Targeting an anchored phosphatase-deacetylase unit restores renal ciliary homeostasis
Figures
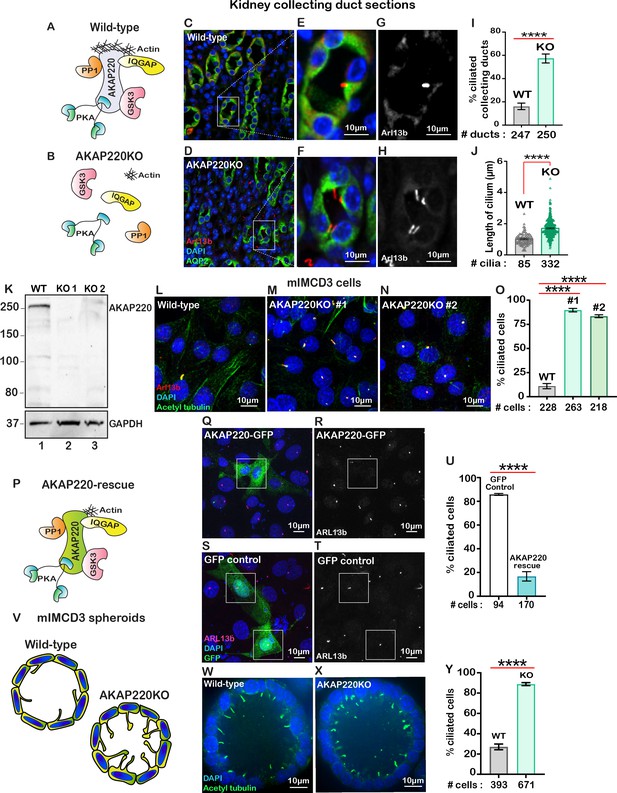
Loss of AKAP220 enhances ciliogenesis.
(A) Schematic of AKAP220 interaction with selected binding partners. (B) Disruption of this signaling complex upon removal of AKAP220. Protein kinase A (blue), Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (pink), Protein phosphatase 1 (orange) and IQGAP (yellow) are indicated. (C–H) Immunofluorescent staining of kidney collecting ducts with Arl13b (red), Aquaporin-2 (green) and DAPI (blue) from (C) wild-type and (D) AKAP220KO mice. (E and F) Enlarged sections from wild-type and AKAP220KO mice. (G and H) Gray scale images of Arl13b. (I) Quantification (% ciliated collecting ducts) in wild-type (gray bar) and AKAP220KO (green bar). ****p<0.0001. (J) Quantification of cilia length (µm) in wild-type (gray bar) and AKAP220KO (green bar). ****p<0.0001. Crispr-Cas9 gene editing of AKAP220 in mIMCD3 cells. (K) Immunoblot detection of AKAP220 (top) and GAPDH loading control (bottom) from wild-type (lane 1) and AKAP220KO (lane 2) cell lysates. (L–N) Immunofluorescent detection of primary cilia with acetyl tubulin (green), Arl13b (red) and DAPI (blue) in wild-type, and two independent clones of AKAP220KO mIMCD3 cells. (O) Quantification (% ciliated cells) from wild-type (gray column), AKAP220KO#1 (green column) and AKAP220KO#2 (dark green column). ****p<0.0001, N=3. (P) Schematic depicting reformation of the signaling complex upon rescue with AKAP220. Immunofluorescent detection of Arl13b (pink), GFP (green) and DAPI (blue) in (Q) pEGFP-AKAP220 or (S) GFP-control transfected AKAP220KO mIMCD3 cells. Gray scale image of Arl13b in (R) control cells and (T) AKAP220-rescued cells. (U) Quantification (% ciliated cells) in pEGFP-AKAP220 (black bar) or GFP-control cells (teal bar). ****p<0.0001, N=3. (V) Schematic of wild-type and AKAP220KO mIMCD3 spheroids. Immunofluorescent staining with acetyl tubulin (green) and DAPI (blue) in (W) wild-type and (X) AKAP220KO spheroids. (Y) Quantification (% ciliated cells) in wild-type (gray column) and AKAP220KO (green column) spheroids. ****p<0.0001, N=3. All error bars are s.e.m. p Values were calculated by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. Scale bars (10 µm). Number of cells analyzed indicated below each column.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Percent ciliated collecting ducts in kidney sections.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig1-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 1—source data 2
Length of primary cilia in kidney sections.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig1-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 1—source data 3
Rescue of GFP-AKAP220 in AKAP220KO mIMCD3 cells.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig1-data3-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 1—source data 4
Percent ciliated cells measured in spheroids.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig1-data4-v2.xlsx

Quantification of cilia number in gene-edited mIMCD3 cells.
Immunofluorescent staining of Arl13b (red), acetyl tubulin (green), and DAPI (blue) in serum starved (0.5% FBS, 24 hr) (A) wild-type and (D) AKAP220KO mIMCD3 cells. Gray scale images of Arl13b (B and E) and acetyl tubulin (C and F) show multiple cilia in the AKAP220KO cell. (G) Quantification (% ciliated cells) in wild-type (purple column), AKAP220KO (green column). ****p<0.0001. Number of cells analyzed are indicated below each bar.

Deletion of AKAP150 has no effect on primary cilia development.
Crispr-Cas nine gene editing was used to delete the murine anchoring protein AKAP150 in mIMCD3 cells. Double knockout cells were also produced lacking AKAP220 and AKAP150. Immunofluorescent staining with ciliary markers Arl13b (green) and acetyl tubulin (red) in (A) wild-type, (B) AKAP150KO and (C) AKAP220-150KO mIMCD3 cells. DAPI serves as a nuclear marker. (D) Quantification (% ciliated cells) in wild-type (mauve column), AKAP150KO (orange column), AKAP220-150KO (pink column), and AKAP220KO (coral column). Number of cells analyzed are indicated below each bar. ****p<0.0001, ns=non-significant, N=3. All error bars are s.e.m. p Values were calculated by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. Scale bars (10 µm).
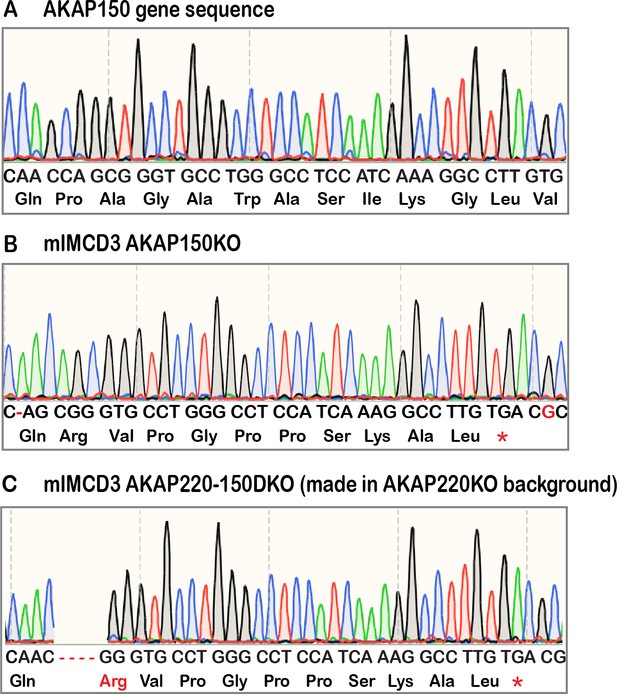
Sequencing data for CRISPR-Cas9 gene edited mIMCD3 cells.
Sequencing analysis data shows (A) intact AKAP150 in wild-type AKAP150, and deletions of AKAP150 in (B) AKAP150KO cells and (C) AKAP220-150 double knockout cells made in AKAP220KO background.
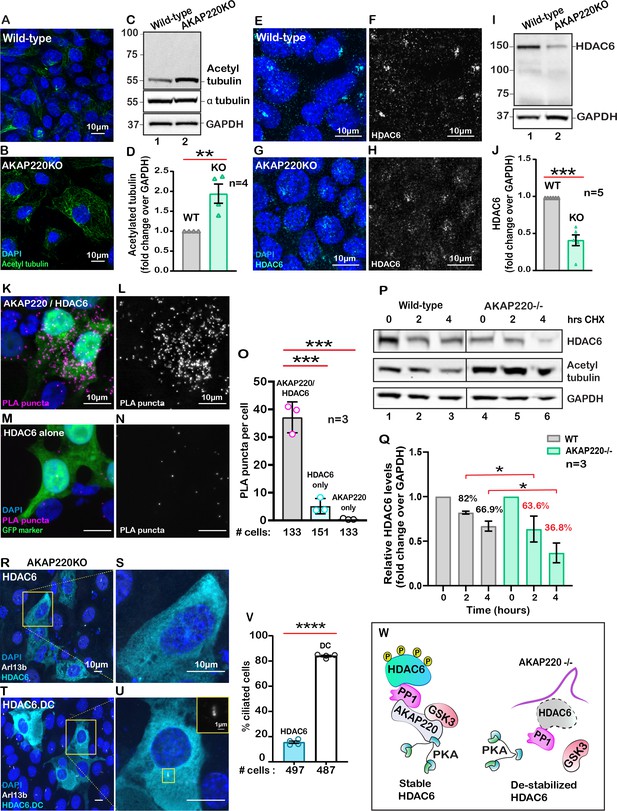
AKAP220 influences tubulin deacetylation.
Immunofluorescent detection of acetyl tubulin (green) and DAPI (blue) in (A) wild-type and (B) AKAP220KO mIMCD3 cells. (C) Immunoblot detection of acetylated tubulin (top), alpha tubulin (mid) and GAPDH loading control (bottom), in wild-type (lane 1) and AKAP220KO (lane 2) cell lysates. (D) Quantification by densitometry of acetylated tubulin in wild-type (gray column) and AKAP220KO (green column) lysates. **p<0.01, N=4. Immunofluorescent staining of HDAC6 (cyan) and DAPI (blue) in (E) wild-type and (G) AKAP220KO cells. Gray scale images of HDAC6 in (F) wild-type and (H) AKAP220KO cells. (I) Immunoblot detection of HDAC6 (top) and GAPDH as loading control (bottom) in wild-type (lane 1) and AKAP220KO (lane 2) cell lysates. (J) Quantification by densitometry of HDAC6 in wild-type (gray column) and AKAP220KO (green column) lysates. ***p<0.001, N=5. (K) Proximity ligation (PLA) detection of V5-AKAP220/HDAC6 subcomplexes (pink), DAPI (blue) in cells expressing GFP (green) as a transfection marker. (L) Gray scale image highlights V5-AKAP220/HDAC6 PLA puncta. (M and N) Control PLA experiments in cells treated with anti-HDAC6 antibody alone. (O) Amalgamated data (PLA puncta/cell) from three independent experiments is presented. Cycloheximide pulse-chase assay investigated HDAC6 stability. (P) Immunoblot of HDAC6 (top), acetylated tubulin (mid) and loading control GAPDH (bottom) from wild-type (lanes 1–3) and AKAP220KO (lanes 4–6) from mIMCD3 cells treated with cycloheximide. Data collected over a time course (0–4 hr). (Q) Quantification of amalgamated data by densitometry (N=3). HDAC6 levels in wild-type (gray) and AKAP220KO (green) are indicated. Levels of protein (%) are normalized to wild-type control (no treatment, 0 hr). (R-V) AKAP220KO mIMCD3 cells were transfected with (R) flag-HDAC6 or (T) catalytically inactive mutant HDAC6.DC. Immunofluorescent detection of HDAC6 (cyan), Arl13b (white) and DAPI (blue). Enlarged sections depict (S) loss of primary cilium upon overexpression of active HDAC6 and (U) intact cilium upon overexpression of inactive mutant HDAC6.DC. (V) Quantification (% ciliated cells) in AKAP220KO cells transfected with flag-HDAC6 (black column) and HDAC6.DC (cyan column). ****p<0.0001, N=3. (W) Schematic of how recruitment to the AKAP220-signaling complex stabilizes HDAC6 through local phosphorylation. All error bars are s.e.m. p Values were calculated by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. Scale bars (10 µm). Number of cells analyzed indicated below each column.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Densitometry of acetylated tubulin western blots.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig2-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Densitometry of HDAC6 western blots.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig2-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 3
Densitometry of HDAC6 in cycloheximide-chase experiments.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig2-data3-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 4
Percent ciliated AKAP220KO cells transfected with Flag-HDAC6 or HDAC6.DC.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig2-data4-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 5
Quantification of puncta in proximity ligation assay.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig2-data5-v2.xlsx

Further characterization of AKAP220-HDAC6 interface.
HDAC6 accumulates at the base of primary cilia. Immunofluorescent detection of acetyl tubulin (green), HDAC6 (red), and DAPI (blue) in (A) wild-type and (C) AKAP220KO mIMCD3 cells. Gray scale images of HDAC6 in (B) wild-type and (D) AKAP220KO show localization of the deacetylase at the base of primary cilia.

Additional Proximity ligation (PLA) controls.
Proximity ligation (PLA) detection of V5-AKAP220/HDAC6 subcomplexes (pink), DAPI (blue) in cells expressing GFP (green) as a transfection marker in mIMCD3 cells (A) transfected with V5-AKAP220 only and (C) AKAP220/HDAC6 untransfected. (B) and (D) gray scale image highlights V5-AKAP220/HDAC6 PLA puncta. (E) Amalgamated data (PLA puncta/cell) from three independent experiments is presented.
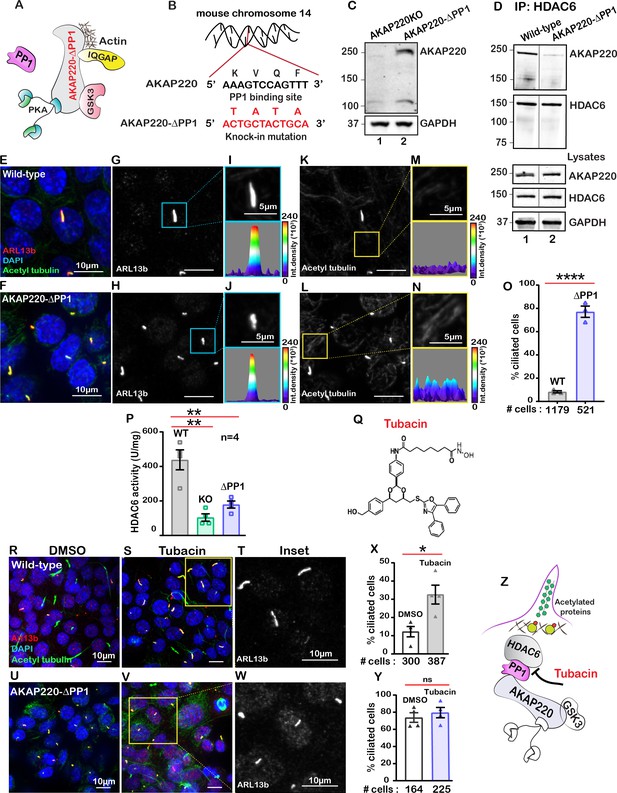
Anchored protein phosphatase one is necessary for HDAC6 activity.
(A) Schematic of AKAP220-ΔPP1. Binding partners are indicated. Gene editing deleted the principal phosphatase binding site (KVQF) on AKAP220. (B) Nucleotide sequencing reveals substitution of the KVxF motif. (C) Immunoblot detection of AKAP220 (top) and GAPDH loading control (bottom) in AKAP220KO (lane 1) and AKAP220-ΔPP1 (lane 2) mIMCD3 cell lysates. (D) Loss of PP1-targeting motif in AKAP220 negatively impacts association with HDAC6. Co-immunoprecipitation studies show that wild-type AKAP220 recruits HDAC6 (lane 1). AKAP220-ΔPP1 recruits less HDAC6 (lane 2). Immunoblot detection of AKAP220 (top), HDAC6 (mid) in cell lysates and GAPDH loading controls (bottom) reveal that equivalent levels of both proteins were present in mIMCD3 cell lysates. (E–O) Immunofluorescent detection of acetyl tubulin (green), Arl13b (red), and DAPI (blue) in (E) wild-type and (F) AKAP220-ΔPP1 cells. Gray scale images of Arl13b in (G) wild-type and (H) AKAP220-ΔPP1 cells. A single enlarged cilium (top) and corresponding three-dimensional surface plots (bottom) from (I) wild-type and (J) AKAP220-ΔPP1 cells. Gray scale images of acetylated tubulin in (K) wild-type and (L) AKAP220-ΔPP1 cells. Enlarged sections from (K and L) (top) and corresponding three-dimensional surface plots (bottom) from (M) wild-type and (N) AKAP220-ΔPP1 cells. (O) Quantification (% ciliated cells) in wild-type (gray) and AKAP220-ΔPP1 (blue). ****p<0.0001, N=3. (P) HDAC6 activity levels (A.U.) in wild-type (gray), AKAP220KO (green) and AKAP220-ΔPP1 (blue) cells as assessed by Bioline’s activity assay. **p<0.01, N=4. (Q) Chemical structure of HDAC6 inhibitor tubacin. (R-Y) Tubacin enhances ciliogenesis in the presence of native AKAP220. Wild-type mIMCD3 cells treated with (R) DMSO or (S) tubacin (2 µM) for 4 hr. Immunofluorescent staining with acetyl tubulin (green), Arl13b (red), and DAPI (blue). (T) Higher magnification gray scale image of Arl13b staining. (X) Quantification (% ciliated cells) in DMSO (white) and tubacin-treated (gray) wild-type cells. *p<0.05, ns=non-significant; N=3. (U–Y) Tubacin has no effect on AKAP220-ΔPP1 cells. (U) DMSO and (V and W) tubacin-treated AKAP220-ΔPP1 cells. (Y) Quantification (% ciliated cells) and analysis as described above in DMSO (white) and tubacin-treated (blue). (Z) Schematic of proposed tubacin mechanism of action on AKAP220-signaling complex. All error bars are s.e.m. p Values were calculated by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. Scale bars (10 µm). Number of cells analyzed indicated below each column.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Percent ciliated DMSO or tubacin-treated mIMCD3 cells.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx

Characterization of AKAP220-ΔPP1 cell line.
CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing was used to substitute the PP1-targeting KVQF motif in AKAP220 gene to generate AKAP220-ΔPP1 mIMCD3 cells. Sequencing analysis data shows (A) wild-type PP1-binding region in AKAP220 and (B) modified TATA region in AKAP220-ΔPP1. (C) AKAP220-ΔPP1 does not recruit PP1. Immunoblot detection shows PP1 (top panel) in WT AKAP220 immune complexes (lane 1), but not in AKAP220-ΔPP1 immune complexes (lane 2).
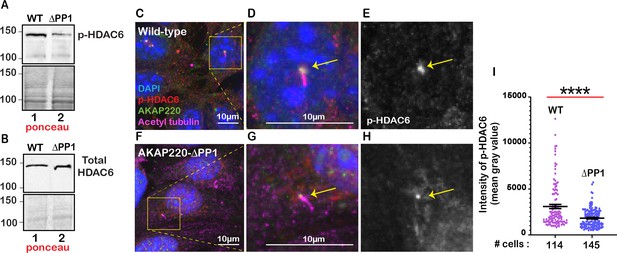
Investigating if AKAP220-HDAC6 interaction is altered in the AKAP220-ΔPP1 cells.
(A) Western blot of phosphorylated HDAC6 (top panel) in wild-type (lane 1) and AKAP220-ΔPP1 (lane 2) mIMCD3 cells. Ponceau blot (bottom panel) depicts equal loading. (B) Western blot of HDAC6 (top panel) in wild-type (lane 1) and AKAP220-ΔPP1 (lane 2) mIMCD3 cells. Ponceau blot (bottom panel) depicts equal loading. (C-I) Immunofluorescence images of AKAP220 (green), phospho-HDAC6(red), Acetyl tubulin (pink) and DAPI (blue) in (C) wild-type and (F) AKAP220-ΔPP1 cells. Enlarged portions depicting localization of proteins at the base of the primary cilium in (D) wild-type and (G) AKAP220-ΔPP1 cells. Gray scale images depict localization and level of p-HDAC6 in (E) wild-type and (H) AKAP220-ΔPP1 cells, respectively. (I) Quantification of p-HDAC6 intensity using ImageJ in wild-type (purple dots) and AKAP220-ΔPP1 (blue dots) mIMCD3 cells. ****p<0.0001. Number of cells analyzed are indicated below each bar.

Serum starvation drives mutant cells to multiciliate.
(A-D) Immunofluorescent staining of Arl13b (red), acetyl tubulin (green), and DAPI (blue) in serum starved (0.5% FBS, 24 hr) (A) AKAP220-ΔPP1 mIMCD3 cells. Gray scale images of (B) Arl13b and (C) acetyl tubulin show multiple cilia in the AKAP220-ΔPP1 cell. (D) Quantification (% ciliated cells) in wild-type (purple column), AKAP220KO (green column) and AKAP220-ΔPP1 (blue column). ****p<0.0001. Number of cells analyzed are indicated below each bar.
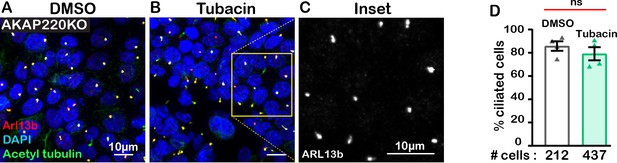
Characterizing tubacin action on cilia number in AKAP220KO cells.
Immunofluorescent staining with ciliary markers acetyl tubulin (green) and Arl13b (red) in (A) DMSO and (B) tubacin-treated AKAP220KO cells. DAPI (blue) serves as a nuclear marker. (C) Expanded gray scale image of Arl13b in tubacin-treated AKAP220KO cells. (D) Quantification (% ciliated cells) in DMSO (black bar) and tubacin-treated (green bar) AKAP220KO cells. The number of cells analyzed from three independent experiments are indicated below the bar for each condition. ns=non-significant. Error bars are s.e.m. p Values were calculated by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. Scale bars (10 µm).
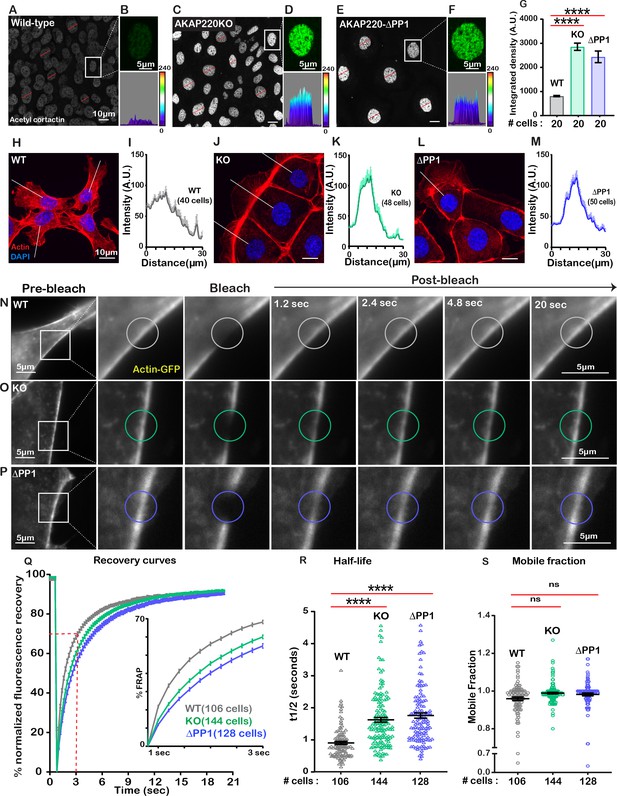
Disrupting the AKAP220-PP1 subcomplex impacts actin reorganization.
Gray scale images of acetylated cortactin in (A) wild-type, (C) AKAP220KO, and (E) AKAP220-ΔPP1 mIMCD3 cells. Magnified images of nuclei (top) and three-dimensional surface plots (bottom) of acetylated cortactin in (B) wild-type, (D) AKAP220KO and (F) AKAP220-ΔPP1 cells. (G) Quantification of amalgamated data (20 cells) from wild-type (gray), AKAP220KO (green), and AKAP220-ΔPP1 (blue) cells. ****p<0.0001, N=3. Scale bars (10 µm). (H-M) Confocal images of actin (red) and DAPI (blue) in (H) wild-type, (J) AKAP220KO, and (L) AKAP220-ΔPP1 cells. Lines indicate sites of line plot analysis to measure actin distribution from nuclei to the lamellipodia in (I) wild-type (gray), (K) AKAP220KO (green) and (M) AKAP220-ΔPP1 (blue) cells. Scale bars (10 µm). (N-S) Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) in mIMCD3 cells. Time course (0–20 s) of GFP-actin imaging in (N) wild-type, (O) AKAP220KO and (P) AKAP220-ΔPP1 cells. (Expanded section) Photobleached portion of cortical actin. (Q) FRAP curves in wild-type (gray), AKAP220KO (green), and AKAP220-ΔPP1 (blue) cells. (Inset) Photo recovery rates over the first 3 s. (R) The t1/2 value for each cell analyzed is presented for wild-type (gray), AKAP220KO (green) and AKAP220-ΔPP1(blue) cells. ****p<0.0001, N=3. (S) The mobile fraction of each cell analyzed is presented for wild-type (gray), AKAP220KO (green), and AKAP220-ΔPP1(blue circles) cells. Non-significant, N=3. Scale bars (5 µm). All error bars are s.e.m. p Values were calculated by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. Number of cells analyzed indicated below each column.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
FRAP curves for lifeact-GFP in mIMCD3 cells.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig4-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 4—source data 2
Half-life measurements for lifeact-GFP in mIMCD3 cells.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig4-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 4—source data 3
Mobile fraction measurements for lifeact-GFP in mIMCD3 cells.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig4-data3-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 4—source data 4
Intensity of actin in mIMCD3 cells by line plot analysis.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig4-data4-v2.xlsx
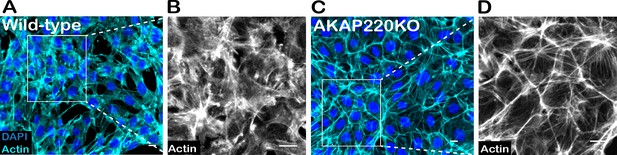
Distribution of actin in confluent mIMCD3 cell culture.
Immunofluorescent detection of actin (cyan) and DAPI (blue) in (A) wild-type and (C) AKAP220KO mIMCD3 cells. Gray scale images of actin in (B) wild-type and (D) AKAP220KO cells show the distribution of actin in confluent cells. Scale bars (10 µm).
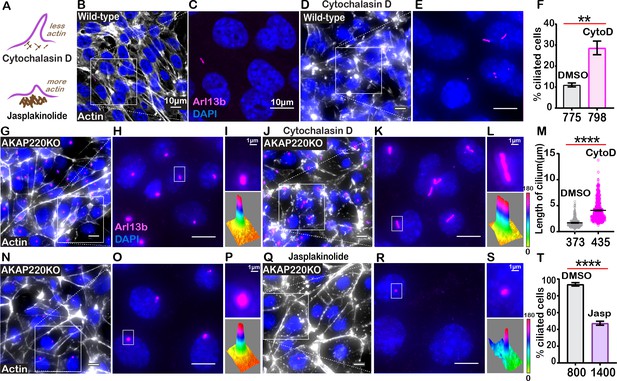
Cilia frequency and development involve f-actin assembly.
(A) Schematic of how actin modulating drugs impact primary cilia. Cytochalasin D depolymerizes actin barriers. Jasplakinolide stabilizes actin filaments. (B–F) Immunofluorescent detection of actin (white), Arl13b (pink), and DAPI (blue) in wild-type mIMCD3 cells treated with (B) DMSO or (D) 200 nM Cytochalasin D. Enlarged regions emphasize cilia frequency in (C) DMSO and (E) Cytochalasin D-treated cells. (F) Quantification (% ciliated cells) in DMSO (gray) and Cytochalasin D (pink) treated cells. **p<0.01, N=3. (G–M) Immunofluorescent detection of actin (white), Arl13b (pink), and DAPI (blue) in (G) DMSO and (J) Cytochalasin-D-treated AKAP220KO cells. (Inset) Expanded field of cells treated with (H) DMSO or (K) Cytochalasin D. Boxed regions in (I and L) focus on a single cilium (top) and three-dimensional surface plot (bottom). The width of the cylindrical region in the 3D surface plot represents cilium length. (M) Quantification of cilia length in DMSO (gray) and Cytochalasin D (pink) treated cells. ****p<0.0001, N=3. (N–T) Immunofluorescent staining of actin (white) and DAPI (blue) of (N) (DMSO) and (Q) (Jasplakinolide)-treated AKAP220KO cells. (Inset) Expanded field of cells treated with (O) DMSO or (R) Jasplakinolide. Boxed regions in (P and S) focus on a single cilium (top) and three-dimensional surface plot (bottom). The width of the cylindrical region in the 3D surface plot represents cilium length. (T) Quantification (% ciliated cells) in DMSO (gray) and Jasplakinolide (purple). ****p<0.0001, N=3. All error bars are s.e.m. p Values were calculated by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. Scale bars (10 µm). Number of cells analyzed indicated below each column.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Percent ciliated in DMSO or Cytochalasin-D-treated wild-type cells.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig5-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 5—source data 2
Cilia length in in DMSO or Cytochalasin-D-treated AKAP220KO cells.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig5-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 5—source data 3
Percent ciliated in DMSO or Jasplakinolide-treated AKAP220KO cells.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig5-data3-v2.xlsx
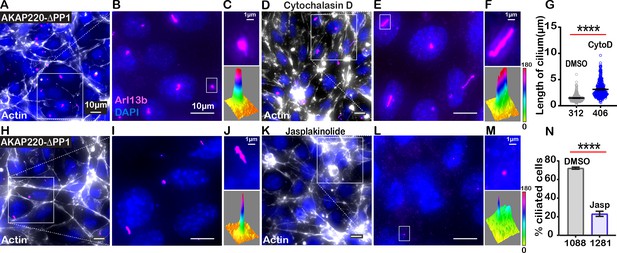
Characterizing the effect of actin-modulating drugs on AKAP220-ΔPP1 cilia.
(A-G) Immunofluorescent detection of actin (white), Arl13b (pink), and DAPI (blue) in (A) DMSO and (D) 200 nM Cytochalasi- D-treated AKAP220-ΔPP1 mIMCD3 cells. (Inset) Expanded field of cells treated with (B) DMSO or (E) Cytochalasin D. Boxed regions in (C and F) focus on a single cilium (top) and three-dimensional surface plot (bottom). The width of the cylindrical region in the 3D surface plot represents cilium length. (G) Quantification of cilia length in DMSO (gray) and Cytochalasin D (pink) treated cells. ****p<0.0001, N=3. (H-N) Immunofluorescent staining of actin (white) and DAPI (blue) of (H) (DMSO) and (K) (Jasplakinolide)-treated AKAP220-ΔPP1 cells. (Inset) Expanded field of cells treated with (I) DMSO or (L) Jasplakinolide. Boxed regions in (J and M) focus on a single cilium (top) and three-dimensional surface plot (bottom). The width of the cylindrical region in the 3D surface plot represents cilium length. (N) Quantification (% ciliated cells) in DMSO (gray) and Jasplakinolide (purple). ****p<0.0001, N=3. All error bars are s.e.m. p Values were calculated by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. Scale bars (10 µm). Number of cells analyzed indicated below each column.
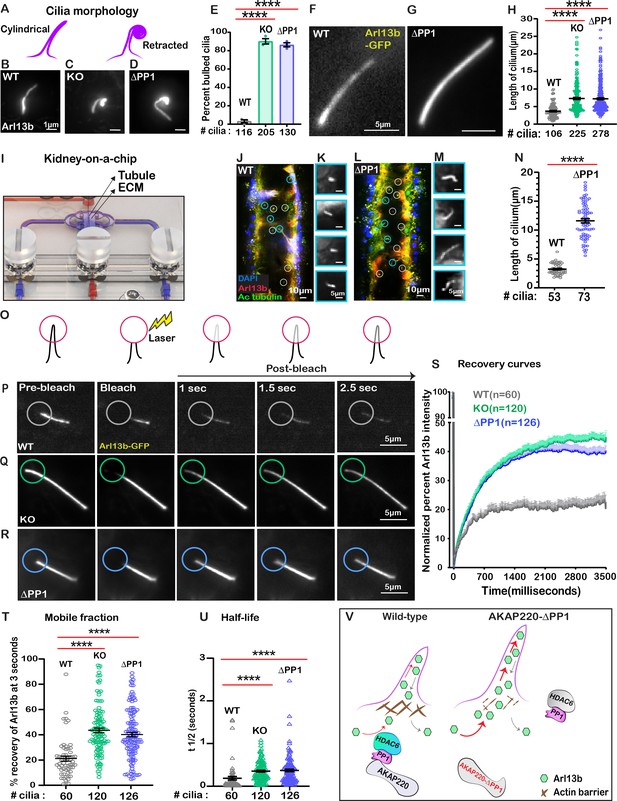
Loss of phosphatase anchoring promotes cilium elongation.
(A) Schematic of cylindrical and retracted cilia morphologies (purple). Super-resolution fixed-cell imaging of Arl13b (gray scale) in (B) wild-type, (C) AKAP220KO, and (D) AKAP220-ΔPP1 cilia. (E) Quantification (% bulbed cilia) in wild-type (gray), AKAP220KO (green), and AKAP220-ΔPP1 (blue) cells. ****p<0.0001, N=3. Scale bars (1 µm). Super-resolution live-cell images of Arl13b-GFP in (F) wild-type and (G) AKAP220-ΔPP1 cilia. (H) Quantification of cilia length in wild-type (gray), AKAP220KO (green), and AKAP220-ΔPP1 (blue) cells. ****p<0.0001, N=3. Scale bars (5 µm). (I) Kidney-on-a-chip device. Location of kidney tubule (Tubule) and extracellular matrix (ECM) are indicated. Confocal imaging of (J) Wild-type and (L) AKAP220-ΔPP1cells cultured in chip device with Arl13b (red), acetyl tubulin (green), and DAPI (blue). Cilia (white circles) are marked. (Insets) Magnified images of representative cilia (cyan circles) from (K) wild-type and (M) AKAP220-ΔPP1 pseudotubules. (N) Quantification of cilia length in wild-type (gray) and AKAP220-ΔPP1 (blue). ****p<0.0001, N=3. Scale bars (10 µm). Inset scale bars (5 µm). (O–U) Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) of Arl13b-GFP in primary cilia. (O) Schematic of how FRAP was measured. (P–R) Super-resolution live-cell images of Arl13b-GFP in (P) wild-type, (Q) AKAP220KO and (R) AKAP220-ΔPP1 cells. Circles mark bleached portion of cilia. (S) FRAP recovery curves of Arl13b over time (3500 ms) in wild-type (gray), AKAP220KO (green), and AKAP220-ΔPP1 (blue) cells. Scale bars (5 µm). (T) Quantification of mobile fraction in wild-type (gray), AKAP220KO (green), and AKAP220-ΔPP1 (blue) cilia. ****p<0.0001, N=3. (U) Half-life of Arl13b in wild-type (gray), AKAP220KO (green), and AKAP220-ΔPP1 (blue) cilia. ****p<0.0001, N=3. (V) Schematic depicting how AKAP220 modulation of the actin barrier influences movement of proteins in and out of primary cilia. All error bars are s.e.m. p Values were calculated by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. Number of cilia analyzed indicated below each column.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Primary cilia length from live cell experiments in mIMCD3 cells.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig6-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 6—source data 2
Length of primary cilia in kidney on a chip device.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig6-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 6—source data 3
FRAP curved for Arl13b-GFP in mIMCD3 cell lines.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig6-data3-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 6—source data 4
Mobile fraction of Arl13b-GFP 3 s after photobleaching.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig6-data4-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 6—source data 5
Half-life of Arl13b-GFP in mIMCD3 cell lines.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig6-data5-v2.xlsx
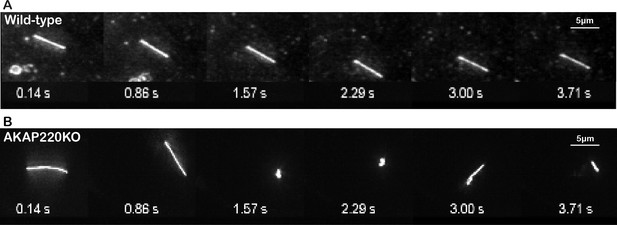
Super resolution videos depicting flexibility of AKAP220KO cilia.
(A) Wild-type and (B) AKAP220KO primary cilia from mIMCD3 cells transduced with Arl13b-GFP were monitored across a time course of 4 s. The AKAP220 cilium is longer and more flexible compared to the wild-type.
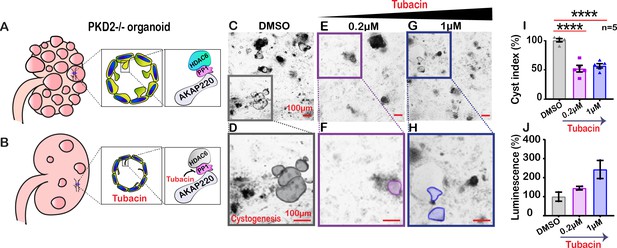
Inactivating HDAC6 reduces renal cystogenesis.
Schematic of polycystic kidneys (A) before and (B) after tubacin treatment. (Insets) Tubacin action on the AKAP220-signaling complex in precystic PKD2-/- organoids derived from WA-09 cells. (C-J) Confocal images of PKD2-/- organoids treated with (C) DMSO, (E) 0.2 µM and (G) 1 µM tubacin. Enlarged regions from (C, E and G) showing cysts in (D) DMSO, (F) 0.2 µM and (H) 1 µM tubacin-treated conditions. Scale bars (100 µm). (I) Quantification (% cyst index) in DMSO (gray), 0.2 µM (purple) and 1 µM (blue) tubacin-treated conditions. ****p<0.0001, N=5. (J) Luminescence assay to detect toxicity of the drug is plotted for DMSO (gray), 0.2 µM (purple) and 1 µM (blue) tubacin-treated conditions. Error bars are s.e.m. p Values were calculated by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Quantification of cyst size in DMSO and tubacin-treated iPSCs.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-fig7-data1-v2.xlsx
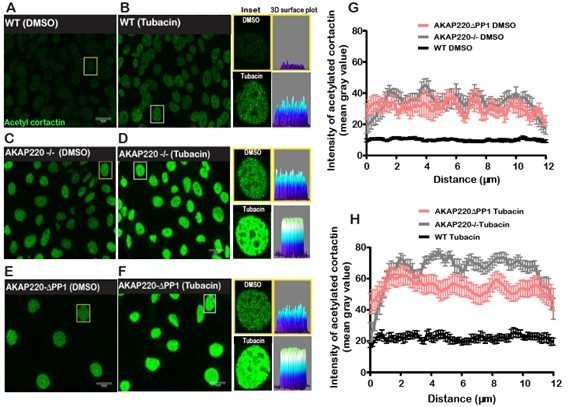
Inhibition of HDAC6 enhances acetylated cortactin in mIMCD3 cells.
Immunofluorescence images of acetylated cortactin in DMSO or Tubacin-treated (A and B) wildtype, C and (D) AKAP220KO and (E and F) AKAP220-ΔPP1 mIMCD3 cells. Insets depict marked nucleus (yellow box, DMSO); (white box, tubacin-treated). Each image and the corresponding 3D surface plots show changes in protein level. (G and H) Quantification of integrated density shows amalgamated data (20 nuclei) from wildtype (black), AKAP220KO (gray), and AKAP220-ΔPP1 (coral) cells.
Videos
Recovery of lifeact-GFP upon photobleaching in wild-type mIMCD3 cells.
Recovery of lifeact-GFP upon photobleaching in AKAP220KO mIMCD3 cells.
Recovery of lifeact-GFP upon photobleaching in AKAP220-ΔPP1 mIMCD3 cells.
Recovery of Arl13b-GFP upon photobleaching in wild-type mIMCD3 cells.
Recovery of Arl13b-GFP upon photobleaching in AKAP220KO mIMCD3 cells.
Recovery of Arl13b-GFP upon photobleaching in AKAP220-ΔPP1 mIMCD3 cells.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody | Acetylated tubulin | Thermo Fisher | Mouse monoclonal 32–2700 RRID:AB_2533073 | IF(1:5000), WB(1:1000) |
| Antibody | ActinRed-555 | Molecular probes | R37112 | Manufacturer instructions |
| Antibody | Arl13b | Proteintech | Rabbit Polyclonal 17711–1-AP RRID:AB_2060867 | IF(1:5000) |
| Antibody | AKAP220 | Santa Cruz Biotech | Goat polyclonal No longer available | IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | AKAP220 | Rockland | Rabbit polyclonal Custom generated | WB (1:500) |
| Antibody | Amersham ECL Mouse IgG, HRP-linked F(ab')₂ fragment (from sheep) | GE Life Sciences | NA9310 RRID:AB_772193 | WB (1:10000) |
| Antibody | Amersham ECL Rabbit IgG, HRP-linked F(ab')₂ fragment (from donkey) | GE Life Sciences | NA9340 RRID:AB_772191 | WB (1:10000) |
| Antibody | Donkey anti-goat IgG-HRP | Santa Cruz | sc-2020 RRID:AB_631728 | WB (1:10000) |
| Antibody | Donkey anti-Mouse IgG, Alexa Fluor 488 | Invitrogen | A-21202 RRID:AB_141607 | IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | Donkey anti-Mouse IgG, Alexa Fluor 555 | Invitrogen | A-31570 RRID:AB_2536180 | IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | Donkey anti-Mouse IgG, Alexa Fluor 647 | Invitrogen | A-11126 RRID:AB_221538 | IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | Donkey anti-Rabbit IgG, Alexa Fluor 488 | Invitrogen | A-21206 RRID:AB_2535792 | IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | Donkey anti-Rabbit IgG, Alexa Fluor 555 | Invitrogen | A-31572 RRID:AB_162543 | IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | Donkey anti-Rabbit IgG, Alexa Fluor 647 | Invitrogen | A-31573 RRID:AB_2536183 | IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | GFP | Rockland | 600-101-215 goat polyclonal RRID:AB_218182 | WB (1:1000), IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | HDAC6 | Proteintech | 12834–1-AP Rabbit Polyclonal RRID:AB_10597094 | IF (1:200) |
| Antibody | V5 | Invitrogen | R960-25 Mouse monoclonal RRID:AB_2556564 | IF (1:500) |
| Cell line (H. sapein) | HEK293 | RRID:CVCL_0045 | Maintained in Scott lab in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS | |
| Cell line (M. musculus) | mIMCD3 | RRID:CVCL_0429 | Maintained in Scott lab in DMEM/F12 supplemented with 10% FBS | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DAPI | Thermo Fisher | 62248 RRID:AB_2307445 | IF (1:1000) |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) | Pierce | TS-20688 | Manufacturer’s instructions |
| Chemical compound, drug | DMEM FluoroBrite | Life Technologies | A1896701 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DMEM/F-12 Hepes | Life Technologies | 11330057 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DMEM, high glucose | Life Technologies | 11965118 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Fetal Bovine Serum | Thermo Fisher | A3382001 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Lipofectamine 2000 Transfection Reagent | Invitrogen | 11668027 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | NuPAGE LDS Sample Buffer 4X | Thermo Fisher | NP0008 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Opti-MEM, Reduced Serum Medium, no phenol red | Life Technologies | 11058021 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | ProLong Diamond Antifade Mountant | Life Technologies | P36961 RRID:SCR_015961 | Manufacturer’s instructions |
| Chemical compound, drug | Polybrene | Santa Cruz | 134220 | Manufacturer’s instructions |
| Chemical compound, drug | Super Signal West Dura Extended Duration Substrate | Thermo Fisher | 34075 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | TransIT-LT1 Transfection Reagent | Mirus | MIR2300 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Trypsin-EDTA (0.25%), phenol red | Gibco | 25200056 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | BCA Protein Assay Kit | Thermo Fisher | 23227 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMD2.G | RRID:Addgene_12259 | gift from Didier Trono; Addgene plasmid #12259 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | psPAX2 | RRID:Addgene_12260 | gift from Didier Trono; Addgene plasmid #12259 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Arl13b-GFP | RRID:Addgene_40879 | gift from Tamara Caspary; Addgene plasmid # 40879 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | lifeact-GFP | RRID:Addgene_58470 | gift from Dyche Mullins; Addgene plasmid # 58470 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pcDNA-HDAC6-flag | RRID:Addgene_30482 | gift from Tso-Pang Yao; Addgene plasmid # 30482 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pEGFP-HDAC6-DC | RRID:Addgene_36189 | gift from Tso-Pang Yao; Addgene plasmid # 36189 | |
| Software, algorithm | Fiji/ImageJ | ImageJ (http://imagej.nih.gov/ij/) | ||
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism | GraphPad Prism (https://graphpad.com) | ||
| Software, algorithm | SoftWoRx | GE Healthcare | ||
| Other | Bolt 4–12% Bis-Tris Plus Gels | Invitrogen | NW04120BOX |
Additional files
-
Source data 1
Original blots included in the manuscript.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-data1-v2.zip
-
Source data 2
Blots with legends added.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-data2-v2.zip
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67828/elife-67828-transrepform-v2.pdf





