A systematic review of population-based studies on lipid profiles in Latin America and the Caribbean
Figures
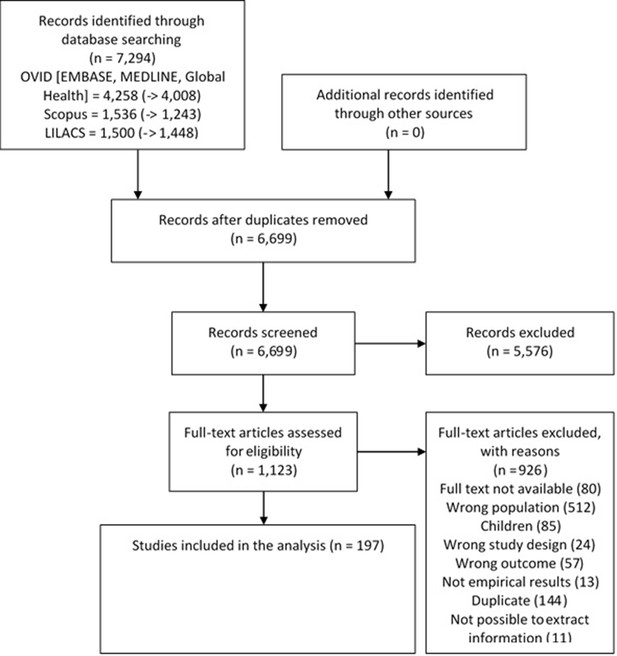
Selection process and number of data sources per year.
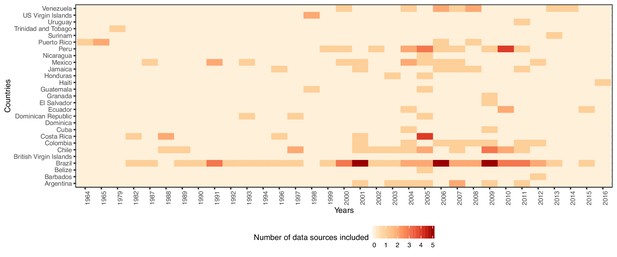
In this figure supplement, we show the number of data sources by country and year of data collection.
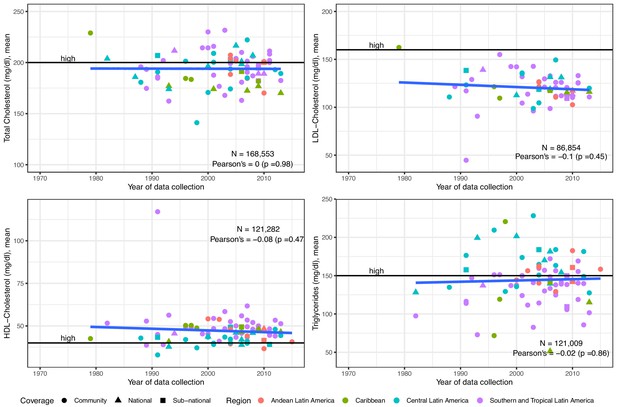
Trends in mean total cholesterol, LDL-Cholesterol, HDL-Cholesterol and triglycerides in Latin America and the Caribbean.
The solid blue line represents a linear regression trend. Year in the x-axis refers to data collection year. Countries within sub-regions are shown in Supplementary file 1, Table 5. Individual estimates are shown in Supplementary file 1, Table 2.
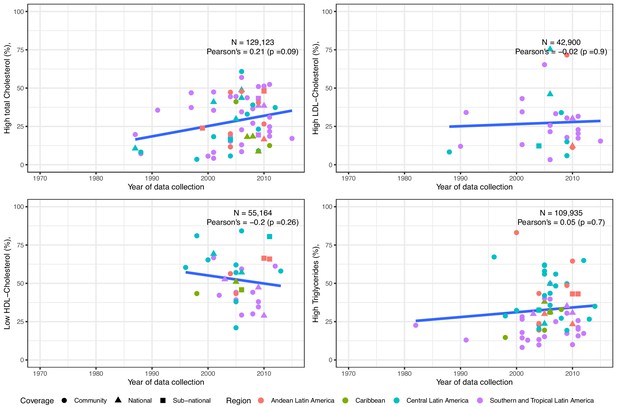
Trends in prevalence of high total cholesterol, high LDL-Cholesterol, low HDL-Cholesterol and high triglycerides in Latin America and the Caribbean. The solid blue line represents a linear regression trend.
Year in the x-axis refers to data collection year. Countries within sub-regions are shown in Supplementary file 1, Table 5. Studies included in this graphics are those with standard clinically relevant definitions. I.e., total cholesterol ≥150 mg/dl,≥200 mg/dl, or ≥240 mg/dl; LDL-Cholesterol ≥100 mg/dl,≥130 mg/dl, or ≥160 mg/dl; HDL-Cholesterol ≤40 mg/dl in men and ≤50 mg/dl in women; triglycerides ≥ 100 mg/dl,≥130 mg/dl,≥150 mg/dl, or ≥200 mg/dl. That is, prevalence estimates based on other definitions were excluded. Individual estimates are shown in Supplementary file 1, Table 3.
Tables
Pooled mean and pooled prevalence estimates since 2005, random-effects meta-analysis.
| Mean (mg/dl) | Lower 95% confidence interval | Upper 95% confidence interval | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total cholesterol (37 studies) | 193.39 | 189.10 | 197.68 |
| LDL-Cholesterol (30 studies) | 119.98 | 116.08 | 123.88 |
| HDL-Cholesterol (42 studies) | 46.55 | 44.99 | 48.12 |
| Triglycerides (39 studies) | 139.27 | 130.57 | 147.98 |
| Prevalence (%) | Lower 95% confidence interval | Upper 95% confidence interval | |
| High total cholesterol - ≥ 200 mg/dl (six studies) | 34.04 | 19.04 | 49.04 |
| High total cholesterol - ≥ 240 mg/dl (five studies) | 20.97 | 13.51 | 28.43 |
| High LDL-Cholesterol - ≥ 130 mg/dl (two studies) | 40.41 | 29.05 | 51.78 |
| High LDL-Cholesterol - ≥ 160 mg/dl (five studies) | 19.73 | 11.57 | 27.89 |
| Low HDL-Cholesterol ≤ 40(men) and ≤50(women) (nine studies) | 48.27 | 36.31 | 60.22 |
| High Triglycerides ≥ 150 mg/dl (12 studies) | 43.12 | 35.40 | 50.85 |
| High Triglycerides ≥ 200 mg/dl (four studies) | 20.48 | 16.28 | 24.69 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Word document with checklist for reporting of systematic reviews; search terms used; risk of bias assessment and rationale; table describing the selected studies along with references; table with the mean levels by selected study; table with prevalence estimates by selected study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57980/elife-57980-supp1-v1.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57980/elife-57980-transrepform-v1.docx