Immunocompetent mouse model for Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus
Figures
MA-CCHFV causes overt clinical disease in wild-type (WT) mice.
(A and B) Groups of 8-week-old male (A) or female (B) WT C57BL/6J mice were infected with 10,000 TCID50 of MA-CCHFV or CCHFV Hoti via the intraperitoneal (IP) route and weighed daily. (A and B) Male and female mice were mock infected for comparison and same data is shown in both panels for comparison. N = 8 mock and four mice per CCHFV-infected group. Data shown as mean plus standard deviation. Statistical comparison performed using two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison to mock-infected mice. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. (C and D) Groups of male (C) or female (D) 8-week-old WT mice were infected with indicated dose of MA-CCHFV via the IP route and weighed daily. N = 5 mice per group. Studies were performed once.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Source data for Figure 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63906/elife-63906-fig1-data1-v2.xlsx
Passage of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV) in mice.
(A–B) Rag1-/- mice, passages 1–9 or wild-type (WT) C57BL6/J mice, passages 10 and 11, were inoculated with indicated source of passaged CCHFV and weighed (A). N = 1 mouse per passage. (C-D) WT C57BL6/J mice were inoculated with tissue-culture grown stocks of CCHFV derived from liver tissue at passages 4, 9, and 11. N = 2 mice per group. Dashed line indicates 100% starting weight for reference.
Male versus female mice infected with MA-CCHFV.
Eight-week-old WT MA-CCHFV were infected with 10,000 TCID50 of MA-CCHFV via the intraperitoneal (IP) route and weighed daily. Data in this figure is duplicated from main text Figure 1A and B and combined here for statistical comparison. p Values calculated with two-way ANOVA and Sidak’s multiple comparison test between male and female MA-CCHFV infected mice. *p<0.05, ****p<0.0001.
Seroconversion of dose-finding study.
Eight-week-old wild-type (WT) C57BL6/J mice were infected with indicated dose of MA-CCHFV and seroconversion at 14 DPI evaluated using whole virion ELISA. Total CCHFV-specific Ig measured in a 1:400 dilution of serum. Dashed line indicates arbitrarily determined threshold for classification of a positive signal.
MA-CCHFV causes clinical disease in multiple laboratory strains of mice.
(A–E) Groups of 8-week-old male or female mice of indicated strains were infected with 1000 TCID50 of MA-CCHFV via the intraperitoneal (IP) route and weighed daily. N = 5 mice per group. Data shown as mean plus standard deviation. Study was performed once.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Source data for Figure 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63906/elife-63906-fig2-data1-v2.xlsx
Lethal infection of young mice with MA-CCHFV.
Three-week-old wild-type (WT) C57BL6/J mice were inoculated with 10,000 TCID50 of MA-CCHFV. Mice were weighed daily (A) and humanely euthanized when they acchieved euthanasia criteria (B). N = 5 mice per group. (A) Dashed line indicates 100% starting weight for reference.
MA-CCHFV replicates to high titers of multiple tissues in wild-type (WT) mice.
Groups of 8-week-old WT C57BL/6J mice were infected with 10,000 TCID50 of MA-CCHFV or CCHFV Hoti via the intraperitoneal (IP) route. At indicated time points, mice were necropsied and viral RNA burdens in tissues evaluated by qRT-PCR. Statistical comparison performed with two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. p-Values between MA-CCHFV and respective sex Hoti-infected mice indicated with * for females, # for males and between MA-CCHFV male and MA-CCHFV female mice with +. Plasma, liver, spleen, kidney, and lung: N = 2–4 (Hoti) and 7–8 (MA-CCHFV) per group per timepoint. Brain: N = 4 per group per timepoint. Study was performed once for Hoti and twice for MA-CCHFV. Data shown as mean plus standard deviation. Dashed line indicates limit of detection. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Source data for Figure 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63906/elife-63906-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx
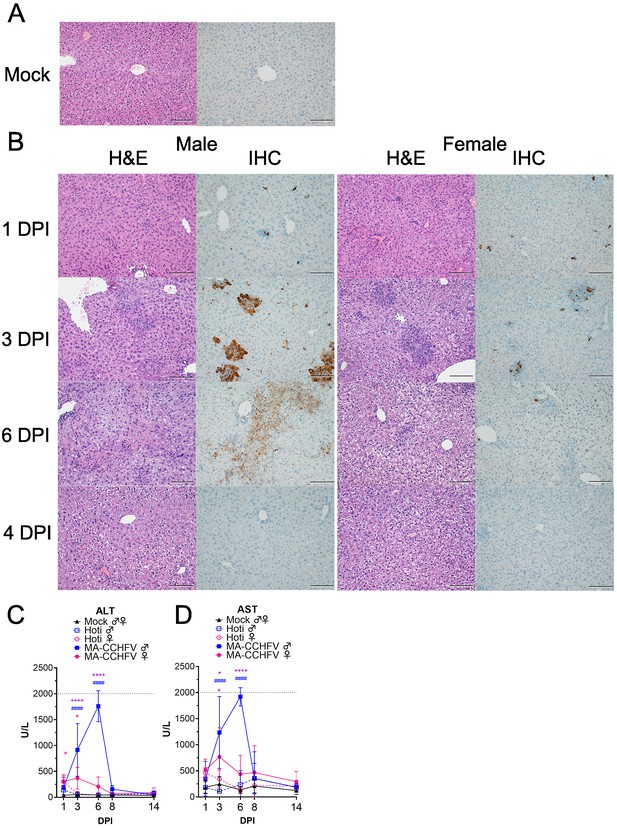
MA-CCHFV causes severe pathology in the livers of WT mice.
(A–D) Groups of 8-week-old wild-type (WT) mice were infected were infected with 10,000 TCID50 of MA-CCHFV or Hoti via the intraperitoneal (IP) route or mock-infected. (A) Representative liver sections from a mock-infected mouse is shown. (B) At indicated timepoints, MA-CCHFV-infected mice were euthanized, liver tissue fixed in formalin and paraffin embedded sections stained with H and E or an antibody against the CCHFV NP to identify viral antigen (IHC). Four mock-infected, four male and four female MA-CCHFV mice were evaluated at each timepoint and representative images shown. Images shown at ×200 magnification and scale bar indicates 100 μm. Study performed once. (C and D) At indicated timepoints, liver enzymes were measured in lithium heparin treated whole blood. ALT = Alanine aminotransferase, AST = Aspartate aminotransferase. N = 6 mock male and female, 4 Hoti-infected and 8 MA-CCHFV infected per group. Study performed once for Hoti and twice for mock and MA-CCHFV-infected mice. Data shown as mean plus standard deviation. Dashed line indicates upper limit of detection. Statistical comparison performed with two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. p-Values between MA-CCHFV and respective sex Hoti-infected mice indicated with * for females, # for males and between MA-CCHFV male and MA-CCHFV female mice with +. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
Histology and IHC of spleens from MA-CCHFV infected mice.
Groups of 8-week-old wild-type (WT) mice were infected were infected with 10,000 TCID50 of MA-CCHFV via the intraperitoneal (IP) route or mock-infected. (A) Representative spleen sections from a mock-infected mouse is shown. (B) At indicated timepoints, MA-CCHFV-infected mice were euthanized, spleen tissue fixed in formalin and paraffin-embedded sections stained with H and E or an antibody against the CCHFV NP to identify viral antigen (IHC). Four mock-infected, four male and four female MA-CCHFV mice were evaluated at each timepoint and representative images shown. Images shown at ×200 magnification and scale bar indicates 100 μm.
MA-CCHFV infection results in inflammatory cytokine responses in wild-type (WT) mice.
Eight-week-old male or female WT mice were infected with 10,000 TCID50 MA-CCHFV via the intraperitoneal (IP) route or mock-infected. At indicated timepoints, cytokine levels in the plasma was measured by 23-plex cytokine assay. Data shown as mean plus standard error. N = 6 mock male and female mice and seven to eight MA-CCHFV mice per sex per timepoint. Study performed twice. Statistical comparison performed with two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. p-Values between MA-CCHFV and mock-infected mice indicated with * for females, # for males and between MA-CCHFV-infected male and female mice with +. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Source data for Figure 5.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63906/elife-63906-fig5-data1-v2.xlsx
Complete cytokine profile of mock, Hoti, or MA-CCHFV-infected mice.
Eight-week-old wild-type (WT) C57BL6/J mice were infected with 10,000 TCID50 of MA-CCHFV or Hoti or mock-infected. At indicated timepoints mice were euthanized and plasma cytokine levels evaluated with 23-plex cytokine assay. The complete cytokine profile is shown with data from main text Figure 5 shown again for comparison. Data shown as mean plus standard error. N = 6 mock male and female, 4 Hoti male or female, and 7–8 MA-CCHFV male or female per group per timepoint.
Type I IFN is required for survival following MA-CCHFV infection.
(A–B) Eight-week-old male or female wild-type (WT) mice were infected with 10,000 TCID50 of CCHFV Hoti, MA-CCHFV via the intraperitoneal (IP) route or mock-infected. At indicated timepoints, plasma IFNα (all subtypes) (A) or IFNβ (B) was quantified by ELISA. N = 4–8 per group. Study performed once for Hoti and twice for mock and MA-CCHFV. Data shown as mean plus standard deviation. Dashed line indicates limit of detection determined from manufacturer provided standard curve. Statistical comparison performed using two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. (C–D) Groups of 8-week-old male or female WT mice or 10- to 13-week-old Ifnar1-/- mice were infected with 10,000 TCID50 of MA-CCHFV via the IP route. Mice were weighed daily (C) and monitored for survival (D). N = 4–5 per group. Study performed once. Data shown as mean plus standard deviation. Statistical comparison between Ifnar1-/- and respective sex WT mice performed using two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test (C) or Log-rank test with Bonferroni’s correction (D). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Source data for Figure 6.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63906/elife-63906-fig6-data1-v2.xlsx
MA-CCHFV is lethal in mice lacking adaptive immunity.
(A–C) Groups of 8-week-old wild-type (WT) mice were infected were infected with 10,000 TCID50 of MA-CCHFV via the intraperitoneal (IP) route or mock-infected. At indicated timepoints CCHFV-specific IgM (A) or IgG (B) in the plasma was measured by whole-virion ELISA. N = 5–6 per timepoint for mock and 7–8 per timepoint for MA-CCHFV. Study performed twice. Data shown as mean plus standard deviation. (C) At day 14 PI, T-cell responses in the spleen were measured by IFNγ ELISpot. Splenocytes were stimulated with overlapping peptide pools derived from the CCHFV NP (1 – 5), concanavalin A (Con A) or DMSO-vehicle alone. N = 2 for mock and four for MA-CCHFV infected. Study performed once. Data shown as mean plus standard deviation. (D and E) Groups of 8-week-old WT or Rag1-/- mice were infected with 10,000 TCID50 of MA-CCHFV via the IP route. Mice were weighed daily (C) and monitored for survival (D). N = 5 per group. Study performed once. Data shown as mean plus standard deviation. Statistical comparison between Rag1-/- and respective sex WT mice performed using two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test (C) or Log-rank test with Bonferroni’s correction (D).
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Source data for Figure 7.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63906/elife-63906-fig7-data1-v2.xlsx
Tables
Mutations identified in MA-CCHFV.
| Mutant Frequency (%) | % AA Conservation among | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Segment | SNP (Hoti>Mutant) | Coding Change (Hoti>Mutant) | Domain | Passage 4 | Passage 9 | MA-CCHFV | CCHFV Strains |
| S | A739G | NP I228M | Arm | 93 | 87 | 88 | 100 (I) |
| A806G | NP K251E and NSs F26S | Arm and Unknown | 95 | 100 | 99 | NP 100 (K); NSs 88 (L), 12 (F) | |
| M | A1502G | R475R | GP38 | 3 | 35 | 54 | |
| G2671A | C865Y | NSm | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 (C) | |
| T4068C | L1331L | Gc | 98 | 100 | 100 | ||
| L | G6097A | S2007N | Unknown | 83 | 97 | 98 | 71 (S), 29 (N) |
| C8135T | V2686V | RdRp | 83 | 95 | 96 | ||
| C9919T | P3281L | Unknown | 85 | 96 | 96 | 100 (P) | |
| G11618A | E3847E | Unknown | 85 | 98 | 97 | ||
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Other | Hoti | This paper | Virus strain | |
| Other | MA-CCHFV | This paper | Virus strain |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Complete histological and IHC findings of formalin-fixed tissue sections from CCHFV-infected mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63906/elife-63906-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
Complete blood chemistry of CCHFV-infected mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63906/elife-63906-supp2-v2.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63906/elife-63906-transrepform-v2.docx