The YTHDF proteins ECT2 and ECT3 bind largely overlapping target sets and influence target mRNA abundance, not alternative polyadenylation
Figures
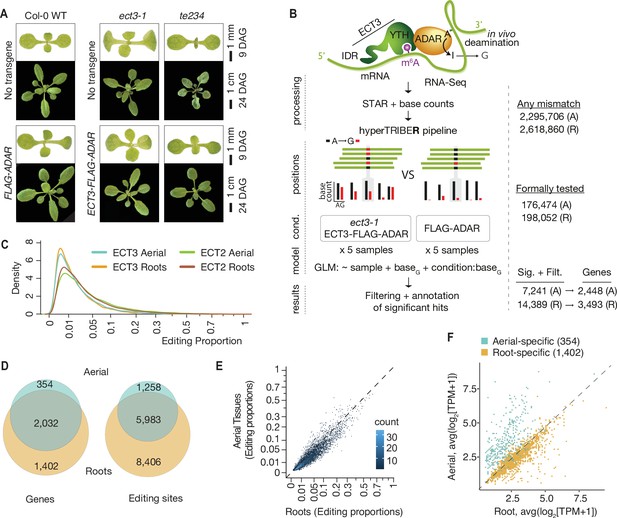
Identification of ECT3 targets using HyperTRIBE.
(A) Phenotypes of wild type, ect3-1, and te234 (ect2-1/ect3-1/ect4-2) mutants with (lower panels) or without (upper panels) ECT3pro:ECT3-FLAG-DmADARE488Qcd-ECT3ter (ECT3-FLAG-ADAR) or ECT3pro:FLAG-DmADARE488Qcd-ECT3ter (FLAG-ADAR) transgenes, at 9 or 24 days after germination (DAG). (B) Experimental design for ECT3-HyperTRIBE (ECT3-HT) target identification. After quantifying nucleotide base counts from mapped RNA-seq libraries of ect3-1/ECT3-FLAG-ADAR and FLAG-ADAR lines, all positions with mismatches were passed into the HyperTRIBER pipeline (Rennie et al., 2021) to call significant editing sites. Identified sites were further filtered to remove SNPs and retain only A-to-G mismatches. The number of sites in either aerial (A, dissected apices) or root (R, root tips) tissues at each stage is indicated. (C) Density of editing proportions for significant editing sites in aerial tissues and roots of ect3-1/ECT3-FLAG-ADAR and ect2-1/ECT2-FLAG-ADAR (Arribas-Hernández et al., 2021) lines. (D) Overlap between ECT3-HT target genes and editing sites in roots and aerial tissues, out of the set of genes commonly expressed in both tissues. (E) Scatterplot of the editing proportions of significant editing sites in ECT3-HT for aerial versus root tissues. (F) Scatterplot showing the expression in aerial and root tissues (mean log2 (TPM+1) over the five ECT3-HT control samples) of the genes that are identified as targets only in aerial tissues or only in roots. GLM, generalized linear model.
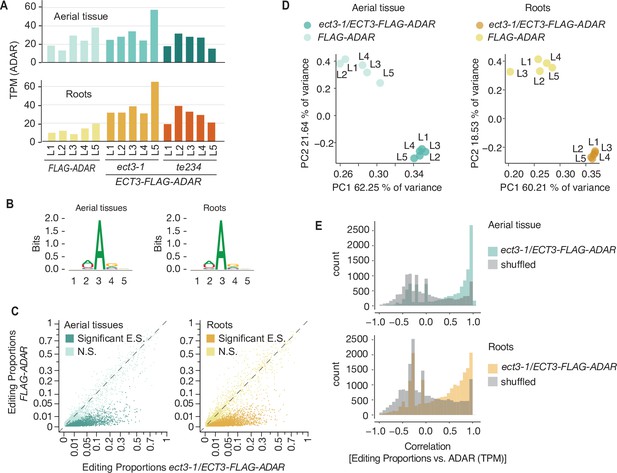
Identification of ECT3 targets using HyperTRIBE (extended data).
(A) Expression levels of ECT3-FLAG-ADAR or FLAG-ADAR in apices (aerial tissues) or root tips of 10-day-old seedlings of the 5+5+5 independent transgenic lines (L1–L5) used for experiments in this article. (B) Consensus motif identified at significant editing sites of ect3-1/ ECT3-FLAG-ADAR lines. (C) Scatterplot of the editing proportions (E.P.=G/(A+G)) of potential and significant editing sites (E.S.) of ect3-1/ECT3-FLAG-ADAR lines compared to the FLAG-ADAR controls. (D) Principal component analysis of editing proportions at significant editing sites in ECT3-HT. (E) Distribution of the correlations between editing proportions and ADAR expression (TPM) for significant editing sites in ect3-1/ECT3-FLAG-ADAR lines. Background correlations are based on randomly shuffling ADAR expression for each site. N.S., not significant.
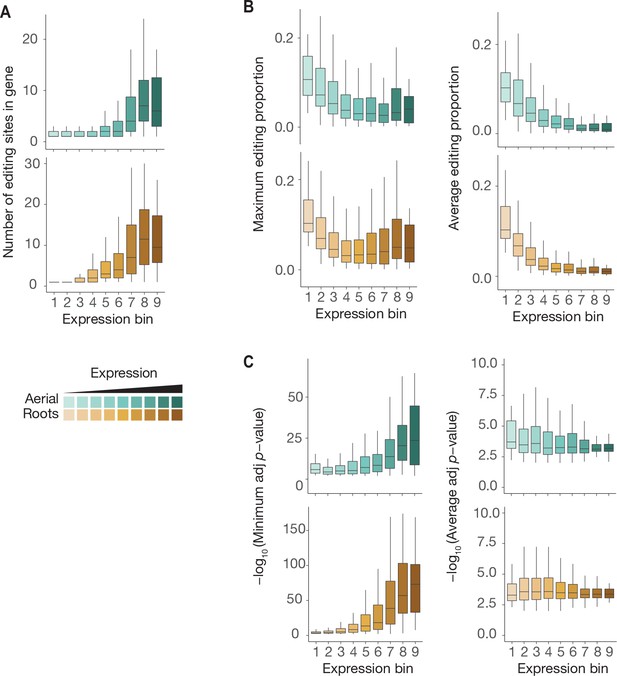
Characteristics of ECT3-HyperTRIBE editing sites relative to target expression levels.
(A–C) Number of significant editing sites (A), maximum or average editing proportions (B), and significance of editing sites according to either minimum or average −log10(adjusted p-value) per gene (C) in ECT3-HT targets split according to their expression levels (mean log2(TPM+1) over the five ECT3-HT control samples), in both aerial and root tissues.
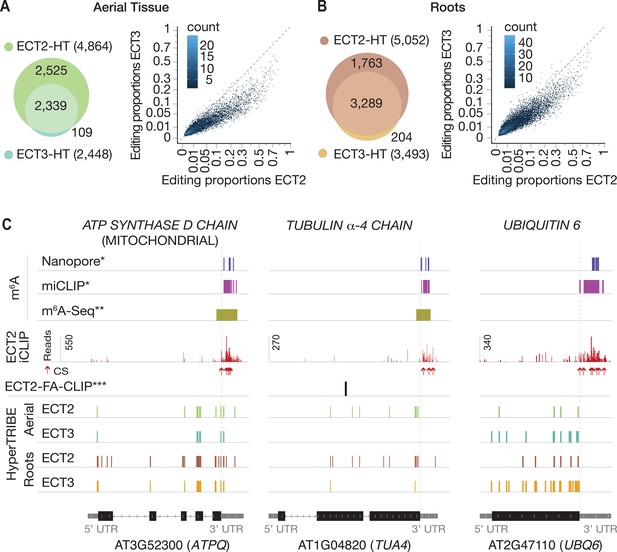
ECT3 targets are fewer and largely contained within ECT2 targets.
(A, B) Left panels: overlap of ECT2-HT and ECT3-HT targets, for the set of commonly expressed genes, in aerial (A) and root (B) tissues. Right panels: Scatter plots showing the editing proportions of editing sites between ECT2-HT and ECT3-HT, for all significant positions common to both sets, separately for aerial (A) and root (B) tissues. (C) Examples of common ECT2 and ECT3 targets showing the distribution of ECT2/3-HT editing sites in either aerial or root tissues along the transcript. The distribution of ECT2-iCLIP reads and crosslink sites (CS) (Arribas-Hernández et al., 2021), FA-CLIP peaks***, and m6A sites*, ** is also shown. * Parker et al., 2020; ** Shen et al., 2016; *** Wei et al., 2018.
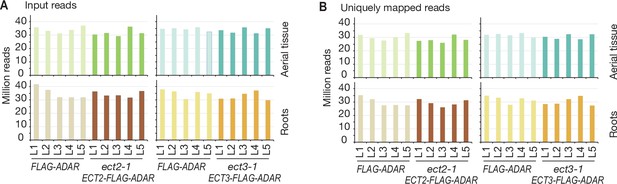
Sequencing depth of ECT2 and ECT3 HyperTRIBE RNA-seq data.
(A, B) Number of input reads (A) and uniquely mapped reads (B) for ECT2-HT and ECT3-HT RNA-seq samples.

ECT2 and ECT3 target each other and themselves.
Distribution of ECT2/3-HT editing sites and ECT2-iCLIP peaks along ECT2/3/4-encoding transcripts. ECT2 is a target of ECT3, particularly clearly in roots, and ECT3 is a target of ECT2 according to ECT2-HT in aerial tissues (not confirmed by ECT2-iCLIP [Arribas-Hernández et al., 2021]). Although self-targeting of ECT2 and ECT3 may also be taken into consideration, it is important to notice that these targeted transcripts originate from transgenes. ECT4 (right panel) does not appear as ECT2/3 target, but its low expression levels might account for a false negative. ECT2-iCLIP reads and peaks (Arribas-Hernández et al., 2021), FA-CLIP peaks***, and m6A sites*, ** are shown as a reference. * Parker et al., 2020; ** Shen et al., 2016; *** Wei et al., 2018.
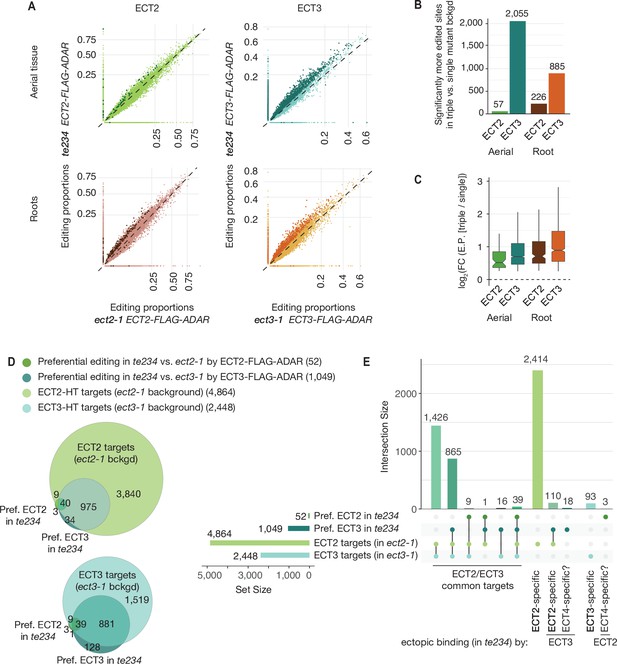
Redundancy between ECT2 and ECT3.
(A) Scatterplots comparing the editing proportions of ECT2- and ECT3-FLAG-ADAR observed in triple versus single mutant backgrounds in aerial and root tissues. They include all positions significantly edited with respect to FLAG-ADAR controls (p-value<0.01, log2(FC)>1) in either background, with dots on the axes reflecting positions not significantly edited in one of the two backgrounds. Dots in darker shades indicate positions more highly edited in one background compared to the other (p-value<0.1, log2(FC)>0.25 or log2(FC)<−0.25). (B) Barplots showing the number of positions significantly more edited in triple versus single mutant background for each tissue and ECT protein. Positions significantly less edited in the triple mutant background were fewer than 12 in all cases. (C) Boxplots showing fold changes in editing proportions between the triple and single mutant backgrounds for the two ECT proteins and tissues studied. (D, E) Venn diagrams (D) and Upset plot (E) showing the overlap between the ECT2-HT (Arribas-Hernández et al., 2021) and ECT3-HT target sets (in single mutant backgrounds) with the groups of genes with more highly edited positions in the triple mutant background in aerial tissues (the equivalent for roots is shown in Figure 3—figure supplement 2).

Expression levels (TPM) of the FLAG-ADAR-containing transgenes in all HyperTRIBE lines.
TPMs for the five lines of every type have been averaged for simplicity. Notice that the expression of ECT2/3-FLAG-ADAR transgenes is highly comparable in triple and single mutant backgrounds, ruling out the possibility of higher editing proportions in the triple mutant background due to higher abundance of the transgene. The expression of ECT3-FLAG-ADAR is generally lower than that of ECT2-FLAG-ADAR, as expected from the relative abundance of the endogenous transcripts (Arribas-Hernández et al., 2018).
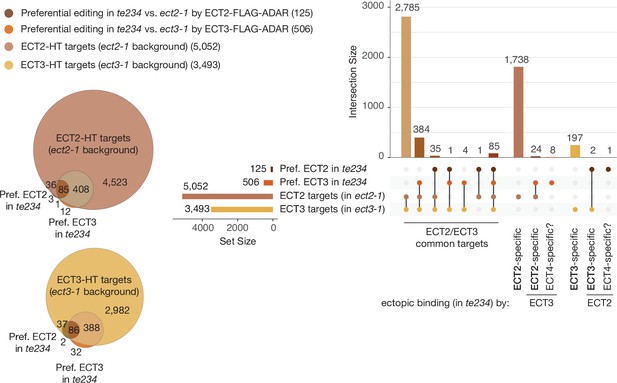
Overlap between ECT2/3-HT targets in single and triple mutant backgrounds in roots.
Venn diagrams (left) and Upset plot (right) showing the overlap between the ECT2-HT (Arribas-Hernández et al., 2021) and ECT3-HT target sets (in single mutant backgrounds) with the groups of genes with more highly edited positions in the triple mutant background in roots (the equivalent for aerial tissues is shown in Figure 3D and E).
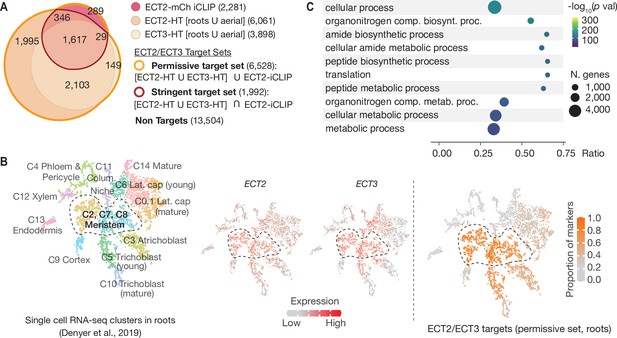
ECT2 and ECT3 targets are co-expressed with ECT2 and ECT3 in proliferating cells and enriched in biosynthetic processes.
(A) Overlap between ECT2-iCLIP target genes with ECT2-HT and ECT3-HT target gene sets. Regions outlined in bold orange and red indicate the defined permissive and stringent ECT2/3 target sets in whole seedlings, respectively (aerial and root-specific target sets are shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 1). Non-targets are all expressed genes (with detectable transcript levels in the corresponding HyperTRIBE RNA-seq data sets) that are not in the permissive target set. (B) Left: t-SNE plot for scRNA-seq data in roots from Denyer et al., 2019, with cells colored according to their cell-type cluster definitions (see Figure 4—figure supplement 2 for details). Center: ECT2 and ECT3 single-cell expression levels overlayed on to the t-SNE plot (Ma et al., 2020). Right: t-SNE plot with cell-type clusters shaded according to the proportion of marker genes from Denyer et al., 2019 that are targets of ECT2 or ECT3 in roots. Dashed enclosed region indicates clusters that contain meristematic cells. (C) The 10 most significantly enriched GO terms among ECT2/3 targets (permissive set). GO, gene ontology.

ECT2 and ECT3 target sets in aerial and root tissues (separately).
(A, B) Overlap between HyperTRIBE target sets of ECT2 and ECT3 in aerial (A) or roots (B) tissues, and ECT2-iCLIP (whole seedlings). Genes contained within the outlined sets in roots constitute the permissive (orange outline) and stringent (dark red outline) ECT2/3 target sets (Supplementary file 4) for the subsequent transcriptome analyses of sorted root protoplasts. Non-targets are all genes with detectable transcript levels in the ECT2 or ECT3 (aerial or root) HT RNA-seq data sets that are not in the permissive target set.
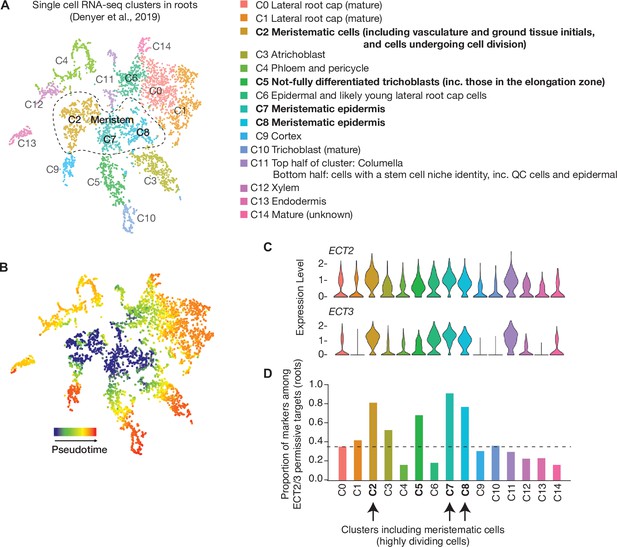
ECT2/ECT3 targets are co-expressed with ECT2/3 in highly dividing root cells.
(A) t-SNE plot for scRNA-seq data in roots from Denyer et al., 2019, with cells colored according to their cell-type cluster definitions described on the right side (https://www.zmbp-resources.uni-tuebingen.de/timmermans/plant-single-cell-browser-arabidopsis-root-atlas/ and personal communication with Thomas Denyer). Dashed-enclosed region indicates clusters that contain meristematic cells. (B) Temporal reference map derived from pseudo-time analysis of cells (Denyer et al., 2019) illustrates the progressive maturation of cells from the meristem core (reproduced with permission from Ma et al., 2020). (C) Violin plot showing ECT2 and ECT3 single-cell expression levels in the different clusters defined in (A). These plots and their corresponding gray-red shaded t-SNE plots in Figure 4B (center panels) were obtained from the above-mentioned website (Ma et al., 2020). (D) Box plot showing the proportion of marker genes from Denyer et al., 2019, which are targets of ECT2 or ECT3 in roots. These values were used to obtain the corresponding gray-orange shaded t-SNE plot shown in Figure 4B (right panel).
© 2019, Denyer et al. Figure 4B and Figure 4-figure supplement 2 have been adapted from Figure 1A from Denyer et al., 2019
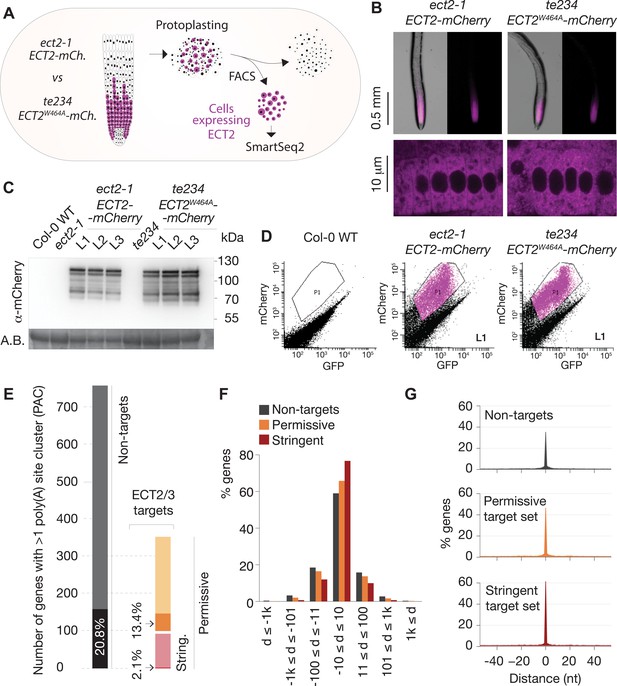
Poly(A) sites in ECT2/3 targets do not change upon loss of ECT2/3/4 function.
(A) Experimental design. The experiment was performed once, using three biological replicates (independent lines) per group (genotype). (B) Expression pattern of ECT2-mCherry in root tips of ect2-1 ECT2-mCherry and te234 ECT2W464A-mCherry genotypes by fluorescence microscopy. (C) Protein blot showing expression levels of ECT2-mCherry in the 3+3 lines of ect2-1 ECT2-mCherry and te234 ECT2W464A-mCherry used as biological replicates for FACS selection of ECT2-expressing cells. Amido black (A.B.) is used as loading control. (D) Fluorescence profile (mCherry vs. GFP fluorescence) of root cells (protoplasts) from the transgenic lines in (C). The complete set of lines/samples is shown in Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Non-transgenic Col-0 WT is shown as control for background autofluorescence. Cells with a fluorescence profile within the outlined areas were selected for RNA extraction, Smart-seq2 library construction, and sequencing. (E) Genes with more than one poly(A) site cluster (PAC) in the different target/non-target sets. Dark shades are genes in which the dominant PAC in te234 ECT2W464A-mCherry samples differs from the one in ect2-1 ECT2-mCherry. (F, G) Distribution of distances (d [nt]) of the most common poly(A) site between te234 ECT2W464A-mCherry and ect2-1 ECT2-mCherry samples for all genes where the most common poly(A) site could be determined in both genotypes (6648 non-targets, 4072 permissive targets, and 1486 stringent targets). Negative values are upstream (5′) and positive values are downstream (3′) relative to the gene orientation. (F) Distances are binned by ±10, ±100, ±1000, and >1000 bp. (G) Distances are plotted by nucleotide in a ±40 bp window.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Original (uncropped) membrane from Figure 5C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72377/elife-72377-fig5-data1-v2.zip
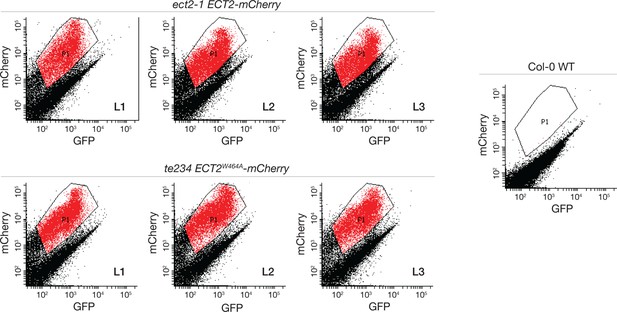
FACS-sorting of root protoplasts expressing ECT2-mCherry.
Fluorescence profile (mCherry vs. GFP fluorescence) of root cells (protoplasts) from the transgenic lines used as replicates for transcriptomic analyses (Figures 5 and 7). Non-transgenic Col-0 WT is shown as control for background autofluorescence. Cells with a fluorescence profile within the outlined areas were selected for RNA extraction, Smart-seq2 library construction, and sequencing.
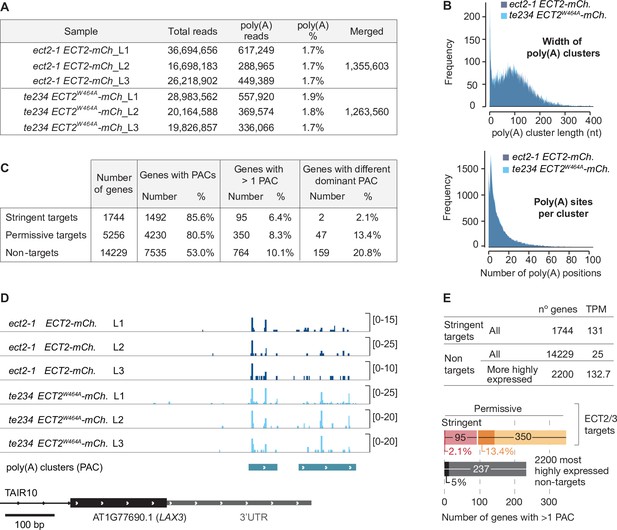
Poly(A) sites do not change in ECT2/3 targets upon loss of ECT2/3/4 function (extended data).
(A) Summary of poly(A)-containing reads (i.e., reads with at least nine untemplated As) after removal of reads mapping upstream of purine-rich sites. These reads were used for cluster identification, yielding 17,028 putative poly(A) site clusters (PACs), from which 14,667 were retained after further filtering of potential false positives (see Materials and methods). (B) Features of PACs. (Upper panel) Genomic distance between most upstream and most downstream poly(A) sites within each cluster (median length of 105 bp). (Lower panel) Total number of genomic positions within the cluster where at least one read with an untemplated poly(A) tail was detected (median of 12 poly(A) sites per cluster). (C) PACs sorted by ECT2/3 target status. Percentages of genes with more than one PAC refer to the number of genes with PACs. Percentages of genes with a dominant PAC (defined as the cluster with the most reads) that is different between te234/ECT2W464A-mCherry and ect2-1/ECT2-mCh samples refer to the number of genes with more than one PAC. (D) Variation in dominant polyadenylation sites for the non-ECT2/3-targeted transcript LAX3, an example of gene with different dominant PAC. Independently of the fact that the total amount of poly(A) reads is generally higher in te234/ECT2W464A-mCherry compared to ect2-1/ECT2-mCh samples (notice that the scales have been adjusted for optimal comparison of PAC usage within samples), the ratio between the number of reads in the upstream and the downstream clusters is different in the two genotypes. Transcript annotation is based on TAIR10. (E) Mean TPMs (Smart-seq2 data of sorted protoplasts, combining all six samples) of genes in the different ECT2/3 targets groups (upper panel). The significantly lower likelihood for ECT2/3 targets to have a different dominant PAC upon loss of ECT2/3/4 function depletion compared to non-targets (Figure 5E) could be due to differences in transcript abundance between the target and non-target groups. Looking at only the 2200 most highly expressed non-target genes, only 5.5% of these genes have a different dominant PAC in te234/ECT2W464A-mCherry than ect2-1/ECT2-mCh samples (lower panel, dark shading refers to genes with different dominant PAC as in Figure 5E), significantly smaller than the percentage for all non-target genes (20.8%, Figure 5E) (p=3.2e−9, Fisher’s exact test).
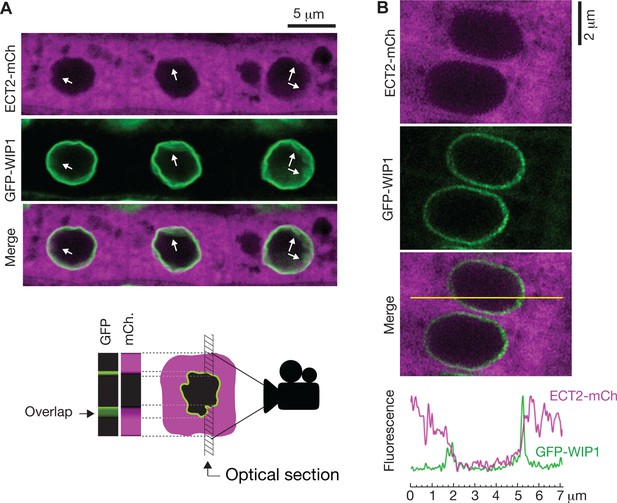
ECT2 is not in the nucleus.
(A) Standard confocal microscopy of root cells co-expressing ECT2-mCherry and GFP-WIP1. White arrows indicate areas in which apparent spills of ECT2-mCherry signal into the nucleus overlap with blurry GFP signal from the nuclear envelope, a sign of not-perpendicularity between the envelope and the optical plane as exemplified on the cartoon at the bottom. (B) Airyscan super-resolution confocal microscopy of root cells as in (A). The image is cropped from a larger picture shown in Figure 6—figure supplement 1. mCherry and GFP fluorescence signals along the yellow line show absence of ECT2-mCherry inside the limits of the GFP-labeled nuclear envelope.
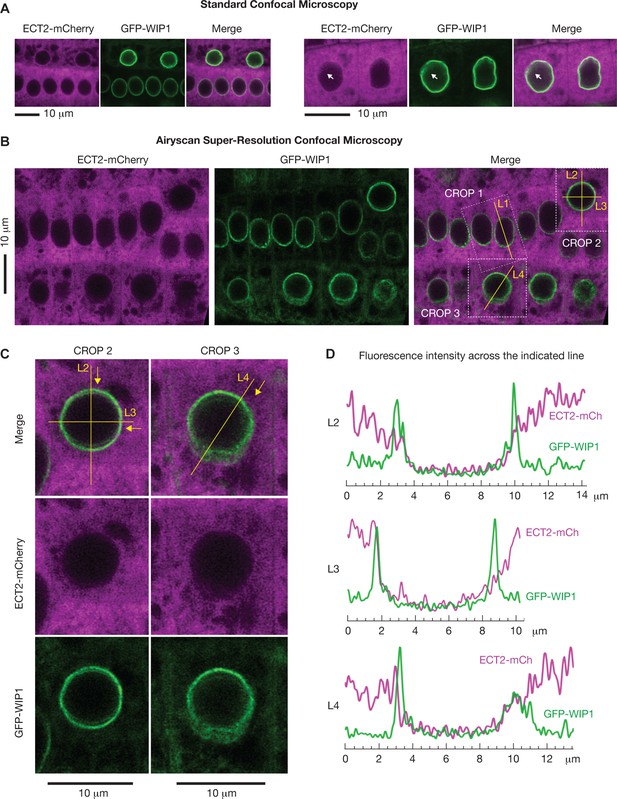
Super-resolution confocal microscopy of cells co-expressing ECT2-mCherry and the nuclear envelope marker GFP-WIP1.
(A) Standard confocal microscopy of root cells co-expressing ECT2-mCherry and GFP-WIP1 as in Figure 6A. (B–D) Airyscan super-resolution confocal microscopy of root cells as in (A). White dashed outlines in (B) are magnified in (C) (crops 2 and 3), and mCherry/GFP fluorescence along the yellow lines (L2–4) is plotted in (D). Yellow arrows indicate the direction of the fluorescence plots from left to right. Magnification of crop 1 and fluorescence intensity along L1 is shown in Figure 6B.
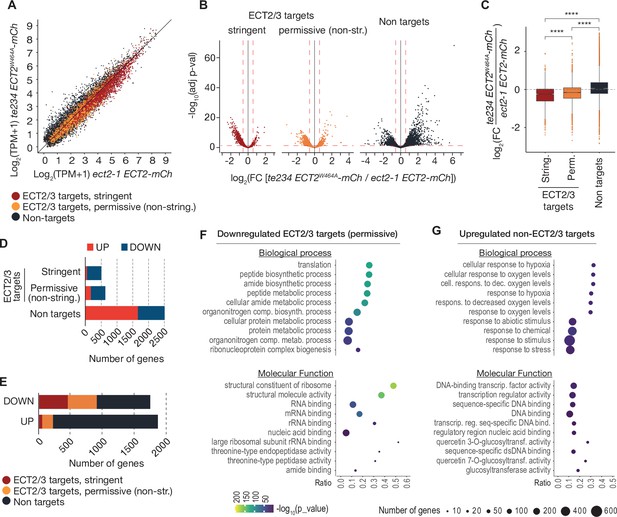
ECT2/3 targets are generally less abundant in cells without ECT2/3/4 function.
(A) Scatterplot of TPM expression values in Smart-seq2 libraries of root protoplasts expressing ECT2-mCherry in te234/ECT2W464A-mCherry versus ect2-1/ECT2-mCherry samples. (B) Volcano plots reveal genes differentially expressed between the genotypes described in (A). (C) Boxplots of log2 fold change expression values between te234/ECT2W464A-mCherry and ect2-1/ECT2-mCherry samples. (D, E) Bar plots showing the amount of significantly upregulated and downregulated genes in ECT2/3 targets and non-targets. (F, G) List with the 10 most significantly enriched GO terms among significantly downregulated ECT2/3 targets (permissive set) (F), or upregulated non-targets (G) upon loss of ECT2/3/4 function. GO, gene ontology.

Differential expression analysis using intact root tips of ect2/ect3/ect4 knockout plants recapitulates the results obtained with sorted protoplasts.
(A) Principal component analysis of transcriptome expression values (TPM) in Smart-seq2 libraries from FACS-sorted root protoplasts of te234/ECT2W464A-mCherry and ect2-1/ECT2-mCherry 5-day-old seedlings (left panel), or in RNA-seq libraries obtained from root tips of te234 and wild type 4-day-old seedlings (right panel). (B) Boxplots of log2 fold change expression values between the genotype-pairs described in (A). (C) Volcano plots showing genes differentially expressed between the genotype-pairs described in (A). Upregulated non-ECT2/3 targeted transcription factors and stress-responsive genes are marked. (D, E) List with the 10 most significantly enriched GO terms among significantly upregulated ECT2/3 targets (permissive set) (D), or downregulated non-targets (E) in root tips of te234 compared to wild type. GO, gene ontology.
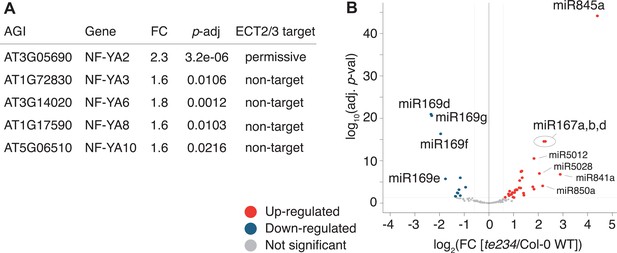
miRNA profile in root tips of ect2/ect3/ect4 knockout plants.
(A) Differential expression analysis of te234 versus Col-0 WT in 4-day-old root tips shows that expression of several stress-related NF-YA transcription factors (miR169defg targets) is induced in te234 plants. FC, Fold Change [te234/WT]. (B) Volcano plot showing miRNAs differentially expressed in te234 versus Col-0 WT in 4-day-old root tips.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (Arabidopsis thaliana) | ECT2 | TAIR10 | AT3G13460 | EVOLUTIONARILY CONSERVED C-TERMINAL REGION 2 |
| Gene (Arabidopsis thaliana) | ECT3 | TAIR10 | AT5G61020 | EVOLUTIONARILY CONSERVED C-TERMINAL REGION 3 |
| Gene (Arabidopsis thaliana) | ECT4 | TAIR10 | AT1G55500 | EVOLUTIONARILY CONSERVED C-TERMINAL REGION 4 |
| Gene (Arabidopsis thaliana) | WIP1 | TAIR10 | AT4G26455 | WPP DOMAIN INTERACTING PROTEIN 1 |
| Gene (Drosophila melanogaster) | ADAR Isoform N | Genebank, FlyBase, NCBI | CG12598 NM_001297862 | Adenosine deaminase acting on RNA |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | SALK_002225 C (ect2-1) | NASC | N657472, N2110120 | |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | SALK_077502 (ect3-1) | NASC | N577502, N2110123 | |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | te234 (ect2-1/ect3-1/ect4-2) | Arribas-Hernández et al., 2018 | N2110132 | Donated to NASC and ABRC |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | ECT3pro:FLAG-DmADARE488Qcd-ECT3ter | This paper (see Methods) | Seed requests to pbrodersen@bio.ku.dk | |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | ect3-1/ECT3pro:ECT3-FLAG-DmADARE488Qcd-ECT3ter | This paper (see Methods) | Seed requests to pbrodersen@bio.ku.dk | |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | te234/ECT3pro:ECT3-FLAG-DmADARE488Qcd-ECT3ter | This paper (see Methods) | Seed requests to pbrodersen@bio.ku.dk | |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | ect2-1/ECT2pro:ECT2-FLAG-DmADARE488Qcd-ECT2ter | Arribas-Hernández et al., 2021 | ||
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | te234/ECT2pro:ECT2-FLAG-DmADARE488Qcd-ECT2ter | Arribas-Hernández et al., 2021 | ||
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | ect2-1/ECT2pro:ECT2-mCherry-ECT2ter | Arribas-Hernández et al., 2018; Arribas-Hernández et al., 2020 | N2110839, N2110840 | Donated to NASC and ABRC |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | te234/ECT2pro:ECT2W464A-mCherry-ECT2ter | Arribas-Hernández et al., 2018; Arribas-Hernández et al., 2020 | N2110847, N2110848 | Donated to NASC and ABRC |
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | GFP:WIP1 | Xu et al., 2007 | ||
| Genetic reagent (A. thaliana) | ect2-1/+ GFP: WIP1ECT2pro:ECT2- mCherry-ECT2ter | This paper (see Methods) | Seed requests to pbrodersen@bio.ku.dk | |
| Antibody | anti-mCherry (rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | ab183628 | Used for WB (1:1000) |
| Chemical compound, drug | Glufosinate-ammonium (PESTANAL) | Sigma | 45520 77182-82-2 | Used for selection of transgenic lines |
| Sequence-based reagent | USER cloning primers | This paper (Appendix) | Used for cloning. Sequences are in the Appendix | |
| Commercial assay or kit | RNeasy Plus Micro kit (inc RLT buffer) | QIAGEN | Cat. # 74,034 | Used for RNA-extraction of FACS-sorted protoplasts |
| Commercial assay or kit | Illumina DNA Nextera Flex kit (now called Illumina DNA Prep) | Illumina | Cat. # 20018704 | Used for Smart-seq2 library preparation |
| Commercial assay or kit | NEBNext small RNA library prep set for Illumina | NEB | Cat. # E7330S | Used for sRNA-seq library preparation |
| Software, algorithm | R | https://www.R-project.org/ | Used for data analyses | |
| Software, algorithm | hyperTRIBER | Rennie et al., 2021; https://github.com/sarah-ku/hyperTRIBER; https://github.com/sarah-ku/targets_arabidopsis | Used for calling significant ADAR-edited sites | |
| Software, algorithm | cutadapt | Kechin et al., 2017 | Used for trimming Smart-seq2, mRNAseq and sRNA-seq reads | |
| Software, algorithm | STAR | Dobin et al., 2013 | Used for mapping Smart-seq2, mRNAseq and sRNA-seq reads | |
| Software, algorithm | nanoPARE and PAS analysis pipelines | Schon et al., 2018; https://github.com/Gregor-Mendel-Institute/nanoPARE; https://github.com/maschon0/ect_polyA_analysis | Used for PAS/PAC analyses | |
| Software, algorithm | bedtools | Quinlan and Hall, 2010 | Used to merge polyadenylation clusters | |
| Software, algorithm | Salmon | Patro et al., 2017 | Used for transcript quantification (Smart-seq2 and mRNAseq) | |
| Software, algorithm | featureCounts | Liao et al., 2014 | Used for sRNA-seq quantification | |
| Software, algorithm | DESeq2 | Love et al., 2014 | Used for DEA (Smart-seq2, mRNAseq and sRNA-seq) | |
| Software, algorithm | gprofiler2 | Raudvere et al., 2019 | Used for GO-term enrichment analysis | |
| Software, algorithm | ggplot2 | https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org | Used to generate plots | |
| Software, algorithm | ImageJ | Schindelin et al., 2012 | Used to generate fluorescence intensity plots | |
| Software, algorithm | IGV (Integrative Genomics Viewer) | Robinson et al., 2011 | Used to navigate and represent genomic data |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
ECT3 HyperTRIBE data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72377/elife-72377-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
ECT2 and ECT3 HyperTRIBE data in triple versus single mutants.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72377/elife-72377-supp2-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 3
ECT2/ECT3-target sets.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72377/elife-72377-supp3-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 4
Poly(A) site selection data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72377/elife-72377-supp4-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 5
Differential expression analysis of ect2/ect3/ect4 mutants (mRNA).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72377/elife-72377-supp5-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 6
Differential expression analysis of ect2/ect3/ect4 mutants (miRNAs).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72377/elife-72377-supp6-v2.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72377/elife-72377-transrepform1-v2.pdf





