SMA-miRs (miR-181a-5p, -324-5p, and -451a) are overexpressed in spinal muscular atrophy skeletal muscle and serum samples
Figures
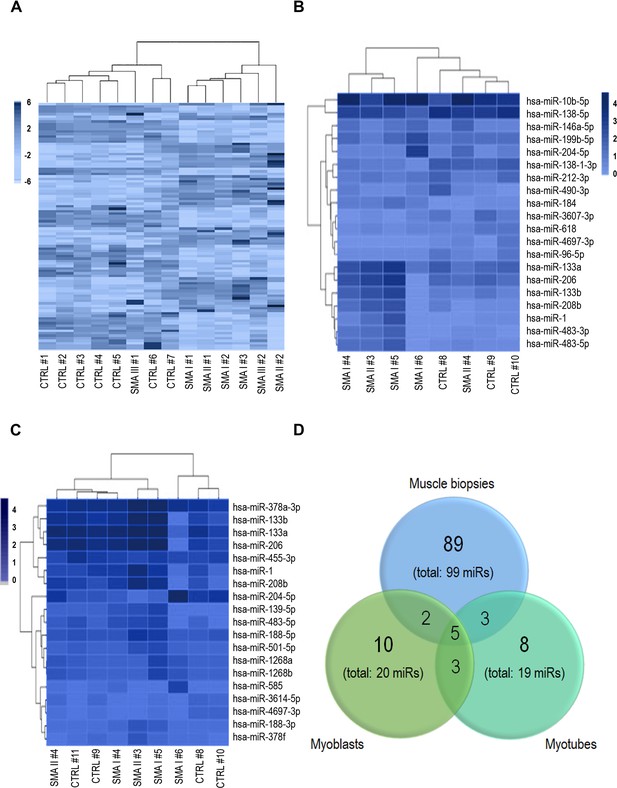
Heatmaps obtained by the whole miRNome analysis of muscle biopsies (A), myoblasts (B), and myotubes (C) of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) patients and controls; patient and control samples display a separate clusterization.
99, 20, and 19 miRs were found deregulated in SMA in muscle biopsies, myoblasts, and myotubes, respectively; (D) Venn’s diagram showing the five miRNAs shared among the three groups, three between myoblasts and myotubes, two between myoblasts and biopsies, and three between myotubes and biopsies.
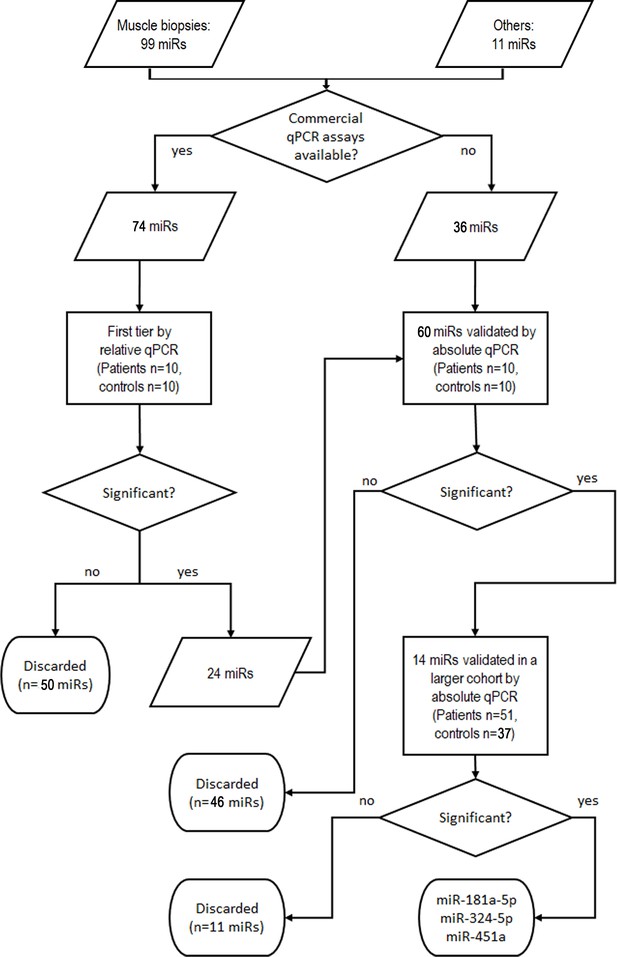
Validation pipeline of miRNAs identified by whole miRNome analysis in serum samples of patients and controls.
‘Others’ indicates miRs that were identified in other studies or with key function in skeletal muscle.
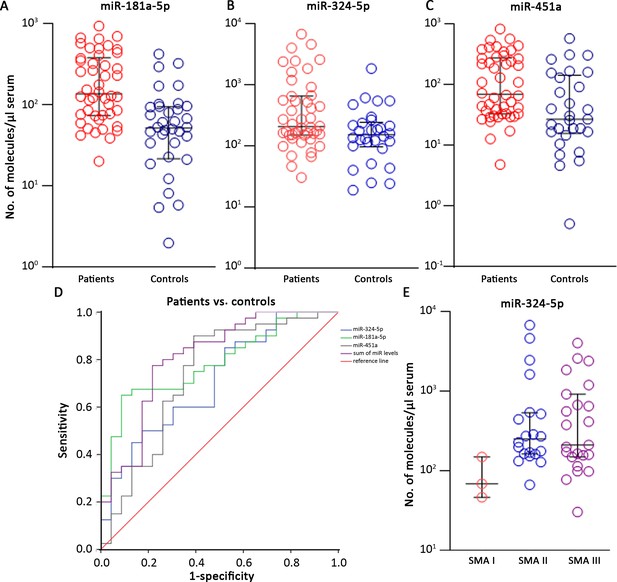
The SMA-miRs (miR-181a-5p [A], miR-324-5p [B] and miR-451a [C]) were significantly upregulated in serum samples of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) patients (p=4.3 * 10–4; 0.02; 0.004, respectively).
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves showed that the quantification of SMA-miRs has 80% sensitivity and 75% specificity in distinguishing patients from controls (D). Correlation of miR-324-5p with SMA type (E): the levels in SMA II and SMA III patients were significantly increased compared to those of SMA I patients (p=0.03 and 0.04, respectively).
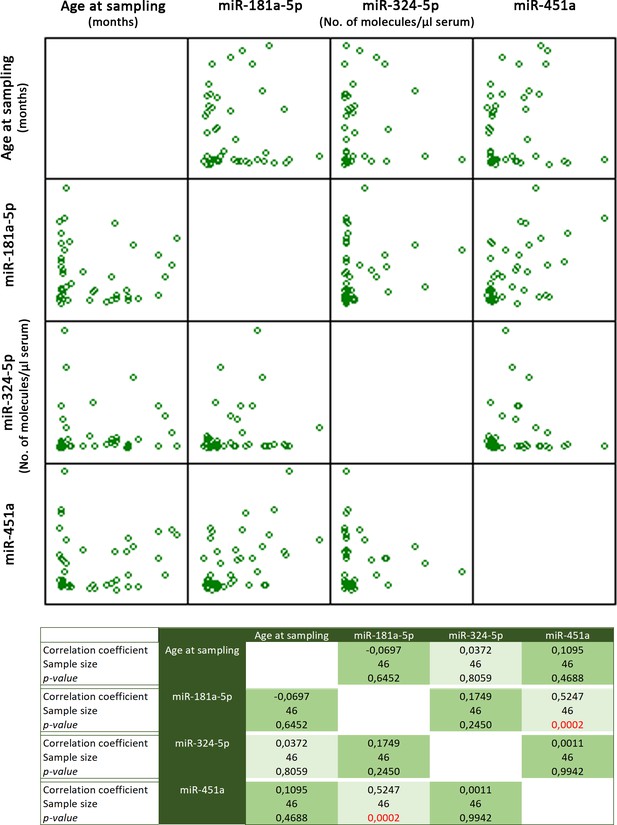
Multiple variable correlation of miR-181a-5p, -324-5p, and -415a levels and age at sampling.
In red, the only significant correlation, between miR-181a-5p and miR-451a (p=0.0002).
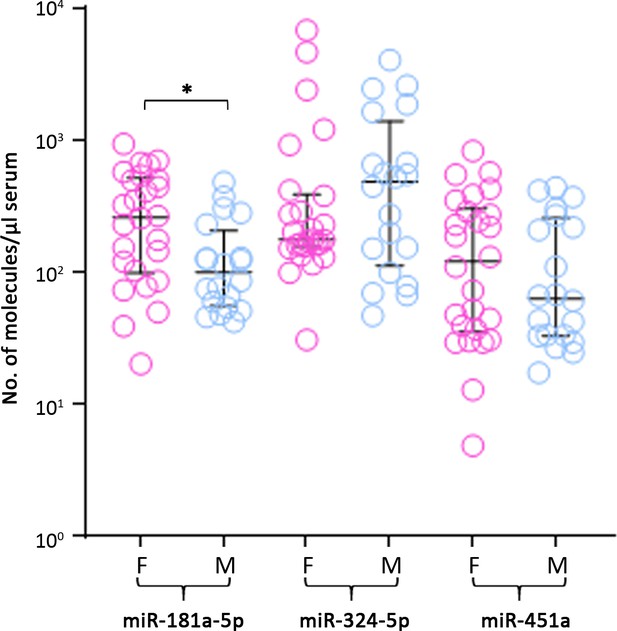
Comparison of levels of miR-181a-5p, -324-5p, and -451a in male and female patients; only miR-181a-5p showed a significant difference in females compared to males (*p=0.024).
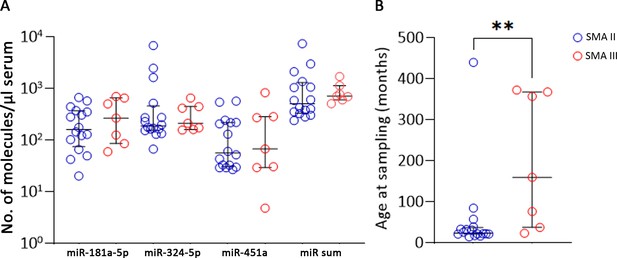
Analysis of type II and III patients with three SMN2 copies; the two groups were not different for miRs levels (p>0.05, A) but showed a significant difference in age (**p=0.0092, B).
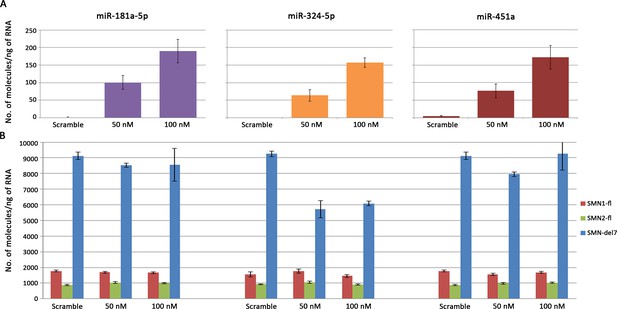
Transfections of SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells with SMA-miR mimics (final concentration: 50 or 100 nM).
In spite of the huge increase in SMA-miR levels (A), SMN1/SMN2 transcripts remained unchanged, except for the SMNΔ7 isoform in cells treated with miR-324-5p, which was reduced by 50%, independently of the mimic concentration (B).
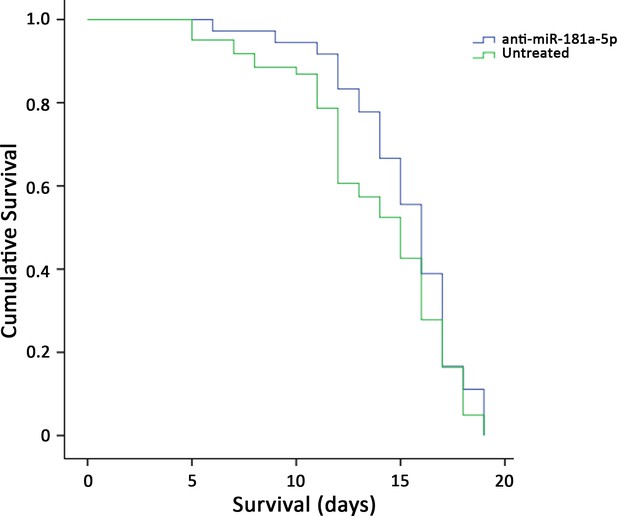
Survival curves of SMNΔ7-mice treated with intrathecal injection of anti-miR-181a-5p (n = 36) and untreated (n = 71); the overall survival remained unchanged (p>0.05).
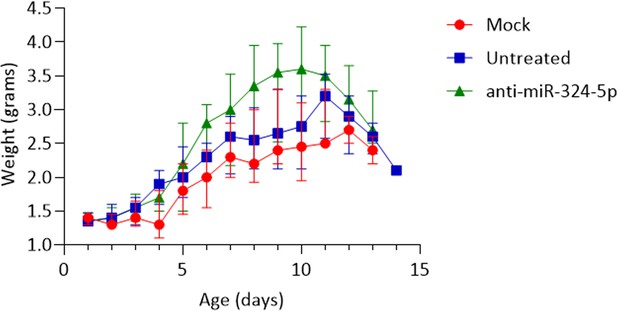
SMNΔ7 mice treated with anti-miR-324-5p showed a significant transient increase in body weight, between P7 and P10 (p=0.002).
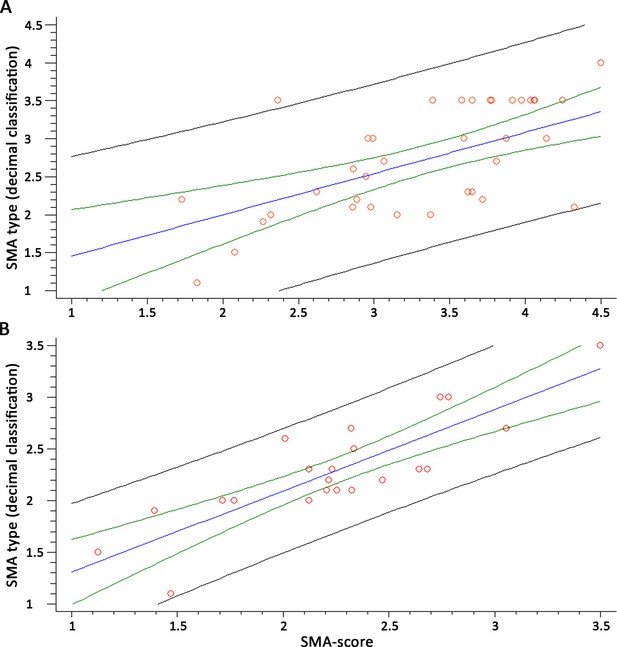
The spinal muscular atrophy score (SMA-score) predicts the phenotypic severity in SMA patients.
Correlation between the SMA-score and the clinical decimal SMA subtype in the whole cohort (A) and aged <6 years (B). Red circles are individual samples, the blue line indicates the expected distribution, the green line indicates the 95% confidence interval, and the black lines are the prediction interval.
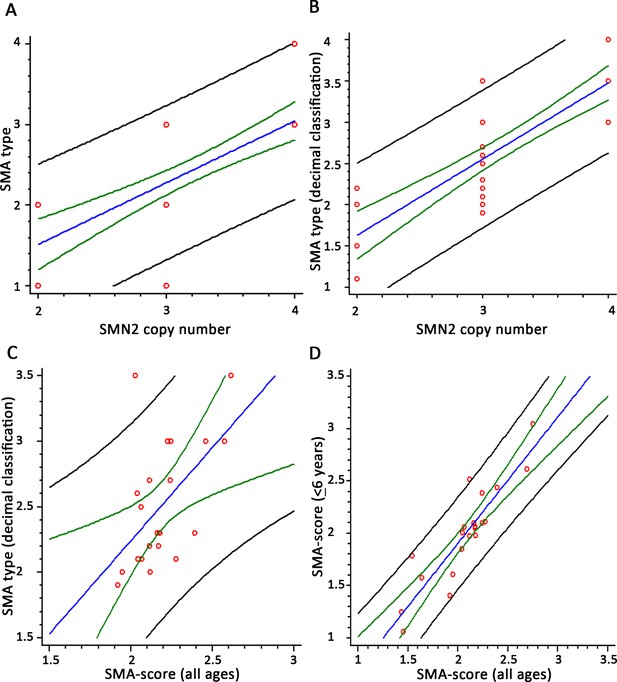
Linear correlation analysis among SMN2 copy number and spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) type, estimated by the standard classification (A; R2 = 52.45%, n = 41, p<10–5) and the decimal classification (B; R2 = 67.04%, n = 39, p<10-5).
Correlation with SMA-score and SMA type estimated by the decimal classification in patients with three SMN2 copies (C; R2 = 30.04, n = 21, p=0.008). Linear correlation analysis among SMA-scores obtained with the two equations (all ages vs. <6 years) (D; R2 = 80.31, n = 21, p<10-5). Red circles are individual samples, the blue line indicates the expected distribution, the green line indicate the 95% confidence interval, and the black lines are the prediction interval.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (Homo sapiens) | SMN1 | GenBank | HGNC:HGNC:11,117 | |
| Gene (Homo sapiens) | SMN2 | GenBank | HGNC:HGNC:11,118 | |
| miR (Homo sapiens) | hsa-miR-181a-5p | miRBase | MIMAT0000256 | |
| miR (Homo sapiens) | hsa-miR-324-5p | miRBase | MIMAT0000761 | |
| miR (Homo sapiens) | hsa-miR-451a | miRBase | MIMAT0001631 | |
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus) | SMNΔ7 miceFVB.Cg-Grm7Tg(SMN2)89Ahmb Smn1tm1Msd Tg(SMN2*delta7)4,299Ahmb/J | Jackson Laboratory | Stock number: 005025 | Hum Mol Genet 14(6):845–57, 2005 |
| Genetic reagent (Homo sapiens) | miRCURY LNA microRNA mimic: hsa-miR-181a-5p, hsa-miR-324-5p, hsa-miR-451a | Exiqon | 50–100–200 nM | |
| Genetic reagent (Homo sapiens) | miRCURY LNA microRNA antogomiR: hsa-miR-181a-5p, hsa-miR-324-5p, hsa-miR-451a | Exiqon | 0.1 nM | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | Primary myoblasts | Italian Telethon Network of Genetic Biobanks | 6756, 6760, 6762, 6816, 7147, 8823, 8655, 8537 | |
| Biological sample (Homo sapiens) | Muscular biopsies | Italian Telethon Network of Genetic Biobanks | 10370, 10351, 8023, 4688, 10543, 10583, 7669, 5944, 5824, 5717, 6760, 6438, 6082, 5379, 7689, 5842, 9814 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | See Supplementary file 3 | IDT (Integrated DNA Technologies) | ||
| Commercial assay or kit | TruSeq Small RNA Sample Preparation kit | Illumina | TruSeq Small RNA Library Prep Kit – RS-200-0024 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | miRCURY RNA Isolation Kit – Biofluids | Exiqon | ||
| Commercial assay or kit | Universal cDNA synthesis kit II | Exiqon | ||
| Commercial assay or kit | Pick-&-Mix miRNA PCR Panel 96-well | Exiqon | ||
| Commercial assay or kit | E.Z.N.A PX Blood RNA Kit | Omega bio-tek | SKU: R1057-01 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | High Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Catalog number: 4368814 | |
| Software, algorithm | Illumina Genome Analyzer | Illumina | ||
| Software, algorithm | RealTime StatMinerVersion 4.1 | |||
| Software, algorithm | Statgraphics Centurion XV software | StatPoint Inc | ||
| Software, algorithm | SPSS 18.0 software | SPSS | RRID:SCR_002865 |
miRs differentially expressed in spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), as reported in previous studies.
| hsa-miR | miRNome | Relative qPCR | Absolute qPCR* | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-19a-3p | Upregulated | Upregulated | <10 molecules/µl serum; p=0.42 | Haramati et al., 2010; Gonçalves et al., 2018 |
| miR-23a-3p | Downregulated | Upregulated | 150–200 molecules/µl serum; 10 patients/controls analyzed; p=0.62 | Kaifer et al., 2019 |
| miR-206 | Nonsignificant | Upregulated | 50–100 molecules/µl serum; 15 patients/controls analyzed; p=0.24 | Valsecchi et al., 2015; Catapano et al., 2016; Bonanno et al., 2020 |
| miR-9 | Nonsignificant | Not tested | <10 molecules/µl serum; p=0.30 | Catapano et al., 2016 |
| miR-132 | Nonsignificant | Not tested | Not tested | Catapano et al., 2016 |
| miR-146a | Upregulated | Upregulated | <5 molecules/µl serum; p=0.10 | Sison et al., 2017 |
| 4miR-431 | Nonsignificant | Not tested | Not tested | Wertz et al., 2016 |
| miR-183 | Nonsignificant | Not tested | Not tested | Kye et al., 2014 |
-
*
p-Values refer to the significance of comparison of the miR levels in patients and controls by Mann–Whitney U-test. p-values < 0.05 were considered significant.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Demographic and genetic characteristics of subjects who underwent muscle biopsy.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68054/elife-68054-supp1-v3.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Clinical and molecular characteristics of subjects included in the present study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68054/elife-68054-supp2-v3.docx
-
Supplementary file 3
Primer sequences.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68054/elife-68054-supp3-v3.docx
-
Supplementary file 4
List of deregulated miRs in whole miRNome analyses (patients vs. controls).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68054/elife-68054-supp4-v3.docx
-
Supplementary file 5
Assessment by relative and/or absolute qPCR of miR levels in serum samples of patients and controls.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68054/elife-68054-supp5-v3.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68054/elife-68054-transrepform1-v3.docx





