CASP microdomain formation requires cross cell wall stabilization of domains and non-cell autonomous action of LOTR1
Figures
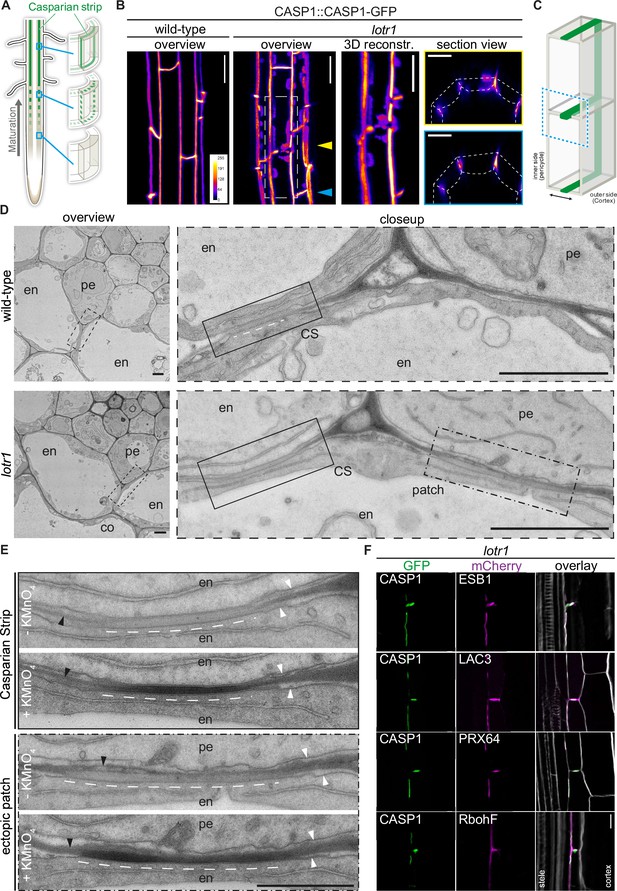
Ectopic domain formation in lotr1.
(A) Schematic representation of endodermal maturation with stages of Casparian Strip (CS) development (green). Elongated endodermal cells focalize CASP1-GFP into aligned micro-domains which are subsequently fused into a continuous ring around each endodermal cell. (B) CASP1-GFP localization in wildtype and lotr1 with focus on patch localization. Images depict maximum intensity projections of z-stack Figure . and 3D reconstruction image depicts region indicated in lotr1 overview image, section view images are annotated by yellow (top) and blue (bottom) arrows. Overview images scale bars: 20 µm; 3D reconstruction & section views scale bars: 10 µm. (C) 3D schematic for visualization of median endodermal cell section with annotated cell faces. (D) TEM section of wildtype and lotr1 obtained at 2 mm from root tip. Overview of section with focus on regular CS and adjacent ectopic patch. Please note the tight plasma membrane-attachment to the CS that is a further feature of CS presence. Closeup indicated by dashed black line in overview image; en = endodermis, pe = pericycle, co = cortex, scale bars = 2 µm. (E) Consecutive TEM sections of lotr1 at 2 mm from root tip, with and without KMnO4 staining, position indicated in lower panels of (D). Dark deposits indicate electron-dense MnO2 precipitation caused by reaction with lignin. Note that in the case of ectopic patches, the staining is restricted to the endodermal side of the cell wall. In addition, plasma membrane-attachment to the CS is only occurring at the endodermal side. en = endodermis, pe = pericycle, white arrows indicate plasma membranes, black arrows highlight cell wall middle lamellae, interspaced white line depicts extend of CS-like cell wall morphology, scale bar = 1 µm. (F) Localization of enzymes necessary for CS lignification in wildtype Col-0 and lotr1, pictures depict cells as seen in (C). Cellulosic cell walls are stained with Calcofluor White and depicted in white in overlay images, scale bar = 10 µm.
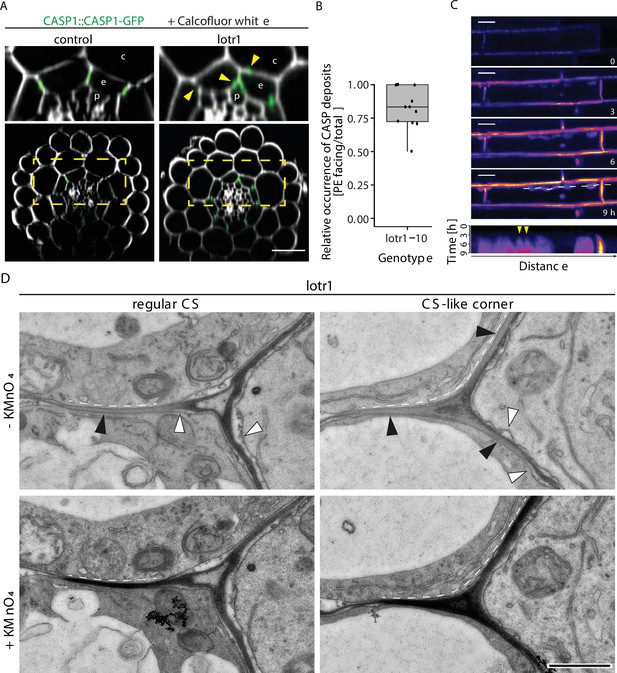
Establishment of ectopic domain formations in lotr1.
(A) Localization of ectopic deposition of CASP1-GFP (green). Section view of z-stack through roots 5–10 cells after onset of protoxylem differentiation, cell wall stained with Calcofluor White (white) and crops shown on top outlined in overview pictures below (dashed yellow line); scale bar = 50 um, c = cortex, e = endodermis, P = pericycle. (B) Quantification of ectopic CASP1-GFP patches. Number and position of ectopic patches were determined per cell and depicted as ratio of patches facing pericycle cells vs total patch number, maximum of 3 cells counted per seedling, ntotal = 11. (C) Deposition of CASP1-GFP in lotr1. CASP1-GFP fluorescence depicted throughout CSD formation in lotr1; scale bars = 5 um. Kymograph image at bottom illustrates fluorescence over time in line indicated above, individual patch formation visible as independent pyramid-like structures (yellow arrows). (D) Consecutive TEM sections at 2 mm from root tip, with and without KMnO4 staining. Dark deposits indicate electron-dense MnO2 precipitation caused by reaction with lignin; en = endodermis, pe = pericycle, black arrows indicate CS-like cell wall with attached plasma membranes, white arrows highlight plasmolyzed membranes detached from the cell wall, scale bar = 1 µm.
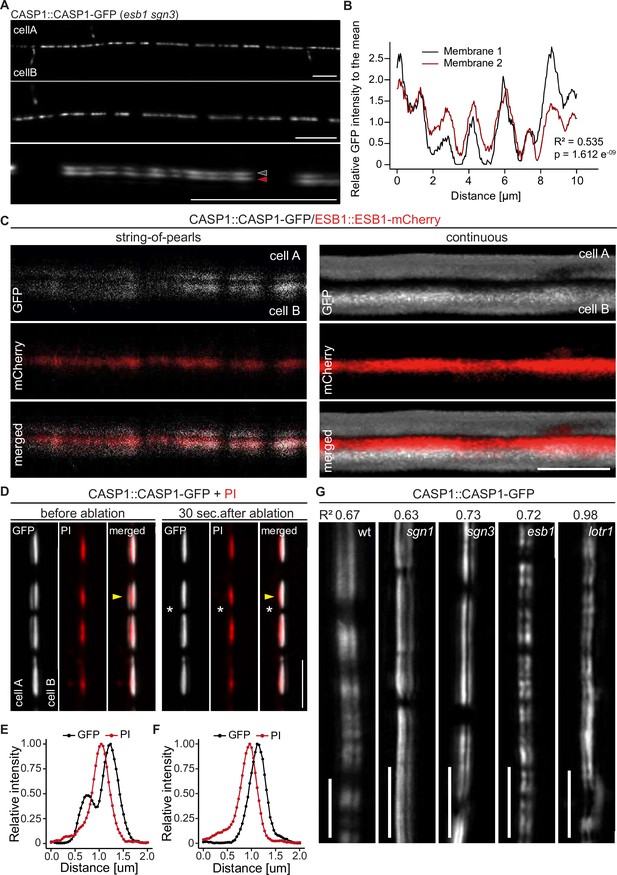
CASP deposition is coordinated between neighboring endodermal cells.
(A) Double membrane phenotype visible with CASP1::CASP1-GFP during string-of-pearls stage of CS development, scale bars depict 10 µm. Red and gray arrows indicate separate membranes measured in (B). (B) Comparison of GFP intensity between adjacent membranes indicated in (A). Pixel intensity was measured along each membrane and relative GFP intensity was adjusted to mean intensity of each membrane. Correlation of original intensities (R-squared) was determined by fitting of a linear model with indicated probability of fit (p-value). (C) Localization of CSD marker CASP1-GFP in comparison to cell wall protein ESB1-mCherry at early and mature CSs, scale bar depicts 5 µm. (D) Double membrane phenotype of CASP1-GFP before and after ablation of one adjacent endodermal cell in early CSs. Cell walls (red) are stained with Propidium iodide (PI), yellow arrows indicate intensity profiles measured in F-I; asterisks indicate ablated cell, scale bars = 5 µM. (E + F) Quantification of CASP1-GFP and PI intensity before and after cell ablation. Intensity was quantified in a 7-pixel wide line indicated in (D) and (E). (G) Double membrane phenotype in CS mutants, scale bars = 5 um. R2 value depicts Spearman rho correlation coefficients of fluorescence of 5-pixel wide lines following each membrane.
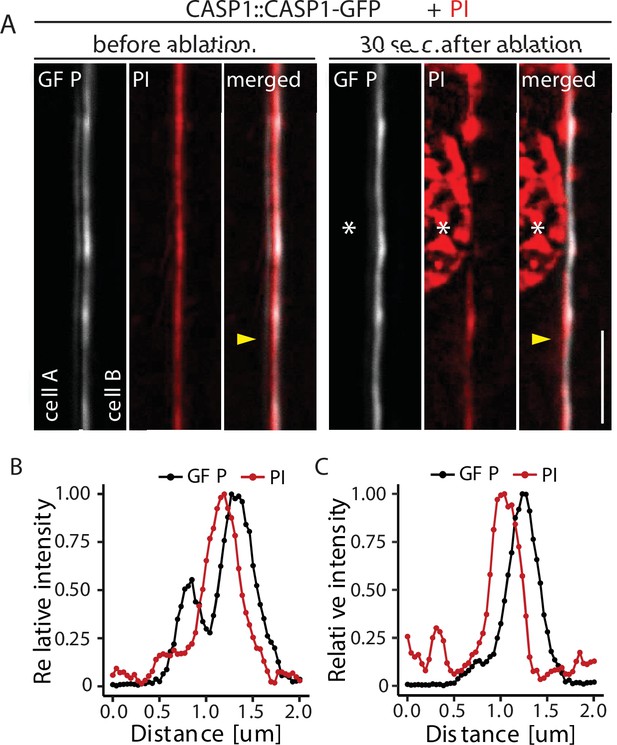
CASP1-GFP membrane coordination.
Double membrane phenotype of CASP1-GFP before and after ablation of one adjacent endodermal cell in early CSs. Cell walls (red) are stained with Propidium iodide (PI), yellow arrows indicate intensity profiles measured in F-I; asterisks indicate ablated cell, scale bars = 5 µM. (E + F) Quantification of CASP1-GFP and PI intensity before and after cell ablation. Intensity was quantified in a 7-pixel wide line indicated in (D) and (E).
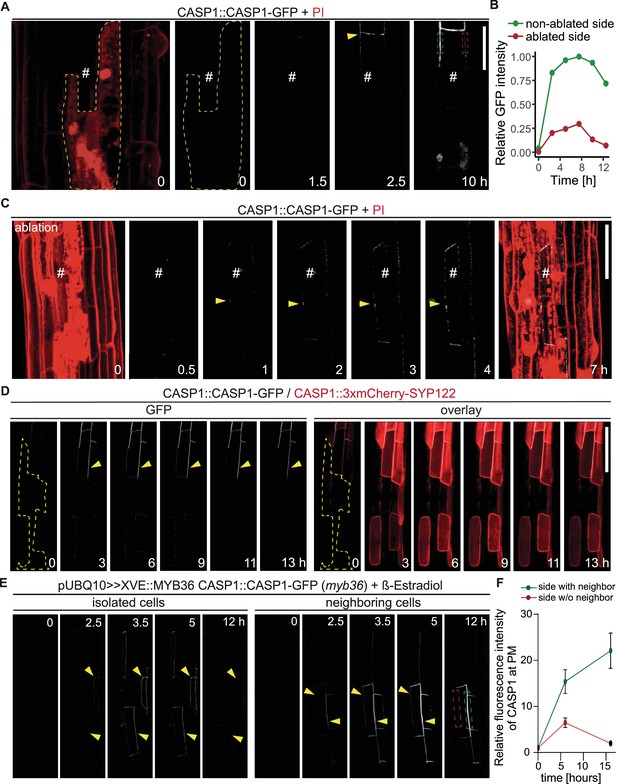
Endodermal neighbors are required for proper CSD establishment.
(A) Endodermal cell ablation leads to instability of the CSD in membranes facing dead cells. Endodermal cells were ablated 3–5 cells prior to onset of CASP1-GFP (white) expression and followed over indicated time spans. First image depicts overview after ablation with cells outlined with PI; # depicts remaining live endodermal cell, dashed yellow line depicts cell outlines of ablated cells, arrow indicates onset of CASP expression, dashed green and red rectangles indicate quantification areas shown in (B), scale bar = 20 µm. (B) Quantification of GFP fluorescence over time in membranes facing live (green) and dead (red) adjacent endodermal cells. Intensity depicted in relation to maximum total GFP intensity. (C) Ablation of all adjacent endodermal cells prevents fusion of CSDs. Endodermal neighbors were ablated at timepoint 0 and CASP1-GFP expression (white) followed over time in remaining cell (#), PI (red) highlighted cell outlines and confirmed destruction of cells; yellow arrow indicates initial CASP microdomains, scale bar = 50 um. (D) CASP instability in membranes facing ablated cells is independent from CASP expression. Cells ablated 3–5 cells prior to onset of CASP expression, cell outline depicted with dashed yellow line, arrow indicates stable CASP formation, scale bar = 100 um. (E) CASP fusion occurs only if both neighboring cells reach expression threshold. Endodermal differentiation was induced via 0.5 µM β-estradiol and CASP1-GFP expression followed over the next 12 hr. Yellow arrows indicate CASP deposits in the membrane, dashed green and red rectangles indicate areas for quantification shown in (F). (F) Quantification of GFP fluorescence over time in membranes reaching local stability threshold (green) and those below the threshold (red).
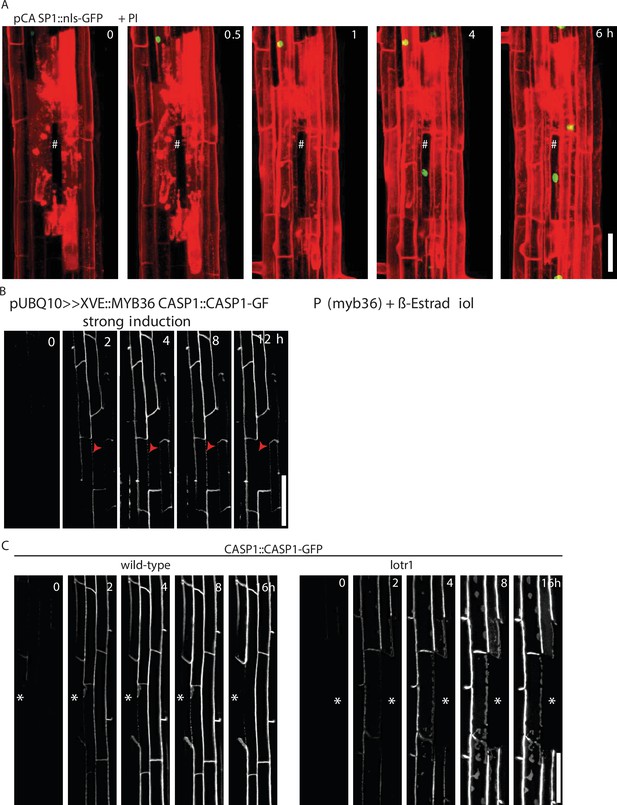
Cell ablation impacts CS establishment.
(A) CASP1 promoter activity highlighted by nls-GFP (green) after ablation of all neighboring cells prior to onset of expression, PI (red) outlines cells and confirmed cell destruction. Scale bar = 50 um. (B) Endodermal differentiation was induced via 0.5 µM β-estradiol and CASP1-GFP expression (white) followed over the next 12 hr. Red arrows indicate unstable CASP deposits in the membrane, scale bar = 50 µm. (C) CSD formation in wildtype and lotr1. Single endodermal cells ablated 3–4 cells prior to onset of CASP expression, * depicts ablated cell, scale bar = 50 um.
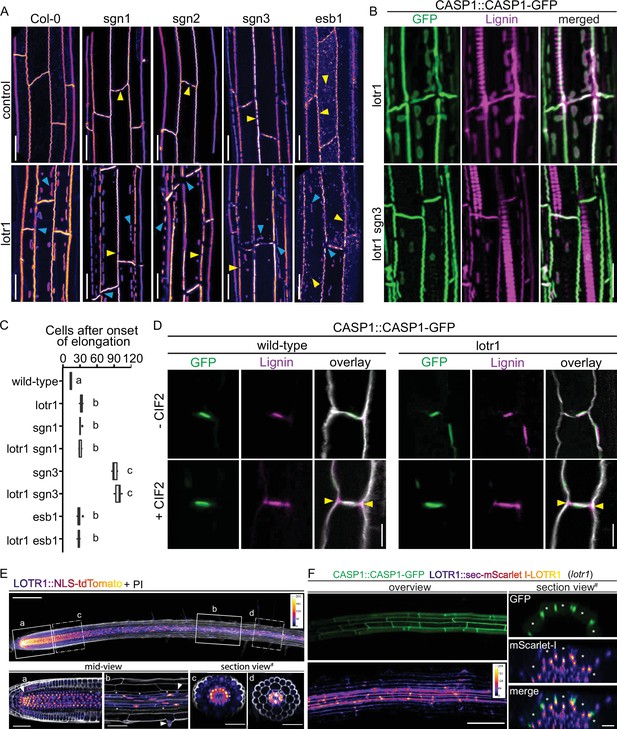
LOTR1 restricts CSD establishment through independent pathway.
(A) CASP1-GFP fluorescence of known CS mutants in wildtype and lotr1 background. Yellow arrows indicate parental CS mutant phenotype while blue arrows highlight lotr1 specific phenotypes; scale bar = 20 µm. (B) Enhanced lignification in lotr1 is SCHENGEN-dependent. Ectopic lignin (magenta) accumulates in lotr1 at disruptions of the CASP1-GFP (green) marked CSD. Lignification of the central domain and ectopic patches is unaffected by disruption of SGN3, scale bar = 20 µm. (C) Apoplastic barrier phenotypes of lotr1 double mutants. Formation of apoplastic barrier was determined by penetrance of apoplastic tracer PI to the stele; n = 10, significance determined by one-way ANOVA and separate groups identified with Tukey-Kramer test. (D) SCHENGEN-pathway is unaffected in lotr1. Wildtype and lotr1 seedlings were treated for 24 hr with 100 µM synthetic CIF2 peptide and lignin accumulation (magenta) outside the regular CSD domain (green) analysed. Cell walls were stained with Calcofluor White, yellow arrows indicate ectopic lignin accumulation, scale bar = 5 µm. (E) LOTR1 expression indicates additional roles. Promoter activity highlighted by tdTomato fluorescence in 5-day-old seedlings; cells outlined by Propidium iodide (white); mid-view regions depicted below highlighted by continuous rectangles (a,b) and section views indicated by dash-dotted lines (c,d), inlay shows color profile of LOTR1 expression intensity. a Single-plane section through root meristem region, arrow indicates cortex-daughter cell. b Single-plane section after cell elongation, arrows indicate expression in endodermis (top arrow) and epidermis (bottom arrow). c Maximum-intensity projection of section view of z-stack through meristem region indicated in top picture. d Maximum-intensity projection of section view of z-stack through mature region indicated in top picture; * denotes endodermal cell lineage, scale bars: top: 100 µm; a,b: 20 µm; c,d: 50 µm. (F) Complementation of lotr1 phenotype. N-terminal fusion construct expressed under native LOTR1 promoter complements ectopic CSD phenotype. Scale bars: left 100 µm, section views 20 µm.
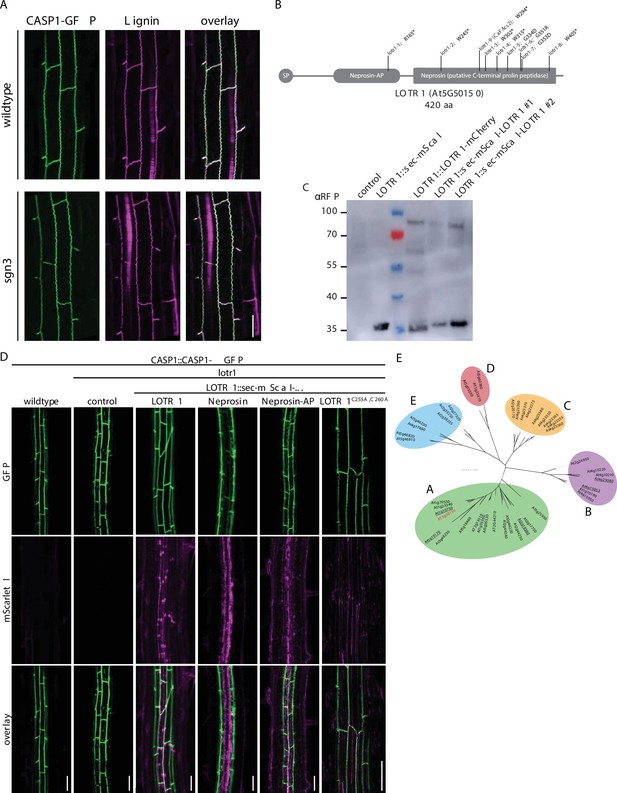
Investigation of putative post-translational processing in LOTR1.
(A) Lignin accumulation (magenta) in wildtype and sgn3 with CSDs labeled by CASP1-GFP (green). (B) Schematic view of LOTR1 with position of identified loss-of-function alleles indicated. (C) Processing of LOTR1. Root protein extracts separated via SDS-PAGE and LOTR1-fragments detected by anti-RFP antibody (Chromotek 6G6). Note that C-terminal fusion construct LOTR1::LOTR1-mCherry does not complement the lotr1 phenotype, but shows processing/degradation fragments. Both weak (#1) and strong (#2) C-terminal complementation lines lack processing/degradation fragments. (D) Complementation analysis of the lotr1 CASP1-GFP phenotype using truncated versions consisting of only LOTR1’s Neprosin domain (Neprosin), the putative autoinhibitory Neprosin-AP domain (Neprosin-AP), or full-length LOTR1 with conserved cysteines C255 and C260 mutated (LOTR1C255A,C260A), scale bars = 50 µm. (E) Phylogenetic analysis of HOMOLOGS-OF-LOTR1 (HOLO) family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Homologs of LOTR1 in A. thaliana were identified and grouped into five subfamilies by phylogenetic distance, LOTR1 (At5g50150) highlighted in red, underlined genes have predicted N-terminal transmembrane domains.
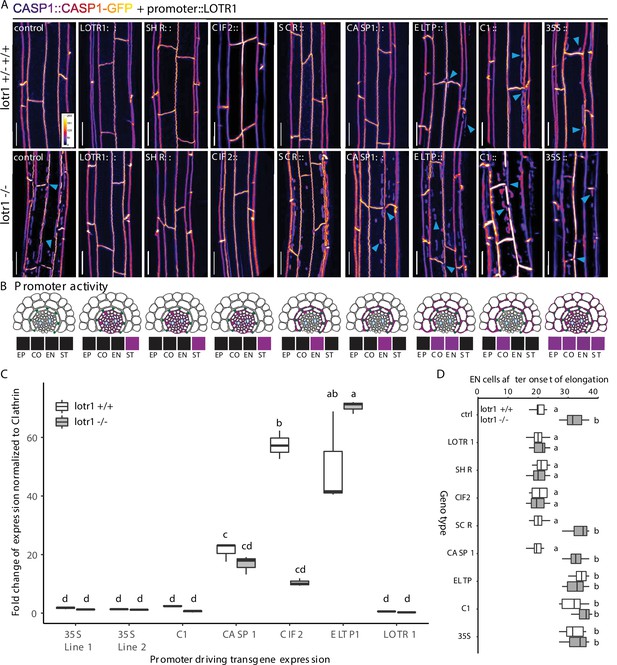
Stele-specific LOTR1 restricts CSD establishment.
(A) Mis-expression of LOTR1 in cortical cells causes dominant loss-of-function phenotypes. CASP1-GFP phenotypes of seedlings expressing LOTR1-complementation construct (used in Figure 4F) under indicated promoters. Presented pictures represent typical phenotypes observed in more than five independent lines; blue arrows indicate lotr1-like phenotypes; EP = epidermis, CO = cortex, EN = endodermis, ST = stele; scale bars = 20 µm. (B) Schematics of promoter activity to highlight cell-type specific expressions are based on publicly available microarray expression data obtained from the BAR eFP browser (Winter et al., 2007), as well as diverse publications that provide detailed characterisations of these promoters Promoters are as follows: SHR, SHORT ROOT; CIF2, CASPARIAN STRIP INTEGRITY FACTOR 2;SCR, SCARECROW; CASP1, CASPARIAN STRIP DOMAIN PROTEIN 1; ELTP, LTPG15, LIPID TRANSFER PROTEIN G 15; C1, CORTEX 1. Expression indication for LOTR1 was modeled according to the patterns shown in Figure 4E/F. (C) Transgene expression comparison of lines presented in (A) by qRT-PCR. The data presented here are representative of three biological replicates (n = 3) analysed. NOTE: Transgene expression levels do not correlate with occurrence of dominant phenotypes observed in A. Statistical difference was determined using ANOVA to search for significant interactions between expression level, transgene presence and genetic background. Significant interactions were grouped by a post-hoc Tukey-Kramer test and depicted with letters. (D) Apoplastic barrier phenotypes of tissue specific complementation lines in wildtype (white) and lotr1 (grey) background. Cells after onset of elongation counted until penetrance of PI was blocked. n = 10, significance determined via one-way ANOVA and independent groups identified via Tukey-Kramer post-hoc test.
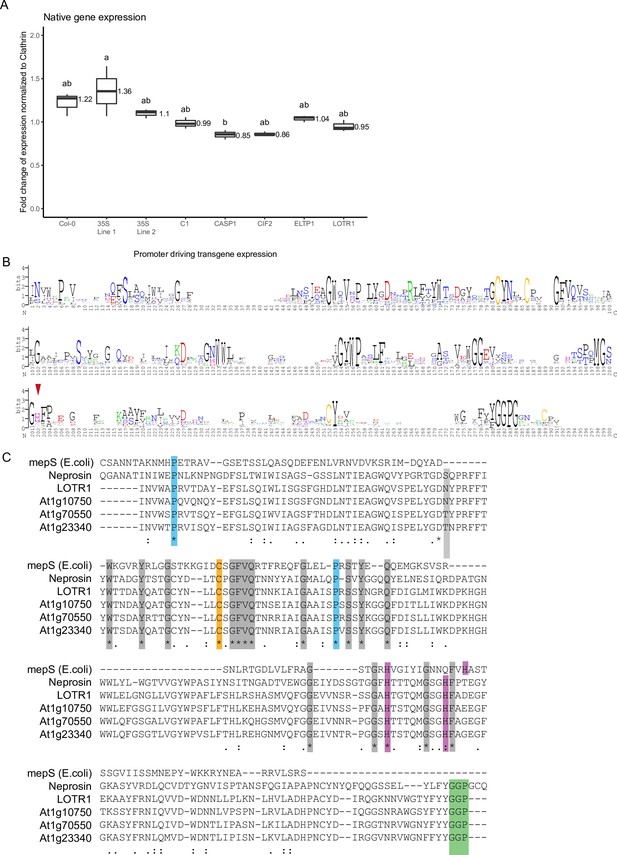
Neprosin domain analysis in the HOLO family.
(A) Native LOTR1 expression is not dramatically changed in lines transformed with tissue-specific expression constructs used in Figure 5A. The data presented here are representative of three biological replicates (n = 3) analyzed. Statistical difference was determined using ANOVA to search for significant interactions between expression level, transgene presence and genetic background. Significant interactions were grouped by a post-hoc Tukey-Kramer test and depicted with letters. (B) Conservation of Neprosin domain throughout the HOLO-family, including LOTR1. Putative catalytic triade amino acids aligning with E. coli mepS marked with red arrows. (C) Sequence alignment of E. coli mepS, Neprosin, LOTR1 and its closest homologs At1g23340 (HOLO2), At1g70550 (HOLO3), and At1g10750 (HOLO4).
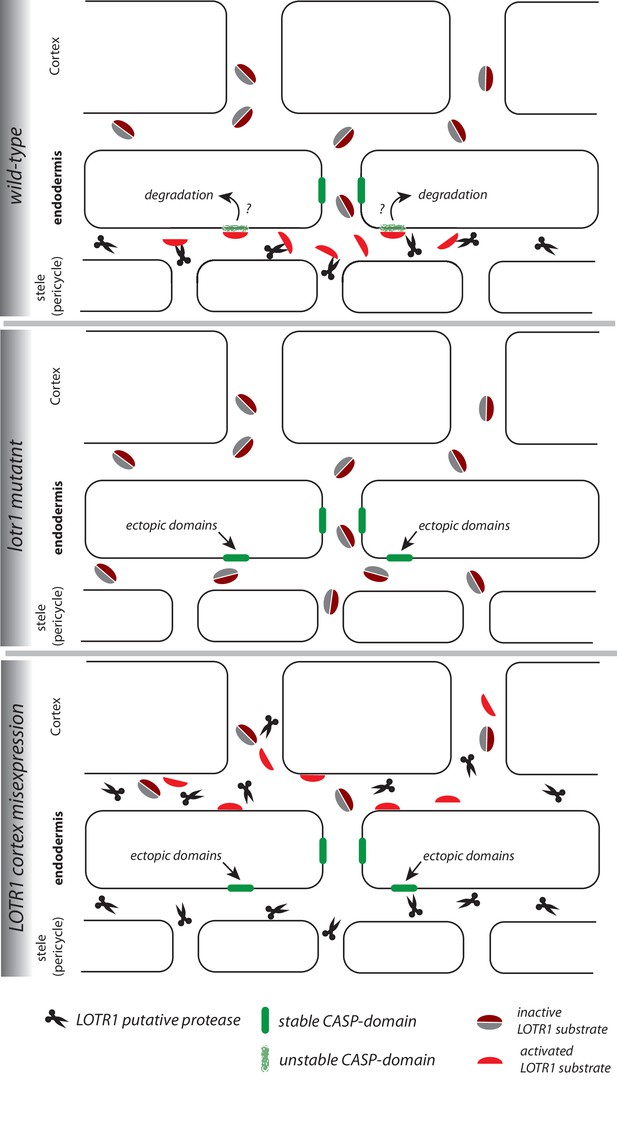
Speculative model of LOTR1 function.
The following model for LOTR1 function is simply one scenario that can plausibly integrate the data on LOTR1’s predicted activity, expression, subcellular localization, as well as phenotypes by loss-of-function and dominant-interference by misexpression. Wild-type: LOTR1 is a predicted protease (scissors), experimentally determined to be expressed in the stele and to localize in the cell wall. We speculate that LOTR1 cleaves a cortex-derived substrate (grey, dark-red coffee bean, inactive), activating it in the stele (red half-bean, active). This substrate then inhibits ectopic CASP-domain formation (green) at the stele-facing endodermal surface by unknown means. lotr1 mutant: Absence of LOTR1 would not allow activation of the ectopic CASP-domain inhibitor in the endodermal, stele-facing apoplast, leading to the observed formation of ectopic, stable CASP-domain predominantly at the stele-facing side of the endodermal surface. LOTR1 cortex mis-expression: This model explains the observation that cortical mis-expression of LOTR1 dominantly interferes with wild-type LOTR1 action, if it would precociously cleave and activate the LOTR1 substrate, not allowing it to reach the stele to be activated by wild-type LOTR1. This would lead to the observed, similar phenotype than the lotr1 knock-out.
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69602/elife-69602-transrepform1-v2.docx
-
Source data 1
Source data files.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69602/elife-69602-supp1-v2.zip
-
Supplementary file 1
Table S1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69602/elife-69602-supp2-v2.xlsx





