A phenotypic screening platform utilising human spermatozoa identifies compounds with contraceptive activity
Figures
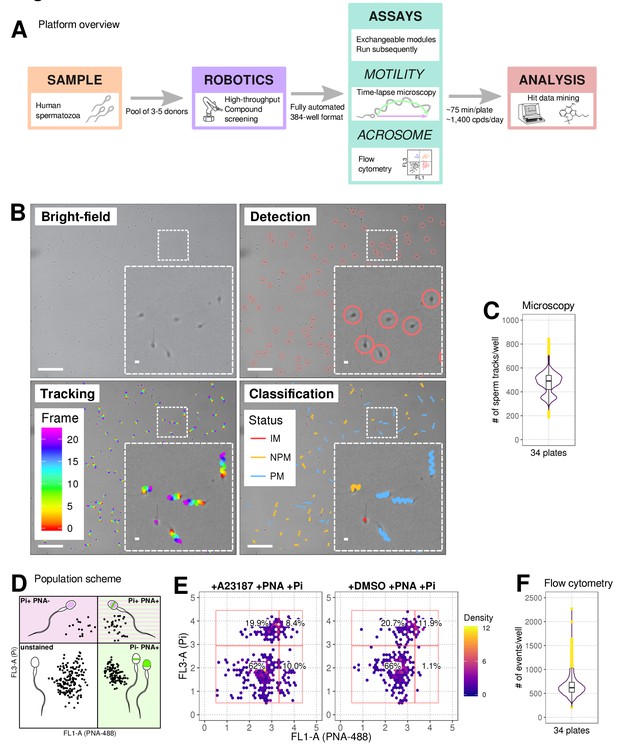
Phenotypic Assay workflows.
(A) Graphical summary of modular screening workflow where motility measurement is followed by acrosome reaction (AR) measurement allowing a screening throughput of >1400 compounds per donor pool (B) Steps in imaging and analysis: human sperm are recorded with brightfield illumination (first panel) then sperm heads detected using a particle tracking algorithm (second panel) which are then tracked across the timelapse series of images (third panel) and subsequently classified (fourth panel). Each panel contains a zoomed-in subsection of the field. Colour coding for tracking distance and kinetic classification is shown in the panel insets: Tracking panel - rainbow gradient (showing progression over time); Classification panel - red for immotile (IM), yellow for non-progressively motile (NPM) and blue for progressively motile (PM). Scale bars: 100 μm (main images), 5 μm (insets). (C) Sperm counts per well after microscopy and detection shown in a combined violin/box plot. Colours: purple violin outline (probability density of values), yellow dots (outliers of boxplot). (D) Graphical summary of the expected populations determined by flow cytometry based on distribution of cells measured with FL3-A (Pi) vertical axis and FL1-A (PNA-488) horizontal axis: dead cells (upper left, Pi+ PNA-); dead and acrosome-reacted (upper right, Pi+ PNA+); unstained/live/non-reacted (lower left) and live acrosome-reacted (lower right, Pi-PNA+). (E) Example flow cytometry data comparing sperm treated with the Ca2+ ionophore (A23187) which induces AR (left panel) with sperm from DMSO-treated well (right panel). Colours indicate event density. (F) Combined violin/box plot data showing flow cytometry event counts per well. Colours and label as in (C).
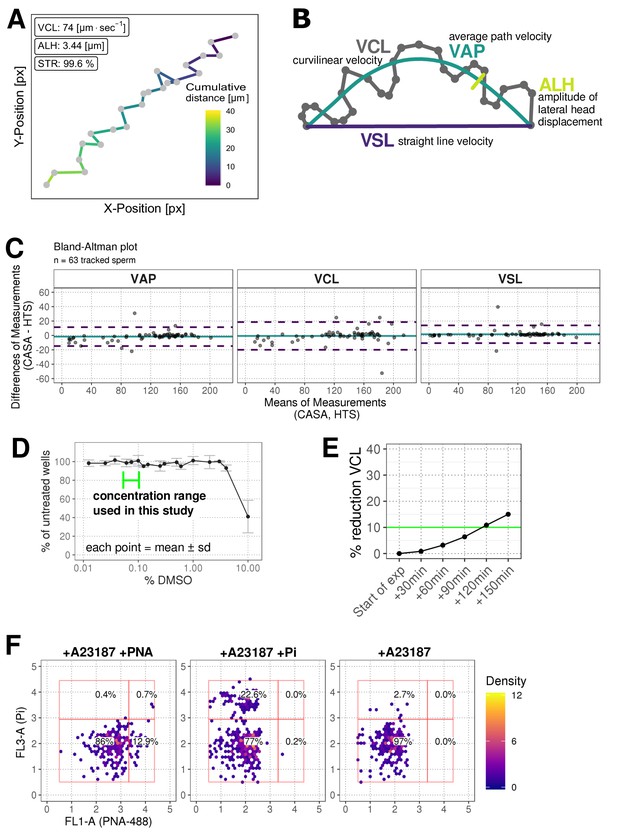
Further characterisation of phenotypic assays.
(A) Example data for a single sperm track with x and y coordinates being used to calculate standard sperm kinetics. Colour represents the cumulative distance travelled in microns. Acronyms: VCL (curvilinear velocity), ALH (amplitude of lateral head displacement; maximum value), STR (straightness ratio). (B) Explanation of main kinematic parameters (VCL, VSL [straight line velocity], VAP [average path velocity] and ALH). (C) Comparison of data from the standard computer-assisted semen analysis (CASA) with the high-throughput system using a Bland-Altman plot of VAP, VCL and VSL. Colours: turquoise line (mean of differences), dashed purple lines (limit of agreement, mean of differences + /- 1.96 * SD). (D) Effect of DMSO on sperm motility (VCL) relative to untreated wells. Green line represents concentration range used in this study (0.0625–0.1%) (E) Effect of pre-dispense incubation time on sperm motility (% reduction in VCL). Colours: green line (arbitrary 10% cut-off). (F) Plots of FL3-A vs FL1-A for the flow cytometry assay controls using acrosome specific PNA-488 dye (FL-1) and cell viability marker propidium iodine (Pi, FL-3) upon addition of A23187 Ca-ionophore. Panels from left to right: with ionophore and acrosome stain; with ionophore and propidium iodide only, with ionophore but unstained. Colours: red rectangles show population gates; coloured hexagons show event density (bin size = 40).
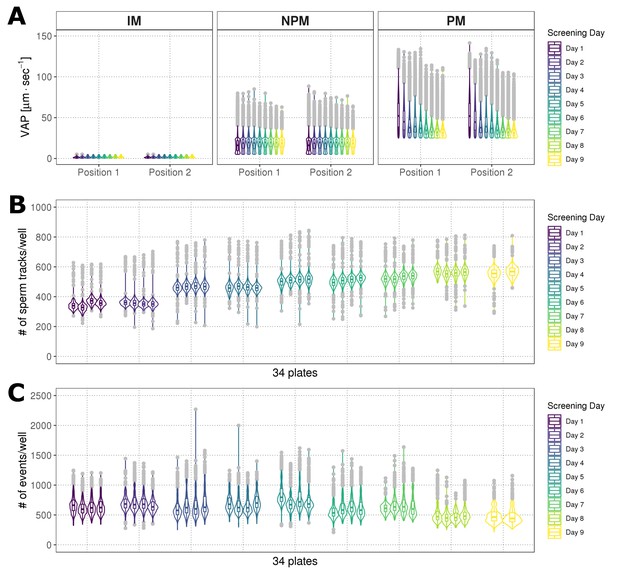
Screening consistency over time analysis.
(A) Distribution of average path velocities (VAP) for sperm motility classes (IM = immotile; NPM = non progressively motile; PM = progressively motile), using data from two positions within each well (Position 1, Position 2), represented as combined box/violin plot. Each box/violin plot is a summary of a screening day (n = 4, 384-well plates). Colours: each screening day is represented as a different colour; grey = boxplot outliers. (B) Distribution of numbers of tracked sperm per well across screening days, represented as combined box/violin plot. Each box/violin plot is a summary of one screening plate. Colours as in (A). (C) Distribution of events identified in the flow cytometry assay, represented as combined box/violin plots. Each box/violin plot is a summary of a screening plate. Colours as in (A).
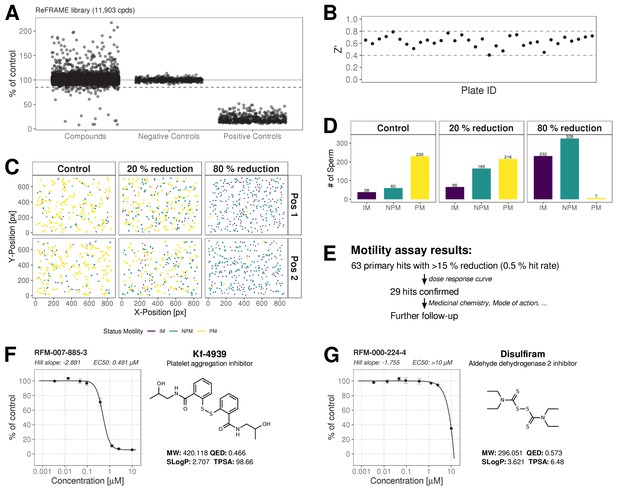
ReFRAME Library Screening: Motility Assay Results.
(A) Primary screening results of the motility assay. Each dot represents a well (either compound or control well) showing % of DMSO control (Curvilinear Velocity: VCL). Positive controls (Pristimerin), negative controls (DMSO) and individual compound datapoints are shown. The dashed line showing the 15% of control (reduction in VCL) – the cut-off for primary hit selection. Total number of compounds = 11,903, excluding wells with auto-focus errors and with ‘sticky’ compounds which have been excluded from analysis. See dataset (http://doi.org/10.5061/dryad.jdfn2z36z) Figure 2—source code 1. (B) Assay robustness: the standard high throughput screening metric, Z' (see Materials and methods; Zhang et al., 1999) was used to determine the performance of the assay for all screening plates. Dashed lines indicate min/max Z' values. (C) Tracking data visualizations of 3 example wells showing sperm tracks of both imaging positions (Position 1 [Pos. 1] and Position 2 [Pos. 2] respectively) within the wells. A DMSO control well (left panels ‘Control’) shows a large number of progressively motile (PM) sperm (yellow) with few non-progressively motile (NPM) sperm (green and very few immotile (IM) sperm (purple) – this is in contrast to the shorter tracks and higher levels of NPM and IM in the middle panel (‘20% reduction’) for a compound that shows 20% inhibition of motility (i.e. 80% of control) and the right hand panel (‘80% reduction’) for a compound showing 80% inhibition (i.e. 20% of control), showing almost all cells are in the IM and NPM classes. (D) Histogram of sperm tracks quantification of the data show in (C). (E) Summary of motility assay hit rate (0.5%) and reconfirmation rate (0.24%). (F-G) Dose response confirmation of two hits. 8-point 3-fold dilution curves are shown with 10 μM as the highest concentration. Two data points per concentration (n = 2, data point is mean ± SD). Each curve is a 4-parameter logistic fit. Each plot shows estimated values Hill Slope and EC50. The chemical structure of the hit compound is shown as well as some annotation and physicochemical properties. Physicochemical properties were calculated using RDKit, Python and KNIME: SlogP = partition coefficient (Wildman and Crippen, 1999); TPSA is the Topological Polar Surface Area (Ertl et al., 2000); MW is the exact Molecular weight; QED = Quantitative Estimate of Drug-likeness (Bickerton et al., 2012).
-
Figure 2—source code 1
R Code for Figure 2 primary motility assay.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/51739/elife-51739-fig2-code1-v2.r
-
Figure 2—source code 2
R Code for Figure 2—source data 1 dose response confirmation motility assay.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/51739/elife-51739-fig2-code2-v2.r
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Dose response and additional data for primary motility hits.
Compound names and nominal target/functional annotation shown on left along with chemical structure and physico-chemical properties. The 8-point dose response curves for each hit with estimated Hill slope, EC50 and Efficacy [% max reduction] are shown on the right. Two data points per concentration (n = 2); data points are Mean ± SD. A 4-parameter logistic fit has been performed using R package: dr4pl. Calculated EC50 values and Efficacy (% max effect) in the motility assay are shown in the right hand section. CC50 values for HEK293 and HepG2 CellTiter-Glo cytotoxicity assays performed by CALIBR (www.reframedb.org) are shown in the right hand section. Note: 0 = inactive in cytotoxicity assay. The chemical structure of the hit compound is shown as well as some annotation and physicochemical properties (for nomenclature description see Figure 2). See Figure 2—source data 2 along with Figure 2—source code 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/51739/elife-51739-fig2-data1-v2.pdf
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Dose response confirmation data motility assay.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/51739/elife-51739-fig2-data2-v2.csv
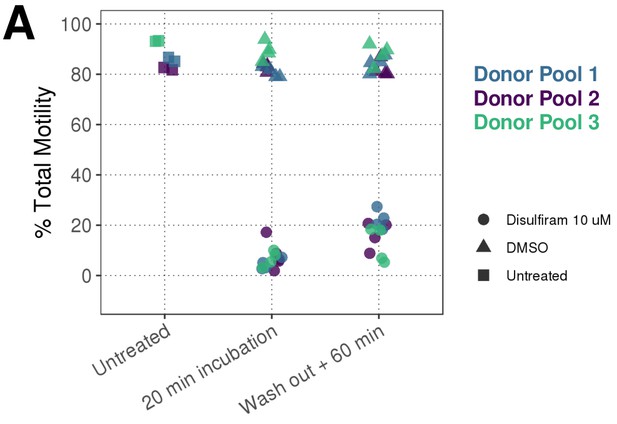
Disulfiram Washout CASA measurement of percentage total motility in samples: prior to treatment (Squares); 20 mins after treatment with DMSO (triangles) or 10 μM disulfiram (circles); 60 min after washout of compound/DMSO.
Different donor pools analysed on three different days are represented by the three different colours. Data shown are four technical replicates per donor pool for DMSO/Disulfiram and two technical replicates for the untreated samples. For each measurement a minimum of 200 cells were recorded. See Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1 along with Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source code 1 .
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source code 1
R code for Figure 2—figure supplement 1 Disulfiram washout assay.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/51739/elife-51739-fig2-figsupp1-code1-v2.r
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Disulfiram washout data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/51739/elife-51739-fig2-figsupp1-data1-v2.csv
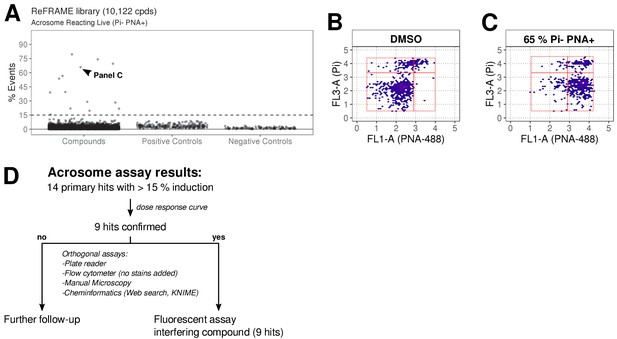
ReFRAME library screening: ar assay results.
(A) Results of primary screening of the library using the acrosome assay (live cells, acrosome reacting, Pi- PNA+ population). Each dot represents a well (either compound or control well). Shown is % Events (number of events in Pi- PNA+ gate relative to total events in the sampled well). Datapoints for compounds, negative controls (DMSO) and positive controls (A23187) are shown. Black dashed line = 15% threshold for primary hits selection. See Figure 3—source data 1 along with Figure 3—source code 1. (B-C) Data from two example wells: a DMSO well (left panel) and a well with 65% Pi- PNA+ population (right panel). (D) Summary of acrosome assay results before and after triage.
-
Figure 3—source code 1
R Code for Figure 2 primary acrosome assay.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/51739/elife-51739-fig3-code1-v2.r
-
Figure 3—source code 2
R Code for Figure 3—source data 2 dose response confirmation acrosome assay.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/51739/elife-51739-fig3-code2-v2.r
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Primary screening data acrosome assay.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/51739/elife-51739-fig3-data1-v2.csv
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Dose response and additional data for primary AR hits.
Compound names and nominal target/functional annotation shown on left along with chemical structure and physico-chemical properties. The 8-point dose response curves for each hit with estimated Hill slope, EC50 and Efficacy [% max induction] values are shown on the right. Two data points per concentration (n = 2); data points are Mean ± SD. A 4-parameter logistic fit has been performed using R package: dr4pl. CC50 values for HEK293 and HepG2 CellTiter-Glo cytotoxicity assays performed by CALIBR (www.reframedb.org) are shown in the right hand section. Note: 0 = inactive in cytotoxicity assay. Physicochemical properties were calculated using RDKit, Python and KNIME: SlogP = partition coefficient (Wildman and Crippen, 1999); TPSA is the Topological Polar Surface Area (Ertl et al., 2000); MW is the exact Molecular weight; QED = Quantitative Estimate of Drug-likeness (Bickerton et al., 2012). See Figure 3—source data 3 along with Figure 3—source code 2 .
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/51739/elife-51739-fig3-data2-v2.pdf
-
Figure 3—source data 3
Dose response confirmation data acrosome assay.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/51739/elife-51739-fig3-data3-v2.csv
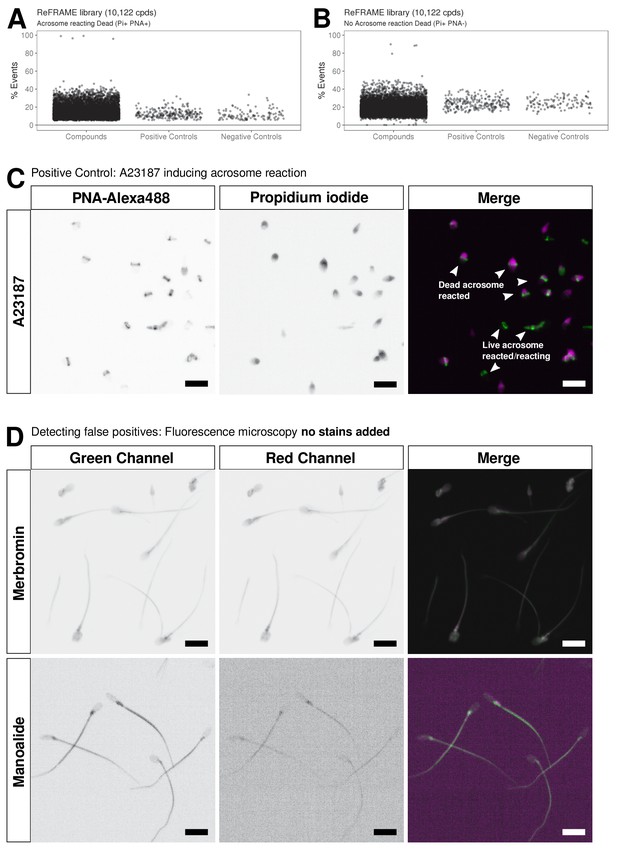
Further analysis of AR screening data and triaging strategy.
Results are shown of primary screening data for two of the other populations in the flow cytometry assay: (A) Acrosome reaction positive and propidium iodide positive (PI+ PNA+) events and (B) acrosome reaction negative and propidium positive (Pi+ PNA-) events. Shown is % Events (number of events relative to total events per well). Datapoints for compounds, negative controls (DMSO) and positive controls (A23187) are shown. See Figure 3—source data 1 along with Figure 3—source code 1 . (C) Control experiment showing microscopy images of A23187-induced acrosome-reacted sperm. Shown are individual channels (greyscale) for acrosome signal stained with PNA-Alexa488 (green band in merged image) and DNA stained with Propidium iodide indicating lack of cell viability (purple in merged image). Scale bar = 10 μM. (D) Orthogonal assay to eliminate fluorescent compounds: Two primary hits were analyzed using fluorescence microscopy without addition of staining reagents: top panels show the non-specific fluorescence of Merbromin and in bottom panels fluorescence of Manoalide which stains only significantly in the midpiece/tail. Grey scale images are shown in the left two panels and a merged image on the right. Key: green channel = Ex 488 nm with Em bandpass filter BP 525/50 nm; red channel = Ex 561 nm; Em Bandpass filter BP600/37 nm). Scale bar = 10 μM.
Videos
Movie was generated using a brightfield image sequence for a typical control well (left pane), a well where a compound reduced motility by 20% (middle pane) and one where it reduced it by 80% (right pane).
Movie was generated using a brightfield image sequence for a typical control well (left pane), a well where a compound reduced motility by 20% (middle pane) and one where it reduced it by 80% (right pane).
Tracking is overlayed in each panel. Colour coding is detailed in Figure 2.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biological sample (Homo sapien) | Live spermatozoa | Donated semen samples | Local ethical approval (13/ES/0091) | |
| Antibody | Lectin PNA (Arachis hypogaea), Alexa Fluor 448 Conjugate | ThermoFisher Scientific | ThermoFisher:L21409; RRID: AB_2315178 | Stored as 1 mg/mL stock in DMSO; used at 1:1000 final dilution |
| Commercial assay or kit | Propidium Iodide; Live/Dead Sperm Viability kit, | ThermoFisher Scientific | ThermoFisher:L7011, | Stored as 2.4 mM stock; used at a 1:2000 final dilution |
| Chemical compound, drug | ReFRAME (Repurposing, Focused Rescue, and Accelerated Medchem) library | CALIBR at the Scripps Institute; Publication (Janes et al., 2018) | www.reframedb.org | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Pristimerin | Merck | Merck:530070 | Stored as 10 mM stock in DMSO; used at final concentration of 20 µM |
| Chemical compound, drug | calcium ionophore (A23187) | Sigma-Aldrich | Sigma-Aldrich:C7522 | Stored as 10 mM stock in DMSO, used at a final concentration of 10 µM) |
| Chemical compound, drug | Disulfiram | Tocris | Tocris:3807 | Stored as 10 mM stock in DMSO, used at 10 μM final concentration |
| Software, algorithm | Trackpy v0.4.1 | Zenodo. (http://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1226458) | Publication: (Crocker and Grier, 1996); Publication: (Allan, 2018) | |
| Software, algorithm | FFMPEG | FFmpeg Developers (http://ffmpeg.org) | RRID:SCR_016075 | |
| Software, algorithm | Bioconductor packages | Bioconductor (https://bioconductor.org) | RRID:SCR_006442 | flowCore, flowDensity, flowWorkspace, ggcyto |
| Software, algorithm | HDF5 | HDF Group (www.hdfgroup.org) | ||
| Software, algorithm | dr4pl | Dr4pl (https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/dr4pl/index.html) | ||
| Software, algorithm | Code used for data analysis | This paper | The R code used for data analysis is included in the supplement files accompanying this paper | |
| Software, algorithm | KNIME | Berthold et al., 2008 | https://www.knime.com | |
| Software, algorithm | RDKit | RDKit, 2018 | https://www.rdkit.org |
Additional files
-
Source data 1
Data of Supplementary file 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/51739/elife-51739-data1-v2.csv
-
Source data 2
Data of Supplementary file 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/51739/elife-51739-data2-v2.csv
-
Supplementary file 1
Compounds that had a significant effect on sperm motility.
Summary of dose response experiments of primary motility hits with estimated EC50 and Efficacy [% reduction] values. Information and names were provided by Calibr. See Source data 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/51739/elife-51739-supp1-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Compounds that had a significant effect on Acrosome Reaction.
Summary of dose response experiments of primary acrosome hits with estimated EC50 and Efficacy [% increase] values. Information and names were provided by Calibr. Note that none of these compounds passed orthogonal counter screening and are considered as assay interfering compounds/false positives. See Source data 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/51739/elife-51739-supp2-v2.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/51739/elife-51739-transrepform-v2.docx





