The role of higher-order thalamus during learning and correct performance in goal-directed behavior
Figures
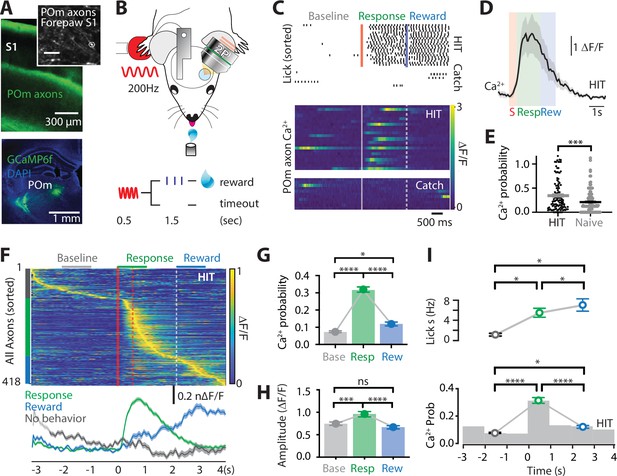
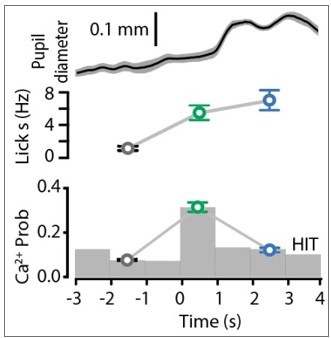
Ca2+ activity of POm axonal projections in forepaw S1 during tactile goal-directed behavior.
(A) The Ca2+ indicator GCaMP6f was locally injected into the POm (bottom) which sends axonal projections to layers 1 and 5 of the forepaw S1 (top). Inset, in vivo two-photon Ca2+ image of POm axonal projections in forepaw S1 (depth, 60 μm; scale bar, 10 μm). (B) Two-photon Ca2+ imaging of GCaMP6f-expressing POm axons in forepaw S1 was performed in head-restrained mice trained to report the detection of a tactile stimulus (200 Hz, 500 ms) by licking a reward port. Correct responses (HIT) were rewarded with sucrose water reward (10 μl, 10% sucrose). (C) Top, raster plot showing a typical behavioral response (licks) sorted into correct HIT performance and Catch (no-stimulus) trials. Gray, spontaneous; red, tactile stimulus; green, response epoch; blue, reward epoch. Blue line, reward delivery. Bottom, example of Ca2+ activity pattern during correct performance and Catch trials from the POm axon in (A). Each row represents a single trial, sorted according to trial number. (D) Mass average with standard error of the mean (SEM; shaded area) of all stimulus-evoked Ca2+ transients in all axons during correct goal-directed performance (HIT; black). Behavioral epochs indicated by color bars (red, stimulus; green, response; blue, reward). (E) Probability of evoking a Ca2+ response during correct HIT behavior (black) compared with tactile-evoked activity in the naive state (gray, n = 113 axons; Mann–Whitney test). (F) Top, Ca2+ activity pattern during HIT performance in the tactile goal-directed task. Each row is an independent axon normalized to maximum fluorescence and sorted by the timing of the peak amplitude (gray, baseline; red, stimulus; green, response epoch; blue, reward epoch). Red lines, stimulus delivery. Dashed line, reward delivery. Bottom, average Ca2+ response in POm axons active during the stimulus and response epoch (green), reward epoch (blue); baseline (no behavior; gray). (G) The probability of a Ca2+ transient in POm axons during baseline (gray), response epoch (green), reward epoch (blue). n = 418 axons, 11 mice. Friedman test + Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. (H) The amplitude of Ca2+ transients in POm axons evoked during baseline (gray), response epoch (green), and reward epoch (blue). n = 239 axons, 11 mice with evoked Ca2+ transients. Friedman test + Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. (I) Top, average lick frequency during spontaneous (gray), stim/response (green), and reward (blue) epochs during correct HIT behavior. Bottom, histogram of Ca2+ transient probability in POm axons. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
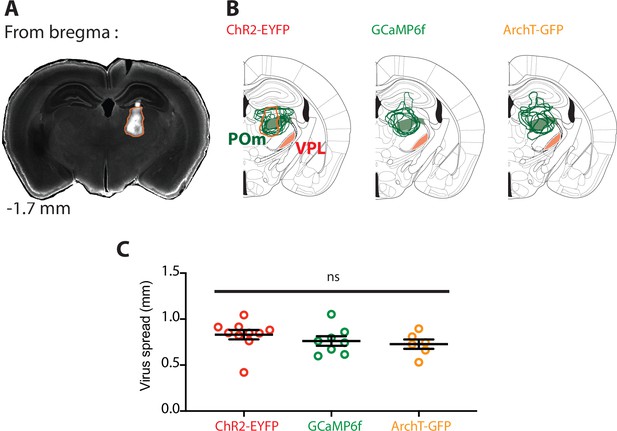
Targeting and spread of AAV injections in the POm nucleus.
(A) Representative example of injection site in the mouse thalamus illustrating localized viral expression in the POm nucleus. (B) Overlay of the virus expression profile from the injection of ChR2-EYFP (left), GCaMP6f (middle), and ArchT-GFP (right) into the POm (green). The location of the other thalamic nuclei which primarily projects to forepaw S1, the ventral posterolateral nucleus (VPL, red) is included for comparison. (C) Plot comparing the virus spread for the different injections.
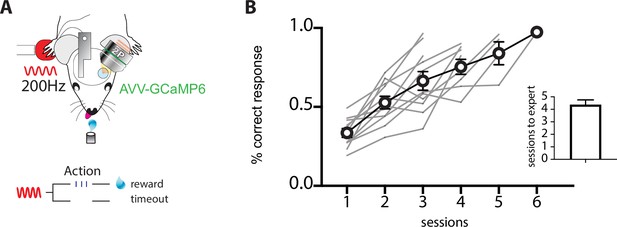
Mice rapidly learn the tactile goal-directed task.
(A) Behavioral task design. Mice were habituated to head restraint and trained to report the detection of a tactile stimulus (200 Hz, 500 ms) by licking a reward port. Correct responses were rewarded with sucrose water reward (10 μl, 10% sucrose). Incorrect responses were punished with a time-out. (B) Performance of mice in the tactile goal-directed task improved in subsequent sessions, taking on average 4 days to reach expert performance (>80% correct; n = 11 mice).
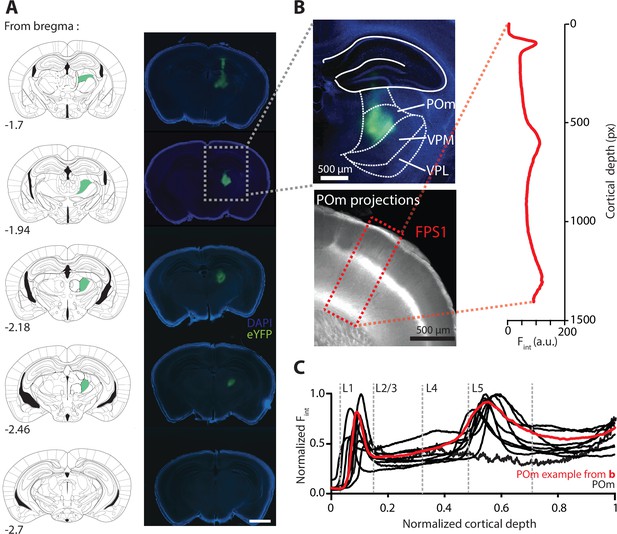
AAV-mediated expression of ChR2-eYFP in the POm nucleus of the thalamus and its axonal projections in forepaw S1.
(A) Representative example of ChR2-eYFP in the mouse thalamus illustrating localized viral expression in the POm nucleus. Left, outline of cortical slices at different rostracaudal locations indicating the POm nucleus (green) from Paxinos and Franklin, 2001. Right, corresponding brain sections showing the virus expression profile in the thalamus. Scale bar, 1 mm. (B) Top, enlarged fluorescence image showing ChR2-eYFP expression profile in POm nucleus from example in (A). The location of the ventral posteromedial nucleus (VPM) and ventral posterolateral nucleus (VPL) is illustrated for comparison. Bottom, POm axonal projection profile in the forepaw area of S1 (FPS1) from example in (A). Inset, fluorescence intensity (Fint) measured as a function of cortical depth (in pixels [px]) in forepaw S1 (FPS1; rectangle). (C) Plot comparing the intensity profiles within FPS1 in 10 different animals with injections localized in the POm nucleus.
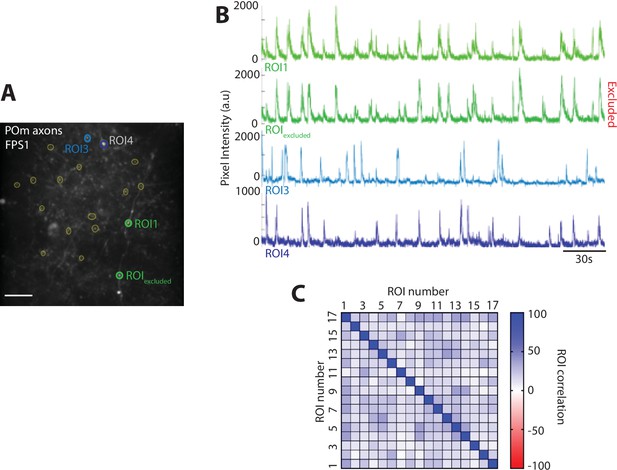
Region of interest (ROI) selection and exclusion criterion.
(A) Example field of view (FOV), ROIs are selected using the standard deviation (STD) image from the concatenated images of the entire imaging session. (B) Fluorescence traces for ROIs shown in (A). ROI1 and ROIexcluded have similar fluorescence activity and ROIexcluded is excluded from further analysis. (C) Spearman correlation matrix of the activity profile of all ROIs from the example FOV in (A). ROIs that have a correlation greater than 95% have been removed from further analysis. Spearman correlation is performed on all FOVs to exclude correlated ROIs.
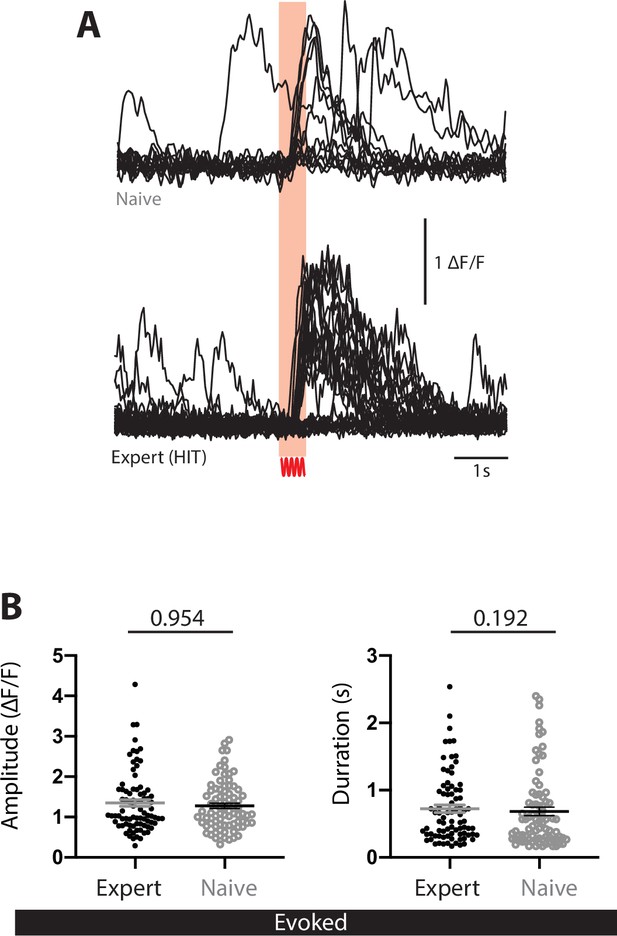
Tactile-evoked activity of POm axons projecting to forepaw S1 in naive and expert mice.
(A) Example Ca2+ responses from a typical POm axon in (top) a naive mouse during forepaw tactile stimulus (200 Hz, 500 ms) and (bottom) an expert mouse during correct HIT performance in an action goal-directed task. (B) Peak amplitude (left) and duration (right) of evoked Ca2+ transients in expert (black) and naive (gray) mice. Expert data were randomized and a sample of equal size to naive was used for statistical analysis. Mann–Whitney test was performed for significance testing.
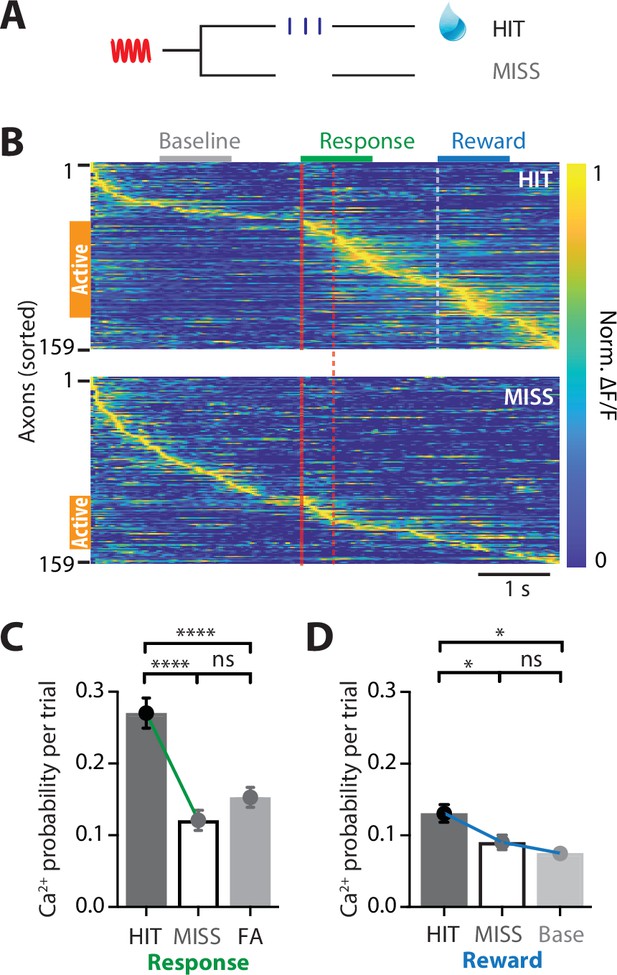
POm axonal projections in forepaw S1 have greatest activity during correct behavioral performance in a tactile goal-directed task.
(A) Behavioral task design. Two-photon Ca2+ imaging of GCaMP6f-expressing POm axons in forepaw S1 was performed in head-restrained mice trained to report the detection of a tactile stimulus (200 Hz, 500 ms) by licking a reward port. Mice received sucrose water reward (10 μl, 10% sucrose) during correct responses (HIT), whereas incorrect responses (MISS) were unrewarded. (B) Ca2+ activity patterns in POm axons with Ca2+ transients evoked during HIT (top) and MISS (bottom) behavior during the tactile goal-directed task (n = 159 axons, 6 mice). Gray, baseline; red, stimulus; green, response epoch; blue, reward epoch. Each row is an independent axon normalized to maximum fluorescence and sorted by the timing of the peak amplitude for both HIT and MISS trials. Orange bar denotes axons that were ‘active’ during the behavior. (C) The probability of a Ca2+ transient evoked during the response epoch in HIT (solid), MISS (empty), and false alarm (FA; dark gray) behavior. Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test (HIT vs MISS) and Mann–Whitney test (FA vs HIT and MISS). (D) The probability of a Ca2+ transient evoked during the same time period as the reward epoch in HIT (solid), MISS (empty), and baseline (light gray). Friedman test + Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
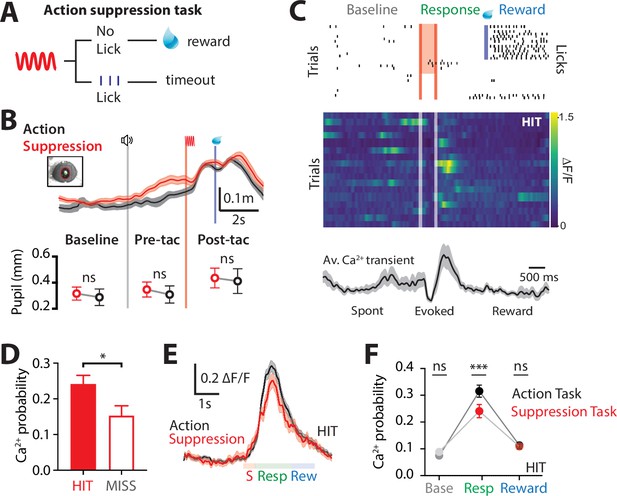
Ca2+ dynamics in POm axonal terminals during suppression of a goal-directed action.
(A) Behavioral task design. Two-photon Ca2+ imaging of POm axon terminals was performed in head-restrained mice trained to suppress a previously learned goal-directed action. Mice were trained to withhold licking in response to forepaw stimulation (200 Hz, 500 ms) for 1.5 s to get a reward (10 μl, 10% sucrose water). (B) Top, average pupil diameter with SEM (shaded area) during correct performance in the ‘suppression’ goal-directed task (red) and ‘action’ goal-directed task (black). Bottom, comparison of pupil dilation during the ‘action’ and ‘suppression’ goal-directed tasks in baseline, pre-tactile stimulus (pre-tac) and post-tactile stimulus (post-tac) epochs (n = 6 mice: Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test). Gray line, trial start; red line, stimulus, blue line, reward delivery. (C) Top, raster plot showing the typical licking response during correct performance of the task. Gray, spontaneous; red, stimulus; green, response epoch; blue, reward epoch. Blue line, reward delivery. Middle, Ca2+ activity pattern in an example axon during HIT trials. Bottom, average Ca2+ activity pattern with SEM (shaded area) in HIT trials for the example axon (n = 17 trials). Red line, stimulus delivery; blue line, reward delivery. (D) Probability of evoking a Ca2+ transient during HIT (correct suppression of licking behavior; red) and MISS (no suppression of licking behavior; red empty). n = 144 axons, 6 mice; Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test. (E) Overlay of the mass average with SEM (shaded area) of the normalized Ca2+ activity pattern during correct performance in the suppression goal-directed task shown in (C) (red) and action goal-directed task (black). (F) Probability of evoked Ca2+ transients during baseline, response, and reward epochs in the ‘suppression’ goal-directed task (red) and ‘action’ goal-directed task (black). Mann–Whitney test. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
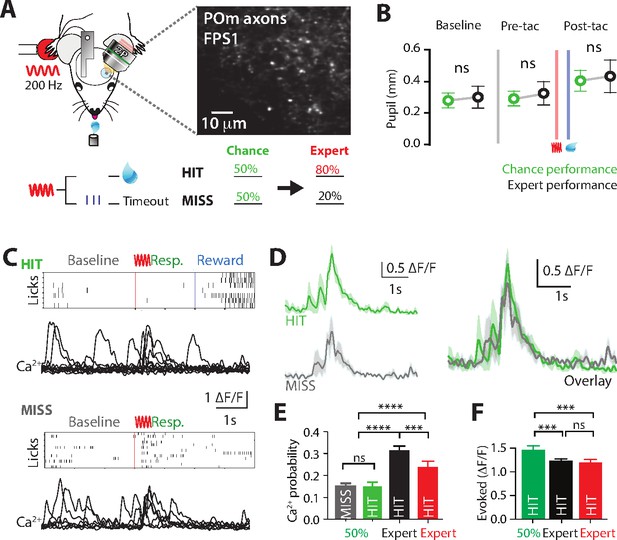
Ca2+ activity of POm axonal projections in forepaw S1 during chance performance and behavioral switching.
(A) Behavioral task design. Ca2+ imaging from POm axons in forepaw S1 was performed as mice transitioned from the ‘action’ goal-directed task to the ‘action–suppression’ goal-directed task (50% correct performance, green). (B) Average pupil dilation during baseline, pre-tactile stimulation (pre-tac) and post-tactile stimulation (post-tac) during the ‘switch’ (green) and ‘action’ task (black; n = 6). Red bar, tactile stimulus; blue bar, reward delivery. (C) Example licking behavior and associated Ca2+ responses from an example axon during HIT (top) and MISS (bottom) trials. (D) (left) Individual and (right) overlay of average with SEM (shaded area) of evoked Ca2+ transients during correct (green) and incorrect (light blue) performance from example in (C). (E) The probability of a Ca2+ transient in MISS (gray) and HIT (green) trials during chance performance (gray), and expert HIT performance in ‘action’ (black) and ‘suppression’ (red) tasks. (F) Peak amplitude of evoked Ca2+ transients during HIT trials in the action (black), switch (green), and suppression (red) behavioral task. Error bars indicate the mean ± SEM. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
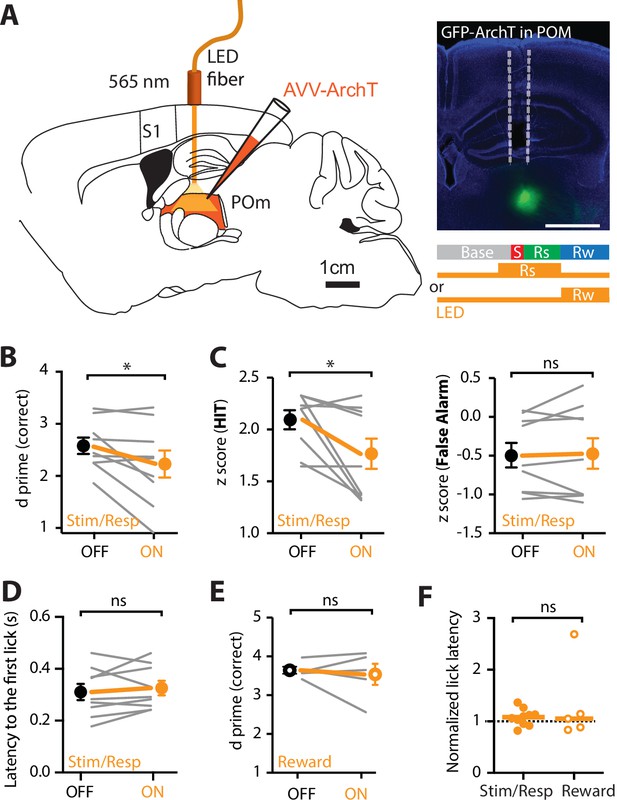
Optogenetic inactivation of the POm during an active goal-directed task.
(A) Left, experimental design. The inhibitory opsin, archaerhodopsin (ArchT) was unilaterally injected into the POm and a fiber-optic cannula was chronically inserted into the brain. Right, localized ArchT spread in POm and fiber-optic track (dotted line), bar = 1 mm. POm was photoinactivated (590 nm, 5 mW, 2 s) either 500 ms prior to, and during the stimulus (S) and response (Rs) epochs (Stim/Resp), or during the reward epoch (Rw) in expert mice performing the ‘action’ goal-directed task. (B) Behavioral performance (d prime) for LED OFF vs LED ON during the stim/response epoch (n = 9 mice). Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test. (C) z-Score during (left) HIT and (right) false alarm for LED OFF vs LED ON during the stim/response epoch (n = 9 mice). Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test. (D) Latency to the first response lick in LED OFF vs LED ON during the stim/response epoch. Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test. (E) Behavioral performance (d prime) during LED OFF and LED ON during the reward epoch in expert mice performing the ‘action’ goal-directed task (n = 5 mice). Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test. (F) Normalized latency to the first response lick during LED ON in the stim/response epoch (solid) and reward (empty) epoch (normalized to the latency to the first lick during LED OFF). Line, median. Mann–Whitney test. Individual values are shown. *p < 0.05.
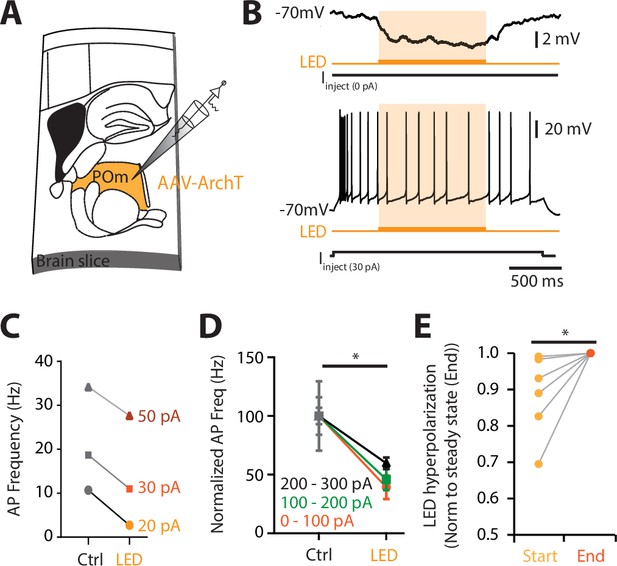
POm neurons are partially photoinhibited by 590 nm LED.
(A) The inhibitory opsin, archaerhodopsin (ArchT) was unilaterally injected into the POm and after 10–14 days, the brain was sectioned into 300-μm thick slices. Whole-cell patch clamp voltage recordings were then performed in POm neurons expressing ArchT. (B) Voltage recording during 590 nm light exposure from an example POm neuron (top) at rest and (bottom) during a current step injection (30 pA; 2 s). (C) Photoinhibition caused a decrease in evoked action potentials during different current steps (20, 30, and 60 pA) for example in (B). Control (Ctrl) firing was determined during current step injection in the absence of LED. (D) Action potential firing evoked during current step injections (0–100, 100–200, and 200–300 pA) was partially inhibited during LED (0–100 pA, p = 0.031; 100–200 pA, p = 0.016; 200–300 pA, p = 0.004; Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test). (E) Voltage response at rest at the start of the LED pulse (300 ms, light orange) normalized to the steady-state ‘end’ voltage (300 ms prior to end of pulse; p = 0.031; Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test). Note, photosuppression would be less effective in vivo than in vitro due to different light penetration and scattering.
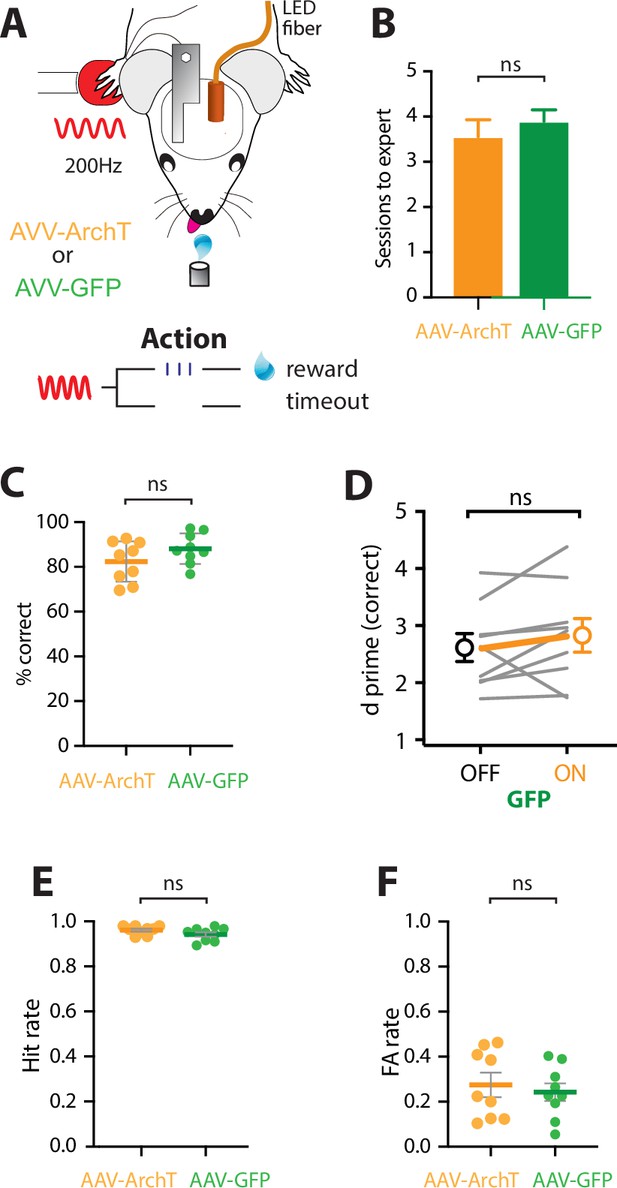
LED in POm does not alter goal-directed behavior.
(A) Behavioral task design. Mice were either injected with the inhibitory opsin, AAV-ArchT or the Green Fluorescent Protein control, AAV-GFP. Mice were then habituated to head-restraint and trained to report the detection of a tactile stimulus (200 Hz, 500 ms) by licking a reward port. Correct responses were rewarded with sucrose water reward (10 μl, 10% sucrose). Incorrect responses were punished with a timeout. (B) The number of training sessions required to reach expert performance (>80% correct) in the tactile goal-directed task in mice previously injected with AAV-ArchT (orange) or AAV-GFP (green). (C) Performance, measured as percent correct, in expert mice (p = 0.15; unpaired t-test). (D) Behavioral performance (d prime) for LED OFF vs ON trials (n = 9 mice) in mice previously injected with AAV-GFP (green). (E) Hit rate in expert mice (p = 0.11; unpaired t-test). (F) False alarm (FA) rate in expert mice (p = 0.21; unpaired t-test). Mice are considered expert when >80% correct performance in the tactile goal-directed task. AAV-ArchT, orange, n = 9 mice; AAV-GFP, green, n = 9 mice. All data passed normality test (Shapiro–Wilk test).
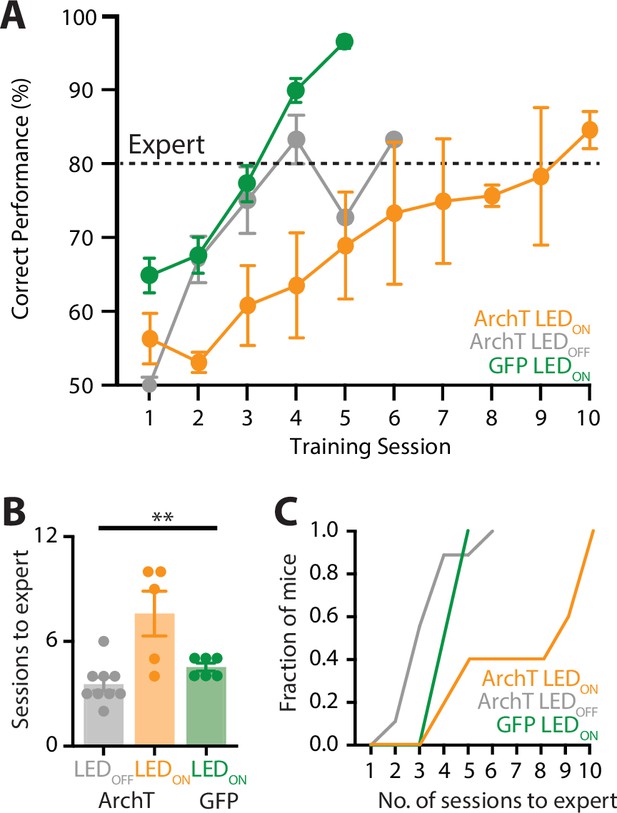
Optogenetic inactivation of the POm during learning of a goal-directed task.
(A) Mice were injected with either a control AAV (GFP; green) or the inhibitory opsin, archaerhodopsin (ArchT) into the POm and trained in the ‘action’ goal-directed task. A fiber-optic cannula was inserted to the POm and LED (590 nm, 5 mW, 2 s) was either ON (ArchT, orange; GFP, green) or OFF (ArchT, gray) during all training sessions. Dotted line indicates expert (>80% correct) performance. (B) The number of training sessions required for mice to reach expert (>80% correct) performance in mice injected with ArchT (LED OFF, gray; LED ON, orange) or GFP (LED ON, green). Kruskal–Wallis test. (C) The number of sessions for mice to reach expert (>80% correct) performance. **p < 0.01.