Control of Arabidopsis shoot stem cell homeostasis by two antagonistic CLE peptide signalling pathways
Figures
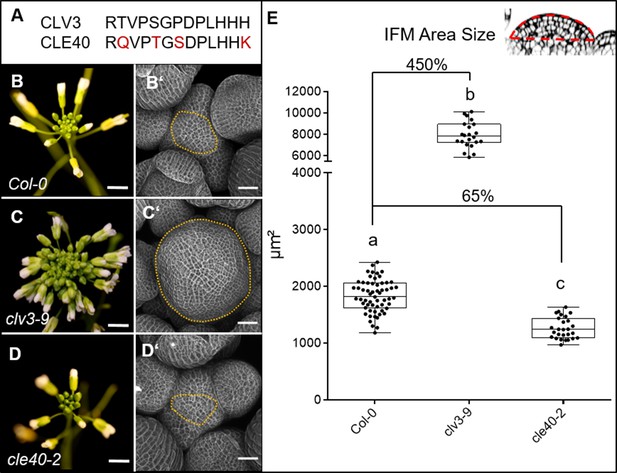
CLV3 and CLE40 exert opposite effects on meristem size.
(A) The amino acid (AA) sequences of the mature CLV3 and CLE40 peptides differ in four AAs (differences marked in red). (B) Col-0 inflorescence at 6 weeks after germination (WAG) with flowers. (B´) Inflorescence meristem (IFM) at 6 WAG, maximum intensity projection (MIP) of a z-stack taken by confocal microscopy. (C) clv3-9 inflorescence at 6 WAG (C´) MIP of a clv3-9 IFM at 6 WAG. (D) Inflorescence of cle40-2 at 6 WAG (D´) MIP of a cle40-2 IFM. (E) Box and whisker plot of IFM sizes of Col-0 (N = 59), clv3-9 (N = 22) and cle40-2 (N = 27) plants. Scale bars: 10 mm (B–D), 50 µm (B’–D’), Statistical groups were assigned after calculating p-values by ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison test (differential grouping from p≤0.01). Yellow dotted lines in (B´–D´) enclose the IFM, red line in the inset meristem in (E) indicates the area that was used for the quantifications in (E).
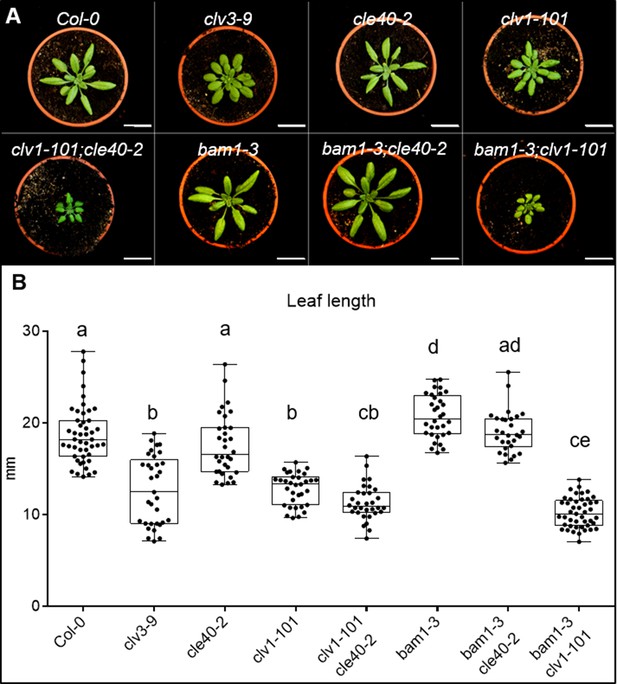
Mutants from the CLV pathway show differences in their leaf lengths.
(A) Wild-type (Col-0) and different single and double mutants (clv3-9, cle40-2, clv1-101, clv1-101;cle40-2, bam1-3, bam1-3;cle40-2, bam1-3;clv1-101) at 4 weeks after germination (WAG). (B) Leaf lengths were measured and plotted. Wild-type (Col-0 N = 47), cle40-2 (N = 32) and bam1-3;cle40-2 (N = 29) mutant plants do not show a significant difference in leaf length to each other. While bam1-3 (N = 32) mutants exhibit in average significantly longer leaves than wild-type plants, the single mutants clv3-9 (N = 33) and clv1-101 (N = 33) and the double mutants clv1-101;cle40-2 (N = 32) and bam1-3;clv1-101 (N = 45) show significantly shorter leaves. Statistical groups were assigned after calculating p-values by ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison test (differential grouping from p≤0.01).
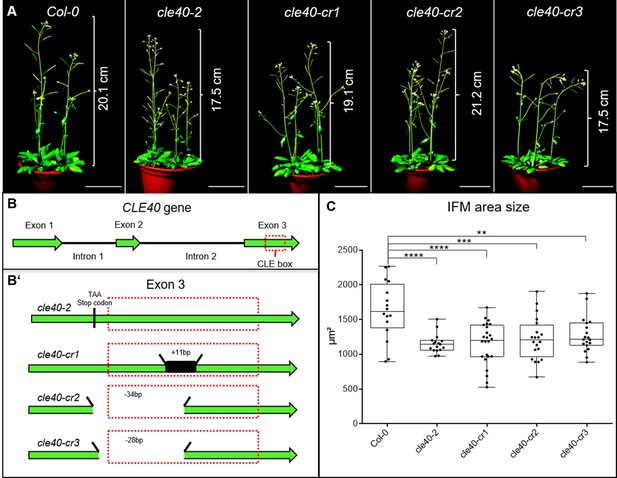
cle40 mutants have smaller meristems.
(A) Wild-type A. thaliana plants (Col-0) and cle40 mutants (cle40-2, cle40-cr1, cle40-cr2, cle40-cr3) at 6 weeks after germination (WAG). All plants show a similar height ranging from 17.5 cm to 21.2 cm and do not have an obvious plant phenotype. (B) Schematic representation of the CLE40 gene, consisting of three exons (green arrows) and two introns. Exon 3 carries the crucial CLE box (dashed red line). (B’) Schematic representation of all four cle40 mutations. All four lines have mutations in or before the CLE box domain in exon 3. cle40-2 mutants were created by transposon mutagenesis, resulting in a stop codon in front of the CLE box (Stahl et al., 2009). cle40-cr1, cle40-cr2 and cle40-cr3 mutants were created using the CRISPR-Cas9 method (Yamaguchi et al., 2017). cle40-cr1 has an 11 bp insertion inside the CLE box domain while cle40-cr2 and cle40-cr3 have a deletion of –34 bp and –28 bp within the CLE box. (C) At 6 WAG, inflorescence meristem (IFM) of wild-type (Col-0 N = 16) and cle40 mutant plants were dissected and the area of each meristem was imaged and measured. All four cle40 mutants show significantly reduced IFM sizes compared to Col-0 plants (cle40-2 N = 17, cle40-cr1 N = 24, cle40-cr2 N = 20, cle40-cr3 N = 19). Statistical stars were assigned after calculating p-values by ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (differential grouping from p≤0.01).
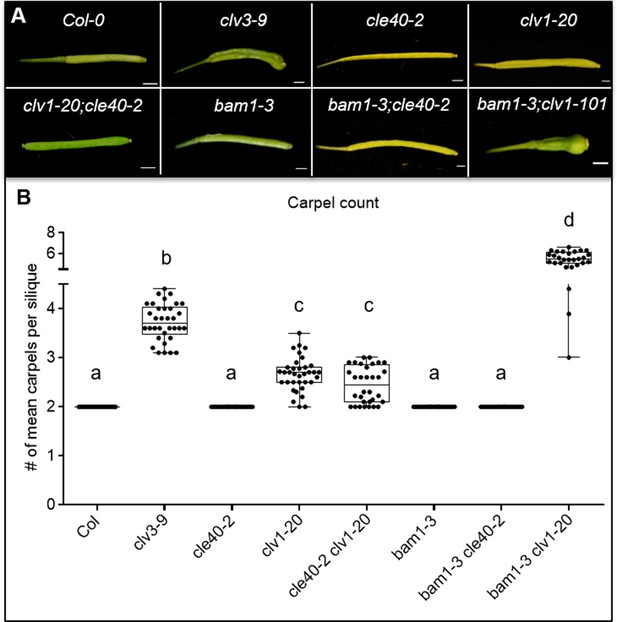
Siliques of various mutants differ in their carpel number.
(A) Carpels of Arabidopsis thaliana plants at 6 weeks after germination (WAG) in wild-type (Col-0) or different mutant backgrounds: clv3-9, cle40-2, clv1-20, clv1-20;cle40-2, bam1-3, bam1-3;cle40-2, bam1-3;clv1-101. (B) Carpel number was counted and plotted. Wild-type (Col-0 N = 290), cle40-2 (N = 300), bam1-3 (N = 300) and bam1-3;cle40-2 (N = 280) mutant plants always develop tow carpels, while clv3-9 (N = 340) plants exhibits 3–5 carpels and clv1-20 (N = 350) and clv1-20;cle40-2 (N = 320) mutants show in average 2–3 carpels. The double mutant bam1-3;clv1-20 (N = 280) develops six carpels in average. N: number depicts number of siliques. Statistical groups were assigned after calculating p-values by ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison test (differential grouping from p≤0.01).
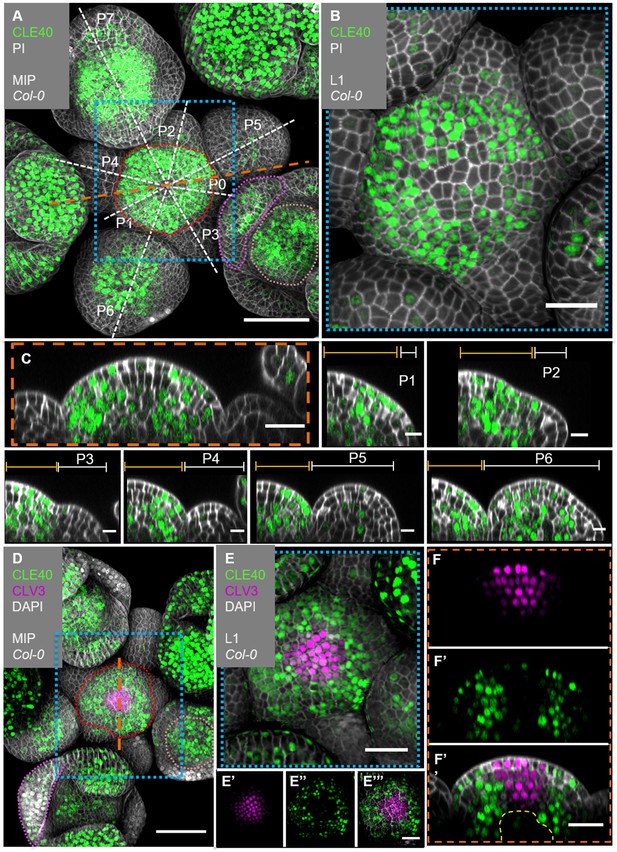
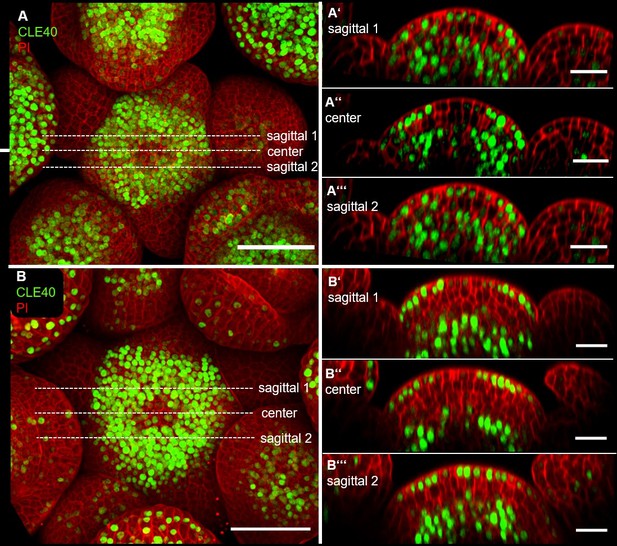
CLE40 and CLV3 show complementary expression patterns in the inflorescence meristem (IFM).
(A) Maximum intensity projection (MIP) of an inflorescence at 5 weeks after germination (WAG) expressing the transcriptional reporter CLE40:Venus-H2B//Col-0 showing CLE40 expression in the IFM, older primordia and sepals (N = 23). (B) The L1 projection shows high expression in the epidermis of the periphery of the IFM and only weak expression in the central zone (CZ). (C) Longitudinal section through the IFM shows expression of CLE40 in the periphery, but downregulated expression in the CZ. (P1 –P6) Longitudinal section through primordia show no CLE40 expression in young primordia (P1–P4), but in the centre of older primordia (P5–P6). (D) The MIP of the double reporter line of CLE40 and CLV3 (CLE40:Venus-H2B;CLV3:NLS-3xmCherry//Col-0) shows CLV3 expression in the CZ surrounded by CLE40 expression in the periphery (N = 12). (E–E’’’) The L1 projection shows CLV3 (E’) expression in the centre of the IFM and CLE40 (E’’) expression in a distinct complementary pattern in the periphery of the IFM. (F) The longitudinal section through the centre of the IFM shows CLV3 expression in the CZ while CLE40 (F’) is mostly expressed in the surrounding cells. (F’’) CLE40 and CLV3 are expressed in complementary patterns. Dashed blue lines indicate magnified areas, dashed white and orange lines indicate planes of longitudinal sections, dashed red line in (A) and (D) marks the IFM area, the dashed pink line marks the sepals, the dashed rose line marks the FMs and dashed yellow line in (F’’) the OC. Scale bars: 50 µm (A, D), 20 µm (B, C, E, E’’’, F’’), 10 µm (P0–P6), PI: propidium iodide; L1: visualization of layer 1 only; P1–P7: primordia at consecutive stages.
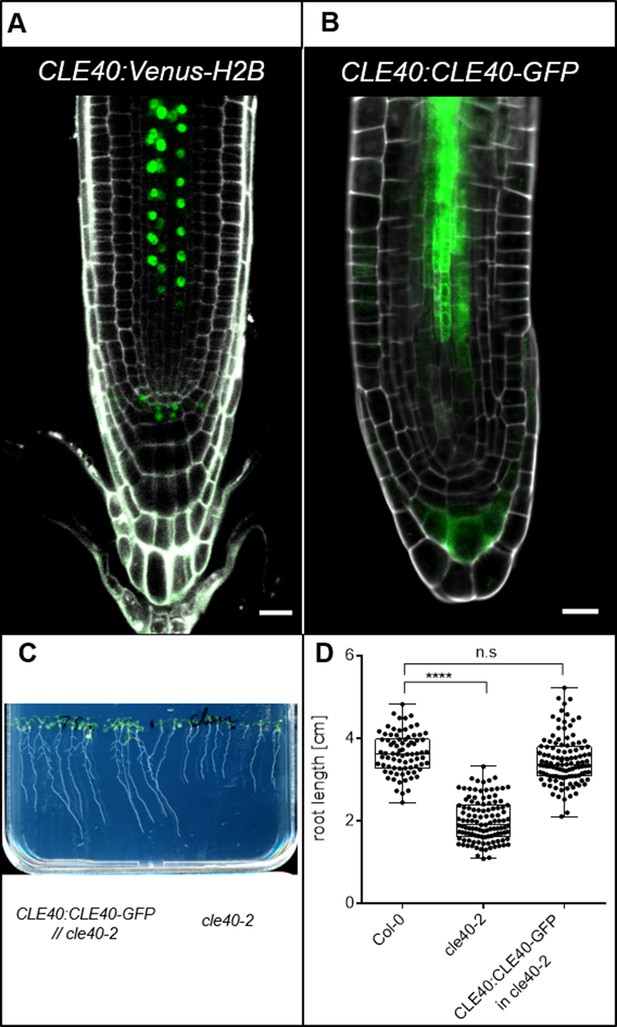
CLE40 transcriptional and translational reporter lines display same expression patterns.
(A) The CLE40:Venus-H2B reporter line shows expression in the columella cells (CC) of the distal root meristem (DRM) and in the stele of main root at 5 days after germination (DAG). (B) The translational CLE40:CLE40-GFP reporter shows also expression of CLE40 in the stele and CCs of the DRM of lateral roots. (C) Roots of cle40-2 mutants carrying the translational CLE40:CLE40-GFP//cle40-2 and cle40-2 mutants seedlings at 11 DAG. (D) Root length of cle40-2 mutants in comparison to Col-0 and cle40-2 mutants carrying a CLE40:CLE40-GFP construct at 11 DAG. The CLE40:CLE40-GFP transgene restores wild-type root growth in cle40-2 mutants. Stars indicate significant differences after calculating p-values by ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (differential grouping from p≤0.0001), N ≥ 79.
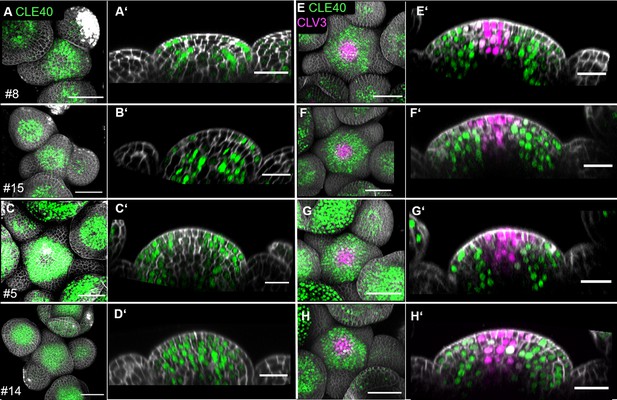
CLE40 and CLV3 expression in multiple inflorescence meristem (IFM).
(A–E) Maximum intensity projections (MIPs) of four independent T1 lines of IFMs at 5 weeks after germination (WAG) expressing the transcriptional reporter CLE40:Venus-H2B//Col-0 showing CLE40 expression in the IFM, flower meristem (FMs) and sepals. (A’–E’) XZ sections through the IFM of (A–E), respectively. XZ sections show expression of CLE40 in the periphery, but downregulated expression in the central zone (CZ) and organizing centre (OC). (F–J) MIP of four different IFMs at 5 WAG expressing the transcriptional reporter CLE40:Venus-H2B;CLV3:NLS-3xmCherry//Col-0 showing CLE40 expression in the IFM, FMs and sepals and CLV3 expression in the CZ. (F’–J’) XZ sections through the IFM of (F–J), respectively. XZ sections show expression of CLE40 in the periphery, but downregulated expression in the CZ and OC. CLV3 is expressed in the stem cells in the CZ in a cone-shaped pattern. Dashed orange line indicates the planes of longitudinal sections; Scale bars: 50 µm (A–J), 20 µm (A’–J’).
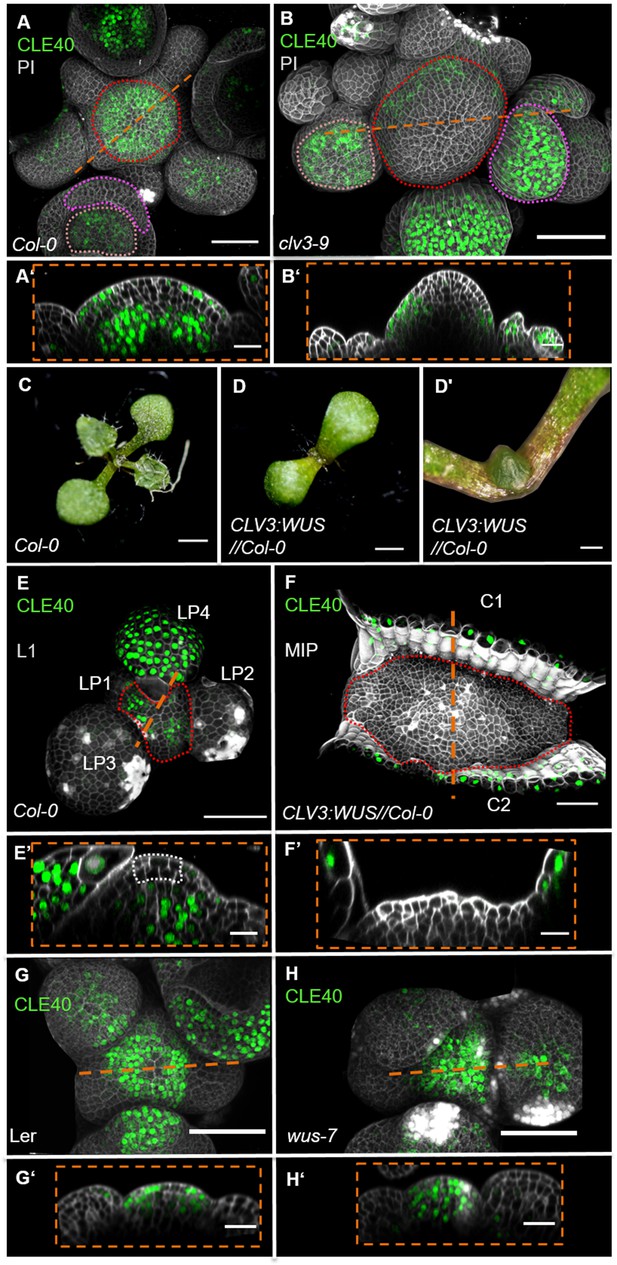
WUS-dependent repression of CLE40 expression in the shoot meristem.
(A) Maximum intensity projection (MIP) of CLE40 expression (CLE40:Venus-H2B//Col-0) at 5 weeks after germination (WAG), (A’) Longitudinal optical section through the centre of the inflorescence meristem (IFM) (indicated by orange line in A) reveals no CLE40 expression in the central zone (CZ) and the centre of the meristem. Cells in the L2 layer also show less CLE40 expression. High CLE40 expression is found in the peripheral zone (PZ) (N = 23). (B) MIP of CLE40 expression in a clv3-9 mutant (CLE40:Venus-H2B//clv3-9) shows expression only in the PZ of the meristem, in flower meristems (FMs) and in sepals (N = 6). (B’) Longitudinal optical section through the IFM depicts no CLE40 expression at the tip and the centre of the meristem. CLE40 expression is only detected in cells at the flanks of the IFM and in sepals. (C) Arabidopsis seedling at 10 days after germination (DAG). (D) Seedling expressing WUS from the CLV3 promoter, 10 DAG. (D’) Magnification of seedling in (D). The meristem fasciates without forming flowers. (E) L1 projection, vegetative seedling with CLE40 expression in the PZ and leaf primordia starting from LP4, at 10 DAG (N = 5). (E’) Longitudinal section of (E) with CLE40 expression primordia and rib meristem or periphery. (F) MIP of fasciated meristem as in (D). CLE40 expression can only be found in the cotyledons (C1 and C2) next to the meristem (N = 5). (F’) Longitudinal optical section shows CLE40 expression only in the epidermis of cotyledons. (G, G’) MIP (G) and longitudinal optical section (G’) of CLE40 expression (CLE40:Venus-H2B//Ler) in a wild- type (Landsberg erecta [L.er]) background at 5 WAG shows no signal in the CZ or OC. CLE40 is confined to the PZ and the centre of older flower primordia, and to sepals (N = 8). (H, H’) MIP of CLE40 in a wus-7 background shows expression through the entire IFM and in the centre of flower primordia. The longitudinal optical section (H’) reveals that CLE40 is also expressed in the CZ as well as in the OC of the IFM (N = 12). Dashed orange lines indicate the planes of longitudinal sections, dashed red line in (A), (B), (E) and (F) marks the IFM area, the dashed pink line in (A) and (B) marks the sepals, the dashed rose line in (A) and (B) marks the FMs, the dashed white line in (E’) marks the CZ. Scale bars: 50 µm (A, B, G, H), 20 µm (A’, B’, E, E’, F, F’, G’, H’), 1 mm (C, D), 500 µm (D’). PI: propidium iodide; L1: layer 1 projection; C: cotyledon; LP: leaf primordium.
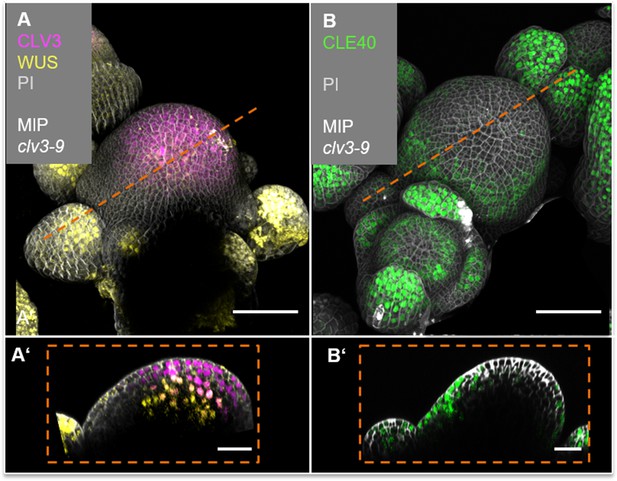
CLE40 expression is lacking in the central zone (CZ) and organizing centre (OC).
(A) Maximum intensity projection (MIP) of CLV3 and WUS expression (CLV3:NLS-mCherry;WUS:NLS-GFP//clv3-9) in a clv3-9 mutant inflorescence meristem (IFM) (N = 5). CLV3 expression is detected at the tip of the meristem, while WUS expression is predominantly found in young primordia surrounding the meristem. (A’) Longitudinal optical section through the IFM shows an extended expression domain of CLV3 in the CZ and WUS-expressing cells in OC of the IFM. (B) MIP of a clv3-9 mutant IFM expressing CLE40:Venus-H2B. CLE40 is expressed in the peripheral zone (PZ) of the IFM, in flower primordia and in mature sepals (N = 6). (B’) Longitudinal optical section through the IFM shows CLE40 expression in the outer layers of the PZ while it is lacking in the CZ and OC, where CLV3 and WUS are expressed. Dashed orange line indicates the planes of longitudinal optical sections; Scale bars: 50 µm (A, B), 10 µm (A’, B’). PI: propidium iodide.
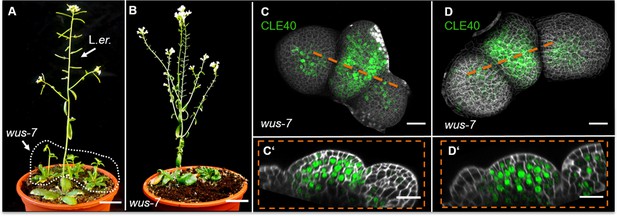
CLE40 expression is extended in wus-7 mutants.
(A) Landsberg erecta (L.er.) wild-type plant at 5 weeks after germination (WAG) shows normal plant growth, while wus-7 mutants at 5 WAG are delayed in their development (dashed white line). (B) wus-7 mutant at 8 WAG. wus-7 mutants develop inflorescence meristems (IFMs) but give rise to sterile flowers that lack inner organs. (C, D) Maximum intensity projection (MIP) of wus-7 IFMs at 5 WAG expressing CLE40:Venus-H2B. CLE40 expression is detected through the entire meristem and in the centre of primordia (N = 12). (C’, D’) Longitudinal optical sections through the meristem show CLE40 expression in an extended pattern in the peripheral zone (PZ) and the organizing centre (OC). Dashed white line in (A) encloses homozygous wus-7 mutants, dashed orange line indicates the planes of longitudinal optical sections; Scale bars: 20 mm (A, B), 20 µm (C–D’).
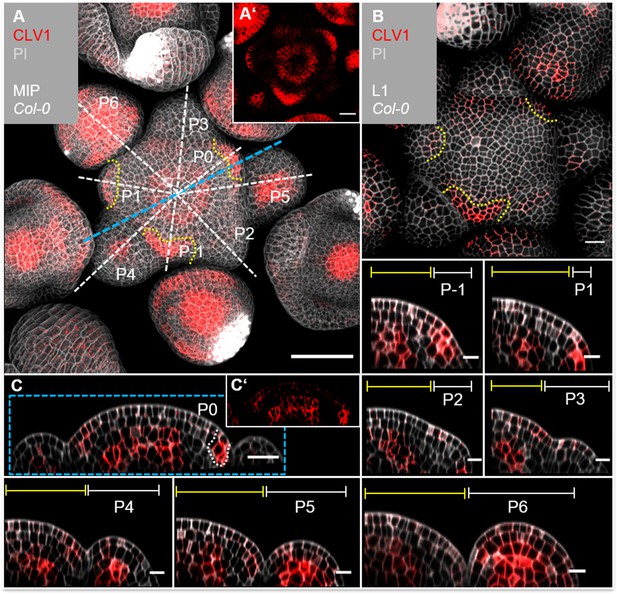
CLV1 is expressed in the organizing centre (OC) and cells of incipient organ primordia.
(A) Maximum intensity projection (MIP) of CLV1 under its endogenous promoter (CLV1:CLV1-GFP//Col-0) at 5 weeks after germination (WAG) shows CLV1 expression in the OC of the meristems, inflorescence meristem (IFM) and flower meristems (FMs), in incipient organ primordia (P-1–P1) and in sepals (N = 15). (A’) MIP of the IFM from (A) without propidium iodide (PI) staining. (B) In the layer 1 (L1) projection, CLV1 expression is detected in cells of incipient organs. (C) Longitudinal section through the IFM shows CLV1 expression in the OC and P0. (C’) XZ section from (C) without PI staining. (P-1–P6) CLV1 expression is detected in incipient organ primordia in L1 and L2 (-P1, P0), in the L2 of P1 and in the OC of the IFM and FMs from P4 to P6. Dashed white and blue lines indicate the planes of longitudinal sections, yellow dashed lines in (A) and (B) mark incipient organ primordia (P-1–P1), yellow lines (P-1–P6) indicate the IFM region, white lines mark the primordium. Scale bars: 50 µm (A), 20 µm (B, C), 10 µm (P1–P6), P: primordium.
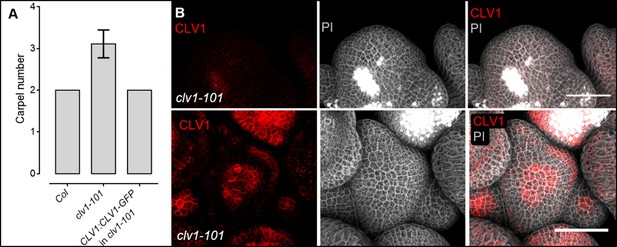
The translational CLV1:CLV1-GFP reporter line rescues the carpel and shoot phenotype of clv1-101 mutants.
(A) Column bar plot shows the average carpel number of Col-0 (N = 260), clv1-101 (N = 320) and clv1-101 carrying the construct CLV1:CLV1-GFP (N = 360) at 5 weeks after germination (WAG). For each plant, 10–20 siliques were analysed. (B) The translational CLV1:CLV1-GFP construct rescues the meristem phenotype of clv1-101 plants. In plants segregating for the CLV1:CLV1-GFP rescue construct, those that lack CLV1 expression (red channel) exhibit a fasciated (bigger) meristem (grey channel) (upper panel). The bottom panel shows CLV1 expression in the centre and the L1 of the meristem and the meristem has a (red channel) wild-type-like structure and size (grey channel). Both inflorescence meristems (IFMs) are from the same segregating T2 line.
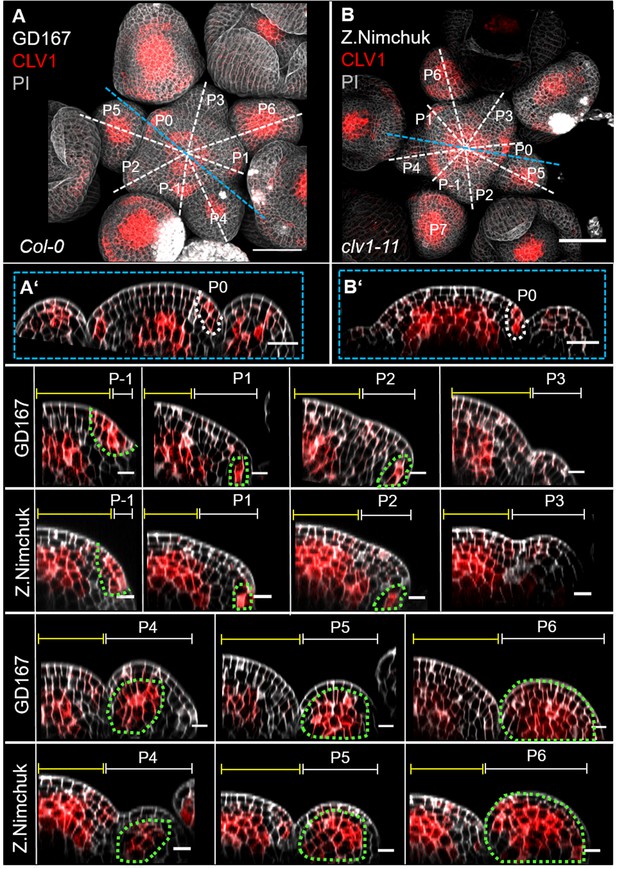
Two independent translational CLV1 reporter lines show exactly the same expression pattern.
(A) Maximum intensity projection (MIP) of the translational CLV1 (CLV1:CLV1-GFP//Col-0) reporter line used in this study at 5 weeks after germination (WAG) shows CLV1 expression in the organizing centre (OC) of the meristems, inflorescence meristem (IFM) and flower meristems (FMs), in incipient organ primordia (P-1–P1) and in sepals. (B) MIP of the translational CLV1 (CLV1:CLV1-2xGFP//clv1-11) reporter line published by Z. Nimchuk in 2011 at 5 WAG shows CLV1 expression in the OC of the meristems, IFM and FMs, in incipient organ primordia (P-1–P1) and in sepals. (A’, B’) Longitudinal cross-section through the centre of the IFMs of both translational reporter lines (GD167 and Z. Nimchuk) shows CLV1 expression in the OC and P0. (P-1–P6) CLV1 expression is detected in incipient organ primordia in L1 and L2 (-P1, P0), in the L2 of P1 and P2 and in the OC of the IFM and FMs from P4 to P6 in both CLV1 reporter lines (GD167 and Z. Nimchuk). Dashed white and blue lines indicate the planes of optical XZ sections, green dashed lines in P-1–P6 mark cells expressing CLV1 in the primordia, yellow lines (P-1–P6) indicate the IFM region and white lines mark the primordium. Scale bars: 50 µm (A, B), 20 µm (A', B'), 10 µm (P1–P6). PI: propidium iodide; P: primordium.
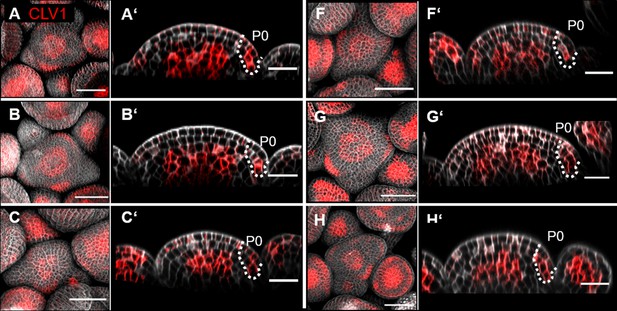
CLV1 expression in multiple inflorescence meristem (IFMs).
(A–H) Maximum intensity projection (MIP) of six different IFMs at 5 weeks after germination (WAG) expressing the translational reporter CLV1:CLV1-GFP//Col-0 showing CLV1 expression in the centre of the IFM and flower meristems (FMs) and in incipient primordia. (A’–H’) Longitudinal sections through the centre of the IFM of (A–H), respectively. XZ sections show expression of CLV1 in the organizing centre (OC) in the IFM and FMs and in cells in the L2 and L1 of P0. Dashed white line marks P0. Scale bars: 50 µm (A–H), 20 µm (A’–H’).
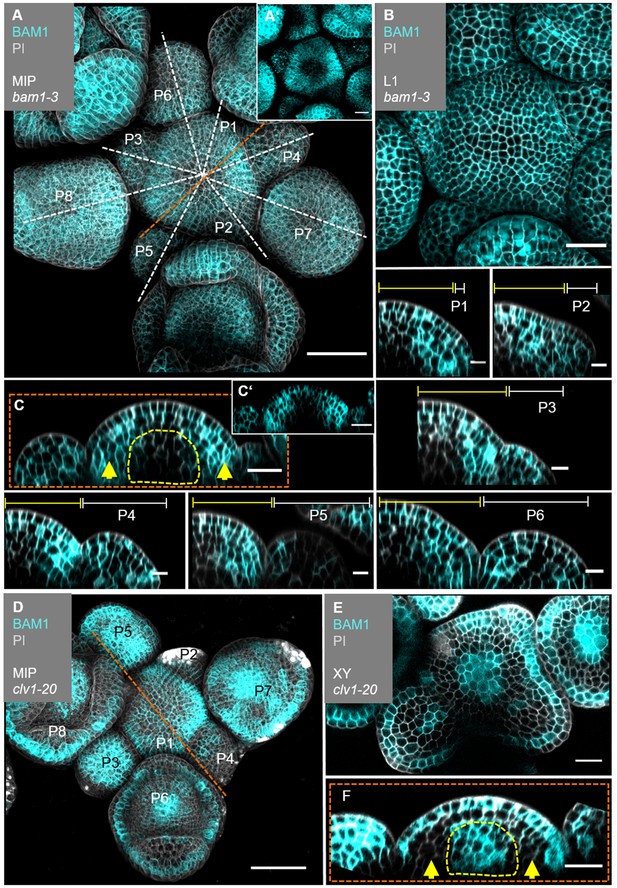
BAM1 expression is elevated in the flanks of the inflorescence meristem (IFM) and not detectable in the organizing centre (OC).
(A) Maximum intensity projection (MIP) of BAM1 under its endogenous promoter (BAM1:BAM1-GFP//bam1-3) at 5 weeks after germination (WAG). BAM1 expression is detected nearly throughout the entire inflorescence (IFM, flower meristem [FM], sepals) with weak expression in the central zone (CZ) of IFM and FMs (N = 15). (A’) MIP of the IFM from (A) without propidium iodide (PI) staining. (B) The layer 1 (L1) projection of the IFM shows ubiquitous expression of BAM1. (C) Longitudinal optical section through the IFM shows elevated BAM1 expression in the flanks (yellow arrows) and a lack of BAM1 expression in the OC. (C’) XZ section from (C) without PI staining. (P1–P6) BAM1 expression is found in all primordia cells. (D) MIP of BAM1 in a clv1-20 mutant (BAM1:BAM1-GFP//bam1-3;clv1-20). BAM1 expression is detected in most parts of the inflorescence, especially in the centre of the IFM and FMs (N = 9). (E) Cross-section (XY) of the IFM (from D) shows BAM1 expression in a clv1-20 mutant in the CZ (IFM and FMs) and the L1/L2. (F) Longitudinal optical section through the meristem (from D) shows BAM1 expression in the OC and the L1, while no BAM1 expression is detected in the peripheral zone (PZ) (yellow arrows). Dashed white and orange lines indicate longitudinal sections; dashed yellow lines in (C) and (F) mark the OC area, yellow lines (P1–P6) indicate the IFM region, white lines (P1–P6) mark the primordium and yellow arrows indicate high (C) or no (F) BAM1 expression in the PZ. Scale bars: 50 µm (A, D), 20 µm (B, C, E, F), 10 µm (P1–P6). P: primordium.
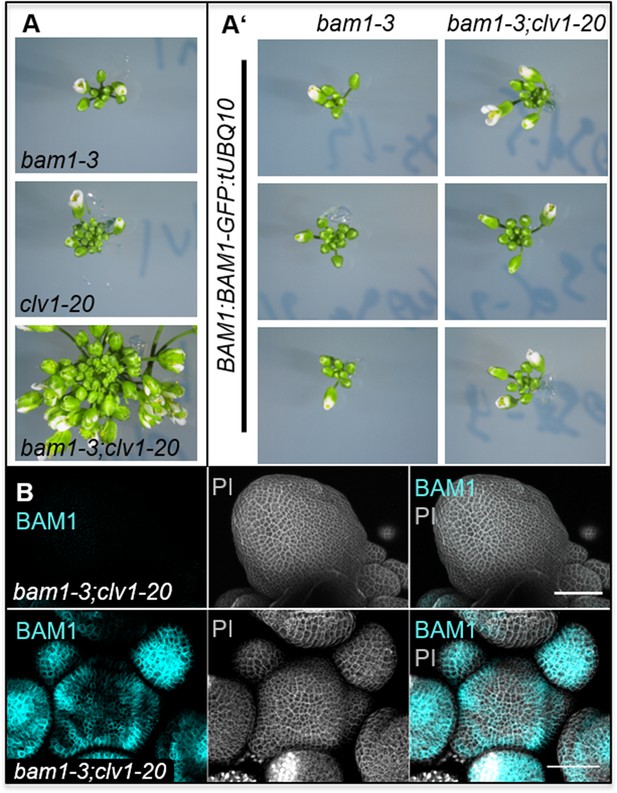
The translational BAM1:BAM1-GFP reporter line rescues the shoot phenotype of the double mutant bam1-3;clv1-20.
(A) Inflorescences (IFs) of bam1-3, clv1-20 at bam1-3;clv1-20 at 5 weeks after germination (WAG). The IF of clv1-20 mutants is enlarged compared to bam1-3 mutants. IFs of bam1-3;clv1-20 have a highly increased number of flowers and show an highly fasciated inflorescence meristem (IFM) compared to bam1-3 and clv1-20 mutants. (A’) IFs of bam1-3 mutants carrying the translational BAM1:BAM1-GFP show a wild-type-like IF and double mutants of bam1-3;clv1-20 plants carrying the BAM1:BAM1-GFP construct have IFs comparable to clv1-20 mutants. (B) The translational BAM1:BAM1-GFP construct rescues the fasciated meristem phenotype of bam1-3;clv1-20 plants. The upper panel shows no BAM1 expression (cyan channel) and a highly fasciated meristem (grey channel). The bottom panel shows BAM1 expression of the BAM1:BAM1-GFP construct in the IFM and primordia (cyan channel). Endogenous BAM1 expression rescues the fasciated meristem phenotype of bam1-3;clv1-20 (grey channel). Both meristems are from the same T2 line. Scale bars: 50 µm (B).
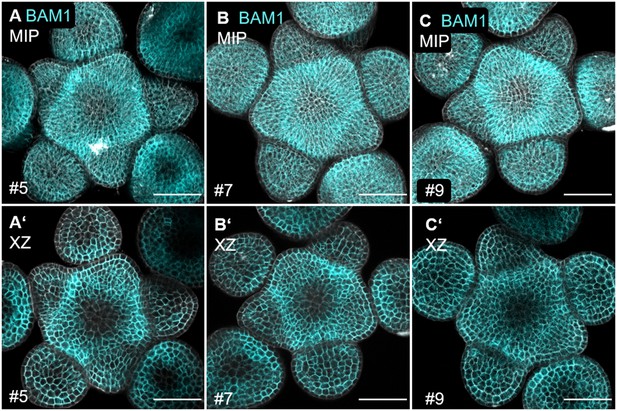
The translational BAM1 reporter line shows similar expression in three independent T1 lines.
(A–C) Maximum intensity projections (MIPs) of three independent T1 lines of inflorescence meristems (IFMs) at 5 weeks after germination (WAG) expressing the translational reporter BAM1:BAM1-GFP//bam1-3 showing BAM1 expression in the IFM, flower meristems (FMs) and sepals. (A’–C’) XY sections of (A–C), respectively. XY sections show expression of BAM1 in all primordia and in the periphery of the IFM, but downregulated expression in the centre.
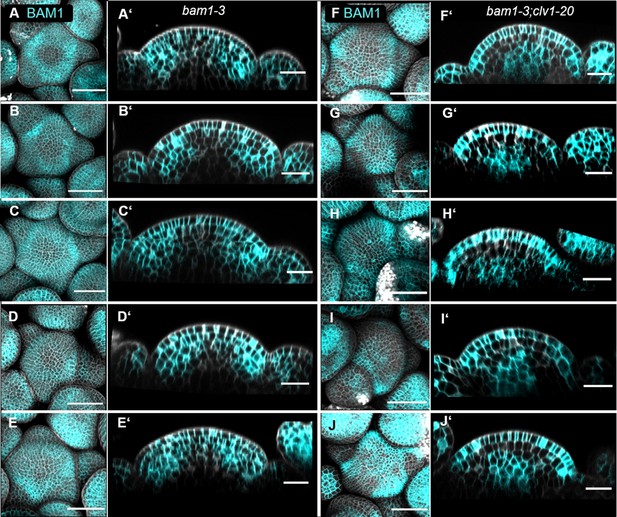
Expression of the translational BAM1 reporter (BAM1:BAM1-GFP) shifts from the PZ in bam1-3 mutants to the organizing centre (OC) and L1 in bam1-3;clv1-20 double mutants.
(A–E) Maximum intensity projection (MIP) of five different inflorescence meristems (IFMs) at 5 weeks after germination (WAG) expressing the translational reporter BAM1:BAM1-GFP//bam1-3 showing BAM1 expression in the IFM and all primordia. (A’-–E’) XZ sections through the IFM of (A–E), respectively. XZ sections show expression of BAM1 in the peripheral zone (PZ), but downregulated expression in the OC. (F–J) MIP of five different IFMs at 5 WAG expressing the transcriptional reporter BAM1:BAM1-GFP//bam1-3;clv1-20. (F’–J’) XZ sections through the IFM of (F–J), respectively. XZ sections show that the expression of BAM1 shifted to the OC and L1 in a clv1-20 mutant background. Scale bars: 50 µm (A–J), 20 µm (A’–J’).
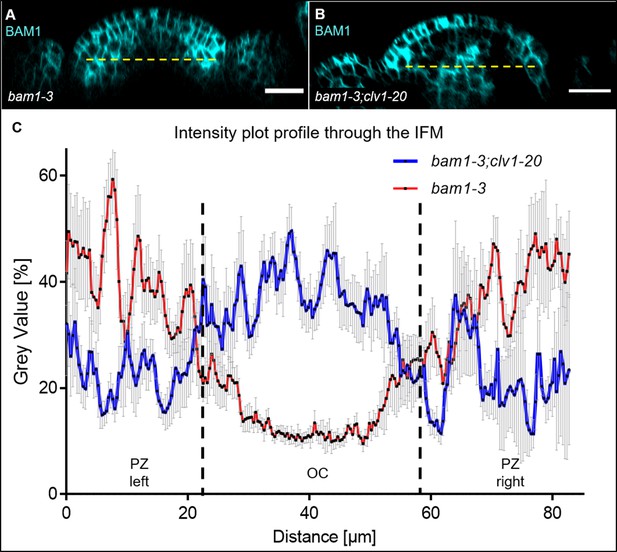
Quantification of expression pattern of the translational BAM1 reporter line in bam1-3 (N = 9) and bam1-3;clv1-20 (N = 9) mutants.
(A) Optical XZ section through the centre of an inflorescence meristem (IFM) carrying the BAM1:BAM1-GFP//bam1-3 construct. BAM1 expression is elevated in the peripheral zone (PZ), downregulated in the organizing centre (OC) and weakly expressed in the primordia. (B) Longitudinal section through the IFM of a bam1-3;clv1-20 double mutant carrying the BAM1:BAM1-GFP construct. BAM1 expression is elevated in the L1, downregulated in the PZ and highly expressed in the OC. (C) Intensity plot profile of grey values through the centre of the XZ cross-sections of bam1-3 and bam1-3;clv1-20 mutants expressing the BAM1:BAM1-GFP reporter line (yellow dashed lines in A and B). For each genotype, nine meristems were analysed and the mean value (red and blue lines) with its standard deviation (error bars: grey) was plotted. Scale bars: 20 µm (A, B).
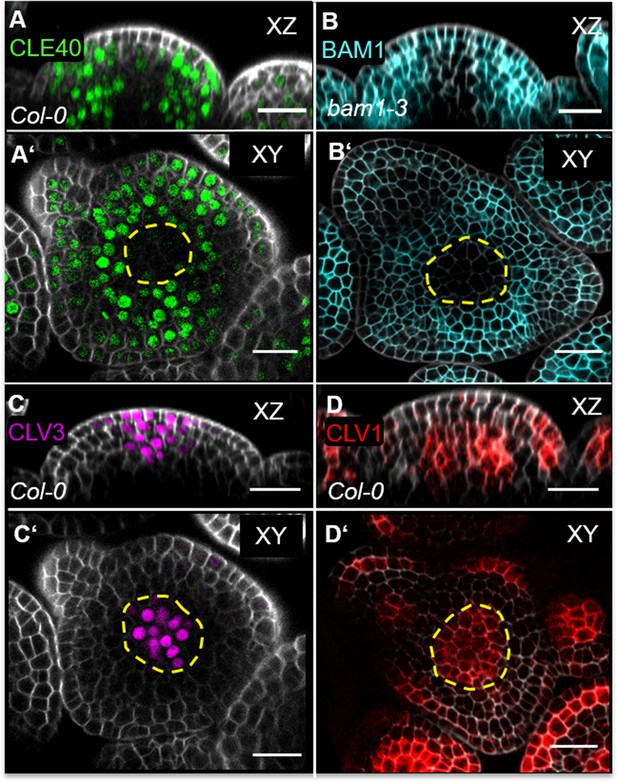
BAM1 and CLV1 are receptors for CLE40 and CLV3, respectively.
(A, A’) Longitudinal and cross-sections of CLE40 (CLE40:Venus-H2B//Col-0) through the inflorescence meristem (IFM) show CLE40 expression in the peripheral zone (PZ) while no CLE40 expression is detected in the central zone (CZ) or the organizing centre (OC) (dashed yellow line). (B, B’) In longitudinal sections of BAM1 (BAM1:BAM1-GFP//bam1-3) through the IFM, elevated BAM1 expression in the PZ and young primordia can be detected, while low expression is found in the CZ and no expression is observed in the OC (dashed yellow line). (C, C’) Longitudinal and transversal section of CLV3 through the IFM (CLV3:NLS-3xmCherry//Col-0) shows CLV3 expression in the CZ (dashed yellow line). (D, D’) The native expression of CLV1 (CLV1:CLV1-GFP//Col-0) in an longitudinal and transversal section through the IFM is depicted in the OC (dashed yellow line) and in cells of the L1 and L2 close to emerging primordia. Scale bars: 20 µm (A–D’), yellow dashed lines indicate the OC (in A’, B’, D’) or the CZ (C’).
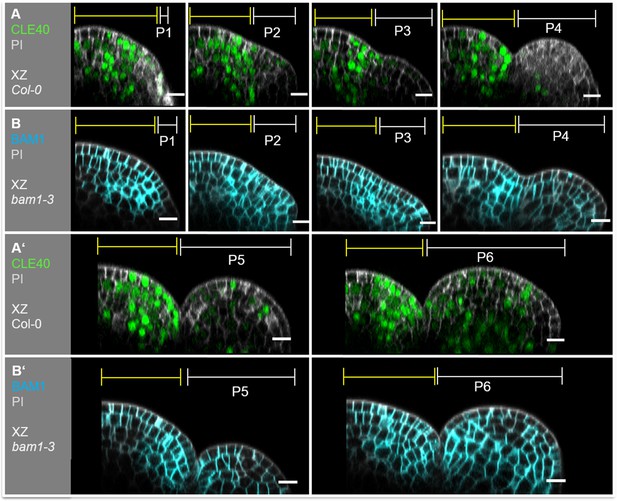
Expression patterns of CLE40 and BAM1 overlap in the inflorescence meristem (IFM).
Longitudinal sections through an IFM and its developing primordia P1–P6 expressing either (A) CLE40 (CLE40:Venus-H2B) (N = 23) or (B) BAM1 (BAM1:BAM1-GFP) (N = 15). In the IFM, CLE40 and BAM1 expression patterns overlap in the peripheral zone (PZ), while both genes are lacking in the organizing centre (OC). No CLE40 expression is detected in young primordia in P1–P3. From P4 on a faint signal in central zone (CZ) of the primordia express CLE40. Its expression expands in P5 and can be found in almost all cells of P6. BAM1 is expressed ubiquitously in all primordia from P2 to P6. Yellow lines (P1–P6) indicate the IFM region, white lines (P1–P6) mark the primordium, Scale bar: 10 µm, P: primordium.
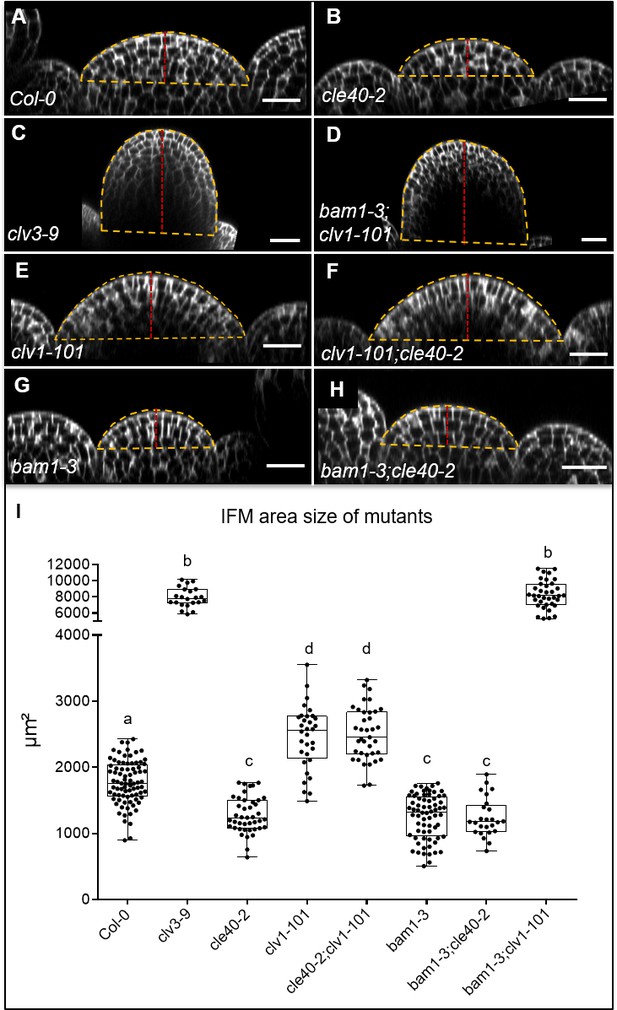
Inflorescence meristem (IFM) size of single and double mutants.
XZ sections through the centre of IFMs of (A) Col-0, (B) cle40-2, (C) clv3-9, (D) bam1-3;clv1-101, (E) clv1-101, (F) clv1-101;cle40-2, (G) bam1-3 and (H) bam1-3;cle40-2 plants. (I) Box and whisker plot of the IFM area size of Col-0 (N = 82), various single (clv3-9 [N = 22], cle40-2 [N = 42], clv1-101 [N = 32], bam1-3 [N = 68]) and double mutants (cle40-2;clv1-101 [N = 37], cle40-2;bam1-3 [N = 25] and bam1-3;clv1-101 [N = 36]) at 6 weeks after germination (WAG).The yellow dashed line depicts the area of the meristem that was measured, and the dashed red line indicates the height of the meristems. Scale bar: 20 µm (A–H). Statistical groups were assigned after calculating p-values by ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison test (differential grouping from p≤0.01).
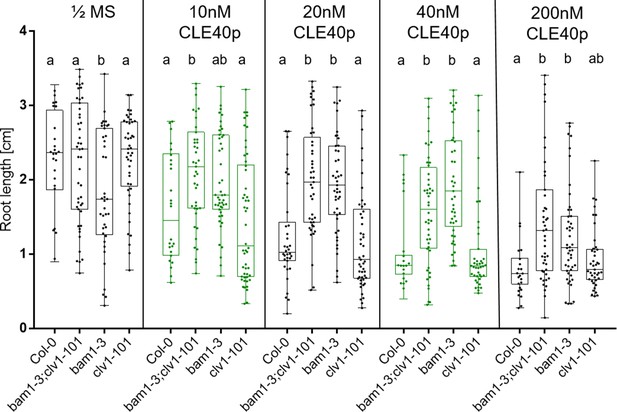
bam1-3 and bam1-3;clv1-101 mutants are resistant to CLE40 peptide treatment.
Root length of Col-0, bam1-3;clv1-101, bam1-3, and clv1-101 plants grown on ½ Murashige & Skoog (MS) media containing no CLE40 peptide, 10 nM, 20 nM, 40 nM or 200 nM CLE40 peptide were measured at 11 days after germination (DAG). Col-0 and clv1-101 plants show a reduced root length compared to bam1-3 and bam1-3;clv1-101 mutant plants when grown on CLE40 peptide. Statistical groups were assigned after calculating p-values by ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison test (differential grouping from p≤0.01).
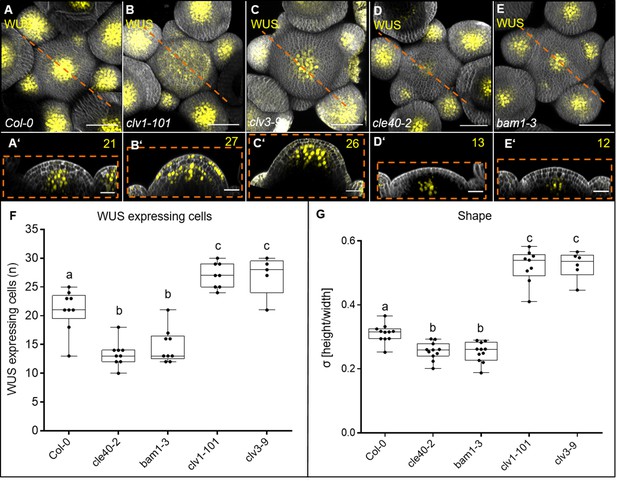
CLE40 and BAM1 promote WUS expression.
(A–E’) Maximum intensity projection (MIP) and longitudinal optical section of inflorescences at 5 weeks after germination (WAG) expressing the transcriptional reporter WUS:NLS-GFP in a (A, A’) Col-0, (B, B’) clv1-101, (C, C’) clv3-9, (D, D’) cle40-2 and (E, E’) bam1-3 background. In (A) wild-type plants, the WUS domain is smaller compared to the expanded WUS domain in (B) clv1-101 and (C) clv3-9 mutants. The WUS domain of (D) cle40-2 and (E) bam1-3 mutants is decreased compared to wild-type plants. Longitudinal optical sections of (B’) clv1-101 and (C’) clv3-9 mutants expand along the basal-apical axis while the meristem shape of (D’) cle40-2 and (E’) bam1-3 mutants is flatter compared to (A’) wild-type plants,. (F) Box and whisker plot shows the number of WUS-expressing cells in a single plane through the organizing centre (OC) of inflorescence meristems (IFMs) of Col-0 (N = 9), cle40-2 (N = 9), bam1-3 (N = 9), clv1-101 (N = 8) and clv3-9 (N = 5). (G) At 5 WAG, bam1-3 (N = 11) and cle40-2 (N = 11) mutants have flatter meristems than wild-type plants (decreased σ value compared to Col-0 [N = 11]), while clv1-101 [N = 9] and clv3-9 [N = 6] mutants increase in their IFM height showing a higher σ value. Scale bars: 50 µm (A–E), 20 µm (A’–E’), Statistical groups and stars were assigned after calculating p-values by ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison test (differential grouping from p≤0.01). yellow numbers: WUS-expressing cells in the CZ; σ value: height/width of IFMs.
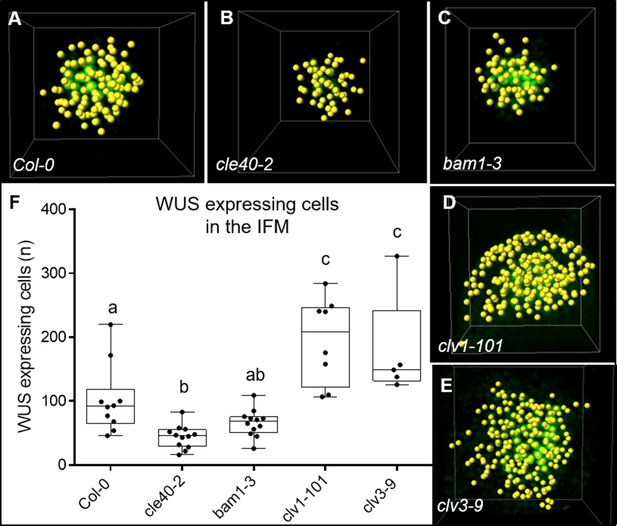
Number of WUS-expressing cells in the inflorescence meristem (IFM) of various mutant backgrounds detected with Imaris software.
(A–E) Spot detection of WUS-expressing cells in the IFMs of (A) Col-0, (B) cle40-2, (C) bam1-3, (D) clv1-101 and (E) clv3-9 mutants via Imaris software. (F) Box and whisker plot shows the number of WUS-expressing cells that were detected by the Imaris software in the IFMs of Col-0 (N = 9), cle40-2 (N = 9), bam1-3 (N = 9), clv1-101 (N = 8) and clv3-9 (N = 5). Statistical groups were assigned after calculating p-values by ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison test (differential grouping from p≤0.05).
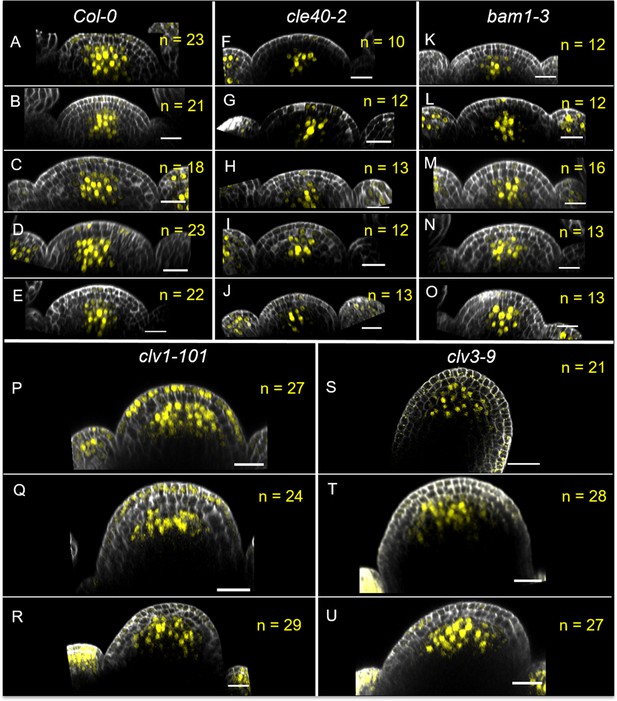
Number of WUS-expressing cells in a longitudinal section through the meristem in multiple inflorescence meristems (IFMs).
(A–U) Longitudinal optical sections through the IFM of 3–5 (A–E) Col-0, (F–J) cle40-2, (K–O) bam1-3, (P–R) clv1-101 and (S–U) clv3-9 plants expressing the transcriptional reporter WUS:NLS-GFP. Scale bars: 20 µm (A–U), yellow numbers: WUS-expressing cells in the central zone (CZ).
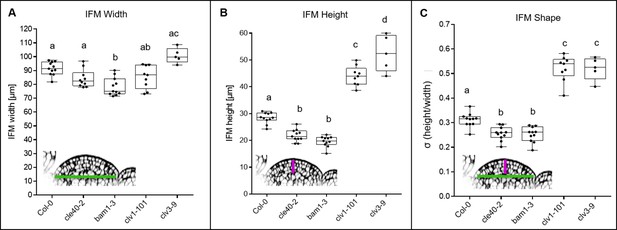
Inflorescence meristem (IFM) height, width and shape at 5 weeks after germination (WAG).
(A) The width of Col-0 (N = 11), cle40-2 (N = 10), bam1-3 (N = 11), clv1-101 (N = 9) and clv3-9 (N = 5) mutants at 5 WAG does not significantly differ from each other. The average width lays between 85 and 100 µm. Wild-type plants are in average 90 µm wide while clv3-9 mutants depict the widest meristem average of 100 µm. Only bam1-3 mutants have with an average of 79 µm a significantly smaller meristem wide compared to wild-type plants. (B) The height of cle40-2 (~22 µm) and bam1-3 (~23 µm) mutants is significantly shorterat 5 WAG compared to wild-type plants (~28 µm). In contrast, clv1-101 and clv3-9 have significantly higher meristems than Col-0, cle40-2 and bam1-3 mutants. (C) The σ-value represents the shape of the meristem and is defined by the quotient of height and width. cle40-2 and bam1-3 mutants have a significantly smaller σ-value compared to wild-type plants, resulting in flatter meristems. clv1-101 and clv3-9 have an average of 0.55, a significantly higher σ-value and thus have more dome-shaped meristems. Green line in the inset meristem in (A) indicates the width that was used for the quantifications in (A); magenta line in the inset meristem in (B) indicates the height that was used for the quantifications in (B); green and magenta lines in the inset meristem in (C) indicate the width and height that was used for the quantifications in (C). Statistical groups were assigned after calculating p-values by ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison test (differential grouping from p≤0.01).
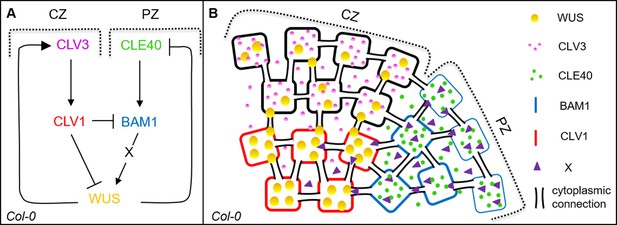
Schematic model of two intertwined signalling pathways in the shoot meristem.
(A, B) Schematic representation of two negative feedback loops in the inflorescence meristem (IFM) of Arabidopsis thaliana. CLV3 in the central zone (CZ) binds to the LRR receptor CLV1 to activate a downstream signalling cascade which leads to the repression of the transcription factor WUS. In a negative feedback loop WUS protein moves to the stem cells to activate CLV3 gene expression. In the peripheral zone (PZ) of the IFM, a second negative feedback loop controls meristem growth by CLE40 and its receptor BAM1. CLE40 binds to BAM1 in an autocrine manner, leading to the activation of a downstream signal ‘X’ which promotes WUS activity. WUS protein in turn represses the expression of the CLE40 gene. Arrows indicate a promoting effect, and the blocked line indicates a repressing signal.
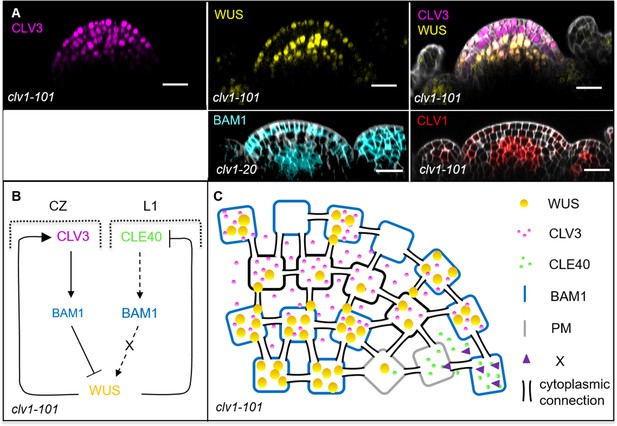
Schematic model of the two intertwined signalling pathways in a clv1-101 mutant background.
(A) Longitudinal sections of inflorescence meristems (IFMs) show the expression patterns of CLV3 (N = 8), WUS (N = 8), BAM1 (N = 9) and CLV1 (N = 5) in a clv1 mutant. Compared to wild-type plants, the expression of CLV3 and WUS is expanded and WUS is found in a patchy pattern in the layer 1 (L1). BAM1 expression shifts to the central zone (CZ) and is found in an elevated expression in the L1. (B, C) Schematic representation of two intertwined negative feedback loops in the IFM of a clv1-101 mutant. The lack of CLV1 leads to a shift of BAM1 expression to the organizing centre (OC) and to an elevated expression in the L1. In the L3, BAM1 can partly substitute for CLV1 and thus CLV3 can act via BAM1 in order to repress WUS activity. The elevated expression of BAM1 in the L1 overlaps in very few cells with CLE40 expression in the periphery and leads to a weak activation of the downstream signal ‘X’ that promotes WUS activity. Since WUS expression is only partly repressed by the CLV3-BAM1 signalling pathway, the WUS domain is extended and leads to an increase in stem cells (expanded CLV3 expression). WUS is now also detected in the L1 of the meristem, together with BAM1 expression. Scale bars: 20 µm (A).
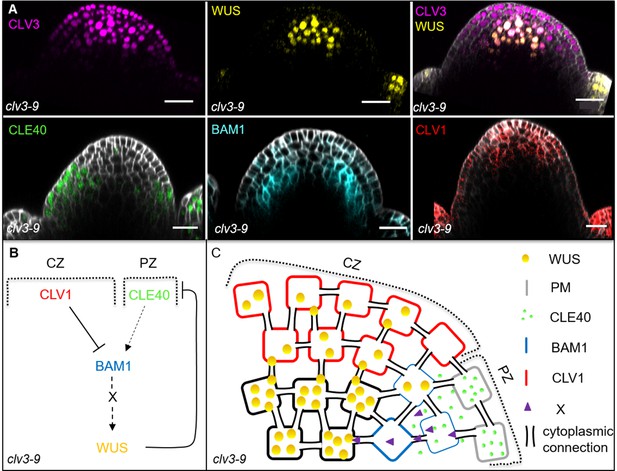
Schematic model of the intertwined signalling pathways in a clv3-9 mutant background.
(A) Longitudinal optical sections of inflorescence meristem (IFMs) show the expression patterns of CLV3 (N = 5), WUS (N = 5), CLE40 (N = 6), BAM1 (N = 5) and CLV1 (N = 5) in a clv3-9 mutant. Compared to wild-type plants, the meristem is highly increased in its size along the apical-basal axis and the expression of CLV3 and WUS is expanded in the central zone (CZ) and organizing centre (OC). CLE40 expression is limited to the outer layers of the meristems’ periphery and excluded from the CZ and OC, while BAM1 expression shifts towards the inner layers of the peripheral zone (PZ). CLV1 expression is found at the tip and not in the centre of the fasciated meristem. (B, C) Schematic representation of two intertwined negative feedback loops in the IFM of a clv3-9 mutant. The lack of CLV3 leads to a fasciated meristem with increased number of stem cells and thus an expanded CZ and a decreased PZ. Since no CLV3 peptide is available, CLV1 is not activated and expression of CLV1 shifts from the OC to the tip of the CZ, where it represses BAM1 expression. BAM1 is expressed in the inner layers of the PZ, while CLE40 expression is found in the outer layers of the PZ since it is repressed by the expanded WUS domain in the centre of the meristem. Thus only very few cells express both, BAM1 and CLE40, and hence, nearly no WUS-promoting factor ‘X’ is produced and the CLV3-CLV1 signalling pathway does not repress WUS activity. Scale bars: 20 µm (A).
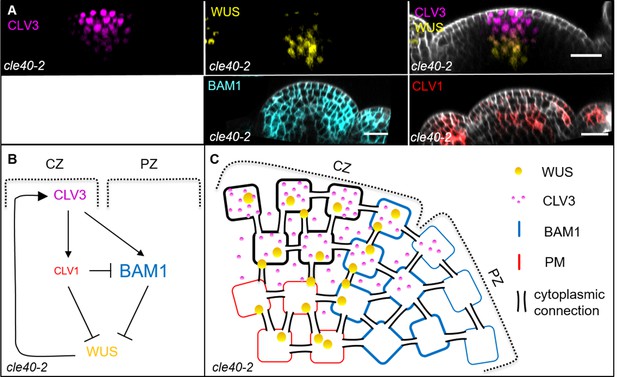
Schematic model of the intertwined signalling pathways in a cle40-2 mutant background.
(A) Longitudinal optical sections of inflorescence meristems (IFMs) show the expression patterns of CLV3 (N = 9), WUS (N = 9), BAM1 (N = 7) and CLV1 (N = 9) in a cle40-2 mutant. CLV3 expression is similar to wild-type plants, in the central zone (CZ). WUS expression is found in the organizing centre (OC), but in less cells than in Col-0 plants. BAM1 expression appears to be broader compared to wild-type plants, while CLV1 expression seems to be decreased in its intensity. (B, C) Schematic representation of two intertwined negative feedback loops in the IFM of a cle40-2 mutant. In cle40-2 mutants, CLV1 expression seems to be decreased and leads to a broader BAM1 expression compared to wild-type plants. Since expression of BAM1 is now also found in the CZ, CLV3 is able to bind CLV1 and BAM1 in the OC and CZ, respectively, leading to a double repression signalling cascade from the centre of the meristem. In the peripheral zone (PZ), the downstream signalling cascade of BAM1 is not activated through CLE40 and thus the WUS-promoting factor ‘X’ is not being expressed and the WUS domain is confined to the centre of the OC. Scale bars: 20 µm (A).
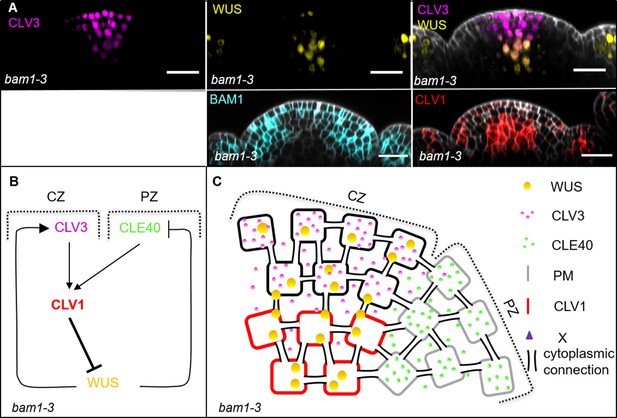
Schematic model of the intertwined signalling pathways in a bam1-3 mutant background.
(A) Longitudinal optical sections of inflorescence meristems (IFMs) show the expression patterns of CLV3 (N = 9), WUS (N = 9), BAM1 (N = 15) and CLV1 (N = 7) in a bam1-3 mutant. CLV3 expression is similar to wild-type plants at the tip of the meristem in a cone-shaped domain. WUS expression is found in the organizing centre (OC), but in less cells than in Col-0 plants. CLV1 expression seems to be increased in its intensity compared to wild-type plants. (B, C) Schematic representation of two intertwined negative feedback loops in the IFM of a bam1-3 mutant. In bam1-3 mutants, CLV1 expression appears to be increased. Since BAM1 is lacking in the periphery, the WUS-promoting diffusion factor ‘X’ is not being produced and thus WUS expression is decreased and confined to the centre of the OC, similar to cle40-2 plants. With the loss of BAM1, the main receptor for CLE40 is missing, and thus CLE40 peptide now might signal through CLV1, leading to a stronger repression of WUS from the centre of the meristem. Scale bars: 20 µm (A).
Tables
Mutants analysed in this study.
| Allele | Gene | Mutation | Reference | Background |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bam1-3 | AT5G65700 | T-DNA | Alonso et al., 2003;SALK_015302 | Col-0 |
| cle40-2 | AT5G12990 | Transposon mutation | Stahl et al., 2009 | Col-0 |
| cle40-cr1 | AT5G12990 | CRISPR | Yamaguchi et al., 2017 | Col-0 |
| cle40-cr2 | ||||
| cle40-cr3 | ||||
| clv3-9 | AT2G27250 | EMS | Brand et al., 2000 | Col-0 |
| clv1-20 | AT1G75820 | T-DNA | SALK_008670 | Col-0 |
| clv1-101 | AT1G75820 | T-DNA | Kinoshita et al., 2010;CS858348 | Col-0 |
| wus-7 | AT2G17950 | EMS | Graf et al., 2010 | L.er. |
Primers and methods used for genotyping.
| Allele | Method | Primer | PCR product |
|---|---|---|---|
| bam1-3 | PCR | bam1-3_F: ctaacgactctccgggagctbam1-3_R: taaggaccacagagatcaggattacLbaI_R: tggttcacgtagtgggccatcg | WT amp.: 1208 bpmutant amp.: 998 bp |
| cle40-2 | dCAPS | cle40-2_F: GGAGAAACACAAGATACGAAAGCCATGcle40-2_R: ATTGTGATTTGATACCAACTTAAAA | Restriction enzyme: AseIWT amp.: 460 + 200 bpmutant amp.: 410 + 200 + 60 bp |
| cle40-cr1 | dCAPS | cle40-cr_F: ATGGCGGCGATGAAATACAAcle40-cr_R: GTTACGCTTTGGCATCTTTCC | Restriction enzyme: BamHIWT amp.: 750 bpmutant amp.: 491 + 259 bp |
| cle40-cr2 | |||
| cle40-cr3 | |||
| clv1-20 | PCR | clv1-20_F: TTTGAATAGTGTGTGACCAAATTTGAclv1-20_R: TCCAATGGTAATTCACCGGTGLBa.1: TGGTTCACGTAGTGGGCCATCG | WT amp.: 860 bpmutant amp: 1200 bp |
| clv1-101 | PCR | clv1-101_F: TTCTCCAAATTCACCAACAGGclv1-101_R: CAACGGAGAAATCCCTAAAGGWiscLox_LT6_R: AATAGCCTTTACTTGAGTTGGCGTAAAAG | WT amp.: 1158 bpmutant amp.: 896 bp |
| wus-7 | dCAPS | wus-7_F: CCGACCAAGAAAGCGGCAACAwus-7_R: AGACGTTCTTGCCCTGAATCTTT | Restriction enzyme: XmnIWT amplification: 216 bpmutant amp.: 193 + 23 bp |
Entry vectors used for cloning.
| Name | Description | Bacterial resistance | Backbone | Reference/origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| proBAM1(pGD288) | BAM1 promoter3522 bp upstream from transcription start | Ampicillin | pGGA000 | Grégoire Denay |
| proCLE40 | CLE40 promoter2291 bp upstream from translational start codon | Kanamycin | pENTR/D-TOPO | Rene Wink |
| proCLV3 | CLV3 promoter1480 bp upstream from transcription start | Ampicillin | pGGA000 | Jenia Schlegel |
| proCLV1 | CLV1 promoter5759 bp upstream from transcription start | Ampicillin | pGGA000 | Patrick Blümke |
| omega-element(pGGB002) | Omega-element | Ampicillin | pGGB000 | Lampropoulos et al., 2013 |
| SV40 NLS(pGGB005) | SV40 NLS (SIMIAN VIRUS 40 NUCLEARLOCALIZATION SIGNAL) | Ampicillin | pGGB000 | Lampropoulos et al., 2013 |
| BAM1_CDS(pGD351) | BAM1 coding region genomic region of BAM1 START to one codon before STOP, including introns, internal BsaI sites removed | Ampicillin | pGGC000 | Grégoire Denay |
| CLV1_CDS | CLV1 coding region2946 bp coding region amplified from genomic Col-0 DNA without STOP codon and internal BsaI site removed | Ampicillin | pGGC000 | Jenia Schlegel |
| 3x-mCherry(pGGC026) | 3x mCherry | Ampicillin | pGGC000 | Lampropoulos et al., 2013 |
| linker-GFP(pGD165) | linker(10aa)-eGFP | Ampicillin | pGGD000 | Grégoire Denay |
| d-dummy(pGGD002) | d-dummy | Ampicillin | pGGD000 | Lampropoulos et al., 2013 |
| tCLV3 | CLV3 terminator1257 bp downstream of transcription stop | Ampicillin | pGGE000 | Jenia Schlegel |
| tUBQ10(pGGE009) | UBQ10 terminator | Ampicillin | pGGE000 | Lampropoulos et al., 2013 |
| BastaR(pGGF008) | pNOS:BastaR (chi sequence removed):tNOS | Ampicillin | pGGF000 | Lampropoulos et al., 2013 |
| D-AlaR(pGGF003) | pMAS:D-AlaR:tMAS | Ampicillin | pGGF000 | Lampropoulos et al., 2013 |
Destination vectors used to generate transgenic A. thaliana reporter lines.
| Name | Backbone | Promoter | N-tag | CDS | C-tag | Terminator | Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAM1:BAM1-GFP | pGGZ001 | proBAM1 | Ω-element(pGGB002) | BAM1-CDS | linker-GFP(pGD165) | tUBQ10 (pGGE009) | D-Alanin(pGGF003) |
| CLE40:Venus-H2B | pMDC99 | proCLE40 | - | Venus | H2B | T3A | Hygromycin |
| CLV1:CLV1-GFP | pGGZ001 | proCLV1 | Ω-element(pGGB002) | CLV1-CDS | linker-GFP(pGD165) | tUBQ10 (pGGE009) | BastaR(pGGF008) |
| CLV3:NLS-3xmCherry | pGGZ001 | proCLV3 | SV40 NLS | 3x-mCherry(pGGC026) | d-dummy(pGGD002) | tCLV3 | BastaR(pGGF008) |
Primers used for cloning the entry vectors.
| Name | Primer |
|---|---|
| proBAM1(pGD288) | F: AAAGGTCTCAACCTATGATCCGATCCTCAAAAGTATGTAR: AAAGGTCTCATGTTTCTCTCTATCTCTCTTGTGTG |
| BAM1_CDS(pGD351) | F: TTTGGTCTCAGGCTCTATGAAACTTTTTCTTCTCCTTCR:TTTGGTCTCACTGATAGATTGAGTAGATCCGGCBsaI-site_#1_F: CTTGATCTCTCCGGACTCAACCTCTCCGGBsaI-site_#1_R: CCGGAGAGGTTGAGTCCGGAGAGATCAAGBsaI-site_#2_F: CTCATGTTGCTGACTTTGGACTCGCTAAATTCCTTCAAGBsaI-site_#2_R: CTTGAAGGAATTTAGCGAGTCCAAAGTCAGCAACATGAG |
| proCLE40 | F: CACCGTTAAGCCAAGTAAGTACCACACAGCR: CATTTCAAAAACCTCTTTGTG |
| proCLV1 | F: AAAGGTCTCAACCTGACTATTGTTTATACTTAGTTGR: TTTGGTCTCATGTTCATTTTTTTAGTGTCCTC |
| CLV1_CDS | F: AAAGGTCTCAGGCTTAATGGCGATGAGACR: TTTGGTCTCACTGAACGCGATCAAGTTCBasI-site_#1_F: CTAAAGGACACGGACTGCACGACTGBasI-site_#1_R: CAGTCGTGCAGTCCGTGTCCTTTAGBasI-site_#2_F: CTTAGAGTATCTTGGACTGAACGGAGCTGGBasI-site_#2_R: CCAGCTCCGTTCAGTCCAAGATACTCTAAG |
| proCLV3 | F: AAAGGTCTCAACCTCGGATTATCCATAATAAAAACR:AAAGGTCTCATGTTTTTTAGAGAGAAAGTGACTGAG |
| tCLV3 | F: TTTGGTCTCTCTGCCGCCCTAATCTCTTGTTR: TTTGGTCTCGTGATATGTGTGTTTTTTCTAAACAATC |
Arabidopsis lines that were analysed in this study.
| Name/construct | Background | Plant resistance | Generation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAM1:BAM1-GFP | bam1-3 | D-Ala | T4 | This study |
| BAM1:BAM1-GFP | bam1-3;clv1-20 | D-Ala | F3 | This study |
| BAM1:BAM1-GFP | bam1-3;clv3-9 | D-Ala | F3 | This study |
| BAM1:BAM1-GFP | bam1-3;cle40-2 | D-Ala | F3 | This study |
| CLE40:Venus-H2B | Col-0 | Hygromycin | T5 | This study |
| CLE40:Venus-H2B | clv3-9 | Hygromycin | F3 | This study |
| CLE40:Venus-H2B | wus-7 | Hygromycin | F2 | This study |
| CLE40:Venus-H2B | CLV3:WUS//Col-0 | Hygromycin/Basta | T1* | This study |
| CLE40:CLE40-GFP | Col-0 | N/A | T3 | Stahl et al., 2009 |
| CLV1:CLV1-GFP | Col-0 | Basta | T4 | This study |
| CLV1:CLV1-GFP | bam1-3 | Basta | F3 | This study |
| CLV1:CLV1-GFP | clv3-9 | Basta | F3 | This study |
| CLV1:CLV1-GFP | cle40-2 | Basta | F3 | This study |
| CLV1:CLV1-2xGFP | clv1-11 | Basta | N/A | Nimchuk et al., 2011 |
| CLV3:NLS-3xmCherry | CLE40:Venus-H2B//Col-0 | Basta/hygromycin | F3 | This study |
| CLV3:NLS-mCherryWUS:NLS-GFP | Col-0 | Kanamycin | N/A | Anne Pfeiffer |
| CLV3:NLS-mCherryWUS:NLS-GFP | cle40-2 | Kanamycin | F3 | This study |
| CLV3:NLS-mCherryWUS:NLS-GFP | bam1-3 | Kanamycin | F3 | This study |
| CLV3:NLS-mCherryWUS:NLS-GFP | clv1-101 | Kanamycin | F3 | This study |
| CLV3:NLS-mCherryWUS:NLS-GFP | clv3-9 | Kanamycin | F3 | This study |
-
*
Plants do not overcome seedling stage.
Microscopy settings used for imaging.
| Fluorophore/staining | Excitation (nm) | Emission (nm) | MBS | Detector | Light source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DAPI | 405 | 410–490 | 405 | PMT | Diode |
| GFP | 488 | 500–545 | 488/561 | GaAsP | Argon laser |
| Venus | 514 | 518–540 | 458/514 | GaAsP | Argon laser |
| mCherry | 561 | 570–640 | 458/561 | PMT | DPSS laser |
| PI | 561 | 595–650 | 488/561 | PMT | DPSS laser |
-
PMT, photomultiplier tubes; DPSS, diode-pumped solid state.
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Arabidopsis thaliana) | Columbia (Col-0) | NASC ID: N22625 | ABRC: CS22625 | |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | bam1-3 | Alonso et al., 2003; NASC ID: N515302 | ABRC: SALK_015302 | T-DNA mutation in Col-0 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | cle40-2 | Stahl et al., 2009 | NA | Transposon mutation Col‑0 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | cle40-cr1/2/3 | Yamaguchi et al., 2017 | NA | CRISPR in Col-0 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | clv3-9 | Hobe et al., 2003 | NA | EMS in Col-0 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | clv1-20 | Alonso et al., 2003; NASC ID: N508670 | ABRC: SALK_008670 | T-DNA mutation in Col-0 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | clv1-101 | Alonso et al., 2003; NASC ID: N858348 | ABRC: CS858348 | T-DNA mutation in Col-0 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | wus-7 | Graf et al., 2010; | NA | EMS in L.er. background Gift from J. Lohmann lab |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | BAM1:BAM1-GFP | This study | NA | Transgenic line in bam1‑3 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | BAM1:BAM1-GFP | This study | NA | Transgenic line in bam1‑3;clv1‑20 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | BAM1:BAM1-GFP | This study | NA | Transgenic line in bam1‑3;clv3-9 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | BAM1:BAM1-GFP | This study | NA | Transgenic line in bam1‑3;cle40-2 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | CLE40:Venus-H2B | This study | NA | Transgenic line in Col-0 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | CLE40:Venus-H2B | This study | NA | Transgenic line in clv3-9 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | CLE40:Venus-H2B | This study | NA | Transgenic line in wus-7 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | CLE40:Venus-H2B | This study | NA | Transgenic line in CLV3:WUS/Col-0 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | CLE40:CLE40-GFP | Stahl et al., 2009 | NA | Transgenic line in Col-0 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | CLV1:CLV1-GFP | This study | NA | Transgenic line in Col-0 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | CLV1:CLV1-GFP | This study | NA | Transgenic line in clv1-101 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | CLV1:CLV1-GFP | This study | NA | Transgenic line in bam1-3 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | CLV1:CLV1-GFP | This study | NA | Transgenic line in clv3-9 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | CLV1:CLV1-GFP | This study | NA | Transgenic line in cle40-2 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | CLV1:CLV1-2xGFP | Nimchuk et al., 2011 | NA | Transgenic line in clv1-11 backgroundGift from Z. Nimchuk lab |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | CLV3:NLS-3xmCherry | This study | NA | Transgenic line in CLE40:Venus-H2B/Col-0 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | CLV3:NLS-mCherry WUS:NLS-GFP | Anne Pfeiffer | NA | Transgenic line in Col-0 backgroundGift from J. Lohmann lab |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | CLV3:NLS-mCherry WUS:NLS-GFP | This study | NA | Transgenic line in cle40-2 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | CLV3:NLS-mCherry WUS:NLS-GFP | This study | NA | Transgenic line in bam1-3 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | CLV3:NLS-mCherry WUS:NLS-GFP | This study | NA | Transgenic line in clv1-101 background |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | CLV3:NLS-mCherry WUS:NLS-GFP | This study | NA | Transgenic line in clv3-9 background |
| Strain, strain background (Agrobacterium tumefaciens) | A. tumefaciens GV3101 pMP90 pSoup | Lifeasible | Cat# ACC-101 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pGGZ001 | Lampropoulos et al., 2013 | Addgene | RRID:Addgene_48868 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pGGB002 | Lampropoulos et al., 2013 | Addgene | RRID:Addgene_48820 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pGGE009 | Lampropoulos et al., 2013 | Addgene | RRID:Addgene_48841 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pGGF003 | Lampropoulos et al., 2013 | Addgene | RRID:Addgene_48844 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pGGC026 | Lampropoulos et al., 2013 | Addgene | RRID:Addgene_48831 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pGGD002 | Lampropoulos et al., 2013 | Addgene | RRID:Addgene_48834 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pGGF008 | Lampropoulos et al., 2013 | Addgene | RRID:Addgene_48848 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMDC99 | Curtis and Grossniklaus, 2003 | NA | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pBAM1/pGGA000 | This study | NA | Entry vector used for cloningSee Tables 4 and 5 for details |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | BAM1-CDS/pGGC000 | This study | TAIR: AT5G65700 | Entry vector used for cloningSee Tables 4 and 5 for details |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCLV1-/pGGA000 | This study | NA | Entry vector used for cloningSee Tables 4 and 5 for details |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | CLV1-CDS/pGGC000 | This study | TAIR: AT1G75820 | Entry vector used for cloningSee Tables 4 and 5 for details |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCLE40/pGGA000 | This study | NA | Entry vector used for cloningSee Tables 4 and 5 for details |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCLV3/pGGA000 | This study | NA | Entry vector used for cloningSee Tables 4 and 5 for details |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCLV3/pGGE000 | This study | NA | Entry vector used for cloningSee Tables 4 and 5 for details |
| Sequence-based reagent | Cloning primers | This study | NA | Table 5 |
| Sequence-based reagent | Genotyping primers | This study | NA | Table 2 |
| Chemical compound, drug | BASTA non-selective herbicide | Bayer CropScience | 84442615 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Synthetic CLE40 | Peptides&Elephants | NA | |
| Software, algorithm | ImageJ v 1.53c | Schneider et al., 2012 | https://imagej.net/software/fiji/ | RRID:SCR_003070 |
| Software, algorithm | MorphoGraphX | Barbier de Reuille et al., 2015 | https://www.mpipz.mpg.de/MorphoGraphX/ | |
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism v8.0.0.224 | NA | GraphPad Prism (https://graphpad.com) | RRID:SCR_002798 |
| Software, algorithm | Imaris | NA | http://www.bitplane.com/imaris/imaris | RRID:SCR_007370 |