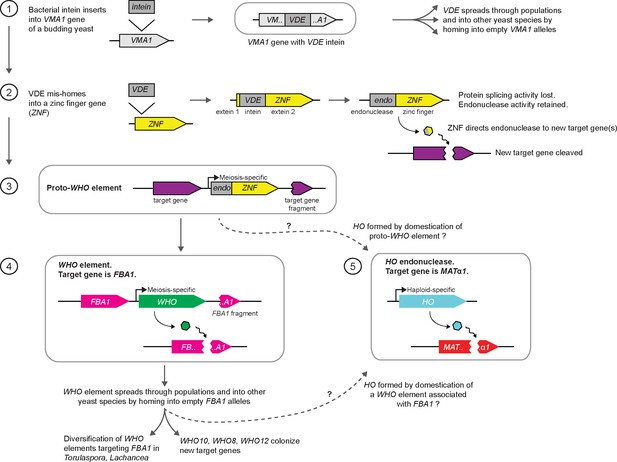
The yeast mating-type switching endonuclease HO is a domesticated member of an unorthodox homing genetic element family
Figures
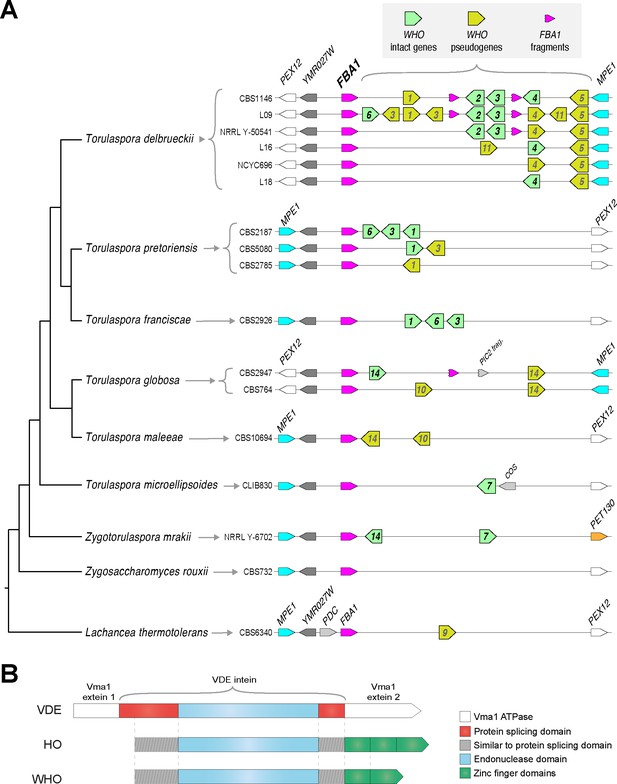
Genomic organization and domain structure of WHO genes.
(A) Polymorphic clusters of WHO genes and pseudogenes downstream of FBA1 in Torulaspora species. Multiple alleles are shown for T. delbrueckii, T. pretoriensis, and T. globosa. WHO genes are indicated by their family number. Fragments of the 3’ end of the FBA1 gene are marked. Genomic views are schematic and not drawn to scale. The phylogenetic tree is based on Shen et al. (2018). (B) Domain structure of HO, VDE and WHO proteins. The protein splicing domain is formed from two regions of the protein that flank the endonuclease domain (Moure et al., 2002).
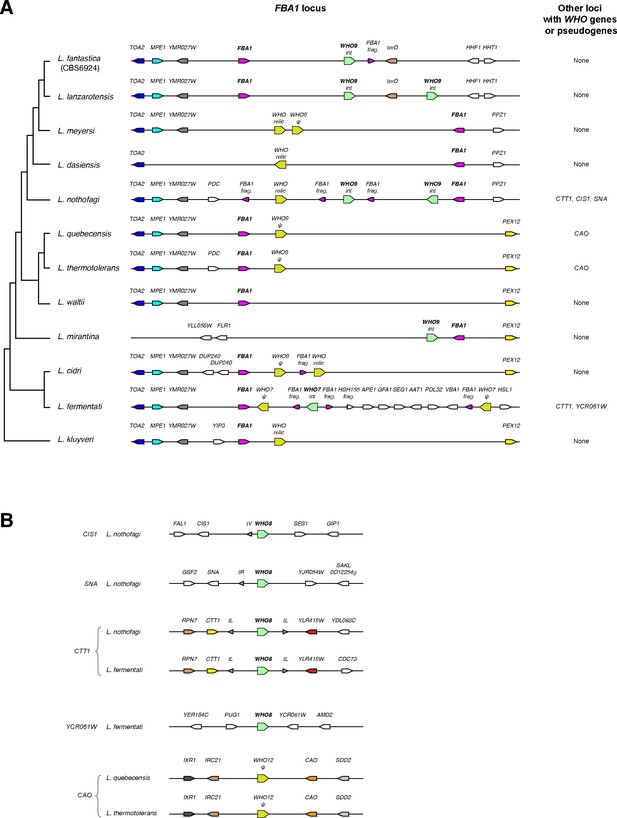
Genomic organization and domain structure of WHO genes in Lachancea species.
(A) WHO genes and pseudogenes downstream of FBA1 in Lachancea species. Fragments of the 3’ end of FBA1 are marked. For WHO genes, ‘int’ indicates an intact gene, ‘ψ” indicates a substantial pseudogene, and ‘relic’ indicates a highly degraded pseudogene. Genomic views are schematic and not drawn to scale. The phylogenetic tree is based on Vakirlis et al. (2016). (B) All WHO genes at locations other than FBA1 in Lachancea species.
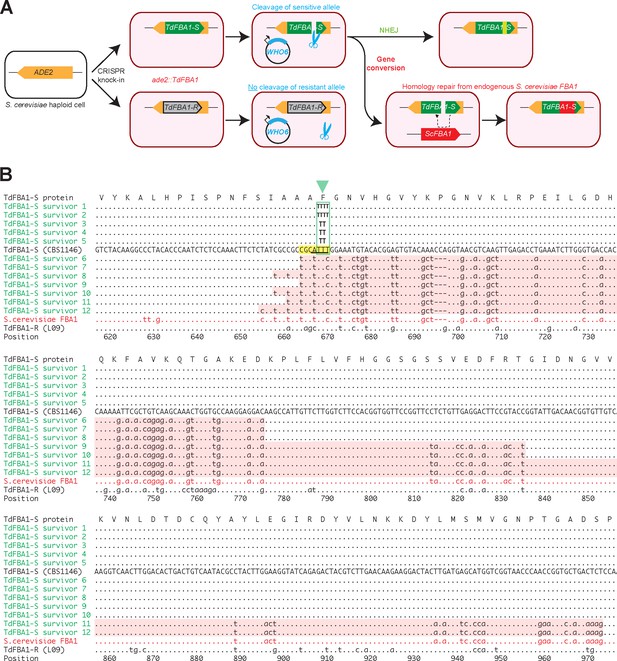
WHO6 induces allele-specific DNA cleavage of the T. delbrueckii FBA1 gene, with DNA repair by gene conversion or NHEJ.
(A) Summary of the experiment. Haploid S. cerevisiae strains, containing a non-expressed T. delbrueckii FBA1 ORF (TdFBA1-S or TdFBA1-R alleles) integrated at ADE2, were transformed multiple independent times with plasmids expressing WHO6 or WHO6-HA. In all transformations of strains containing the TdFBA1-S allele, the only colonies that survived expression of WHO6 were ones in which TdFBA1-S underwent DNA cleavage and repair by gene conversion or imprecise NHEJ, changing its sequence and making it resistant to further cleavage. (B) Gene conversion and imprecise NHEJ events in TdFBA1-S. The reference DNA sequence (uppercase) shows the 3’ end of the TdFBA1-S allele from T. delbrueckii strain CBS1146. Survivors 1–5 are transformants in which TdFBA1-S was cleaved by Who6 and repaired by imprecise NHEJ near position 668 (green box and triangle; survivors 1 and 2 have a 1 bp insertion, and survivors 3–5 have a 1 bp deletion, relative to the sequence TTT in the reference). Survivors 6–12 are transformants in which TdFBA1-S was cleaved by Who6 and partially overwritten by gene conversion with the endogenous S. cerevisiae FBA1 gene. Gene conversion regions are highlighted with pink backgrounds. The TdFBA1-R allele from T. delbrueckii strain L09, which is the natural host of WHO6, is also shown; this allele acquired no sequence changes among 10 independent pWHO6 transformants examined. A putative Who6 recognition site (yellow) and cleavage site with 4 bp 3’ overhang (underlined) are marked. Survivors 10 and 11 are from transformations with pWHO6-HA; all other survivors are from transformations with pWHO6. The complete TdFBA1 gene was sequenced from all transformants but only positions 616 to 975 are shown; there were no changes outside this region.
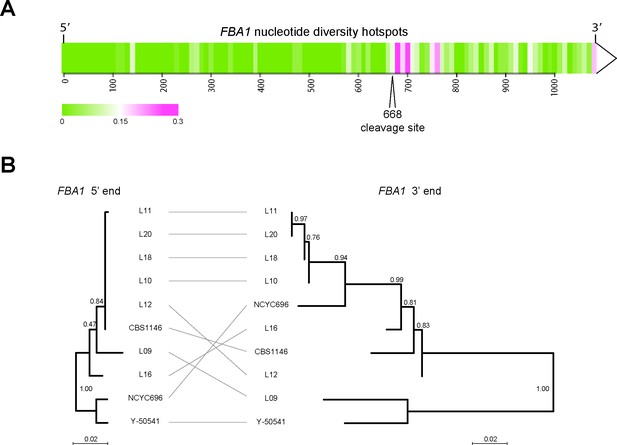
Different evolutionary dynamics of the 5’ and 3’ parts of T. delbrueckii FBA1.
(A) Heatmap showing regions of nucleotide sequence diversity (π) among 15 sequenced FBA1 alleles from T. delbrueckii isolates, plotted in 10 bp windows. (B) Inconsistency of phylogenetic trees obtained from the 5’ and 3’ ends of FBA1 alleles from different T. delbrueckii strains (5’ end: bases 1–667; 3’ end: bases 669–1083). The alleles from strains CBS1146 and L09 are also called TdFBA1-S and TdFBA1-R, respectively. The trees are drawn to the same scale and were generated from nucleotide sequences using PhyML as implemented in Seaview v4.5.0 (Gouy et al., 2010) with default parameters. Bootstrap support from 1000 replicates is shown.
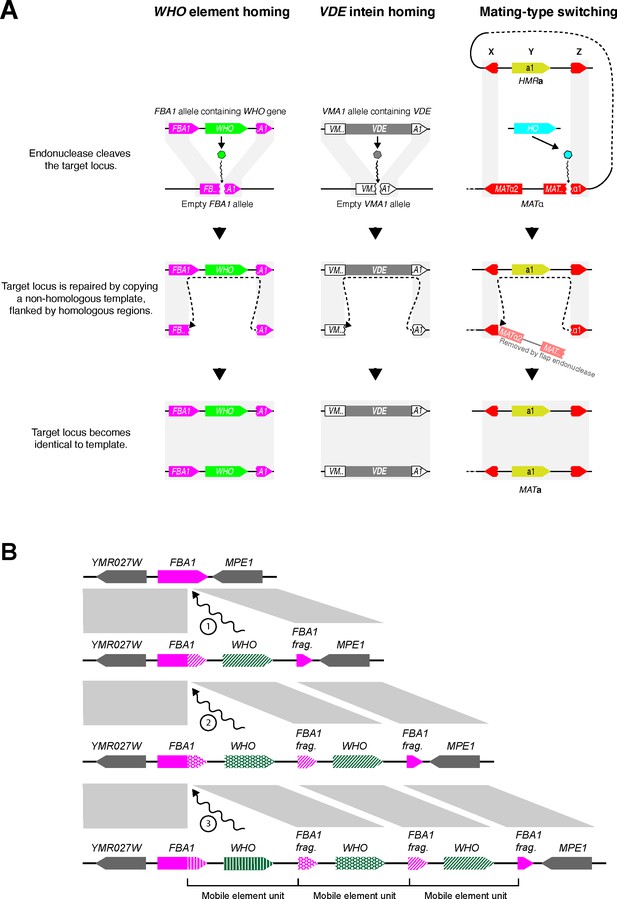
Proposed mechanism of WHO element homing.
(A) Similarity of mechanisms of action of WHO, VDE and HO. The mechanism we propose for WHO elements integrating at FBA1 is compared to the known mechanisms for VDE integrating into VMA1 and for HO-mediated switching of the MAT locus (Gimble and Thorner, 1992; Lee and Haber, 2015). WHO and VDE homing occur between allelic chromosomes in a diploid cell, whereas mating-type switching occurs between MAT and HML/HMR loci in a haploid cell. Gray rectangles indicate regions of sequence identity. The column on the right shows mating-type switching from MATα to MATa in S. cerevisiae. Switching from MATa to MATα occurs by an identical mechanism; the core of the HO recognition site (CGCAACA) is the first 7 nucleotides of the Z region, which is present in both of the MAT alleles even though it is part of the MATα1 gene sequence. The HO gene is on a different chromosome than MAT-HML-HMR. (B) Model for WHO cluster formation by successive integration of WHO elements. Every time a WHO element integrates into the locus, the 3’ end of the full-length FBA1 gene is replaced. The previous 3’ end is pushed rightwards, together with any older WHO genes, after which they can decay into pseudogenes. The complete WHO mobile element unit consists of a WHO gene and the upstream 3’ end of FBA1, which confers resistance to it.
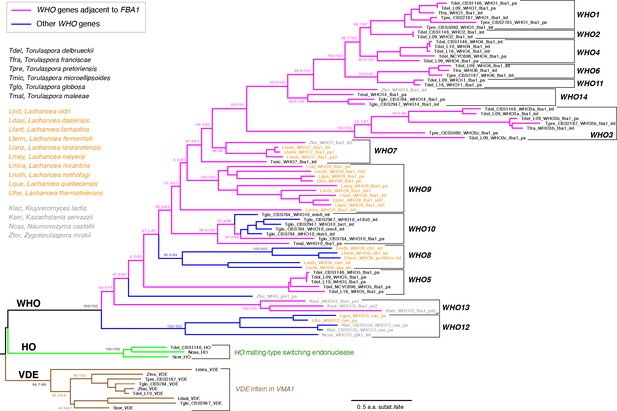
Families of WHO genes and their phylogenetic relationship to HO and VDE.
Magenta branches indicate WHO genes that are located at the FBA1 locus, and blue branches indicate WHO genes that are not beside FBA1. 14 WHO families are marked by brackets. Individual WHO gene names are colored by their source genus (black, Torulaspora; orange, Lachancea; gray, other genera). WHO gene names indicate the source species and strain number (if multiple strains were analyzed), WHO family (in uppercase), the name of a neighboring gene in the genome (in lowercase), and the suffix ‘int’ for intact WHO genes or ‘ps’ for WHO pseudogenes. Protein sequences were aligned using MUSCLE and filtered with Gblocks as implemented in Seaview v4.5.0 (Gouy et al., 2010). Badly degraded pseudogenes (relics) were not included. The tree was constructed by maximum likelihood using IQ-TREE v1.6.12 (Trifinopoulos et al., 2016), utilizing the built-in model finder option. Numbers on branches show support values from SH-aLRT and 1000 ultrafast bootstraps, separated by a slash (Trifinopoulos et al., 2016). The tree was rooted using VDE because WHO and HO share a zinc finger domain.
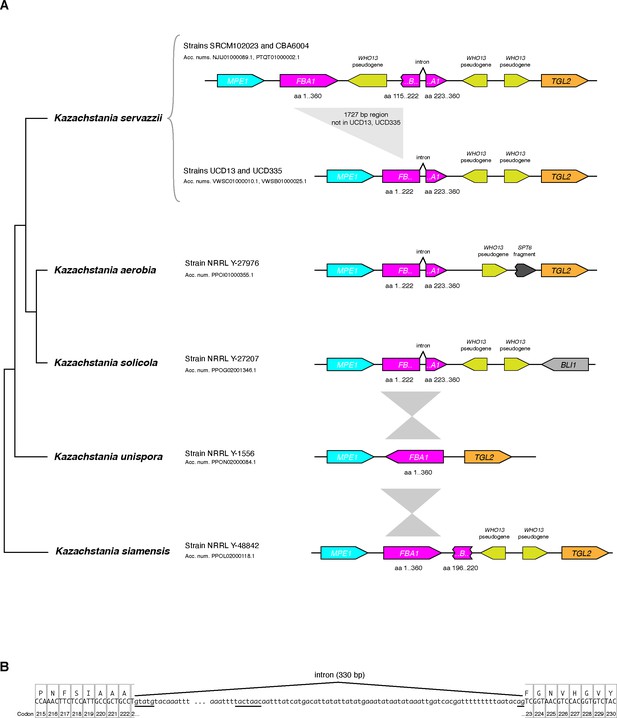
Some Kazachstania species have an intron in FBA1 at a location corresponding to the WHO cleavage site in Torulaspora.
(A) Genome organization around FBA1 in Kazachstania servazzii and its close relatives. Data from 4 strains of K. servazzii are shown. FBA1 genes, exons and fragments are colored magenta and their amino acid coordinates in the Fba1 protein are indicated. The phylogenetic tree topology is from Shen et al. (2018) and Vaughan-Martini et al. (2011). The genomes of 13 other species of Kazachstania that are outgroups to the ones shown here have no FBA1 intron and no WHO genes (data from Shen et al., 2018). (B) Sequence of the intron in the FBA1 gene of K. servazzii strain UCD13. The intron is located between the first and second bases of codon 223. Intron sequence is shown in lowercase, with exons and their translations in uppercase. Core intron sequence motifs are underlined.
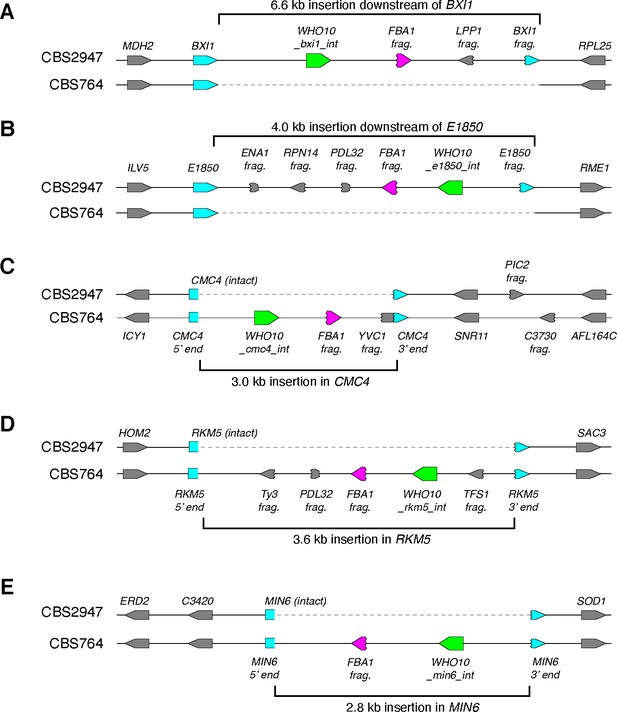
WHO10 is an active mobile genetic element in T. globosa and integrates into loci other than FBA1.
Each panel shows a pair of allelic regions from T. globosa strains CBS2947 and CBS764T. Intact WHO10 genes are shown in green, FBA1 fragments in magenta, and host genes in blue. (A-E) Five strain-specific insertions of WHO10 elements into different host loci. At the BXI1 and E1850 loci of CBS2947 (A,B), the 3’ end of the host gene became duplicated, whereas at the CMC4, RKM5 and MIN6 loci of CBS764 (C-E) the host gene was disrupted by the insertion and no part of it became duplicated. All the integrations contain a fragment of FBA1 immediately downstream of WHO10, and most also contain fragments of other genes. Genes are named after their S. cerevisiae orthologs where possible. E1850 is the T. globosa ortholog of T. delbrueckii TDEL0E01850, a gene with no homolog in baker’s yeast.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (Torulaspora delbrueckii) | FBA1 | Gordon et al., 2011 | TDEL0B06660; NCBI: XM_003679958 | Strain CBS1146; TdFBA1-S allele |
| Strain, strain background (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) | IMX585 | Mans et al., 2015 | S. cerevisiae strain with integrated CAS9 gene | |
| Strain, strain background (Torulaspora delbrueckii) | L09; L10; L11; L12; L13; L15; L16; L18; L19; L20 | This paper | Strain collection of Lallemand, Inc | |
| Strain, strain background (Torulaspora delbrueckii) | NCYC696 | National Collection of Yeast Cultures (UK) | ||
| Strain, strain background (multiple Torulaspora species) | All CBS strains | Westerdijk Fungal Biodiversity Institute (Netherlands) | ||
| Strain, strain background (Torulaspora pretoriensis) | UWOPS 83–1046.2 | MA Lachance, University of Western Ontario (Canada) | ||
| Strain, strain background (Zygotorulaspora mrakii) | NRRL Y-6702 | CP Kurtzman, USDA Agricultural Research Service | ||
| Strain, strain background (Naumovozyma castellii) | Y056 (NRRL Y-12630T); Y174 (CBS4310); Y287 (CBS3006); Y668 (CBS1579) | Jure Piškur, Lund University (Sweden) | See Spírek et al., 2003 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMEL13 plasmid | Mans et al., 2015 | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | ADE2.Y sgRNA template | DiCarlo et al., 2013 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pIL75-KanMX plasmid | Liachko and Dunham, 2014 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pWHO6 | This paper | DNA sequence is in Supplementary file 3 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pWHO6-HA | This paper | DNA sequence is in Supplementary file 3 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pGFP-HA | This paper | DNA sequence is in Supplementary file 3 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Sc ade2::TdFBA1-S repair template | This paper | DNA sequence is in Supplementary file 3 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Sc ade2::TdFBA1-R repair template | This paper | DNA sequence is in Supplementary file 3 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Primers for PCR of Sc ade2::TdFBA1 locus | This paper | 5’-TGACCACGTT AATGGCTCC-3’ and 5’-CACCAGCTCCA GCGATAATTG-3’ | |
| Software, algorithm | SPAdes assembler | Bankevich et al., 2012 | V3.11.1 | RRID:SCR_000131 |
| Software, algorithm | HGAP3 assembler | Chin et al., 2013 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
T. delbrueckii genome sequence data used in this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/55336/elife-55336-supp1-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Other genome sequence data used in this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/55336/elife-55336-supp2-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 3
Sequences of the plasmids pWHO6, pWHO6-HA and pGFP-HA, and of the ade2::TdFBA1-S and ade2::TdFBA1-R constructs.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/55336/elife-55336-supp3-v2.txt
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/55336/elife-55336-transrepform-v2.docx