The inherent flexibility of receptor binding domains in SARS-CoV-2 spike protein
Figures
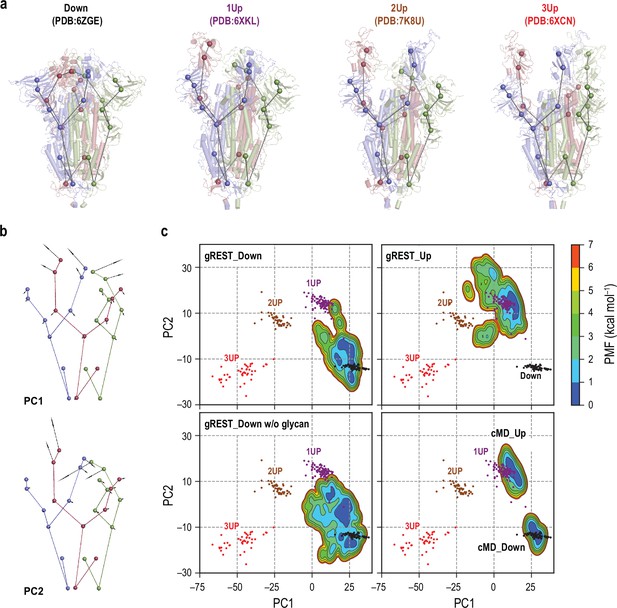
Comparisons of spike (S) protein structures in molecular dynamics (MD) simulations with cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures.
(a) Twenty-seven coarse-grained beads representations of four representative cryo-EM structures: Down (PDB ID: 6ZGE), 1Up (6XKL), 2Up (7K8U), and 3Up (6XCN). Chains A, B, and C in S-protein are shown in red, blue, and green, respectively. (b) The lowest two modes (PC1 and PC2) in principal component analysis of the 27-beads model of 289 cryo-EM structures. PC1 and PC2 respectively represent a symmetric and an anti-symmetric Down-to-Up motion of the receptor binding domains. The vector direction of PC1 is reversed so that it points from Down to Up for better visualization. The vectors are magnified 100 times for clarity. (c) Free-energy landscapes at 310 K along the PC1 and PC2 obtained from the simulations: (top) gREST_SSCR simulations with glycans starting from Down (500 ns) and Up (300 ns), (bottom left) gREST_SSCR simulation without glycans from Down (150 ns), (bottom right) conventional MD simulations with glycans starting from either Down or Up. The positions of cryo-EM structures are also shown for comparison. Wherein, Down, 1Up, 2Up, and 3Up conformations are shown in black, purple, brown, and red dots, respectively.
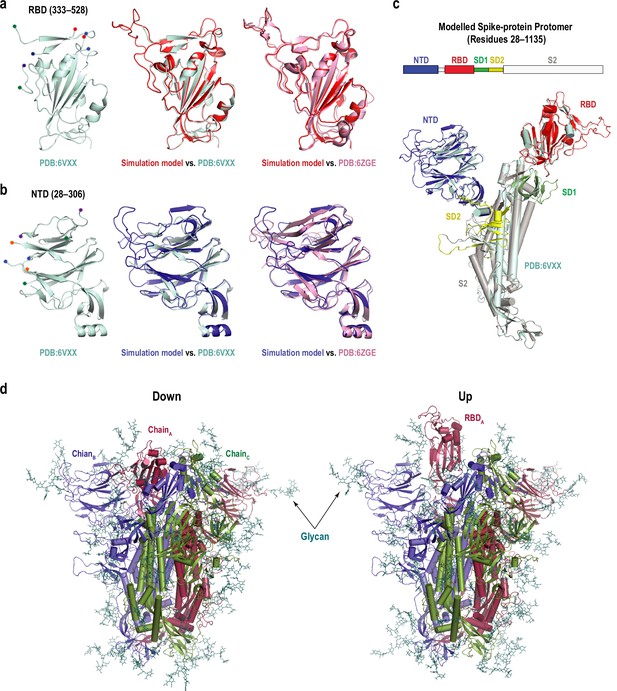
Structural model of the spike protein used in this study.
(a) Left: cartoon representation of the receptor binding domain (RBD) in the original cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure (PDB:6VXX). The terminal residues before and after the missing loops are highlighted with colored dots. Middle: superimposition of our simulation model, which was modeled from PDB:6LZG (red) to PDB:6VXX (cyan). Right: comparison between our simulation model (red) and more recent high-resolution cryo-EM structure in Down conformation (PDB:6ZGE) (pink). (b) Left: cartoon representation of the N-terminal domain (NTD) in the original cryo-EM structure (PDB:6VXX). The terminal residues before and after the missing loops are highlighted with colored dots. Middle: superposition of our simulation model (blue) to PDB:6VXX (cyan). Right: comparison between our simulation model (blue) and PDB:6ZGE (pink). (c) Superposition of the modeled protomer (residues 28–1135) to PDB:6VXX (cyan). Besides missing residues in the RBD and NTD, three other regions were also modeled using Modeller (Sali and Blundell, 1993). The head of the protomer is composed of S1 and S2 subunits. S1 includes NTD (blue), RBD (red), SD1 (green), and SD2 (yellow). Part of S2 that was included in the simulation model (gray). (d) Full models used in the simulation of Down and 1Up conformations, where 19 glycans per protomer were added. The protomers are shown in red, blue, and green cartoon for chains A, B, and C, respectively, and glycans are shown as deep teal sticks.
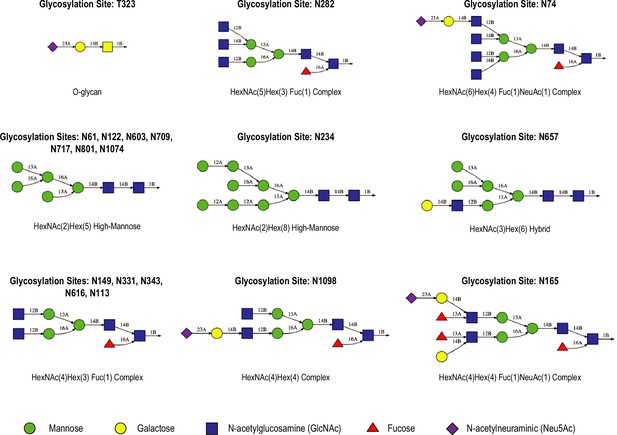
Glycans in our spike protein models.
Schematic representations of the glycan structures and types used in gREST_Down and gREST_Up simulations including the location of the glycosylation sites.
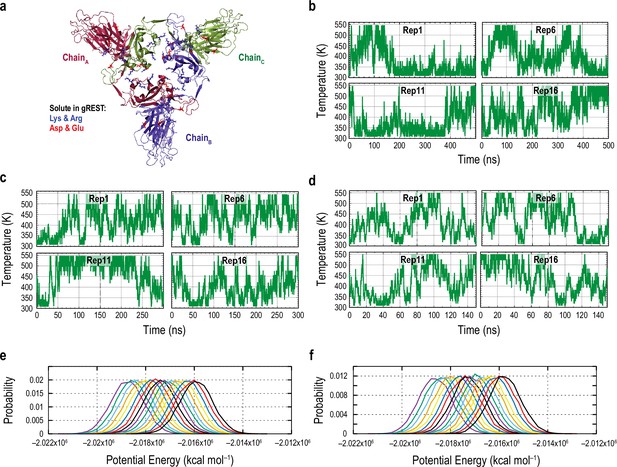
Performance of the gREST_SSCR simulations.
(a) Top view the S1 subunit, where the positively and negatively charged residues used for solute region in gREST are shown as blue and red sticks, respectively. (b, c, d) Time courses of the temperature in the selected replicas (1, 6, 11, and 16) in the 500 ns gREST_Down (b), 300 ns gREST_Up (c), and 150 ns gREST_Down w/o glycan simulations (d). All three simulations showed random walk in the temperature space. (e, f) Probability distribution of the potential energies of the sorted temperatures in gREST_Down (e) and gREST_Up simulations (f), both of which showed sufficient overlaps between temperature parameters.
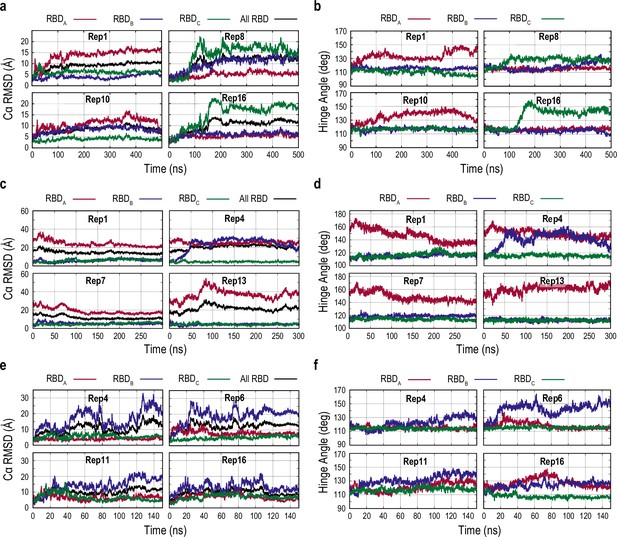
Characterization of the receptor binding domain (RBD) conformational change in the three gREST_SSCR simulations.
(a, c, e) Time courses of the root mean square deviation (RMSD) of the Cα atoms with respect to Down structure upon fitting the Cα atoms of the S2 subunit in the selected replicas from the gREST_Down (a), gREST_Up (c), and gREST_Down w/o glycan simulations (e). RMSD of the individual RBDs (red, blue, and green for chains A, B, and C, respectively) as well as all three RBDs (black) are shown. (b, d, f) Time courses of the hinge angle of RBDs in the gREST_Down (b), gREST_Up (d), and gREST_Down w/o glycan simulations (f).
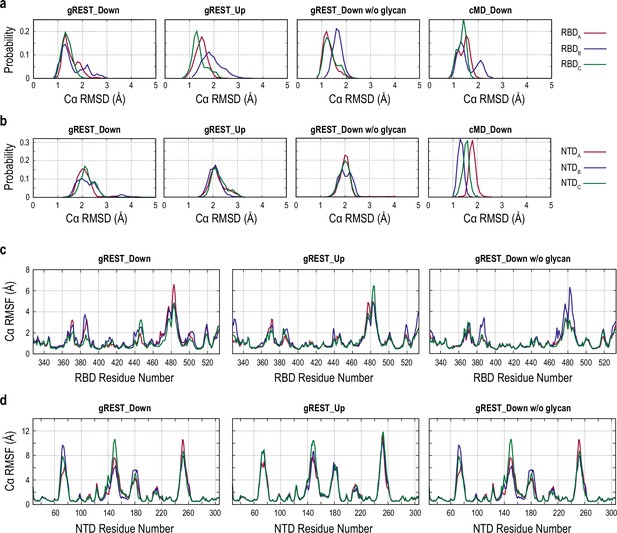
Analysis of the intra-domain stability of receptor binding domain (RBD) and N-terminal domain (NTD) in the gREST_SSCR simulations.
(a, b) Probability distribution of the Cα root mean square deviation (RMSD) of the RBDs (a) and NTDs (b) at 310 K of the gREST_Down, gREST_Up, and gREST_Down w/o glycan simulations as well as our previous 1 μs conventional molecular dynamics (cMD) simulation of the Down conformation (Mori et al., 2021). (c, d) Root mean square fluctuation (RMSF) of the Cα atoms of the RBDs (c) and NTDs (d) in the gREST_Down, gREST_Up, and gREST_Down w/o glycan simulations.
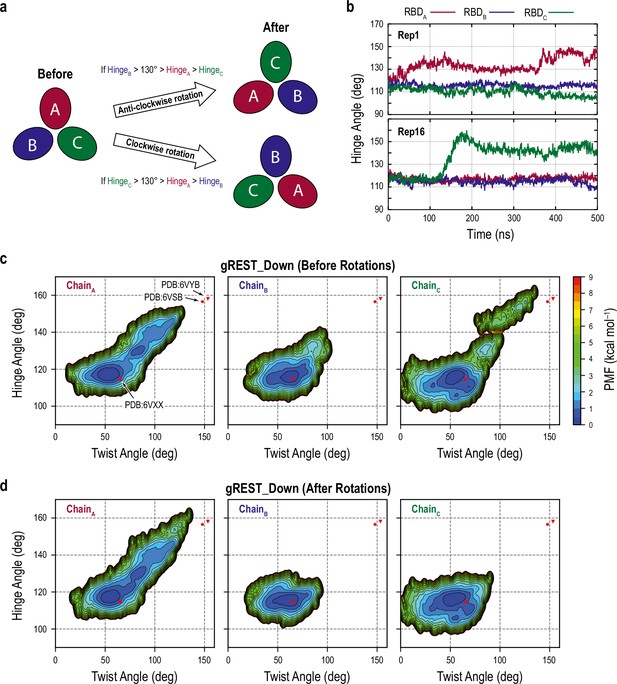
Scheme of the protomer rotation and analysis of the rotated trajectories of the gREST_Down simulation.
(a) Schematic representation of the rotation scheme and criteria that was used to define structural changes of receptor binding domains (RBDs). First, hinge angle of each RBD is calculated. Then, if the hinge angle of RBDB is larger than 130° and larger than those of RBDA and RBDC, all three chains are rotated anticlockwise, where the chain index is changed from A to C, B to A, or C to B. Similarly, if RBDC has the hinge angle more than 130° and its larger than hinge angles of RBDA and RBDB, all chains are rotated clockwise. If RBDA originally has the largest hinge angle, no rotation is applied. Rotation was applied to all frames of the selected replicas whose the majority of its snapshots had the above criteria. (b) Time courses of the hinge angle in replicas 1 (upper panel) and 16 (lower panel) from the gREST_Down simulation, where RBDA and RBDC showed the largest hinge angle, respectively. This shows the indistinguishability of RBD in our simulation and the need for rotation scheme for further analysis. (c, d) Free-energy landscape along the hinge and twist angles of the three chains before (c) and after the protomer rotation (d). Without the rotation scheme (c), Up-like conformations are observed in both chains A and C due to the indistinguishability of RBD.
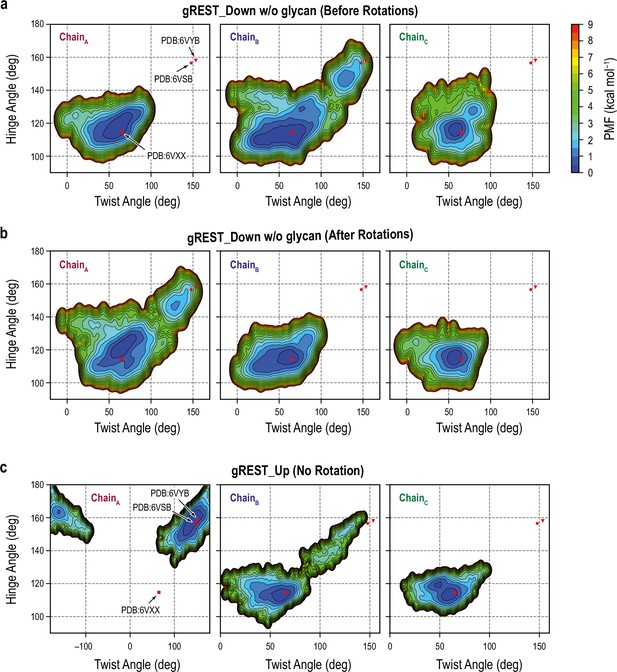
Free-energy landscape (FEL) along the hinge/twist angles in the gREST_Down w/o glycan and gREST_Up simulations.
(a, b) FEL in chains A, B, and C before (a) and after the rotation (b) in the gREST_Down w/o glycan simulation. The FELs show significant receptor binding domain (RBD) changes in chain B (or A) and to less extent in chain C. (c) FEL in chains A, B, and C without rotation in the gREST_Up simulation. The FELs show very large twist angles in RBDA as well as the formation of Up conformation in RBDB, demonstrating the formation of 2Up-like conformations.
Down-to-1Up transition of replica 16 in gREST_Down simulation.
1Up-to-2Up transition of replica 4 in gREST_Up simulation.
Down-to-1Up transition of replica 6 in gREST_Down w/o glycan simulation.
Representative receptor binding domain (RBD) conformations from molecular dynamics (MD) simulations vs. cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) PDB structures.
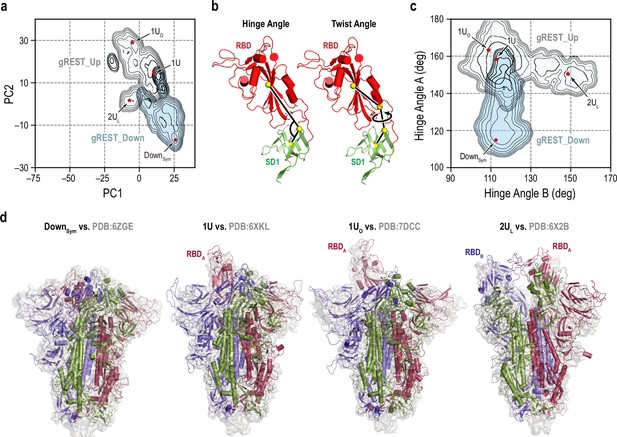
(a) An overlay of the two free-energy landscapes at 310 K along the PC1 and PC2 obtained from gREST_Down (light blue) and gREST_Up (light cyan) simulations. The red dots represent the positions of four representative RBD conformations: symmetric Down (DownSym), 1RBD Up (1U and 1UO) and 2RBDs Up-like (2UL) conformations. (b) Definitions of the hinge and twist angles representing the RBD conformations. The hinge angle is determined by three centers of masses (COMs, yellow spheres) of the core and top residues of SD1 (green, Cα atoms only) and the core residues of RBD (red, Cα atoms only). The twist angle is determined by the aforementioned COMs with an extra COMs of the bottom residues of RBD. (c) An overlay of two free-energy landscapes at 310 K along the hinge angles in RBDA and RBDB obtained from gREST_Down (light blue) and gREST_Up (light cyan) simulations. (d) Four representative conformations from MD simulations (cartoon representation) in comparison with cryo-EM structures (light gray surface). Chains A, B, and C in spike (S) protein are shown in red, blue, and green, respectively.
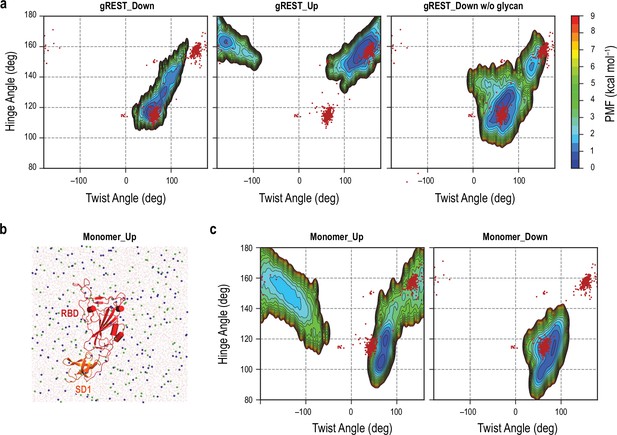
Free-energy landscape (FEL) along the hinge/twist angles in the gREST_SSCR simulations in comparisons with the conventional molecular dynamics (cMD) simulations for receptor binding domain (RBD)/SD1 monomer and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures.
(a) FEL of RBDA in all three gREST_SSCR simulations. Note that these FELs are identical with those in Figure 1—figure supplement 6d (left), 6c (left), and 7b (left). 891 cryo-EM protomers are shown as red dots. This reflects the flexibility of RBD not only in simulations but also in cryo-EM structures. (b) Snapshot at 100 ns in the cMD simulation of RBD/SD1 monomer, where the system is solvated with 0.15 M NaCl solution. (c) FEL of RBD/SD1 monomer starting from Up (left) and Down (right) conformations, highlighting the flexibility of RBD in the absence of protein environment.
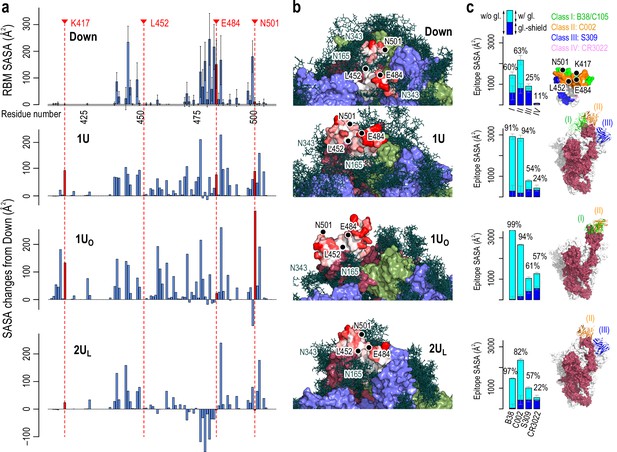
Accessibility of receptor binding motif (RBM).
(a) Per-residue solvent accessible surface area (SASA) values of the RBM (residues 410–510) in Down conformation (top) and their changes in Up conformations (bottom three). SASA values were calculated using the probe radius of 7.2 Å. Four mutational residues, K417, L452, E484, and N501, are highlighted in red. (b) The surface representation of RBM SASA (white to red for 0–260 Å2, the maximum value in Down, the values higher than this are truncated for consistent color scheme). Chains A, B, and C in the protein are shown in red, blue, and green surfaces, respectively, while a collection of glycans from 10 snapshots are shown in stick representation. (c) Epitope SASA and glycan shielding of four types of neutralized antibodies, B38 (Class I), C002 (Class II), S309 (Class III), and CR3022 (Class IV). Sum of SASA with glycans (cyan) and the glycan shield (blue) gives SASA without glycans. The ratio of the SASA with glycan over that without glycans is shown. The right-most column shows the putative interaction models with three classes of antibodies: Class III (S309, PDBID: 6WPT, blue), Class II (C002, PDBID: 7K8T, orange), and Class I (C105, PDBID: 6XCM, green).
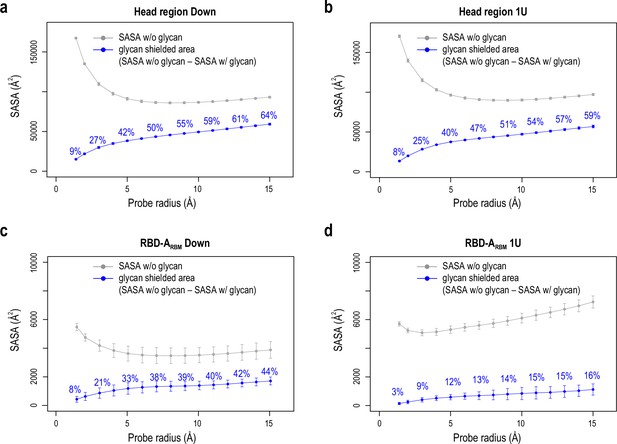
Glycan shield of spike (S) protein.
(a, b) Solvent accessible surface area (SASA) of the head region of S-protein and the glycan shielded area, calculated for Down and 1U conformations at different probe radii from 1.4 to 15 Å (from a sphere of water to that of antibody scale). The subtraction of the glycan shielded area (blue) from SASA without glycan (gray) gives SASA with glycan (an area between gray and blue curves). The ratio (%) of the glycan shielded area over SASA without glycan is also shown. (c, d) SASA of the receptor binding motif (RBM, residues 410–510) and the glycan shielded area, calculated for Down and 1U conformations. The results are consistent with the previous work by Amaro and co-workers (Pavlova et al., 2021).
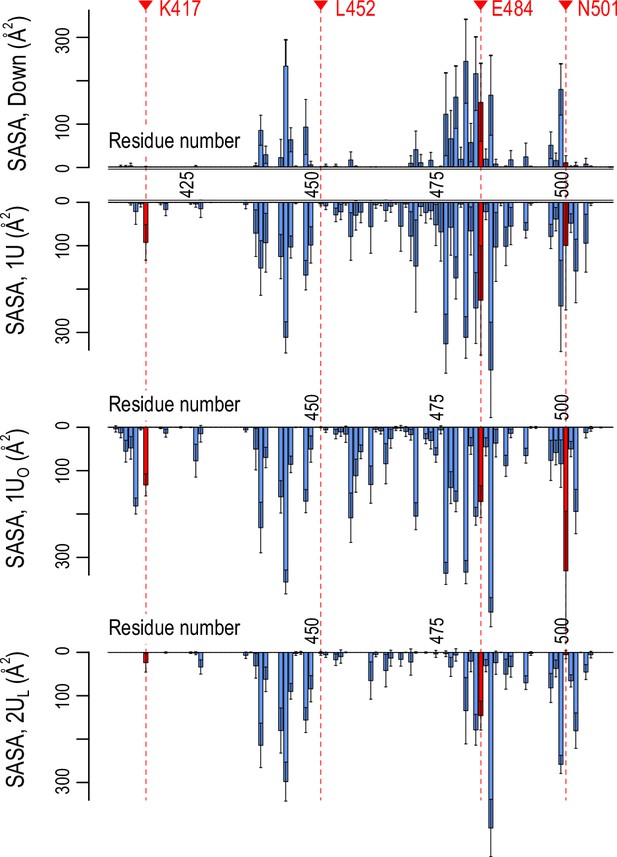
Accessibility of receptor binding motif (RBM).
Per-residue solvent accessible surface area (SASA) values of the RBM (residues 410–510) in Down (top) and three Up conformations (1U, 1UO, and 2UL, bottom three). SASA values were calculated using the probe radius of 7.2 Å. Four mutational residues, K417, L452, E484, and N501, are highlighted in red.
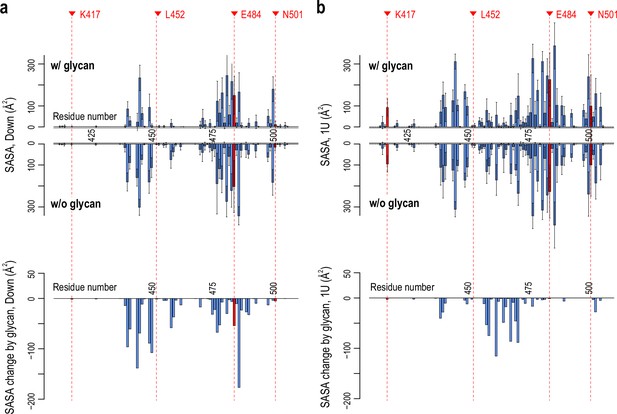
Glycan effect on the accessibility of receptor binding motif (RBM).
(a) Per-residue solvent accessible surface area (SASA) values of the RBM (residues 410–510) in Down conformation with and without glycan (top) and their changes (SASA w/ glycan – SASA w/o glycan, bottom). (b) Per-residue RBM SASA values in 1U conformation with and without glycan and their changes. Four mutational residues, K417, L452, E484, and N501, are highlighted in red.
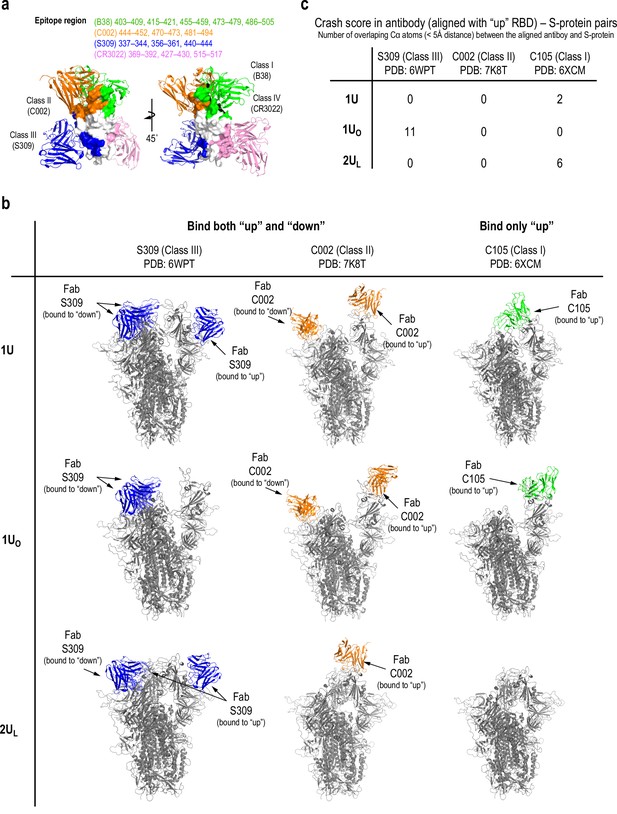
Putative interaction models with antibodies.
(a) The surface representation of receptor binding domain (RBD) epitopes for neutralizing antibodies: green: B38 (Class I), orange: C002 (Class II), blue: S309 (Class III), and pink: CR3022 (Class IV). The structures of spike (S) protein-bound antibodies are also shown in cartoon representation. The structures (PDBIDs 6WPT, 7K8T, and 6XCM for S309, C002, and C105, respectively) and epitope residues were taken from the paper by Barnes and co-workers (Hsieh et al., 2020). (b) The putative interaction with antibodies modeled by aligning the antibody structures from cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) with each of 1U, 1UO, and 2UL conformations. The structures of three antibodies, S309 (Class III), C002 (Class II), and C105 (Class I), were aligned with each conformation. Note that the class II/III antibodies bind both ‘Up’ and ‘Down’ conformations, while Class I binds only ‘Up’ conformation. For example, in 1U, S309 and C002 also bind to the ‘Down’ RBDs when sterically allowed (in 1U, two ‘Down’ RBDs bind S309, while one ‘Down’ RBD binds C002 due to steric hindrance). (c) The crash score between the antibody aligned with ‘Up’ RBD and S-protein. We defined the crash score as the number of overlapping Cα atoms (<5 Å distance) between the aligned antibody and S-protein. To avoid the confusion, the notations of ‘Up’ and ‘Down’ are used for RBD conformations in general.
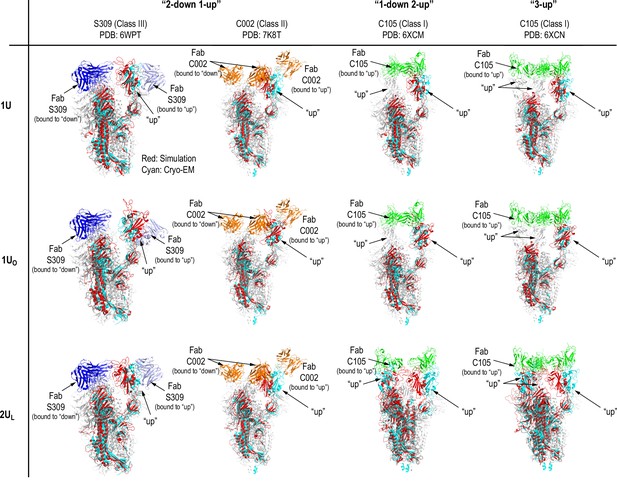
Comparison of Up structures from molecular dynamics (MD) simulations with cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures.
The structures of 1U, 1UO, and 2UL from our simulations were aligned with the cryo-EM structures of spike (S) protein complexed with three types of neutralizing antibodies (nAbs): Class III (S309-S complex, PDBID: 6WPT), Class II (C002-S complex, PDBID: 7K8T), and Class I (C105-S complex, PDBID: 6XCM and 6XCN). The chain A, which involves ‘Up’ receptor binding domain (RBD), of the simulation structure was aligned to the corresponding chain of the cryo-EM structures using Cα atoms. The aligned structures were colored in red and the corresponding chain of cryo-EM structures were in cyan. Note that Class I nAbs bind only ‘Up’ RBD, while Class II/III nAbs bind both ‘Up’ and ‘Down’ RBDs. In the cryo-EM structure of S309-S complex, nAb bound to ‘Up’ RBD was not resolved, thus the S309 orientation was modeled using the S309-RBD structure resolved for ‘Down’ RBD (colored in light blue). To avoid the confusion, the notations of ‘Up’ and ‘Down’ are used to represent RBD conformation in general.
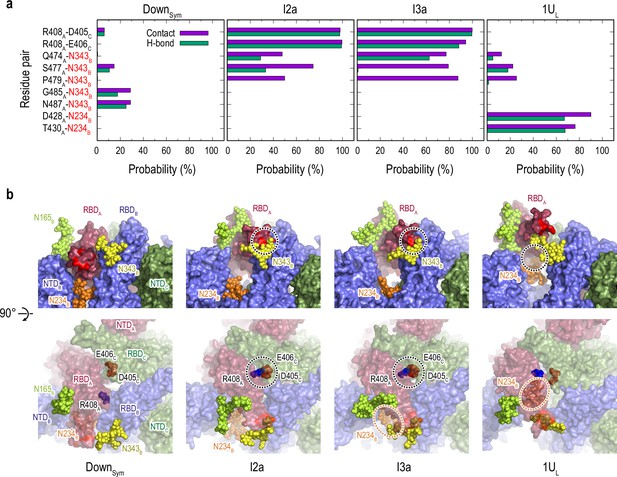
Protein-protein and protein-glycan interactions critical for Down-to-Up transition.
(a) Probability of finding the hydrogen bond (green) and contact (purple) pairs between protein residues or protein-glycans that markedly change along the transition pathway (DownSym, I2a, I3a, and 1UL). All hydrogen bond (probability of finding of >50%) and contact pairs (probability of finding of >70%) are shown in Figure 4—figure supplements 7 and 8, respectively. (b) Typical snapshots of the protein-protein and protein-glycan interactions along the transition pathway. Chains A, B, and C in the protein are shown in red, blue, and green surfaces, respectively. Glycans at N165, N234, and N343 are shown with spheres in lime, orange, and yellow color, respectively. The transient N343B-RBDA contact is highlighted in red surface (top). The salt-bridges formed by R408A (blue), E406C (brown), and D405C (red) are also highlighted with black dashed circles (top and bottom), while the location of N234 glycan is highlighted with orange dashed circles.
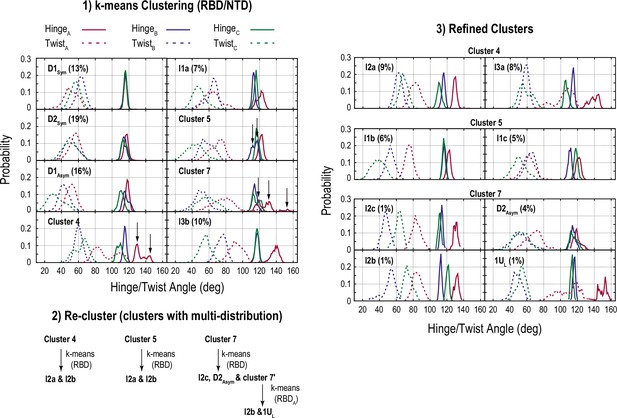
Clustering for the conformations obtained from the gREST_Down simulation.
Schematic representation of the clustering steps and the resultant distributions of the hinge and twist angles are illustrated. (1) First, all conformations at 310 K were classified into eight clusters using the k-means clustering algorithm, upon fitting S2 and selecting receptor binding domain (RBD) and N-terminal domain (NTD). Then, the distributions of the hinge/twist angles in each cluster were examined. Here, clusters that had multiple peaks are highlighted by black arrows. (2) The clusters with multiple distributions (4, 5, and 7) were further classified into two or three clusters, where only RBD was used as a clustering criterion. (3) The obtained clusters were further examined, and cluster 7′ was classified into two clusters. Finally, the hinge/twist angle distributions in all refined clusters are shown in the right panel.
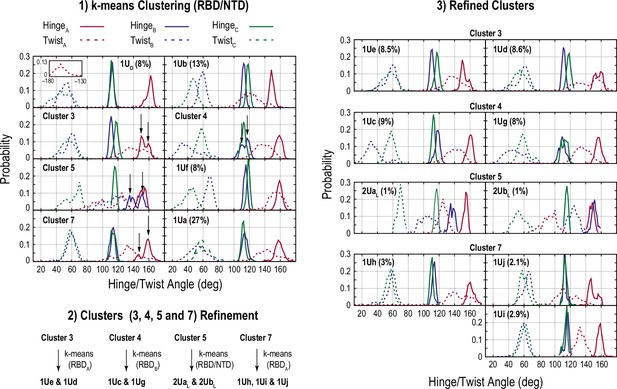
Clustering for the conformations obtained from the gREST_Up simulation.
The scheme is almost same as in Figure 4—figure supplement 1.
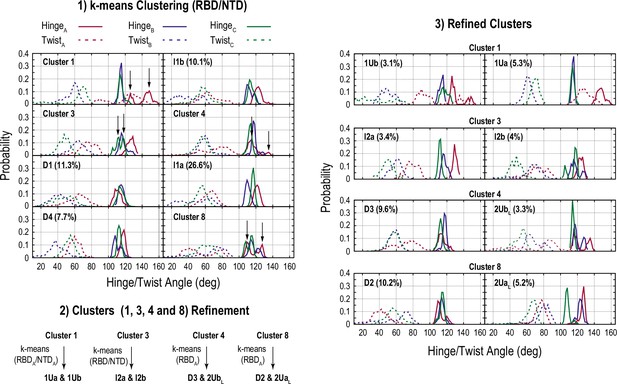
Clustering for the conformations obtained from the gREST_Down w/o glycan simulation.
The scheme is almost same as in Figure 4—figure supplement 1.
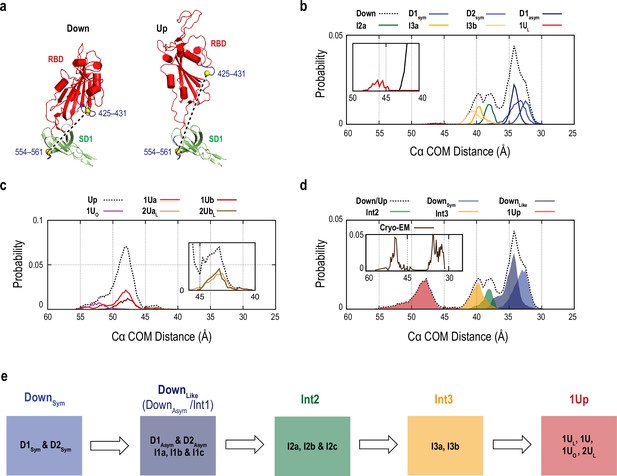
Simulated single molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer (smFRET) distance using the gREST_SSCR trajectory data.
(a) The residues used in the calculation of the smFRET-like distance are illustrated in blue. The distance was estimated based on the center of mass (COM) of the Cα atoms of the residues 425–431 in receptor binding domain (RBD) and 554–561 in SD1 (yellow spheres). (b) Probability distribution of the smFRET-like distance (black dashed line) in the conformations obtained at 310 K in the gREST_Down simulation. Contributions from main clusters (DownSym (D1Sym and D2Sym), DownAsym (D1asym), Intermediates 2 and 3 (I2a, I3a, and I3b), and 1Up-like (1UL) conformations) are also shown. (c) Probability distribution of the smFRET-like distance (black dashed line) in the gREST_Up simulation. Main clusters including 1Ua, 1Ub, 1UO, 2UaL, and 2UbL are also shown. (d) Probability distribution of the smFRET-like distance, where the gREST_Down (b) and gREST_Up (c) were combined with the experimental statistical ration of 77% and 23%. The distribution of macro-clusters that align with the experiment data are also shown. For comparison, the distribution of 891 cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) protomer is also shown in the small panel. (e) Schematic representation of the constituent of the macro-clusters used in (d). For complete description of the formation of macro-clusters from micro-clusters, see Supplementary file 1C,.
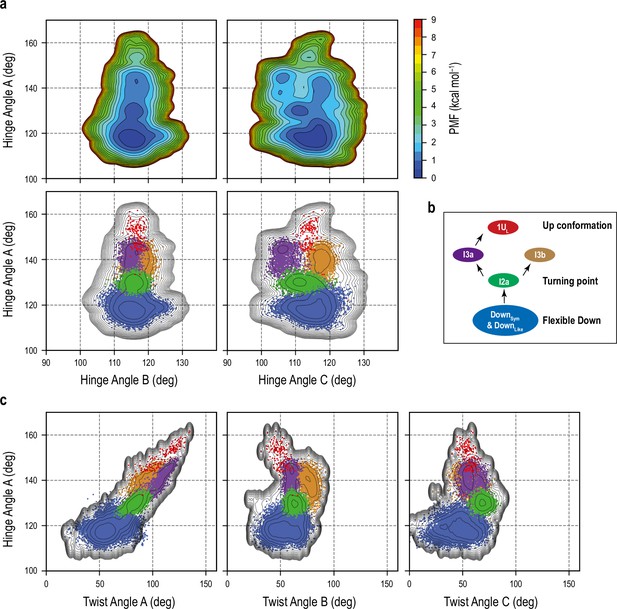
Transition pathway from Down to 1Up in the gREST_Down simulation.
(a) Top: free-energy landscapes (FELs) along the HingeA/ HingeB and HingeA/ HingeC angles, and Bottom: projection of the five main clusters [DownSym and DownLike (blue), I2a (green), I3a (purple), I3b (brown), and 1UL (red)] onto the FEL. The results suggest an independent motion of RBDA from other RBD hinge motions during the conformational transition from Down to Up. (b) Proposed transition pathway from flexible Down to I2a then I3a and finally 1UL. (c) Projection of the five main clusters onto the HingeA/TwistA, HingeA/TwistB, and HingeA/TwistC maps.
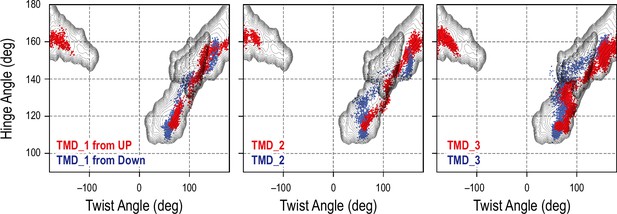
Comparison between targeted molecular dynamics (TMD) and gREST_SSCR simulations.
Projection of our previous TMD Down-to-Up (blue) or Up-to-Down (red) simulations (Mori et al., 2021) onto the overlapped free-energy landscape along the hinge/twist angles in the gREST_Down and gREST_Up simulations. In TMD, the simulation time is 20 ns for TMD_1 and TMD_2 and 50 ns for TMD_3, where the different random seeds were used.

Contact analysis for the main clusters in gREST_Down and gREST_Up simulations.
Probability of the residue-residue contacts in the receptor binding domain (RBD)/RBD (a), RBD/N-terminal domain (NTD) (b), and RBD/S2 interfaces (c) was analyzed for the main clusters DownSym, DownLike (DAsym and Int1), I2a, I3a, 1UL, top populated 1Up cluster (1Ua), 1Up/open conformation (1UO), and 2Up-like conformation (2UaL and 2UbL). Contact pairs are selected based on a minimum of 75% probability in any clusters. Pair that involve protein-glycan interactions are highlighted with red color for the glycan part. (a) Contacts between RBDA/RBDB, RBDB/RBDC, and RBDC/RBDA are shown in purple, green, and blue, respectively. (b) Contacts between RBD/NTD, where the same colors are used to show RBDA/NTDB, RBDB/NTDC, and RBDC/NTDA, respectively. (c) Contacts between RBD/S2 showing RBDA/S2B, RBDB/S2C, and RBDC/S2A in purple, green, and blue, respectively.
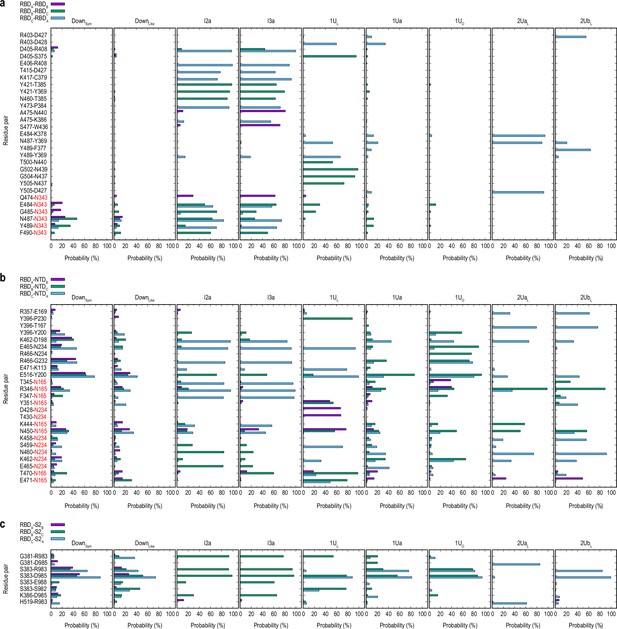
Hydrogen bond analysis for the main clusters in gREST_Down and gREST_Up simulations.
Probability of the residue-residue hydrogen-bonding in the receptor binding domain (RBD)/RBD (a), RBD/N-terminal domain (NTD) (b), and RBD/S2 interfaces (c) was analyzed. Hydrogen bonding pairs are selected based on a minimum of 50% probability in any clusters. The color definitions are same as in Figure 4—figure supplement 7.
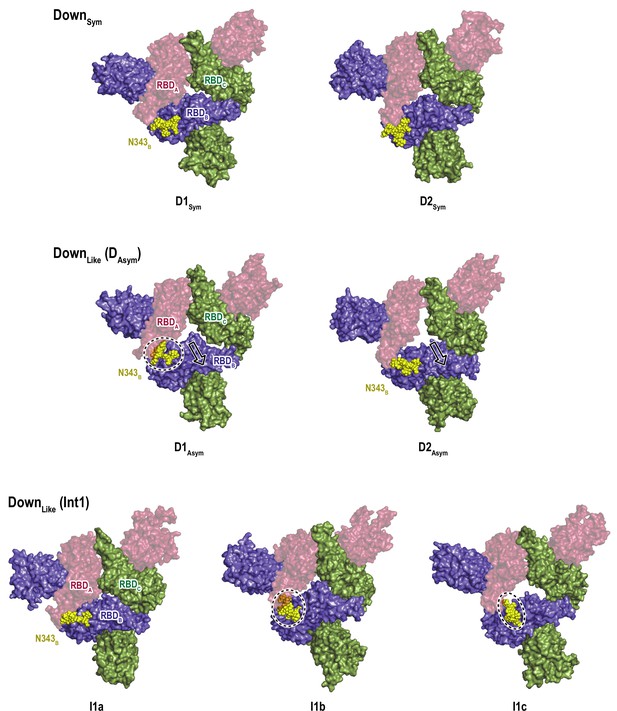
Relationship between the sideway motion of RBDB and intrusion of the glycan at N343B.
Cluster centers of DownSym and DownLike (DAsym and Int1) conformations are shown to highlight the sideway motion of RBDB that allows the glycan N343 (yellow sphere) to intrude underneath RBDA. Black dashed circles highlight the change in N343B position.
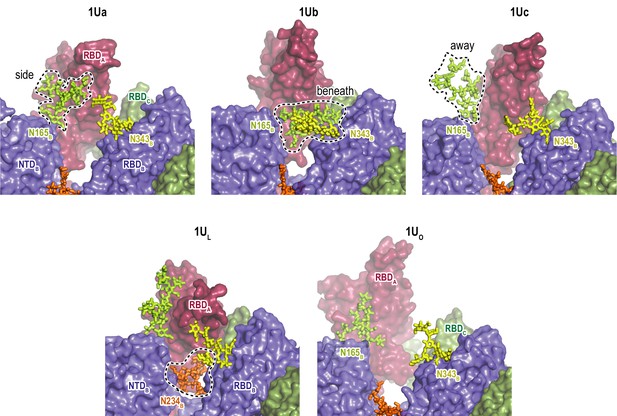
Glycan interaction sites in various Up conformations.
Structures of the cluster centers of top populated 1Up (1Ua, 1Ub, and 1Uc) and 1Up/open conformations (1UO) in the gREST_Up simulation are shown. For comparison, the cluster center of 1Up_like (1UL) in the gREST_Down simulation is also shown. Three glycans N165B (lime), N234B (orange), and N343B (yellow) are shown with the stick model, highlighting the diversity of glycan interactions in Up conformations.
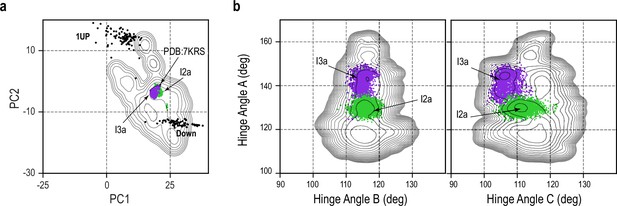
Stability of I2a and I3a along transition pathway.
(a) Free-energy landscape (FEL) along PC1-PC2 of gREST_Down simulation shown as black contour. I2a and I3a are shown as green and purple dots, respectively. Down and one-Up cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure projection are also shown as black dots. (b) FELs of HingeA/HingeB and HingeA/HingeC are shown as black contour. Projection of I2a and I3a are also shown.
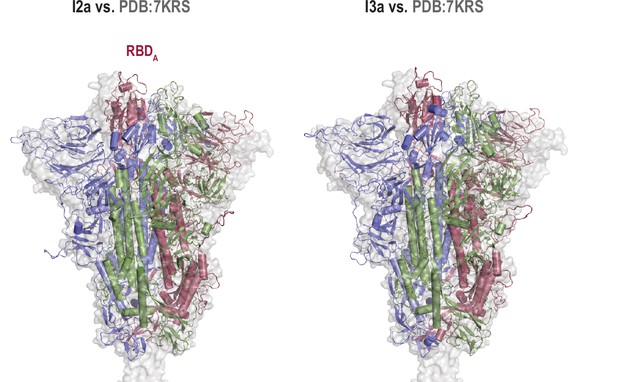
Intermediate structures align with cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures.
Superposition of the cartoon representation of I2a and I3a intermediate structures with D614G spike mutant cryo-EM structure of intermediate state (PDB:7KRS).
Protein-glycans interactions along Down-to-1Up transition pathway.
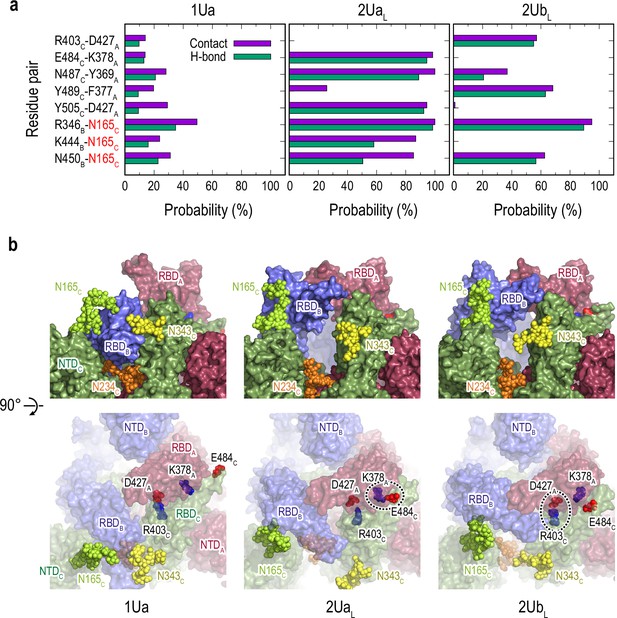
Selected protein-protein and protein-glycan interactions along the 1Up-to-2Up transition.
(a) Probability of finding the hydrogen bond (green) and contact (purple) pairs throughout the transition pathway (1Ua, 2UaL, and 2UbL). Where the conformational transition of RBDB induces RBDA/RBDC interactions. All hydrogen bonds and contact pairs are shown in Figure 4—figure supplements 7 and 8 respectively. (b) Typical snapshots of the protein-protein and protein-glycan interactions along RBDB transition pathway. Chains A, B, and C in the protein are shown in red, blue, and green surfaces, respectively. Glycans at N165, N234 and N343 are shown with spheres in lime, orange, and yellow colors, respectively. Positive and negatively charged residues are shown as blue and red spheres, respectively. The transient salt-bridges formed by K378A/E484C and D427A/R403C are also highlighted with black dashed circles.
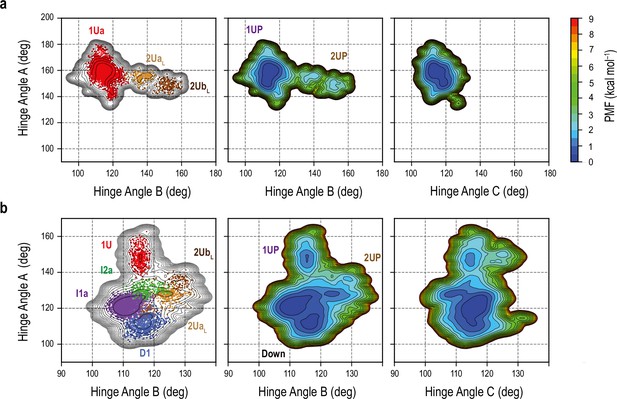
Free-energy landscape (FEL) in the gREST_Up and gREST_Down w/o glycan simulations.
(a) FEL along the HingeA/HingeB (middle) and HingeA/HingeC (right) as well as the projection of the top populated clusters (1Up (1Ua) and 2Up-like clusters (2UaL and 2UbL)) onto the FEL (left) in the gREST_Up simulation are illustrated. (b) FEL in the gREST_Down w/o glycan along HingeA/HingeB (middle) and HingeA/HingeC (right). Main clusters along Down-to-1Up and Down-to-2Up-like conformations are shown in left.
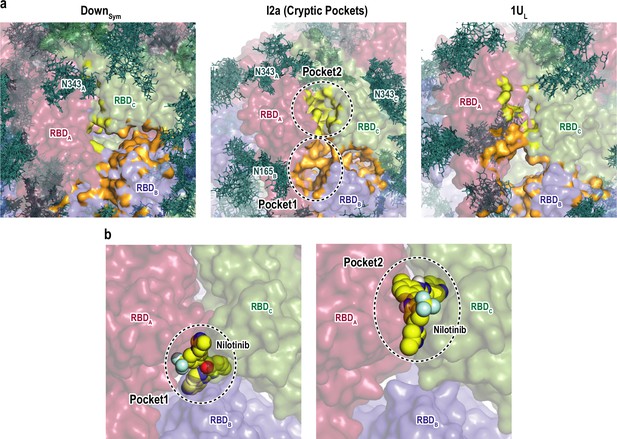
Druggable cryptic pockets in the transition intermediates.
(a) Snapshots of receptor binding domain (RBD) interface in Down symmetric (DownSym), Intermediate 2a (I2a), and 1Up-like (1UL) conformations. Chains A, B, and C in the protein are shown in red, blue, and green surfaces, respectively, while a collection of glycans from 10 snapshots are shown in stick representation. The cryptic pockets predicted for I2a using P2Rank software are shown in orange (Pocket1) and yellow (Pocket2), respectively. These pockets disappear in both DownSym and 1UL. (b) Nilotinib docked poses (top and third ranked) to two cryptic pockets in I2a by Autodock Vina. The pockets are highlighted with black dashed circles and the nilotinib is shown in sphere representation in yellow.
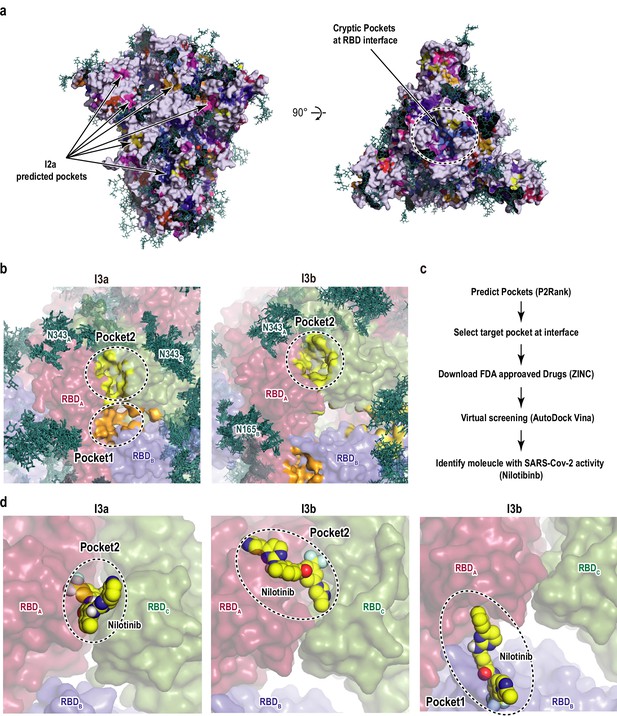
Cryptic pockets and ligand binding in receptor binding domain (RBD).
(a) Results of the binding pocket search for I2a predicted by P2Rank software (Krivák and Hoksza, 2018). The spike protein is shown as gray surface, while all other colors represent predicted pockets. Glycans are shown as deep teal sticks, and cryptic pockets at the RBD interface are highlighted by black circle in the top view (right). (b) Cryptic pockets at the RBD interface in the main intermediate clusters I3a and I3b. RBDA, RBDB, and RBDC are shown as red, blue, and green surfaces, respectively, and Pocket1 and Pocket2 are shown as yellow and orange surfaces, respectively. Glycans from 10 different conformations that were close to the cluster centers are shown as deep teal sticks. (c) Scheme for the identification of cryptic pockets and virtual screening used in this study. (d) Binding of nilotinib to the predicted cryptic pockets in I3a and I3b. Nilotinib is shown as the sphere model with yellow carbon atoms.
Tables
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of spike (S) protein performed in this study.
| Name | Model | Method | Simulations length |
|---|---|---|---|
| gREST_Down | Spike Down w/ glycans | gREST_SSCR | 500 ns × 16 replicas |
| gREST_Up | Spike Up w/ glycans | gREST_SSCR | 300 ns × 16 replicas |
| gREST_Down w/o glycan | Spike Down w/o glycans | gREST_SSCR | 150 ns × 16 replicas |
| Monomer_Down | RBD/SD1 monomer Down | cMD | 300 ns × 1 run |
| Monomer_Up | RBD/SD1 monomer Up | cMD | 300 ns × 2 runs |
| cMD_Down* | Spike Down w/ glycans | cMD | 1000 ns × 1 run |
| cMD_Up* | Spike Up w/ glycans | cMD | 1000 ns × 1 run |
-
*
cMD_Down and cMD_Up are the same simulations as shown in our previous study Mori et al., 2021.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
List of PDBs, clusters and lignads.
(A) Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures used in the principal component analysis (PCA). (B) Definition of protomer coarse-grained particles representing rigid domains for PCA. (C) List of clusters for gREST_Down, gREST_Up, and gREST_Down w/o glycan simulations. (D) The receptor binding domain (RBD) interface cryptic pockets predicted by P2Rank. (E) List of the top-ranked molecules from the virtual screening of 2115 FDA approved drugs to RBD interface in I2a, I3a, and I3b intermediate structures. (F) Nilotinib binding energy to I2a, I3a, and I3b intermediates.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/75720/elife-75720-supp1-v2.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/75720/elife-75720-transrepform1-v2.pdf





