Chronic postnatal chemogenetic activation of forebrain excitatory neurons evokes persistent changes in mood behavior
Figures
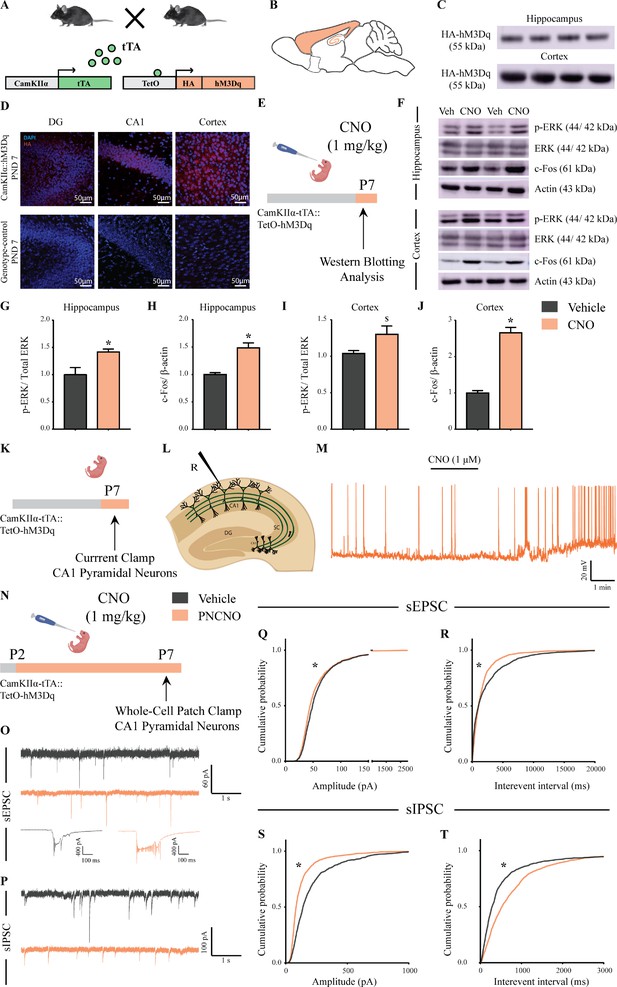
Selective expression and activation of hM3Dq DREADD in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons in CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic mice during the postnatal window.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental strategy for the generation of the bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq mouse line to selectively drive the expression of the hM3Dq DREADD in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons. tTA – tetracycline transactivator. (B) Shown is a schematic sagittal view of the mouse brain indicating the region of hM3Dq DREADD expression. (C) Western blots indicate expression of the HA-tag in the hippocampus and the cortex confirming the presence of HA-tagged hM3Dq DREADD (n = 4). (D) Shown are representative confocal images indicating expression of hM3Dq DREADD in the DG, CA1, and cortex as identified by HA immunofluorescence, which was not observed in the genotype-control mice (n = 3 per group). (E) Shown is the experimental paradigm to assess activity-related signaling signatures following acute CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons at P7. The mice were fed a single dose of either CNO (1 mg/kg) or vehicle and sacrificed 15 min later for western blotting analysis (n = 4 per group). (F) Representative western blots indicate the expression of the neuronal activity-related proteins, p-ERK and c-Fos in the hippocampus and cortex of CNO and vehicle-treated CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic mouse pups. Densitometric quantification revealed a significant CNO-mediated, hM3Dq DREADD activation evoked increase in p-ERK/ERK (G) and c-Fos (H) expression in the hippocampi of CNO-treated pups as compared to the vehicle-treated controls (n = 4 per group). In the cortex, hM3Dq DREADD activation resulted in a trend toward an increase in p-ERK/ERK (I) and a significant increase in c-Fos (J) protein levels in the CNO-treated pups. Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. *p<0.05, $p=0.07 as compared to vehicle-treated controls using the two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test. (K–L) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm for whole-cell patch clamp recording from the somata of CA1 pyramidal neurons at P7 in acute hippocampal slices derived from drug-naïve, bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq mouse pups. R – Recording electrode. (M) Bath application of CNO (1 μM) to acute hippocampal slices resulted in hM3Dq DREADD activation mediated robust spiking activity of CA1 pyramidal neurons (n = 3 cells). (N) Experimental paradigm to assess the effects of chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using whole-cell patch clamp recording. CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic mouse pups were fed either CNO (1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P2 to P7 followed by recording of sEPSCs and sIPSCs. (O) Shown are representative sEPSC traces of vehicle and PNCNO-treated mice at P7. Top traces: examples of small amplitude events. Bottom traces: examples of large-amplitude events. (P) Shown are representative sIPSC traces of vehicle and PNCNO-treated mice at P7. (Q) PNCNO-treated mice showed significantly altered cumulative probability of sEPSC amplitude with a small decrease at lower amplitudes (<100 pA) and a significant increase in large-amplitude events characterized by a long-tail as compared to vehicle-treated controls. (R) PNCNO-treated mice showed a significant decline in the cumulative probability of sEPSC interevent intervals as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 7 cells for vehicle; n = 10 cells for PNCNO). PNCNO-treated mice showed a significant decrease in sIPSC amplitude (S), and a concomitant increase in sIPSC interevent intervals (T) as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 6 cells for vehicle; n = 8 cells for PNCNO). Results are expressed as cumulative probabilities. *p<0.001 as compared to PNCNO-treated group using Kolmogorov-Smirnov two-sample comparison.
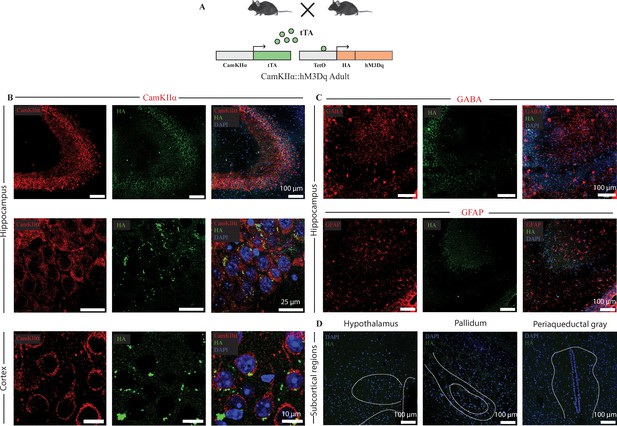
Selective expression of the HA-tagged hM3Dq DREADD in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons in adult CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic mice.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental strategy for the generation of the bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq mouse line to selectively drive the expression of the HA-tagged hM3Dq DREADD in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons. tTA – tetracycline transactivator. (B) Shown are representative confocal images indicating expression of the HA-tagged hM3Dq DREADD in the Hippocampus (upper and middle panels), and cortex (lower panel) as identified by HA/CamKIIα double immunofluorescence. The HA-tagged hM3Dq DREADD appears to be localized to the membrane of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons as observed in higher magnification photomicrographs. (C) HA-tagged hM3Dq DREADD expression was not observed in either GABA-positive neurons (upper panel), or GFAP-positive astrocytes (lower panel). (D) Immunofluorescence experiments revealed the lack of expression of HA-tagged hM3Dq DREADD in subcortical brain regions. Shown here is the lack of expression for the HA-tagged hM3Dq DREADD in the hypothalamus, pallidum and periaqueductal gray in sections stained for HA expression. All immunofluorescence experiments to address co-localization of the HA-tagged hM3Dq DREADD with neuronal excitatory and inhibitory markers, and astrocyte markers were performed on n = 4 per group.
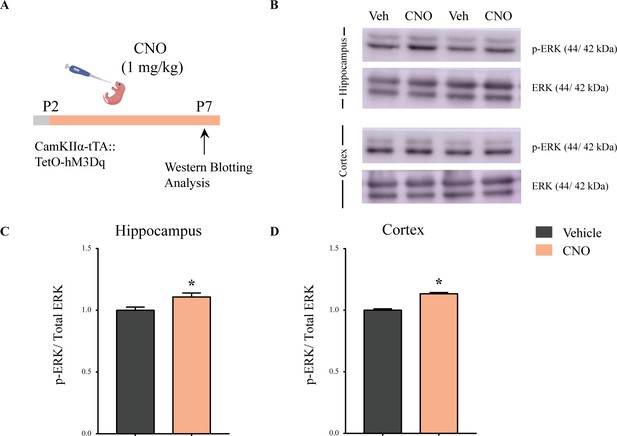
Enhanced p-ERK/ERK expression following chronic postnatal hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons.
(A) Experimental paradigm to assess the influence of chronic PNCNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons on p-ERK/ERK expression. CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic mouse pups were fed either CNO (1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P2 to P7, followed by sacrifice on P7 for western blotting analysis. (B) Representative western blots indicate the expression of the neuronal activity-related protein p-ERK, as compared to total ERK levels in the hippocampus and cortex of vehicle and chronic PNCNO-treated CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic mouse pups. Densitometric quantification revealed a significant hM3Dq DREADD activation mediated increase in p-ERK/ERK in the hippocampus (C) and the cortex (D) of the CNO-treated pups as compared to the vehicle-treated controls. Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. *p<0.05 as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 4 per group) using the two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test.
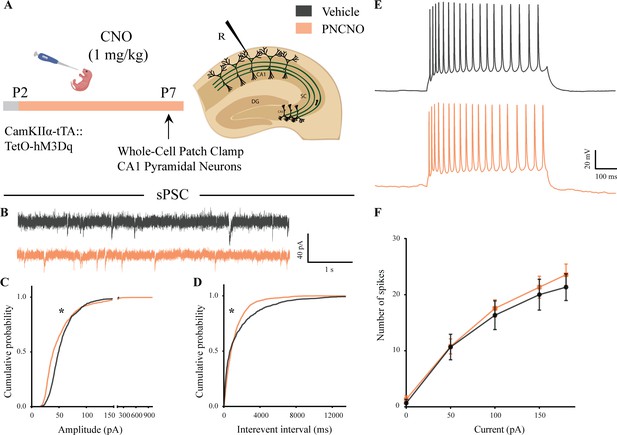
Spontaneous network activity and intrinsic excitability following chronic postnatal hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons.
(A) Shown is the experimental paradigm to assess the effects of chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using whole-cell patch clamp. CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic mouse pups were fed either CNO (1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P2 to P7, followed by recording of input-output characteristics and sPSCs. Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm for current clamp recording from the somata of CA1 pyramidal neurons at P7. (B) Shown are representative sPSC traces of vehicle and PNCNO-treated mice at P7. (C) PNCNO-treated mice showed significantly altered cumulative probability of sPSC amplitude with a small decrease at lower amplitudes (<100 pA) and a significant increase in large-amplitude events characterized by a long-tail as compared to vehicle-treated controls. (D) PNCNO-treated mice showed a significant decline in the cumulative probability of sPSC interevent intervals as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 7 cells for vehicle; n = 10 cells for PNCNO). Results are expressed as cumulative probabilities. *p<0.001 as compared between vehicle and PNCNO-treated group using Kolmogorov-Smirnov two-sample comparison. (E) Representative traces of spikes generated by CA1 pyramidal neurons following a current injection of 100 pA. (F) No significant change was observed in the input-output characteristics of the PNCNO-treated pups as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 6 cells for vehicle; n = 9 cells for PNCNO).
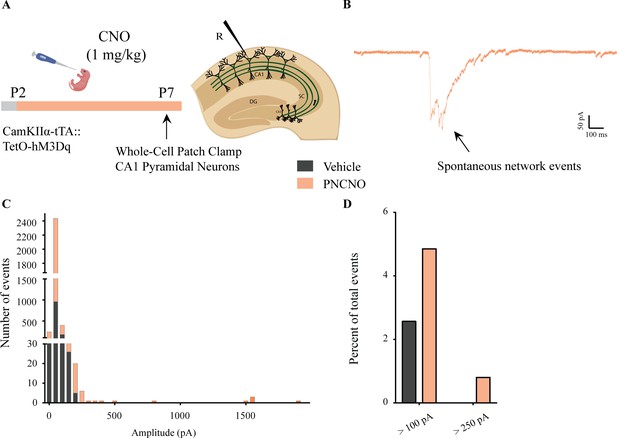
Distribution of spontaneous network events following chronic postnatal hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons.
(A) Shown is an experimental paradigm to assess the effects of chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using whole-cell patch clamp. CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic mouse pups were fed either CNO (1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P2 to P7 followed by recording of sPSCs (n = 7 cells for vehicle; n = 10 cells for PNCNO). (B) Example trace of a large-amplitude spontaneous network event observed in the CA1 pyramidal neuron of a PNCNO-treated pup. (C) Distribution plot for sPSC amplitudes showing a long-tail of large-amplitude events in PNCNO-treated mice. (D) Quantification of percent of total events with amplitude >100 pA and >250 pA. No event >250 pA was observed in vehicle-treated pups.
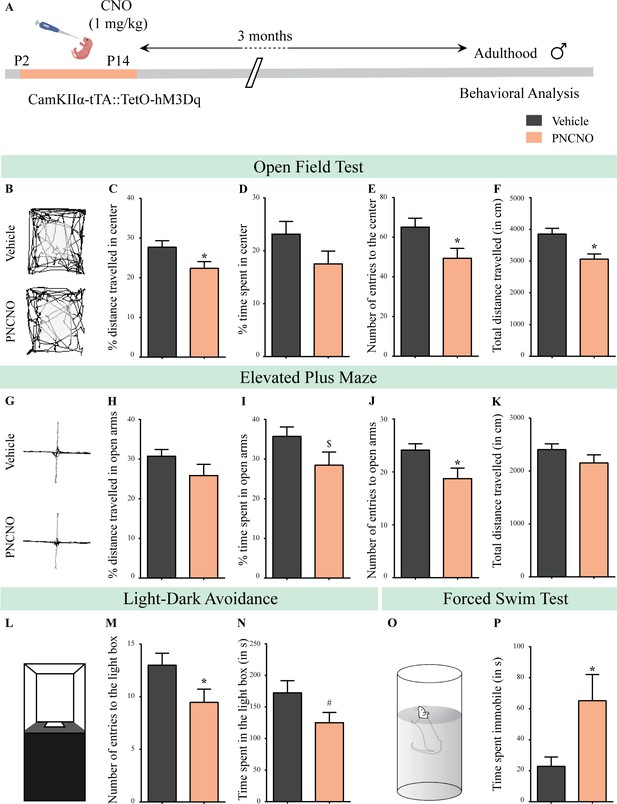
Chronic chemogenetic activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons during the early postnatal window results in a long-lasting increase in anxiety- and despair-like behavior in adult male mice.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm to induce chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq mouse pups that were fed CNO (PNCNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P2 to P14 and then left undisturbed for 3 months prior to behavioral analysis performed in adulthood on male mice. (B) Shown are representative tracks of vehicle or PNCNO-treated CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic adult male mice in the open field test (OFT). A history of chronic postnatal hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons resulted in increased anxiety-like behavior on the OFT in adulthood, as noted by a significant decrease in the percent distance traveled in center (C), number of entries to the center (E), and the total distance traveled in the OFT arena (F) in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 15 per group). The percent time spent in the center was not significantly altered (D) in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls. (G) Shown are representative tracks of vehicle or PNCNO-treated CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic adult mice on the elevated plus maze (EPM). Adult mice with chronic postnatal hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons exhibited increased anxiety-like behavior on the EPM as revealed by a significant decrease in the number of entries to the open arms (J), and a trend toward a decrease in percent time spent in the open arms (I) in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 15 per group). The percent distance traveled in the open arms (H) and the total distance traveled in the EPM arena (K) was not altered in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls. (L) Shown is a schematic of the light-dark box used to assess anxiety-like behavior. Chronic postnatal hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons resulted in an increased anxiety-like behavior in the LD box test in adulthood, as revealed by a significant decline in the number of entries to the light box (M), and a trend toward decline in the time spent in the light box (N) in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 15 per group). (O) Shown is a schematic representation of the forced swim test (FST) apparatus used to assess despair-like behavior. Chronic postnatal hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons resulted in an increased despair-like behavior on the FST in adulthood, as revealed by a significant increase in time spent immobile (P) in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 13 per group). Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. *p<0.05, $p=0.08, #p=0.07; as compared to vehicle-treated controls using the two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Source data for Figure 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56171/elife-56171-fig2-data1-v2.xlsx
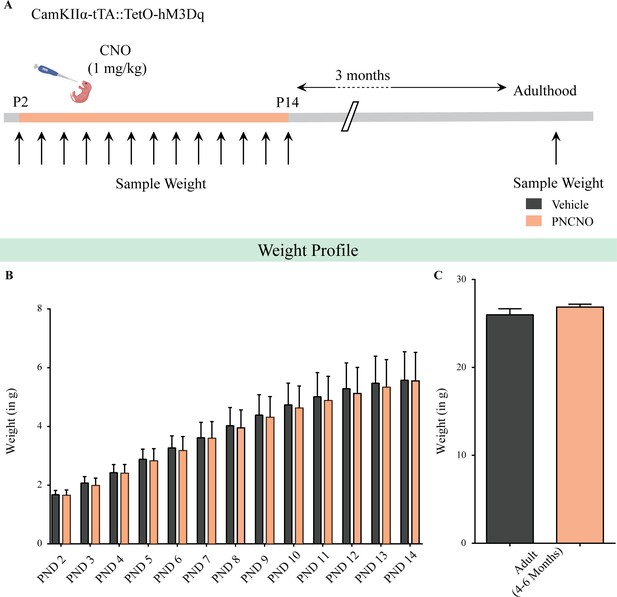
Chronic chemogenetic activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons during the early postnatal window does not alter weight during CNO administration and in adulthood.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm used to determine the influence of chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons in CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic mouse pups from P2 to P14 on gross weight during the time of treatment and in adulthood. (B) CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic mouse pups fed with CNO (1 mg/kg) once daily from P2 to 14 did not show any significant change in gross weight across the duration of treatment as compared to their vehicle-treated controls (n = 9 for vehicle; n = 11 for PNCNO). (C) Adult CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic mice with a history of postnatal CNO treatment from P2 to 14 did not show any significant change in gross adult weight as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 9 for vehicle; n = 11 for PNCNO). Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M.
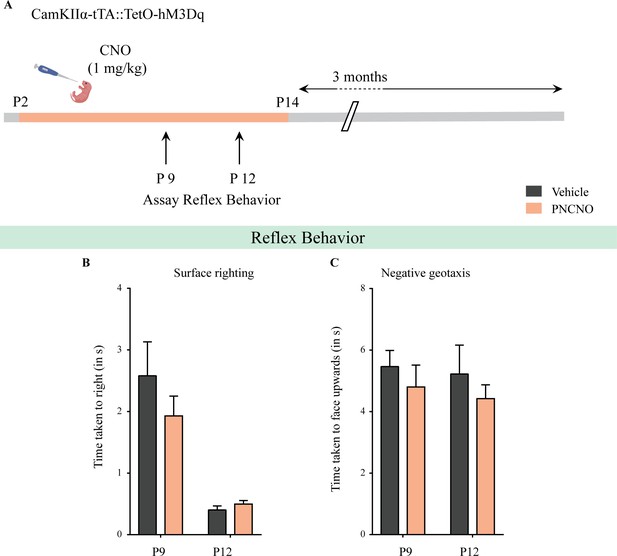
Chronic chemogenetic activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons during the early postnatal window does not alter the developmental emergence of reflex behaviors.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm used to determine the influence of chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons in CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic mouse pups from P2 to P14 on the postnatal emergence of reflex behaviors. (B) Surface righting was not significantly altered at P9 (n = 10 for vehicle; n = 11 for PNCNO) and P12 (n = 12 for vehicle; n = 16 for PNCNO) in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls. (C) Negative geotaxis was not significantly altered at P9 (n = 12 for vehicle; n = 19 for PNCNO) and P12 (n = 12 for vehicle; n = 16 for PNCNO) in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls. Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M.
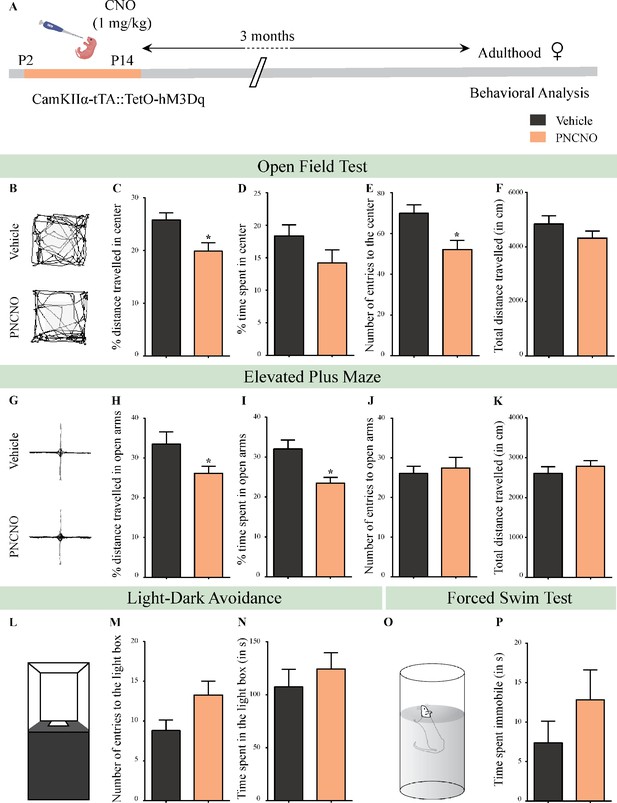
Chronic chemogenetic activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons during the early postnatal window results in a long-lasting increase in anxiety-like behavior in adult female mice.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm to induce chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq mouse pups that were fed CNO (PNCNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P2 to P14, and then left undisturbed for 3 months prior to behavioral analysis performed in adulthood on female mice. (B) Shown are representative tracks of vehicle or PNCNO-treated CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic adult female mice in the open field test (OFT). A history of chronic postnatal hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons resulted in increased anxiety-like behavior on the OFT in adulthood, as noted by a significant decrease in the percent distance traveled in center (C), and the number of entries to the center (E) in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls. The percent time spent in the center (D), and the total distance traveled in the OFT arena (F) were not significantly altered across treatment groups (n = 11 per group). (G) Shown are representative tracks of vehicle or PNCNO-treated CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic adult mice on the elevated plus maze (EPM). Adult female mice with chronic postnatal hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons exhibited increased anxiety-like behavior on the EPM as revealed by a significant decrease in the percent distance traveled in the open arms (H), and a decrease in percent time spent in the open arms (I) in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls. The number of entries to the open arms (J) and the total distance traveled in the EPM arena (K) was not altered in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 11 per group). (L–N) Shown is a schematic of the light-dark box used to assess anxiety-like behavior. Chronic postnatal hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons did not alter anxiety-like behavior in the LD box test in adulthood in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 11 per group). (O) Shown is a schematic representation of the forced swim test (FST) apparatus used to assess despair-like behavior. Chronic postnatal hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons did not influence despair-like behavior on the FST (P) in adulthood in PNCNO-treated female mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 14 for vehicle; n = 11 for PNCNO). Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. *p<0.05 as compared to vehicle-treated controls using the two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test.
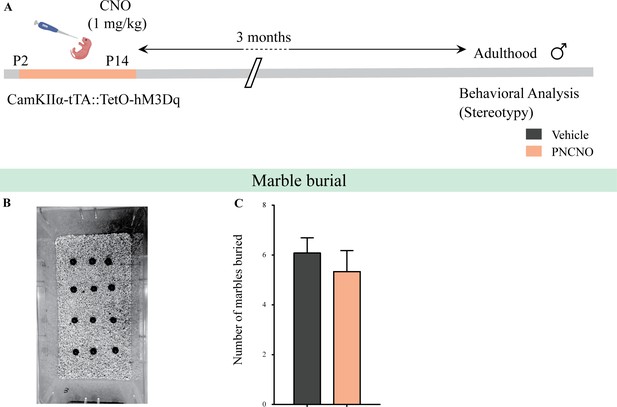
Chronic chemogenetic activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons during the early postnatal window does not alter repetitive behavior in adult male mice.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm to induce chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq mouse pups that were fed CNO (PNCNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P2 to P14 and then left undisturbed for 3 months prior to behavioral analysis to assess repetitive behavior on the marble burial test performed in adult male mice. (B) Shown is a representative image of marble burial test. PNCNO-treated mice did not show any significant difference in the number of marbles buried (C) as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 12 per group). Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M.
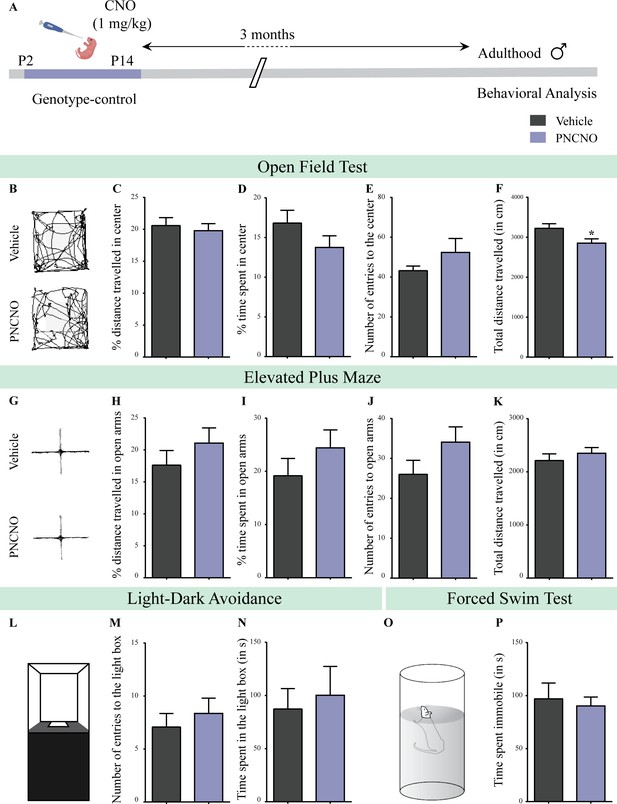
Chronic CNO administration during the early postnatal window does not influence anxiety- and despair-like behavior in genotype-control, adult male mice.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm to assess the influence of chronic CNO administration in genotype-control mice. Mouse pups, single-positive for either CamKIIα-tTA or TetO-hM3Dq and referred to as genotype-controls, were fed CNO (PNCNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P2 to P14 and then left undisturbed for 3 months prior to behavioral analysis performed in adulthood on male mice. (B) Shown are representative tracks of vehicle or PNCNO-treated genotype-control adult male mice in the open field test (OFT). A history of chronic postnatal CNO treatment did not influence anxiety-like behavior on the OFT in adulthood, with no change observed in the percent distance traveled in center (C), percent time spent in the center (D) and the number of entries to the center (E) of the OFT arena in PNCNO-treated genotype-control mice as compared to vehicle-treated genotype-control group (n = 13 for vehicle; n = 11 for PNCNO). We noted a small, but significant decline in the total distance traversed in the OFT arena (F) in the PNCNO-treated genotype-control mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls. (G) Shown are representative tracks of vehicle or PNCNO-treated genotype-control male mice on the elevated plus maze (EPM). Chronic postnatal CNO treatment did not alter anxiety-like behavior on the EPM, with no change observed in percent distance traveled (H), percent time spent (I), or number of entries (J) in the open arms of the EPM between PNCNO-treated genotype-control mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 13 for vehicle; n = 14 for PNCNO). The total distance traveled in the EPM arena (K) was also not different between the two groups. (L) Shown is a schematic of the light-dark box used to assess anxiety-like behavior. Chronic postnatal CNO administration did not influence anxiety-like behavior in the LD box test in adulthood, with no change noted for either the number of entries to the light box (M) or the time spent in the light box (N) in PNCNO-treated genotype-control mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 13 for vehicle; n = 14 for PNCNO). (O) Shown is a schematic representation of the forced swim test (FST) apparatus used to assess despair-like behavior. Chronic postnatal CNO administration did not influence despair-like behavior on the FST in adulthood, with no change in time spent immobile (P) in PNCNO-treated genotype-control mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 12 per group). Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. *p<0.05 as compared to vehicle-treated genotype-controls using the two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test.
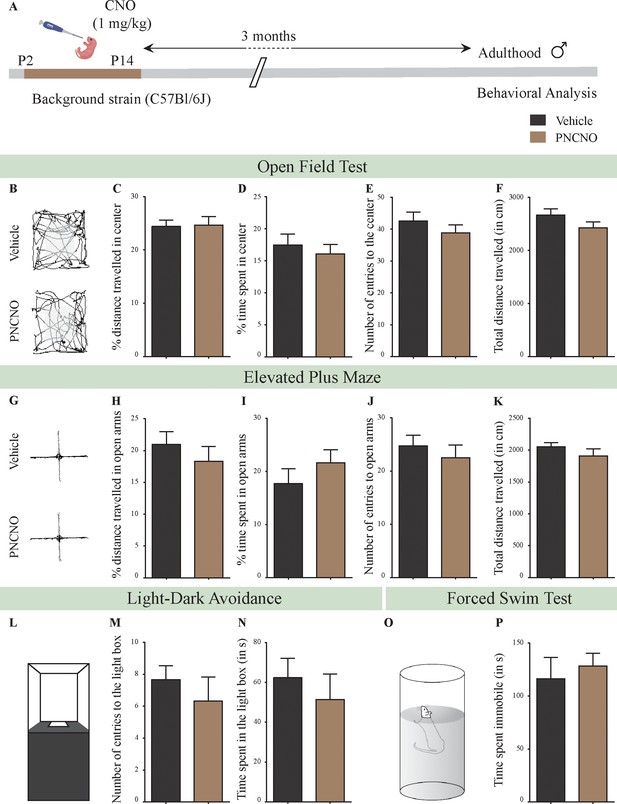
Chronic CNO administration during the early postnatal window does not influence anxiety- and despair-like behavior in C57BL/6J adult male mice.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm to assess the influence of chronic CNO administration in the background strain for the bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq, namely the C57BL/6J mouse strain. C57BL/6J mouse pups were fed CNO (PNCNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P2 to P14 and then left undisturbed for 3 months prior to behavioral analysis performed in adulthood on male mice. (B) Shown are representative tracks of vehicle or PNCNO-treated background strain, adult male mice in the open field test (OFT). A history of chronic postnatal CNO treatment did not influence anxiety-like behavior on the OFT in adulthood, with no change observed in the percent distance traveled in center (C), percent time spent in the center (D), the number of entries to the center (E), or the total distance traversed in the OFT arena (F) in PNCNO-treated background strain mice as compared to the vehicle-treated background strain control group (n = 12 per group). (G) Shown are representative tracks of vehicle or PNCNO-treated background strain male mice on the elevated plus maze (EPM). Chronic postnatal CNO treatment did not alter anxiety-like behavior on the EPM, with no change observed in percent distance traveled (H), percent time spent (I), number of entries (J) in the open arms of the EPM, or the total distance traveled in the EPM arena (K) between PNCNO-treated background strain mice as compared to vehicle-treated background strain controls (n = 12 per group). (L) Shown is a schematic of the light-dark box used to assess anxiety-like behavior. Chronic postnatal CNO administration did not influence anxiety-like behavior in the LD box test in adulthood, with no change noted for either the number of entries to the light box (M) or the time spent in the light box (N) in PNCNO-treated background strain mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 12 per group). (O) Shown is a schematic representation of the forced swim test (FST) apparatus used to assess despair-like behavior. Chronic postnatal CNO administration did not influence despair-like behavior on the FST in adulthood, with no change in time spent immobile (P) in PNCNO-treated background strain mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 12 per group). Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M.
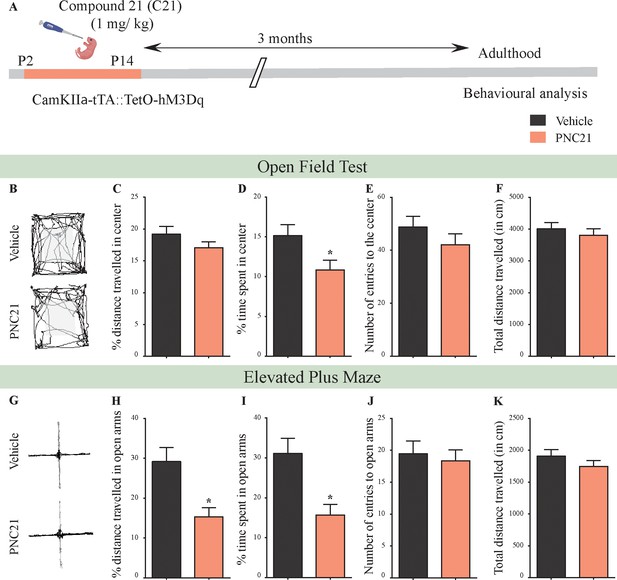
Chronic chemogenetic activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons during the early postnatal window using the DREADD agonist Compound 21 (C21) results in a long-lasting increase in anxiety-like behavior in adult male mice.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm to induce chronic C21-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq mouse pups that were fed C21 (PNC21; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P2 to P14 and then left undisturbed for 3 months prior to behavioral analysis performed in adulthood on male mice. (B) Shown are representative tracks of vehicle or PNC21-treated CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic adult male mice in the open field test (OFT). A history of chronic postnatal hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons resulted in increased anxiety-like behavior on the OFT in adulthood, as noted by a significant decrease in the percent time spent in center (D) (n = 15 per group). The percent distance traveled in center (C), number of entries to the center (E), and total distance traveled (F) was not altered in PNC21-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls. (G) Shown are representative tracks of vehicle or PNC21-treated CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic adult mice on the elevated plus maze (EPM). Adult mice with chronic postnatal hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons exhibited increased anxiety-like behavior on the EPM as revealed by a significant decrease in percent distance traveled in the open arms (H), as well as percent time spent in the open arms (I) (n = 15 per group). The number of entries to open arms (J) and the total distance traveled in the EPM arena (K) was not altered in PNC21-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls. Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. *p<0.05 as compared to vehicle-treated controls using the two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test.
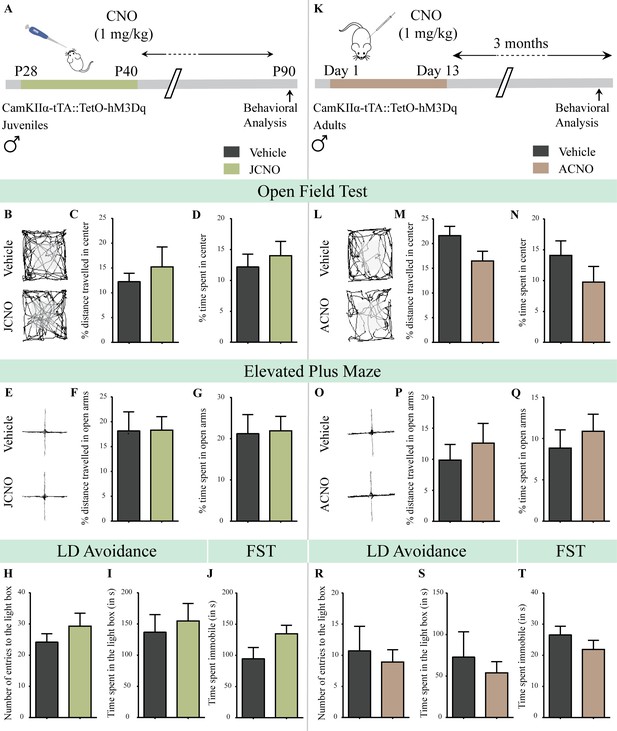
Chronic chemogenetic activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons during the juvenile window or in adulthood does not evoke any long-lasting changes in anxiety- and despair-like behavior in male mice.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm to induce chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq juvenile male mice that were fed CNO (JCNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P28-P40 and then left undisturbed till 3 months of age prior to behavioral analysis. (B) Shown are representative tracks of vehicle or JCNO-treated CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic adult male mice in the open field test (OFT). A history of chronic juvenile hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons does not evoke any persistent change in anxiety-like behavior on the OFT in adulthood, with no difference observed in the percent distance traveled in the center (C) and the percent time spent in the center (D) of the OFT arena in JCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 11 for vehicle; n = 8 for JCNO). (E) Shown are representative tracks of vehicle or JCNO-treated CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic adult mice on the elevated plus maze (EPM). Adult mice with chronic juvenile hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons did not exhibit any persistent changes in anxiety-like behavior on the EPM, with no change observed for the percent distance traveled (F) and the percent time spent (G) in the open arms of the EPM arena across treatment groups (n = 11 for vehicle; n = 10 for JCNO). Anxiety-like behavior was also assessed on the light-dark avoidance test and no significant alterations were seen in the number of entries to the light box (H) or the time spent in the light box (I) across treatment groups (n = 11 for vehicle; n = 10 for JCNO). A history of chronic juvenile hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons did not evoke any persistent change in despair-like behavior in the forced swim test (FST), with no difference observed in the time spent immobile (J) in JCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 11 per group). (K) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm to induce chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq adult male mice (3–4 months of age) that received CNO (ACNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle via intraperitoneal administration (once daily for thirteen days) and were left undisturbed for 3 months prior to behavioral analysis. (L) Shown are representative tracks of vehicle or ACNO-treated CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic adult male mice in the open field test (OFT). A history of chronic hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons in adulthood does not evoke any persistent change in anxiety-like behavior on the OFT, with no difference observed in the percent distance traveled in the center (M) and the percent time spent in the center (N) of the OFT arena in ACNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 7 for vehicle; n = 11 for ACNO). (O) Shown are representative tracks of vehicle or ACNO-treated CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic adult mice on the elevated plus maze (EPM). Chronic hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons in adulthood did not evoke any persistent changes in anxiety-like behavior on the EPM, with no change observed for the percent distance traveled (P) and the percent time spent (Q) in the open arms of the EPM arena across treatment groups (n = 7 for vehicle; n = 11 for ACNO). Anxiety-like behavior was also studied on the light-dark avoidance test and no change was observed in the number of entries to the light box (R) or the time spent in the light box (S) across treatment groups (n = 7 for vehicle; n = 11 for ACNO). Chronic hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons in adulthood did not evoke any persistent change in despair-like behavior in the forced swim test (FST), with no difference observed in the time spent immobile (T) in ACNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 10 for vehicle; n = 9 for ACNO). Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Source data for Figure 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56171/elife-56171-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx
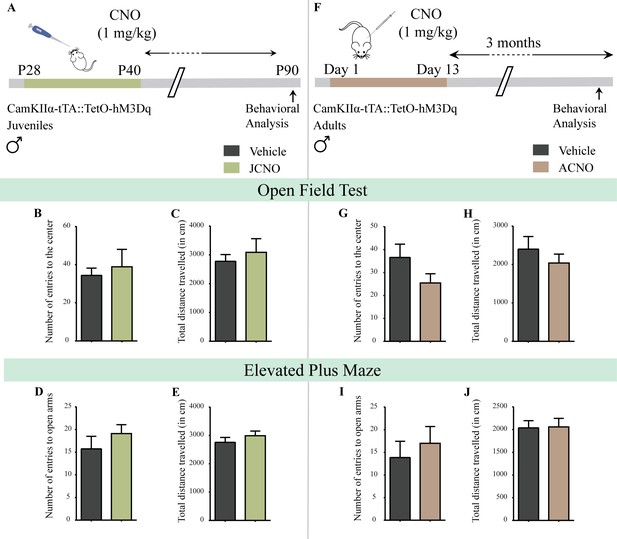
Chronic chemogenetic activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons during the juvenile window or in adulthood does not evoke any long-lasting changes in anxiety-like behavior in male mice.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm to induce chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq juvenile male mice that were fed CNO (JCNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P28-P40 and then left undisturbed till 3 months of age prior to behavioral analysis. A history of chronic juvenile hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons does not evoke any persistent change in anxiety-like behavior on the OFT in adulthood, with no difference observed in the number of entries to the center (B) and the total distance traveled in the OFT arena (C) in JCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 11 for vehicle; n = 8 for JCNO). Adult mice with chronic juvenile hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons did not exhibit any persistent changes in anxiety-like behavior on the EPM, with no change observed for the number of entries to the open arms (D) and the total distance traveled in the EPM arena (E) across treatment groups (n = 11 for vehicle; n = 10 for JCNO). (F) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm to induce chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq adult male mice (3–4 months of age) that received CNO (ACNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle via intraperitoneal administration (once daily for thirteen days) and were left undisturbed for 3 months prior to behavioral analysis. A history of chronic hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons in adulthood does not evoke any persistent change in anxiety-like behavior on the OFT, with no difference observed in the number of entries to the center (G) and the total distance traveled in the OFT arena (H) in ACNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 7 for vehicle; n = 11 for ACNO). Chronic hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons in adulthood did not evoke any persistent changes in anxiety-like behavior on the EPM, with no change observed for the number of entries to the open arms (I) and the total distance traveled in the EPM arena (J) across treatment groups (n = 7 for vehicle; n = 11 for ACNO). Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M.
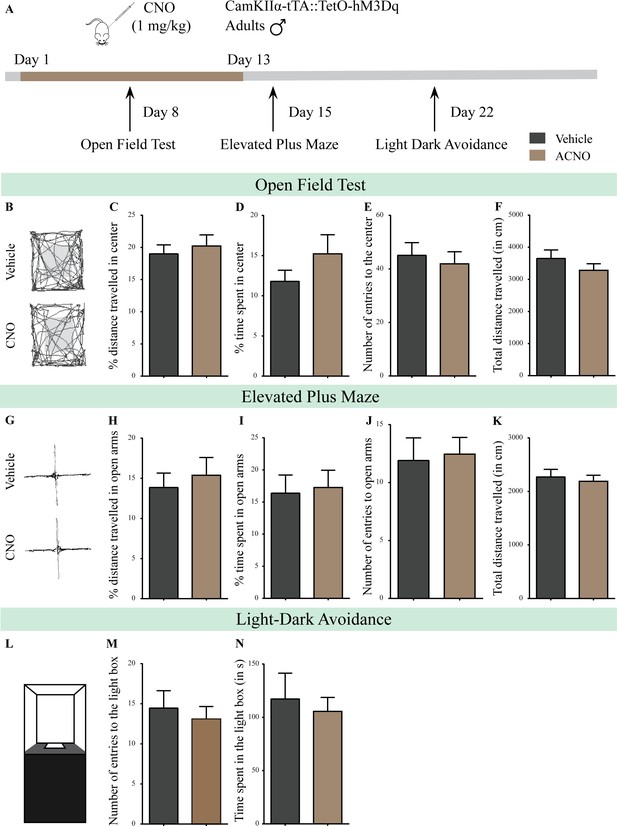
Chronic chemogenetic activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons in adulthood does not evoke any long-lasting changes in anxiety-like behavior in male mice during or soon after cessation of CNO treatment.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm to induce chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq adult male mice (3–4 months of age) that received CNO (ACNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle via intraperitoneal administration (once daily for thirteen days) and were assayed for anxiety-like behavior during (OFT- performed on Day 8) and soon after cessation of CNO treatment (EPM performed on Day 15; LD avoidance test performed on Day 22). (B) Shown are representative tracks of vehicle or ACNO-treated bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq adult male mice in the open field test (OFT). Chronic CNO treatment in adulthood did not influence anxiety-like behavior on the OFT as tested on Day 8 of a 13 day treatment regime, with no change observed in the percent distance traveled in center (C), percent time spent in the center (D), the number of entries to the center (E), or the total distance traversed in the OFT arena (F) in ACNO-treated male mice as compared to the vehicle-treated controls (n = 11 per group). (G) Shown are representative tracks of vehicle or ACNO-treated adult male mice on the elevated plus maze (EPM). Chronic CNO treatment did not alter anxiety-like behavior on the EPM soon after cessation of CNO treatment, with no change observed in percent distance traveled (H), percent time spent (I), number of entries (J) in the open arms of the EPM, or the total distance traveled in the EPM arena (K) between ACNO-treated CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 11 per group). (L) Shown is a schematic of the light-dark box used to assess anxiety-like behavior. Chronic CNO administration did not influence anxiety-like behavior in the LD box test in adulthood soon after cessation of CNO treatment, with no change noted for either the number of entries to the light box (M) or the time spent in the light box (N) in ACNO-treated bigenic adult male mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 11 per group). Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M.
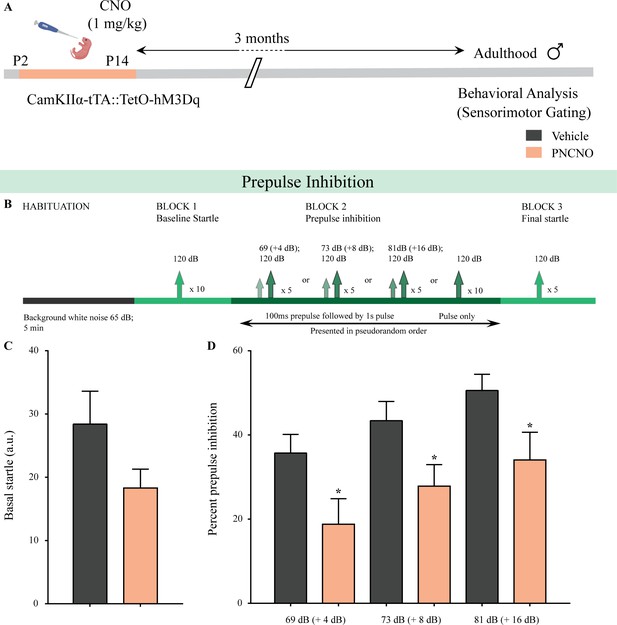
Chronic chemogenetic activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons during the early postnatal window evokes impaired sensorimotor gating in adulthood.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm to induce chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq mouse pups that were fed CNO (PNCNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P2 to P14 and then left undisturbed for 3 months prior to behavioral analysis for sensorimotor gating, using the prepulse inhibition (PPI) test, in adulthood on male mice. (B) Shown is the test paradigm for PPI to assess sensorimotor gating. Adult male mice with a history of postnatal CNO administration (PNCNO) did not show any significant change in basal startle response (C) as compared to vehicle-treated controls. PNCNO-treated adult mice exhibited deficits in sensorimotor gating, as noted via a significant decrease in prepulse inhibition (PPI)(D) at + 4 dB (69 dB), + 8 dB (73 dB), and + 16 dB (81 dB) above background noise (65 dB) when compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 12 per group). Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. *p<0.05, as compared to vehicle-treated controls using two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test.
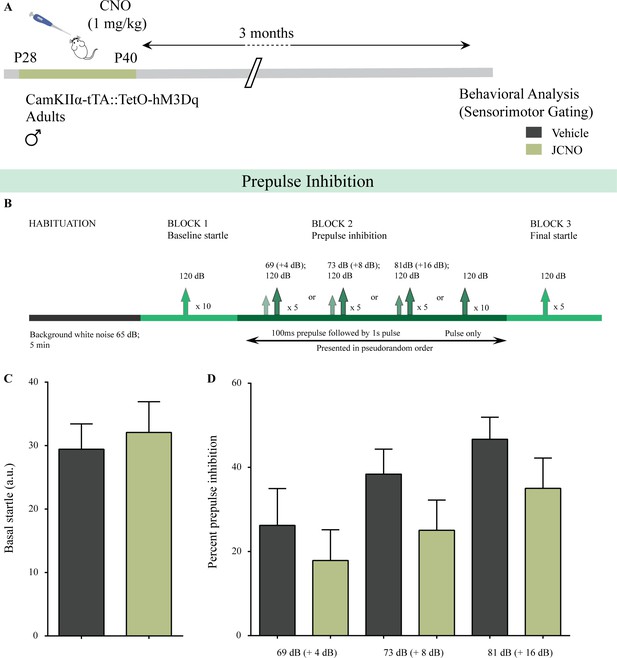
Chronic chemogenetic activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons during the juvenile window does not alter sensorimotor gating behavior.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm to induce chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq juvenile male mice (P28-40) that were fed CNO (JCNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle, and subjected to behavioral analysis using the prepulse inhibition (PPI) test in adulthood. (B) Shown is the experimental paradigm for PPI to assess sensorimotor gating. JCNO-treated mice did not show any significant change in basal startle response (C) as compared to vehicle-treated controls. (D) Prepulse inhibition at + 4 dB (69 dB), + 8 dB (73 dB), and + 16 dB (81 dB) above background noise (65 dB) was unaltered in JCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 8 for vehicle and n = 9 for JCNO). Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M.
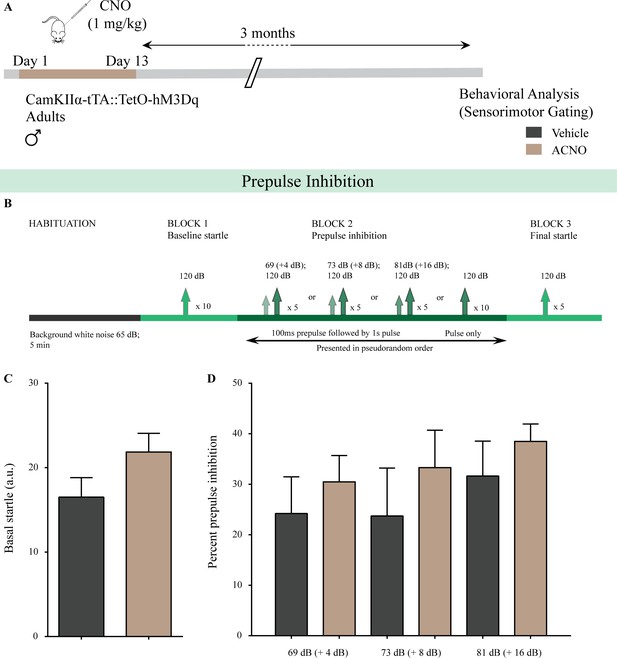
Chronic chemogenetic activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons in adulthood does not alter sensorimotor gating behavior.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm to induce chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq adult male mice (3–4 months of age) that received CNO (ACNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle via intraperitoneal administration (once daily for thirteen days) and were left undisturbed for 3 months prior to behavioral analysis using the prepulse inhibition (PPI) test. (B) Shown is the experimental paradigm for PPI to assess sensorimotor gating. ACNO-treated mice did not show any significant change in basal startle response (C) as compared to vehicle-treated controls. (D) Prepulse inhibition at + 4 dB (69 dB), + 8 dB (73 dB), and + 16 dB (81 dB) above background noise (65 dB) was unaltered in ACNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 10 per group). Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M.
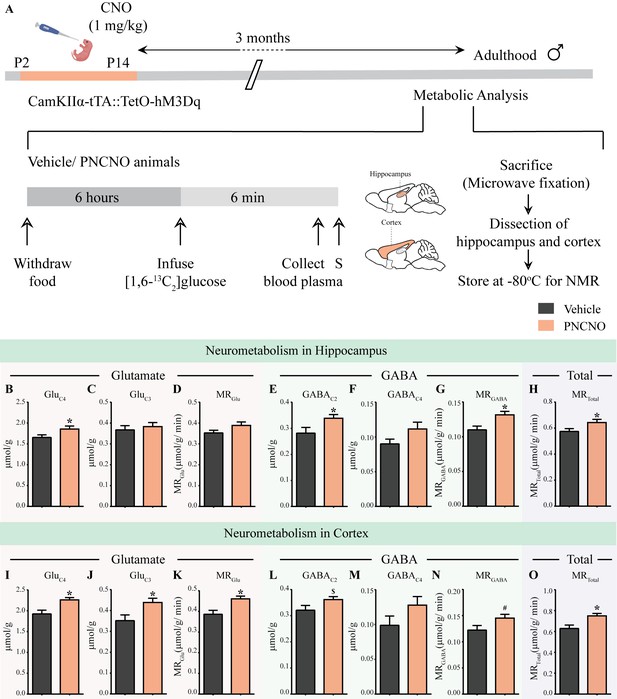
Chronic chemogenetic activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons during the early postnatal window results in long-lasting alterations in neurotransmitter cycling flux and neuronal metabolic rate in hippocampus and cortex.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm to induce chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq mouse pups that were fed CNO (PNCNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P2 to P14 and then left undisturbed for 3 months prior to metabolic analysis performed in adulthood on male mice using 1H-[13C]-NMR spectroscopy. Adult male mice, with a history of PNCNO or vehicle administration, were subjected to fasting for 6 hr, following which [1,6-13C2]glucose was infused via the tail-vein. Blood plasma was collected and mice were sacrificed 6 min following glucose infusion, followed by dissection of hippocampus and cortex for NMR analysis. PNCNO-treated mice exhibited a higher rate of glutamate and GABA synthesis from [1,6-13C2]glucose in the hippocampus as revealed by significantly higher levels of 13C-labeled metabolites GluC4 (B) and GABAC2 (E) as compared to vehicle-treated controls. Levels of 13C-labeled metabolites GluC3 (C) and GABAC4 (F) was not altered across treatment groups in the hippocampus. No significant change was observed in the metabolic rate of glucose oxidation in glutamatergic neurons of the hippocampus (D) across treatment groups. There was a significant increase in the metabolic rate of glucose oxidation in GABAergic neurons of the hippocampus (G) and the overall neuronal metabolic rate of the hippocampus (H), in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls. PNCNO-treated mice had a higher rate of glutamate and GABA synthesis from [1,6-13C2]glucose in the cortex as revealed by significantly higher levels of 13C-labeled metabolites GluC4 (I), GluC3 (J), and the metabolic rate of glucose oxidation in glutamatergic neurons of the cortex (K) as compared to vehicle-treated controls. There was a trend toward an increase in levels of 13C-labeled metabolite GABAC2 (L) and the metabolic rate of glucose oxidation in GABAergic neurons of the cortex (N) in the PNCNO-treated mice as compared to the vehicle-treated controls. The levels of 13C-labeled GABAC4 (M) was not altered across treatment groups. There was a significant increase in the overall neuronal metabolic rate of the cortex (O), in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 7 per group). Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. *p<0.05, $p=0.08, #p=0.06; as compared to vehicle-treated controls using the two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test.
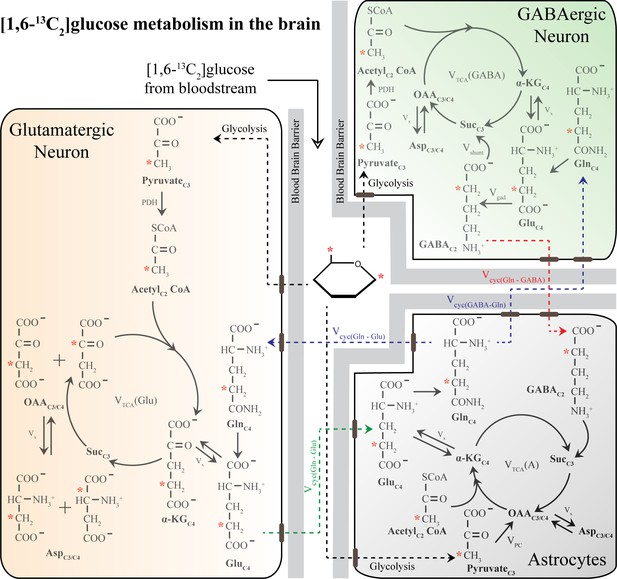
Schematic of 13C labeling of various metabolites from [1,6-13C2]glucose in a three-compartment metabolic model [1,6-13C2]glucose is converted to PyruvateC3 via glycolysis and subsequently enters the TCA cycle.
Metabolism of [1,6-13C2]glucose in glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons produces GluC4, which is then decarboxylated to GABAC2 by GAD enzyme in GABAergic neurons. The glutamate–glutamine and GABA-glutamine cycle operating between neurons and astrocytes produce GlnC4. Other versions of 13C-labeled glutamate (GluC4) and GABA (GABAC4) are produced in the subsequent metabolism of GluC4 and GABAC2. In the astrocytes, PyruvateC3 can enter the TCA cycle via the pyruvate carboxylate pathway and subsequently produce the 13C-labeled metabolites namely GlnC2, GluC2, and GABAC4. Only the first round of TCA cycle is depicted here for simplicity. Abbreviations: αKG: α-ketoglutarate; OAA: oxaloacetate; Asp: aspartate; Suc: succinate; GABA: γ-aminobutyric acid; GAD: glutamic acid decarboxylase; Glu: glutamate; Gln: glutamine; Vcyc(GABA-Gln): GABA-glutamine cycling flux; Vcyc(Glu-Gln): glutamate–glutamine cycling flux; Vgad: glutamate decarboxylase flux; Vgln: glutamine synthesis rate; Vpc: pyruvate carboxylase flux; Vshunt: flux of GABA shunt; VTCA(A): Astroglial TCA cycle flux; VTCA(GABA), GABAergic TCA cycle flux; VTCA(Glu): glutamatergic TCA cycle flux; Vx: exchange rate between a ketoglutarate and glutamate. ∗ represents the position of the 13C carbon.
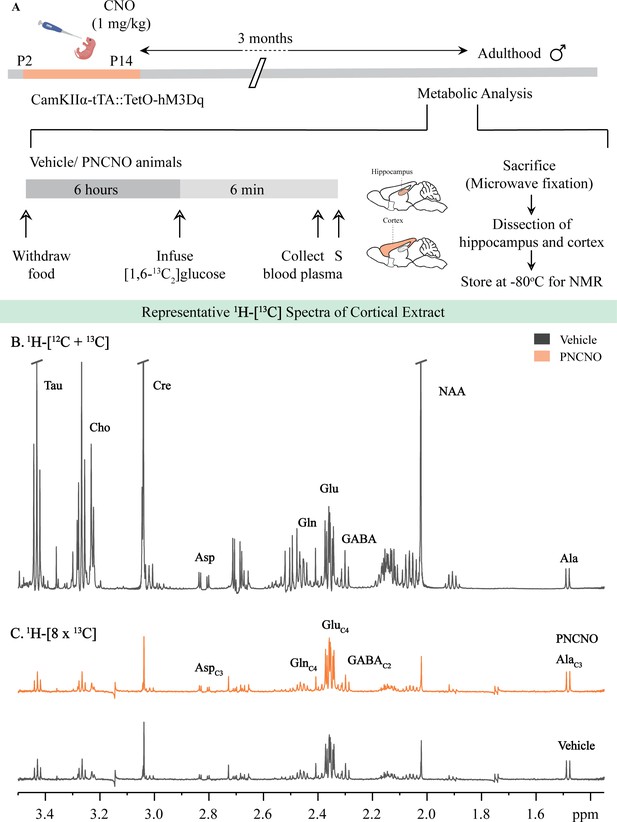
Representative 1H-[13C]-NMR spectra from the cortex of vehicle and PNCNO-treated CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq adult male mice.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm to induce chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq mouse pups that were fed CNO (PNCNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P2 to P14 and then left undisturbed for 3 months prior to metabolic analysis performed in adulthood on male mice using 1H-[13C]-NMR spectroscopy. Adult male mice, with a history of PNCNO or vehicle administration, were subjected to fasting for 6 hr, following which [1,6-13C2]glucose was infused via the tail-vein. Blood plasma was collected and mice were sacrificed 6 min following glucose infusion, followed by dissection of hippocampus and cortex for NMR analysis. (B) 1H-[12C + 13C] spectra represents the total concentration of metabolites. (C) 1H-[8 × 13C] depicts 13C labeling of metabolites from [1,6 - 13C2]glucose. Peak labels: Asp: aspartate; Ala: alanine; Cho: Choline; Cre: Creatine; NAA: N-acetylaspartate; GABA: γ-aminobutyric acid; Glu: glutamate; Gln: glutamine; AlaC3: alanine-C3; AspC3: asparate-C3; GABAC2: GABA-C2; GlnC4: glutamine-C4; GluC4: glutamate-C4.
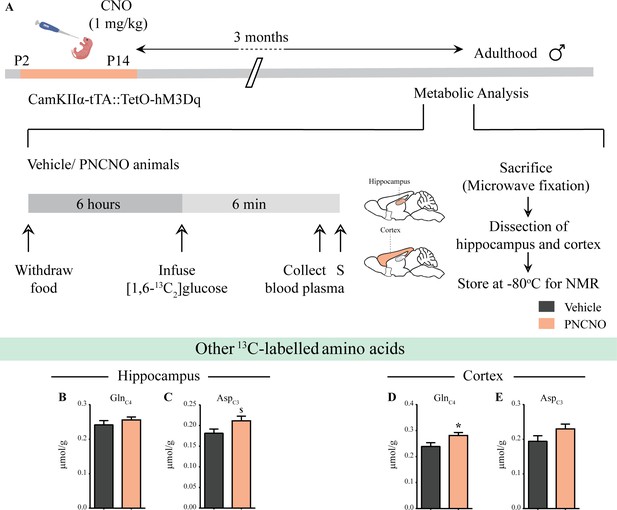
Influence of chronic chemogenetic activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons during the early postnatal window on the levels of other 13C-labeled metabolites in the hippocampus and cortex in adult male mice.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm to induce chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq mouse pups that were fed CNO (PNCNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P2 to P14 and then left undisturbed for 3 months prior to metabolic analysis performed in adulthood on male mice using 1H-[13C]-NMR spectroscopy. Adult male mice, with a history of PNCNO or vehicle administration, were subjected to fasting for 6 hr, following which [1,6-13C2]glucose was infused via the tail-vein. Blood plasma was collected and mice were sacrificed 6 min following glucose infusion, followed by dissection of hippocampus and cortex for NMR analysis. (B) No significant change was observed in the levels of GlnC4 in the hippocampus across treatment groups. (C) There was a trend toward an increase observed in the 13C-labeled metabolite, AspC3 in the hippocampi of PNCNO-treated adult male mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls. (D) A significant increase was noted in the 13C-labeled GlnC4 in the cortex of PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls. (E) No significant change was observed in the levels of AspC3 in the cortex across treatment groups (n = 7 per group). Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. *p<0.05, $p=0.07; as compared to vehicle-treated controls using the two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test.
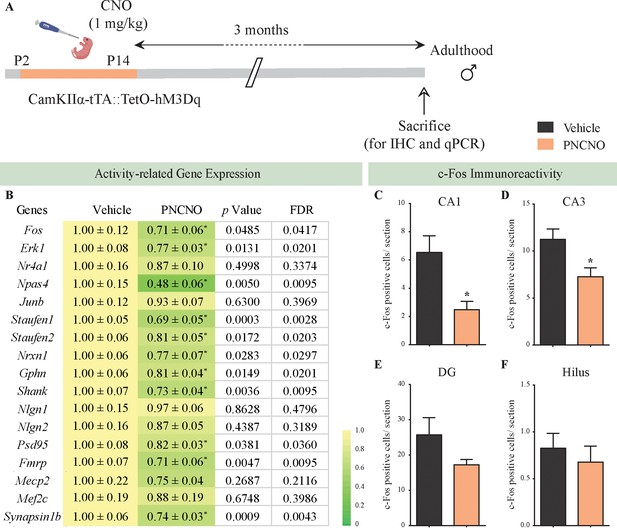
Chronic chemogenetic activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons during the early postnatal window results in a long-lasting decline in neuronal activity-related gene expression, and c-Fos immunopositive cell numbers, in the adult hippocampus.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm to induce chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq mouse pups that were fed CNO (PNCNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P2 to P14 and then left undisturbed for 3 months prior to qPCR analysis for neuronal activity-related gene expression and c-Fos immunohistochemistry performed in adulthood on male mice. (B) Shown are normalized gene expression levels for specific neuronal activity-related genes in PNCNO-treated mice represented as fold-change of their vehicle-treated controls (n = 11 per group). Heat maps indicate the extent of gene regulation. *p<0.05 as compared to vehicle-treated controls using the two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test. Also shown are false-discovery rate (FDR) corrected p values. Cell counting analysis for c-Fos immunopositive cells within the hippocampus, indicated a significant reduction in the number of c-Fos positive cells/section within the CA1 (C) and CA3 (D) hippocampal subfields in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 10 for vehicle; n = 12 for PNCNO). c-Fos immunopositive cell numbers were unaltered in the DG (E) and the hilar subfield (F) of the hippocampus in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls. Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. *p<0.05 as compared to vehicle-treated controls using the two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
List of qPCR primers.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56171/elife-56171-fig6-data1-v2.xlsx
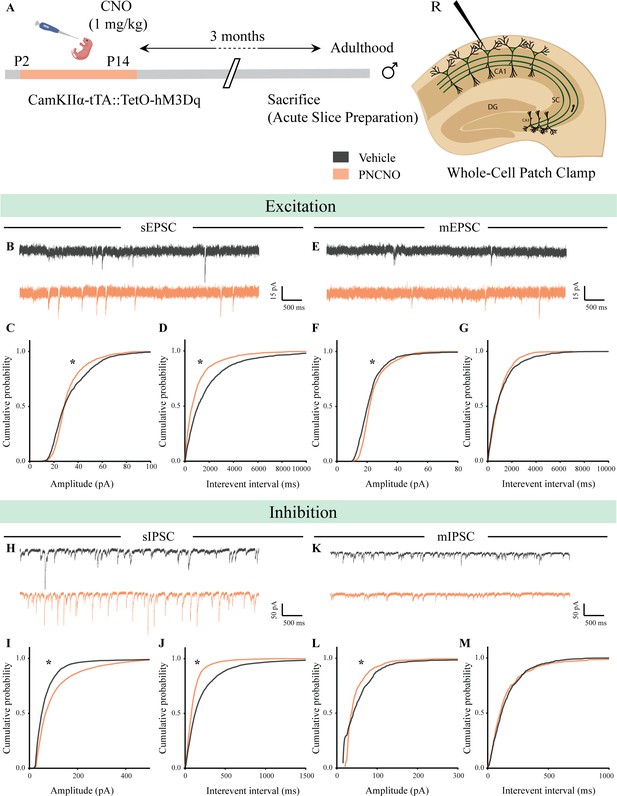
Chronic chemogenetic activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons during the early postnatal window alters excitatory and inhibitory spontaneous currents in the hippocampi of adult male mice.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm to induce chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq mouse pups that were fed CNO (PNCNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P2 to P14 and then left undisturbed for 3 months prior to electrophysiological analysis, in acute hippocampal slices derived from adult male mice. Whole-cell patch clamp was performed to record sEPSCs/mEPSCs and sIPSCs/mIPSCs in the somata of CA1 pyramidal neurons. R – Recording electrode. (B) Shown are representative sEPSC traces of CA1 pyramidal neurons from vehicle and PNCNO-treated mice. (C) PNCNO-treated mice showed significantly altered cumulative probability of sEPSC amplitude with a small increase at lower amplitudes (<30 pA) and a significant decline in large-amplitude events as compared to vehicle-treated controls. (D) PNCNO-treated mice showed a significant decline in the cumulative probability of sEPSC interevent intervals as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 8 cells for vehicle; n = 5 cells for PNCNO). (E) Shown are representative mEPSC traces of CA1 pyramidal neurons from vehicle and PNCNO-treated mice. (F) PNCNO-treated mice showed significantly enhanced cumulative probability of sEPSC amplitude as compared to vehicle-treated controls. (G) No significant change was observed in the cumulative probability of sEPSC interevent intervals in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 5 cells for vehicle; n = 6 cells for PNCNO). (H) Shown are representative sIPSC traces of CA1 pyramidal neurons from vehicle and PNCNO-treated mice. PNCNO-treated mice showed a significant increase in the cumulative probability of sIPSC amplitude (I), along with a significant decline in the cumulative probability of sIPSC interevent intervals (J) as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 8 cells for vehicle; n = 7 cells for PNCNO). (K) Shown are representative mIPSC traces of CA1 pyramidal neurons from vehicle and PNCNO-treated mice. (L) PNCNO-treated mice showed a significant decline in the cumulative probability of mIPSC amplitude as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 6 cells for vehicle; n = 7 cells for PNCNO). (M) No significant change was observed in the cumulative probability of mIPSC interevent intervals across treatment groups. Results are expressed as cumulative probabilities. *p<0.001 as compared to PNCNO-treated group using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov two-sample comparison.
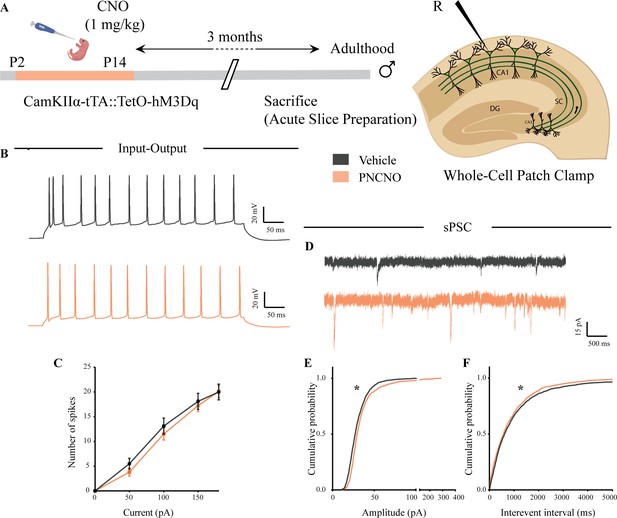
Chronic chemogenetic activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons during the early postnatal window does not change intrinsic excitability but alters spontaneous network activity in the hippocampi of adult male mice.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm to induce chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq mouse pups that were fed CNO (PNCNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P2 to P14 and then left undisturbed for 3 months prior to electrophysiological analysis, in acute hippocampal slices derived from adult male mice. Whole-cell patch clamp was performed to record sPSCs and input-output characteristics in the somata of CA1 pyramidal neurons. R – Recording electrode. (B) Shown are representative traces of spikes generated by CA1 pyramidal neurons following a current injection of 100 pA in vehicle and PNCNO-treated adult male mice. (C) No significant change was observed in the input-output characteristics of CA1 pyramidal neurons in acute hippocampal slices derived from PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 18 cells for vehicle; n = 25 cells for PNCNO). Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. (D) Shown are representative sPSC traces of CA1 pyramidal neurons from vehicle and PNCNO-treated mice. (E) PNCNO-treated mice showed significantly enhanced cumulative probability of sPSC amplitude in addition to the presence of a long-tail as compared to vehicle-treated controls. (F) PNCNO-treated mice showed a significant decline in the cumulative probability of sPSC interevent intervals as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 8 cells for vehicle; n = 6 cells for PNCNO). Results are expressed as cumulative probabilities. *p<0.001 as compared between vehicle and PNCNO-treated group using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov two-sample comparison.
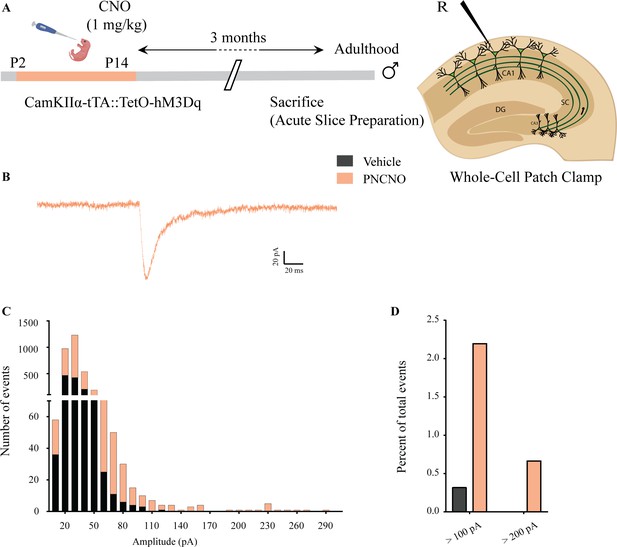
Effect of chronic chemogenetic activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons during the early postnatal window on the distribution of spontaneous network events in hippocampi of adult male mice.
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm to induce chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq mouse pups that were fed CNO (PNCNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P2 to P14 and then left undisturbed for 3 months prior to electrophysiological analysis, in acute hippocampal slices derived from adult male mice. Whole-cell patch clamp was performed to record sPSCs in the somata of CA1 pyramidal neurons. R – Recording electrode. (B) Shown is an example trace of a large-amplitude spontaneous network event observed in a CA1 pyramidal neuron of a PNCNO-treated mouse. (C) Distribution plot for sPSC amplitudes showing a long-tail of large-amplitude events in PNCNO-treated mice. (D) Quantification of percent of total events with amplitude >100 pA and >200 pA. No event >200 pA was observed in vehicle-treated controls.
Tables
Effects of chronic postnatal hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons on intrinsic membrane properties.
| Postnatal Day 7 | CA1 pyramidal neurons | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intrinsic Properties | ||||||
| Group | RMP (mV) | Input resistance (MΩ) | τ (ms) | Sag (mV) | Sag (%) | Accomodation index |
| Vehicle | −55.96 ± 1.923 | 310.2 ± 39.43 | 34.77 ± 4.62 | −10.09 ± 2.65 | 10.15 ± 2.42 | 0.32 ± 0.06 |
| PNCNO | −51.66 ± 1.151$ | 352.3 ± 35.23 | 33.62 ± 3.65 | −8.99 ± 1.66 | 9.10 ± 1.22 | 0.48 ± 0.09 |
-
CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic mouse pups were fed either CNO (1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P2 to P7, and whole-cell patch clamp was performed at P7 to determine intrinsic membrane properties. No significant effect was noted for input resistance, membrane time constant (τ), sag voltage, percent sag and accommodation index across treatment groups. We noted a trend toward an increase in resting membrane potential (RMP) in hippocampi derived from the PNCNO-treated mouse pups as compared to vehicle-treated controls. $p=0.06 as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 6 cells for vehicle; n = 9 cells for PNCNO) using the two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test.
Influence of chronic chemogenetic activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons during the early postnatal window on the total levels of metabolites relative to [2-13C]glycine in the hippocampus and cortex in adult male mice.
| [1,6-13C]glucose Infusion | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration of brain metabolites determined relative to [2-13C]glycine (µmol/g) | ||||||||||||
| Brain Region | Group | Glu | GABA | Gln | Asp | NAA | Ala | Lac | Ino | Tau | Cho | Cre |
| Hippocampus | Vehicle | 13.5 ± 0.3 | 3.6 ± 0.2 | 5.0 ± 0.1 | 2.3 ± 0.1 | 8.9 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 3.0 ± 0.6 | 7.3 ± 0.2 | 8.6 ± 0.2 | 2.3 ± 0.1 | 13.5 ± 0.2 |
| PNCNO | 13.7 ± 0.3 | 3.7 ± 0.2 | 4.8 ± 0.1 | 2.5 ± 0.1 | 9.0 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.1* | 2.3 ± 0.2 | 7.5 ± 0.2 | 8.5 ± 0.2 | 2.3 ± 0.1 | 13.5 ± 0.3 | |
| Cortex | Vehicle | 13.5 ± 0.3 | 3.4 ± 0.1 | 4.7 ± 0.1 | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 9.5 ± 0.4 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 7.0 ± 1.3 | 6.0 ± 0.2 | 9.1 ± 0.1 | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 12.9 ± 0.1 |
| PNCNO | 14.0 ± 0.2 | 3.3 ± 0.1 | 4.5 ± 0.1 | 3.2 ± 0.1$ | 9.6 ± 0.4 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 5.3 ± 0.5 | 6.0 ± 0.1 | 9.1 ± 0.2 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 12.9 ± 0.2 | |
-
Chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons was achieved using bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq mouse pups that were fed CNO (PNCNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P2 to P14 and then left undisturbed for 3 months prior to metabolic analysis performed in adulthood on male mice and NMR spectroscopy on the hippocampus and cortex was performed to acquire 1H-[12C + 13C] spectra. The concentration of metabolites was determined relative to [2-13C]glycine. Glu: Glutamate; GABA: γ-aminobutyric acid; Gln: Glutamine; Asp: Aspartate; NAA: N-acetylaspartate; Suc: Succinate; Ala: Alanine; Lac: Lactose; Ino; Inositol; Tau: Taurine; Cho: Choline; Cre: Creatine. Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M (n = 7 per group). *p<0.05, $p=0.06; as compared to vehicle-treated controls using the two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test.
Effect of chronic chemogenetic activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons during the early postnatal window on intrinsic membrane properties in adulthood.
| Adults | CA1 pyramidal neurons | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intrinsic properties | ||||||
| Group | RMP (mV) | Input resistance (MΩ) | τ (ms) | Sag (mV) | Sag (%) | Accomodation index |
| Vehicle | −62.3 ± 0.655 | 195.1 ± 10.89 | 18.87 ± 1.574 | −4.282 ± 0.288 | 4.956 ± 0.317 | 0.375 ± 0.054 |
| PNCNO | −62.81 ± 0.682 | 180.2 ± 10.46 | 18.66 ± 1.269 | −3.603 ± 0.397 | 4.173 ± 0.420 | 0.392 ± 0.046 |
-
Chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons was performed using bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq mouse pups that were fed CNO (PNCNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P2 to P14 and then left undisturbed for 3 months prior to electrophysiological analysis, in acute hippocampal slices derived from adult male mice. Whole-cell patch clamp was performed to determine intrinsic properties in the somata of CA1 pyramidal neurons. RMP: Resting membrane potential, τ: Membrane time constant. Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 18 cells for vehicle; n = 25 cells for PNCNO).
Additional files
-
Source data 1
Summary of statistical analysis.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56171/elife-56171-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56171/elife-56171-transrepform-v2.pdf





