Functional characterization of a ‘plant-like’ HYL1 homolog in the cnidarian Nematostella vectensis indicates a conserved involvement in microRNA biogenesis
Figures
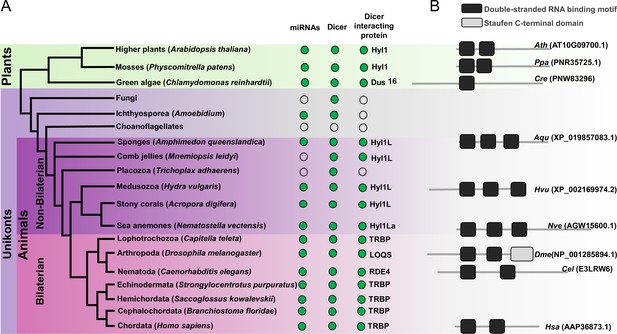
Schematic representation of a phylogenetic tree of Eukaryotes at the phylum level.
(A) Phylogenetic tree representing the presence (green circles) and absence (open circles) of microRNAs (miRNAs), Dicer, and Dicer interacting proteins in different plant and animal phyla. The names of representatives of different phyla are given in brackets. The names of Dicer interacting proteins are given near the green circles. (B) Domain structure of different Dicer interacting proteins predicted by using the Pfam (https://pfam.xfam.org/). NCBI gene ID is shown in brackets.
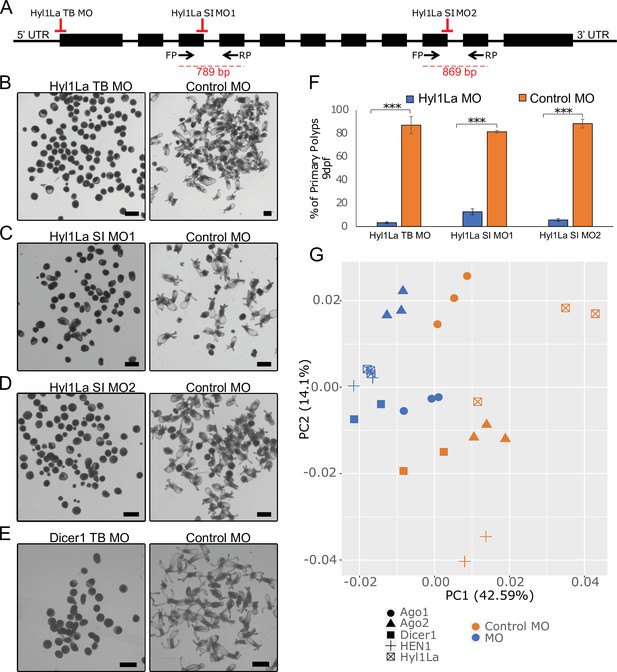
Developmental defects in different morphants of Hyl1-like a (Hyl1La).
(A) Schematic representation of the Hyl1La gene showing the intron-exon junction as defined by comparing the transcript (NCBI Accession KF192067.1) to the Nematostella vectensis genome. The positions targeted by different morpholinos used in the study are shown by red symbols. The black arrows represent the position of primers designed for the validation of splicing morpholino and the product size is indicated below. (B–D) Images of 9 days post-fertilization (dpf) animals showing similar developmental defects in different morphants. (E) Images of 10 dpf Dicer1 morphants showing similar developmental defects to Hyl1La morphants. Scale bars are 500 µm. (F) Bar chart representing percentage of developed and undeveloped animals for each of the morphants. More than 80% of Hyl1La-depleted animals did not develop into the primary polyp stage after 9 dpf. Data was taken in triplicates, in each n = 200, ***p < 0.001 (Student’s t-test). (G) Principal component analysis (PCA) plot of the miRNA expression following the knockdown of miRNA biogenesis components: Hyl1La, HEN1, Dicer2, AGO1, and AGO2. Morphants are in blue and control in orange, different symbols represent different miRNA biogenesis components and their respective controls from the same experiment.
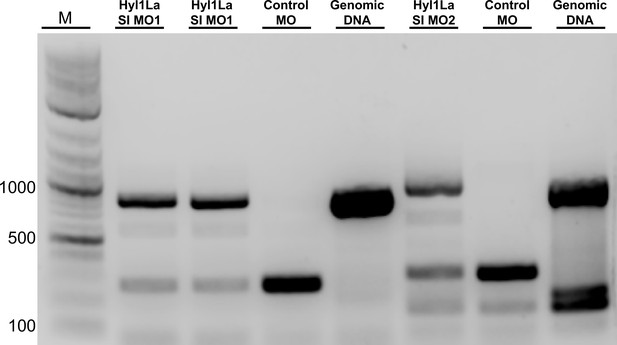
Gel image showing aberrant splicing of Hyl1-like a (Hyl1La).
cDNAs were amplified by using two different primer sets for different morpholinos (Hy1La SI MO1 and Hyl1La SI MO2). The control morpholino lane showed the band of spliced Hyl1La while the Hyl1La SI morpholino lane showed the band of size equivalent for intron retention. The genomic DNA was amplified by using the same primer pairs to check the size and primer efficiency (Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1).
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Related to Figure 2—figure supplement 1 – This data includes the gel image of aberrant Hyl1-like a (Hyl1La) splicing after different morpholinos injections.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-fig2-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
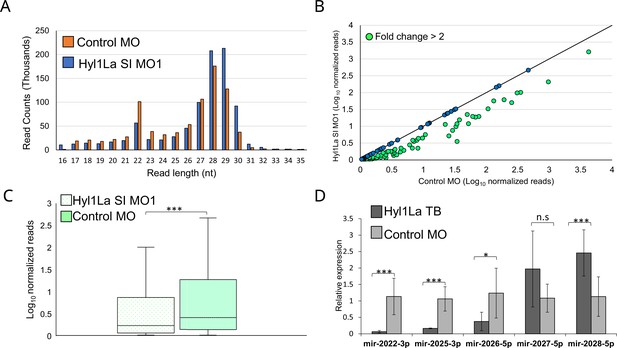
Hyl1-like a (Hyl1La) morphants show reduced expression of microRNAs (miRNAs).
(A) Average read length distribution of small RNA reads after adapter removal. (B) Scatter plot representing normalized read counts of miRNAs in control and treated animals. Each dot represents the average expression of an individual miRNA. The miRNAs showing a depletion greater than twofold are indicated in green. The axes are scaled to Log10 of normalized read counts. The data represents the mean of three independent biological replicates. (C) Box plot showing the average abundance of miRNA read counts in Hyl1La SI MO1 and control MO. A significant reduction of miRNA read counts is noted in Hyl1La SI MO1 (p < 0.0001, Wilcoxon signed-rank test). The data represents the mean of three independent biological replicates ± SD. (D) Bar plot showing the expression of miR-2022, miR-2025, miR-2026, miR-2027, and miR-2028 as quantified using stem-loop PCR in translation-blocking (TB) and control morpholino. The data represents the mean of three independent biological replicates ± SD. ***p < 0.001, **p ≤ 0.01, *p ≤ 0.05 (Student’s t-test), n.s. (not significant).

Effect of Hyl1-like a (Hyl1La) depletion on microRNAs (miRNA) expression.
The expression of miR-2022, miR-2025, miR-2026, miR-2027, and miR-2028 was checked by using the stem-loop PCR between the Hyl1La SI MO1 vs. control MO and Hyl1La SI MO2 vs. control MO. The data represents the mean of four independent biological replicates ± SD. ***p < 0.001, **p ≤ 0.01, *p ≤ 0.05, (Student’s t-test), n.s. (not significant).
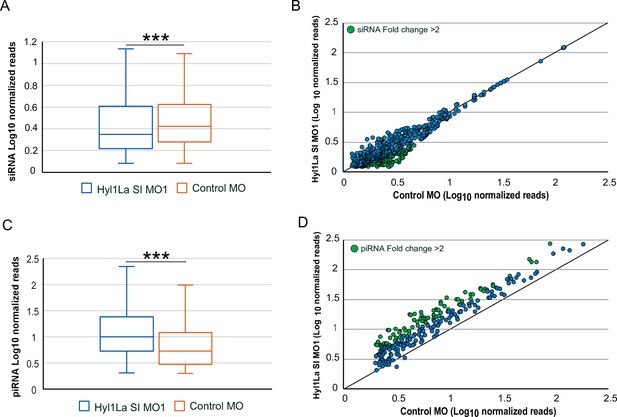
Effect of Hyl1-like a (Hyl1La) depletion on siRNA and piRNA expression.
(A) Box plot showing the average of abundance of siRNA read counts in Hyl1La SI MO1 and control MO. A significant slight reduction of siRNA read counts is noted in Hyl1La SI MO1 (p < 0.00001, Wilcoxon signed-rank test). The data represents the mean of three independent biological replicates ± SD. (B) Scatter plot representing normalized read counts of siRNAs in control and treated animals. Each dot represents the average expression of an individual siRNA. The siRNAs showing a depletion greater than twofold are indicated in green. The axes are scaled to Log10 of normalized read counts. The data represents the mean of three independent biological replicates. (C) Box plot showing the average of abundance of piRNA read counts in Hyl1La SI MO1 and control MO. A significant upregulation of piRNA read counts is noted in Hyl1La SI MO1 (p < 0.00001, Wilcoxon signed-rank test). The data represents the mean of three independent biological replicates ± SD. (D) Scatter plot representing normalized read counts of piRNAs in control and treated animals. Each dot represents the average expression of an individual piRNA. The piRNAs showing an upregulation greater than twofold are indicated in green. The axes are scaled to Log10 of normalized read counts. The data represents the mean of three independent biological replicates.
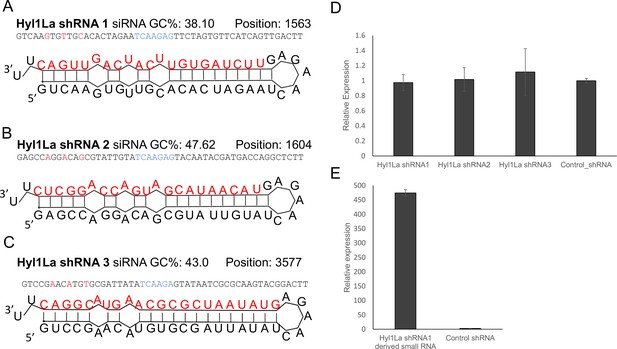
Structure of short-hairpin RNA (shRNA) precursors and their effect on Hyl1-like a (Hyl1La) expression.
(A–C) Structure of different shRNAs designed from different positions of Hyl1La gene along with GC content and their position are shown. In the shRNA sequence, the red color shows the nucleotides edited for mismatch and blue color represents loop region. The red colored nucleotides on precursor’s structure indicate the small RNA derived from the shRNAs. (D) Real-time quantification of Hyl1La from animals injected with different shRNAs relative to control. The data represents the mean of three independent biological replicates ± SD. (E) Quantification of small RNAs produced from Hyl1La shRNA1. The quantification was performed by using stem-loop qRT-PCR.
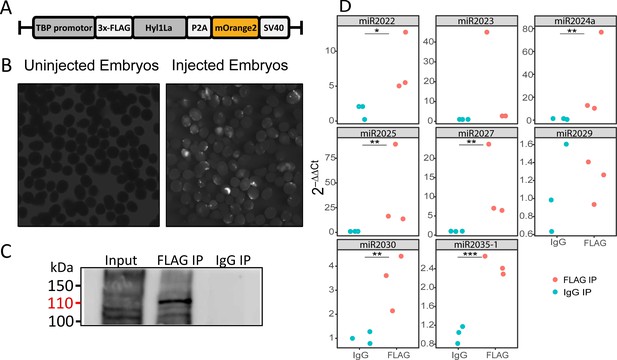
RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) and qRT-PCR.
(A) Schematic representation of the FLAG-Hyl1-like a (Hyl1La) construct with a TBP promoter, a self-cleaving P2A sequence, a memOrange2 gene, and the polyadenylation signal SV40. (B) The plasmid-injected and -uninjected embryos were visualized under a florescence microscope after 2 days. The injected embryos were showing the expression of memOrange2 (right side). (C) Immunoprecipitation (IP) of 3 × FLAG-Hyl1La with mouse anti-FLAG antibody or whole mouse IgG by using Protein G Magnetic Beads. The input and IP samples were subjected to Western blot with mouse anti-FLAG antibody. The red arrow (110 kDa) indicates the 3 × FLAG-Hyl1La (Figure 5—source data 1 and Figure 5—source data 2). (D) pre-miRNA expression of eight different miRNAs were measured using the qRT-PCR. The Y-axis represents the 2-ΔΔCt values of three independent biological replicates. ***p < 0.001, **p ≤ 0.01, *p ≤ 0.05 (Student’s t-test).
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Related to Figure 5C – Western blot of FLAG-Hyl1-like a (Hyl1La) after immunoprecipitation.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-fig5-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 5—source data 2
Related to Figure 5C – Figure includes the image of Western Blot Protein Ladder used as a size ruler.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-fig5-data2-v2.zip
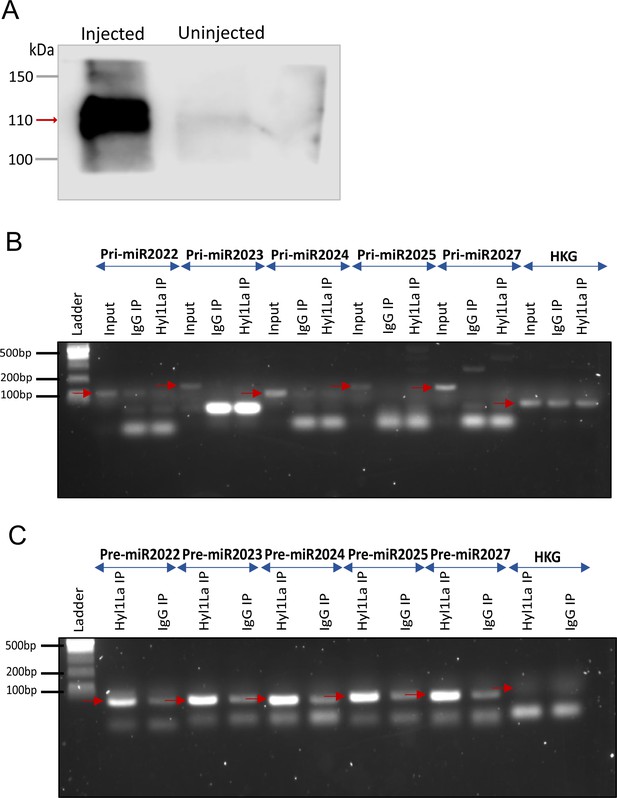
RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) and PCR (related to Figure 5B–D).
(A) Western blot of 3 × FLAG-Hyl1-like a (Hyl1La) with mouse anti-FLAG antibody (Figure 5—source data 1 and Figure 5—source data 2). Gel image showing RT-PCR amplified (B) pri-miRNA (primary miRNA) and (C) pre-miRNA (precursor miRNA) transcripts. The pri- and pre-miRNA were amplified with their specific primers from RNA isolated from samples immunoprecipitated with mouse anti-FLAG antibody (Hyl1La IP)/whole mouse IgG (IgG IP). The red arrow indicates the expected product size. Ubiquitin was taken as control housekeeping gene (HKG) (Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 3 and Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 4).
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Related to Figure 5—figure supplement 1A – Western blot of FLAG-Hyl1-like a (Hyl1La) with anti-FLAG antibody.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-fig5-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 2
Related to Figure 5—figure supplement 1A – Figure includes the image of Western Blot Protein Ladder used as a size ruler.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-fig5-figsupp1-data2-v2.zip
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 3
Related to Figure 5—figure supplement 1B – Gel image of PCR amplified pri-microRNA (miRNA).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-fig5-figsupp1-data3-v2.zip
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 4
Related to Figure 5 – Figure supplement 1C – Gel image of PCR amplified pre-microRNA (miRNA).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-fig5-figsupp1-data4-v2.zip
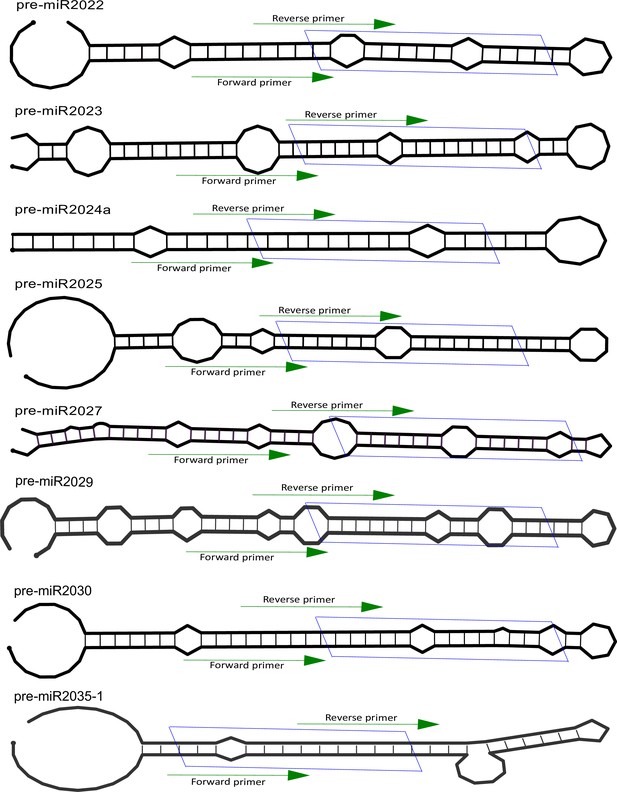
Position of primers on pre-microRNA (miRNA).
The secondary structure of miRNA precursors used in this study for identification of functional interaction with Hyl1-like a (Hyl1La). The green arrow indicates the primer positions used for pre-miRNA quantification. The blue box represents position of miRNA/miRNA* duplex.

Position of pre- and pri-microRNA (miRNA) primers on probable sequence of pri-miRNA.
The probable sequence of pri-miRNA taken from the Nematostella genome browser (https://simrbase.stowers.org/). The underlined sequences represent the pre-miRNA. The sequences with purple and green color represent primer position for pri- and pre-miRNA, respectively.
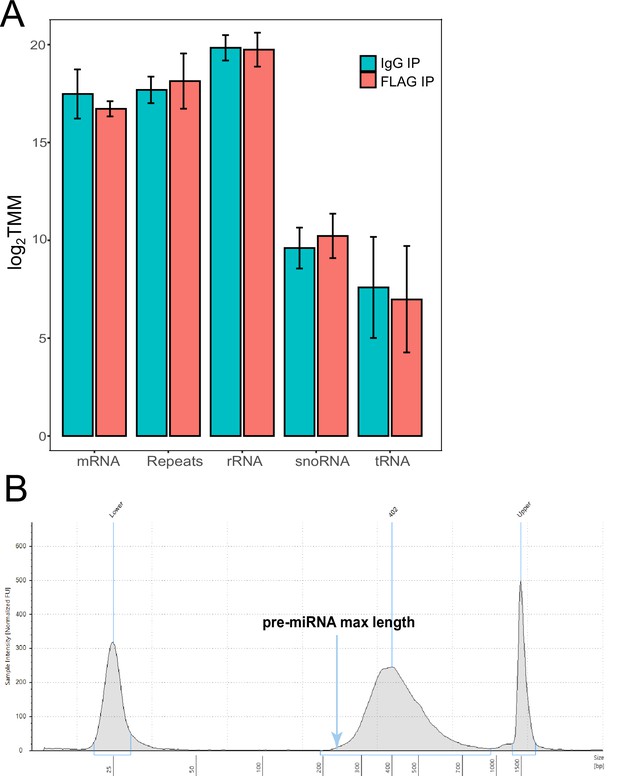
RNA-seq of RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP).
(A) Immunoprecipitation RNA sequencing of FLAG-Hyl1-like a (Hyl1La). Read counts mapped to the Nematostella genome were Log2 and trimmed mean of M (TMM) normalized. A combination of coding (messenger RNA [mRNA]), non-coding RNA (rRNA, snoRNA, tRNA) and repetitive elements were quantified for both FLAG-Hyl1La and IgG. Error bars correspond to standard deviation among replicates (n = 4). All comparisons were not significant (Student’s t-test). (B) Representation of size distribution of libraries generated from RIP samples, validated with TapeStation system (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA).
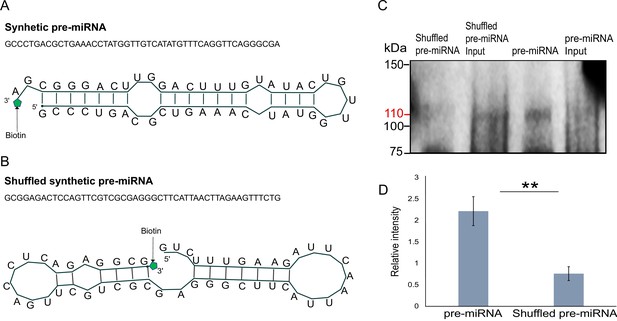
In vitro binding assay.
(A) The sequence and secondary structure of biotin-labeled synthetic pre-microRNA (miRNA) used for in vitro binding assay. (B) The sequence and secondary structure of biotin-labeled shuffled synthetic pre-miRNA used as negative control for in vitro binding assay. (C) Pull-down of biotin-labeled synthetic pre-miRNA and shuffled pre-miRNA negative control using streptavidin magnetic beads. The pull-down samples were subjected to Western blot with mouse anti-FLAG antibody (Figure 6—source data 1; Figure 6—source data 2; Figure 6—source data 3; Figure 6—source data 4; Figure 6—source data 5; Figure 6—source data 6). (D) Relative intensity of Western blot bands with mouse anti-FLAG antibody, showing pull-down of biotin-labeled synthetic pre-miRNA and shuffled pre-miRNA negative control. Error bars correspond to standard deviation among replicates (n = 3). **p ≤ 0.01 (Student’s t-test).
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Related to Figure 6C – Western blot of biotin pull-down with anti-FLAG antibody – replicate1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-fig6-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 6—source data 2
Related to Figure 6C – Figure includes the image of Western Blot Protein Ladder used as a size ruler – replicate1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-fig6-data2-v2.zip
-
Figure 6—source data 3
Related to Figure 6C – Western blot of biotin pull-down with anti-FLAG antibody – replicate2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-fig6-data3-v2.zip
-
Figure 6—source data 4
Related to Figure 6C – Figure includes the image of Western Blot Protein Ladder used as a size ruler – replicate2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-fig6-data4-v2.zip
-
Figure 6—source data 5
Related to Figure 6C – Western blot of biotin pull-down with anti-FLAG antibody – replicate3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-fig6-data5-v2.zip
-
Figure 6—source data 6
Related to Figure 6C – Figure includes the image of Western Blot Protein Ladder used as a size ruler – replicate3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-fig6-data6-v2.zip
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (Nematostella vectensis) | Hyl1La | GenBank | KF192067 | |
| Strain, strain background (Nematostella vectensis) | Lab strain, Rhode River, MD | Lab strain | Sea anemone species | |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | NEB 5-alpha Competent E. coli (High Efficiency) (DH5α) | New England Biolabs | C2987I | Chemically competent cells |
| Antibody | Monoclonal mouse anti-FLAG M2 antibody (Mouse monoclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | F1804-50UG | IP (5 µg per test) WB (1:500) |
| Antibody | Peroxidase-AffiniPure Goat Anti-Mouse IgG (Goat polyclonal) | Jackson ImmunoResearch | 115-035-146 | WB (1:10,000) |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pER242 (plasmid) | Admoni et al., 2020 | Used as backbone | |
| Sequence-based reagent | PCR Primers | Integrated DNA Technologies | In this paper | See Materials and methods and Supplementary file 7 |
| Sequence-based reagent | DNA template of shRNA | Integrated DNA Technologies | In this paper | See Materials and methods |
| Sequence-based reagent | Morpholino | Gene Tools | In this paper | See Materials and methods |
| Chemical compound, drug | Trizol | Thermo (Ambion) | 15596026 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tryptone | Merck Millipore | 61930505001730 | For bacterial media |
| Chemical compound, drug | Yeast extract purified for Microbiology | Merck Millipore | 61931105001730 | For bacterial media |
| Chemical compound, drug | Agar purified for Microbiology | Merck Millipore | 61939005001730 | For bacterial media |
| Chemical compound, drug | Ampicillin | ROTH | K029.1 | For bacterial media |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dextran Alexa Fluor 488 | Thermo (Molecular Probes) | D22910 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Red sea salt | Red sea | For Nematostella vectensis growth | |
| Chemical compound, drug | L-Cysteine | Merck Millipore | 1028380100 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tween20 | Sigma-Aldrich | P9416-100ML | |
| Chemical compound, drug | NP40 | Sigma-Aldrich | NP40S-100ML | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Skim milk | BD | 232100 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Bovine serum albumin (fraction V) | MP | 160069 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tris-glycine-SDS buffer | Bio-Rad | 1610772 | For SDS-PAGE |
| Chemical compound, drug | Total mouse IgG | Sigma-Aldrich | I5381-1MG | IP (5 µg per test) |
| Commercial Assay, kit | SuperScript III Reverse Transcriptase | Thermo (Invitrogen) | 18080044 | |
| Commercial Assay, kit | iScript cDNA Synthesis Kit | Bio-Rad | 1708891 | |
| Commercial Assay, kit | Fast SYBR Green Master Mix | Thermo (ABI) | AB-4385612 | |
| Commercial Assay, kit | Q5 High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase | New England Biolabs | M0493S | |
| Commercial Assay, kit | AmpliScribe T7-Flash Transcription Kit | Lucigen | ASF3507 | |
| Commercial Assay, kit | Quick-RNA Miniprep | Zymo Research | R1054 | |
| Commercial Assay, kit | NucleoSpin Gel and PCR Clean-up | Macherey-Nagel | MAN-740609.50 | |
| Commercial Assay, kit | NEBuilder HiFi DNA Assembly Master Mix | New England Biolabs | E2621S | |
| Commercial Assay, kit | CloneJet cloning kit | Thermo (Fermentas) | K1231 | |
| Commercial Assay, kit | HiSpeed Plasmid Midi Kit | Qiagen | 12643 | |
| Commercial Assay, kit | PureLink Quick Plasmid Miniprep Kit | Thermo (Invitrogen) | K210010 | |
| Commercial Assay, kit | NextSeq 500/550v2 Kits (75 cycles) | Illumina | FC-404–2005 | |
| Commercial Assay, kit | NEBNext Multiplex Small RNA Library Prep Set for Illumina (1-12) – 24 rxns | New England Biolabs | NEB-E7300S | |
| Commercial Assay, kit | Pierce RNA 3' End Biotinylation Kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 20160 | |
| Commercial Assay, kit | Ovation SoLo RNA-seq systems kit | Tecan Genomics | 0500–32 | |
| Commercial Assay, kit | SureBeads Protein G Magnetic Beads | Bio-Rad | 1614023 | For IP |
| Commercial Assay, kit | Streptavidin Magnetic Beads | New England Biolabs | S1420S | For pull-down |
| Commercial Assay, kit | RNase Inhibitor, Murine | New England Biolabs | M0314L | |
| Commercial Assay, kit | cOmplete ULTRA Tablets, Mini, EASYpack Protease Inhibitor Cocktail | Roche | 05892970001 | |
| Commercial Assay, kit | Protease Inhibitor Cocktail Set III, EDTA-Free | Merck-Millipore | 539134–1ML | |
| Commercial Assay, kit | 4–15% Mini-PROTEAN TGX Precast Protein Gels | Bio-Rad | 4561083 | For Western blot |
| Commercial Assay, kit | Trans-Blot Turbo Mini 0.2 µm PVDF Transfer Packs | Bio-Rad | 1704156 | For Western blot |
| Software, algorithm | miRDeep2 | doi:10.1093/nar/gkr688 (2012) | Small RNA analysis | |
| Software, algorithm | The UEA small RNA Workbench | doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bts311 | Small RNA analysis | |
| Software, algorithm | Trimmomatic (v3.4) | doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170. Epub 2014 Apr 1 | Total RNA analysis | |
| Software, algorithm | STAR (v2.7.9) | doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bts635 | Total RNA analysis | |
| Software, algorithm | RSEM | doi:10.1186/1471-2105-12-323 | Total RNA analysis | |
| Software, algorithm | shRNA design | doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2019.01.005 | https://www.invivogen.com/sirnawizard/index | |
| Software, algorithm | Protein Domain Search | https://pfam.xfam.org/search#tabview=t | ||
| Software, algorithm | Homologs search | https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi/Proteins |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
The morpholino (MO) clones that are showing the intron retention.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) and their expression.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-supp2-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 3
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) and their expression for meta-analysis.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-supp3-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 4
Pre-microRNA (miRNA) and pri-miRNA Ct values.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-supp4-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 5
RNA-seq.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-supp5-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 6
In vitro binding assay band intensities.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-supp6-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 7
Primers used in this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-supp7-v2.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-transrepform1-v2.docx
-
Source data 1
Source data file of gels and blots with relevant bands labelled.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-data1-v2.zip
-
Source data 2
Source data of original gels and blots.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69464/elife-69464-data2-v2.zip





