Structure and ion-release mechanism of PIB-4-type ATPases
Figures
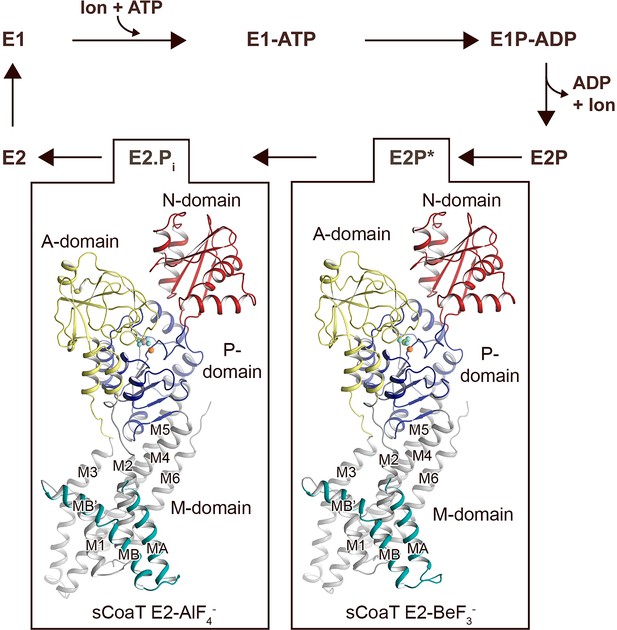
Overall architecture and reaction cycle.
The sCoaT structures reveal that PIB-4-ATPases comprise soluble A-, P-, and N-domains, shown in yellow, blue, and red, respectively, as well as a transmembrane domain with eight helices: MA and MB, in cyan, and M1–M6, in grey, and that the PIB-4-topology lacks classical so-called heavy-metal-binding domain. The transport mechanism of P-type ATPases depends on ATP-dependent phosphorylation and auto-dephosphorylation, and includes four principal conformations, E1, E1P, E2P, and E2, where P denotes phosphorylation. The determined structures are trapped in two transition states following ion release – an occluded late E2P (E2P*) and an occluded transition state of dephosphorylation, E2.Pi.
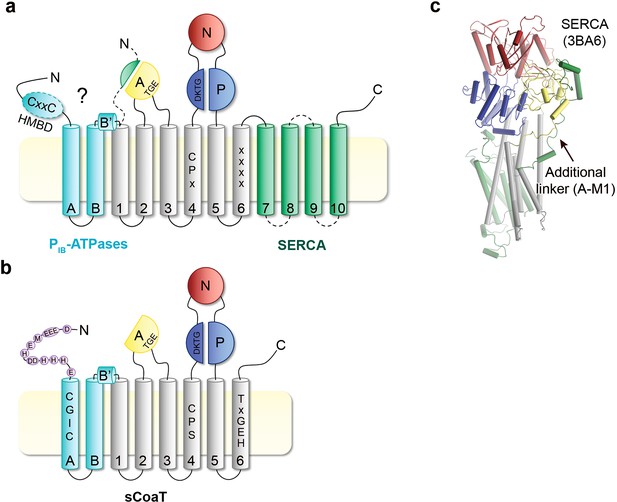
Topology comparison.
Topological differences between PIB-ATPases and classical P-type ATPases such as sCoaT and SERCA, respectively. (a) Schematic topology of P-type ATPases showing features unique to PIB-ATPases (the so-called heavy-metal-binding domain, HMBD, and transmembrane helices MA–MB in cyan) and SERCA (an extended A-domain, an additional A-domain linker, and M7–M10 transmembrane helices in green). Location of key residues in the M-domain for PIB-ATPases are highlighted. (b) The structure of SERCA (PDB ID 3BA6), coloured as the schematic topology highlighting the additional linker to the A-domain. (c) Topology of the PIB-4-ATPase sCoaT. The present work discloses the presence of helices MA, MB, MB’, and that the core of PIB-4-ATPases is devoid of classical HMBD, representing a previously elusive matter. The cysteine pair (CGIC in the sequence) in the N-terminus of sCoaT is rather positioned in MA. The N-terminus of sCoaT is rich in methionine, cysteine, histidine, aspartate, and glutamate residues (shown as purple circles), amino acids that can bind metal.
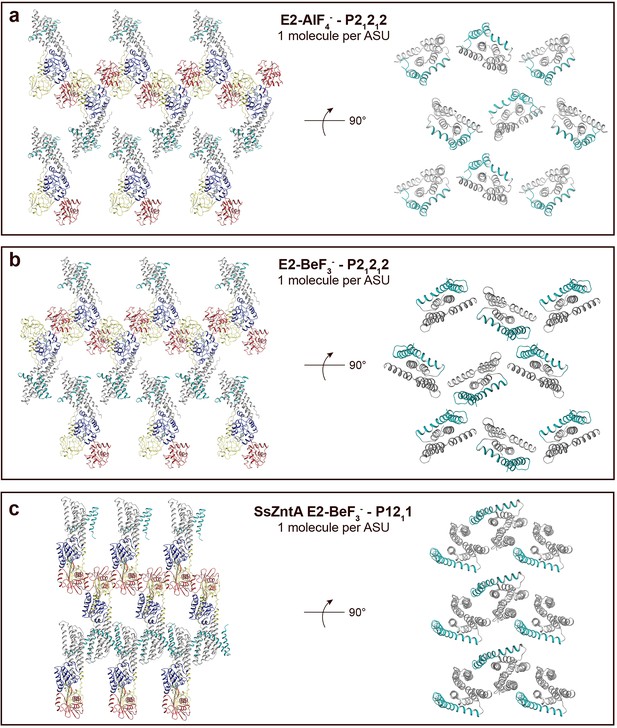
Crystal packing of sCoaT E2-AlF4− compared to the E2-BeF3− crystal form of ZntA from Shigella sonnei (SsZntA, PDB ID: 4UMV).
The domains are coloured as in Figure 1b. (a) sCoaT E2-AlF4− (P21212, with one molecule per asymmetric unit). Left: view of the membrane layer. Right: 90° rotation view (compared to panel to the left) showing only the transmembrane domains. Equivalent views of the sCoaT E2-BeF3− (P21212) (b) and the SsZntA E2-BeF3− (P1211) (c) crystal forms. Note the loose packing of the sCoaT crystals compared to that of SsZntA E2-BeF3−.
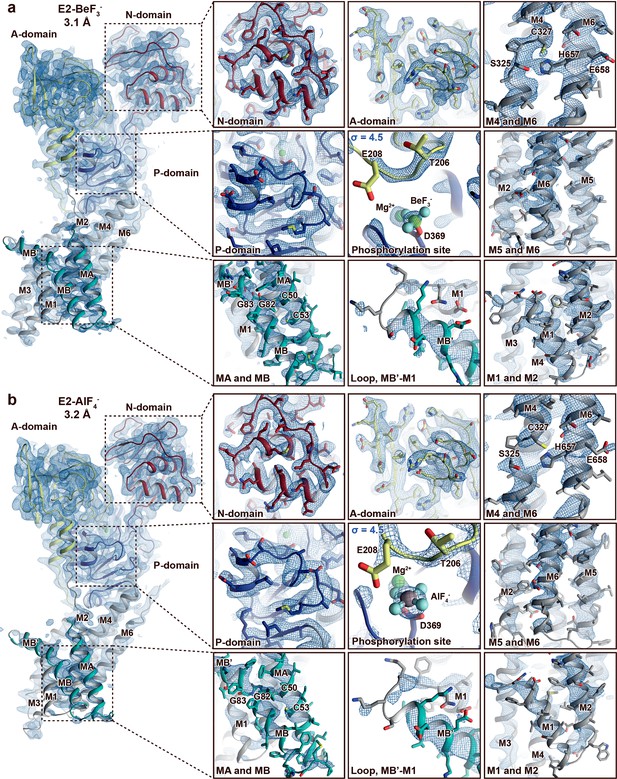
Electron density quality.
Final, sharpened, 2Fo-Fc electron density at σ = 1.0 (blue mesh) if not otherwise stated. The overall resolution is indicated and the structures are coloured as in Figure 1. (a) E2-BeF3− and (b) E2-AlF4−. The quality of the maps differs between structures and domains. The A-, P-, and N-domains are well resolved in both structures. The M-domain is in general less well resolved than the soluble domains, and the domain is somewhat more well resolved in the E2-BeF3− structure than in E2-AlF4− structure. Nevertheless, it is still clear that MA and MB are present and that C50 and C53 in the N-terminus are membrane embedded and not part of a heavy-metal-binding domain (HMBD). This is relevant, as CXXC is otherwise a pattern typically linked to a solvent-exposed metal-binding site in HMBDs of other PIB groups.
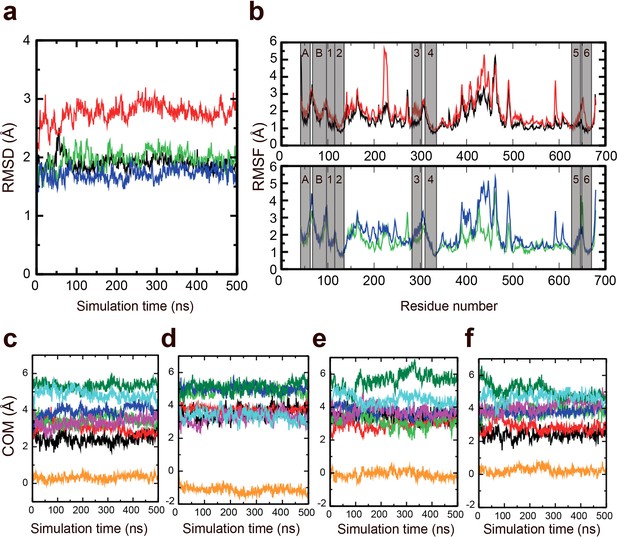
Stability of the M-domain.
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were performed to assess the stability of the M-domain. (a) Root mean square deviation of the M-domain in AlF4− (black), AlF4−-repeat (red), BeF3− (green), and BeF3−-repeat (blue) simulations. (b) RMSF of the M-domain in the AlF4− and AlF4−-repeat simulations (upper) and BeF3− and BeF3−-repeat simulations (lower) across the Cα atoms. The transmembrane (TM) helices region are marked in transparent grey. Evolution of the centre-of-mass of TM helices in the (c) AlF4−, (d) AlF4−-repeat, (e) BeF3−, and (f) BeF3-repeat simulations. The TM helices are shown in different colours: MA (black), MB (red), M1 (green), M2 (blue), M3 (magenta), M4 (orange), M5 (dark green), and M6 (cyan).
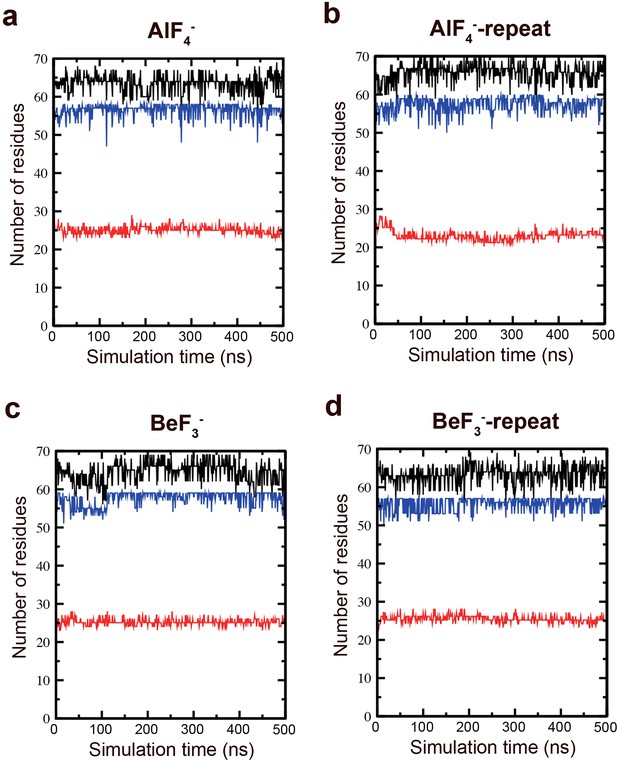
Secondary structure stability of the M-domain.
MD simulations were performed to assess the secondary structure stability of the M-domain. Total structure (black), helix (blue), and coil (red) secondary structural elements in the (a) AlF4−, (b) AlF4−-repeat, (c) BeF3−, and (d) BeF3−-repeat simulations.
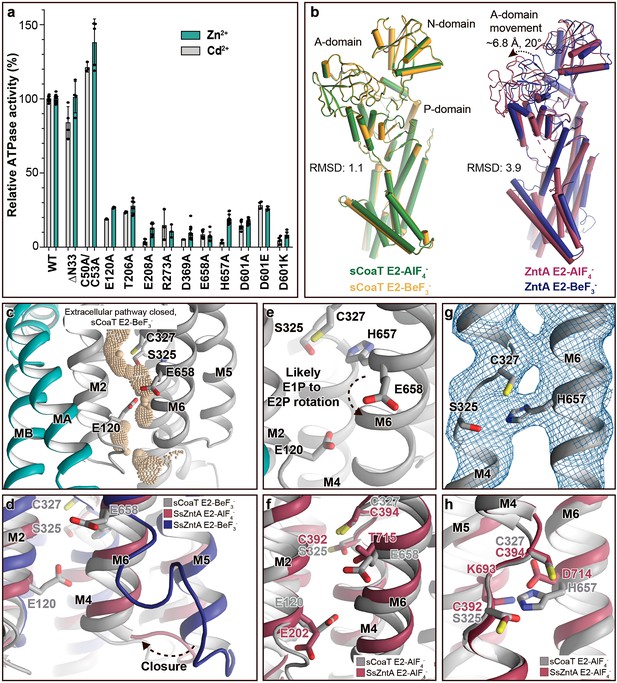
Mechanistic insight into the function of PIB-4-ATPases.
(a) Functional ATPase assay in lipid–detergent solution with targeted residues in sequential order. The wild-type (WT)-specific activity using the employed experimental conditions in the presence of 50 μM metal is 1.00 ± 0.01 μmol mg−1 min−1 with Zn2+ and 2.80 ± 0.06 μmol mg−1 min−1 with Cd2+, comparable to the activity previously measured for PIB-4-ATPases. For biological averages and SD, see Figure 2—figure supplement 1e. (b) Comparisons of E2-AlF4− and E2-BeF3− structures of sCoaT and the equivalent of SsZntA (PDB ID of SsZntA structures: 4UMV and 4UMW). All superimpositions were performed based on the P-domain, and the RMSD values for the overall structures are indicated. (c) Identified cavity (wheat) in the E2-BeF3− structure using the software HOLE. The E2-BeF3− and the E2-AlF4− (not shown) structures are occluded, lacking continuous connection between the ion-binding site to the outward environment. (d) The conformational changes that likely allow for closure of the release pathway, as illustrated from the E2-BeF3− structure of SsZntA to the E2-AlF4− structures of sCoaT or SsZntA. (e–h) Close views of ion-binding and -release residues in the M-domain of sCoaT and SsZntA. (e) The orientation of E658 is incompatible with high-affinity binding, and is likely contributing to ion release. (f) Release likely takes place via E658 and E120. (g) The sandwiched position between S325 and C327 of H657, including the final 2Fo-Fc electron density (blue). (h) The position of H657 in sCoaT overlaps with the one of K693 in SsZntA, and both likely serve as in-built counterions.
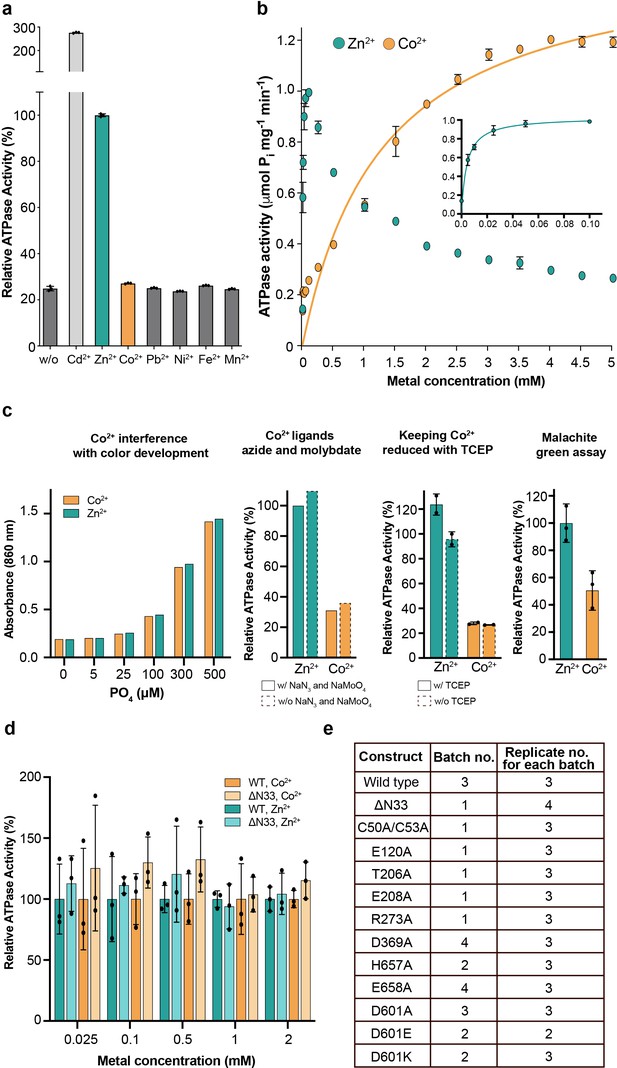
Metal selectivity screening and reproducibility.
(a) Screen of different transition metals, tested at 50 μM each. There is clear metal-dependent ATPase activity with Zn2+ (1.0 ± 0.01 µmol mg−1 min−1) and Cd2+ (2.8 ± 0.05 µmol mg−1 min−1), comparable to the activity previously measured for PIB-4-ATPases and also to Zn2+-dependent activity of SsZntA (0.59 ± 0.02 μmol mg−1 min−1) Wang et al., 2014. In contrast, only low ATPase activity (about 5% of the wild-type, corrected for the background observed with no metal added) was detected with Co2+ for sCoaT. (b) Titration of zinc and cobalt. Co2+-induced ATPase activity predominates above 1 mM, while at lower concentrations Zn2+ stimulates activity at a faster rate. The data yield KM values of 1.3 mM and 4.1 µM for Co2+ and Zn2+, respectively. The corresponding for the SsZntA related pump EcZntA is 10 µM with Zn2+ (Mitra and Sharma, 2001). (c) Screening of assay conditions and assay type. (d) The effect of the N-terminal tail on the ion specificity. Relative activity in the presence of Co2+ and Zn2+ (100% is equal to the activity measured for wild-type at every measured metal type and concentration), respectively, at five different metal concentrations, suggesting that the tail is no major determinant for metal specificity. (e) Biological and technical replicates exploited to generate the error bars in Figure 2a.
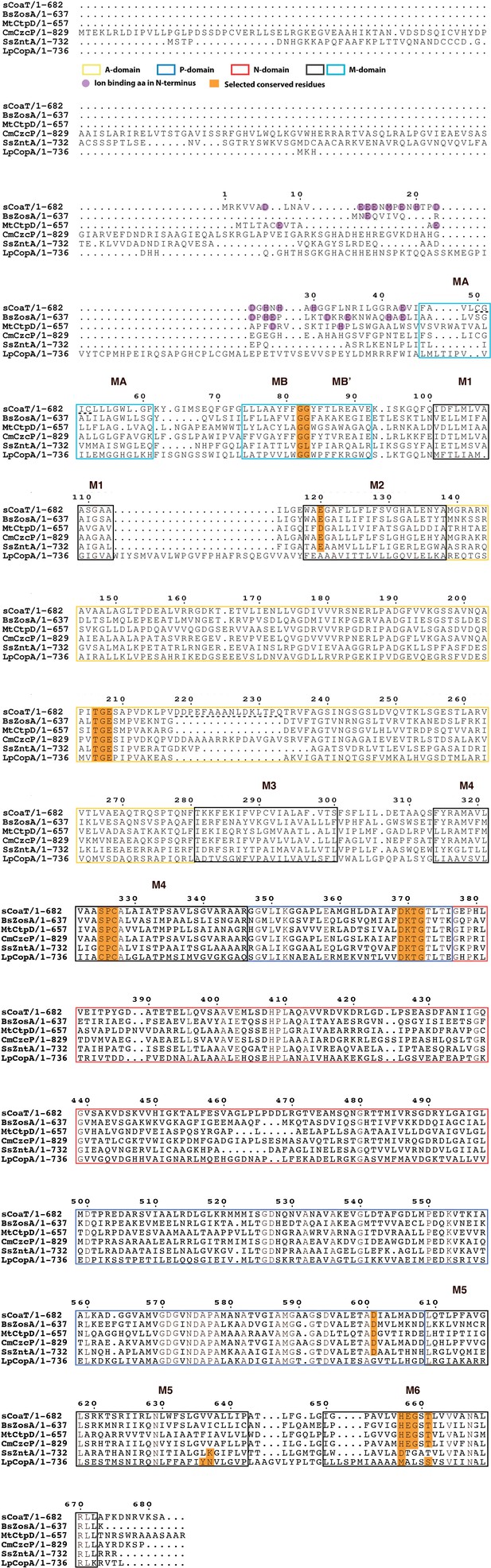
Sequence alignment of selected PIB-ATPases.
Sequence alignment of four PIB-4-ATPases, sCoaT from Sulfitobacter sp. NAS-14.1 CmCzcP from Cupriavidus metallidurans, BsZoa from Bacillus subtilis and MtCtpD from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The PIB-1-ATPase LpCopA from Legionella pneumophila and the PIB-2-ATPase SsZntA from Shigella sonnei are also included for comparison.
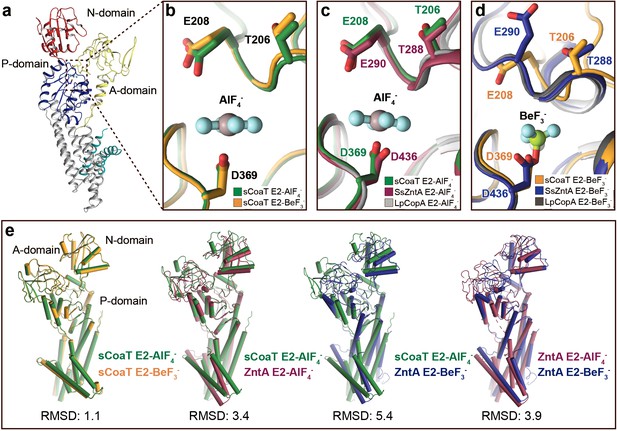
Comparison of E2 states overall and close views of the phosphorylation site.
The TGE loop in the E2-BeF3−-stabilized sCoaT (E2P*) is preorganized for dephosphorylation, which is not the case for SsZntA and LpCopA. (a) The overall E2P* structure of sCoaT showing the region of focus in panels b–d. (b), Comparison of the TGE loop in the two sCoaT structures, with only minor differences. (c) Comparison of sCoaT E2.Pi with the equivalent structures of SsZntA and LpCopA (PDB ID: 4UMW and 4BYG). (d) Comparison of sCoaT E2P* with the equivalent structures of SsZntA and LpCopA (PDB ID: 4UMV and 4BBJ). (e) Comparisons of E2-AlF4− and E2-BeF3− structures of sCoaT and SsZntA (PDB ID of SsZntA structures: 4UMV and 4UMW). All superimpositions were performed based on the P-domain, and the RMSD values based on the overall structure are listed below the structural alignments. Alignment of the E2-BeF3− and E2-AlF4− structures of sCoaT demonstrates that they are very similar (RMSD = 1.1), and comparison to the equivalent structures of SsZntA support the conclusion from (a–d) that both structures have been captured in occluded E2.Pi transition states.
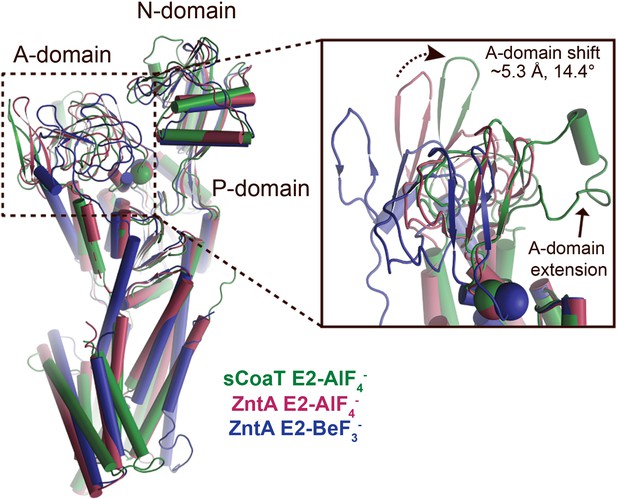
A-domain differences.
Superimposition of the E2-AlF4− structures of sCoaT (determined here, shown in green) and SsZntA (PDB ID 4UMW, purple) and the E2-BeF3− structure of SsZntA (PDB ID 4UMV, blue). The overall structures are shown to the left. The inset represents a close-view of the A-domain, showing that the sCoaT structure is more alike the SsZntA E2-AlF4− structure. The peripheral part of the A-domain in sCoaT is shifted closer to the P-domain, whereas the area around the conserved TGE motif (the Glu of the TGE motif is visualized as a sphere) superposes well with SsZntA. Like SERCA, the A-domain of sCoaT possesses a surface-exposed extension which is however not present in PIB-1- and PIB-2-ATPases.
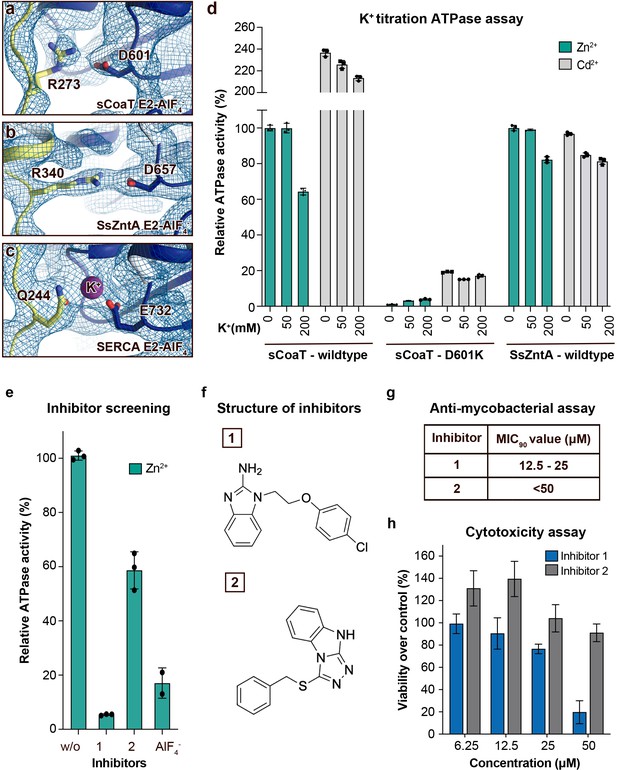
Regulation and inhibition.
(a–c) Close views of the regulatory point-of-interaction between the A- and P-domains in the E2-AlF4− structures of sCoaT, SsZntA, and SERCA (PDB IDs 4UMW and 1XP5) with the corresponding 2Fo-Fc electron density shown at σ = 1.0 (blue mesh). (a) sCoaT (coloured as in Figure 1) with interaction between D601 and R273. (b) SsZntA (shown as panel a) with interaction between D657 and R340. (c) SERCA (shown as in panel a) with bound K+ (purple) between E732 and Q244. (d) Functional ATPase assay in lipid–detergent solution of sCoaT (wild-type and D601K forms) as well as SsZntA (wild-type), using protein samples purified in the absence of K+ and Na+ (see Methods). The mean + SD of technical replicates is shown (n = 3). KCl leaves the function of sCoat and SsZntA essentially unaffected in the presence of Zn2+ (cyan) or Cd2+ (grey). The equivalent form of sCoaT D601K has previously been exploited to demonstrate K+ dependence in the Na,K-ATPase (Schack et al., 2008). Collectively, these data suggest that the P-/A-domain site regulation is K+ independent in PIB-ATPases, in contrast to classical P-type ATPases. (e–h) Evaluation of the effect on selected identified novel inhibitors on activity of protein, as well as survival of mycobacteria and primary human macrophages. (e) Effect of two inhibitors (300 μM) on the activity of sCoaT assessed in lipid–detergent solution in the presence of Zn2+. For comparison, the commonly used P-type ATPase inhibitor AlF4− (500 μM) is included. (f) The structure of inhibitors 1 and 2. (g) The minimal inhibitory concentration to kill 90% (MIC90) of mycobacteria for inhibitors 1 and 2. The mean MIC90 value for inhibitor 1 is 18.75 µM, while for inhibitor 2 it is over 50 µM. The values are based on four separate experiments. (h) The cytotoxic effect of different concentrations of inhibitors 1 and 2 on primary human macrophages (ATP assay). The standard error of mean (SEM) of nine replicates is shown (n = 9).
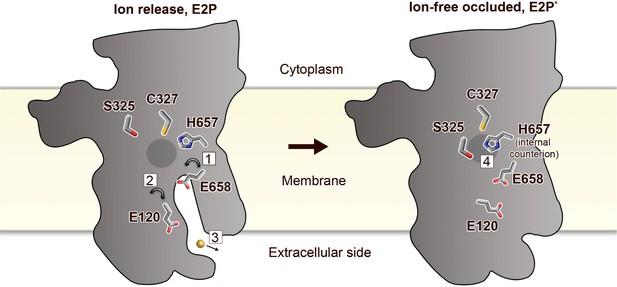
Putative ion-release and reocclusion mechanism of PIB-4-ATPases.
Schematic model illustrating the transmembrane domain (the soluble domains have been removed for clarity) of two separate states, an E2P and an occluded E2P* conformation as the determined structure (E2-BeF3−), respectively. Zinc or cadmium release from the high-affinity-binding site in the M-domain is likely permitted through re-orientation of E658 (1) in the E1P to E2P transition, thereby lowering the affinity for the occluded ion. E120 serves as a transient linker between the high-affinity-binding site and the outward environment (2). Following ion-release (3) H657 shifts to a sandwiched position between S325 and C327 (4), acting as a built-in counter ion, preventing backtransfer of the released ion, and allowing completion of the reaction cycle.
Tables
Data collection and refinement statistics.
Statistics for the highest resolution shell are shown in parentheses.
| E2-BeF3− | E2-AlF4− | |
|---|---|---|
| Data collection | ||
| Wavelength (Å) | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Space group | P 21 21 2 | P 21 21 2 |
| Cell dimensions | ||
| a, b, c (Å) | 89.0 94.5 128.8 | 89.6 93.7 128.3 |
| a, b, g (°) | 90 90 90 | 90 90 90 |
| Resolution (Å) | 47.3–3.1(3.22–3.11) | 45.6–3.3(3.37–3.25) |
| Rmerge (%) | 11.4 (276.3) | 15.5 (246) |
| I / σI | 17.8 (1.12) | 8.5 (0.98) |
| CC1/2 | 1 (0.475) | 0.99 (0.37) |
| Completeness (%) | 97.3 (99.8) | 99.2 (99.9) |
| Redundancy | 13.3 (13.8) | 6.1 (6.6) |
| Refinement | ||
| Resolution (Å) | 47.3–3.1(3.22–3.11) | 45.6–3.3(3.37–3.25) |
| No. reflections | 19,643 (1963) | 17,466 (1714) |
| Rwork / Rfree (%) | 24.4/26.8 | 21.8/25.5 |
| No. of atoms | ||
| Protein | 4,695 | 4,695 |
| Ligand/ion | 5 | 6 |
| Water | 10 | 0 |
| Average B-factors | ||
| Protein | 135.91 | 152.54 |
| Ligand/ion | 84.15 | 86.47 |
| Solvent | 79.62 | |
| R.m.s. deviations | ||
| Bond lengths (Å) | 0.004 | 0.003 |
| Bond angles (°) | 0.77 | 0.83 |
| Ramachandran statistics | ||
| Favoured (%) | 97.8 | 96.9 |
| Allowed (%) | 2.2 | 3.1 |
| Outliers (%)ClashscoreMolProbity score | 0.01.050.85 | 0.07.891.62 |
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (Sulfitobacter sp. (strain NAS-14.1)) | NAS141_02821 | Synthetic | Uniprot: A3T2G5 | |
| Cell line (Escherichia coli) | C41(DE3) | Sigma-Aldrich | Chemically competent cells | |
| Cell line(Mycobacterium bovis) | BCG Montreal | ATCC 35735 | ||
| Software, algorithm | Phenix | RRID:SCR_014224 | https://www.phenix-online.org/ | |
| Software, algorithm | ISOLDE | https://doi.org/10.1107/S2059798318002425 | https://isolde.cimr.cam.ac.uk/ | |
| Software, algorithm | UCSF ChimeraX | RRID:SCR_015872 | https://www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimerax/ | |
| Software, algorithm | COOT | RRID:SCR_014222 | http://www2.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/personal/pemsley/coot/ | |
| Software, algorithm | Pymol | RRID:SCR_000305 | http://www.pymol.org/ |





