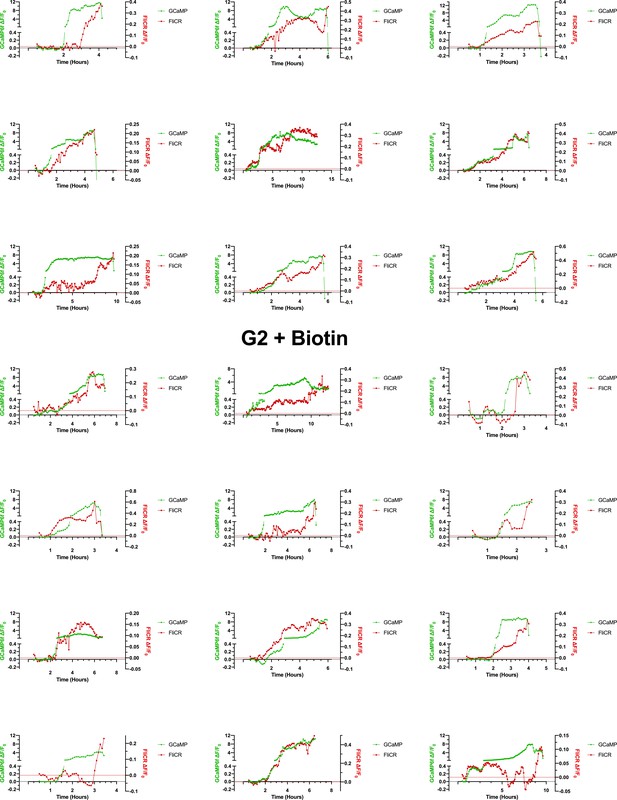
The RUSH-G2-mediated Ca2+ influx occurs concurrently with a modest depolarization of the cell (Na+ influx), followed by complete depolarization prior to cell death.
The G2-mediated Ca2+-influx occurs alongside a Na+ influx (as measured via membrane voltage) (n = 21). Cytoplasmic Ca2+ continues to increase for several hours while the membrane potential either steadily increases alongside it, or becomes erratic and then undergoes depolarization prior to cell death.
The G2-mediated Ca2+ influx occurs concurrently with the influx of Na+.
CHO cells were co-transfected with RUSH-G2, GCaMP6f, and FliCR for 24 hr prior to imaging. On the day of the experiment cells were treated with 80 µM biotin and imaged every 5 min from 0.5 to 12 hr post-biotin (the cells represented here, from Figure 5, underwent lysis by 5 hr). Cells that displayed the established phenotype of Ca2+ influx followed by cell swelling were selected. Scale bar = 20 µm.
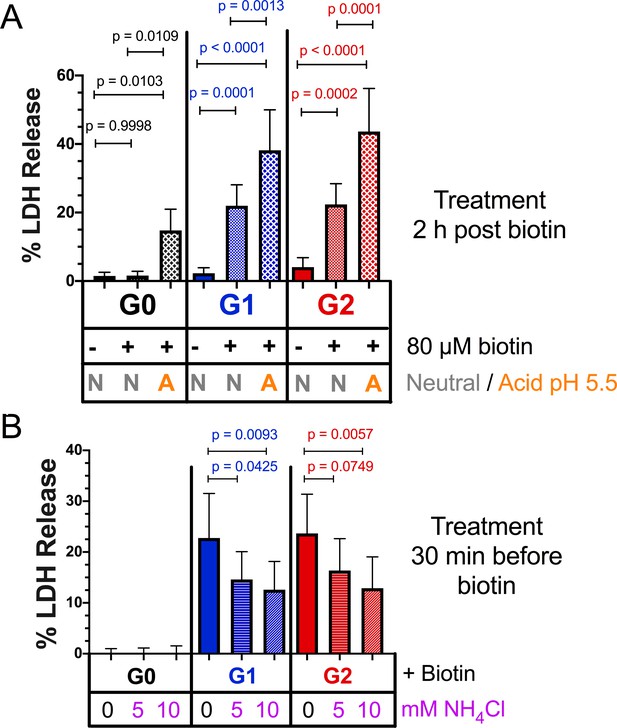
Acidic activation of APOL1 drives channel formation and cytotoxicity.
(a) Acidification and neutralization of RUSH-APOL1 transfected HEK293 cells causes G0 to become cytotoxic and exacerbates the cytotoxicity of G1 and G2. 24 hr after transfection cells were treated with or without 80 µM biotin. 2 hr post-biotin, cells were incubated with media +/- succinic acid at pH 5.5 for 1 hr followed by neutralization. Cytotoxicity was measured 24 hr post-biotin (n = 13). (b) Pre-treatment with ammonium chloride protects against the cytotoxicity of G1 and G2. RUSH-APOL1 transfected HEK293 cells were treated with the indicated amounts of ammonium chloride 30 min prior to biotin treatment. Cytotoxicity was then measured 8 hr after biotin-mediated release (n = 11). (a–b) Cytotoxicity was measured via release of lactate dehydrogenase. A two-way ANOVA comparing treated and untreated cells within each respective genotype was performed.
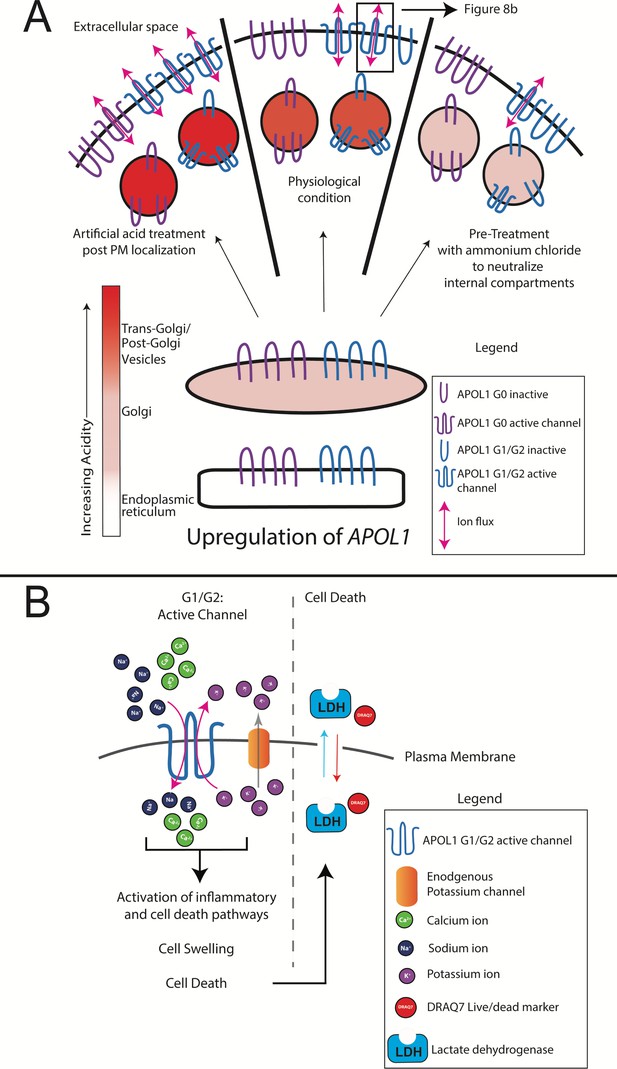
Model of RRV-mediated cytotoxicity: G1 and G2 form cation channels at the PM.
(a) Proposed model of APOL1 trafficking and cytotoxicity. All variants of APOL1 will traffic to the PM, en route they will encounter acidification and neutralization along the secretory pathway, steps required for channel formation. However, while G1 and G2 are able to form cation channels when overexpressed, G0 does not. We hypothesize that G1 and G2 are more sensitive to pH-activation than G0, leading to channel formation. Artificial acidification of cells after localization of APOL1 to the PM caused G0 to become toxic. The increase in G1 and G2 cytotoxicity post-artificial acidification demonstrates that not all APOL1 at the PM is in a channel conformation. Protection against cytotoxicity due to pre-treatment with the weak base ammonium chloride signifies the requirement for acid-activation. (b) At the PM, G1 and G2 channels will lead to an influx of extracellular Na+ and Ca2+, initiating a cascade of events that eventually lead to cell death. Cell death is represented by the assays utilized in this study (release of cytoplasmic lactate dehydrogenase or influx of the live/dead stain DRAQ7).
Videos
Expression of G1 and G2 leads to a Ca2+ influx prior to cell swelling.
FT293 cells were transfected with GCaMP6f 24 hr before imaging. Cells were then incubated with 3 µM DRAQ7 and with or without 50 ng/mL doxycycline to induce APOL1 expression. Cells were imaged via widefield from 4.5 to 30 hr post induction, and dual color images were taken every 10 min. Scale bars = 50 µm.
Expression of RUSH-G1 and G2 leads to Ca2+ influx, swelling, and lysis only after release from the ER.
HEK293 cells were co-transfected with RUSH-APOL1 and GCaMP6f for 24 hr. Prior to imaging, 3 µM DRAQ7 was added and cells were treated with or without 80 µM biotin to release APOL1 from the ER. Cells were imaged via widefield from 1 to 18 hr post-biotin treatment, and dual color images were taken every 5 min. Scale bars = 20 µm.
Expression and ER release of RUSH-G1 and G2 leads to Ca2+ influx and lysis in CHO cells.
CHO cells were co-transfected with RUSH-APOL1 and GCaMP6f for 24 hr. Prior to imaging, cells were treated with or without 80 µM biotin to release APOL1 from the ER. Cells were imaged via widefield from 1 to 12 hr post biotin treatment, and images were taken every 5 min. Scale bars = 20 µm.
Expression and release of RUSH-G1 and G2 does not induce ER Ca2+ release.
CHO cells were co-transfected with RUSH-APOL1, GCaMP6f, and ER-LAR-GECO for 24 hr prior to imaging. On the day of the experiment cells were treated with 80 µM biotin and imaged for 0.5–12 hr post treatment. Cells that displayed the established phenotype of Ca2+ influx followed by cell swelling were selected. Dual color images were taken every 5 min. Scale bars = 20 µm.
Replacement of NaCl with choline Cl or KCl does not affect the G2-mediated Ca2+ influx.
CHO cells were co-transfected with RUSH-G2 and GCaMP6f for 24 hr prior to imaging. On the day of the experiment cells were treated with 80 µM biotin and incubated in media containing 150 mM Na+ (130 mM NaCl), 85 mM Na+ and 65 mM choline+, or 85 mM Na+ and 65 mM K+. The G2-mediated Ca2+ influx was unaffected by reduced Na+. 3 different fields are shown for each condition. Cells were imaged every 5 min from 0.5 to 12 hr post-biotin. Scale bar = 100 µm.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recombinant DNA reagent (Homo sapiens) | APOL1-G0 | NCBI | BC143038.1 | cDNA |
| Recombinant DNA reagent (Homo sapiens) | APOL1-G1 | NCBI | AF305428.1 | cDNA |
| Recombinant DNA reagent (Homo sapiens) | APOL1-G2 | 1000 genomes project, this paper | cDNA *Constructed from mutagenesis from APOL1-G0. Protein coding sequence based off of 1000 genomes data | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent PRG977 | PRG977 | Regeneron | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent and transfected construct pcDNA5/FRT/TO | pcDNA5 | Thermo Fisher | V652020 | APOL1 variants cloned into this plasmid to generate stable cell line (FT293-APOL1_ |
| Recombinant DNA reagent and transfected construct pOG44 | p0G44 | Thermo Fisher | V600520 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent and transfected pcDNA6/Tet-repressor | pcDNA6/Tet-repressor | Thermo Fisher | R25001 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent and transfected Str-KDEL-SBP-EGFP-GPI | RUSH | Addgene | 65293 | Gift from Franck Perez. APOL1 variants cloned into this plasmid for transfection into cells (RUSH-APOL1). GFP and GPI anchor removed |
| Recombinant DNA reagent and transfected pGP-CMVB-GCaMP6f | GCaMP6f | Addgene | 40755 | A gift from Douglas Kim and the GENIE project |
| Recombinant DNA reagent and transfected CMV-ER-LAR-GECO1 | ER-LAR-GECO | Addgene | 61244 | A gift from Robert Campbell |
| Recombinant DNA reagent and transfected CMV-FliCR | FliCR | Addgene | 74142 | A gift from Robert Campbell |
| Sequence based reagent | APOL1_G0 K150E mutagenesis primers | This paper | PCR primer pair | F:5'TGAAAGAGTTTCCTCGGTTGAAAAGTGAGCTTGAGGATAAC R:5'GTTATCCTCAAGCTCACTTTTCAACCGAGGAAACTCTTTCA |
| Sequence based reagent | APOL1-G0 E150 Conversion to G1 mutagenesis Round 1 (S243G) | This paper | PCR primer pair | F:5'CGGATGTGGCCCCTGTAGGCTTCTTTCTTGTG R:5'CACAAGAAAGAAGCCTACAGGGGCCACATCCG |
| Sequence based reagent | APOL1-G0 E150 Conversion to G1 mutagenesis Round 2 (I384M) (Round 1 as template) | This paper | PCR primer pair | F:5'GGAGCTGGAGGAGAAGCTAAACATGCTCAACAATAATTATAAGA R:5'TCTTATAATTATTGTTGAGCATGTTTAGCTTCTCCTCCAGCTCC |
| Sequence based reagent | APOL1-G0 E150 Conversion to G12 mutagenesis | This paper | PCR primer pair | F: 5'AGCTAAACATTCTCAACAATAAGATTCTGCAGGCGGAC R: 5'GTCCGCCTGCAGAATCTTATTGTTGAGAATGTTTAGCT |
| Sequence based reagent | Insertion of APOL1 cDNA into pcDNA 5 vector | This paper | PCR primer pair | F: 5'ATGATATCGCCACCATGGAGGGAGCTG R: 5'ATCTCGAGTCATCACAGTTCTTGGTCCGCCTG |
| Sequence based reagent | Insertion of APOL1 cDNA into RUSH vector | This paper | PCR primer pair | F: 5'ATGCCCTGCAGGAGAGGAAGCTGGAGCGAGG R: 5'ATGCTCTAGACTATCACAGTTCTTGGTCCGCC |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HEK293 | ATCC | CRL-1573 | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | FlpIn HEK 293 | Thermo Fisher | Gift from Dr. Christian Brix Folsted Andersen. Converted into FlpIn TREX293 | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | Conditionally Immortalized Human podocytes | Saleem et al., 2002 | Gift from Dr. Moin Saleem and Dr. Jeffrey Kopp | |
| Cell line (Cricetulus griseus) | CHO | ATCC | CCL-61 | |
| Antibody | Mouse anti-APOL1 | Proteintech | 66124–1-Ig | WB 1:2000 IF 1:800 |
| Antibody | Rabbit anti-APOL1 | Proteintech | 11486–2-AP | WB 1:5000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit anti-GAPDH | Proteintech | 10494–1-AP | WB 1:5000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit anti-Calnexin | Stressgen | SPA-860 | IF 1:200 |
| Antibody | Goat anti-mouse 680RD | LICOR | 92568070 | WB 1:10,000 |
| Antibody | Donkey anti-rabbit 800CW | LICOR | 925–32213 | WB 1:10,000 |
| Antibody | anti-rabbit Alexa 488 plus | Thermo Fisher | A32731 | IF 1:1500 |
| Antibody | anti-mouse Alexa 647 | Thermo Fisher | A21236 | IF 1:1000 |
| Chemical compound, drug | HCS Nuclear Mask | Thermo Fisher | H10325 | IF 1:400 |
| Chemical compound, drug | DRAQ7 | Abcam | ab109202 | Live cell microscopy 3 µM |
| Chemical compound, drug | Thapsigargin | Thermo Fisher | T7458 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Interferon gamma | R and D Systems | 285IF100 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Lactate dehydrogenase assay | Promega | G1781 | Cytotox 96 Non-Radioactive Cytotoxicity Assay |
| Commercial assay kit | MultiTox-Fluor Multiplex Cytotoxicity Assay | Promega | G9201 | |
| Commercial assay kit | Quik Change II Mutagenesis Kit | Agilent | 200523 | |
| Software | TrackMate | Tinevez et al., 2017 | ||
| Software | Prism | GraphPad | ||
| Software | R-multicomp package | Hothorn et al., 2008 |