Processing of the ribosomal ubiquitin-like fusion protein FUBI-eS30/FAU is required for 40S maturation and depends on USP36
Figures
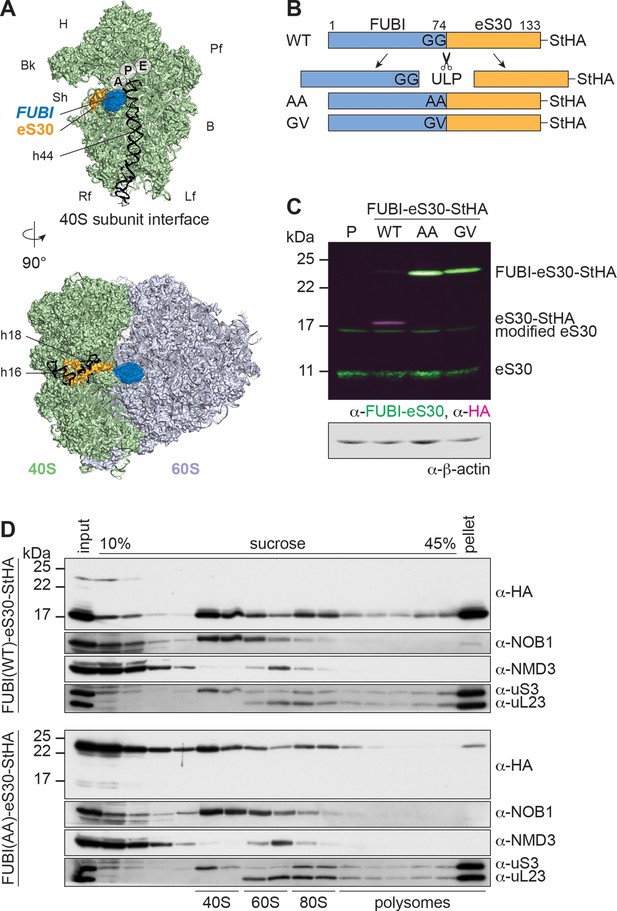
Mutant, non-cleavable FUBI-eS30 can be incorporated into (pre-)40S particles.
(A) Structures (PDB ID: 4UG0 Khatter et al., 2015) of the human 40S subunit shown from the subunit interface (top) and of the 80S ribosome viewed from the mRNA entry channel (bottom), highlighting the hypothetical location of FUBI (blue) at the N terminus of eS30 (orange). FUBI (PDB ID: 2L7R, state 1 (Lemak, 2011), marked with an opaque blue shape) was manually positioned in PyMOL avoiding molecular contacts in the surface representation mode. Ribosomal A-, P-, and E-sites are indicated and the 18S rRNA helices h44 (G1702–C1833), h18 (U595–A641), and h16 (C527–G558) are highlighted in black. B, body; Bk, beak; H, head; Lf, left foot; Pf, platform; Rf, right foot; Sh, shoulder. (B) Schematic representation of C-terminally StHA-tagged FUBI-eS30 wild-type (WT) and mutant G73,74A (AA) and G74V (GV) constructs used in this study. The C-terminal diglycine motif of FUBI (G73,G74) was mutated to impair FUBI removal by ubiquitin-like protease(s) (ULP). (C) Immunoblot of tetracycline-inducible HeLa cell lines expressing the indicated FUBI-eS30-StHA constructs using anti-FUBI-eS30/FAU and anti-HA primary antibodies. Fluorescent secondary antibodies against anti-FUBI-eS30/FAU (green) and anti-HA (magenta) antibodies were detected simultaneously. P, parental cells. Note that the StHA tag adds ~7 kDa to the (FUBI-)eS30 protein constructs. eS30 runs at a higher MW than the expected 7 kDa, likely due its high content in positively charged residues. (D) Extracts from FUBI-eS30-StHA WT (top) or AA mutant (bottom) HEK293 cell lines were separated on a linear 10–45% sucrose gradient by centrifugation. Expression of the FUBI-eS30-StHA constructs was induced with 0.1 µg/ml tetracycline for 17 hr. Input, gradient, and pellet fractions were analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Source data for Figure 1C and D with relevant bands labeled on the uncropped original blots.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70560/elife-70560-fig1-data1-v2.png.zip
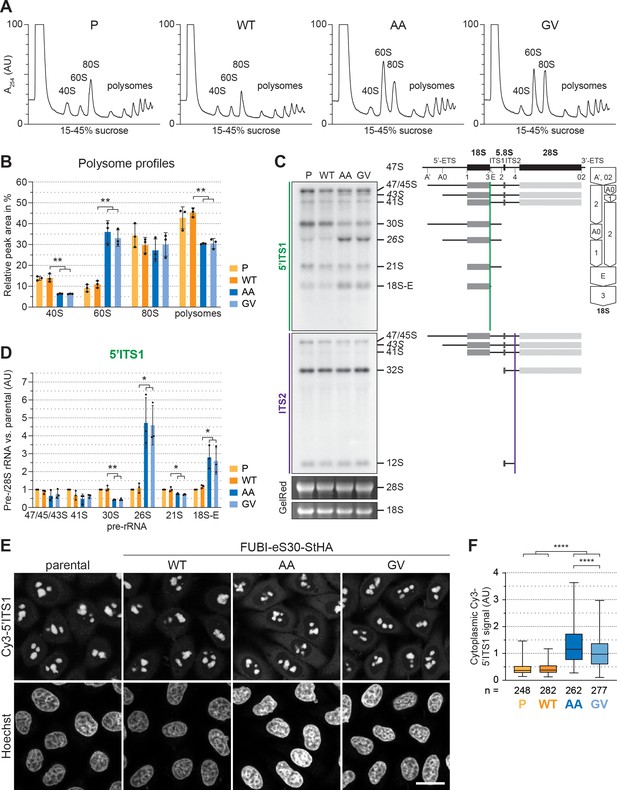
40S ribosome biogenesis is defective upon expression of non-cleavable FUBI-eS30 mutants.
(A) Extracts from parental (P), wild-type (WT) or mutant (AA, GV) FUBI-eS30-StHA HEK293 cell lines were separated on a linear 15–45% sucrose gradient by centrifugation and analyzed by polysome profiling recording the absorption at 254 nm. (B) Quantification of three biological replicates of polysome profiles as shown in (A) determining the relative areas beneath the A254 traces of 40S, 60S, 80S, and the first five polysome peaks. Unpaired t-test, mean ± SD, N = 3, **p < 0.01. (C) Northern blot analysis of total RNA extracted from parental (P), WT or mutant (AA, GV) FUBI-eS30-StHA HeLa cell lines using radioactively labeled probes hybridizing to the 5’ region of ITS1 (5’ITS1) or the ITS2. Mature 28S and 18S rRNAs were visualized by GelRed staining of the gel. The short-lived 43S and 26S rRNA precursors are labeled in italics. The rRNA precursors are schematically indicated on the right including the probe binding sites (colored lines) and the processing sites (dashed lines). On the very right, a simplified processing scheme indicates the generation of 18S rRNA precursors by successive endo- and exonucleolytic processing in two parallel pathways according to Henras et al., 2015. (D) Quantification of the indicated pre-rRNA species based on the 5’ITS1 signal normalized to mature 28S rRNA in three biological replicates as shown in (C), expressed as fold changes relative to the parental cell line. Unpaired t-test, mean ± SD, N = 3, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Quantification pre-rRNAs based on the ITS2 signal is shown in Figure 2—figure supplement 1. (E) Fluorescence in situ hybridization of parental, WT or mutant (AA, GV) FUBI-eS30-StHA HeLa cell lines using a Cy3-labeled 5’ITS1 probe (Rouquette et al., 2005). To enhance lower gray levels, γ value was set to 1.5 in parallel for all images. DNA was stained with Hoechst. Scale bar, 20 µm. (F) Quantification of cytoplasmic Cy3-5'ITS1 signals measured in three biological replicates of the experiment shown in (E). Box plots represent the range, quartiles, and mean of the measured signals for the indicated total number of cells (n) per cell line (P, WT, AA, GV). Unpaired t-test, N = 3, n ≥ 46, ****p < 0.0001. Note that, for unknown reason, there is a small but significant difference between the AA and GV mutants.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Source data for Figure 2C with relevant areas labeled on the uncropped edited images.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70560/elife-70560-fig2-data1-v2.png.zip
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Unedited image of the ITS1 blot shown in Figure 2C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70560/elife-70560-fig2-data2-v2.tiff.zip
-
Figure 2—source data 3
Unedited image of the ITS2 blot shown in Figure 2C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70560/elife-70560-fig2-data3-v2.tiff.zip
-
Figure 2—source data 4
Unedited image of the gel shown in Figure 2C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70560/elife-70560-fig2-data4-v2.tif.zip
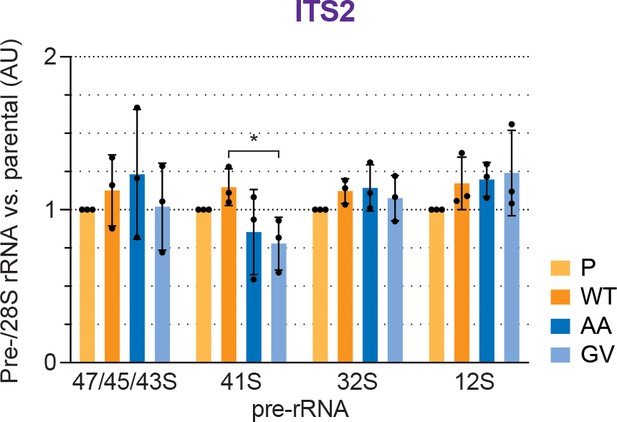
Quantification of pre-rRNAs based on the ITS2 signal.
Quantification of the indicated pre-rRNA species based on the ITS2 signal, normalized to mature 28S rRNA in three biological replicates as shown in Figure 2C, expressed as fold changes relative to the parental cell line. Unpaired t-test, mean ± SD, N = 3, *p < 0.05.
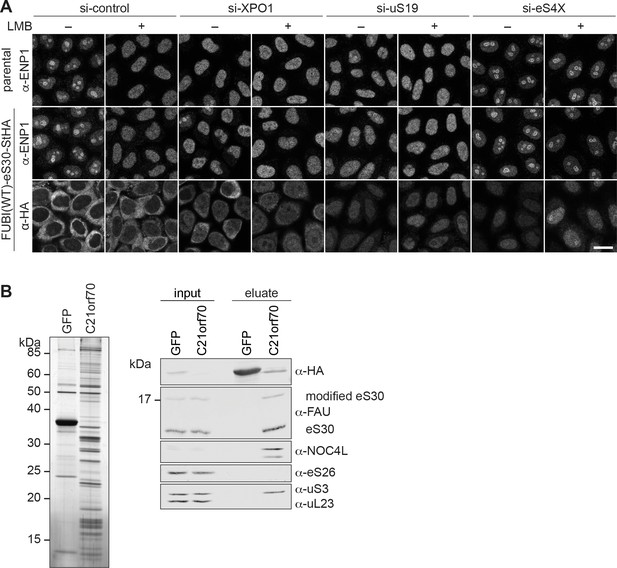
eS30 joins pre-40S ribosomal subunits in the nucleus.
(A) Parental and tetracycline-inducible FUBI(WT)-eS30-StHA HeLa cell lines were treated with the indicated siRNAs (5 nM, 48 hr) and LMB (+; 20 nM, 90 min) before fixation. Cells were immunostained with an antibody against the 40S RBF ENP1. FUBI(WT)-eS30-StHA expressing cells were co-stained with an anti-HA antibody. Scale bar, 20 µm. (B) StrepTactin affinity purification of HASt-GFP (GFP) and HASt-C21orf70 (C21orf70) from HEK293 cell lysates. Eluates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by silver staining (left) and together with the input lysates analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies (right).
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Source data for Figure 3B with relevant areas labeled on the uncropped edited image of the gel and with relevant bands labeled on the uncropped original blots.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70560/elife-70560-fig3-data1-v2.png.zip
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Unedited image of the gel shown in Figure 3B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70560/elife-70560-fig3-data2-v2.tif.zip
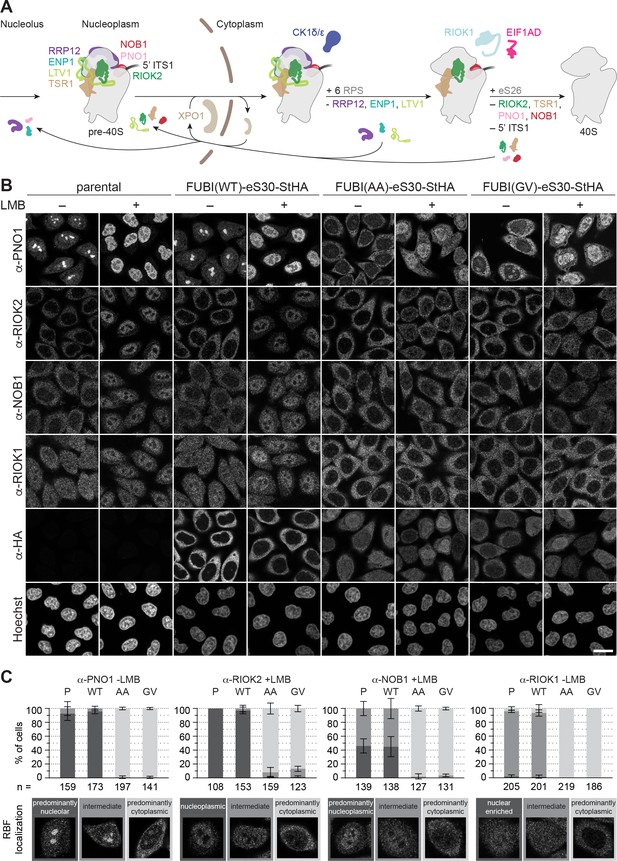
Non-cleavable FUBI-eS30 mutants have a dominant-negative effect on late cytoplasmic steps of 40S subunit biogenesis.
(A) Scheme of pre-40S maturation focusing on late nucleoplasmic to cytoplasmic maturation steps and highlighting the RBFs mentioned in the text. Nucleoplasmic pre-40S particles containing 18S-E pre-rRNA with its characteristic 5' ITS1 remnant and bound to various RBFs can be exported in an XPO1-dependent manner. In the cytoplasm, late-assembling RPS are incorporated, the 3' overhang of 18S rRNA is cleaved off by the endonuclease NOB1, and the RBFs are released and recycled. Together, these sequential maturation steps lead to the formation of a mature 40S subunit. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of parental, WT or mutant (AA, GV) FUBI-eS30-StHA HeLa cell lines using the indicated antibodies against the constructs (HA) and the 40S RBFs PNO1, RIOK2, NOB1, and RIOK1. Note that HA and RIOK2 co-immunostaining was performed in parallel with Hoechst staining of DNA. Where indicated, cells were treated with leptomycin B (LMB; 20 nM, 90 min) to inhibit XPO1-mediated nuclear export prior to fixation of cells. Scale bar, 20 µm. (C) Quantification of RBF localization for selected conditions of the experiment shown in (B). Percentage of cells assigned to the respective phenotypic classes exemplified below was determined from three or in case of PNO1 -LMB four biological replicates for the indicated total number of cells per condition and cell line (n).
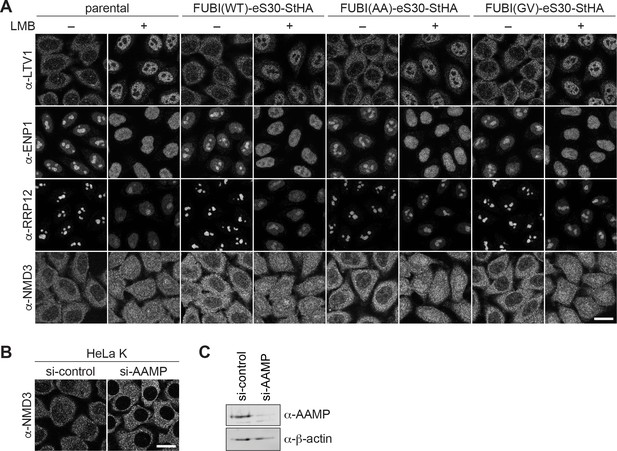
Expression of non-cleavable FUBI-eS30 mutants affects nucleolar but not early cytoplasmic 40S or cytoplasmic 60S biogenesis.
(A) The localizations of the 40S RBFs LTV1, ENP1, and RRP12 and of the 60S RBF NMD3 were analyzed in parental, WT or mutant (AA, GV) FUBI-eS30-StHA HeLa cell lines by immunostaining. Where indicated, cells were treated with 20 nM LMB for 90 min or for 4 hr in case of anti-NMD3 staining before fixation. Scale bar, 20 µm. (B) Anti-NMD3 immunofluorescence analysis of HeLa K cells treated with control or AAMP siRNA (10 nM, 72 hr). Scale bar, 20 µm. (C) Immunoblot analysis of (B) using the indicated antibodies showed efficient depletion of AAMP.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Source data for Figure 4—figure supplement 1C with relevant bands labeled on the uncropped original blots.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70560/elife-70560-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v2.png.zip
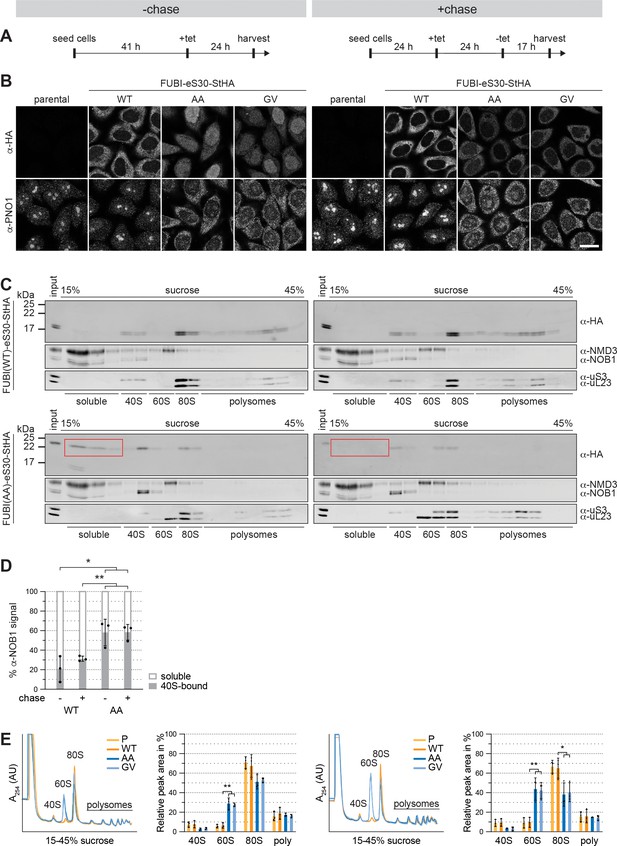
Non-cleavable FUBI-eS30 mutants induce a persistent 40S ribosomal subunit biogenesis defect.
(A) Flowchart of the timeline for the tetracycline (tet)-mediated induction of FUBI-eS30-StHA expression in HeLa cell lines without (left panel) or with (right panel) a chase period in tet-free medium. All cells were harvested at the same time for subsequent analysis by immunofluorescence or polysome profiling. (B) Parental, WT or mutant (GA, GV) FUBI-eS30-StHA HeLa cell lines were treated as in (A) and immunostained with antibodies against the constructs (HA) and the 40S RBF PNO1. Scale bar, 20 µm. (C) Extracts of WT or mutant (AA) FUBI-eS30-StHA HeLa cell lines matching the samples in (B) were separated on a linear 15–45% sucrose gradient by centrifugation. Gradient fractions were analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies against the constructs (HA), 60S and 40S RBFs (NMD3 and NOB1, respectively) and ribosomal proteins of the small and large subunits (uS3 and uL23, respectively). Note the decrease of FUBI-eS30(AA)-StHA in the light fractions after the chase (respective fractions marked by red boxes). (D) Quantification of the soluble and 40S-bound anti-NOB1 signal in the respective sucrose gradient fractions of three biological replicates of the experiment shown in (C). Unpaired t-test, mean ± SD, N = 3, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. (E) Polysome profiles of parental (P, light orange), WT (dark orange), AA (dark blue), or GV (light blue) FUBI-eS30-StHA HeLa cell lines matching the samples in (B). The relative areas beneath the A254 traces of the 40S, 60S, 80S, and the first three polysome peaks of three biological replicates were measured and quantified. Unpaired t-test, mean ± SD, N = 3, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Source data for Figure 4—figure supplement 2C with relevant bands labeled on the uncropped original blots.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70560/elife-70560-fig4-figsupp2-data1-v2.png.zip
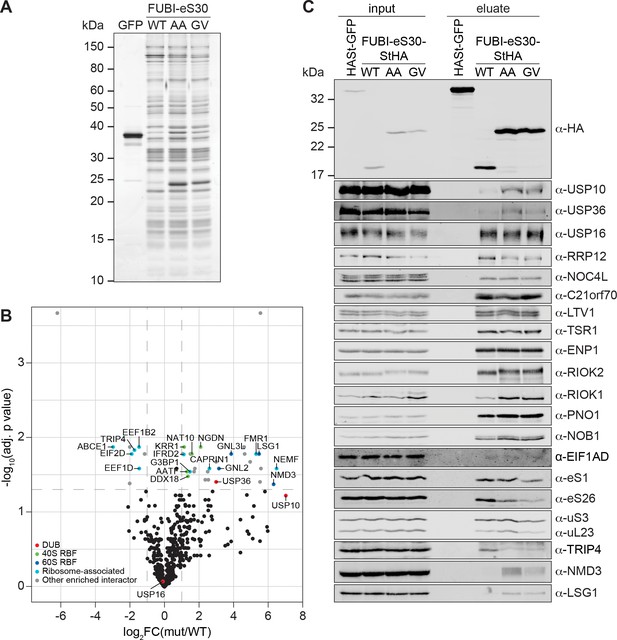
Identification of candidate proteases by differential affinity purification mass spectrometry of FUBI-eS30-StHA constructs.
(A) StrepTactin affinity purification of HASt-GFP (GFP), WT or mutant (AA, GV) FUBI-eS30-StHA from HEK293 cell lysates. Eluates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by silver staining or mass spectrometry. (B) Results of the proteomic analysis of three biological replicates as in (A). The spectral counts of proteins that were compared to HASt-GFP confidently enriched on FUBI-eS30-StHA baits (SAINT Bayesian false discovery rate < 1%) were normalized to their size in amino acids. The log2 fold change of the average number of the spectral counts of the confident interactors identified on the non-cleavable AA and GV mutants (mut) vs. WT FUBI-eS30-StHA (log2FC(mut/WT)) are plotted against the negative log10 of the adjusted p value (-log10(adj. p value)). All confidently identified DUBs are labeled, significantly enriched interactors (|log2FC| > 1 and adj. p value < 0.05, demarcated with dashed lines) are categorized as indicated and individual proteins are labeled. Data before and after normalization and filtering are shown in Supplementary file 1. (C) Inputs and eluates of StrepTactin affinity purification performed as in (A) were analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Source data for Figure 5A and C with relevant areas and bands labeled on the uncropped gel and uncropped original blots, respectively.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70560/elife-70560-fig5-data1-v2.png.zip
-
Figure 5—source data 2
Unedited image of the gel shown in Figure 5A.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70560/elife-70560-fig5-data2-v2.tif.zip
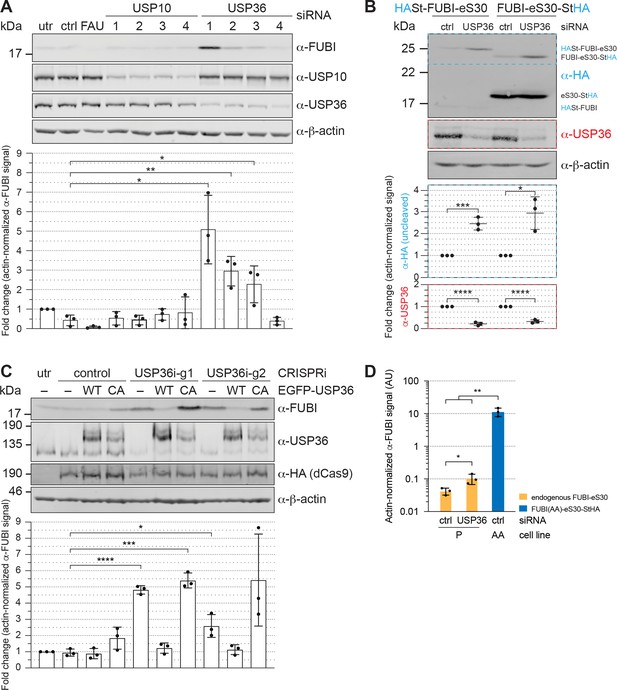
USP36 is required for FUBI-eS30 processing in vivo.
(A) Immunoblot analysis of HeLa K cells that were either left untreated (utr), treated with control (ctrl) siRNA or siRNAs against the indicated factors (48 hr, 10 nM, except for FAU/FUBI-eS30: 5 nM) using the indicated antibodies. Quantification of the fold change of the actin-normalized anti-FUBI signal from three biological replicates shows a significant accumulation of uncleaved FUBI-eS30 upon depletion of USP36 by three different siRNAs. Unpaired t-test, mean ± SD, N = 3, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. (B) Immunoblot analysis of HASt-FUBI-eS30 and FUBI-eS30-StHA HEK293 cell lines treated with si-control (ctrl) or si-USP36-1 (USP) (20 nM, 48 hr) using the indicated antibodies. Note that the linkers between FUBI-eS30 and the tags differ slightly between the two constructs, causing their different running behavior. Actin-normalized anti-HA and anti-USP36 signals in dashed colored boxes of three biological replicates were quantified. Unpaired t-test, mean ± SD, N = 3, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. (C) Immunoblot analysis of a USP36 CRISPRi-rescue experiment using the indicated antibodies. Parental (–) and EGFP-USP36 WT or catalytically inactive C131A mutant (CA) HeLa cell lines were left untreated (utr) or transfected for 72 hr with a plasmid encoding HA-tagged KRAB-dCas9 and a control single guide RNA (sgRNA) or a sgRNA targeting a site in the promoter region of USP36 (USP36i-g1, USP36i-g2). Expression of the rescue constructs in the respective cell lines was induced 24 hr prior to CRISPRi transfection by addition of tetracycline. Quantification of the fold change of the actin-normalized anti-FUBI signal from three biological replicates confirmed rescue of USP36 depletion by CRISRPi with WT EGFP-USP36 but not the catalytically inactive CA mutant. Unpaired t-test, mean ± SD, N = 3, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. (D) Parental (P) and FUBI(AA)-eS30-StHA (AA) HeLa cell lines were treated with the indicated siRNAs (si-control (ctrl), si-USP36-1 (USP36); 15 nM, 48 hr). Expression of FUBI(AA)-eS30-StHA was induced with 0.1 µg/ml tetracycline for 24 hr. FUBI immunoblot signals of endogenous, uncleaved FUBI-eS30 (in P) and of FUBI(AA)-eS30-StHA (in AA) were quantified and normalized to actin. Unpaired t-test, mean ± SD, N = 3, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Source data for Figure 6 with relevant areas labeled on the uncropped original blots.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70560/elife-70560-fig6-data1-v2.png.zip
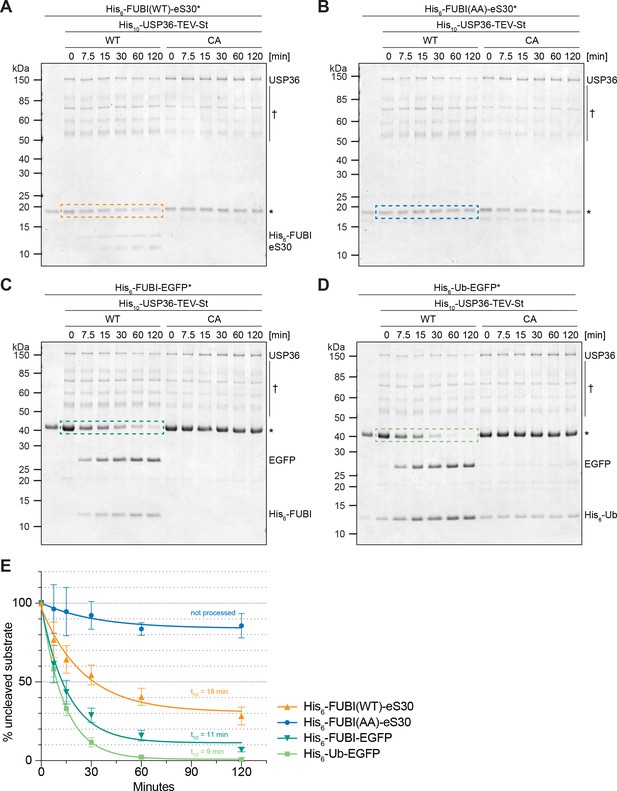
USP36 cleaves linear authentic and artificial UB(L) substrates in vitro.
In vitro processing assays for which 2.5 µM (A) His6-FUBI(WT)-eS30, (B) His6-FUBI(AA)-eS30, (C) His6-FUBI-EGFP, and (D) His6-Ub-EGFP were incubated with 0.5 µM His10-USP36-TEV-St WT or CA mutant at 37°C. Samples taken at the indicated time points (0, 7.5, 15, 30, 60, 120 min) were analyzed on Coomassie brilliant blue-stained gels. Unprocessed substrates are marked with an asterisk (*). Note that the enzyme preparation contains USP36 degradation products (marked with a dagger (†), see Figure 7—figure supplement 1). (E) Quantification of USP36-dependent processing based on the levels of the uncleaved substrates, highlighted by dashed colored boxes in panels (A to D), each normalized to t = 0 min from three technical replicates. Half-lives (t1/2) of fitted one-phase exponential decay curves are indicated for processed substrates.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Source data for Figure 7 with relevant areas labeled on the uncropped images of the gels.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70560/elife-70560-fig7-data1-v2.png.zip
-
Figure 7—source data 2
Unedited image of the gels shown in Figure 7.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70560/elife-70560-fig7-data2-v2.tif.zip
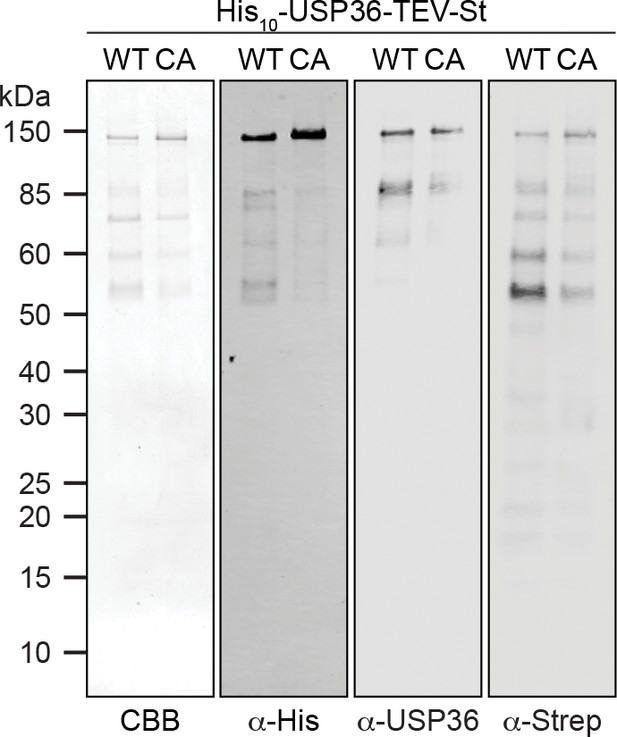
Analysis of purified His10-USP36-TEV-St.
Purified WT and CA His10-USP36-TEV-St (0.5 µM) were analyzed by Coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) staining of the gel or by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies.
-
Figure 7—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Source data for Figure 7—figure supplement 1 with relevant areas labeled on the uncropped gel and uncropped original blots.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70560/elife-70560-fig7-figsupp1-data1-v2.png.zip
-
Figure 7—figure supplement 1—source data 2
Unedited image of the gel shown in Figure 7—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70560/elife-70560-fig7-figsupp1-data2-v2.tif.zip
Tables
.
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HEK293 Flp-In T-REx | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# R78007 RRID:CVCL_U427 | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HEK293 Flp-In T-REx FUBI-eS30-StHA | This paper | See Materials and methods, Cell culture, cell lines, and treatments | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HEK293 Flp-In T-REx FUBI(AA)-eS30-StHA | This paper | AA: G73,74A See Materials and methods, Cell culture, cell lines, and treatments | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HEK293 Flp-In T-REx FUBI(GV)-eS30-StHA | This paper | GV: G74V See Materials and methods, Cell culture, cell lines, and treatments | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HEK293 Flp-In T-REx HASt-C21orf70 | (Zemp et al., 2014) DOI: 10.1242/jcs.138719 | ||
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HEK293 Flp-In T-REx HASt-FUBI-eS30 | This paper | See Materials and methods, Cell culture, cell lines, and treatments | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HEK293 Flp-In T-REx HASt-GFP | (Wyler et al., 2011) DOI: 10.1261/rna.2325911 | ||
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HeLa Flp-In T-REx | (Häfner et al., 2014) DOI: 10.1038/ ncomms5397 | Obtained from T. Mayer (University of Konstanz) | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HeLa Flp-In T-REx FUBI-eS30-StHA | This paper | See Materials and methods, Cell culture, cell lines, and treatments | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HeLa Flp-In T-REx FUBI(AA)-eS30-StHA | This paper | AA: G73,74A See Materials and methods, Cell culture, cell lines, and treatments | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HeLa Flp-In T-REx FUBI(GV)-eS30-StHA | This paper | GV: G74V See Materials and methods, Cell culture, cell lines, and treatments | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HeLa FRT/TetR | Other | Obtained fromM. Beck (EMBL, Heidelberg) | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HeLa FRT/TetR EGFP-USP36 | This paper | See Materials and methods, Cell culture, cell lines, and treatments | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HeLa FRT/TetR EGFP-USP36(CA) | This paper | CA: C131A See Materials and methods, Cell culture, cell lines, and treatments | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HeLa Kyoto, HeLa K | Other | RRID:CVCL_1922 | Obtained from D. Gerlich (IMBA, Vienna) |
| Antibody | anti-AAMP (rabbit polyclonal) | This paper | WB (1:800) See Materials and methods, Antibodies | |
| Antibody | anti-β-actin (mouse monoclonal) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Cat# sc-47778 RRID:AB_626632 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-C21ORF70 (rabbit polyclonal) | (Montellese et al., 2020) DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkx253 | WB (1:500) | |
| Antibody | anti-EIF1AD | Proteintech | Cat# 20528-1-AP RRID:AB_10693533 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-ENP1 (rabbit polyclonal) | (Zemp et al., 2009) DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200904048 | IF (1:15,000) WB (1:1000) | |
| Antibody | anti-eS1 (RPS3A) (rabbit polyclonal) | (Wyler et al., 2011) DOI: 10.1261/rna.2325911 | WB (1:1000) | |
| Antibody | anti-eS26 (RPS26) (rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat# ab104050 RRID:AB_10710999 | WB (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti-FAU (FUBI-eS30) (rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat# ab135765 | WB (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti-FUBI (rabbit polyclonal) | This paper | WB (1:2000) See Materials and methods, Antibodies | |
| Antibody | anti-HA (mouse monoclonal) | Enzo Life Sciences | ENZ-ABS120-0200 | IF (1:2000) WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-His (mouse monoclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# H1029 RRID:AB_260015 | WB (1:2000) |
| Antibody | anti-LSG1 (rabbit polyclonal) | (Wyler et al., 2014) DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.08.013 | WB (1:3000) | |
| Antibody | anti-LTV1 (rabbit polyclonal) | (Zemp et al., 2009) DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200904048 | IF (1:4000) WB (1:2000) | |
| Antibody | anti-NMD3 (rabbit polyclonal) | (Zemp et al., 2009) DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200904048 | IF (1:1000) WB (1:10,000) | |
| Antibody | anti-NOB1 (rabbit polyclonal) | (Zemp et al., 2009) DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200904048 | IF (1:5000) WB (1:2000) | |
| Antibody | anti-NOC4L (rabbit polyclonal) | (Wyler et al., 2011) DOI: 10.1261/rna.2325911 | WB (1:5000) | |
| Antibody | anti-PNO1 (DIM2) (rabbit polyclonal) | (Zemp et al., 2009) DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200904048 | IF (1:2000) WB (1:2000) | |
| Antibody | anti-RIOK1 (rabbit polyclonal) | (Widmann et al., 2012) DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E11-07-0639 | IF (1:8000) WB (1:1000) | |
| Antibody | anti-RIOK2 (rabbit polyclonal) | (Zemp et al., 2009) DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200904048 | IF (1:5000) WB (1:5000) | |
| Antibody | anti-RRP12 (rabbit polyclonal) | (Wyler et al., 2011) DOI: 10.1261/rna.2325911 | IF (1:2000) WB (1:1000) | |
| Antibody | anti-Strep (mouse monoclonal) | IBA GmbH | Cat# 2-1507-001 RRID:AB_513133 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-TRIP4 (rabbit polyclonal) | This paper | WB (1:50,000) See Materials and methods, Antibodies | |
| Antibody | anti-TSR1 (rabbit polyclonal) | ##(Zemp et al., 2014)# DOI: 10.1242/jcs.138719 | WB (1:10,000) | |
| Antibody | anti-uL23 (RPL23A) (rabbit polyclonal) | (Wyler et al., 2011) DOI: 10.1261/rna.2325911 | WB (1:200) | |
| Antibody | anti-uS3 (RPS3) (rabbit polyclonal) | (Zemp et al., 2009) DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200904048 | WB (1:1000) | |
| Antibody | anti-USP10 (rabbit polyclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# HPA006731 RRID:AB_1080495 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-USP16 (rabbit polyclonal) | Bethyl Laboratories | Cat# A301-615A RRID:AB_1211387 | WB (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti-USP36 (rabbit polyclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# HPA012082 RRID:AB_1858682 | IF (1:1000) WB (1:250) |
| Antibody | goat anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 594 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A-11005, RRID:AB_2534073 | IF (1:250) |
| Antibody | goat anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 488 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A-11008, RRID:AB_143165 | IF (1:250) |
| Antibody | goat anti-mouse Alexa Fluor Plus 680 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A32729 RRID:AB_2633278 | WB (1:10,000) |
| Antibody | goat anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor Plus 800 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A32735, RRID:AB_2633284 | WB (1:10,000) |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pC2Pi/control | (Boneberg et al., 2019) DOI: 10.1261/rna.069609.118 | See Materials and methods, Molecular cloning | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pC2Pi/USP36i-g1 | This paper | USP36 guide 1 See Materials and methods, Molecular cloning | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pC2Pi/USP36i-g2 | This paper | USP36 guide 2 See Materials and methods, Molecular cloning | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCDNA5/FRT/TO/FUBI-eS30-StHA | This paper | See Materials and methods, Molecular cloning | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCDNA5/FRT/TO/FUBI(AA)-eS30-StHA | This paper | AA: G73,74A See Materials and methods, Molecular cloning | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCDNA5/FRT/TO/FUBI(GV)-eS30-StHA | This paper | GV: G74V See Materials and methods, Molecular cloning | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCDNA5/FRT/TO/EGFP-USP36 | This paper | See Materials and methods, Molecular cloning | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCDNA5/FRT/TO/EGFP-USP36(CA) | This paper | CA: C131A See Materials and methods, Molecular cloning | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCDNA5/FRT/TO/HASt-FUBI-eS30 | This paper | See Materials and methods, Molecular cloning | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pDEST/LTR/Flag-HA-USP36 | Addgene (Sowa et al., 2009) DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.04.042 | Cat# 22579 RRID:Addgene_22579 | See Materials and methods, Molecular cloning |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pET-28b(+)/His6-FUBI-EGFP | This paper | See Materials and methods, Molecular cloning | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pET-28b(+)/His6-Ub-EGFP | This paper | See Materials and methods, Molecular cloning | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pFBD/EGFP/His10-USP36-TEV-St | This paper | pFBD: pFastBac Dual See Materials and methods, Molecular cloning | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pFBD/EGFP/His10-USP36(CA)-TEV-St | This paper | pFBD: pFastBac Dual, CA: C131A See Materials and methods, Molecular cloning | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pQE30/His6-FUBI-eS30 | This paper | See Materials and methods, Molecular cloning | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pQE30/His6-FUBI(AA)-eS30 | This paper | AA: G73,74A See Materials and methods, Molecular cloning | |
| Sequence-based reagent | QuikChange primers for FUBI(AA)-eS30 | Sigma-Aldrich | 5'-GCAGGCCGCATGCTTGcAGcTAAAGTTCATGGTTCC-3', 5'-GGAACCATGAACTTTAgCTgCAAGCATGCGGCCTGC-3' See Materials and methods, Molecular cloning | |
| Sequence-based reagent | QuikChange primers for FUBI(GV)-eS30 | Sigma-Aldrich | 5'-GGCCGCATGCTTGGAGtTAAAGTTCATGGTTCC-3', 5'-GGAACCATGAACTTTAaCTCCAAGCATGCGGCC-3' See Materials and methods, Molecular cloning | |
| Sequence-based reagent | QuikChange primers for USP36(CA) | Sigma-Aldrich | 5'-CCACAACCTaGGCAACACCgcCTTTCTCAATGCCACC-3', 5'-GGTGGCATTGAGAAAGgcGGTGTTGCCtAGGTTGTGG-3' See Materials and methods, Molecular cloning | |
| Sequence-based reagent | QuikChange primers for USP36(NdeI) | Sigma-Aldrich | 5’- CCGTGTGCAAGAGCGTCagcGAtACaTAtGACCCCTACTTGGAC-3’, 5'-GTCCAAGTAGGGGTCaTAtGTaTCgctGACGCTCTTGCACACGG-3' See Materials and methods, Molecular cloning | |
| Sequence-based reagent | 5'ITS1 | Microsynth (Rouquette et al., 2005) DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600752 | 5'-CCTCGCCCTCCGGGCTCCGTTAATGATC-3' See Materials and methods, Northern blot analysis | |
| Sequence-based reagent | ITS2 | Microsynth (Rouquette et al., 2005) DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600752 | 5'-GCGCGACGGCGGACGACACCGCGGCGTC-3' See Materials and methods, Northern blot analysis | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Cy3-5'ITS1 | Microsynth (Rouquette et al., 2005) DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600752 | 5'-CCTCGCCCTCCGGGCTCCGTTAATGATC-3' See Materials and methods, Fluorescence in situ hybridization | |
| Sequence-based reagent | si-AAMP | Microsynth | 5’-CAGGAUGGCAGCUUGAUCCUA-3 See Materials and methods, RNA interference | |
| Sequence-based reagent | si-control | Qiagen | Cat# 1027281 | Allstars Negative Control siRNA See Materials and methods, RNA interference |
| Sequence-based reagent | si-eS4X (RPS4X) | Qiagen | 5’-CUGGAGGUGCUAACCUAGGAA-3’ See Materials and methods, RNA interference | |
| Sequence-based reagent | si-FAU (FUBI-eS30) | Qiagen | 5’-CCGGCGCUUUGUCAACGUUGU-3’ See Materials and methods, RNA interference | |
| Sequence-based reagent | si-uS19 (RPS15) | Microsynth (Rouquette et al., 2005) DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600752 | 5’-UCACCUACAAGCCCGUAAA-3’ See Materials and methods, RNA interference | |
| Sequence-based reagent | si-USP10-1 | Qiagen | 5'-UCGCUUUGGAUGGAAGUUCUA-3' See Materials and methods, RNA interference | |
| Sequence-based reagent | si-USP10-2 | Qiagen | 5’-UACGUCAACACCCAUGAUAGA-3’ See Materials and methods, RNA interference | |
| Sequence-based reagent | si-USP10-3 | Qiagen | 5’-AACACAGCUUCUGUUGACUCU-3’ See Materials and methods, RNA interference | |
| Sequence-based reagent | si-USP10-4 | Qiagen | 5’-AAGAACUAGUUCUUACUUCAA-3’ See Materials and methods, RNA interference | |
| Sequence-based reagent | si-USP36-1 | Qiagen, Microsynth | 5’-CAAGAGCGUCUCGGACACCUA-3’ See Materials and methods, RNA interference | |
| Sequence-based reagent | si-USP36-2 | Qiagen | 5’-UCCGUAUAUGUCCCAGAAUAA-3’ See Materials and methods, RNA interference | |
| Sequence-based reagent | si-USP36-3 | Qiagen | 5’-CCGCAUCGAGAUGCCAUGCAU-3’ See Materials and methods, RNA interference | |
| Sequence-based reagent | si-USP36-4 | Qiagen | 5’-UUCCUUGUGAGUAGCUCUCAA-3’ See Materials and methods, RNA interference | |
| Sequence-based reagent | si-XPO1 (CRM1) | Microsynth (Zemp et al., 2009) DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200904048 | 5’-UGUGGUGAAUUGCUUAUAC-3’ See Materials and methods, RNA interference | |
| Chemical compound, drug | cycloheximide, CHX | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# C7698 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Leptomycin B | LC Laboratories | Cat# L-6100 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | tetracycline, tet | Invitrogen | Cat# 550205 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Proteomic analysis of the interactome of WT and non-cleavable FUBI-eS30-StHA.
(S2-1) Spectral counts and SAINT Bayesian false discovery rates (BFDRs) of proteins identified in affinity purification mass spectrometry experiments of HASt-GFP (GFP), FUBI-eS30-StHA wild-type (WT), G73,74A (AA) or G74V (GV) performed in three independent biological replicates. (S2-2) Spectral counts of the confidently identified interactors with a BFDR < 0.01 for at least one bait were normalized to protein length (per 1000 amino acids, UniProt database) after addition of a pseudocount of 0.1. The average spectral counts identified on the individual (AA, GV) and combined (mut) non-cleavable mutants compared to WT FUBI-eS30-StHA were determined as a log2 fold change (log2FC). The enrichment of interactors on mut vs. WT was tested by ANOVA (p value and adjusted p values using FDR correction). Significantly enriched interactors (|log2FC| > one with an adjusted p value < 0.05) were categorized as deubiquitinase (DUB), 40S ribosome biogenesis factor (RBF), 60S RBF, ribosome-associated, or other enriched interactor.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70560/elife-70560-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70560/elife-70560-transrepform-v2.docx





