Human cytomegalovirus antagonizes activation of Fcγ receptors by distinct and synergizing modes of IgG manipulation
Figures
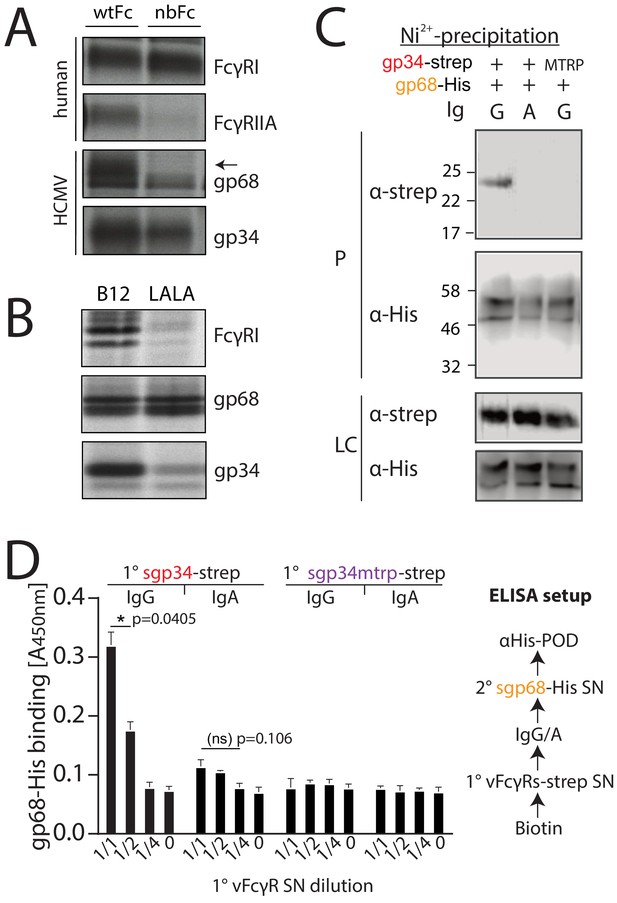
gp34 and gp68 simultaneously bind to IgG using distinct epitopes.
(A) CV-1 cells were infected with rVACVs expressing gp34, gp68, or the host Fc-receptors FcγRIIA and FcγRI at a multiplicity of infection of 4 for 14 hr before metabolic labeling. Proteins were precipitated using either wtFc or nbFc coupled with CNBr-activated Sepharose. Dissociated immune complexes were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE. IP, immunoprecipitation. Shown is one out of two independent experiments. (B) CV-I cells were infected and metabolically labeled as above. Lysates were incubated with B12 or B12-LALA and IgG was precipitated using PGS. All samples were de-glycosylated using EndoH resulting in double bands for gp68 (Sprague et al., 2008). Shown is one out of two independent experiments. (C) Soluble vFcγRs were tested for simultaneous IgG1 (Rtx) binding by Ni-NTA-Sepharose co-precipitation and subsequent immunoblot in the presence of IgG (Rtx). gp34 and gp34mtrp were streptavidin-tagged; gp68 was 6xHis-tagged. All samples were deglycosylated using PNGaseF resulting in double bands for gp68 (Sprague et al., 2008). LC = loading control, P = precipitate. Shown is one out of two independent experiments. (D) Soluble vFcγRs as in B were tested for simultaneous IgG1 (Rtx) binding via ELISA as schematically depicted. An anti-CD20 IgA molecule served as a negative control. The 1° sgp34-strep or sgp34mtrp layers were generated by incubation of titrated amounts of supernatants from soluble vFcγR producing cells on coated biotin. Supernatants were diluted in PBS. 2° sgp68-His detection was performed using 1:2 diluted supernatant accordingly. Graph shows averages from two independent experiments performed in technical replicates (Figure 1—source data 1). Error bars = SD. Two-way ANOVA.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Relates to Figure 1D bar graph.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63877/elife-63877-fig1-data1-v2.xlsx
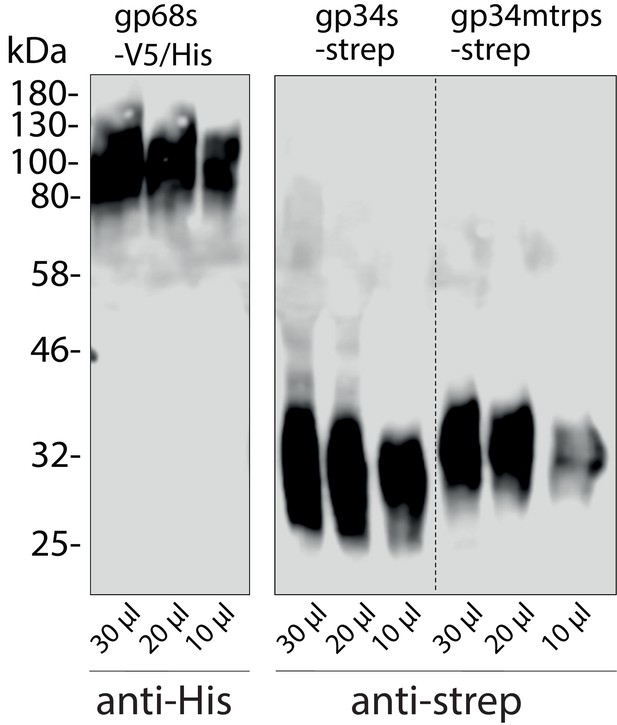
Immunoblot detection of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) glycoproteins in the supernatant of Hek293T producer cells.
Soluble constructs of gp34 or gp34mtrp (sgp34 and sgp34mtrp, both streptavidin-tagged) or gp68 (gp68s, 6xHis-tagged) lacking a transmembrane domain and cytosolic tail were recombinant expressed in transfected 293 T cells. Indicated volumes of cell culture supernatant were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and subsequent immunoblot using tag-specific HRP-conjugated antibodies.
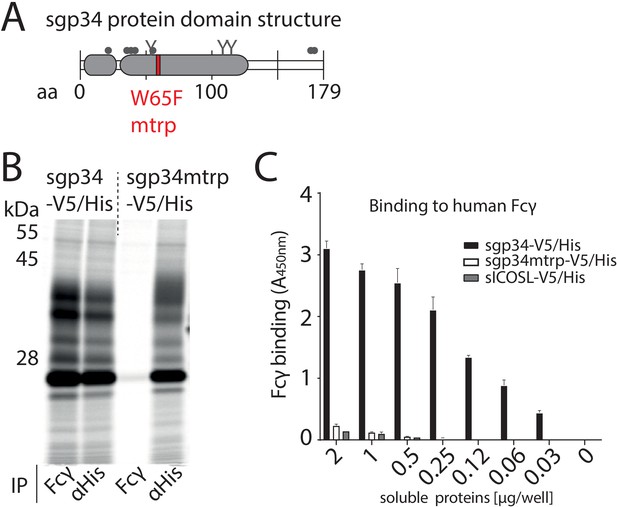
Fcγ-binding deficient mutant of gp34.
(A) Schematic depiction of soluble gp34 of AD169 (sgp34) with indicated signal peptide (small gray box) and Ig-like domain (large gray box), O-glycosylation sites (gray dots), N-glycosylation sites (Y), and the position of the mutated tryptophan (mtrp, W65F) in red. (B) The mtrp variant of gp34 shows strongly reduced binding to human IgG-Fc. Hela cells transiently expressing sgp34 or sgp34mtrp were metabolically labeled with 35S for 2 hr. Cell lysates were precipitated (IP) using Protein-A-Sepharose to pull down polyclonal rabbit-anti-His antibody (Bethyl) or a human Fcγ fragment (Rockland). Precipitates were EndoH digested and analyzed on a 10–13% gradient SDS-PAGE gel and visualized by phosphoimaging (Typhoon FLA 7000, GE Healthcare). (C) Sgp34mtrp binding to Fcγ is abolished in ELISA. Human Fcy fragments (1 µg/well) were immobilized and incubated with sgp34-V5/His or sgp34mtrp-V5/His at indicated concentrations. sgp34/sgp34mtrp binding was measured by HRP-conjugated anti-His antibody detection. Soluble human ICOS ligand ectodomain (sICOSL) served as a negative control.
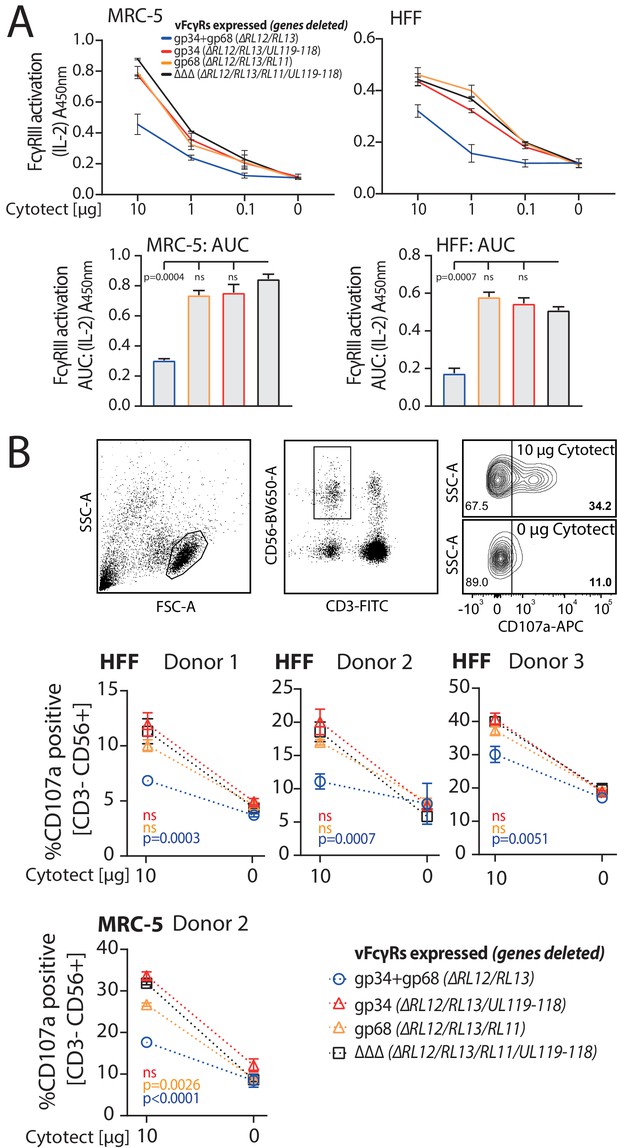
gp34 and gp68 synergistically antagonize FcγR activation.
(A) MRC-5 or human foreskin fibroblasts (HFF) cells were infected with human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) AD169 mutant viruses lacking different combinations of vFcγRs (Multiplicity of Infection [MOI] = 3, for 72 hr) and incubated with titrated amounts of Cytotect. FcγR activation was measured as mIL-2 production of BW5147-FcγRIII reporter cells. Error bars: SD of two independent experiments. Bar graphs show area under curve (AUC) comparison (0.1 cut-off). Error bars: SD. One-way ANOVA. (B) Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) assay: HFF or MRC-5 cells were infected as in A and incubated upon opsonization with Cytotect with PBMCs of three different donors for 6 hr. NK cell CD107a positivity was measured using flow cytometry. Gating strategy shown for one representative experiment of MRC-5 cells infected with HCMV AD169/pBAC2 ∆RL12/UL119-118 incubated with PBMCs from Donor 2. Error bars: SD of two independent experiments performed in technical replicates. Error bars smaller than graph symbols are not shown. Two-way ANOVA compared to ΔΔΔ.
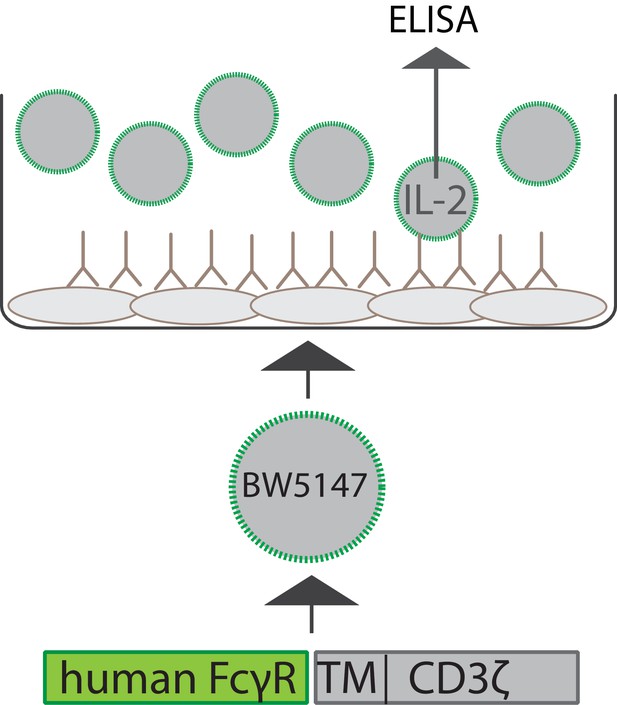
Schematic depiction of the experimental setup of a cell-based FcγR activation assay.
Infected or antigen-transfected cells are opsonized using virus-specific or antigen-specific antibody preparations. BW5147 reporter cells stably expressing chimeric human FcγR receptor ectodomains fused to the transmembrane and cytosolic domains of mouse CD3ξ are then incubated on the opsonized cells. FcγR activation can be quantified by measurement of secreted mouse IL-2 (mIL-2) via an IL-2-specific sandwich ELISA.
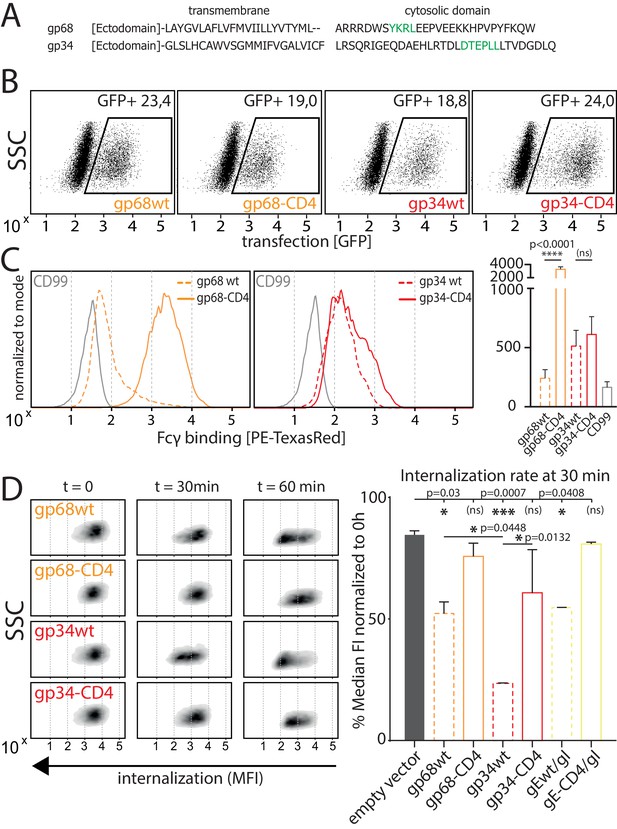
Native gp34 efficiently internalizes immune complexes.
(A) Sequence alignment of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) AD169 BAC-2 encoded glycoproteins gp34 (RL11, P16809) and gp68 (UL119-118, P16739). Cellular localization motifs are highlighted in green. (B) 293 T cells stably expressing CD20. 293 T-CD20 cells were transfected with indicated constructs encoded by a pIRES_eGFP vector. Transfected cells were gated via GFP expression using flow cytometry. (C) GFP positive cells from B were measured for surface expression of vFcγRs judged by Fcγ binding. Unaltered native full-length molecules (wt) were compared to CD4-tailed variants via a TexasRed-conjugated human Fcγ fragment. CD99 expression from a pIRES_eGFP vector served as a non-Fcγ-binding negative control. Bar graph shows data from three individual experiments. Error bars = SD. One-way ANOVA. (D) Internalization of CD20/Rtx immune complexes in dependence of vFcγR expression was measured by loss of surface signal over time in a pulse-chase approach detecting residual surface complexes via a PE-conjugated mouse-anti-human-IgG antibody. 293 T cells stably expressing CD20 were transfected with the indicated constructs. HSV-1 gE was co-transfected with gI to form a functional heterodimer (Ndjamen et al., 2014). Left: Exemplary experiment comparing internalization rates between native vFcγRs (wt) and their respective CD4-tailed variants. Right: Internalization rates 1 hr post pulse. Two independent experiments (Figure 3—source data 1). Error bars = SD. One-way ANOVA.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Relates to Figure 3D bar graph.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63877/elife-63877-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx

Alignment of selected herpesvirus glycoproteins present on the surface of an infected cell.
Green = localization signal. Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) gp34 (RL11, P16809), gp68 (UL119-118, P16739), gB (UL55, P06473), gp95 (RL12, P16810), and gpRL13 (RL13, Q6SWC9). HSV-1 gE (US8, P04488). MCMV m138 (m138, Q83151). RhCMV pRh05 (RL11A, Kolb et al., 2019).
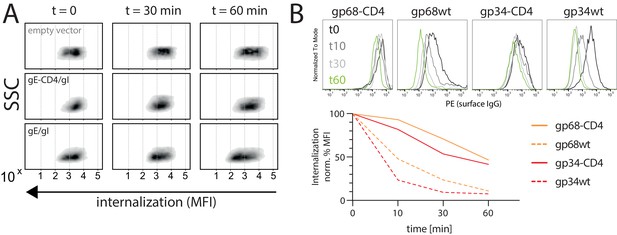
Internalization of CD20/Rtx immune complexes and non-immune IgG in dependence of vFcγR expression.
Internalization kinetics was measured by loss of surface signal over time in a pulse-chase approach detecting residual surface complexes via a PE-conjugated mouse-anti-human-IgG antibody. 293 T cells stably expressing CD20 were transfected with the indicated constructs. (A) HSV-1 gE was co-transfected with gI to form a functional heterodimer. Exemplary experiment showing internalization in empty vector transfected cells compared to gE/gI or gE-CD4/gI co-transfected cells. (B) Internalization of non-immune IgG is increased by gp34 over gp68 and reduced with respective CD4-tailed constructs. Cells expressing vFcγRs were pre-incubated with Cytotect at a 1:500 dilution. Graph shows Mean Fluorescence Intensity (MFI) normalized to t0 (100% = highest value for each data set) and t60 (0% = 0 MFI).
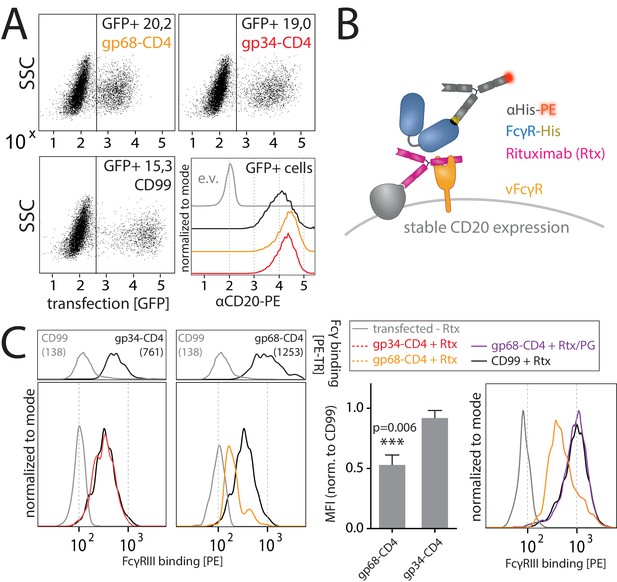
gp68 blocks binding of human FcγRIII to immune complexes.
(A) 293 T-CD20 cells were transfected with indicated constructs encoded on a pIRES_eGFP vector. CD99 served as a non-Fcγ-binding control. Gating strategy and CD20 expression in dependence of vFcγR or CD99 co-expression. CD20 was detected using a PE-labeled αCD20 antibody. (B) Schematic depiction of the experimental flow cytometry setup to measure FcγR binding to cell surface IC. (C) Expression of vFcγRs or CD99 differentially modulates binding of FcγRIII to CD20/Rtx complexes. Total IgG binding by vFcγRs is demonstrated by Fc binding (PE-TexasRed-conjugated Fcγ fragment) compared to CD99 (upper panels). MFI are indicated in brackets. Pre-incubation of Rtx with Protein G counteracts block of FcγRIII binding mediated by gp68. Bar graph: Comparing the blocking effect of vFcγRs over four independent experiments normalized to CD99 (Figure 4—source data 1). Error bars = SD. Two-tailed t-test.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Relates to Figure 4C bar graph.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63877/elife-63877-fig4-data1-v2.xlsx
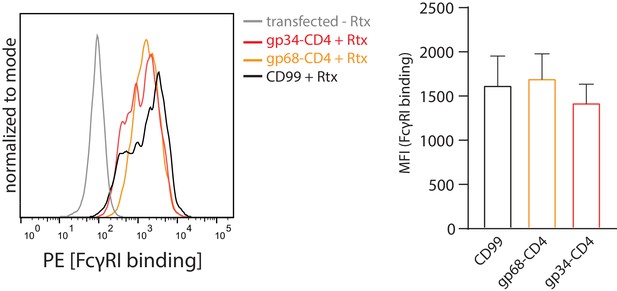
gp68 is not able to block FcγRI binding to IC.
Hek293T cells stably expressing CD20 and opsonized with Rtx were assayed for FcγRI ectodomain binding in the presence or absence of gp68-CD4 as described in Figure 4. Error bars = SD. Three independent experiments (Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1). One-way ANOVA, no significant differences were calculated.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Relates to Figure 4—figure supplement 1 bar graph.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63877/elife-63877-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v2.xlsx
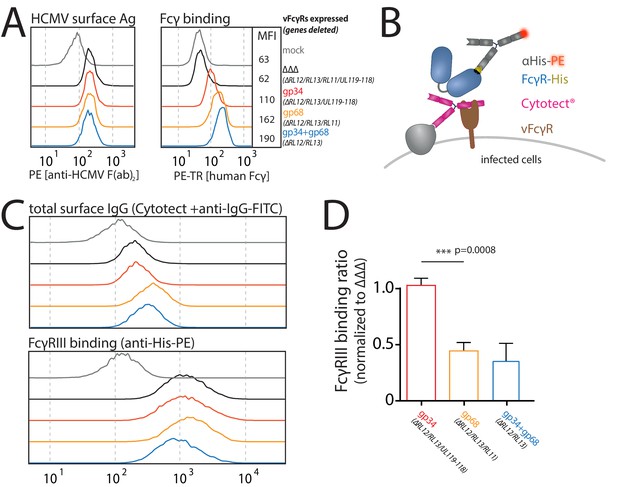
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) gp68, but not gp34 blocks binding of human FcγRIII to opsonized HCMV-infected cells.
MRC-5 cells were infected with mutant HCMV Ad169 viruses lacking different vFcγR encoding genes at MOI = 2 and measured 72dpi via flow cytometry. ΔΔΔ = ΔRL11/ΔRL12/ΔUL119-118. ΔUL119 = ΔUL119-118. (A) Left: Infected cells were measured for surface expression of antigens using Cytotect derived F(ab’)2 fragments detected via polyclonal rabbit anti-human-IgG-FITC. Right: The same cells were measured for surface binding of human Fcγ using a TexasRed conjugated human Fcγ fragment. (B) Schematic depiction of the experimental setup to measure human FcγR binding to immune complexes in dependence of vFcγR deletion. (C) Representative experiment showing the binding of soluble ectodomains of His-tagged human FcγRIIIA to infected cells opsonized with Cytotect and the total surface bound IgG. FcγR binding was detected via αHis-PE staining. Effects on FcγRIIIA binding are obscured by total surface IgG binding varying between viruses. (D) Three independent experiments testing FcγRIII binding to infected cells incubated with Cytotect are shown in one graph. FcγRIII binding to infected cells pre-incubated with Cytotect was calculated as MFI ratio between FcγR-binding and surface-IgG to account for differences in surface attachment of human antibodies in the presence of different combinations of vFcγRs. FcγRIIIA binding was normalized to ΔΔΔ for each individual experiment (Figure 5—source data 1). Error bars = SD, one-way ANOVA.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Relates to Figure 5D bar graph.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63877/elife-63877-fig5-data1-v2.xlsx
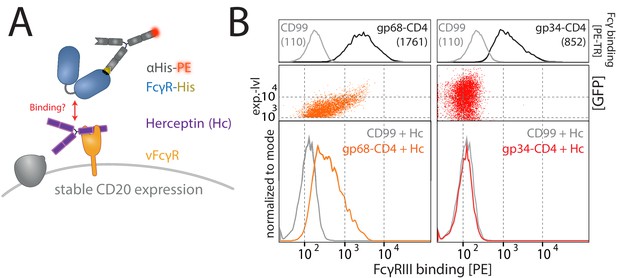
Gp68, but not gp34, binds IgG simultaneously to FcγRIII.
(A) Schematic of the experimental setup. As in Figure 4, using HER-2-specific Herceptin (Hc) replacing Rtx. Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) vFcγRs gp34 or gp68 were transiently expressed by 293 T cells stably expressing CD20. Expression of the non-vFcγR glycoprotein CD99 served as a negative control. Transfected cells were identified via GFP expression (p_IRES-eGFP polycistronic vector). FcγRIII/CD16 binding was assessed via flow cytometry. (B) Gp68, but not gp34, mediates binding of FcγRIII/CD16 via non-immune IgG (Hc). Binding is dependent on the expression level of gp68 (upper panel) judged by GFP intensity. Total IgG bound by vFcγRs was assessed via binding of PE-TexasRed-conjugated Fcγ fragments compared to CD99 (upper panels). MFI are indicated in brackets.
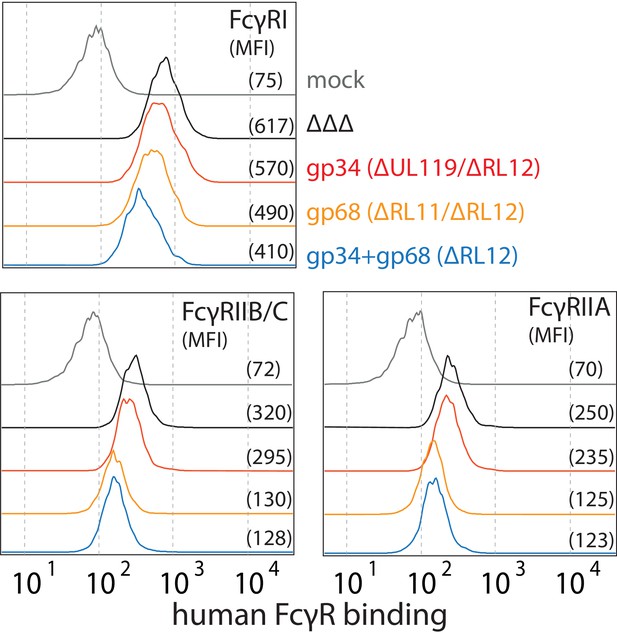
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) gp68 reduces binding of human FcγRII ectodomains to opsonized-infected cells.
MRC-5 cells were infected with mutant HCMV AD169 pBAC2-derived viruses lacking different vFcγR encoding genes at MOI = 2 and measured 72dpi via flow cytometry. ΔΔΔ = ΔRL11/ΔRL12/ΔUL119-118. ΔUL119 = ΔUL119-118. Experiments testing FcγR binding to infected cells incubated with Cytotect were conducted as described in Figure 6. Gating was adjusted to account for differences in surface attachment of human antibodies in the presence of different combinations of vFcγRs.
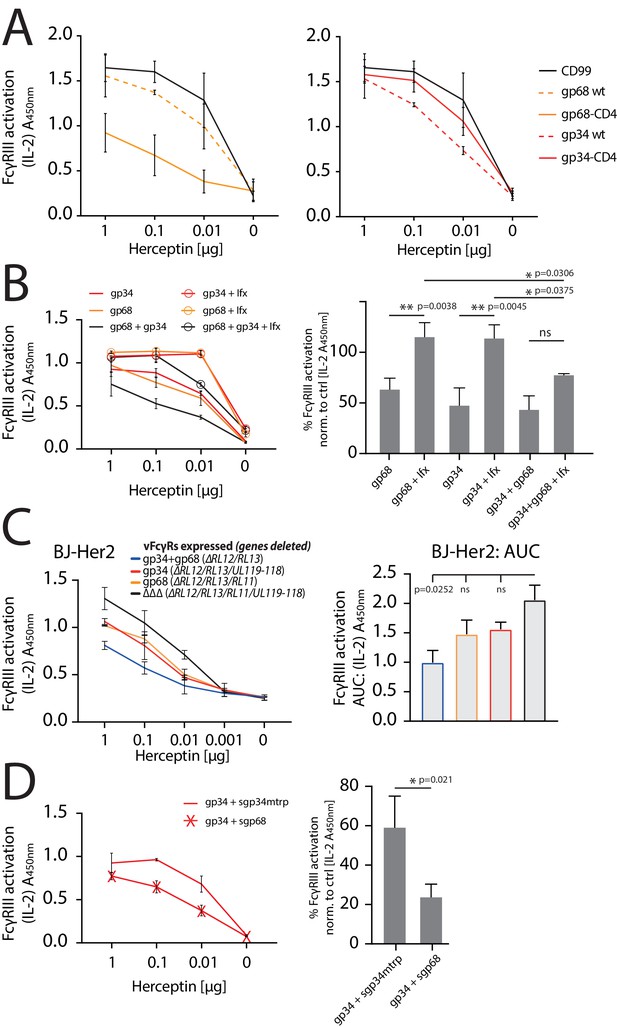
gp34 and gp68 synergistically antagonize.
FcγRIIIA in the absence and presence of non-immune IgG and show cooperativity. (A) Increased membrane-residence enhances antagonistic potential of gp68 and reduces antagonistic potential of gp34. Hela cells were co-transfected as indicated in combination with Her2 antigen and incubated with titrated amounts of Herceptin followed by FcγRIII activation assessment. Three independent experiments performed in technical replicates. Error bars = SD. (B) Non-immune IgG counteracts antagonistic potential of vFcγRs. Hela cells were co-transfected as indicated in combination with Her2 antigen and incubated with titrated amounts of Herceptin (µg per 100 µl) followed by FcγRIII activation assessment. FcγR activation was assessed in the absence or presence of excess of non-immune IgG by addition of 1 µg per 100 µl Infliximab (Ifx). Hc, Ifx, and reporter cells were added concomitantly. Titrations show one exemplary experiment. Error bars = SD. Bar graphs show combined averages from three independent experiments performed in technical replicates at 0.01 µg Hc normalized to CD99 control (Figure 6—source data 1). Error bars = SD. Two-way ANOVA. (C) gp34 and gp68 antagonize FcγRIIIA activation individually in the context of viral infection. BJ-Her2 cells were infected with the indicated human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) AD169 deletion mutants (MOI = 2). 72 hr post infection, cells were opsonized with titrated amounts of Herceptin and incubated with FcγRIIIA reporter cells. mIL-2 expression was quantified via anti-mIL-2 sandwich ELISA. Two independent experiments performed in technical replicates. Error bars = SD. Bar graph shows area under curve (AUC) comparison (Figure 6—source data 2). Error bars = SD. One-way ANOVA. (D) gp68 cooperatively enhances antagonistic potential of gp34. Hela cells were co-transfected with gp34 and Her2 antigen and incubated with titrated amounts of Herceptin followed by FcγRIII activation assessment. gp34 expressing cells were supplemented with sgp68 or sgp34mtrp from soluble vFcγR producer cells at a 1:4 dilution. Soluble vFcγRs and reporter cells were incubated concomitantly after removal of pre-incubation with Hc to avoid saturation of sgp68 with unbound Hc. Titrations show one exemplary experiment. Error bars = SD. Bar graphs show combined averages from three independent experiments performed in technical replicates at 0.01 µg Hc normalized to CD99 control (Figure 6—source data 3). Error bars = SD. Unpaired t-test.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Relates to Figure 6B bar graph.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63877/elife-63877-fig6-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 6—source data 2
Relates to Figure 6C bar graph.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63877/elife-63877-fig6-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 6—source data 3
Relates to Figure 6D bar graph.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63877/elife-63877-fig6-data3-v2.xlsx
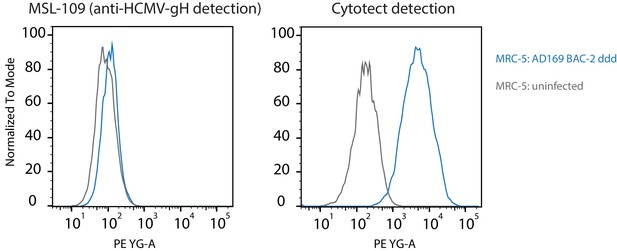
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) gH surface expression on HCMV-infected cells.
MRC-5 cells were infected using a vFcγR-deleted (ddd) AD169 BAC-2 derived mutant virus (MOI = 2) and gH surface expression was detected at 72hpi using MSL-109 (humanized anti-HCMV gH, 10 µg/ml) and a PE-conjugated anti-human-IgG secondary antibody. For comparison, detection using an anti-HCMV serum pool (Cytotect 1 µg/ml) under the same conditions is shown on the right. Exemplary experiment.
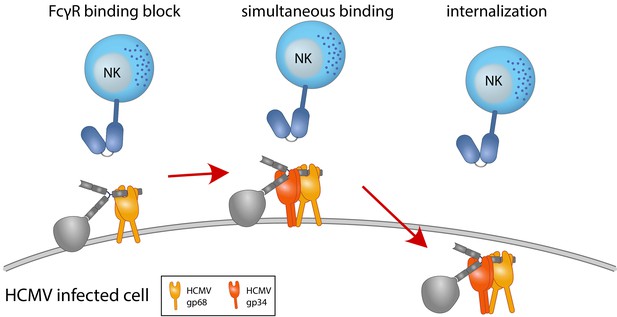
Graphical summary.
NK cells elicit a powerful antibody-mediated antiviral response through antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). gp68 (ochroid) binds IgG in a 2:1 ratio reducing, but not abolishing accessibility of immune complexes to FcγRIII+ (dark blue) immune effector cells such as NK cells. gp34 (red, natively forming a dimer [Sprague et al., 2008]) effectively internalizes immune complexes making them unavailable to surveilling FcγRIII+ effector cells but cannot compete with FcγRIII for a similar binding region on IgG. Supported by functional evaluation, we propose a model in which g34 and gp68 work in cooperation to achieve efficient antagonization of antibody-mediated effector mechanisms.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (HCMV) | UL119-118 | This paper | MN900952.1 | |
| Gene (HCMV) | RL11 | This paper | MN900952.1 | |
| Gene (Homo sapiens) | CD4 | This paper | BT019791.1 | |
| Gene (HSV-1) | US8 | This paper | MN136524.1 | |
| Gene (HSV-1) | US7 | This paper | MN136524.1 | |
| Strain, strain background E. coli | NEB5-alpha | NEB | C2987 | Made chemically competent for cloning via CaCl2 |
| Strain, strain background (HCMV) | AD169-BAC2 | doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2020 | MN900952.1 | |
| Genetic reagent Mus musculus | BW5147 FcγR-reporter cells | doi:10.1016/j.jim.2012.09.006 | ||
| Genetic reagent (H. sapiens) | Hek-CD20 | Kindly provided by Irvin Chen, UCLA | Lentiviral transduction | |
| Genetic reagent (H. sapiens) | BJ-Her2 | This paper | Lentiviral transduction as in doi:10.1128/JVI.01923-10 | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | Hela | ATCC | CCL-2 | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | MRC-5 | ECACC | 05090501 | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | HFF Human foreskin fibroblasts | Kindly provided by Dieter Neumann-Haefelin and Valeria Kapper-Falcone, Institute of Virology, Freiburg, Freiburg, Germany | HF-99/7 | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | BJ-5ta | ATCC | CRL-4001 | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | 293T-CD20 | Kindly provided by Irvin Chen, UCLA, USA | ||
| Cell line (M. musculus) | BW5147 | Kindly provided by Ofer Mandelboim, Hadassah Hospital, Jerusalem, Israel | FcR-expressing cell lines as in Corrales-Aguilar et al., 2013 | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | PBMC | Primary human cells | Primary cells isolated from human donors | |
| Transfected construct (H. sapiens) | Her2/Erbb2 | gBlock by IDT | NM_004448 | Construct to generate stably expressing BJ cells |
| Transfected construct (H. sapiens) | gp68 | gBlock by IDT | UL119-118 of MN900952.1 | Cloning via added flanking Nhe1 and BamH1 restriction sites |
| Transfected construct (H. sapiens) | gp34 | gBlock by IDT | RL11 of MN900952.1 | Cloning via added flanking Nhe1 and BamH1 restriction sites |
| Transfected construct (H. sapiens) | gE | gBlock by IDT | US8 of MN136524.1 | Cloning via added flanking Nhe1 and BamH1 restriction sites |
| Transfected construct (H. sapiens) | gI | gBlock by IDT | US7 of MN136524.1 | Cloning via added flanking Nhe1 and BamH1 restriction sites |
| Transfected construct (H. sapiens) | gp68-CD4 | gBlock by IDT | UL119-118 of MN900952.1 fused to human CD4 TM and cytosolic tail BT019791.1 | Cloning via added flanking Nhe1 and BamH1 restriction sites |
| Transfected construct (H. sapiens) | gp34-CD4 | gBlock by IDT | RL11 of MN900952.1 fused to human CD4 TM and cytosolic tail BT019791.1 | Cloning via added flanking Nhe1 and BamH1 restriction sites |
| Transfected construct (H. sapiens) | gE-CD4 | gBlock by IDT | US8 of MN136524.1 fused to human CD4 TM and cytosolic tail BT019791.1 | Cloning via added flanking Nhe1 and BamH1 restriction sites |
| Antibody | Cytotect Human plasma pool polyclonal | Biotest | Titration as indicated in this study, 1:100 in flow cytometry | |
| Antibody | αCD107a-APC mouse monoclonal | BD FastImmune | Clone H4A3 | 1:50 in flow cytometry |
| Antibody | αCD56-BV650 mouse monoclonal | Biolegend | Clone 5.1H11 | 1:50 in flow cytometry |
| Antibody | αCD3-FITC mouse monoclonal | Biolegend | Clone UCHT1 | 1:50 in flow cytometry |
| Antibody | αhuman-IgG-PE mouse monoclonal | BD | 1:100 in flow cytometry | |
| Antibody | αHis-PE mouse monoclonal | Miltenyi Biotec | 1:100 in flow cytometry | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Human Fcγ-TexasRed | Rockland | Human IgG-Fc fragment | |
| Antibody | Rituximab Humanized monoclonal | Roche, University Hospital Freiburg Pharmacy | Titration as indicated in this study, 1:100 in flow cytometry | |
| Antibody | Herceptin Humanized monoclonal | Roche, University Hospital Freiburg Pharmacy | Titration as indicated in this study | |
| Antibody | αCD20-PE mouse monoclonal | Miltenyi Biotec | 1:100 in flow cytometry | |
| Antibody | αhuman IgG-FITC Polyclonal rabbit | ThermoFisher | 1:100 in flow cytometry | |
| Antibody | THE Anti-His-HRP mouse monoclonal | Genscript | 0.5 µg/ml in ELISA | |
| Antibody | MSL-109 Humanized monoclonal | Absolute antibody | 10 µg/ml in flow cytometry | |
| Antibody | B12 Humanized monoclonal | Kindly provided by Ann Hessell, Scripps USA | 1 µg/ml in precipitation | |
| Antibody | B12 LALA Humanized monoclonal | Kindly provided by Ann Hessell, Scripps USA | 1 µg/ml in precipitation | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pIRES-eGFP | Addgene | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pSLFRTKn | doi:10.1128/jvi.76.17.8596-8608 | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | KL-DeltaTRL11-Kana1 | This paper | PCR primer | ACGACGAAGAGGACGAGGACGACAACGTCTGATAAGGAAGGCGAGAACGTGTTTTGCACCCCAGTGAATTCGAGCTCGGTAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | KL-DeltaTRL11-Kana2 | This paper | PCR primer | TGTATACGCCGTATGCCTGTACGTGAGATGGTGAGGTCTTCGGCAGGCGACACGCATCTTGACCATGATTACGCCAAGCTCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | KL-DeltaTRL12-Kana1 | This paper | PCR primer | CGGACGGACCTAGATACGGAACCTTTGTTGTTGACGGTGGACGGGGATTTACAGTAAAAGCCAGTGAATTCGAGCTCGGTAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | KL-DeltaTRL12-Kana2 | This paper | PCR primer | CCTTACAGAATGTTTTAGTTTATTGTTCAGCTTCATAAGATGTCTGCCCGGAAACGTAGCGACCATGATTACGCCAAGCTCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | KL-DeltaUL119-Kana1 | This paper | PCR primer | TTGTTTATTTTGTTGGCAGGTTGGCGGGGGAGGAAAAGGGGTTGAACAGAAAGGTAGGTGCCAGTGAATTCGAGCTCGGTAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | KL-DeltaUL119-Kana2 | This paper | PCR primer | AGGTGACGCGACCTCCTGCCACATATAGCTCGTCCACACGCCGTCTCGTCACACGGCAACGACCATGATTACGCCAAGCTCC |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | sgp68-V5/His | This paper | Ectodomain of UL119-118 from MN900952.1 | V5/His6-tagged. Produced in 293T cells |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | sgp34-V5/His | This paper | Ectodomain of RL11 from MN900952.1 | V5/His6-tagged. Produced in 293T cells |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | sgp34mtrp-V5/His | This paper | Ectodomain of RL11 mtrp mutant from MN900952.1 | V5/His6-tagged. Produced in 293T cells |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | sgp68-strep | This paper | Ectodomain of UL119-118 from MN900952.1 | Streptavidin-tagged. Produced in 293T cells |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | sgp34-strep | This paper | Ectodomain of RL11 from MN900952.1 | Streptavidin-tagged. Produced in 293T cells |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | sgp34mtrp-strep | This paper | Ectodomain of RL11 mtrp mutant from MN900952.1 | Streptavidin-tagged. Produced in 293T cells |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | CD16-Avi/His | Sino Biological | Soluble recombinant FcγRIIIA | Avi/His-tagged 5 µg/ml in flow cytometry |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | CD32A-Avi/His | Sino Biological | Soluble recombinant FcγRIIA | Avi/His-tagged 5 µg/ml in flow cytometry |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | CD32B-Avi/His | Sino Biological | Soluble recombinant FcγRIIB | Avi/His-tagged 5 µg/ml in flow cytometry |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | CD64-Avi/His | Sino Biological | Soluble recombinant FcγRI | Avi/His-tagged 5 µg/ml in flow cytometry |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | wtFc | Kindly provided by Pamela Bjorkman, Caltech USA doi:10.1128/JVI.01476-07 | ||
| Peptide, recombinant protein | nbFc | Kindly provided by Pamela Bjorkman, Caltech USA doi:10.1128/JVI.01476-07 | ||
| Commercial assay or kit | Pierce F(ab')2 Preparation Kit | ThermoFisher | ||
| Commercial assay or kit | Easytag Express | Perkin Elmer | ||
| Software, algorithm | Prism | GraphPad | ||
| Software, algorithm | FlowJo | BD |





