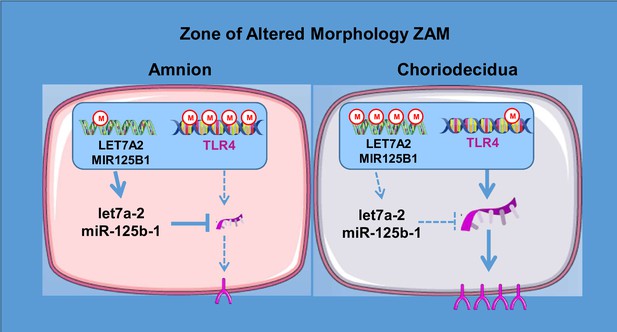
Physiological TLR4 regulation in human fetal membranes as an explicative mechanism of a pathological preterm case
Figures
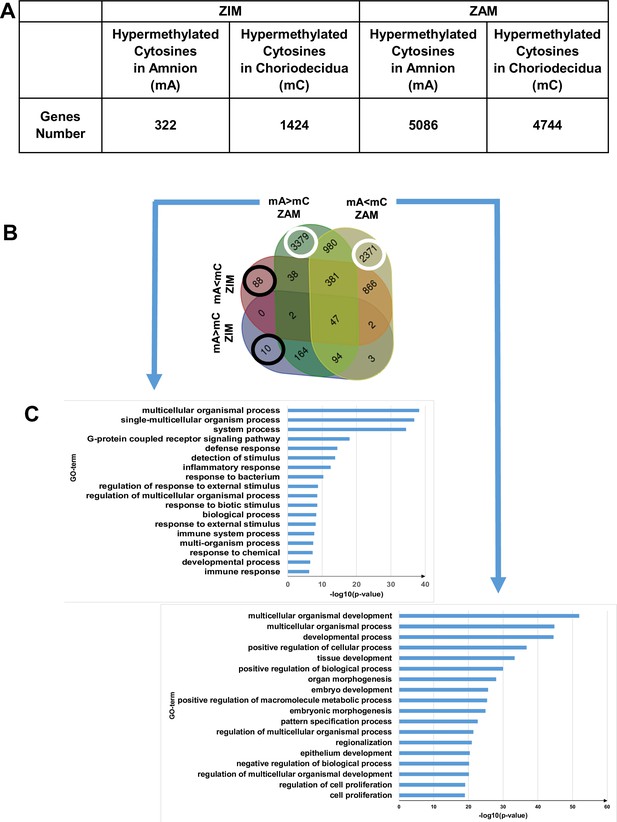
Differential cytosine methylation analysed for the zone of intact morphology (ZIM) and zone of altered morphology (ZAM).
(A) Genes affected by differential methylation between the amnion and choriodecidua, separately studied for the ZIM (left) and ZAM (right). (B) Four-way Venn diagram representing the number of genes with hypermethylated cytosines in the ZIM and ZAM according to methylomic analyses. mA> mC: a specific gene was more methylated in the amnion than in the choriodecidua. mA< mC: a specific gene was less methylated in the amnion than in the choriodecidua. (C) Gene Ontology (GO) term classifications for genes observed specifically in the ZAM: mA> mC (left panel) and mA< mC (right panel). Bonferroni correction was conducted for p-values < 0.01.
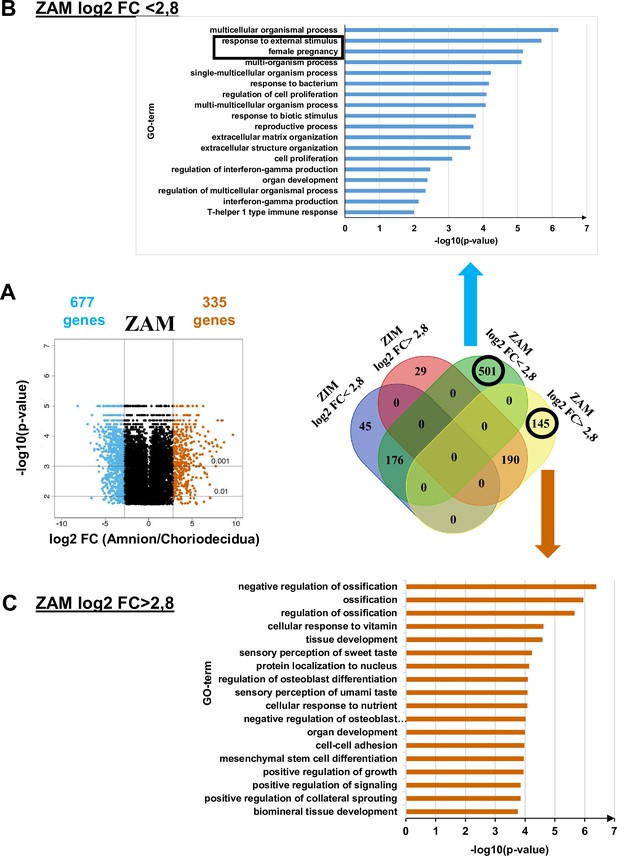
Transcriptomic assay analysed for the zone of altered morphology (ZAM) in fetal membranes.
(A) Volcano plots represent the log10-adjusted p-values vs. the log2-fold change (FC). Up- and downregulated genes are shown in red and blue, respectively, limited by│log2 FC│ = 2.8. They are classified in a four-way-Venn diagram representing the gene numbers in zone of intact morphology (ZIM) and ZAM analyses with│log2 FC│ = 2.8. (B) Gene Ontology (GO) term classifications are shown for genes expressed only in the ZAM for log2 FC <2.8 (Bonferroni correction for p-values < 0.01). (C) GO term classifications are shown for genes expressed only in the ZAM for log2 FC >2.8 (uncorrected p-value < 0.01).
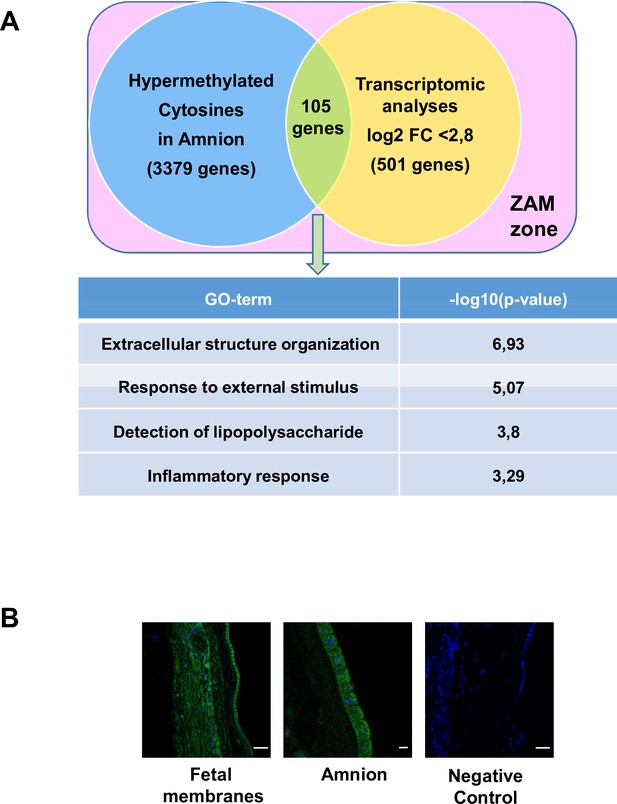
Common genes observed between the mA> mC methylomic results and choriodecidua/amnion transcriptomic analysis in the zone of altered morphology (ZAM).
(A) Gene Ontology (GO) terms’ representative distribution and their log10 p-values are shown for the 105 common genes across both genome-wide studies. (B) Representative TLR4 immunofluorescence (green staining) in the ZAM of fetal membranes in confocal analyses. Cell nuclei were visualised with Hoechst (blue) staining. A negative control was used without a primary antibody. Slides were observed at ×250 magnification for total fetal membranes (left and right): scale bar: 50 µm and ×400 for the amnion (middle): scale bar: 20 µm.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Raw data for toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) immunofluorescence in the fetal membranes by confocal microscopy.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71521/elife-71521-fig3-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Raw data for toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) immunofluorescence in the amnion by confocal microscopy.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71521/elife-71521-fig3-data2-v1.zip
-
Figure 3—source data 3
Raw data for toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) immunofluorescence in the fetal membranes by confocal microscopy(negative control).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71521/elife-71521-fig3-data3-v1.zip
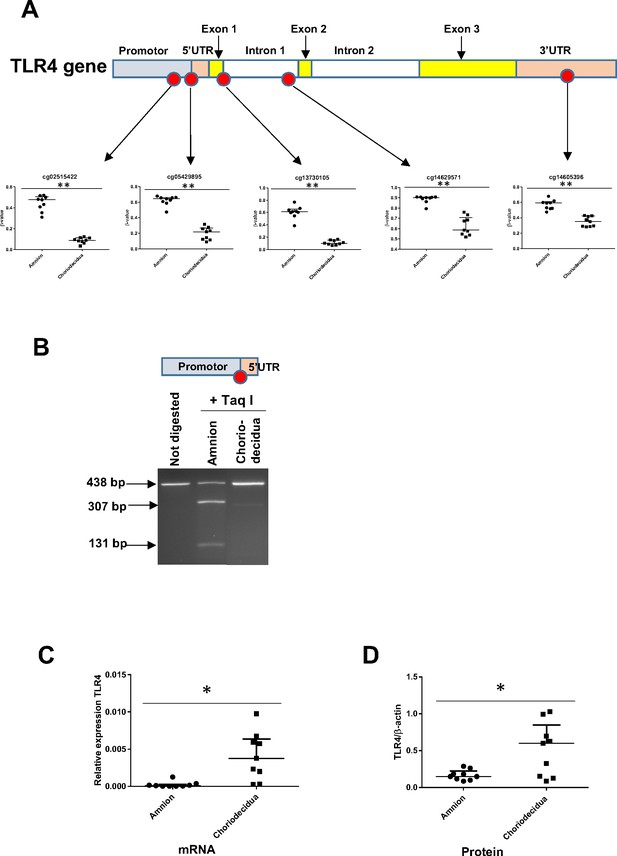
The expression level of the toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) gene is related to its cytosine methylation level in the amnion and choriodecidua from the zone of altered morphology (ZAM).
(A) The median ± interquartile ranges of the DNA methylation levels of the five cg probes on the TLR4 gene in the amnion and choriodecidua ZAMs. Each dot represents the individual β-value for one patient (n = 9). The probe set with significant differential methylation between the amnion and choriodecidua (Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test) is designated by an asterisk (**p-value < 0.01). (B) Control of the difference of methylation for the cg 05429895 between the amnion and choriodecidua after digestion with Taq I PCR products (438 bp) obtained after DNA bisulfite treatment. This probe, after being methylated in the amnion, was sensitive to Taq I and gave two fragments after digestion: 307 and 131 bp. (C) Relative expression of TLR4 transcripts for the nine samples of choriodecidua ZAM were significantly higher than for the amnion ZAM (Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test *p-value < 0.05). (D) The TLR4 protein was significantly overexpressed for the nine samples in the choriodecidua compared with the amnion (Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test *p-value < 0.05).
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Data on β-value for cg probes on the toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) gene for Figure 4A.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71521/elife-71521-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 4—source data 2
Uncropped polyacrylamide gel for Figure 4B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71521/elife-71521-fig4-data2-v1.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 3
Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) data and Western blot data for toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) expression (Figure 4C).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71521/elife-71521-fig4-data3-v1.xlsx
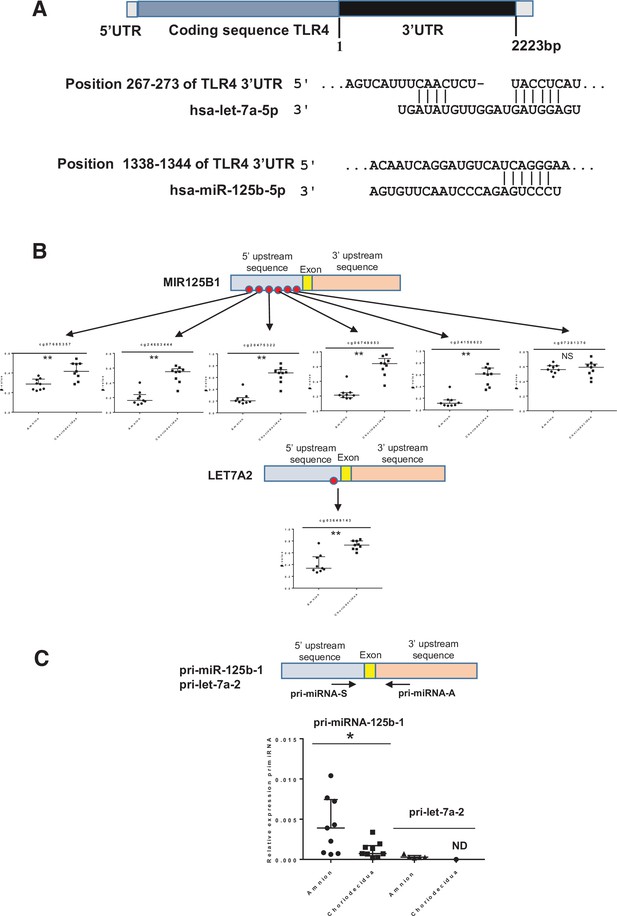
Two miRNAs potentially targeting the human 3’UTR-TLR4 (toll-like receptor 4) are differentially methylated in the zone of altered morphology (ZAM) between the amnion and choriodecidua.
(A) In silico computational target prediction analysis using TargetScan of the human 3’UTR-TLR4. This zone may be targeted by gene coding for MIR125B1 and LET7A2. (B) The median ± interquartile ranges of the DNA methylation cg probe levels for the MIR125B1 (top) and LET7A2 (bottom) genes for the nine samples in the amnion and choriodecidua ZAM. Each dot represents the individual β-value for one patient. The probe set with significant differential methylation between the amnion and choriodecidua (Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test) is designated by an asterisk (**p-value < 0.01, NS = not significant). (C) The relative expression of pri-miR-125b-1 (n = 9) and pri-let-7a-2 (n = 5) was determined. qRT-PCR experiments performed for each zone; tissue demonstrated that pri-miR-125b-1 was significantly overexpressed in the amnion compared with the choriodecidua ZAM, as expected from the differential methylation status (Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test *p-value < 0.05). The pri-let-7a-2 amount could not be rigorously determined (ND) in the choriodecidua.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Data on β-value for cg probes on the MIR125B1 and LET7A2 genes for Figure 5B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71521/elife-71521-fig5-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 5—source data 2
Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) data for pri-miR-125b-1 and pri-let-7a-2 (Figure 5C).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71521/elife-71521-fig5-data2-v1.xlsx
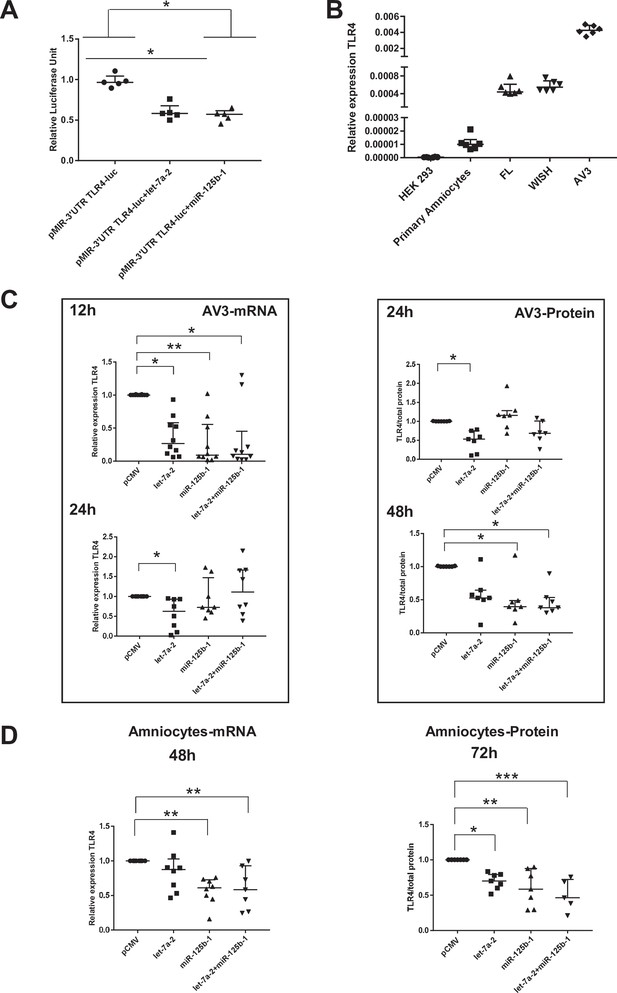
miR-125b-1 and let-7a-2 target the human 3’UTR-TLR4 (toll-like receptor 4) and decrease TLR4 expression.
(A) Targeting of miR-125b-1 and let-7a-2 to the human 3’UTR of TLR4 mRNA using a Luciferase Reporter Gene Assay depending on human 3’UTR-TLR4 (pMIR-3’UTR TLR4-luc). HEK293 cells cotransfected for 48 hr with this construction and expressing plasmid of human pCMV, pre-mir125b1, or let7A2 (n = 5). Luciferase activity was normalised with the pRL-TK-Renilla luciferase level (median ± interquartile range, Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparison test, *p-value < 0.05). The results showed that both miRNAs could target the 3’-UTR zone of the TLR4 gene and decrease luciferase quantity. (B) Determination of endogenous TLR4 expression levels in human cell lines (HEK293 from embryonic kidney and FL, WISH, and AV3 from amniocytes) and in primary amniocyte cells quantified by quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) (n = 6). (C) Effects of miR-125b-1, let-7a-2, and the combination miR-125b-1+ let-7a-2 on TLR4 mRNA expression (n = 10 for 12 hr and n = 8 for 24 hr, left) and TLR4 protein (n = 7, right) in AV3 cells. Cells were transfected with expressing plasmid of human pCMV, or pre-mir125b1, or let7A2 and miR-125b-1+ let-7a-2 for 12 and 24 hr for mRNA and 24 and 48 hr for protein (median ± interquartile range, Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparison test, *p-value < 0.05, **p-value < 0.01). (D) Effects of miR-125b-1, let-7a-2, and the combination miR-125b-1+ let-7a-2 on TLR4 mRNA expression (n = 7 at least, left) at 48 hr and TLR4 protein (n = 5 at least, right) at 72 hr in primary amniocyte cells (median ± interquartile ranges, Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparison test, *p-value < 0.05, **p-value < 0.01, ***p-value < 0.001).
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Data on luciferase activity in HEK293 cells transfected with pMIR-3’UTR toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-luc and pre-mir125b1 or let7A2 (Figure 6A).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71521/elife-71521-fig6-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 6—source data 2
Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) data for toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) expression in Figure 6B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71521/elife-71521-fig6-data2-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 6—source data 3
Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) data and Western blot data for toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) expression in AV3 cells transfected with pre-miRNA (Figure 6C).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71521/elife-71521-fig6-data3-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 6—source data 4
Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) data and Western blot data for toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) expression in amniocytes transfected with pre-miRNA (Figure 6D).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71521/elife-71521-fig6-data4-v1.xlsx
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Supplementary tables 1a to g.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71521/elife-71521-supp1-v1.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71521/elife-71521-transrepform1-v1.docx