The structures of secretory and dimeric immunoglobulin A
Figures
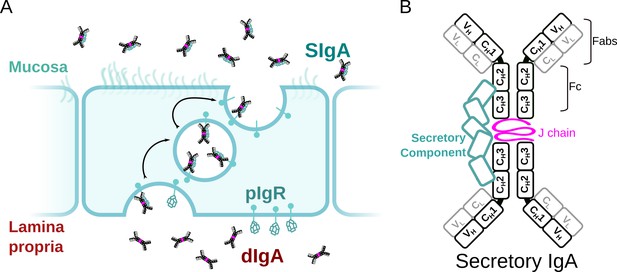
SIgA delivery to the mucosa.
(A) Schematic depicting unliganded pIgR binding to dIgA from the lamina propria on the basolateral surface of an epithelial cell followed by transcytosis to the apical membrane and SIgA release into the mucosa. (B) Schematic showing protein components of SIgA, including two IgA monomers, joining chain (JC), and secretory component (SC). The IgA heavy chain is colored white with a black outline and the light chain is colored white with a gray outline. Each chain is made up of immunoglobulin domains, including IgA heavy chain constant (CH1-3), heavy chain variable (VH), light chain constant (CL), and light chain variable (VL),domains, which are indicated along with antigen-binding fragments (Fabs) and Fc regions.

Sequence identity, similarity, and alignments between mouse and human SIgA components.
(A) Sequence identity and similarity calculated between the indicated mouse and human sequences. (B) Sequences of the mouse SIgA structure components aligned to homologous human sequences. The sequences for individual protein domains are separated by line and labeled; identical residues are highlighted in red. Molecular contacts between JC, SC and each heavy chain observed in the SIgA structure are indicated by squares. Each square denotes an interfacing residue described in the main text and/or within 4 Å of a residue on another chain. Squares are colored according to the key at the bottom of the figure; contacts occurring between the four heavy chains are not indicated.
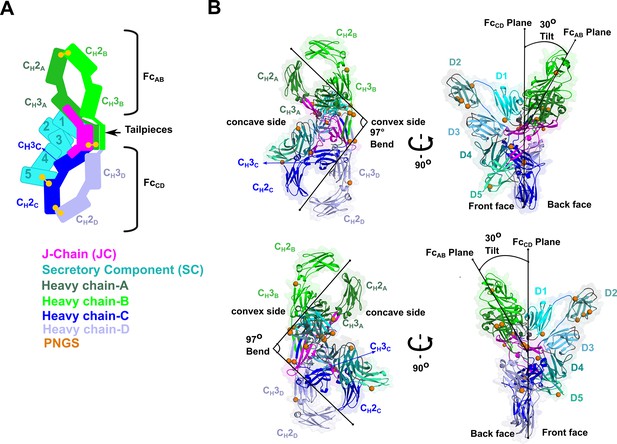
SIgA structure.
(A) Schematic representing ordered domains in the SIgA structure. The relative position of each SIgA component is approximated based on the structure. Chain IDs and corresponding CH domains and Fcs are labeled along with SC domains (1-5). Each SIgA component is depicted in a unique color; J chain (JC), magenta; secretory component (SC), teal; heavy chains A, dark green, B, light green, C, dark blue, and D, light blue, respectively. (B) Cartoon representation (with semi-transparent molecular surface) of the SIgA structure shown in four orientations and colored as in (A). CH and SC domains (D1-D5) are labeled and PNGS are shown as orange spheres. The bend and tilt between the two Fcs are indicated with a line and the angle measured in the structure; the concave and convex sides are labeled, along with the front face and the back face.
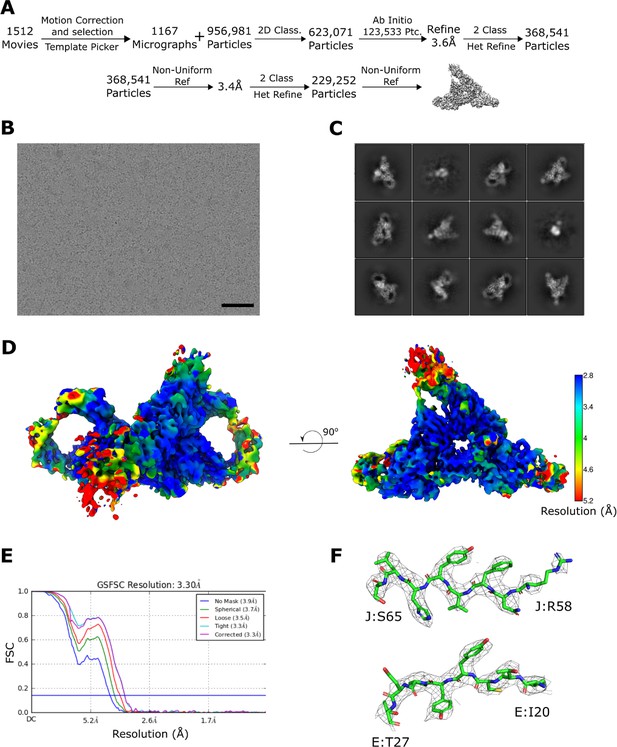
SIgA cryoEM data collection and CryoSparc processing pipeline.
(A) Schematic summary of the data processing pipeline of SIgA reconstruction in cryoSparc2. (B) Representative micrograph (scale bar – 50 nm) and (C) 2D class averages. (D) Local resolution map of the final structure calculated in cryoSparc2 with FSC cut off at 0.143 threshold and prepared in ChimeraX; the scale bar was generated in Chimera. (E) FSC curves for the final reconstruction with reported resolution at FSC = 0.143 shown by the blue horizontal line. (F) Densities from the J and E chains contoured to 8σ and carved at 1.6 Å cutoff.
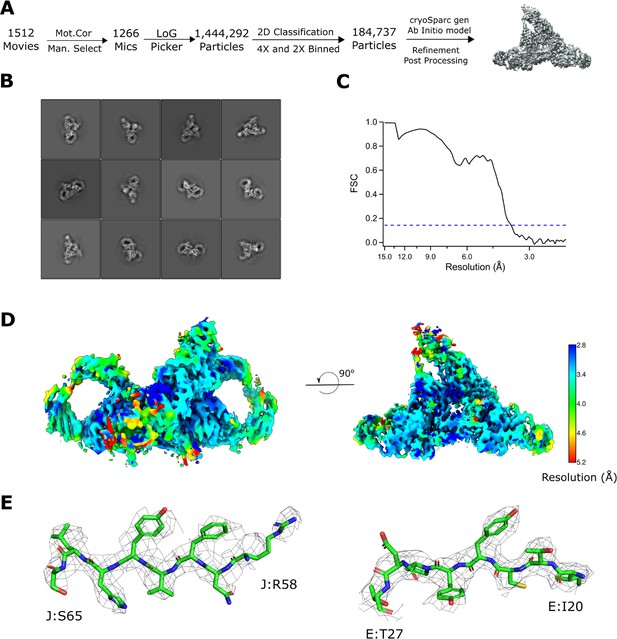
SIgA cryoEM data collection and Relion processing pipeline.
(A) Schematic summary of the data processing pipeline of SIgA reconstruction in Relion. (B) Representative 2D class averages. (C) FSC curve for the final reconstruction with reported resolution at FSC = 0.143 shown by the horizontal dashed line. (D) Local resolution map of the final structure calculated in cryoSparc2 with FSC cut off at 0.143 threshold and prepared in ChimeraX; the scale bar was generated in Chimera. (E) Densities from the J and E chains contoured to 8σ and carved at 1.6 Å cutoff.
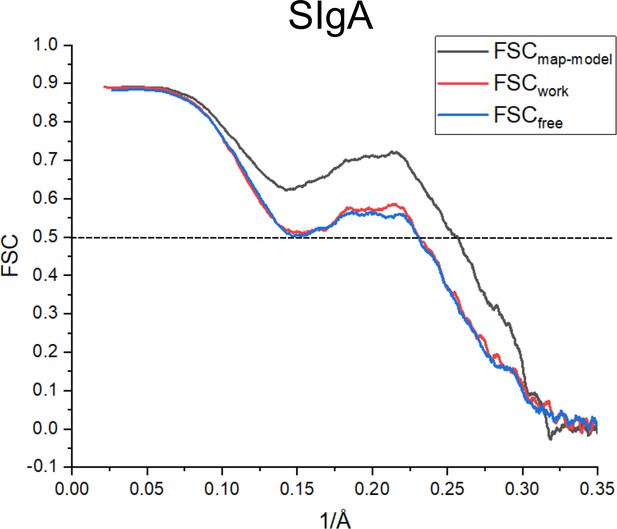
SIgA cross-validation FSC curves.
The FSC curve generated between the final structure and CryoEM map including all data (FSCmap-model) is shown in black and indicates agreement between the map and final model. FSCwork (red) is the FSC curve generated between the final structure refined against half the data (half map 1) and half map 1. FSCfree (blue) is the FSC curve generated between the final structure refined against half map 1 and the other half of the data (half map 2), not used in refinement calculations. Close agreement between, FSCwork and FSCfree indicate that the model has not been overfit to the map.
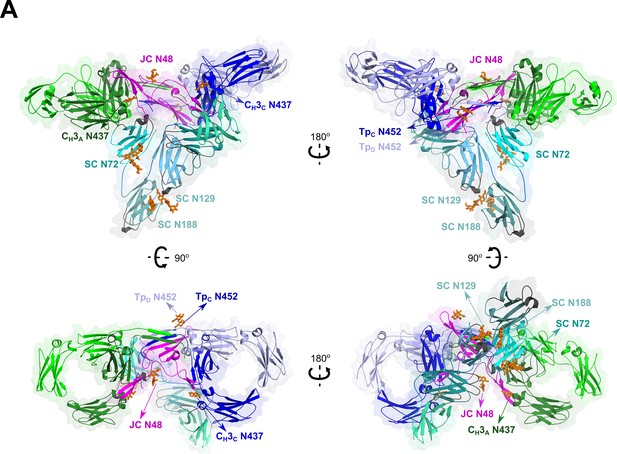
SIgA glycosylation.
Cartoon representations of SIgA structure with ordered glycosylation shown as sticks. The structure is shown in four orientations and colored as in Figure 2.
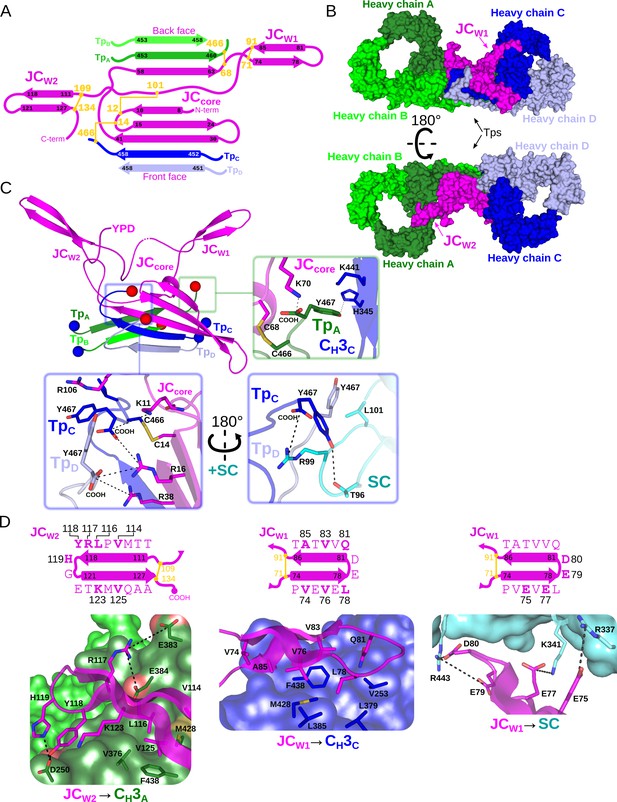
Fc dimer interface and JC structure.
(A) Schematic depicting the topology that arises from JC and its interactions with four Tps and colored as in Figure 2. JC regions (JCW1, JCW2, JCcore, and N- and C termini) are labeled along with TpA-D and their location relative to the front face or back face of SIgA; disulfide bonds are indicated in yellow and the residue boundaries of each β-strand are labeled. (B) SIgA molecular surface representation (SC removed) colored as in Figure 2 and indicating the location of JCW1, JCW2 and Tps relative to each HCA-D in two SIgA orientations. (C) Cartoon representation of JC and Tps complex (same region as shown in panel A) with the N- and C termini of each Tp shown as blue and red spheres, respectively. Regions surrounding the three C-terminal residues of Tp are boxed, TpA (green box), and TpC and TpD (blue boxes), and enlarged. Enlargements show Tp carboxy termini (COOH) and side chain sticks involved in interactions with adjacent Tps, JC, CH3 domains, and SC. The three C-terminal residues of TpB are disordered and not shown. (D) Topology diagram and sequence (top) and structure (bottom) detailing interactions between JCW2 and CH3A (left), JCW1 and CH3C (center), and JCW1 and SC (right) and colored as in A-C. JC residues interacting with CH3 or SC are indicated in bold and numbered in the topology diagram (top) and shown as sticks on a cartoon representation (bottom); CH3 and SC domains are shown as molecular surface representations with interfacing residues shown as sticks. Negatively charged atoms in CH3 that form contacts are shown as a red surface.
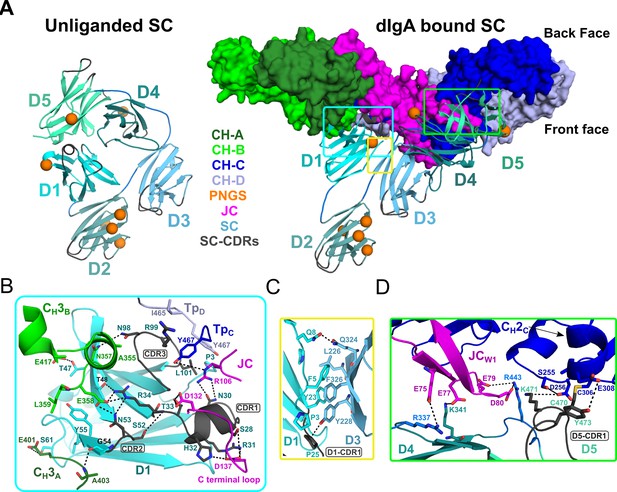
SC Structure.
(A) Cartoon representations of an unliganded mouse SC homology model based on unliganded human SC crystal structure (PDB code 5D4K; left) and the dIgA-bound mouse SC (right). The dIgA is shown as a molecular surface representation; SC domains D1-D5 are show in color gradient from cyan (D1) to pale green (D5), with CDR loops colored gray; PNGS are shown as orange spheres. Regions where SC interfaces with dIgA and other SC domains are boxed. (B-D) Boxed, enlarged views of stabilizing interfaces between SC Fc, JC and other SC domains; colored as in panel A. (B) SC D1 interface with CH3A, CH3B, TpC, TpD. (C) SC D1-D3 interface. (D) SC D4-D5 interface with JC and CH2C. In all panels conserved, interfacing residues are shown as sticks and hydrogen bonds and salt bridges are show as black dashes.
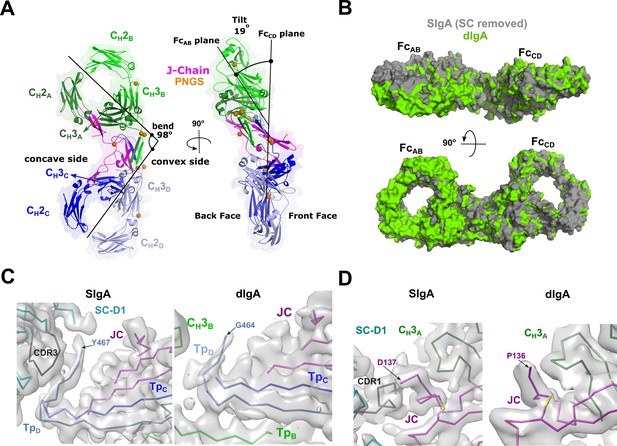
dIgA structure.
(A) Cartoon representation (with semi-transparent molecular surface) of the unliganded dIgA structure shown in two orientations and colored as in Figure 2. The bend and tilt between the two Fcs is indicated with a line and the angle measured in the structure; the concave and convex sides are labeled, along with the front face and the back face and CH domains. PNGS are shown as orange spheres. (B) Molecular surface representation of SIgA (gray; SC removed) aligned to dIgA (green) on the JC from each complex structure. (C) CryoEM maps and structures for SIgA (right) and dIgA (left) detailing the region surrounding TpD. (D) CryoEM maps and structures for SIgA (right) and dIgA (left) detailing the region surrounding the JC C-terminus.
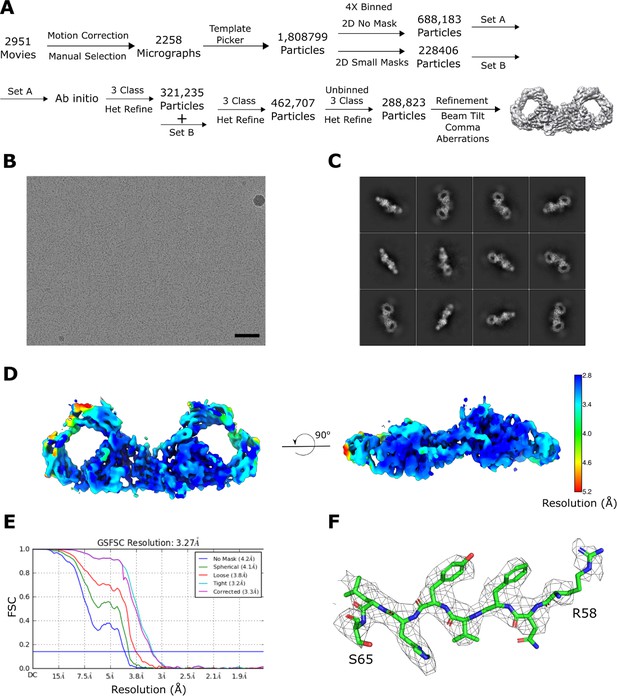
dIgA cryoEM data collection and processing strategy.
(A) Schematic summary of the data processing pipeline of dIgA reconstruction in cryoSparc2. (B) Representative micrograph (scale bar – 50 nm) and (C) 2D class averages. (D) Local resolution map of the final structure calculated in cryoSparc2 with FSC cut off at 0.143 threshold. (E) FSC curves for the final reconstruction with reported resolution at FSC = 0.143 shown by the blue horizontal line. (F) Densities from the J chain contoured to 8σ and carved at 1.9 Å cutoff.
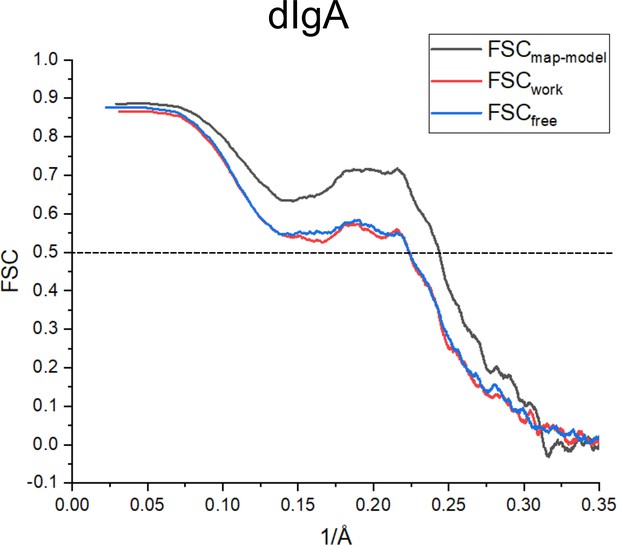
dIgA cross-validation FSC curves.
The FSC curve generated between the final structure and CryoEM map including all data (FSCmap-model) is shown in black and indicates agreement between the map and final model. FSCwork (red) is the FSC curve generated between the final structure refined against half the data (half map 1) and half map 1. FSCfree (blue) is the FSC curve generated between the final structure refined against half map 1 and the other half of the data (half map 2), not used in refinement calculations. Close agreement between, FSCwork and FSCfree indicate that the model has not been overfit to the map.
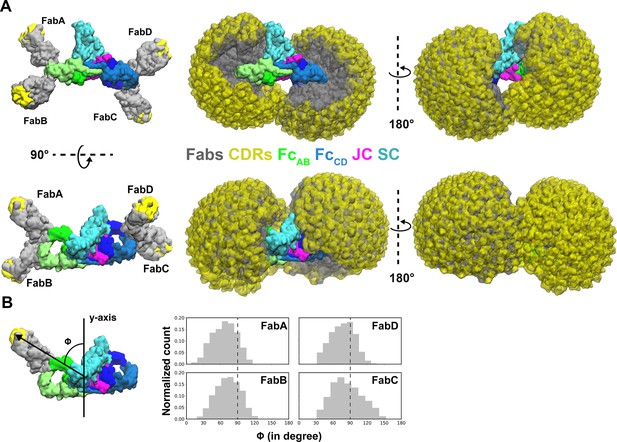
Modeling of Fabs and CDRs on SIgA.
(A) SIgA structure shown with four Fabs, each modeled in a single position as well as all possible positions and shown in multiple orientations. Complex components are colored according to the key (center). (B) The number of positions sampled by Fab CDRs were quantified by measuring the angle (ϕ) between the Fab vector and the y-axis, a vector parallel to the FcAB plane and passing through the center of mass of Fc and JC. The frequency (normalized count) of each angle is shown as a histogram.
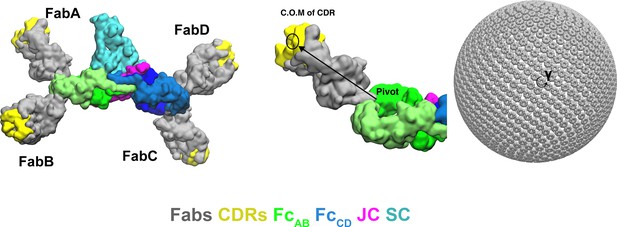
Modeling strategy for the computational search of SIgA Fab positions.
(Left) SIgA structure shown with four modeled Fabs in one orientation. (Right) Schematic showing how Fab positions were modeled by mapping a vector, spanning from the N-terminal residue in the CH2 domain (pivot) to the center of mass (C.O.M) of the CDRs (yellow), onto a Fibonacci spherical lattice (FSL) with one thousand points and γ angle intervals of 45°.
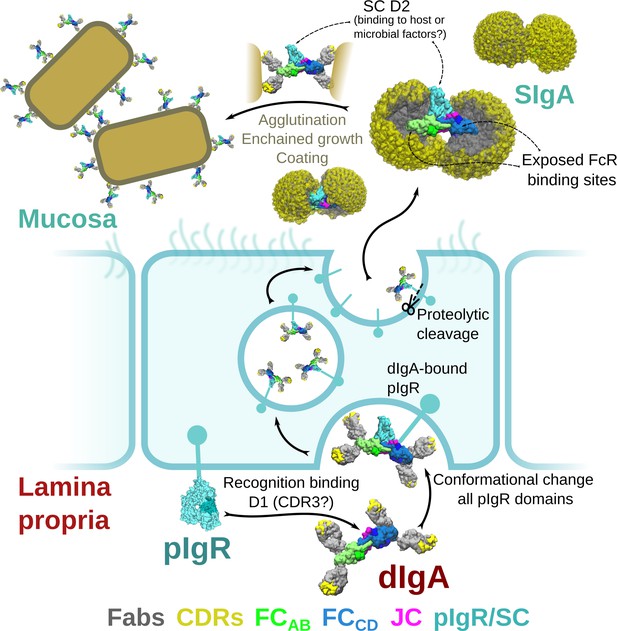
Model for the formation, transport,and function of SIgA.
Schematic summary depicting the unliganded SC structure (pdb code 5D4K) as pIgR bound to basolateral surface of an epithelial cell in its closed conformation and recognizing bent dIgA from the lamina propria. The pIgR binding to dIgA triggers a conformation change that repositions its domains to facilitate numerous stabilizing contacts with dIgA. The dIgA-pIgR complex transcytoses to the apical membrane where the pIgR is proteolytically cleaved, releasing SIgA into the mucosa. In the mucosa, SIgA Fabs (shown in all possible modeled positions) are directed toward the concave side of the antibody ‘looking’ for potential antigens while its Fc-receptor-binding regions are exposed on the convex side and accessible to potential host or microbial receptors. SC domains are also partially exposed; the D2 domain is almost completely accessible, protruding out of the SIgA where it may bind host and bacterial factors. Upon encountering antigen, SIgA Fabs bind, promoting antigen coating, agglutination, or enchained growth.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Other | IGHA_MOUSE | UniProtKB RRID:SCR_004426 | UniProtKB: P01878 | Amino acid sequence of Mus musculus IgA heavy chain constant regions |
| Other | LAC1_MOUSE | UniProtKB RRID:SCR_004426 | UniProtKB: P01843 | Amino acid sequence of Mus musculus lambda-1 light chain constant region |
| Other | IGJ_MOUSE | UniProtKB RRID:SCR_004426 | UniProtKB: P01592 | Amino acid sequence of Mus musculus joining chain |
| Other | PIGR_MOUSE | UniProtKB RRID:SCR_004426 | UniProtKB: O70570 | Amino acid sequence of Mus musculus polymeric Ig Receptor |
| Other | STA121 | Moor et al., 2017 | Variable region of human IgA2 antibody STA121 | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HEK Expi293F | Thermo Fisher RRID:SCR_008452 | Cat#: A14635 RRID:CVCL_D615 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pD2610-v1 | ATUM | Cat#: pD2610-v1-03 | Mammalian expression plasmid |
| Transfected construct (Homo sapiens) | STA121 IgA Heavy chain (HC) in pD2610v1 | Materials and methods of this paper | Construct encoding STA121 heavy chain (HC) variable region fused to Mus musculus IgA HC constant domains | |
| Transfected construct (Homo sapiens) | STA121 IgA light chain (LC) lambda in pD2610v1 | Materials and methods of this paper | Construct encoding STA121 light chain (LC) variable region fused to Mus musculus lambda LC constant domain | |
| Transfected construct (Homo sapiens) | Mouse Secretory component (SC) in pD2610v1 | Materials and methods of this paper | Construct encoding residues 1–567 of Mus musculus pIgR (a.k.a. secretory component; SC) | |
| Transfected construct (Homo sapiens) | Mouse joining chain (JC) in pD2610v1 | Materials and methods of this paper | Construct encoding Mus musculus joining chain (JC) | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | STA121 Secretory IgA | Materials and methods of this paper | Protein complex produced from transfected constructs and containing: STA121 HC, STA121 LC, JC, SC | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | STA121 dimeric IgA | Materials and methods of this paper | Protein complex produced from transfected constructs and containing: STA121 HC, STA121 LC, JC | |
| Other | CaptureSelect LC-lambda (Mouse) Affinity Matrix | Thermo Fisher RRID:SCR_008452 | Cat#: 194323005 | Affinity matrix for protein purification |
| Other | Superose 6 Increase 10/300 GL | GE Healthcare Life Sciences RRID:SCR_000004 | Cat#: 29091596 | Size exclusion column for protein purification |
| Software, algorithm | Rosetta CryoEM refinement package | Wang et al., 2016 | RRID:SCR_015701 | |
| Software, algorithm | Phenix | Afonine et al., 2018a; Afonine et al., 2018b | Phenix RRID:SCR_014224 Phenix.refine RRID:SCR_016736 | |
| Software, algorithm | Pymol Molecular Graphics System | Schrodinger LLC RRID:SCR_014879 | RRID:SCR_000305 | |
| Software, algorithm | RELION-3 | Scheres, 2012; Zivanov et al., 2018 | RRID:SCR_016274 | |
| Software, algorithm | UCSF Chimera | Pettersen et al., 2004; Yang et al., 2012 | RRID:SCR_004097 | |
| Software, algorithm | UCSF ChimeraX | Goddard et al., 2018 | RRID:SCR_015872 | |
| Software, algorithm | cryoSPARC v.2 | Punjani et al., 2017 | RRID:SCR_016501 | |
| Software, algorithm | VMD | Humphrey et al., 1996 | RRID:SCR_001820 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
CryoEM data collection and refinement statistics associated with SIgA and dIgA structures.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56098/elife-56098-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56098/elife-56098-transrepform-v2.docx





