Association of Toll-like receptor 7 variants with life-threatening COVID-19 disease in males: findings from a nested case-control study
Figures
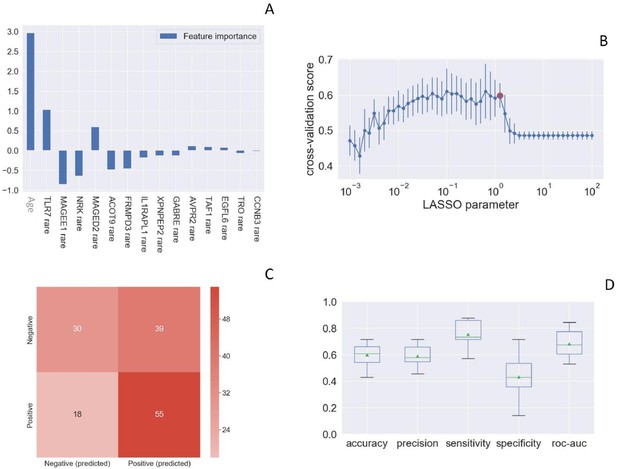
Rare TLR7 variants and association with COVID-19.
LASSO logistic regression on boolean representation of rare variants of all genes of the X chromosome is presented. TLR7 is picked up by LASSO logistic regression as one of the most important genes on the X chr (Panel A). The LASSO logistic regression model provides an embedded feature selection method within the binary classification tasks (male patients with life-threatening COVID-19 vs infected asymptomatic male participants). The upward histograms (positive weights) reflect a susceptible behavior of the features to the target COVID-19, whereas the downward histograms (negative weights) a protective action. Panel B represents the cross-validation accuracy score for the grid of LASSO regularization parameters; the error bar is given by the standard deviation of the score within the 10 folds; the red circle (1.26) corresponds to the parameter chosen for the fitting procedure. Performances are evaluated through the confusion matrix of the aggregated predictions in the 10 folds of the cross-validation (Panel C) and with the boxplot (Panel D) of accuracy (60% average value), precision (59%), sensitivity (75%), specificity (43%), and ROC-AUC score (68%). The box extends from the Q1 to Q3 quartile, with a line at the median (Q2) and a triangle for the average.
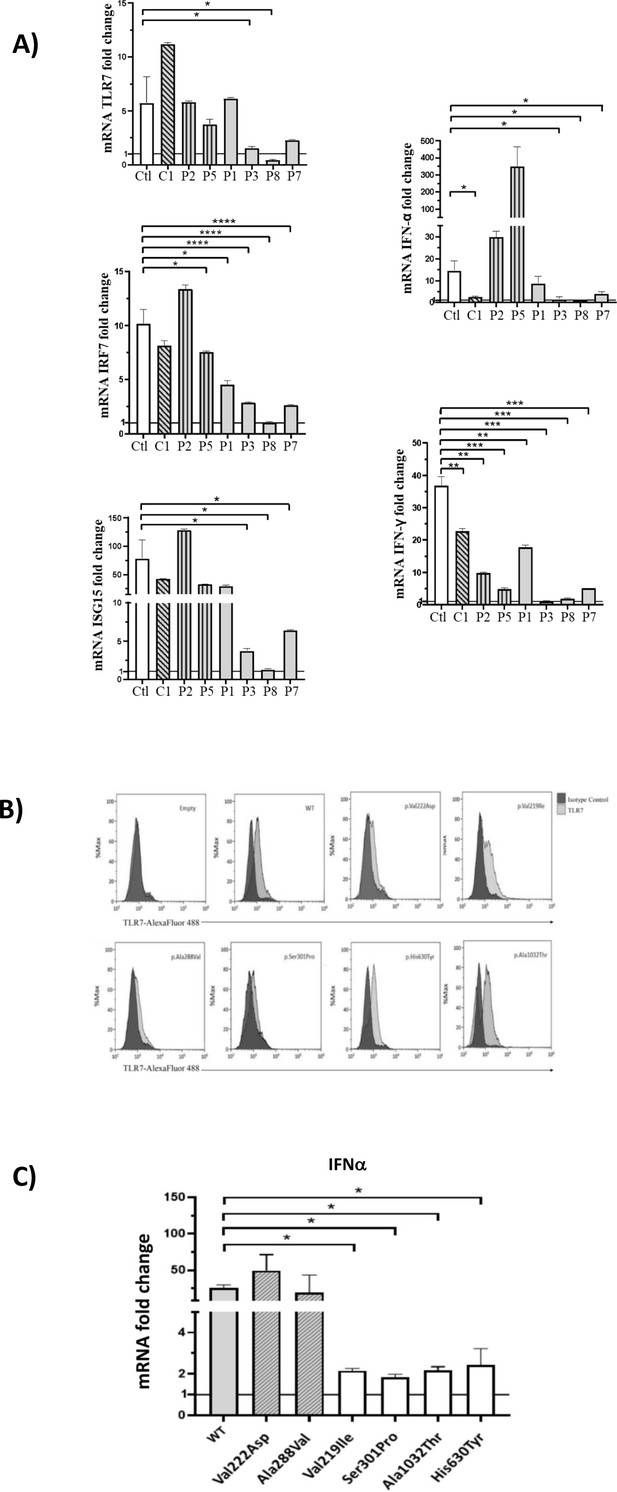
Gene expression profile analysis in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and in HEK293 cells transfected with the functional variants after stimulation with a TLR7 agonist for 4 hr.
(A) 5 × 105 PBMCs from COVID-19 patients and six unaffected male and female controls were stimulated for 4 hr with the TLR7 agonist imiquimod at 5 μg/mL or cell culture medium. Quantitative PCR assay was performed and the 2-ΔΔCt calculated using HPRT1 as housekeeping gene. Fold change in mRNA expression of TLR7 and type 1 IFN-related genes ISG15, IRF7, IFN-ɑ and IFN-γ induced by TLR7 agonist imiquimod was compared with cell culture medium. Ctl indicates healthy controls (white bar); C1, the asymptomatic mutated control (diagonal lines bar); P2, P5, cases with neutral variants (vertical lines bar); P1, P3, P8, P7 cases with functional variants (gray bar) (as in Table 2). (B) Histograms of intracellularly expressed TLR7 protein in HEK293 cells transfected with the different TLR7 plasmids. (C) Gene expression profile analysis of IFN-ɑ in transfected cells after stimulation with the TLR7 agonist imiquimod. WT indicates cells transfected with WT TLR7 plasmid. Quantitative PCR assay was performed and the 2-ΔΔCt calculated using HPRT1 as housekeeping gene. Fold change in mRNA expression induced by imiquimod was compared with cell culture medium. Error bars show standard deviation. p values were calculated for the reduction using an unpaired t test: *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001.
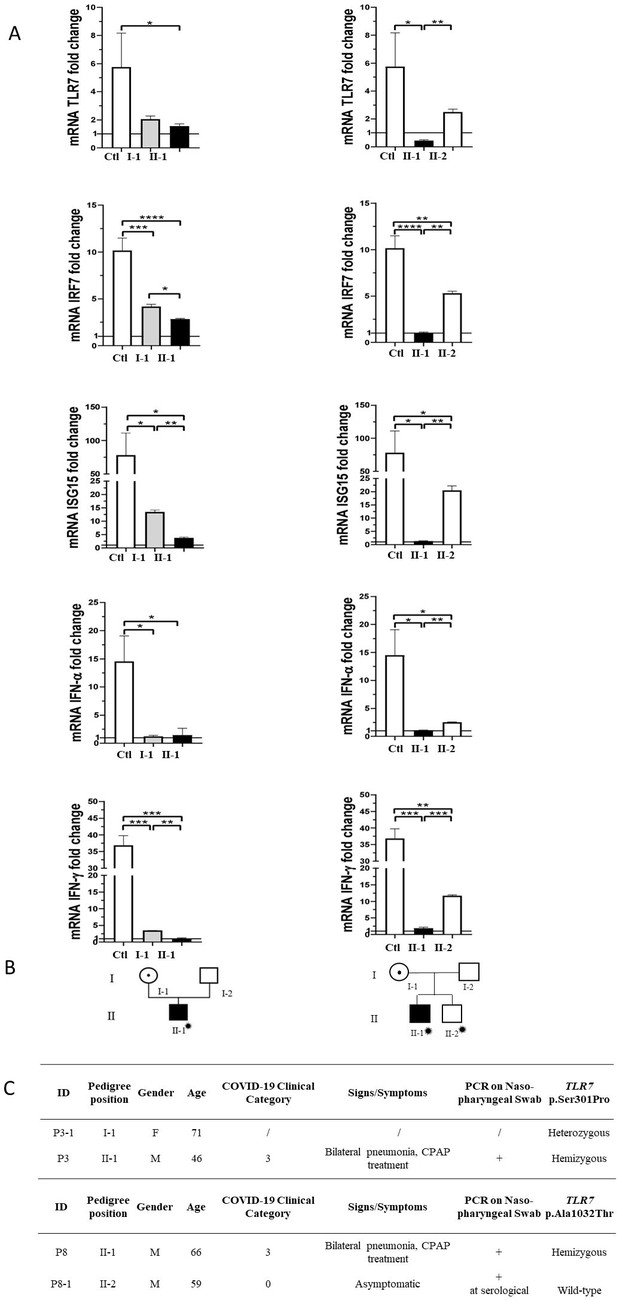
Segregation analysis.
Fold change in mRNA expression following Imiquimod stimulation of TLR7 itself and its main effectors, IRF7, ISG15, IFN-alpha, and IFN-gamma is shown in Panel A. Gray columns represent individuals harboring the TLR7 variant and black columns are severely affected SARS-CoV-2 cases. Pedigree (Panel B) and respective segregation of TLR7 variant and COVID-19 status (Panel C) are also shown. Squares represent male family members; circles, females. Individuals infected by SARS-CoV-2 are indicated by a virus cartoon close to the individual symbol ( ).
).
Tables
Fisher exact test of the overall combined cohorts in young males (<60 years).
| Clinical category | N. wild-type variants (97.84%) | N. pathological variants (2.15%) | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Severely affected males | 129 | 6 | 135 |
| Asymptomatic males | 104 | 0 | 104 |
| Total | 233 | 6 | 239 (Grand Total) |
-
p-value=0.0037.
TLR7 variants in severely affected Italian males -all ages- (cases).
| Nucleotide change | Amino acid change | dbSNP | CADD | ExAC_ NFE | Function* | N. of patients | Clinical category† | Age | Cohort | Patient ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c.901T>C | Ser301Pro | - | 26.4 | N/A | LOF | 1 | 3 | 46 | Italian | P3 |
| c.2759G>A | Arg920Lys | rs189681811 | 16.52 | 0.0002 | LOF‡ | 1 | 4 | 49 | Italian | P6 |
| c.3094G>A | Ala1032Thr | rs147244662 | 22.3 | 0.0006 | LOF | 2 | 3 | 65/66 | Italian | P7/P8 |
| c.655G>A | Val219Ile | rs149314023 | 12.28 | 0.0003 | HYPO | 1 | 4 | 32 | Italian | P1 |
| c.863C>T | Ala288Val | rs200146658 | 15.37 | 0.000012 | Neutral | 1 | 3 | 57 | Italian | P2 |
| c.1343C>T | Ala448Val | rs5743781 | 13.08 | 0.00465 | Neutral | 2 | 3 | 53/58 | Italian | P4/P5 |
-
CADD, Combined Annotation Dependent Depletion; ExAC, Exome Aggregation Consortium; NFE, Non-Finnish European;
*Function: HYPO, hypomorphic; LOF, loss-of-function;
-
†Clinical category: 4, Hospitalized and intubated; 3, Hospitalized and CPAP-BiPAP and high-flows oxygen treated; 2, Hospitalized and treated with conventional oxygen support only; 1, Hospitalized without respiratory support; 0, Not hospitalized oligo/asymptomatic individuals.
‡based on in silico prediction.
Additional files
-
Reporting standard 1
STROBE checklist.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67569/elife-67569-repstand1-v3.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67569/elife-67569-transrepform-v3.pdf





