AKAP6 orchestrates the nuclear envelope microtubule-organizing center by linking golgi and nucleus via AKAP9
Figures
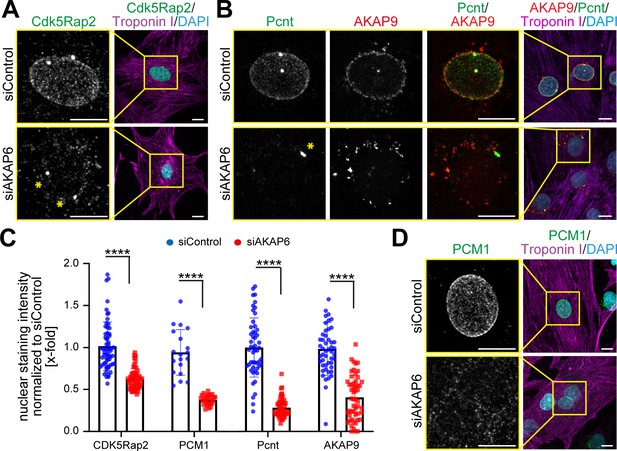
AKAP6 is required for centrosomal protein recruitment and MTOC function at the nuclear envelope.
(A–B) Immunostaining of (A) Cdk5Rap2 (green) or (B) Pcnt (green) and AKAP9 (red) together with cardiac troponin I (magenta, cardiomyocyte-specific) and DNA (DAPI) in rat P3 cardiomyocytes transfected with control-siRNA or AKAP6-siRNA. Asterisks indicate the centrosome. (C) Quantification of A, B, and D as intensity of the signal at the nucleus normalized to siControl. Statistical assay: two-way ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni comparison. ****p<0.0001, n = 60, 60, 19, 28, 58, 46, 56, 46 (from left to right), data are pooled from three independent experiments. Error bars represent the SD. (D) Immunostaining of PCM1 (green), cardiac troponin I (magenta), and DNA (DAPI) in siControl- and siAKAP6-treated P3 cardiomyocytes. Scale bars: 10 µm.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Underlying data for panels D, F and G.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61669/elife-61669-fig1-data1-v1.xlsx

AKAP6 expression is associated with PCM1 localization at the nuclear envelope.
(A) RT-PCR of Akap6 and gapdh utilizing RNA from rat heart samples at different developmental stages as indicated. (B) Quantification of A, as Akap6 band intensity normalized to Gapdh band intensity. (C) Microarray-based temporal expression profile of Akap6 during rat heart development. (D) Immunostaining of AKAP6 (green), PCM1 (red), troponin I (magenta, cardiomyocyte-specific), and DNA (DAPI) in E15 and P3 rat cardiomyocytes. Scale bars: 10 µm.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Underlying data for graphs in panel 1C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61669/elife-61669-fig1-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
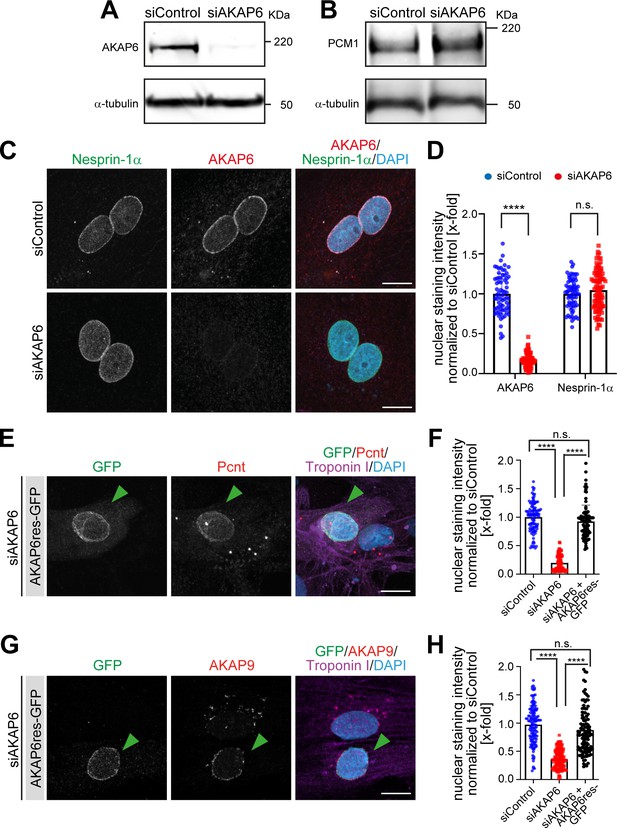
AKAP6 is required for centrosomal protein recruitment and MTOC function at the nuclear envelope.
(A–B) Western blot analysis of (A) AKAP6 or (B) PCM1 expression levels upon siRNA-mediated depletion of AKAP6. Loading control: α-tubulin. (C) Immunostaining of nesprin-1α (green), AKAP6 (red), and DNA (DAPI) in siControl- or si-AKAP6-depleted P3 cardiomyocytes. (D) Quantification of C as nuclear intensity normalized to the mean intensity in siControl. Error bars represent SD. Statistical test: two-way ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni comparison. **** p<0.0001, n.s.: no significance. n = 70, 83, 66, 98 (from left to right), data are from two independent experiments. (E–H) Immunostaining of (E) Pcnt (red) or (G) AKAP9 (red), cardiac troponin I (magenta, cardiomyocyte-specific), and DNA (DAPI) in AKAP6-depleted P3 cardiomyocytes transfected with an siRNA-resistant silent mutant of AKAP6 fused to GFP (AKAP6res-GFP). Transfected cells are denoted with a green arrowhead. (F–H) Quantification of E and G respectively, as nuclear intensity normalized to the mean intensity in siControl. Error bars represent SD. Statistical test: two-way ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni comparison. **** p<0.0001, n.s.: no significance. (F) n = 100 per condition, (H) n = 128, 133, 112 (from left to right), data are from three independent experiments. Scale bars: 10 µm.
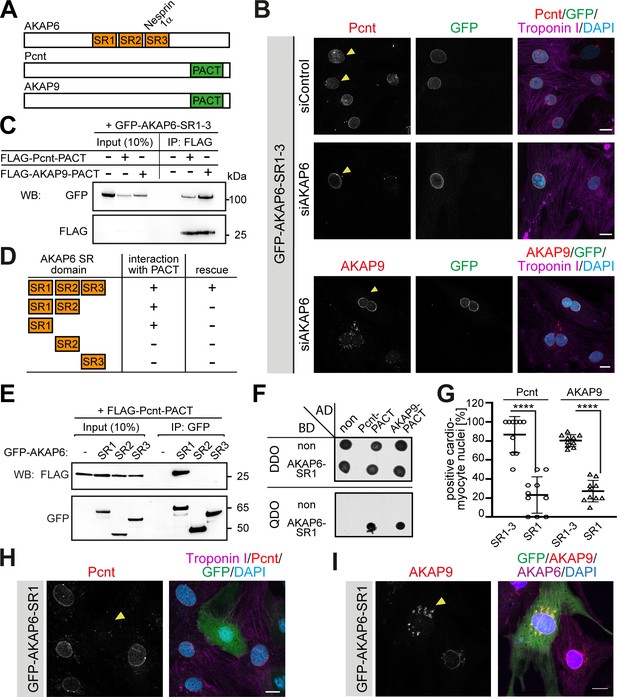
AKAP6 anchors centrosomal proteins to nesprin-1α through its SR domains.
(A) Schematic representation of AKAP6, Pcnt, and AKAP9. (B) Immunostaining of Pcnt (red) or AKAP9 (red), cardiac troponin I (magenta, cardiomyocyte-specific), and DNA (DAPI) in siControl and siAKAP6-treated rat P3 cardiomyocytes transfected with GFP-AKAP6-SR1-3 suggesting that the SR domains of AKAP6 are sufficient to bind to the nuclear envelope and to anchor centrosomal proteins. Transfected cells are indicated with a yellow arrowhead. (C) Immunoprecipitation to demonstrate the interaction of SR1-3 of AKAP6 with the PACT domain of Pcnt or AKAP9. Lysates from HEK293 cells transfected with GFP-AKAP6-SR1-3 in the absence or presence of FLAG-Pcnt-PACT or FLAG-AKAP9-PACT were immunoprecipitated with an anti-FLAG antibody and analyzed by western blotting with antibodies against GFP and FLAG, as indicated. The experiment was performed three times (n = 3); shown is a representative image. (D) Schematic representation of the results in E. +: interaction; -: no interaction. (E) Lysates from HEK293 cells co-transfected with FLAG-Pcnt-PACT and the indicated GFP-AKAP6-SR domains were immunoprecipitated with an anti-GFP antibody and analyzed by western blotting with antibodies against FLAG and GFP; as indicated. The experiment was performed three times (n = 3); shown is a representative image. (F) Yeast-two-hybrid assay. Interactions were tested by monitoring the growth of yeast cells expressing AKAP6-SR1 fused to the DNA binding domain of GAL4 (BD) and Pcnt-PACT or AKAP9-PACT fused to the GAL4 activation domain (AD) proteins on DBO agar plates (double dropout; SD /-Leu /- Trp) (upper), or on QDO plates (quadruple dropout; SD /-Ade /- His/-Leu/-Trp) (lower). Growth on QDO plates indicate interaction. The experiment was performed twice (n = 2); shown is a representative image. (G–I) Immunostaining of (H) Pcnt (red) or (I) AKAP9, cardiac troponin I (magenta, cardiomyocyte-specific), and DNA (DAPI) in P3 cardiomyocytes transfected with GFP-AKAP6-SR1 and subsequent quantification of Pcnt- or AKAP9-positive cardiomyocyte nuclei in transfected cells (G) Transfected cells are labeled with a yellow arrowhead. Data are represented as individual biological replicates, together with mean ± SD. Statistical test: two-way ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni comparison. ****: p<0.0001. n = 10. Scale bars: 10 µm.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Underlying data for graphs in panel 2G.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61669/elife-61669-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx

AKAP6 anchors the Golgi through AKAP9 to the nuclear envelope.
(A) Immunostaining of AKAP9 (green), GM130 (red), and DNA (DAPI) in siControl- and siAKAP6-treated cardiomyocytes. (B) Quantification of A as the GM130 mean intensity in concentric bands of 0.2 µm around the nuclear edge normalized to the total GM130 mean intensity of the cell. 24 cells were analyzed per condition from three independent experiments. Error bars represent the SD. (C) Immunostaining of GM130 (green) and DNA (DAPI) in control, AKAP9- or Pcnt-depleted cardiomyocytes. (D) Quantification of C as in B. 24 (siControl), 17 (siAKAP9) and 26 (siPcnt) cells were quantified per condition and pooled from three independent experiments. Error bars represent the SD. (E) Immunostaining of GM130 (red), cardiac troponin I (magenta, cardiomyocyte-specific), and DNA (DAPI) in P3 cardiomyocytes transfected with GFP-AKAP6-SR1, GFP-AKAP9-PACT or GFP-AKAP6-SR1-3 as control. Transfected cells are labeled with a yellow arrowhead. (F) Immunostaining of GM130 (red), AKAP9 (magenta), and DNA (DAPI) in P3 cardiomyocytes transfected with GFP-AKAP6-SR1-3 or GFP-AKAP9-AK1b. (G) Model representing the tethering of the Golgi to the nuclear envelope through AKAP6 and AKAP9 interaction. AKAP6 bridges AKAP9 to nesprin-1α through its SR domains, while AKAP9 bridges AKAP6 to GM130 through its PACT and N-terminal (AK1b) domains. Scale bars: 10 µm.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Underlying data for graphs in panels B and D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61669/elife-61669-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
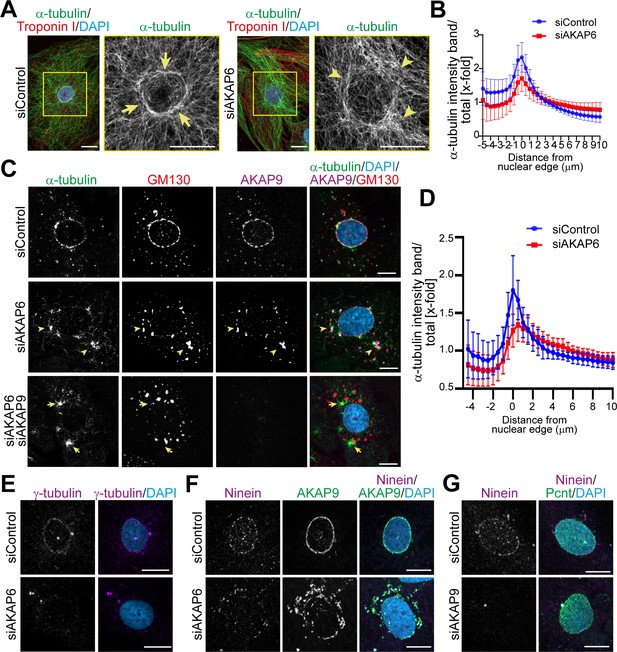
AKAP9-dependent Golgi MTOC in AKAP6-depleted cells.
(A) Immunostaining of α-tubulin (green), cardiac troponin I (red, cardiomyocyte-specific), and DNA (DAPI) in siControl- or siAKAP6-treated P3 cardiomyocytes. Arrows denote the perinuclear microtubule cage in siControl cells, while arrowheads denote disorganized microtubules. (B) Quantification of A as α-tubulin intensity in concentric bands around the nucleus normalized to the total intensity of α-tubulin in the cell, 119 siControl cells and 131 siAKAP6 cells were quantified per condition from four independent experiments. Error bars represent the SD. (C) Immunostaining of α-tubulin (green), GM130 (red), AKAP9 (magenta), and DNA (DAPI) in siControl-, siAKAP6, and siAKAP6 + siAKAP9-treated P3 cardiomyocytes after 2 min of recovery from nocodazole-induced microtubule depolymerization, indicating a switch of MTOC activity from nuclear envelope to Golgi upon AKAP6 depletion (arrowheads). (D) Quantification of α-tubulin intensity in 0.5 µm wide concentric bands in AKAP6-depleted cells, as in C. 37 siControl cells and 48 siAKAP6 cells were quantified per condition from three independent experiments. Error bars represent the SD. (E) Staining of γ-tubulin (magenta) in siControl- or siAKAP6-treated cells. (F–G) Immunostaining of (F) ninein (magenta) and AKAP9 (green) in AKAP6-depleted cells or (G) ninein (magenta) and Pcnt (green) in AKAP9-depleted cells. Scale bars: 10 µm.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Underlying data for graphs in panels B and D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61669/elife-61669-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
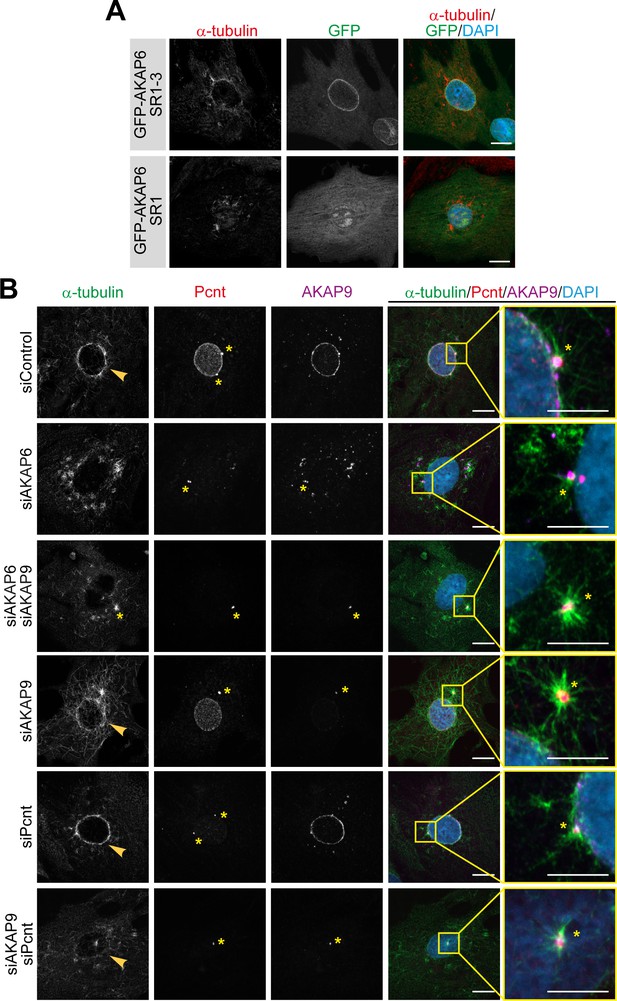
Enhanced centrosomal MTOC activity in AKAP6 and AKAP9 depleted cells.
(A) Immunostaining of α-tubulin (red) and DAPI in P3 cardiomyocytes transfected with GFP-AKAP6-SR1-3 or GFP-AKAP6-SR1 after 2 min of recovery from nocodazole-induced microtubule depolymerization. (B) Immunostaining of α-tubulin (green), Pcnt (red), AKAP9 (magenta), and DNA (DAPI) in the indicated siRNA-treated cardiomyocytes after 2 min of recovery from nocodazole-induced microtubule depolymerization; insets: 5 µm. Asterisk indicates the centrosome and arrowheads indicate nuclear envelop MTOC. Scale bars: 10 µm.

AKAP6 regulates two pools of microtubules at the nuclear envelope.
(A) Immunostaining of α-tubulin (green), GM130 (red), AKAP9 (magenta), and DNA (DAPI) in control, as well as in the indicated siRNA-transfected cells, after 2 min of recovery from nocodazole-induced microtubule depolymerization. Asterisks indicate centrosomal MTOC and arrowheads indicate nuclear envelope MTOC. (B) Quantification of A as α-tubulin intensity in concentric bands around the nucleus normalized to the total intensity of α-tubulin in the cell. 37 siControl cells, 53 siAKAP9 cells, 34 siPcnt cells and 43 siAKAP9+siPcnt cells were quantified per condition, from two independent experiments. Error bars represent the SD. (C) Immunostaining of γ-tubulin (magenta), α-tubulin (green), troponin I (red), and DNA (DAPI) in siRNA-treated cardiomyocytes after 2 min of recovery from nocodazole-induced microtubule depolymerization. (D) Quantification of C, as γ-tubulin intensity at the nuclear envelope normalized to siControl-treated cells. Statistical test: one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni’s comparison. ****: p<0.0001, n.s.: no significance, n = 127, 63, 136, 115 (from left to right), data are pooled from three independent experiments. Error bars represent the SD. (E) Model representing the two pools of microtubules regulated by AKAP6. AKAP6 orchestrates MTOC activity at the nuclear envelope by anchoring both γ-TuRC biding proteins, Pcnt and AKAP9. While Pcnt and AKAP9 cooperate at the nuclear envelope for the nucleation of microtubules, Golgi-dependent microtubule nucleation depends on AKAP9. Scale bars: 10 µm.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Underlying data for graphs in panels B and D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61669/elife-61669-fig5-data1-v1.xlsx
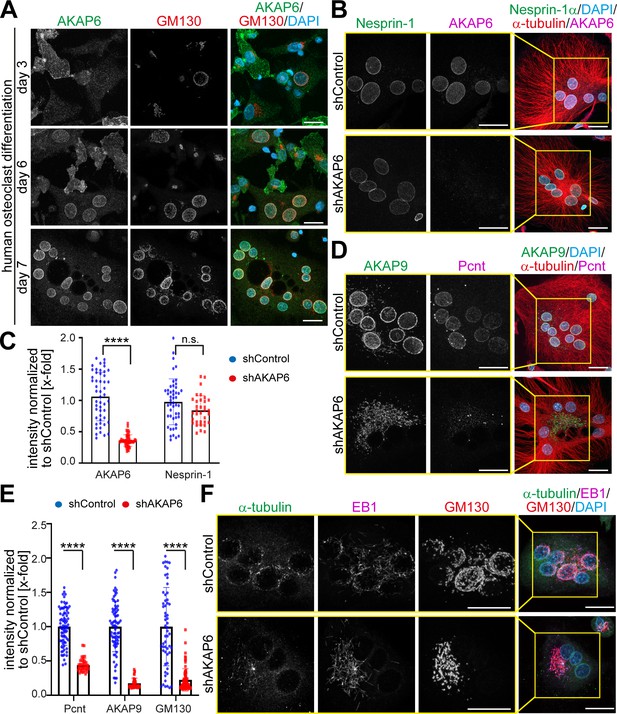
AKAP6 is a key component of nuclear envelope MTOCs.
(A) Immunostaining of AKAP6 (green) and GM130 (red) in human osteoclasts after 3, 6 or 7 days of differentiation. Scale bars: 10 µm. (B) Immunostaining of nesprin-1 (green), AKAP6 (magenta), α-tubulin (red), and DNA (DAPI) in control or AKAP6-depleted osteoclasts. Scale bars: 10 µm. (C) Quantification of B as nuclear intensity normalized to shControl. Error bars represent the SD. n = 48, 48, 34, 34 (from left to right). Data are pooled from three independent donors. Statistical test: two-way ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni comparison. ****: p<0.0001, n.s.: no significance. (D–E) Immunostaining of AKAP9 (green), Pcnt (magenta), α-tubulin (red), and DNA (DAPI) in control and AKAP6-depleted osteoclasts. Scale bars: 10 µm. (E) Quantification of nuclear intensity normalized to shControl. Error bars represent the SD. n = 77, 39, 77, 39, 58, 76 (from left to right). Data were pooled from three independent donors. Statistical test: two-way ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni comparison. ****p<0.0001. (F) Immunostaining of α-tubulin (green), EB1 (magenta), GM130 (red), and DNA (DAPI) in control and AKAP6-depleted osteoclasts, after 15 s of recovery from cold-induced microtubule depolymerization. Scale bars: 20 µm.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Underlying data for graphs in panels C and E.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61669/elife-61669-fig6-data1-v1.xlsx
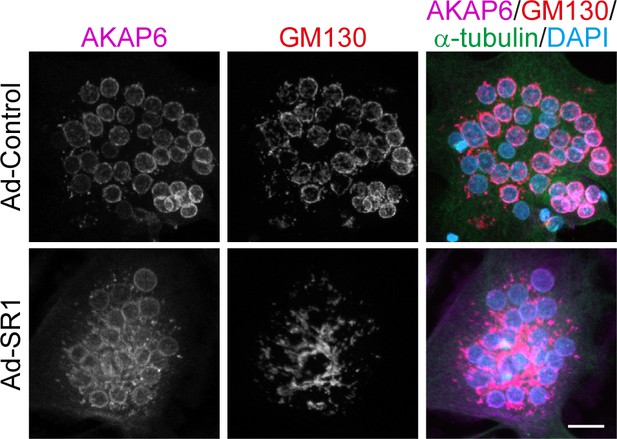
AKAP6 is a key component of nuclear envelope MTOCs.
Immunostaining of AKAP6 (magenta), GM130 (red), α-tubulin (green), and DNA (DAPI) in control and AKAP6-SR1 overexpressing osteoclasts. Overexpression of the SR1 domain of AKAP6 caused displacement of Golgi without displacing endogenous AKAP6 from the nuclear envelope of osteoclasts. Note the cytosolic staining of the SR1 domain. Scale bars: 20 µm.
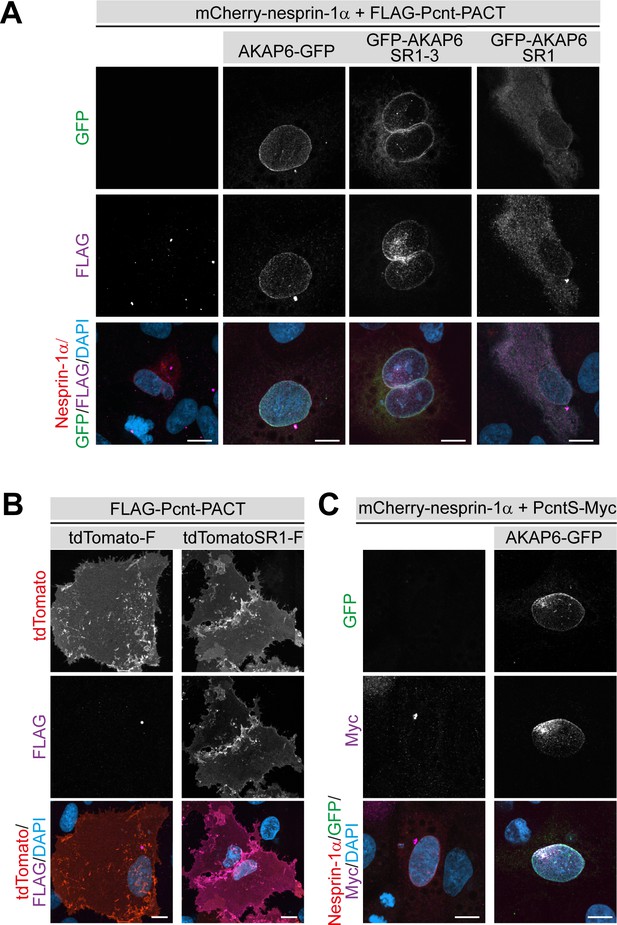
AKAP6 is sufficient to anchor the PACT domain of Pcnt and AKAP9 to the nuclear envelope of nesprin-1α expressing epithelial cells.
(A) ARPE19 epithelial cells co-transfected with mCherry-nesprin-1α, FLAG-Pcnt-PACT, and the corresponding GFP construct, were immunostained with anti-FLAG (magenta) and DNA (DAPI). (B) Immunostaining of FLAG (magenta) in ARPE19 cells co-transfected with tdTomato-Farnesyl (tdTomato-F) or tdTomato-AKAP6-SR1-Farnesyl (tdTomatoSR1-F) together with FLAG-Pcnt-PACT indicating that farnesylated SR1 is sufficient to recruit PACT to the plasma membrane. (C) ARPE19 cells co-transfected with mCherry-nesprin-1α, FLAG-PcntS-Myc with or without AKAP6-GFP, were immunostained with anti-Myc (magenta), and DNA (DAPI). Scale bars: 10 µm.
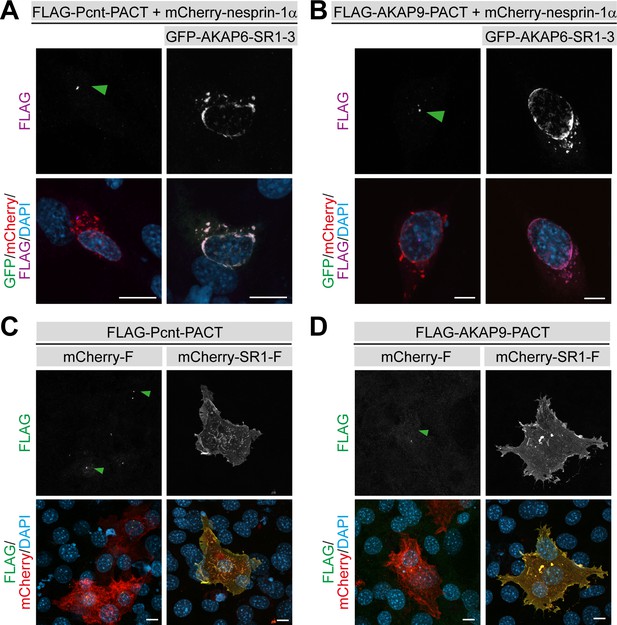
AKAP6 is sufficient to anchor Pcnt and AKAP9 to the nuclear envelope of nesprin-1α cells.
(A–B) NIH3T3 fibroblasts co-transfected with mCherry-nesprin-1α, (A) FLAG-PACT-Pcnt or (B) FLAG-PACT-AKAP9, and GFP-AKAP6-SR1-3 and immunostained with anti-FLAG (magenta) and DAPI. Green arrowhead: centrosomal staining of FLAG-PACT. (C–D) Immunostaining of FLAG (green) in NIH3T3 fibroblasts co-transfected with Cherry-Farnesyl or Cherry-AKAP6-SR1-Farnesyl together with (C) FLAG-Pcnt-PACT or (D) FLAG-AKAP9-PACT indicating that farnesylated SR1 is sufficient to recruit PACT to the plasma membrane. Green arrowhead: centrosomal staining of FLAG-PACT-Pcnt. Scale bars: 10 µm.
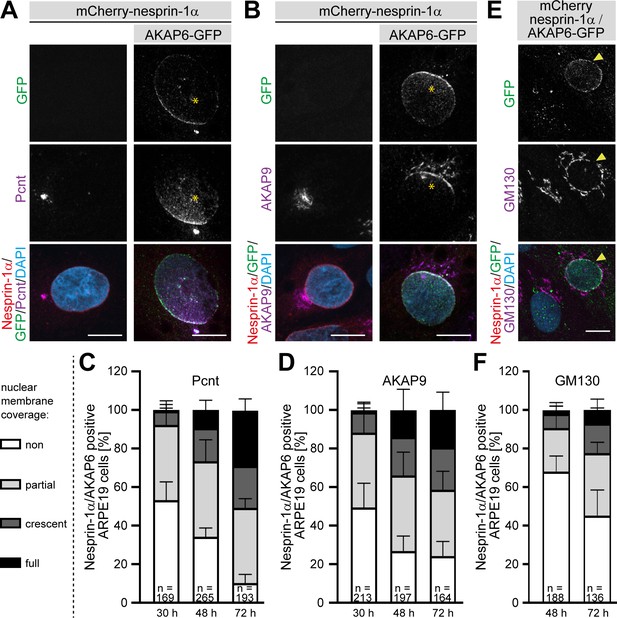
AKAP6 is sufficient to recruit endogenous Pcnt and AKAP9 to the nuclear envelope of nesprin-1α expressing epithelial cells.
(A–B) ARPE19 cells co-transfected with mCherry-nesprin-1α and AKAP6-GFP and immunostained for endogenous (A) Pcnt (magenta) or (B) AKAP9 (magenta) indicating that AKAP6 can recruit endogenous centrosomal proteins to the nuclear envelope of nesprin-1α-expressing cells. Note the partial nuclear localization of Pcnt or AKAP9 near the centrosome (asterisks). (C–D) Percentage of Cherry-nesprin-1α-AKAP6-GFP expressing cells showing non, partial, crescent or full recruitment of Pcnt (C) or AKAP9 (D) to the nuclear envelope. Error bars represent the SD. Data are pooled from four independent experiments. Total number of Cherry-nesprin-1α/AKAP6-GFP expressing cells analyzed are indicated. (E) ARPE19 cells co-transfected with mCherry-nesprin-1α and AKAP6-GFP and immunostained for endogenous GM130 (magenta). Transfected cell is labeled with a yellow arrowhead. (F) Percentage of Cherry-nesprin-1α/AKAP6-GFP expressing cells showing non, partial, crescent or full recruitment of GM130 to the nuclear envelope. Data are represented as individual biological replicates, together with mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Total number of Cherry-nesprin-1α/AKAP6-GFP expressing cells analyzed are indicated. Scale bars: 10 µm.
-
Figure 8—source data 1
Underlying data for graphs in panels C, D and F.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61669/elife-61669-fig8-data1-v1.xlsx
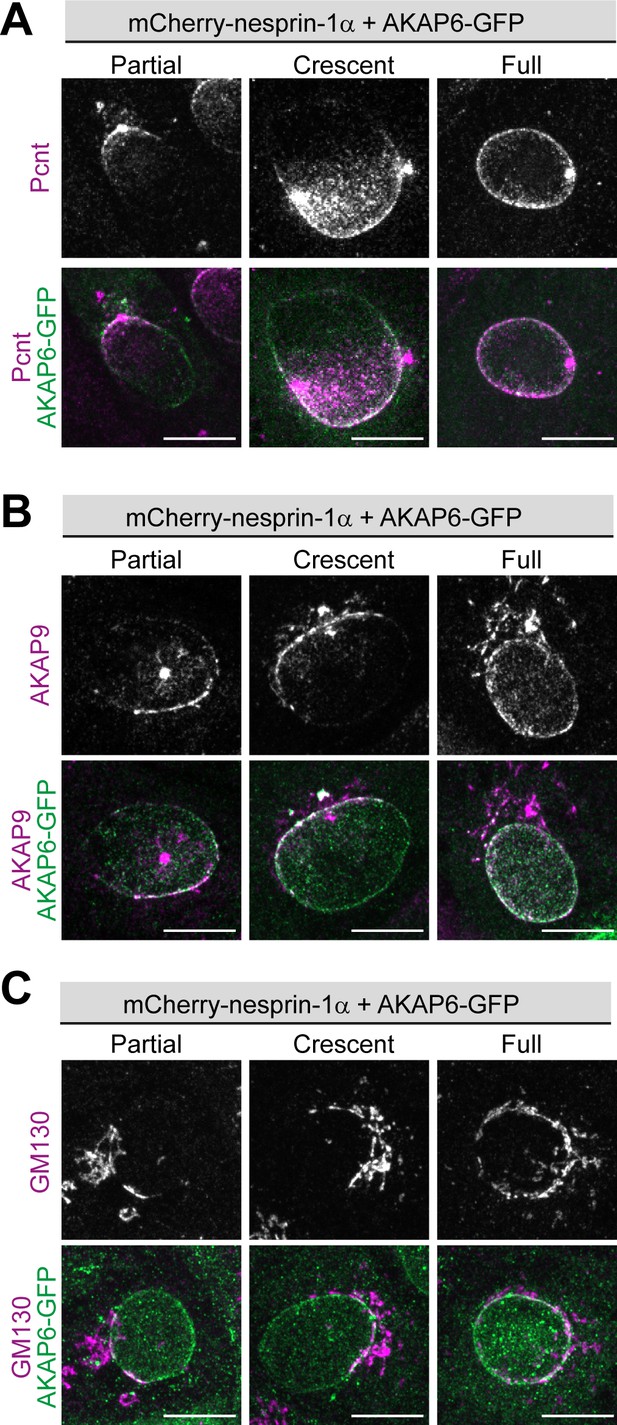
AKAP6 is sufficient to induce recruitment of Pcnt, AKAP9 and GM130 to the nuclear envelope of nesprin-1α cells.
(A–C) Examples of partial, crescent or full recruitment of Pcnt (A), AKAP9 (B) or GM130 (C) of ARPE19 cells co-transfected with mCherry-nesprin-1α and AKAP6-GFP. Scale bars: 10 µm.
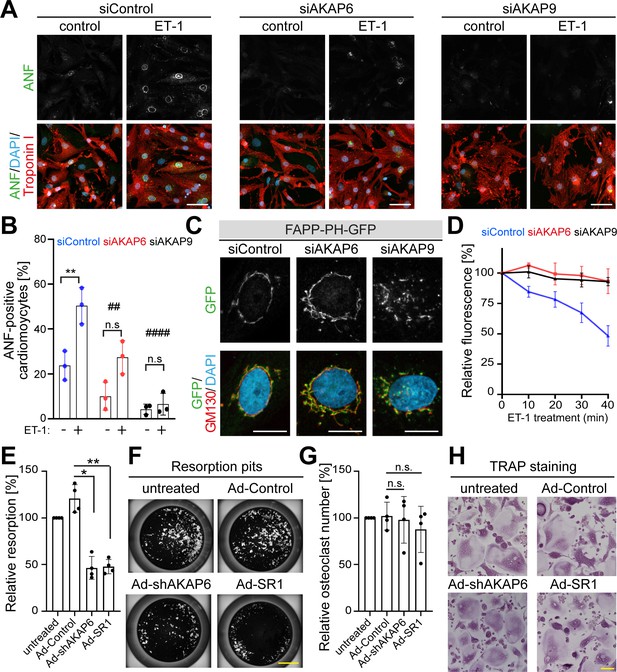
AKAP6 and AKAP9 dependent Golgi localization to the nuclear envelope is required for cell-specific functions in cardiomyocytes and osteoclasts.
(A) Immunostaining of ANF (green), troponin I (red), and DNA (DAPI) of P3 cardiomyocytes transfected with siControl, siAKAP6, or siAKAP9 and stimulated with vehicle or 100 nM ET-1 for 24 hr. Cells were analyzed for a hypertrophic response (perinuclear ANF expression). (B) Quantitative analysis of the percentage of ANF-positive troponin I-positive cardiomyocytes. Data are represented as individual biological replicates, together with mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed with two-way ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni comparison. *: p<0.05, **: p<0.01, ****: p<0.0001, n.s.: no significance; ##: p<0.01, ####: p<0.0001 compared to siControl + ET-1. (C) Immunostaining of GM130 and DNA (DAPI) in control, AKAP6- and AKAP9-depleted cardiomyocytes transfected with FAPP-PH-GFP indicating that depletion of AKAP6 and AKAP9 displaced most of the FAPP-PH-GFP signal from the nuclear envelope. Scale bars: 10 µm. (D) Quantitative analysis of C. Individual regions of GFP fluorescence in siControl-, AKAP6- and AKAP9-treated P3 cardiomyocytes transfected with FAPP-PH-GFP were monitored with confocal microscopy after treatment with vehicle or 100 nM ET-1 and followed for 40 min. Relative fluorescence of GFP was normalized to time 0. 15 cells per condition were measured and pooled from three independent experiments. Error bars represent the SD. (E) Relative resorbed area of osteoclasts transduced with the indicated adenovirus for the last 3 days of differentiation in calcium phosphate-coated wells. Data are ± SD of 4 independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed with One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni comparison. *: p=0.015, **: p<0.01. (F) Representative micro images. Scale bars: 500 μm. (G) Relative osteoclast number after transduction of the indicated virus for the last 3 days of differentiation. TRAP-positive cells with ≥3 nuclei were considered as osteoclasts. Data are mean ± SD of 4 independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed with one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni comparison. n.s.: no significance. (H) Representative images. Scale bars: 100 μm.
-
Figure 9—source data 1
Underlying data for graphs in panels B, D, E and G.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61669/elife-61669-fig9-data1-v1.xlsx
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) | AH109 | Clontech | Reporters: HIS3, ADE2, MEL1, LacZ | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HEK293 | ATCC | Cat# PTA-4488, RRID:CVCL_0045 | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | ARPE19 | ATCC | Cat# CRL-2302, RRID:CVCL_0145 | |
| Cell line (Mus musculus) | NIH3T3 fibroblast cell line | ATCC | Cat# CRL-1658, RRID:CVCL_0594 | |
| Transfected construct | pEGFP-N1 | Clontech | Cat# 6085–1 | |
| Transfected construct (Rattus norvegicus) | pEGFP-N1 AKAP6β | This paper | N/A | |
| Transfected construct (Rattus norvegicus) | pEGFP-N1 AKAP6βsiRNA res | This paper | N/A | |
| Transfected construct (Rattus norvegicus) | pEGFP -C2 AKAP6 -SR1-3 (585–1286) | This paper | N/A | |
| Transfected construct (Rattus norvegicus) | pEGFP -C2 AKAP6 -SR1-2 (585–1065) | This paper | N/A | |
| Transfected construct (Rattus norvegicus) | pEGFP -C2 AKAP6 -SR1 (585–915) | This paper | N/A | |
| Transfected construct (Rattus norvegicus) | pEGFP -C2 AKAP6 -SR2 (915–1065) | This paper | N/A | |
| Transfected construct (Rattus norvegicus) | pEGFP -C2 AKAP6 -SR3 (1065–1286) | This paper | N/A | |
| Transfected construct (Mus musculus) | pmCherry-Nesprin1α | This paper | N/A | |
| Transfected construct (H. sapiens) | pCMV-Tag2b-hAKAP9-CTermin | This paper | N/A | |
| Transfected construct (H. sapiens) | pCMV-Tag2b-hPCNT-CTermin | This paper | N/A | |
| Transfected construct (H. sapiens) | pDsRed-PACT-Myc | Mikule et al., 2007 | ||
| Transfected construct (H. sapiens) | GFP-FLAG-PcntB-Myc | Lee and Rhee, 2012 | ||
| Transfected construct | pGBKT7 | Clontech | Cat# 630443 | |
| Transfected construct (Rattus norvegicus) | pGBKT7-AKAP6-SR1(585–915) | This paper | N/A | |
| Transfected construct | pGADT7 | Clontech | Cat# 630442 | |
| Transfected construct (H. sapiens) | pGADT7-Pcnt-PACT | This paper | N/A | |
| Transfected construct (H. sapiens) | pGADT7-AKAP9-PACT | This paper | N/A | |
| Transfected construct | pmCherry-Farnesyl5 | Addgene | Cat# 55045 | |
| Transfected construct | tdTomato-Farnesyl5 | Addgene | Cat# 58092 | |
| Transfected construct (Rattus norvegicus) | tdTomato-SR1- Farnesyl5(585-915) | This paper | N/A | |
| Transfected construct (Rattus norvegicus) | pmCherry-Farnesyl5 -SR1(585–915) | This paper | N/A | |
| Transfected construct (Rattus norvegicus) | pENTR1-SR1(585–915) | This paper | N/A | |
| Transfected construct (H. sapiens) | pEGFP-C2-AKAP9-1KB | This paper | N/A | |
| Transfected construct | FAPP-PH-GFP | Balla et al., 2005 | ||
| Biological sample (Rattus norvegicus) | E15 cardiomyocytes | This paper | N/A | |
| Biological sample (Rattus norvegicus) | P3 cardiomyocytes | This paper | N/A | |
| Biological sample (H. sapiens) | Osteoclasts | This paper | N/A | |
| Antibody | anti-PCM1 (H-262) (rabbit polyclonal) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Cat# sc-67204, RRID:AB_2139591 | IF: (1:500) WB: (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-PCM1 (G-6) (mouse monoclonal) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Cat# sc-398365, RRID:AB_2827155 | IF: (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti-AKAP6 (rabbit polyclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# HPA048741, RRID:AB_2680506 | IF: (1:500) WB: (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-AKAP6 (mouse monoclonal) | Covance Research Products Inc | Cat# MMS-448P-100, RRID:AB_10094719 | IF: (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti-AKAP6 (rabbit polyclonal) | M.S. Kapiloff (Li et al., 2013) | IF: (1:1000) | |
| Antibody | anti-Pericentrin (rabbit polyclonal) | BioLegend | Cat# PRB-432C, RRID:AB_291635 | IF: (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti-Pericentrin (mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | Cat# ab220784 | IF: (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti-nesprin-1 (MANNES1E) (mouse monoclonal) | G. Morris (Randles et al., 2010) | N/A | IF: (1:100) |
| Antibody | anti-nesprin-1 (rabbit polyclonal) | Covance | Cat# PRB-439P-100, RRID:AB_10094891 | IF: (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti-α-tubulin (mouse monoclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# T9026, RRID:AB_477593 | WB:(1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-tubulin (rat monoclonal) | Abcam | Cat# ab6160, RRID:AB_305328 | IF: (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti-Troponin I (goat polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat# ab56357, RRID:AB_880622 | IF: (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti-γ-tubulin (mouse monoclonal) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Cat# sc-51715, RRID:AB_630410 | IF: (1:100) |
| Antibody | anti-ninein (mouse monoclonal) | Santa Cruz Biotechnolgy | Cat# sc-376420, RRID:AB_11151570 | IF: (1:100) |
| Antibody | anti-AKAP9 (rabbit polyclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# HPA026109, RRID:AB_1844688 | IF: (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti-AKAP9 (mouse monoclonal) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 611518, RRID:AB_398978 | IF: (1:250) |
| Antibody | anti-GM130 (mouse monoclonal) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 610823, RRID:AB_398142 | IF: (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti-Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANF) (rabbit polyclonal) | Millipore | Cat# AB5490, RRID:AB_2155601 | IF: (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti-GFP (mouse monoclonal) | Roche | Cat# 11814460001, RRID:AB_390913 | IF: (1:1000) WB: (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-GFP (rabbit polyclonal) | Novus | Cat# NB600-308, RRID:AB_10003058 | IF: (1:1000) WB: (1:1000) IP: (1.5 µl) |
| Antibody | anti-FLAG (mouse monoclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# F1804, RRID:AB_262044 | IF: (1:2000) WB: (1:1000) IP: (1.5 µl) |
| Antibody | anti-Myc (mouse monoclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 2276, RRID:AB_331783 | IF: (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-Rabbit secondary antibody, Alexa Fluor 488 (donkey) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A-21206, RRID:AB_2535792 | IF: (1:250) |
| Antibody | anti-Rabbit secondary antibody, Alexa Fluor 594 (donkey) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A21207, RRID:AB_141637 | IF: (1:250) |
| Antibody | anti-Rabbit secondary antibody, Alexa Fluor 647 (donkey) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A31573, RRID:AB_2536183 | IF: (1:250) |
| Antibody | anti-Mouse secondary antibody, Alexa Fluor 488 (donkey) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A21202, RRID:AB_141607 | IF: (1:250) |
| Antibody | anti-Mouse secondary antibody, Alexa Fluor 594 (donkey) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A21203, RRID:AB_2535789 | IF: (1:250) |
| Antibody | anti-Mouse secondary antibody, Alexa Fluor 647 (donkey) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A31571, RRID:AB_162542 | IF: (1:250) |
| Antibody | anti-Goat secondary antibody t, Alexa Fluor 594 (donkey) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A32758, RRID:AB_2762828 | IF: (1:250) |
| Antibody | anti-Goat secondary antibody, Alexa Fluor 647 (donkey) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A21447, RRID:AB_2535864 | IF: (1:250) |
| Antibody | anti-rat secondary antibody, Alexa Fluor 488 (donkey) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A-21208, RRID:AB_2535794 | IF: (1:250) |
| Antibody | anti-rat secondary antibody, Alexa Fluor 594 (donkey) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A-21209, RRID:AB_2535795 | IF: (1:250) |
| Antibody | ECL Mouse IgG, HRP-linked whole Ab (sheep) | GE Healthcare | Cat# NA931, RRID:AB_772210 | WB: (1:5000) |
| Antibody | ECL Rabbit IgG, HRP-linked whole Ab (sheep) | GE Healthcare | Cat# NA934, RRID:AB_772206 | WB: (1:5000) |
| Sequence-based reagent | Silencer Select Negative Control No. one siRNA | Thermo Fischer Scientific | Cat# 4390843 | |
| Sequence-based reagent (Rattus norvegicus) | siRNA targeting sequence: rat Akap6 | Thermo Fischer Scientific | Cat# 4390771 s134273 | CAAACGACCUUGAUCAAGAtt |
| Sequence-based reagent (Rattus norvegicus) | siRNA targeting sequence: rat Akap9 | Thermo Fischer Scientific | Cat# 4390771 s97685 | GCUUGAACAUGCGAAAGUUtt |
| Sequence-based reagent | shRNA targeting sequence: rat/mouse/ human Akap6 | This paper | N/A | CGTTTGATTTGCCTCTGCAGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Pcnt FlexiTube siRNA | Qiagen | Cat# SI01709351 | CAGGAACUCACCAGAGACGAA |
| Sequence-based reagent (Rattus norvegicus) | Akap6 RT-PCR | This paper | Forward primer: | GGGTGATTTGTTTGGATTGG |
| Sequence-based reagent (Rattus norvegicus) | Akap6 RT-PCR | This paper | Reverse primer: | TGTCAGAAACACTCCGCTTG |
| Sequence-based reagent (Rattus norvegicus) | Gapdh RT-PCR | This paper | Forward primer: | CAG AAG ACT GTG GAT GGC CC |
| Sequence-based reagent (Rattus norvegicus) | Gapdh RT-PCR | This paper | Reverse primer: | AGT GTA GCC CAG GAT GCC CT |
| Commercial assay or kit | Cold Fusion Cloning Kit with Competent Cells | System Biosciences | Cat# MC010B-1 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Neonatal Heart Disassociation Kit | Miltenyi Biotec | Cat# 130-098-373 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | M-MLV Reverse Transcriptase | Sigma | Cat# M1302 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Lipofectamine LTX | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 15338100 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Lipofectamine RNAiMAX | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 13778150 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Nocodazole | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# M1404 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Brefeldin A (BFA) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# B7651 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Endothelin 1 (ET-1) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# E7764 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Fibronectin | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# F1141 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 4’,6-diamidino-2- phenylindole (DAPI) | Carl Roth | Cat# 6335.1 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Fluoromount-G | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 00-4958-02 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM), high glucose, GlutaMAX | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 61965059 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DMEM 199 medium | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 41150 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Iscove's Modified Dulbecco's Medium (IMDM), GlutaMAX Supplement | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 31980 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) | biowest | Cat# S1810 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Horse Serum | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 16050122 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Penicillin-Streptomycin | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 15140122 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Gentamicin | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 15750060 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DPBS, no calcium, no magnesium | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 14190094 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Opti-MEM I Reduced Serum Medium | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 11058021 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | YPDA Broth | Clontech | Cat# 630306 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | SD–Leu /– Trp with Agar | Clontech | Cat# 630317 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | SD–Ade /– His /– Leu /– Trp with Agar | Clontech | Cat# 630323 | |
| Software, algorithm | Fiji | http://fiji.sc | RRID:SCR_002285 | |
| Software, algorithm | ZEN blue | Carl Zeiss AG | RRID:SCR_013672 | |
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism | GraphPad Prism, | RRID:SCR_002798 | |
| Other | Zeiss LSM800 confocal laser scanning microscope with Airyscan module | Carl Zeiss AG | N/A | |
| Other | Leica TCS SP8 | Leica Microsystems | N/A |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Oligonucleotides used for generating constructs.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61669/elife-61669-supp1-v1.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61669/elife-61669-transrepform-v1.docx





