A low affinity cis-regulatory BMP response element restricts target gene activation to subsets of Drosophila neurons
Abstract
Retrograde BMP signaling and canonical pMad/Medea-mediated transcription regulate diverse target genes across subsets of Drosophila efferent neurons, to differentiate neuropeptidergic neurons and promote motor neuron terminal maturation. How a common BMP signal regulates diverse target genes across many neuronal subsets remains largely unresolved, although available evidence implicates subset-specific transcription factor codes rather than differences in BMP signaling. Here we examine the cis-regulatory mechanisms restricting BMP-induced FMRFa neuropeptide expression to Tv4-neurons. We find that pMad/Medea bind at an atypical, low affinity motif in the FMRFa enhancer. Converting this motif to high affinity caused ectopic enhancer activity and eliminated Tv4-neuron expression. In silico searches identified additional motif instances functional in other efferent neurons, implicating broader functions for this motif in BMP-dependent enhancer activity. Thus, differential interpretation of a common BMP signal, conferred by low affinity pMad/Medea binding motifs, can contribute to the specification of BMP target genes in efferent neuron subsets.
Introduction
Diverse neuronal subtypes are generated by the gene regulatory activities of subtype-specific combinations of transcription factors (Allan and Thor, 2015; da Silva and Wang, 2011; Hobert et al., 2010). In postmitotic neurons, retrograde signaling continues to play prominent roles during neuronal maturation and through life in regulating terminal differentiation and synaptic function (Allan et al., 2003; Angley et al., 2003; Veverytsa and Allan, 2011; Berke et al., 2013; Chou et al., 2013; Kelly et al., 2013; Majdazari et al., 2013; Xiao et al., 2013; DuVal et al., 2014; McCabe et al., 2003; Guha et al., 2004; Lopez-Coviella et al., 2005; Hodge et al., 2007; Pavelock et al., 2007; Miguel-Aliaga et al., 2008; Eade and Allan, 2009; Henríquez et al., 2011). In Drosophila, retrograde BMP signaling occurs within most efferent neurons, regulating a diverse suite of target genes in a subtype-specific manner; for example, the neuropeptide genes unique to each neurosecretory subtype, and the partially overlapping battery of genes that support the growth and strengthening of motor neuron neuromuscular junction synapses (Veverytsa and Allan, 2011; Miguel-Aliaga et al., 2008; Allan et al., 2003; Kim and Marqués, 2010; Vuilleumier et al., 2019; Ball et al., 2010; Marqués et al., 2003). An unresolved question regards how BMP target genes are differentially specified within each of these BMP-activated neuron subtypes. Prevailing models suggest that subtype-specific transcription factors play the primary role in target gene selection, and BMP-responsive DNA motifs within those target gene enhancers encode generic responsiveness to BMP signaling in any neuron (Veverytsa and Allan, 2011; Miguel-Aliaga et al., 2008; Allan et al., 2005). Here we describe our identification of a low affinity BMP-responsive DNA motif that instructively contributes to the differential specification of BMP target genes within efferent neuron subtypes.
In Drosophila efferent neurons, retrograde BMP-signaling is triggered by Glass bottom boat (Gbb) ligand engagement at a presynaptic BMP-Receptor (BMP-R) complex of Wishful thinking (Wit), Thickveins (Tkv), and Saxophone (Sax). This leads to phosphorylation of Mad to pMad (vertebrate SMAD1/5/9) (Allan et al., 2003; McCabe et al., 2003; Aberle et al., 2002; Rawson et al., 2003), which then complexes with Medea (vertebrate SMAD4) (Gao and Laughon, 2007; Gao et al., 2005). This pMad/Medea complex translocates to the nucleus and regulates transcription by binding DNA in a sequence-specific manner at BMP-response elements (BMP-REs) (Kim et al., 1997; Xu et al., 1998; Shi and Massagué, 2003). In the nucleus, Schnurri (Shn) can act as a co-repressor with the pMad/Medea complex at silencer BMP-REs (BMP-SE) to repress target genes (Gao et al., 2005; Pyrowolakis et al., 2004; Charbonnier et al., 2015). Additionally, Brinker (Brk) is a DNA binding default repressor of genes in the absence of BMP-signaling (Barolo and Posakony, 2002; Affolter and Basler, 2007; Hamaratoglu et al., 2014).
Studies of BMP-dependent morphogenesis in the Drosophila embryo and wing imaginal disc have established core principles and sequence preferences for BMP-REs and transcriptional regulators of the BMP pathway. BMP-dependent gene activation is mediated directly by pMad/Medea acting at a bipartite 15 bp BMP-AE; GGCGCCA(N4)GNCV (Weiss et al., 2010; Chayengia et al., 2019). BMP-dependent gene silencing is mediated directly by pMad, Medea, and Shn acting in a complex at a bipartite 15 bp BMP-SE; GRCGNC(N5)GNCT (Gao et al., 2005; Pyrowolakis et al., 2004; Charbonnier et al., 2015). In these complexes, two pMad proteins bind to the 6 bp GC-rich sequence, and a single Medea protein binds to the 4 bp GNCV/GNCT sequence (Gao et al., 2005). An additional widely-utilized mechanism for BMP target gene activation in Drosophila involves brk-dependent de-repression (Affolter and Basler, 2007). Here BMP signaling results in pMad, Medea and Shn binding to multiple BMP-SE motifs in the brk locus (Pyrowolakis et al., 2004; Marty et al., 2000; Torres-Vazquez et al., 2000; Müller et al., 2003). Subsequent reduction in Brk levels relieves its default repression of many genes, which thereby become de-repressed in a BMP-dependent manner (Pyrowolakis et al., 2004; Jaźwińska et al., 1999; Campbell and Tomlinson, 1999; Winter and Campbell, 2004; Minami et al., 1999; Moser and Campbell, 2005).
We recently demonstrated that the BMP-AE motif serves as a widely-deployed BMP-dependent activator of gene expression in larval Drosophila efferent neurons (Vuilleumier et al., 2019). In that study, BMP-AE motifs were shown to confer BMP-dependence on enhancers that were active in diverse patterns across the many subtypes of efferent neurons. This diversity did not appear to be encoded by sequence differences within BMP-AEs. For example, enhancers that included similar 15 bp BMP-AE sequences differed greatly in expression pattern (such as Van 50 and Van 27 reporters), and swapping BMP-AE sequences between enhancers failed to change expression pattern (Vuilleumier et al., 2019). This notion is supported by recent work in Drosophila follicular epithelium and wing imaginal disc showing that the cis-regulatory environment around BMP-AE motifs, bound by other transcription factors, determines the enhancer’s spatiotemporal activity, while the BMP-AE itself acts as a ‘monotonic’, or generic, interpreter of BMP activity (Chayengia et al., 2019).
The integration of BMP-activated pMad/Medea with subtype-specific transcription factors in Drosophila neurons has only been examined in detail in Tv4-neurons (Chayengia et al., 2019). Here a Tv4-neuron-specific transcription factor code and pMad/Medea were found to bind within a Tv4neuron-specific enhancer of the FMRFa gene (Allan et al., 2003; Allan et al., 2005; Miguel-Aliaga et al., 2004; Berndt et al., 2015; Benveniste et al., 1998), at a minimal 25 bp Homeodomain-Responsive Element, and a minimal 39 bp BMP-Responsive Element, respectively (Berndt et al., 2015). Misexpression of combinations of these transcription factors in other efferent neurons (with activated retrograde BMP signaling) led to widespread ectopic FMRFa gene activation (Allan et al., 2003; Eade and Allan, 2009; Allan et al., 2005; Miguel-Aliaga et al., 2004; Berndt et al., 2015; Benveniste et al., 1998; Baumgardt et al., 2009). By contrast, neither ectopic activation nor reduction in BMP signaling was found to alter Tv4-specific FMRFa expression. A parsimonious model emerging from these studies would suggest that activator BMP-RE motifs add a generic BMP-responsive input for an enhancer whose spatiotemporal activity is otherwise determined by subtype-specific transcription factors.
Here we provide evidence for a second model, in which low affinity BMP-RE motifs instructively contribute to subtype-specific gene expression within subsets of BMP-activated efferent neurons. By functional and biochemical dissection of the 39 bp BMP-responsive cis-element of the FMRFa enhancer, we identified a non-canonical minimal pMad/Medea binding motif [GGCGCC(N5)GTAT], which has low affinity (LA) compared to BMP-AE and BMP-SE motifs, that we herein term BMP-LA. Our genetic analysis showed that pMad and Medea act through this motif to directly activate FMRFa expression, without any contribution from brinker or schnurri. Notably, by converting this motif into a high affinity BMP-AE motif, we observed ectopic expression of BMP-dependent reporter activity into other neuronal populations, and a loss of expression in the Tv4-neuron itself. Finally, in silico searches and subsequent enhancer activity analysis revealed other functional instances of this motif in the genome. Overall, our results identify a novel low affinity BMP-RE motif type (BMP-LA), and lead to our proposal that the relative strength of BMP-responsive motifs is utilized to confer subtype-specific expression of BMP target genes in neurons.
Results
A 445 bp enhancer region mediates Tv4-neuron-specific expression of the FMRFa gene (Benveniste et al., 1998; Benveniste and Taghert, 1999). We recently sub-mapped this enhancer and defined two short cis-elements that are together necessary for enhancer activity, but are not individually sufficient (Berndt et al., 2015). Toward defining the information encoded by each cis-element, we found that concatemers for both cis-elements independently generate highly specific Tv4-neuron activity in late embryos. Thus, both contain sufficient information for Tv4-specific activity. This allowed us to explore their transcription factor inputs, leading to their definition as a homeodomain-responsive cis-element (HD-RE) and a BMP-responsive cis-element (BMP-RCE). The HD-RE recruits and is activated by the LIM-homeodomain transcription factor, Apterous, but does not require BMP-signaling for activation. The BMP-RCE requires BMP-signaling for its activity and recruits pMad sequence-specifically at a GGCGCC site (Berndt et al., 2015; Figure 1A).
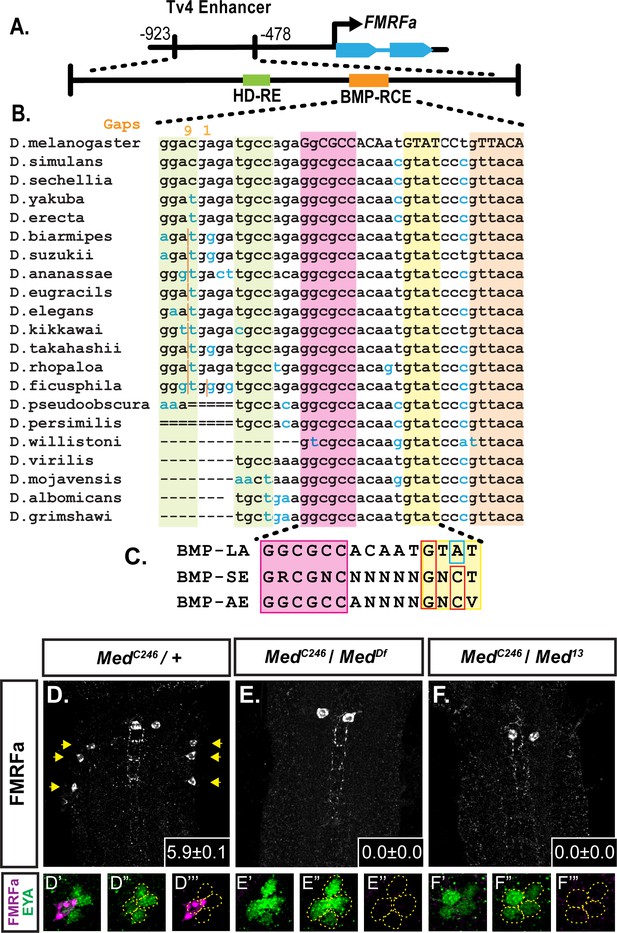
A novel BMP-Response element (BMP-RE) in the Tv4-neuron-specific enhancer of the FMRFa gene.
The 445 bp Tv4-enhancer depicted in (A) contains two cis-elements critical for FMRFa activation, the homeodomain response element (HD-RE that recruits Apterous), and the BMP response element (BMP-RCE) that binds pMad and mediates the BMP-dependence of the Tv4-enhancer. (B) Output from the UCSC Browser shows sequence conservation through the BMP-RE across 21 Drosophila species. Capitalized letters are conserved across all species. Highlighted sequences include the putative Mad/Brinker binding site (magenta), two 5’ optimal GNCV Medea binding sequences with non-canonical spacing (green), and three 3’ sequences that deviate from a non-stringent GNCN sequence in one critical nucleotide (yellow, orange). The yellow GTAT motif is ideally spaced but has a C > A switch. The orange GTTACA contains two motifs (GTTA with a C > T switch, and TACA with a G > T switch). (C) Comparison of a putative FMRFa BMP-RE with the well-defined BMP-SE and BMP-AE motifs. (D-F) FMRFa immunoreactivity in Tv4-neurons is lost in Medea nulls (E,F) compared to controls (D). Insets show mean number of FMRFa-positive Tv4-neurons per VNC ± SD. (D’-F’’) Fluorophore splits of single Tv -clusters in A-C, showing Tv-neurons (circled) labeled by anti-Eya (green) and anti-FMRFa (magenta) expression in each genotype.
The 15 bp FMRFa BMP-responsive cis-element contains a novel pMad/Medea-binding motif
Here we explored how the 39 bp BMP-RCE encodes activity that is BMP-dependent and Tv4-neuron-specific. We previously defined the necessity of a palindromic GGCGGC pMad-binding sequence, but not its associated Medea-binding sequence (Berndt et al., 2015). Here we find two GNCV-types sequences 5’ of the GGCGCC sequence; spaced 3 and 11 nucleotides away (green highlight in Figure 1B). Although not of canonical 5nt length, BMP-AE motifs with altered linker lengths have been shown to retain activity (Weiss et al., 2010; Chayengia et al., 2019; Esteves et al., 2014). We substitution mutagenized the 15 bp region containing these sequences, within the context of a full-length 445 bp Tv4-enhancer (Figure 1—figure supplement 1A). This mutant reported wildtype levels of enhancer activity in Tv4-neurons; therefore, we discounted all sequences 5’ of the pMad-binding site as essential (Figure 1—figure supplement 1B,C).
Within sequences 3’ of pMad-binding site in the remainder of the minimal 39 bp region, there are no consensus GNCV or GTCT motifs. However, three sequences deviate from the consensus by only a single nucleotide, including a perfectly conserved GTAT sequence spaced five nucleotides from the pMad site (yellow highlight in Figure 1B), and a conserved GTTACA spaced 12nt from the pMad motif, with partially overlapping GTTA and TACA sequences (orange highlight in Figure 1B).
pMad and Medea are direct activators of FMRFa
The lack of a canonical Medea site, necessary for BMP-RE motif activity, led us to test if Medea is even required for FMRFa expression. In two different null Medea backgrounds, immunoreactivity to the FMRFa prepropeptide was entirely lost (Figure 1D–F). Anti-Eya staining revealed that all four Tv neurons were generated. We also examined EYFP reporter expression driven from the full length 445 bp TvWT-EYFP enhancer, and from the concatemerized BMP-RCE and HD-RE reporters (Berndt et al., 2015). As expected, TvWT-EYFP and BMP-RCE-EYFP expression were eliminated, while the BMP-insensitive HD-RE-EYFP exhibited expression comparable to controls (Figure 1—figure supplement 1D–I). Thus, Medea is selectively required for the BMP input that activates FMRFa expression.
The apparent dichotomy of Mad and Medea-dependence in the absence of a canonical BMP-RE motif led us to test whether brinker (brk) de-repression accounts for BMP-dependent FMRFa expression (Figure 2A). In numerous Drosophila tissues outside the nervous system, brk-mediated de-repression results in BMP-dependent gene expression (Hamaratoglu et al., 2014). In the absence of BMP-signaling, Brk binds GGCGYY motifs to default repress many genes that are activated upon the onset of BMP signaling (Zhang et al., 2001). In the presence on BMP signaling, pMad, Medea, and Shn bind BMP-SE motifs to repress brk (Pyrowolakis et al., 2004; Marty et al., 2000; Torres-Vazquez et al., 2000; Müller et al., 2003), lowering its expression and resulting in the de-repression of BMP gene targets (Pyrowolakis et al., 2004; Jaźwińska et al., 1999; Campbell and Tomlinson, 1999; Winter and Campbell, 2004; Minami et al., 1999; Moser and Campbell, 2005).
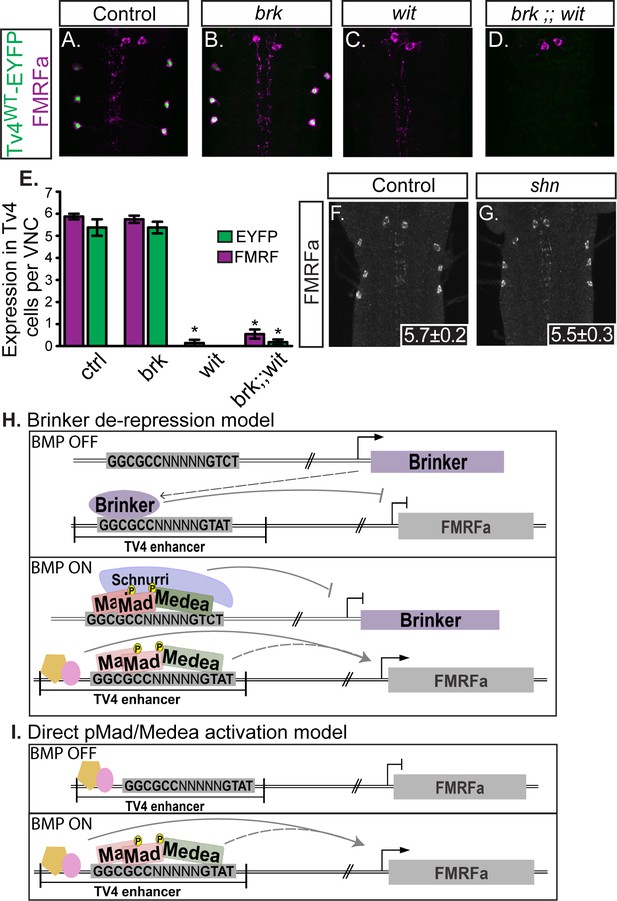
Neither brinker nor schnurri are required for BMP-dependent FMRFa.
(A,B) Expression of the BMP-dependent FMRFa prepropeptide and the Tv4WT-EYFP reporter were not affected in brk mutants. (C,D) Loss of FMRFa prepropeptide and Tv4WT-EYFP in wit nulls was not rescued by the loss of brk in the double mutant of brk and wit. Thus, FMRFa is not lost in wit mutants due to the de-repression of brk. (E) Quantification of data in A-D (n = 7–12 animals per group, *p<0.01 compared to controls using One-way ANOVA with Tukey HSD post-hoc). (F,G) No change in the number of FMRFa-positive Tv4-neurons was observed between control and shn nulls in late stage 17 embryos. Mean ± SD number of FMRFa-positive Tv4-neurons per VNC shown in inset, n = 5 per genotype. (H) In a Brinker de-repression model, brinker would act as an FMRFa repressor by binding to the BMP-LA element (at the GGCGCC motif). When the BMP signaling pathway is active, the activated pMad/Medea complex would translocate to the nucleus and bind to the brk BMP-SE element, recruiting Schnurri, and silencing brk expression. This would allows expression of FMRFa, activated by other transcription factors and/or direct binding of a pMad/Medea complex. (I) In a direct pMad/Medea complex activation model, FMRFa is only expressed when an activated pMad/Medea complex binds to the BMP-LA sequence. Our work indicates that this latter model is likely correct, as neither brk nor shn manipulation modulates BMP-dependent FMRFa expression. Genotypes: Control (TvWT-nEYFP). brk (brkXA/Y;;TvWT-nEYFP/TvWT-nEYFP). wit (TvWT-nEYFP,witA12/TvWT-nEYFP,witB11). brk;;wit (brkXA/Y;; TvWT-nEYFP,witA12/TvWT-nEYFP,witB11). shn control in F (w;shn1/+). shn null in G (shn1/shn1).
The BMP-responsive GGCGCC sequence in the FMRFa BMP-RCE matches this Brk consensus motif (Zhang et al., 2001). If a Brk de-repression model were correct for FMRFa expression (Figure 2H), BMP-induced pMad, Medea, and Schnurri (Shn) would be required to silence brk, resulting in FMRFa de-repression (Marty et al., 2000; Müller et al., 2003). Thus, we would expect that Brk expression would be increased in wit nulls, resulting in FMRFa repression. To test this model genetically, we first examined brkXA/Y hemizygotes, but observed no change in either anti-FMRFa immunoreactivity or Tv4WT-EYFP reporter expression (Figure 2B,E). Second, we tested brk;;wit double mutants to test if the absence of FMRFa in wit mutants is due to upregulation of the brk repressor. Contrary to this hypothesis, FMRFa expression was absent in brk/Y;;witA12/witB11 double mutants (Figure 2D,E), phenocopying wit mutants (Figure 2C,E).
However, this analysis did not rule out the possibility that FMRFa activation requires de-repression by brk as well as direct activation by pMad/Medea, as occurs at BMP-AE motifs regulating dad (Weiss et al., 2010). In such a model, the absence of FMRFa in brk; ;wit nulls may be due to a lack of activation by pMad/Medea. Therefore, we tested FMRFa expression in shn nulls. In this genotype, Brinker and pMad/Medea would all be expressed. In shn (Allan and Thor, 2015) null mutants, we found that FMRFa immunoreactivity was wildtype in late stage 17 embryos, the latest age testable in these mutants due to shn (Allan and Thor, 2015) late embryonic lethality (Figure 2G). Thus, brk de-repression cannot function as the primary mechanism for BMP-dependent FMRFa expression. We conclude that FMRFa is directly activated by pMad/Medea (Figure 2I), with no apparent involvement for shn and brk-mediated de-repression.
The 15 bp FMRFa BMP-RE has reduced pMad/Medea binding relative to canonical BMP-REs
These data led us to test if the pMad/Medea complex is recruited by a non-canonical motif within the FMRFa BMP-RCE. We used an Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) to examine nucleotides essential for pMad/Medea binding. We activated BMP signaling in S2 cells, by transfecting S2 cells with FLAG::Mad, Myc::Medea, and activated BMP type I receptor Thickveins (TkvQD) (Gao et al., 2005). From these cells, we obtained total cell lysates to perform EMSA tests on IRDye700-tagged DNA oligonucleotides containing a 27 bp BMP-RE sequence. In Figure 3, we show that co-transfection of all three plasmids was required for a band shift of the FMRFa BMP-RCE probe by BMP-activated S2 cell lysates. Addition of either an anti-Myc or anti-FLAG IgG to the lysate super-shifted the band, whereas a control IgG had no effect. Thus, a BMP-activated pMad/Medea complex isolated from S2 cells bind and band shift the FMRFa BMP-RCE.
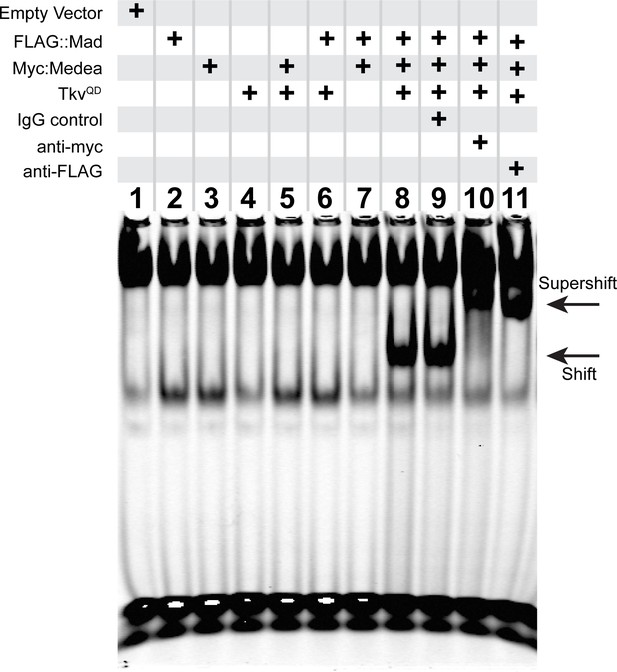
An activated pMad/Medea complex binds to the FMRFa BMP-RE.
EMSA using IRDye700-tagged DNA oligonucleotides of the FMRFa BMP-RE incubated with S2 cell extracts transfected with FLAG::Mad and/or Myc::Medea, and/or activated BMP-receptor TkvQD. Lanes 2–7 showed no specific band shift that differed from empty vector transfected cells (lane 1). Co-transfection of FLAG::Mad, Myc::Medea and TkvQD together generated a strong band shift (lane 8). Addition of antibodies to Myc (lane 10) or FLAG (lane 11) caused a super-shifted band that was not seen upon addition an IgG antibody control (lane 9). Thus, Mad, Medea, and activated Tkv receptor were capable of generating a band-shift of the FMRFa BMP-RE.
Next, we tested which sequences within the BMP-RCE are required for pMad/Medea recruitment. We generated an IRDye-700 tagged wildtype FMRFa BMP-RCE probe comprising a reduced 27 bp FMRFa BMP-RCE (AGAGGCGCCACAATGTATCCCGTTACA), necessary for appropriate in vivo expression (Figure 1—figure supplement 1A). We first tested candidate pMad and Medea binding sites by generating untagged probes with mutant sequence to test their ability to outcompete the wildtype tagged BMP-RE probe when pre-incubated at 10× or 100× excess. We confirmed that mutation of the pMad-binding sequence GGCGCC eliminated binding of the activated pMad/Medea complex (Figure 4A), as previously demonstrated (Berndt et al., 2015). Next, we tested candidate Medea-binding sequences by mutating the GTAT sequence (to TTAT) and the sequence CCCG (to AATT). We found that only mutation of the GTAT sequence reduced binding of the activated pMad/Medea complex (Figure 4B). This indicated that a 15 bp GGCGCC(N5)GTAT motif likely represents the pMad/Medea-recruitment motif for the FMRFa BMP-RCE. We further corroborated these data by comparing the ability of the pMad/Medea complex to bind IRDye-700-tagged BMP-RE oligonucleotides that were either wildtype or contained GTAT mutations predicted to abrogate Medea binding (ACTA or TTAT). Our results demonstrated that pMad/Medea had reduced binding to the mutant sequences (Figure 4—figure supplement 1).
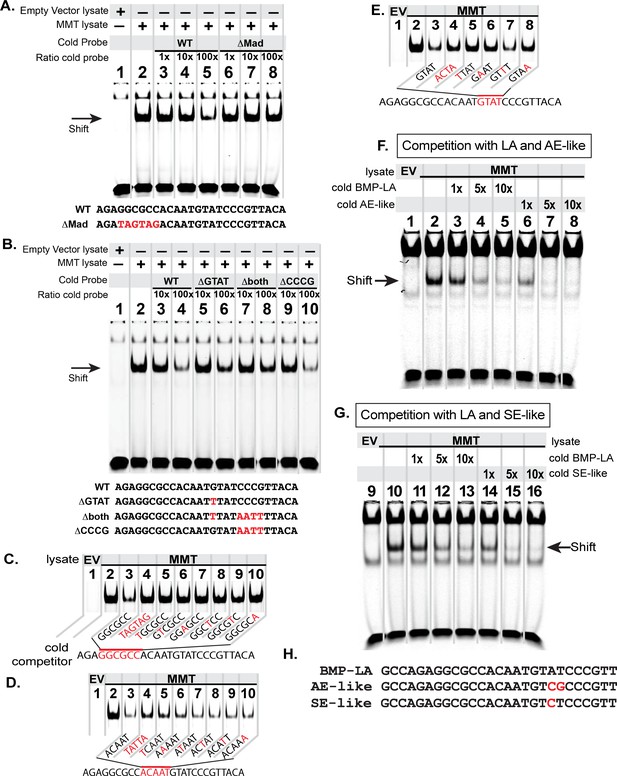
The FMRFa BMP-LA is required for pMad/Medea recruitment but at a lower affinity compared to BMP-AE and BMP-SE motifs.
We performed EMSA gels in which we ran IRDye700-tagged FMRFa BMP-RE DNA oligonucleotides (of sequence AGAGGCGCCACAATGTATCCCGTTACA) pre-incubated with lysates from S2 cells transfected with either empty vectors (EV; lane 1) or FLAG::Mad, Myc::Medea and activated BMP-receptor, TkvQD (MMT lysate; lanes 2–8 or 2–10) (A-B). The MMT lysate generated a band shift indicative of pMad/Medea binding to the tagged probe (lane 2 in A,B). In lanes 3–8 (A) or 3–10 (B), we ran MMT lysates pre-incubated with tagged probe and a stoichiometric excess of untagged (cold) DNA oligonucleotides with either wildtype or mutated sequence (shown below each gel). Loss of a band shift indicates that the untagged probe is capable of binding activated pMad/Medea. (A) We pre-incubated with untagged (cold) competitors of wildtype (WT) sequence or GGCGCC >TAGTAG mutated sequence (ΔMad) in 1×, 10×, 100× excess. At 100× excess, competition by the WT cold probe reduced the band shift (lane 5). In contrast, the mutated cold probe failed to reduce the band shift at 100× excess (lane 8). (B) We pre-incubated with 10x and 100x excess of cold probes of wildtype (WT) or mutated sequences, including of G and C nucleotides within candidate Medea-binding sequences GTAT (>TTAT, termed ΔGTAT), CCCG (>AATT, termed ΔCCCG), and a mutant to both of these sequences (Δboth). At 100× excess, the wildtype (lane 4) and ΔCCCG (lane 10) greatly reduced the band shift to the same extent; thus, the CCCG sequence does not contribute to pMad/Medea binding. By contrast, the ΔGTAT (lane 6) and Δboth (lane 8) cold probes only partially reduced the band shift, indicating that their ability to bind pMad/Medea was compromised. These data suggest that the minimal BMP-RE comprises a GGCGCC(N5)GTAT sequence. (C-D) The MMT lysate generated a band shift indicative of pMad/Medea binding to the tagged probe (lane 2). We added untagged (cold) BMP-RE DNA oligonucleotides at 100× stoichiometric excess with mutations in the sequences shown in red. (C) Nucleotide mutations are shown as red within the pMad-binding site. (D) Nucleotide mutations are shown as red within the linker region. (E) Nucleotide mutations are shown as red within the Medea-binding site. Examining the ability of each cold competitor to compete with tagged FMRFa BMP-RE, we reveal a necessary BMP-RE sequence of GGCGGGacaatGTaT, where capitalized nucleotides are found most necessary for pMad/Medea recruitment. (F,G) In these EMSA, we additionally transfected S2 cell extracts with a 1×, 5×, and 10× stoichiometric excess of untagged competitors (sequences shown in H). (F) Competition for the tagged BMP-LA by the untagged wildtype (BMP-LA) or the AE-like mutant. A 10× excess (lane 5) of untagged wildtype BMP-LA reduced but did not eliminate the band shift (lane 5). By contrast, the BMP-AE-like mutant totally out-competed the tagged BMP-LA at a 5× excess (lane 7 compared to lane 4) and significantly out-competed the tagged BMP-LA even at equimolar ratio (lane 6 compared to lane 3). (G) Competition for the tagged BMP-LA by the untagged wildtype or the SE-like mutant. The SE-like mutant totally out-competed the tagged BMP-LA at a 5× excess (lane 15 compared to lane 12) and significantly out-competed the tagged BMP-LA even at equimolar ratio (lane 14 compared to lane 11).
We wished to define the sequence requirements for this novel 15 bp BMP-Response Element (BMP-RE). Therefore, we examined band shifts of BMP-activated S2 cell lysates pre-incubated with tagged wildtype BMP-RE DNA oligonucleotides and a 100× stoichiometric excess of cold mutants in which a single nucleotide through the 15 bp motif was substitution mutagenized (Figure 4C–E). Mutagenesis of the entire GGCGCC sequence, or any single nucleotide therein, severely reduced binding of pMad/Medea, as shown by an inability to reduce the band shift of the tagged BMP-RE probe (Figure 4C). In addition, mutation of the entire GTAT sequence, or of any nucleotide except the A, greatly reduced the binding of pMad/Medea, as shown by retention of a strong band shift of the tagged BMP-RE probe (Figure 4E). By contrast, mutation of any nucleotide within the linker sequence ACAAT only minimally reduced pMad/Medea binding and the band shift was only minimally retained (Figure 4D). We conclude that a minimal 15 bp element of GGCGCCacaatGTaT is essential for pMad/Medea recruitment in vitro (with capitalized letters being essential).
It is intriguing that the position 14 A nucleotide in the putative GTAT Medea binding motif is the only nucleotide not required for pMad/Medea recruitment to this motif in vitro, as a C in this position was shown to be important for pMad/Medea recruitment to BMP-AE and BMP-SE motifs (Pyrowolakis et al., 2004; Weiss et al., 2010). Due to this loss of a key pMad/Medea recruitment nucleotide, we postulate that this position 14 C > A switch reduces affinity by introducing a nucleotide that fails to contribute to binding, resulting in the observed reduction of pMad/Medea recruitment.
Hereafter, we term the FMRFa BMP-RE motif as a BMP-Low Affinity Activation motif (BMP-LA). We wished to determine if the C > A switch that distinguishes the BMP-LA from the BMP-AE/SE motifs has an impact on BMP-activated pMad/Medea recruitment. To examine this, we tested whether modifying the BMP-LA Medea site to a BMP-AE-like or BMP-SE-like sequence indeed increases its ability to bind pMad/Medea. We generated a series of tagged and untagged DNA oligonucleotides comprising 27 bp of the BMP-LA sequence that was either wildtype at the Medea site, GTAT, or mutated at this site to GACG (BMP-AE-like) or GTCT (BMP-SE-like). By competition EMSA assays, we tested the relative ability of these untagged DNA oligonucleotides to compete for pMad/Medea binding when at 1×, 5×, and 10× stoichiometric ratios relative to the tagged wildtype probe (Figure 4F–G). We found that a wildtype untagged BMP-LA sequence reduced but did not eliminate the band shift generated by its tagged counterpart by 10×. In contrast, both the AE-like and the SE-like sequence mutants proved to be much stronger competitors, totally outcompeting the BMP-LA tagged probe by 5×. Moreover, at equimolar ratios, the untagged wildtype BMP-LA competitor did not substantially alter the tagged probe band shift; however, both AE-like and SE-like mutants reduced the band shift. These data indicate that the GTAT sequence displays low affinity pMad/Medea binding activity relative to the characterized BMP-AE and BMP-SE motifs.
Conversion of the low affinity FMRFa BMP-RE to a high affinity BMP-AE sequence results in ectopic neuronal BMP-dependent activity in vivo
Collectively, our genetic and biochemical data indicated that the BMP-LA motif exhibits low affinity pMad/Medea recruitment. This raised the question as to why the BMP-LA motif is attenuated in this manner, yet conserved across all Drosophila species. To address this, we tested for functional relevance for this motif’s low affinity.
First, we mutated the 445 bp Tv4-enhancer (within the Tv4-nEGFP nuclear-localized reporter) at the GTAT sequence into ACTA (Tv4mGTAT>ACTA-nEGFP) (sequence shown in Supplementary file 1a), in order to eliminate Medea recruitment. We found that the Tv4mGTAT>ACTA-nEGFP reporter exhibited a total loss of expression in Tv4-neurons, and no ectopic expression was detected in other neurons (Figure 5A,B). We conclude that the GTAT sequence is essential. Second, we tested the effect of converting the GTAT motif of BMP-LA to an optimal BMP-AE-like sequence (GTAT > GACG), within the Tv4-nEGFP reporter (Tv4mGTAT>GACG-nEGFP) (sequence shown in Supplementary file 1a). This conversion eliminated Tv4-enhancer activity in Tv4-neurons (Figure 5A,C) but led to strong ectopic reporter activity in other neurons of the VNC (Figure 5D). We noted that all EGFP positive cells were also anti-pMad immunoreactive (Figure 5D’–D”’), suggesting that we had indeed created a high affinity BMP-RE that recruits pMad/Medea to generate BMP-responsive Tv4-enhancer activity in an expanded population of neurons. To confirm this, we tested the wit-dependence of this ectopic reporter activity, by examining the expression of the mutant BMP-AE-like Tv4-enhancer reporter (Tv4mGTAT>GACG-nEGFP) in a wit mutant background (Figure 5D,E). As expected, this eliminated all reporter activity, demonstrating that the low-to-high affinity conversion created a functional BMP-AE that generated BMP-dependent reporter activity in other BMP-activated neurons of the VNC.
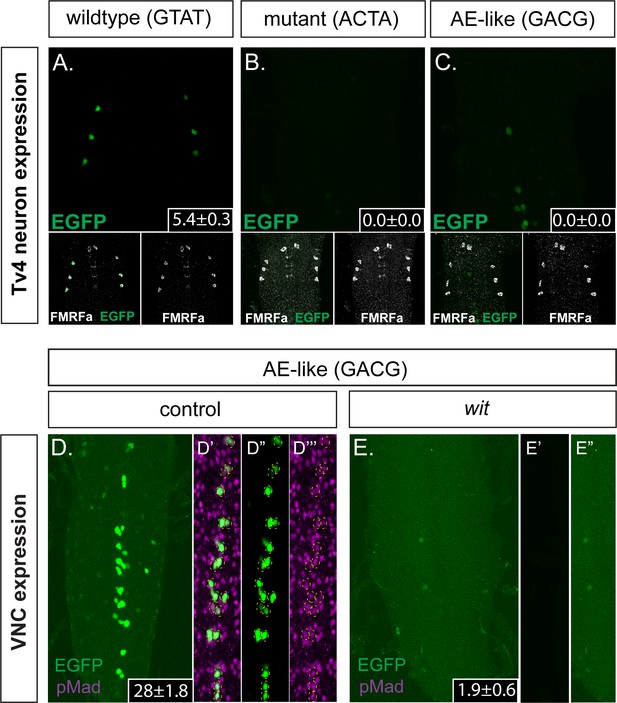
The FMRFa BMP-LA motif has a necessary but low affinity Medea binding site that specifies selective neuronal subtype activity.
(A–C) Conversion of the Medea-binding GTAT site in the wildtype 445 bp Tv4-neuron-specific FMRFa enhancer to a mutant version, ACTA (that reduces pMad/Medea recruitment; termed Tv4 mGTAT>ACTA–nEGFP), resulted in a complete loss of reporter gene expression in Tv4-neurons (B). Conversion of the Medea-binding GTAT site in the wildtype 445 bp Tv4-neuron-specific FMRFa enhancer to an optimal BMP-AE-like sequence (GACG; termed Tv4 mGTAT>GACG–nEGFP) also resulted in a total loss of reporter expression in Tv4-neurons (C). Numbers in insets indicate the mean ± SD number of EGFP-positive Tv4-neurons per VNC, out of the possible six Tv neurons. (D,E) The Tv4mGTAT>GACG–nEGFP reporter generated strong ectopic reporter activity in VNC midline cells (D) that is lost in the absence of neuronal BMP signaling (E; in wit mutants, witA12/witB11). Full z-projections though the whole VNC are shown. Numbers in insets indicate the mean ± SD number of EGFP-positive neurons per VNC. (D’–D’’’) Images of the midline ectopic EGFP expression generated from Tv4mGTAT>GACG–nEGFP. EGFP expression (green) was exclusively expressed in pMad-immunoreactive cells (magenta); all cells are yellow circled.
These data show that the low affinity of BMP-LA is essential for the spatially restricted activity of this cis-element to Tv4-neurons.
Identification of additional functional BMP-responsive BMP-LA motifs through the genome
Following the identification of the novel BMP-LA motif regulating FMRFa expression in Tv4-neurons, we examined if this cis-regulatory motif was unique to FMRFa regulation, or functions to confer BMP-dependence to other cis-regulatory regions. To this end, we identified 178 BMP-LA motifs in the D. melanogaster genome using the motif discovery tool HOMER (v4.10) (Heinz et al., 2010). These were filtered for sequence conservation across 24 sequenced Drosophila species using PhastCons scores (Siepel et al., 2005), reducing the list to 128 BMP-LA with an average PhastCons score over 0.55. Of these 128 BMP-LA, 103 were highly conserved with a score of over 0.9 (Supplementary file 1b).
We selected 24 of the BMP-LA motifs for functional testing in vivo. Of the 24 prioritized motifs, 20 were highly conserved (average PhastCons score >0.9) and chosen in order to optimize the chance of characterizing functional BMP-RE's. Additionally, four motifs with lower scores 0.75–0.55 were tested for functionality (Table 1, Supplementary file 1c). We examined reporter activity driven from these genomic fragments in late third instar larvae (L3). Of the 24 reporters, five showed no expression in the ventral nerve cord (VNC) (Figure 6—figure supplement 1A), while the remaining 19 reporters exhibited low to high reporter activity in the VNC (Table 1). Of these active reporters, 10 exhibited expression in subsets of pMad-positive cells in the VNC, and also numerous pMad-negative glia and neurons (Table 1). The remaining nine active reporters were restricted to pMad-negative glia and neurons (Figure 6—figure supplement 1B). We tested the BMP-responsiveness of the 10 reporters expressed in pMad-positive cells, by placing them in a wit mutant background. Out of those 10 reporters, seven showed reduced reporter expression (Figure 6B), including two (CM5 and CM7) with motifs of lower PhastCons score. Three reporters showed no significant change (Figure 6A, Figure 6—figure supplement 1B). Quantification of reporter expression in the VNC of controls and their corresponding wit mutants revealed a loss of up to 88% of reporter-expressing cells in certain genotypes (Figure 6—figure supplement 2B).
Summary table of expression pattern and wit-responsiveness for BMP-LA containing DNA fragments tested in vivo.
The first column indicates the name for each of the cloned BMP-LA containing DNA fragments; these were sorted based on intensity and pattern of reporter expression. The second column provides information on reporter expression in the VNC, (more plus signs indicate higher intensity), and the final column provides details on expression pattern. The third and fourth columns indicate fragments that exhibited pMad and reporter co-expression, as well as the ones that were shown to be wit-responsive. Bolded letters indicate the enhancer fragments that were further tested for wit-responsiveness. The expression pattern was assessed in wandering third instar larvae.
| DNA fragment | VNC expression | Reporter/pMad stain overlap | Wit responsive | VNC expression details |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CM5 | +++ | √ | √ | neurons and glia |
| CM1 | +++ | √ | √ | medial and lateral neurons |
| CM4 | +++ | √ | √ | medial and lateral neurons |
| CM3 | +++ | √ | √ | medial and lateral neurons |
| CM2 | ++ | √ | √ | medial and lateral neurons |
| CM7 | + | √ | √ | sparse |
| CM6 | + | √ | √ | sparse |
| CM8 | +++ | √ | - | medial neurons |
| CM9 | ++ | √ | - | lateral neurons |
| CM10 | + | √ | - | sparse |
| CM11 | ++ | - | - | neurons and glia |
| CM12 | + | - | - | sparse |
| CM13 | + | - | - | sparse |
| CM14 | + | - | - | sparse |
| CM15 | + | - | - | sparse |
| CM16 | + | - | - | sparse |
| CM17 | + | - | - | low intensity |
| CM18 | + | - | - | low intensity |
| CM19 | + | - | - | low intensity |
| CM20 | - | - | - | none |
| CM21 | - | - | - | none |
| CM22 | - | - | - | none |
| CM23 | - | - | - | none |
| CM24 | - | - | - | none |
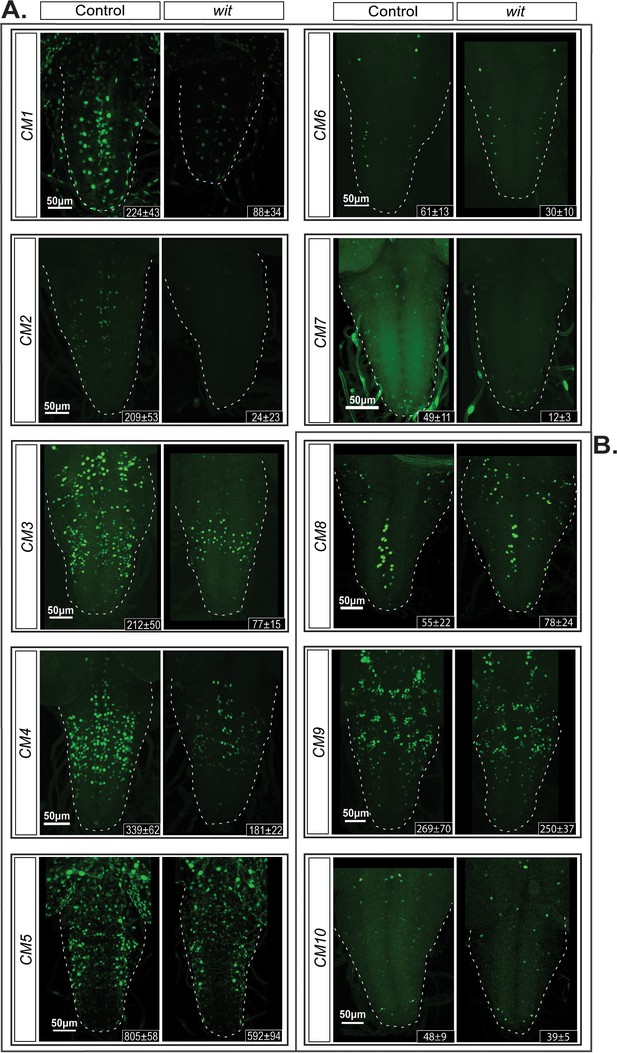
Identification of additional wit-responsive genomic fragments containing the BMP-LA motif.
We identified 10 genomic fragment reporters that exhibited expression in subsets of pMad-positive cells in the VNC and tested their wit-responsiveness. (A) EGFP reporter patterns of three genomic fragments that exhibit no wit-responsive loss of reporter expression in wit mutants (witA12/witB11) compared to controls (witA12/+) in late third Instar larval VNCs. (B) Nuclear EGFP expression patterns driven from seven genomic fragments containing conserved BMP-LAs that were down-regulated in wit mutants (witA12/witB11), compared to controls (witA12/+) in late third Instar larval VNCs. The observed down-regulation ranged from a near-total loss of all neuronal expression to loss of expression in a subset of neurons. Full z-projections though the whole VNC are shown. Genotypes: All control lines shown here were heterozygous (w;;CM#/+); wit mutants (w;;CM#,witA12/witB11).
Next, we tested whether the activity of the identified wit-responsive fragments was dependent on the BMP-LA motif within these genomic fragments. We selected four wit-responsive fragments (CM1, CM2, CM3, and CM7) and one non-wit responsive fragment (CM9; Figure 7A). We introduced nucleotide substitution mutations into the pMad-binding site of the LA (GGCGCC > TGATGA). In all four wit-responsive fragments tested, there was a significant loss of reporter expressing cells (Figure 7B). Finally, having established the necessity of Medea for BMP-dependent activity of the FMRFa BMP-RE, we tested the requirement for Medea in reporter expression these same BMP-dependent CM1, CM2, CM3, and CM7 reporters. In Medea mutant third instar (L3) larvae, reporter expression was reduced in the same pattern as observed in a wit mutant background (Figure 7—figure supplement 1).
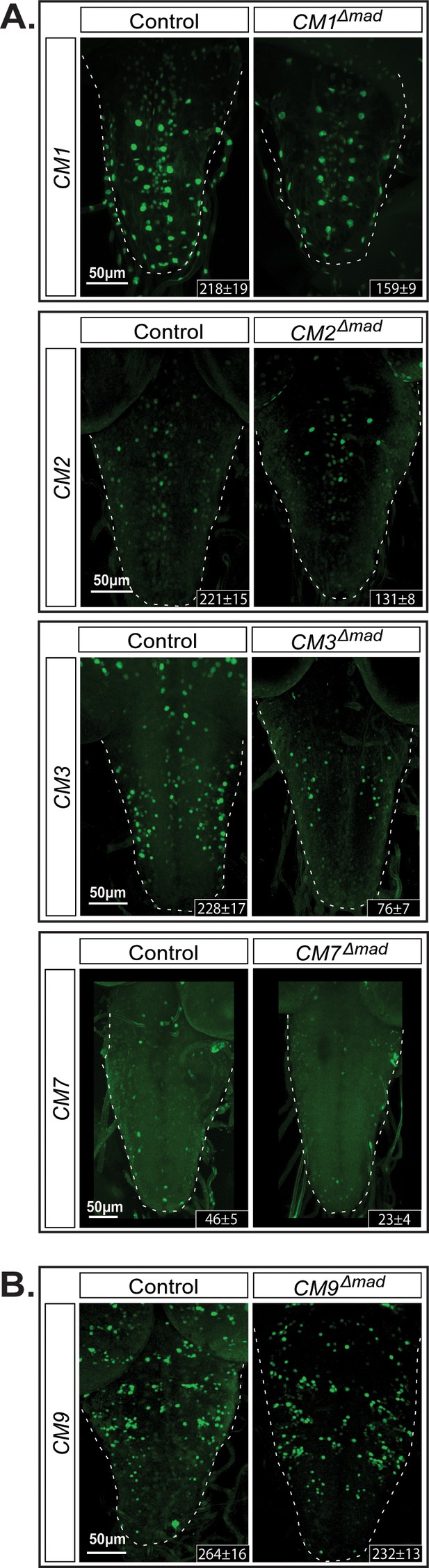
The GGCGCC pMad-binding site is necessary for reporter expression in vivo.
We introduced specific mutations into the pMad-binding site of the BMP-LA motif (GGCGCC >TGATGA) of four wit-responsive fragments (CM1, CM2, CM3, and CM7) and one non-wit responsive fragment (CM9) to verify whether reporter activity was dependent on pMad binding. (A) CM9 showed no significant loss of reporter expression in the CM9Δmad mutant compared to the control. (B) All four wit-responsive fragments exhibited a significant loss of reporter expressing cells; however, this loss was less pronounced than the loss in wit mutants, apart from CM3. Full z-projections though the whole VNC are shown. Genotypes: All control and pMad-binding site mutant lines examined here were heterozygous (w;;CM#/+).
We conclude that the BMP-LA is utilized by numerous cis-regulatory regions in order to generate BMP-dependent enhancer activity in neurons.
Discussion
Retrograde BMP signaling, and BMP responsive DNA motifs in target gene enhancers, have been viewed as functionally equivalent across efferent neuron populations. Therefore, the differential expression of BMP target genes across efferent neuron populations has been attributed to the activity of subtype-specific transcription factors (Veverytsa and Allan, 2011; Miguel-Aliaga et al., 2008; Allan et al., 2005). Here we describe our identification of a low affinity BMP-responsive DNA motif that appears to instructively contribute to differential specification of BMP target genes across efferent neuron subtypes.
Our previous work had identified a 39 bp BMP responsive cis-element within the Tv4-enhancer of FMRFa that is absolutely required for Tv4-enhancer activity, and encodes sufficient information for selective activity in Tv4-neurons (Berndt et al., 2015). Here we reveal that pMad and Medea are recruited to this cis-element by an essential low affinity motif (the BMP-LA). Converting this motif to a high affinity BMP-AE motif led to Tv4-enhancer activity in a broader set of efferent neurons, as would be expected from BMP-AE’s generic responsiveness across many efferent neurons and Drosophila tissues (Vuilleumier et al., 2019; Chayengia et al., 2019). These results provide evidence that low affinity BMP responsive motifs instructively restrict BMP target genes within subsets of efferent neuron.
Low affinity motifs serve widespread roles in restricting gene expression in space and time (Crocker et al., 2015). They function to reduce enhancer activity in order to prevent ectopic expansion of enhancer activity (Wharton et al., 2004; Farley et al., 2015; Jiang and Levine, 1993). They are also required to generate enhancer activity with the appropriate expression domain; for example, Hedgehog regulation of numerous wing imaginal disc and embryonic enhancers requires Ci transcription factor binding to low affinity motifs; increasing their affinity abolished enhancer activity (Ramos and Barolo, 2013). Also, clustered low affinity motifs have been shown to improve discrimination between transcription factors with similar binding preferences, and to locally concentrate transcription factors to ensure robust target gene expression (Crocker et al., 2015).
How does the BMP-LA confer Tv4-neuron specificity? We propose that the BMP-LA does not singularly specify Tv4 neuron activity, but rather imposes a requirement for pMad/Medea cooperative interactions with subtype-specific transcription factors bound to adjacent motifs for combinatorial activation of FMRFa expression. Four primary lines of evidence inform our conclusion. First, lowering or ectopically hyperactivating BMP signaling in other neurons failed to trigger ectopic Tv4-enhancer or FMRFa expression, without also co-misexpressing Tv4-specific transcription factors (Allan et al., 2003; Allan et al., 2005; Miguel-Aliaga et al., 2004; Eade et al., 2012; Berndt et al., 2015). This rules out a model whereby BMP-LA’s lower affinity is tuned for a specific level of BMP signaling only observed in Tv4-neurons. Second, the minimal BMP-responsive, Tv4-specific cis-element within the Tv4-enhancer cannot dispense with a highly conserved sequence 3’ of the BMP-LA. This sequence likely contains binding sites for other transcription factors that synergize with pMad/Medea to specify FMRFa expression in Tv4-neurons. These transcription factor(s) remain unidentified at this time. Third, BMP-LA motifs in other genomic regions confer BMP-dependent enhancer activity across other efferent neurons, suggesting that the BMP-LA imposes a requirement for pMad/Medea synergistic interactions with other transcription factors that combinatorially specifies neuronal subtype expression. Fourth, converting the BMP-LA to a BMP-AE resulted in a loss of reporter expression within its appropriate domain (Tv4-neurons), but an inappropriate expansion of BMP-responsive activation into other efferent neurons. This strongly suggests that the BMP-LA imposes transcription factor interactions that the BMP-AE is unable to replicate in Tv4-neurons; yet are unnecessary for generic BMP-AE activity in other efferent neurons. These specific interactions may occur between transcriptional regulators that require a specific pMad/Medea conformation that is imposed by the BMP-LA sequence. Precedent for this comes from analysis of Schnurri binding to pMad and Medea bound at the BMP-SE, which requires a pMad/Medea conformation that is imposed by a precise 5nt linker between the Mad and Medea binding motifs and also a terminal T at position 15 of the BMP-SE motif (Gao et al., 2005; Pyrowolakis et al., 2004; Müller et al., 2003). No such sequence constraints appear to be required for pMad/Medea activity at the BMP-AE (Weiss et al., 2010; Chayengia et al., 2019). Alternatively, but not mutually exclusively, these specific interactions may occur between other transcription factors bound to adjacent DNA motifs and a pMad/Medea conformation imposed by the BMP-LA sequence. Precedent for such a model comes from evidence that conversion of a low affinity Pax6 site in the chicken DC5 enhancer to a high-affinity site disrupted the formation of an activation competent Sox2-Pax6 complex, and decreased enhancer activity (Kamachi et al., 2001; Uchikawa et al., 2003). Similarly, single nucleotide differences in NF-κB binding sequences determine cofactor specificity for NF-κB dimers (Leung et al., 2004; Pan et al., 2010). A similar instructive role for low affinity motifs in generating exquisitely subtype-specific neuronal gene expression has been proposed in Drosophila (Jafari and Alenius, 2015; González et al., 2019). The exclusive expression of odorant receptor genes in specific olfactory sensory neurons is encoded by arrays of low affinity binding sites for multiple transcription factors. The authors propose that these low affinity motifs provide the necessary environment for the weak and somewhat promiscuous binding for numerous transcription factors that ultimately establishes the cooperative interactions that stabilizes target gene activation in a single neuronal subset.
Our results add to growing evidence that BMP-dependent gene regulation can be profoundly altered by subtle nucleotide substitutions within the 4-nucleotide Medea-recruitment site of these response elements; a BMP-dependent activator (GNCV), a BMP-dependent repressor (GNCT), and a low affinity activator that generates restricted activation (GTAT). The sequence similarity yet diverse functional output of these three BMP-REs reveals the diversity of responses that can be generated from subtle sequence deviations from a core BMP-RE motif. This raises a challenge for computational approaches for BMP-RE motif discovery; a specific high affinity motif will not capture all functional motif instances, but a degenerate motif built from multiple BMP-RE motifs would increase background noise to unacceptably high rates. Moreover, our discovery here of a novel motif with predictive value only increases the promise that more BMP-REs with predictive value will be discovered. However, as demonstrated by numerous studies, accounting for low affinity sites has proven to be beneficial in identifying functional enhancers (Zandvakili et al., 2018; Gurdziel et al., 2015). Therefore, it remains important to identify novel BMP-responsive motifs with demonstrated predictive value in BMP-RE discovery. Regardless, considerable degeneracy has been found in the sequences of BMP-REs (Ross and Hill, 2008) and it is important to acknowledge that in silico BMP-RE discovery will always under-represent functional BMP-REs in any system.
We started this study by sub-mapping a minimal BMP-responsive, Tv4-specific cis-element to a short 27 bp region that contains the canonical GGCGCC pMad-binding site, but no canonical Medea-binding site. After dismissing the expected model that this motif would mediate Brk default repression and BMP-dependent de-repression, we defined a minimal 15 bp GGCGCC(N5)GTAT bipartite motif required for pMad/Medea recruitment. The low affinity of this motif arises from the C > A nucleotide switch at position 14; removing the C nucleotide required for pMad/Medea recruitment to BMP-AE and BMP-SE (Pyrowolakis et al., 2004; Weiss et al., 2010), for an A nucleotide that plays no role in recruitment (Figure 4E). Interestingly, this loss of recruitment activity at motif position 14 leads to increased nucleotide stringency at positions 2, 5, 12, and 13 for pMad/Medea recruitment (Figure 4E), which are either unnecessary or less necessary for recruitment to BMP-AE and BMP-SE (Gao et al., 2005; Pyrowolakis et al., 2004; Weiss et al., 2010). Thus, transversion of one core nucleotide requires compensatory pMad/Medea recruitment activity from other nucleotides within the overall 15 bp motif. This could be viewed as exerting an evolutionary pressure on these remaining nucleotides to not exhibit degeneracy across Drosophila species, which may provide an explanation for why the BMP-LA is so highly conserved. By contrast, other low affinity cis-elements exhibit considerable degeneracy, with the hypothesis being that a high affinity, optimal motif would be highly constrained in nucleotide composition, but there could be a variety of nucleotide substitutions that would result in lower affinity motif (Crocker et al., 2015; Ramos and Barolo, 2013; Crocker et al., 2016; Farley et al., 2016).
Overall, our results show that differential BMP-dependent gene expression in neuronal subtypes is not only conferred by the integration of pMad/Medea into a combinatorial transcription factor code. In addition, sequence variation of the BMP-RE that is bound by pMad/Medea provides additional critical information required to selectively trans-activate gene expression in specific neuronal subtypes. Further work is required to identify transcription factors that bind the highly conserved sequences that flank the BMP-LA motif in the FMRFa Tv4-enhancer, or interact directly with the BMP-LA motif itself. Once such factors are identified, we will be able to directly assess the contribution of pMad/Medea affinity and specific transcription factors to the BMP-LA in order to form subtype-specific, activation-competent complexes.
Materials and methods
Fly genetics
Request a detailed protocolStrains used: MedC246 (McCabe et al., 2004); Med13 (Hudson et al., 1998); MedDf (Df(3R)ED6361) (Ryder et al., 2007); witA12 and witB11 (Aberle et al., 2002); brkXA (Campbell and Tomlinson, 1999); shn1 ( Grieder et al., 1995). Mutants were kept over CyO, Act-GFP TM3, Ser, Act-GFP (Reichhart and Ferrandon, 1998), CyO, twiGAL4, UAS-2xEGFP, or TM3, Sb, Ser, twiGAL4, UAS-2xEGFP (Halfon, 2002). w1118 was used as the control genotype. Flies were maintained at 25°C, 70% humidity.
Reporter transgene construction
Request a detailed protocolTvWT-EYFP, BMP-RE-EYFP, HD-RE-EYFP were generated previously (Berndt et al., 2015). Drosophila transformations were performed by Rainbow Transgenic Flies, Inc (Camarillo, CA). Empty pThunderbird EGFP vector was generated from Tv-nEYFP and from sequence within pHstinger (Berndt et al., 2015; Barolo et al., 2000). Tv4-nEYFP was digested with AscI and SpeI. The multiple cloning site (MCS), HSP70 promoter, EGFP coding sequence, Tra nuclear localization signal, and SV40-polyA sequences from pHstinger (Barolo et al., 2000) were liberated with AscI and SpeI and ligated into the cut Tv-nEYFP backbone. The Tv4-enhancer was PCR-amplified from Oregon-R with XbaI and EcoRI adaptors, restriction digested and ligated into XbaI/EcoRI digested empty Tv4-nEYFP. SOE PCR generated nucleotide substitution and deletion mutants were inserted similarly. Summary of all mutations and concatemerization sequences in Supplementary file 1a. pMad-binding site mutagenesis was performed by Q5 Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA), using primers designed to introduce specific base pair substitutions to the Mad binding site (GCCGGC > tgatga), according to manufacturer`s protocols. All constructs were verified by sequencing before the generation of transgenic fly lines. Fly transformations were performed by Rainbow Transgenic Flies, Inc (Camarillo, CA). All transgenic reporters were integrated into attP2 (Groth et al., 2004).
Immunochemistry
Request a detailed protocolImmunochemistry was performed as previously described (Eade and Allan, 2009; Berndt et al., 2015). Primary antibodies: Rabbit α-FMRFa C-terminal peptide (1:1000, a gift from S. Thor) Baumgardt et al., 2007; Mouse α-Eya (1:100; MAb clone 10H6 DSHB; Iowa University, IA); Rabbit α-pMad (1:100, 41D10, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA), Chicken α-GFP antibody (1:1000, ab13970, Abcam, Ontario, Canada). Donkey anti-Rabbit and anti-Mouse conjugated to DyLight 488, Cy3, Cy5 (1:100, Jackson ImmunoResearch, West Grove, PA).
Image and statistical analysis
Request a detailed protocolSample size and measurements are given as supplementary files for each accompanying figure. Analysis of the reporter constructs was performed on heterozygous reporter lines. Images were acquired with an Olympus FV1000 or a Zeiss Axio Imager VIS LSM880 confocal microscope with settings that avoided pixel intensity saturation. Representative images of Tv neurons being compared in figures were linear contrast enhanced together in Adobe Photoshop CS5 (Adobe Systems, San Jose, CA). All statistical analyses and graphing were performed using Prism 5 or Prism 8.0.1 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA). Normality of sample distribution was determined with Shapiro-Wilk normality tests. All multiple comparisons were done with One-Way ANOVA and a Tukey post-hoc test, or Student’s two-tailed t-test when only two groups were compared. Mann-Whitney U-test was used when the samples were not normally distributed. Differences between groups were considered statistically significant when p<0.05. Data are presented as either Mean ± Standard Deviation (SD).
Quantification of reporter expression
Request a detailed protocolQuantification of native EGFP reporter expression (without anti-GFP immunoreactivity enhancement) in late L3 larval VNCs was performed, in the context of anti-pMad immunoreactivity (to mark nuclei with active BMP-signaling). In all cases, five or more VNC were dissected and imaged for each genotype. All compared tissues were processed with the same reagents, imaged, and analyzed in identical ways. To quantitate reporter activity, we used Bitplane:Imaris v9.2 software (in Spots Mode) to identify reporter-positive nuclei in the VNC (excluding the brain lobes). When comparing control and pMad-binding site mutant genomic fragment reporters, we additionally assessed EGFP positive nuclei that were co-marked by pMad immunoreactivity (by mean intensity thresholding). Imaris settings were established independently for each set of reporters, in order to provide optimal ‘spot’ marking of a verifiable reporter and pMad co-immunoreactive nuclei, with minimal background fluorescence spot marking. Each image was further subtracted, manually, for spots that erroneously labeled background fluorescence.
Gel shift assay
Request a detailed protocolFLAG::Mad, Myc::Medea, and/or TkvQD cDNA sequences were derived from previously described vectors (Gao et al., 2005) and subcloned into a pAc5.1/V5-His vector backbone (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA). Drosophila S2 cells were transfected at a density of 1.5 × 106 S2 cells per mL in a six well dish in 2 mL of media. A total of 2.4 ug of plasmid was used per well with each plasmid constituting 0.8 ug of the total. Total plasmid mass was kept constant by co-transfecting empty pAc5.1 when only one or two protein coding plasmids were used for an experimental condition. Transfections were performed with the XtremeGENE HD transfection kit according to the manufacturer’s recommended protocol (Roche, Ontario, Canada). 48 hr after transfection, cells were harvested and lysed for gel shift assay. Cells were harvested in 15 mL tubes then pelleted by centrifugation (700 g at room temperature for 3 min). The pellets were re-suspended in PBS, transferred to 1.5 mL tubes, and centrifugation repeated as before. Cells were then resuspended in 90 μL ice-cold lysis buffer and the lysis reaction incubated on ice for 15 min. S2 cell lysis buffer contained 100 mM Tris HCl pH 7.6, 0.5% Tween-20, 1 mM DTT, and 1× Roche cOmplete ULTRA EDTA-free Protease inhibitor cocktail. The lysate was cleared by centrifugation at 16.2 × 103 g for 15 min at 4°C. The supernatant was aliquoted into new pre-chilled tubes in 30 uL volumes, snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80°C until use. Oligonucleotides were synthesized and labeled with IRDye 700 by Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT, Indiana). DNA and protein binding was performed by incubating 20 μg of lysate protein with 1 μL of 50 nM IRDye 700-labeled probe in 20 μL of reaction buffer containing 25 mM Tris pH7.5, 35 mM KCl, 80 mM NaCl, 3.5 mM DTT, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.25% Tween 20, 1 μg poly dIdC, 10% glycerol, and 1× Roche cOmplete ULTRA EDTA-free Protease inhibitor cocktail for 30 min at room temperature. If super shifts were performed, then 1 μg of mouse anti-MYC (clone 9E10, Sigma), mouse anti-FLAG (clone M2, Sigma), or mouse IgG (Sigma) was added and incubated for an additional 30 min at room temperature. The DNA-protein complexes were resolved on a 4% non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel for 1.5 hr at 70 V in 1× TGE buffer. After electrophoresis, the gel was imaged immediately by a Licor Odyssey Imager system (Lincoln, NE).
Computational detection of BMP-LA instances
Request a detailed protocolHOMER v4.10 software suite (Heinz et al., 2010) was used to scan the reference dm6 Drosophila genome for the BMP-LA (GGCGCC(N5)GTAT) motif. Base-specific PhastCons scores (Siepel et al., 2005) against 27-insect species were obtained from the UCSC genome browser (https://genome.ucsc.edu/) to annotate each motif instance with evolutionary conservation scores (Supplementary file 1b).
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in the manuscript and supporting files.
References
-
The decapentaplegic morphogen gradient: from pattern formation to growth regulationNature Reviews Genetics 8:663–674.https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2166
-
Transcriptional selectors, masters, and combinatorial codes: regulatory principles of neural subtype specificationWiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Developmental Biology 4:505–528.https://doi.org/10.1002/wdev.191
-
Cell type-specific regulation of the Drosophila FMRF-NH2 neuropeptide gene by Apterous, a LIM homeodomain transcription factorDevelopment 125:4757–4765.
-
BMP-dependent gene repression cascade in Drosophila eggshell patterningDevelopmental Biology 400:258–265.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.02.004
-
The soft touch: low-affinity transcription factor binding sites in development and evolutionEssays on Developmental Biology Part B 117:455–469.https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.ctdb.2015.11.018
-
Retrograde neural circuit specification by target-derived neurotrophins and growth factorsCurrent Opinion in Neurobiology 21:61–67.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2010.07.007
-
Dpp-responsive silencers are bound by a trimeric Mad-Medea complexJournal of Biological Chemistry 280:36158–36164.https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M506882200
-
Flexible interaction of Drosophila smad complexes with bipartite binding sitesBiochimica Et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Gene Structure and Expression 1769:484–496.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbaexp.2007.05.006
-
Thermodynamic model of gene regulation for the Or59b olfactory receptor in DrosophilaPLOS Computational Biology 15:e1006709.https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006709
-
New fluorescent protein reporters for use with the Drosophila Gal4 expression system and for vital detection of balancer chromosomesGenesis : The Journal of Genetics and Development 138:135–138.https://doi.org/10.1002/gene.10136
-
Dpp/BMP signaling in flies: from molecules to biologySeminars in Cell & Developmental Biology 32:128–136.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.04.036
-
The wnt and BMP families of signaling morphogens at the vertebrate neuromuscular junctionInternational Journal of Molecular Sciences 12:8924–8946.https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12128924
-
The molecular and gene regulatory signature of a neuronTrends in Neurosciences 33:435–445.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2010.05.006
-
The Drosophila Medea gene is required downstream of dpp and encodes a functional homolog of human Smad4Development 125:1407–1420.
-
Identification of downstream targets of the bone morphogenetic protein pathway in the Drosophila nervous systemDevelopmental Dynamics 239:2413–2425.https://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.22368
-
Dendrite complexity of sympathetic neurons is controlled during postnatal development by BMP signalingJournal of Neuroscience 33:15132–15144.https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4748-12.2013
-
Schnurri mediates Dpp-dependent repression of brinker transcriptionNature Cell Biology 2:745–749.https://doi.org/10.1038/35036383
-
Generating and interpreting the brinker gradient in the Drosophila wingDevelopmental Biology 286:647–658.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.08.036
-
Mechanisms of transcription factor selectivityTrends in Genetics 26:75–83.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2009.12.003
-
Low-affinity transcription factor binding sites shape morphogen responses and enhancer evolutionPhilosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 368:20130018.https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2013.0018
-
How the smads regulate transcriptionThe International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology 40:383–408.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2007.09.006
-
Schnurri is required for dpp-dependent patterning of the Drosophila wingDevelopmental Biology 227:388–402.https://doi.org/10.1006/dbio.2000.9900
-
A conserved activation element in BMP signaling during Drosophila developmentNature Structural & Molecular Biology 17:69–76.https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1715
-
Repression of dpp targets in the Drosophila wing by brinkerDevelopment 131:6071–6081.https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.01538
-
BMP signaling specifies the development of a large and fast CNS synapseNature Neuroscience 16:856–864.https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3414
-
Brinker is a sequence-specific transcriptional repressor in the Drosophila embryoGenes & Development 15:261–266.https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.861201
Article and author information
Author details
Funding
Canadian Institutes of Health Research (MOP-98011)
- Douglas W Allan
Canadian Institutes of Health Research (MOP-130517)
- Douglas W Allan
The funders had no role in study design, data collection and interpretation, or the decision to submit the work for publication.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge Drs. Stefan Thor (Linkoping University, Sweden), Markus Affolter (University of Basel, Switzerland), Giorgos Pyrowolakis (University of Freiburg, Germany), Robin Vuilleumier, Hugh Brock, T Michael Underhill, Jacob Hodgson, Timothy O'Connor (University of British Columbia, Canada), and the Allan laboratory for their valuable assistance and comments. The authors gratefully acknowledge Drs. Konrad Basler and Johannes Bischof (University of Zurich, Switzerland), Jonathan Benito-Sipos (Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Spain), Allen Laughon (University of Wisconsin - Madison, USA), Stefan Thor (Linkoping University, Sweden), Esther Verheyen (Simon Fraser University. Canada), and the Bloomington Drosophila Stock Centre (Indiana, USA) for genetic, molecular, or immunological reagents.
Copyright
© 2020, Berndt et al.
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 1,166
- views
-
- 157
- downloads
-
- 3
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.
Citations by DOI
-
- 3
- citations for umbrella DOI https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.59650






