Evolutionarily conserved regulation of immunity by the splicing factor RNP-6/PUF60
Figures
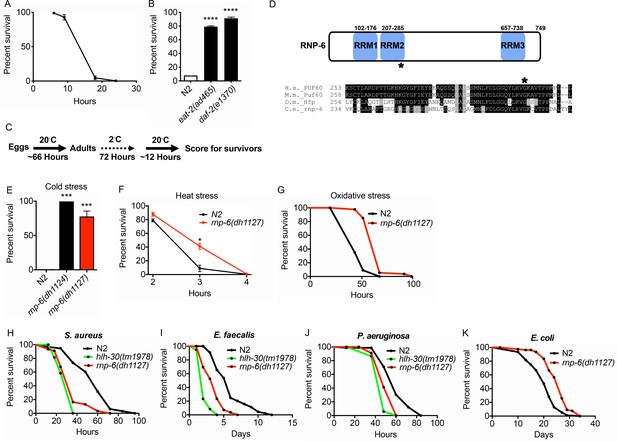
Isolation of the rnp-6 G281D substitution mutant from a cold resistance screen.
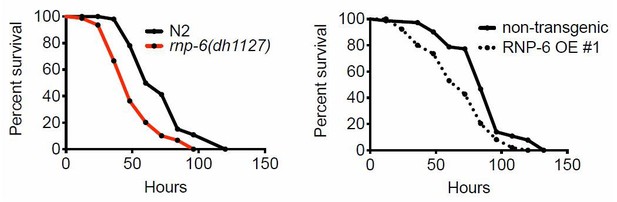
(A) Cold stress survival assay. Low temperature (2°C) incubation kills wildtype young adult worms. (B) daf-2 and eat-2 mutants show enhanced survival after 24 hr incubation at 2°C. (C) Schematic of the cold stress selection experiment. (D) Schematic showing the location of the G281D mutation in rnp-6. RRM stands for RNA recognition motif. The glycine at this position is conserved in human (Homo sapiens), mouse (Mus musculus) and fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster). (E) The CRISPR strain (dh1127) shows the same cold resistant phenotype as the original mutant (dh1124) isolated from the genetic screen. (F) The rnp-6 G281D mutant shows enhanced survival under 35°C heat stress. (G) The rnp-6 G281D mutant shows improved survival under oxidative stress (20 mM paraquat) (p<0.0001, log-rank test.). (H,I,J) Infection survival analysis. rnp-6(dh1127) animals show sensitivity to all the bacteria tested. S. aureus (p<0.0001, log-rank test.), E. faecalis (p<0.0001, log-rank test.) and P. aeruginosa (p=0.0022, log-rank test.). The hlh-30 mutant serves as a positive control of infection sensitivity. (K) Demographic analysis of lifespan. rnp-6(dh1127) mutants have significant lifespan extension when cultured with OP50 bacteria at 20°C (p<0.0001, log-rank test.). Survival and lifespan experiments were performed three times independently. Error bars represent mean ± s.e.m. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, unpaired t-test.
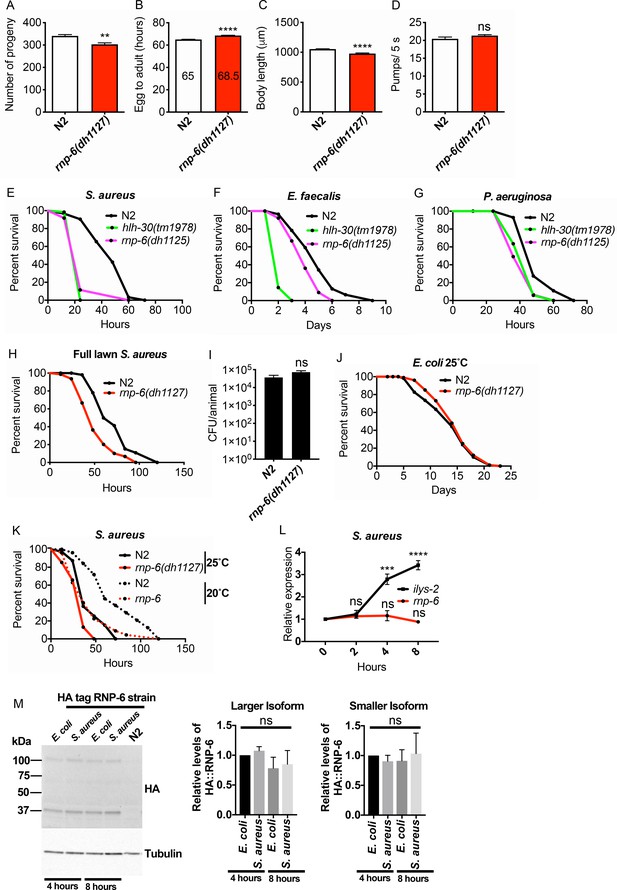
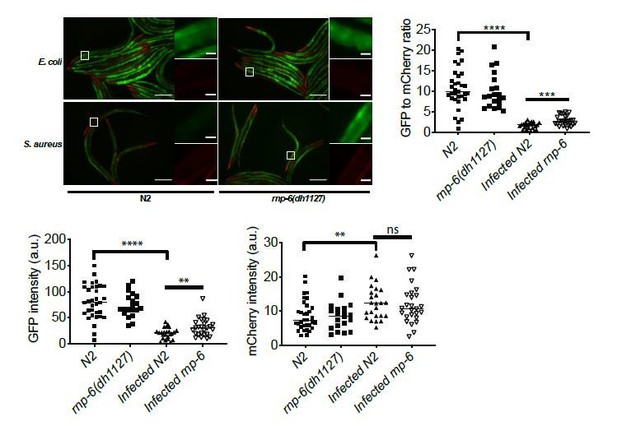
rnp-6 G281D mutation compromises bacterial infection survival, related to Figure 1.
(A) Number of progenies per animal of wildtype and rnp-6(dh1127) worms. rnp-6(dh1127) mutants have a smaller brood size. (B) Development time of wildtype and rnp-6(dh1127) animals. rnp-6(dh1127) mutants take a slightly longer time to reach adulthood. (C) Body length of day one adults. The length of rnp-6(dh1127) mutants is marginally shorter. (D) Pharyngeal pumping rate. rnp-6(dh1127) mutants have identical pharyngeal pumping rate as wildtype animals. (E, F, G) Infection survival analysis. rnp-6(dh1125) mutants show sensitivity to S. aureus (p<0.001), E. faecalis (p<0.01) and P. aeruginosa (p<0.0001, log-rank test.). (H) Infection survival analysis. Chemicalized sterilized (FUDR) animals were infected with full S. aureus lawn. rnp-6(dh1127) mutants are more sensitive under these conditions (p<0.0001, log-rank test.). (I) Bacterial burden at 24 hr post-infection. No significant difference between N2 and rnp-6(dh1127) animals. (J) Demographic analysis of lifespan. rnp-6(dh1127) and wildtype animals have comparable lifespan when cultured with OP50 bacteria at 25°C (non-significant, log-rank test.). (K) Infection survival analysis. rnp-6(dh1127) mutants are sensitive to S. aureus infection at both 20°C (p<0.0001) and 25°C (p<0.001, log-rank test.). (L) qRT-PCR results showing rnp-6 transcript levels remain stable upon S. aureus infection. ilys-2 serves as a positive control here. (M) Western blot results showing the protein levels of rnp-6 do not change upon S. aureus infection. Experiments of panel E, G and J were performed twice. All other experiments were performed three times independently. Error bars represent mean ± s.e.m. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, ns non-significant, unpaired t-test.
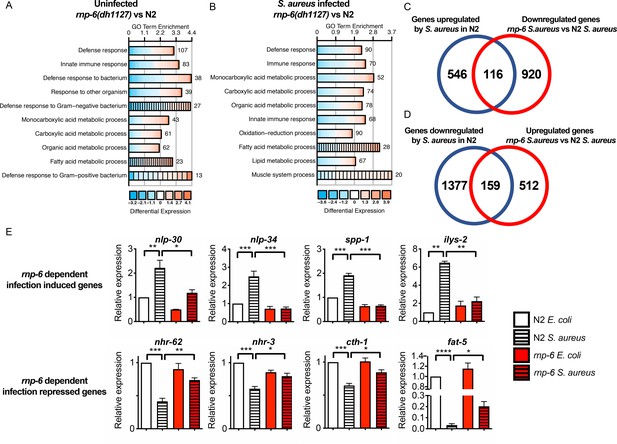
Dysregulation of immune responses in the rnp-6 G281D mutant.
(A,B) GO enrichment analysis using DAVID. RNA sequencing was performed on WT and rnp-6(dh1127) animals under control and S. aureus infected conditions. The 10 most statistically significant terms (based on p-values) are depicted for each comparison (p-values ascending). The enrichment (x axis), fold change (colour coding) and number of genes are shown. (C) Venn diagrams showing the numbers of up-regulated genes by infection and genes that are down-regulated in infected rnp-6(dh1127) when compared to infected N2 animals. rnp-6 dependent infection induced gene are defined as the interception between the two set of genes. (D) Venn diagrams of genes that are down-regulated upon infection and genes that are up-regulated in infected rnp-6(dh1127) when compared to infected wildtype animals. rnp-6 dependent infection repressed genes are defined as the interception between the two set of genes. (E) qRT-PCR results showing rnp-6 G281D substitution compromises induction of antimicrobial genes (nlp-30, nlp-34, spp-1 and ilys-2) upon S. aureus infection. Metabolic genes (nhr-62, nhr-3, cth-1 and fat-5), which are suppressed in wildtype animals upon infection, maintain a higher expression in the rnp-6(dh1127) mutant. Error bars represent mean ± s.e.m. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, unpaired t-test.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
List of differentially expressed genes.
Non-infected.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57591/elife-57591-fig2-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 2
List of differentially expressed genes.
Infected.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57591/elife-57591-fig2-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 3
List of rnp-6 dependent infection induced genes.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57591/elife-57591-fig2-data3-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 4
List of rnp-6 dependent infection repressed genes.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57591/elife-57591-fig2-data4-v2.xlsx
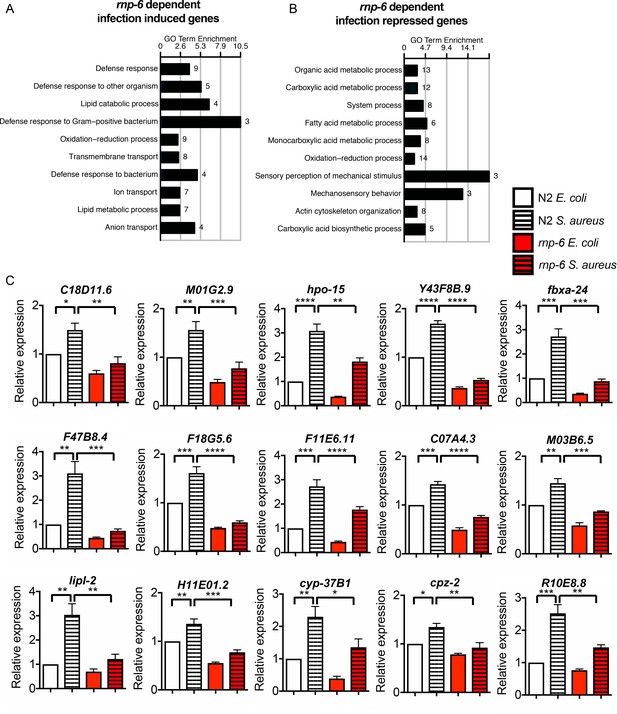
G281D substitution of rnp-6 inhibits transcriptional responses to bacterial infection, related to Figure 2.
(A,B) GO enrichment analysis of rnp-6 dependent infection responsive genes. (C) qRT-PCR results showing rnp-6 G281D substitution compromises induction of infection responsive genes upon S. aureus infection. Animals were harvested 4 hr after the start of infection. Error bars represent mean ± s.e.m. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, unpaired t-test.
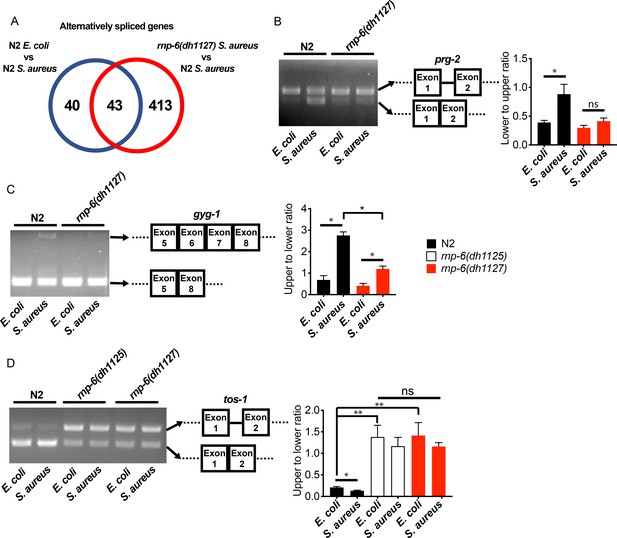
rnp-6 remodels alternate splicing patterns upon infection.
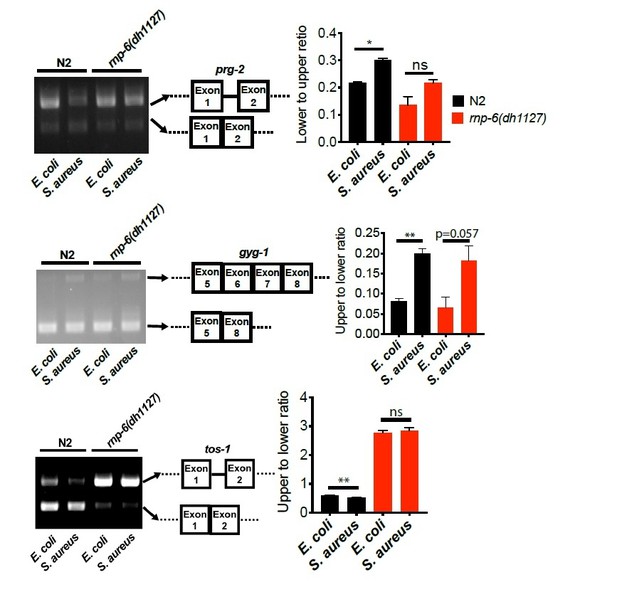
(A) Venn diagrams showing the numbers of alternatively spliced genes induced by S. aureus infection and those that are affected in infected rnp-6(dh1127) when compared to infected N2 animals. (B,C,D) Agarose gel analysis of RT-PCR products of prg-2, gyg-1 and tos-1. In wildtype animals, S. aureus infection induces a shift in splicing patterns, which is suppressed in the rnp-6 G281D mutants. Error bars represent mean ± s.e.m. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ns non-significant, unpaired t-test.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
List of alternatively spliced genes upon S. aureus infection in wildtype animals.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57591/elife-57591-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 3—source data 2
List of alternatively spliced genes between infected wildtype animals and infected rnp-6(dh1127) mutants.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57591/elife-57591-fig3-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 3—source data 3
List of genes whose splicing is affected by both infection and rnp-6.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57591/elife-57591-fig3-data3-v2.xlsx
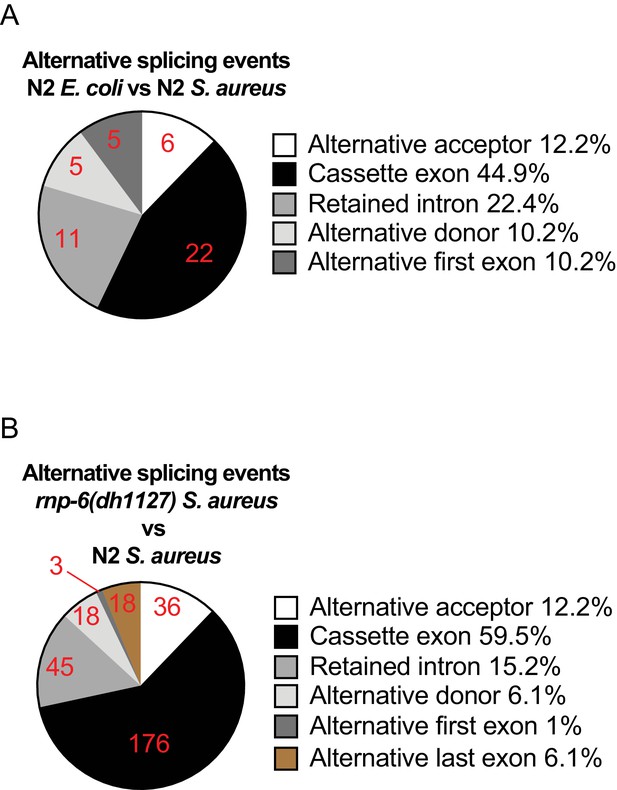
Alternative splicing events induced by infection and rnp-6 G281D substitution, related to Figure 3.
(A,B) Pie charts showing the percentage of each type of alternative splicing events in each indicated comparison. Analysis was performed with SAJR method. The numbers of splicing events are depicted.
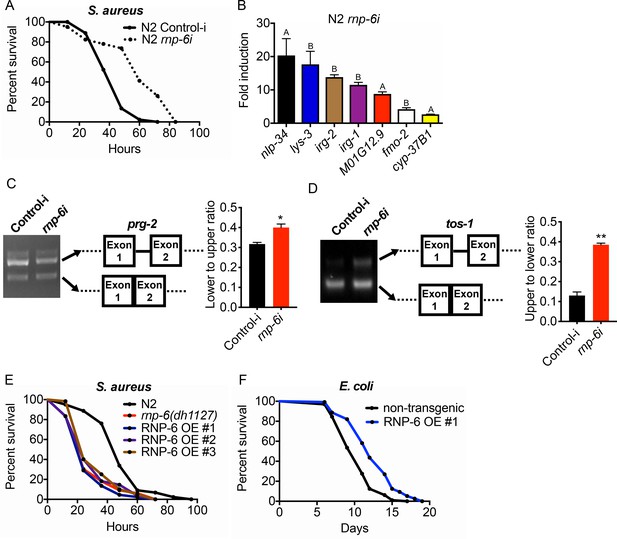
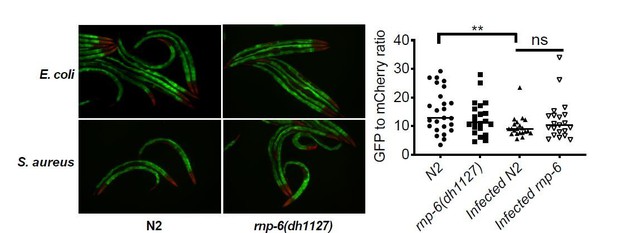
RNP-6 restrains innate immunity in C. elegans.
(A) Infection survival analysis. Young adult worms fed with either control or rnp-6 RNAi HT115 bacteria were infected with S. aureus. rnp-6 RNAi leads to prolonged survival (p<0.0001, log-rank test.). (B) qRT-PCR results showing that wildtype animals grown on rnp-6 RNAi HT115 bacteria have elevated levels of immune-related genes. (nlp-34 p=0.0184, lys-3 p=0.0132, irg-2 p<0.0001, irg-1 p=0.0002, M01G12.9 p=0.0002, fmo-2 p=0.0021, cyp-37B1 p<0.0001, unpaired t-test.). ‘A’ denotes genes that are repressed in the rnp-6 G281D mutant under infection condition. ‘B’ denotes genes that are also slightly induced in the rnp-6 G281D mutant. Error bars represent mean ± s.e.m. (C,D) Agarose gel analysis of RT-PCR products of prg-2 and tos-1. In wildtype animals, rnp-6 RNAi (OP50) induces a shift in splicing patterns. (E) RNP-6 overexpressing strains show enhanced sensitivity upon infection with S. aureus (RNP-6 OE #1, p<0.0001, RNP-6 OE #2 P<0.0001, RNP-6 OE #3 p=0.0006, log-rank test). (F) Demographic analysis of lifespan. Overexpression of RNP-6 prolongs lifespan when the animals are cultured withE. coliOP50 at 25°C (p<0.0001, log-rank test.). Survival and lifespan experiments were performed three times independently. Error bars represent mean ± s.e.m. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, unpaired t-test.
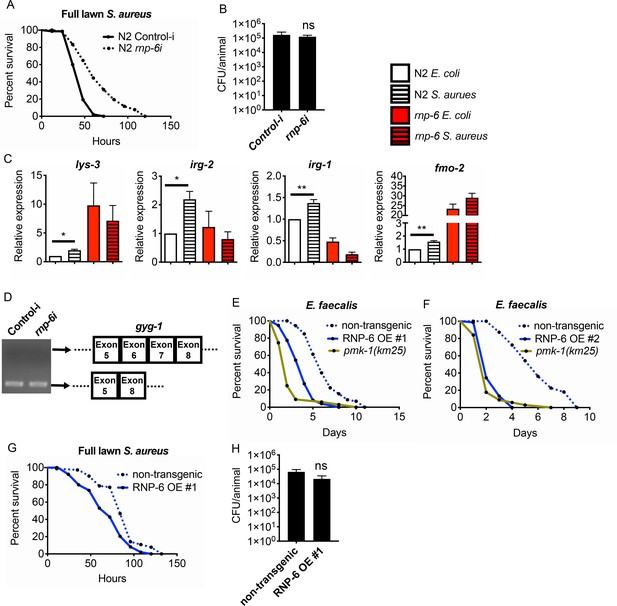
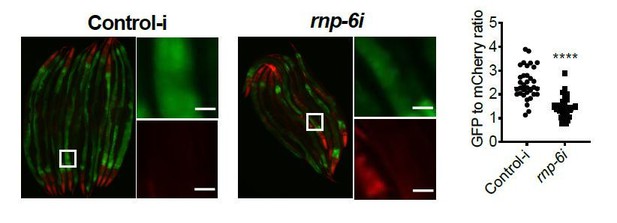
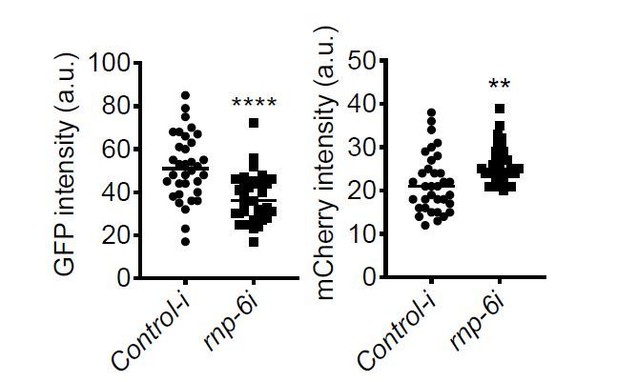
rnp-6 regulates immune gene expression, and its overexpression compromises infection survival, related to Figure 4.
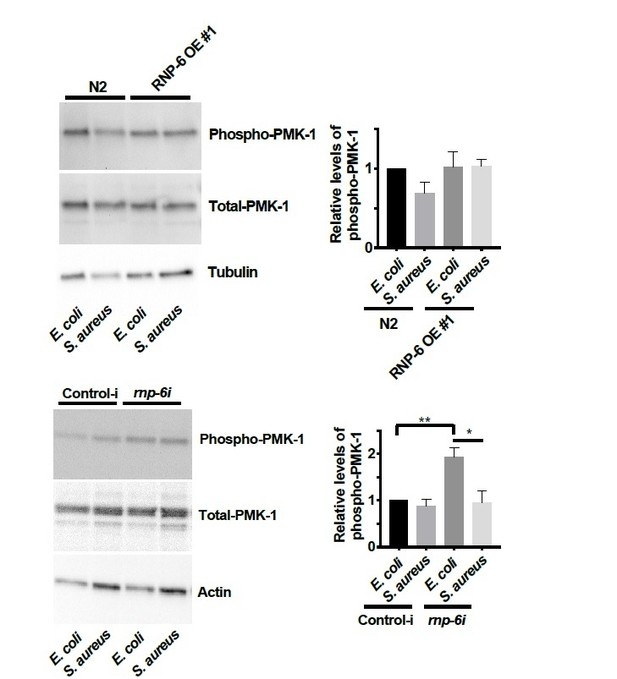
(A) Infection survival analysis. rnp-6 OP50 RNAi prolongs survival of N2 animals under full lawn S. aureus infection condition (p<0.0001, log-rank test.). (B) Bacterial burden at 24 hr post-infection. No significant difference between control-i and rnp-6i treated N2 animals. (C) qRT-PCR results showing rnp-6 G281D substitution leads to differential expression of lys-3, irg-2, irg-1 and fmo-2. Animals were harvest 4 hr after the start of infection. (D) Agarose gel analysis of RT-PCR products of gyg-1. In wildtype animals, rnp-6 RNAi (OP50) has no observable effects on splicing patterns. (E,F) RNP-6 overexpressing strains show sensitivity to E. faecalis (#1 P<0.0001, #2 P<0.0001, log-rank test.). (G) Infection survival analysis. Chemicalized sterilized (FUDR) animals were infected with full lawn S. aureus plates. RNP-6 overexpressing strains show compromised survival under these conditions (p<0.0001, log-rank test.). (H) Bacterial burden at 24 hr post-infection. No significant difference between RNP-6 overexpressing animals and non-transgenic siblings. Error bars represent mean ± s.e.m. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ns non-significant, unpaired t-test.
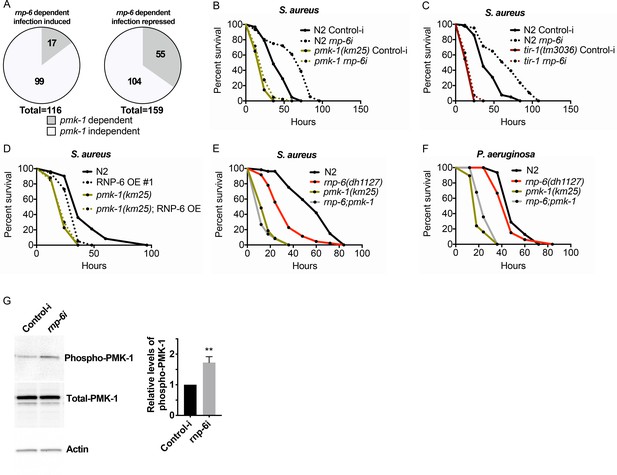
RNP-6 controls PMK-1 activity.
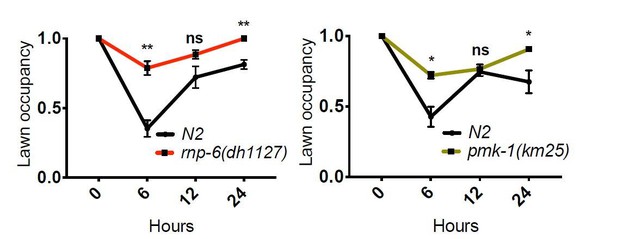
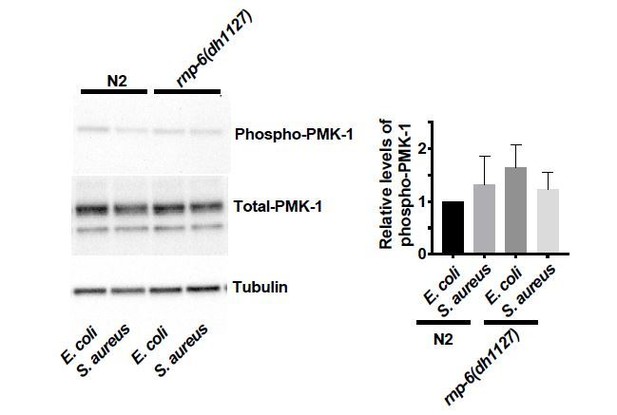
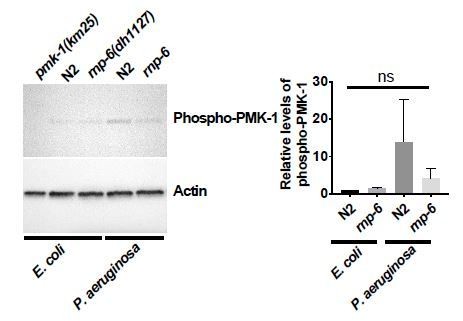
(A) Pie charts showing the portion of rnp-6 dependent infection responsive genes which are also reported to be pmk-1 dependent. 17 out of 116 rnp-6 dependent infection induced genes also have pmk-1 dependent induction (p<0.0001). 55 out of 159 rnp-6 dependent infection repressed genes are up-regulated in pmk-1 deletion mutants (p<0.0001). (B,C) Infection survival analysis. Wildtype, pmk-1(km25) and tir-1(tm3036) animals were fed with either control or rnp-6 RNAi OP50 bacteria and then infected with S. aureus. rnp-6 RNAi does not prolong survival in the pmk-1 or tir-1 deletion mutant (non-significant, log-rank test.). (D) Overexpression of RNP-6 does not further sensitize pmk-1 deletion mutants to S. aureus infection (non-significant, log-rank test.). (E) rnp-6(dh1127) does not further sensitize the pmk-1 deletion mutants to S. aureus infection (non-significant, log-rank test.). (F) rnp-6(dh1127) mutation decreases survival in wildtype background upon P. aeruginosa infection (p=0.0056, log-rank test). However, the double mutant of rnp-6(dh1127) and pmk-1(km25) has enhanced survival relative to pmk-1(km25) alone (p<0.0001, log-rank test). (G) Western blot analysis showing the levels of phosphorylated PMK-1. N2 animals grown on HT115 RNAi bacteria targeting rnp-6 possess higher levels of PMK-1 phosphorylation. **p<0.05. Error bars represent mean ± s.e.m., unpaired t-test. Survival experiments were performed three times independently.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
List of rnp-6 dependent infection induced genes with pmk-1 dependency.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57591/elife-57591-fig5-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 5—source data 2
List of rnp-6 dependent infection repressed genes with pmk-1 dependency.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57591/elife-57591-fig5-data2-v2.xlsx
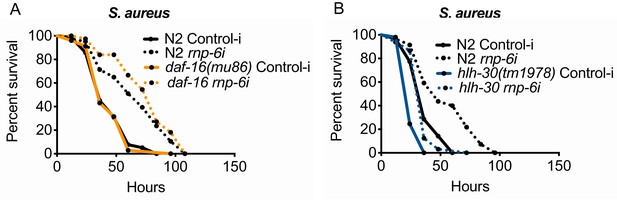
daf-16 and hlh-30 do not play a significant role in rnp-6 mediated immunity, related to Figure 5.
(A,B) Infection survival analysis. rnp-6 OP50 RNAi prolongs survival under S. aureus infection condition in daf-16 (p<0.0001) and hlh-30 (p<0.0001, log-rank test.) mutants.

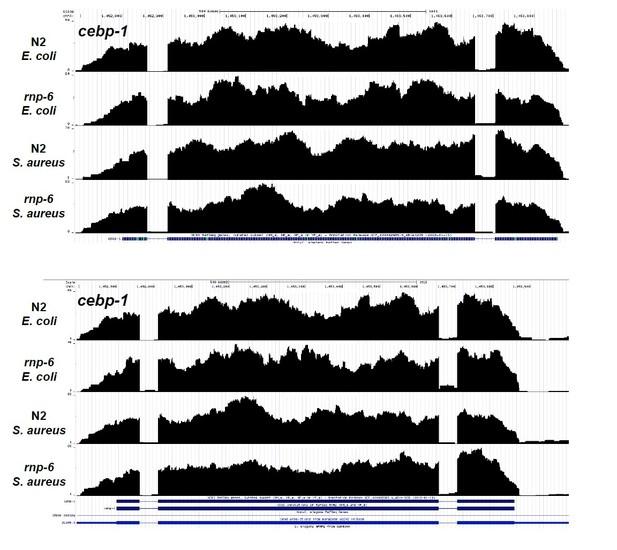
rnp-6 regulates immunity independently of splicing of the PMK-1 MAPK signaling pathway genes, related to Figure 5.
(A–I) Sequencing reads coverage for gene members of the PMK-1 MAPK signaling pathway. These genes are tir-1, nsy-1, sek-1, pmk-1, vhp-1, skn-1, atf-7, riok-1 and cebp-1. The splicing patterns of these genes are not significantly and consistently affected by S. aureus infection or the rnp-6 G281D mutation.
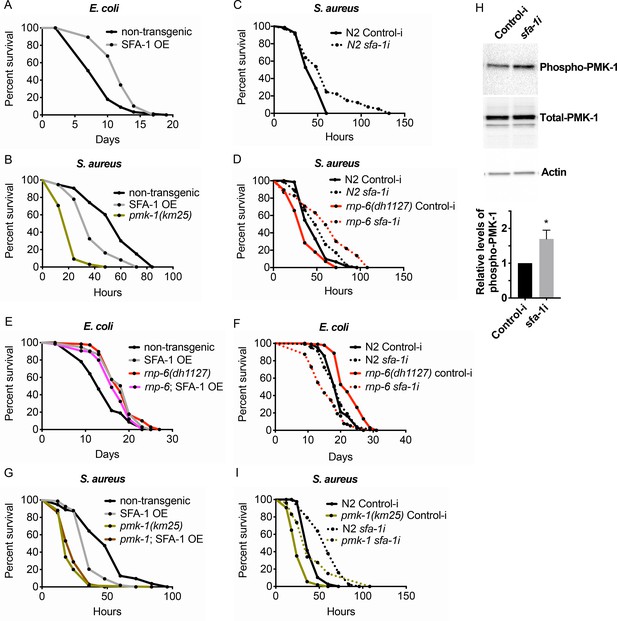
Suppression of immunity by SFA-1.
(A) Demographic analysis of lifespan. Overexpression of SFA-1 extends lifespan when the animals are cultured withE. coliOP50 at 25°C (p<0.0001, log-rank test.). (B) Infection survival analysis. SFA-1 overexpressing animals show significant sensitivity to S. aureus infection (p=0.0165, log-rank test.). The pmk-1 deletion mutant serves as a positive control for infection sensitivity. (C) Wildtype worms grown on control or sfa-1 RNAi OP50 bacteria were infected with S. aureus. sfa-1 knockdown improves survival (p=0.0048, log-rank test.). (D) sfa-1 knockdown using OP50 RNAi bacteria suppresses infection sensitivity of rnp-6(dh1127) mutants (p<0.0001, log-rank test, comparing rnp-6(dh1127) Control-i and rnp-6 sfa-1i). (E) Demographic analysis of lifespan. SFA-1 overexpression does not further extend the lifespan of rnp-6(dh1127) mutants. In fact, SFA-1 overexpression slightly reduces the rnp-6 mutants’ lifespan (p=0.0147, log-rank test.). (F) sfa-1 RNAi (OP50) abolishes rnp-6(dh1127) longevity (p<0.0001, log-rank test, comparing rnp-6(dh1127) Control-i and rnp-6 sfa-1i). (G) SFA-1 overexpression does not further sensitize pmk-1(km25) animals to S. aureus infection (non-significant, log-rank test.). (H) Western blot analysis showing the levels of phosphorylated PMK-1. N2 animals grown on OP50 RNAi bacteria targeting sfa-1 possess higher levels of PMK-1 phosphorylation. Error bars represent mean ± s.e.m., *p<0.05, unpaired t-test. (I) Infection survival analysis. sfa-1 knockdown using OP50 RNAi bacteria extends infection survival upon S. aureus infection in pmk-1(km25) mutants (p<0.0001, log-rank test.). Experiments of panel A and E were performed twice. All other survival and lifespan experiments were performed three times independently.
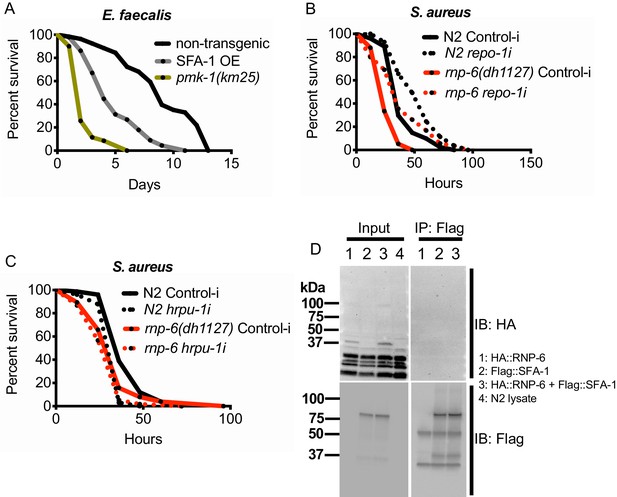
sfa-1 specifically work with rnp-6 to regulate infection survival, related to Figure 6.
(A) Infection survival analysis. SFA-1 overexpression causes sensitivity to E. faecalis (p<0.0001, log-rank test.). (B,C) repo-1 or hrpu-1 RNAi does not fully rescue the sensitivity of rnp-6(dh1127) mutants to S. aureus. (D) Immunoblot of immunoprecipitation experiments between Flag-SFA-1 and HA-RNP-6. No obvious co-immunoprecipitation can be detected, suggesting SFA-1 and RNP-6 do not physically interact.
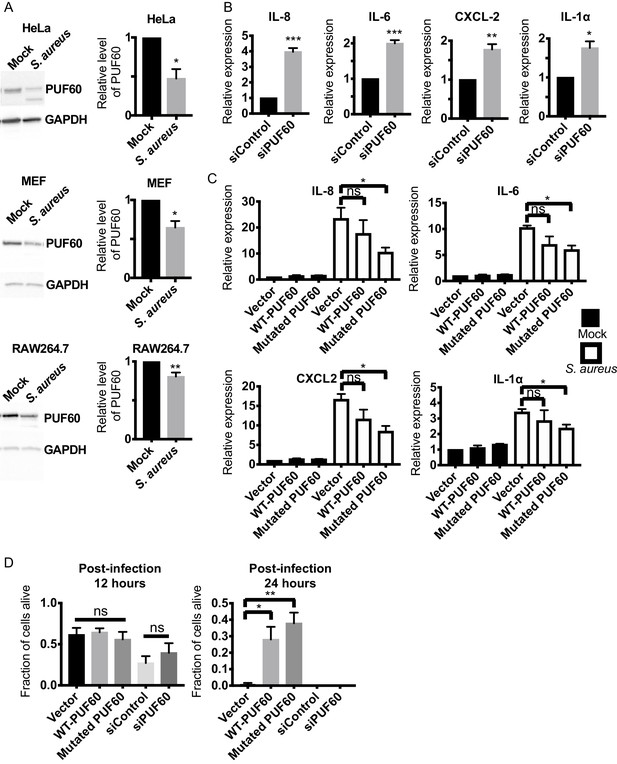
Evolutionary conservation of immuno-suppressive and anti-inflammatory functions of PUF60 in mammalian cells.
(A) Western blot analysis of S. aureus infected HeLa, MEF and RAW264.7 cells at 6 hr post-infection. S. aureus infection significantly reduces the protein levels of PUF60. (B) qRT-PCR results. HeLa cells were transfected with either control non-targeting or PUF60 siRNA. The cells were harvested at post-transfection 48 hr. PUF60 RNAi induces cytokine expression. GAPDH was used for internal normalization. (C) qRT-PCR results of S. aureus infected HeLa cells. Cells were transfected with the indicated expression plasmids. At 48 hr post-transfection, the cells were infected with S. aureus and harvested at 6 hr post-infection. Transfection of the mutated PUF60 (G300D) plasmid significantly reduces the induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Although the trend of cytokine suppression is evident for wildtype PUF60, the effects do not reach statistical significance. RPL13A was used for internal normalization. (D) HeLa cells survival after S. aureus infection. Overexpression of either wildtype or the mutated PUF60 (G300D) improves cell survival at 24 hr post-infection. Cells were transfected with the indicated siRNA or expression plasmids and then infected with S. aureus 48 hr after transfection. Error bars represent mean ± s.e.m. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ns non-significant, unpaired t-test.
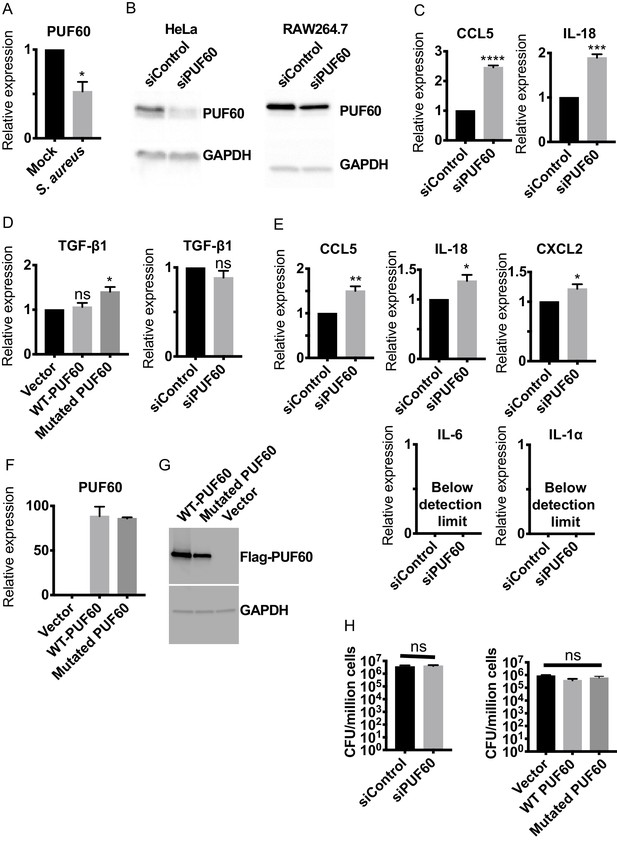
PUF60 suppresses inflammation in mammalian cells, related to Figure 7.
(A) qRT-PCR results of S. aureus infected HeLa cells. At post-infection 6 hr, PUF60 transcript levels are significantly lower in the infected cells. (B) Western blot showing PUF60 levels are reduced upon transfection of PUF60 targeting siRNAs in HeLa and RAW264.7 cells. Cells were harvested 48 hr after transfections. (C, D) qRT-PCR results of HeLa cells transfected with PUF60 expression plasmids or PUF60 targeting siRNAs. Knocking-down PUF60 induces expression of CCL5 and IL-18, but has no effects on TGF- β1 transcript levels. Overexpression of the mutated form (G300D) of PUF60 increases TGF-β1 transcript abundance. Cells were harvested 48 hr after transfections. (E) qRT-PCR results of RAW264.7 cells transfected with PUF60 targeting siRNAs. Knocking-down PUF60 induces expression of CCL5, IL-18 and CXCL2. The transcript levels of IL-6 and IL-1α are below the detection limit. Cells were harvested 48 hr after transfections. (F) qRT-PCR results of HeLa cells transfected with PUF60 expression plasmids. Both wildtype and the mutated form of PUF60 have comparable transcript levels. Cells were harvested 48 hr after transfections. (G) Western blot results of HeLa cells transfected with PUF60 expression plasmids. The protein abundance of wildtype PUF60 is higher than that of the mutated form, although the same amounts of DNA were transfected, and the transcript levels are comparable. Cells were harvested 48 hr after transfections. (H) Intracellular bacterial burden of HeLa cells. Neither PUF60 knockdown nor overexpression affects intracellular bacterial burden right after infection, suggesting PUF60 does not affect bacterial uptake of the cells. Error bars represent mean ± s.e.m. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, ns non-significant, unpaired t-test.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
List of primers.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57591/elife-57591-supp1-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
qPCR primer binding sites for C. elegans targets.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57591/elife-57591-supp2-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 3
qPCR primer binding sites for human targets.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57591/elife-57591-supp3-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 4
qPCR primer binding sites for mouse targets.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57591/elife-57591-supp4-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 5
List of antibodies.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57591/elife-57591-supp5-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 6
Table of survival data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57591/elife-57591-supp6-v2.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57591/elife-57591-transrepform-v2.docx