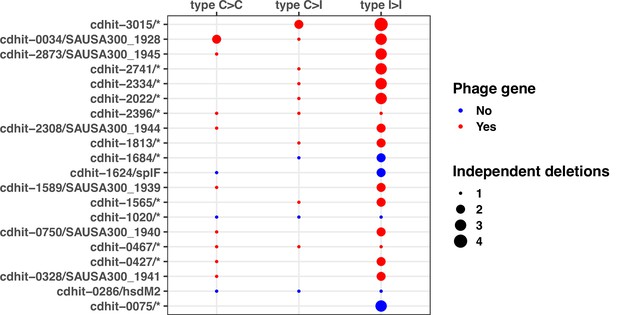
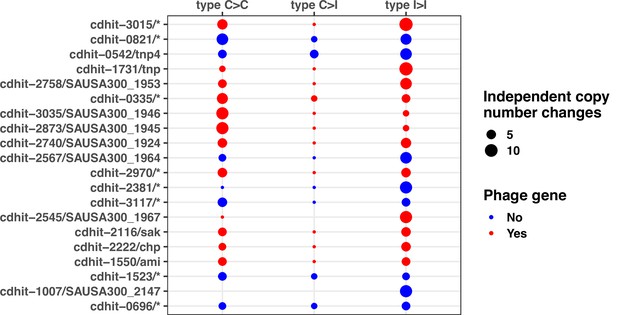
Niche-specific genome degradation and convergent evolution shaping Staphylococcus aureus adaptation during severe infections
Figures
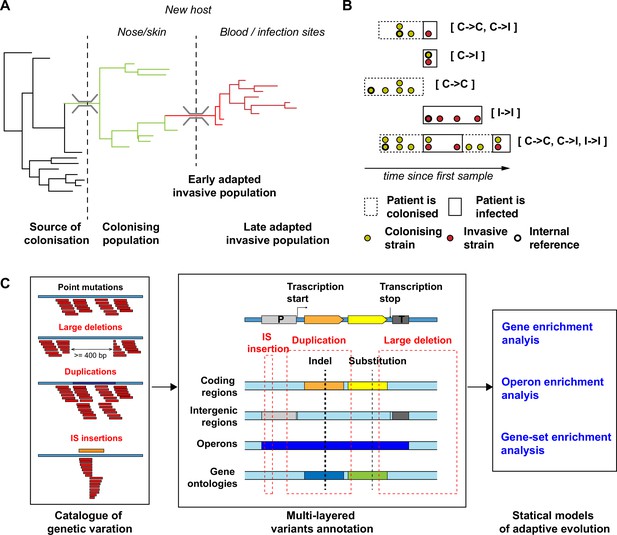
Overview of the S. aureus within-host evolution analysis framework.
(A) Simulated phylogenetic tree illustrating within-host evolution of S. aureus colonisation and infection. This model assumes two genetic bottlenecks (dotted lines); upon transmission and upon transition from colonisation to invasive infection. (B) Sites and timing of within-host samples and number of genomes per sample define five prototypes of within-host evolution studies, each with colonising-colonising (C>C), colonising-invasive (C>I), or invasive-invasive (I>I) comparisons in different combinations: from top to the bottom: multiple colonising samples and one invasive samples; one colonising and one invasive sample; multiple colonising samples; multiple invasive samples; multiple colonising and invasive samples. (C) Approach to capture signals of adaptation across multiple independent episodes of colonisation/infection through detection of multiple genetic mechanisms of adaptation from short reads data and multi-layered functional annotation of the genetic variants using multiple databases including characterisation of intergenic regions (promoters), operon prediction, and gene ontology (GO). Statistical framework for the gene, operon, and gene set enrichment anlaysis (GSEA). Counts of independent mutations with likely impact on the protein sequence (non-synonymous substitutions, frameshifts, stop codon mutations, and insertion sequences [IS] insertions) were computed for each genes with a FPR3757 homologue. Gene counts (with the addition of intergenic mutations in promoter regions) were aggregated in operons and GOs. Gene and operon counts were used to fit Poisson regression models to infer mutation enrichment and significance of the enrichment. GOs counts and gene enrichment significance were used to run a gene-set-enrichment analysis. To illustrate the approach, the example of the gene walR is provided in italic.
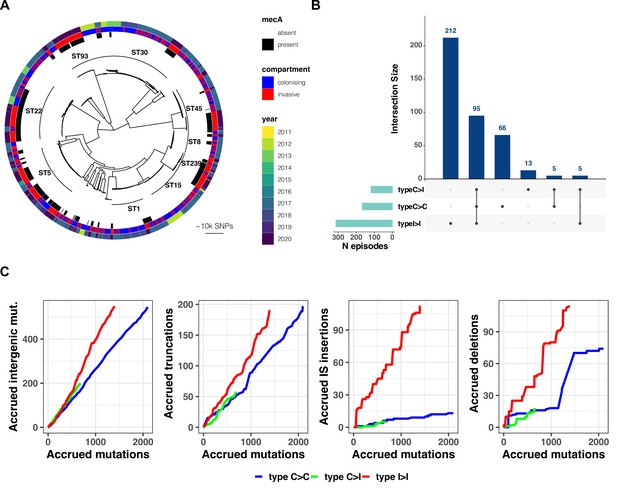
(A) Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of 2590 S. aureus sequences included in the study.
The tree is annotated (starting from the inner circle) with the most prevalent sequence types (ST), presence/absence of the mecA gene, compartment of isolation (colonising or invasive), and year of publication. (B) Summary of 396 independent episodes of S. aureus colonisation or infection categorised according to whether they allowed comparing colonising-colonising (C>C), colonising-invasive (C>I), or invasive-invasive (I>I) strains, or a combination of them. (C) Evidence of a distinctive pattern of adaptation in late infection-adapted strains (type I>I variants). For each type of comparison (type C>C, colonising-colonising; type C>I, colonising-invasive; type I>I, invasive-invasive), the cumulative curves display the accrued number of intergenic mutations, truncating mutations, insertion sequences (IS) insertions, and large deletions as a function of the total number of mutations. Genetic events were counted once per episode, regardless of the number of strains with the mutation. The sequence of mutations events in the cumulative curves is random.
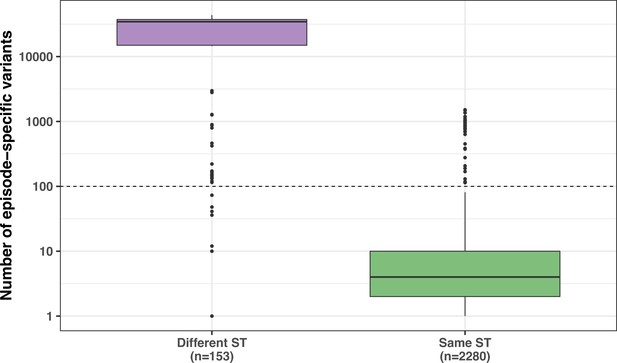
Number of episode-specific variants in same-episode strains having the same sequence type (ST) as the internal reference vs. isolates with a different ST.
The dashed line represents the mutation threshold used to remove genetically unrelated strains with the same episode.
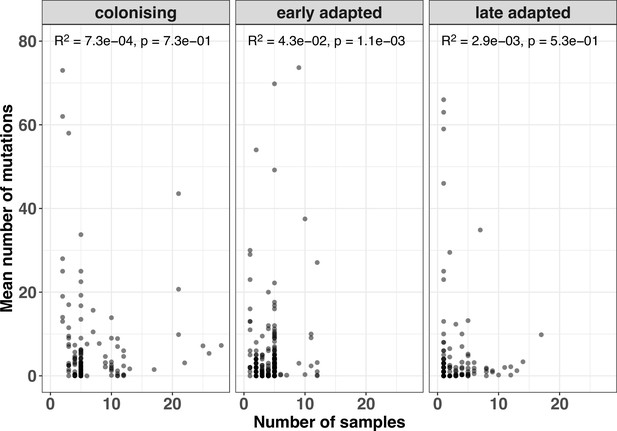
Correlation between number of samples per episode and mean mutation counts.
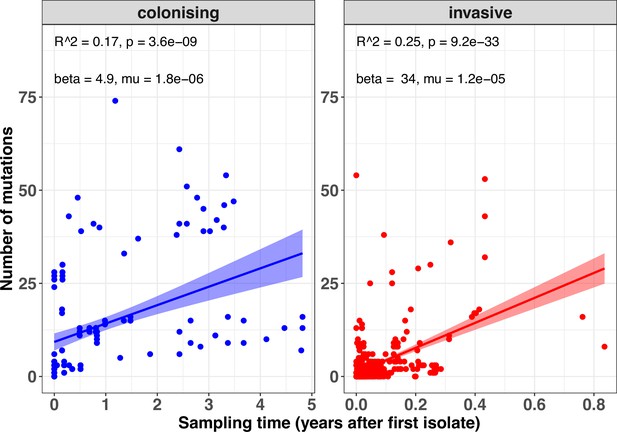
Within-host mutation rates within the colonising and invasive populations.
The scatter plots display the linear relationship between sampling time after the internal reference and number of mutations. Only episodes with at least two strains collected at at least 1 day apart were included. The shaded area around the fitted regression shows the 95% confidence interval (CI). The parameters shown on the top of each plot are the r-squared, p value, regression coefficient β, and the mutation rate μ (mutations site–1 year–1).
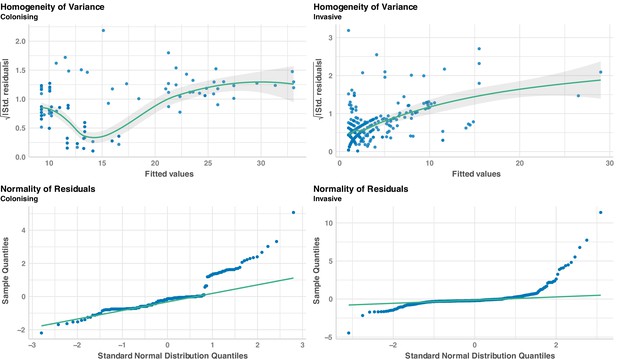
Regression diagnostics to assess linear regressions sampling time after the internal reference and number of mutations.
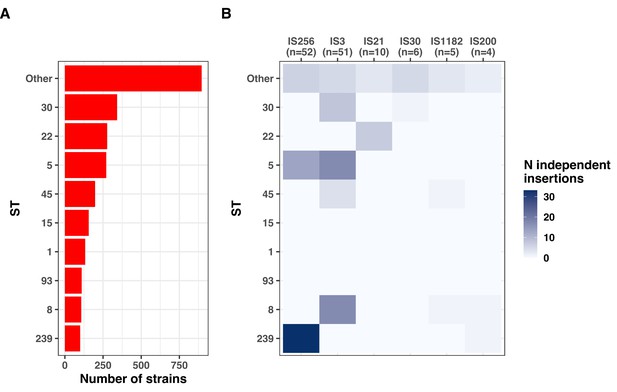
Distribution of new IS insertions by classification of the transposase and by major sequence types (ST).
(A) Distribution of the nine major ST among 2590 strains. (B) Number of independent insertion sequences (IS) insertions by ST group and type of transposase.
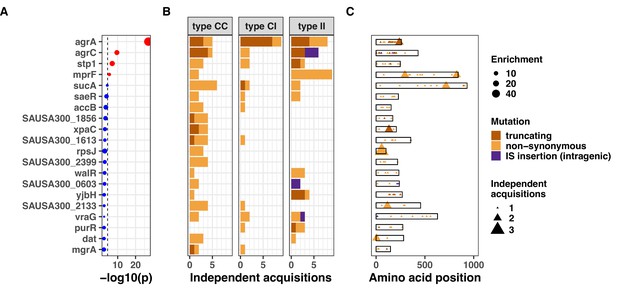
Top 20 genes with the most significant mutation enrichment across the entire dataset.
(A) Significance of the enrichment for protein-altering mutations. The dashed line depicts the Bonferroni-corrected significance threshold, and red circles and blue circles represent genes with p values below and above the Bonferroni threshold, respectively. (B) Bar plots of independent mutations separated in three panels according to the type of variant (type C>C: colonising-colonising; type C>I: colonising-invasive; type I>I: invasive-invasive) and coloured according to the class of mutation. (C) Gene maps with type and positions of mutations.
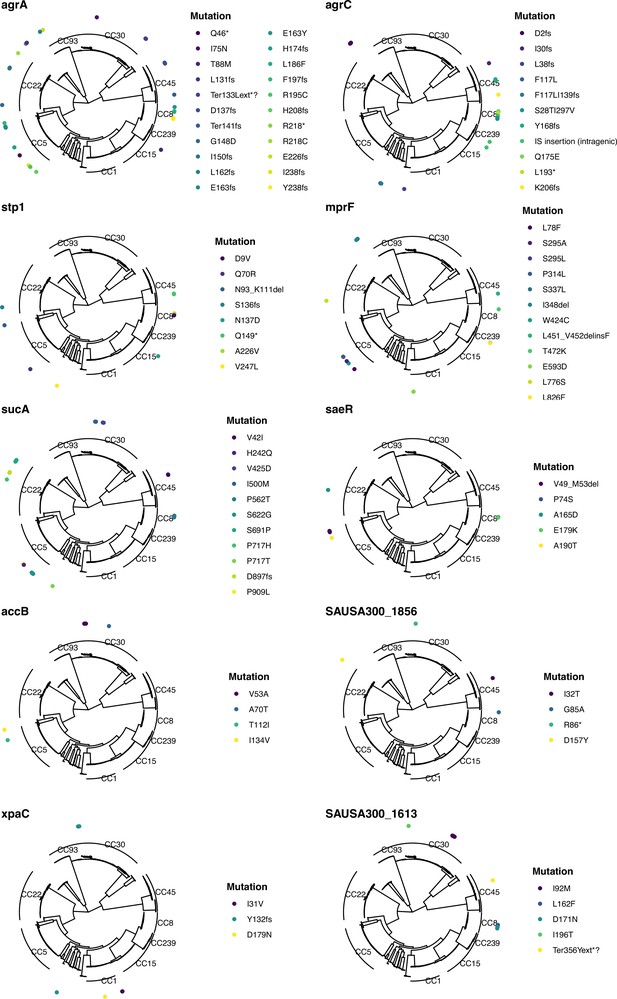
Mapping of mutations in the 10 most significantly enriched mutated genes across the entire dataset.
The maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree was inferred from the core genome alignment of 2590 isolates. The variants are annotated based on SnpEff (*: stop codon; fs: frameshift; ext*?: stop lost).
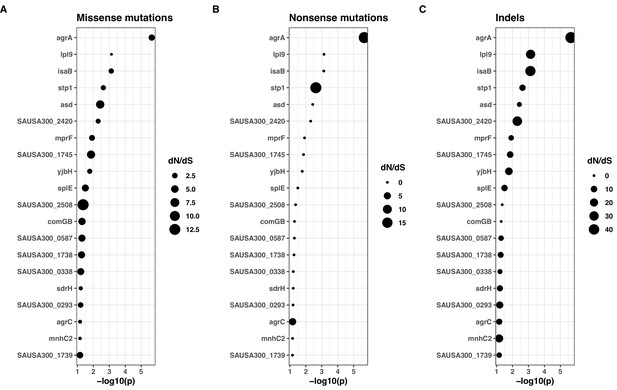
dN/dS values for non-synonymous mutations (A), indels (B), and non-sense mutations (stop codons) (B) for FPR3757 genes.
Only the 20 most significant genes with positive selection (dN/dS for missense mutations >1) are shown.
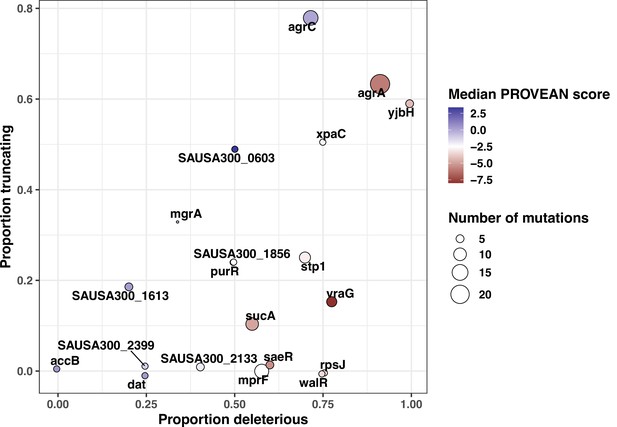
Scatter plot representing in silico inferred functional impact of variants in the 20 most convergent loci.
On the x-axis are shown proportions of predicted deleterious mutations (protein-truncating substitutions with PROVEAN score <–2.5, insertion sequences [IS] insertions), the y-axis shows protein-truncating mutations, the colour of the dots is based on the median PROVEAN score, and the size represents the total number of aggregated mutations.
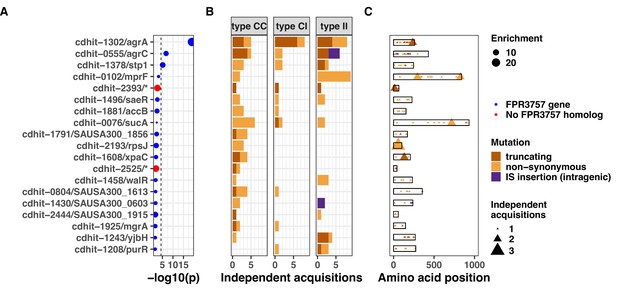
Gene convergence analysis of all mutated genes (i.e. including both genes with FPR3757 homologue and no FPR3757 homologue).
Top 20 genes with the most significant mutation enrichment across the entire dataset. (A) Significance of the enrichment for protein-altering mutations. The dashed line depicts the Bonferroni-corrected significance threshold, and red circles and blue circles represent genes with and without FPR3757 homologue, respectively. (B) Bar plots of independent mutations separated in three panels according to the type of variant (type C>C: colonising-colonising; type C>I: colonising-invasive; type I>I: invasive-invasive) and coloured according to the class of mutation. (C) Gene maps with type and positions of mutations.
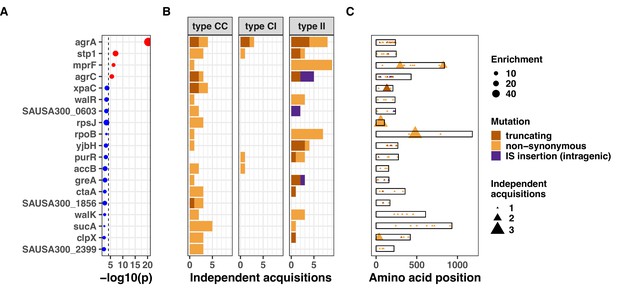
Gene convergence analysis after removing variants in strains included in Young et al., 2017, the largest collection of this analysis (1078 strains and 105 episodes).
Top 20 genes with the most significant mutation enrichment across the entire dataset. (A) Significance of the enrichment for protein-altering mutations. The dashed line depicts the Bonferroni-corrected significance threshold, and red circles and blue circles represent genes with p values below and above the Bonferroni threshold, respectively. (B) Bar plots of independent mutations separated in three panels according to the type of variant (type C>C: colonising-colonising; type C>I: colonising-invasive; type I>I: invasive-invasive) and coloured according to the class of mutation. (C) Gene maps with type and positions of mutations.
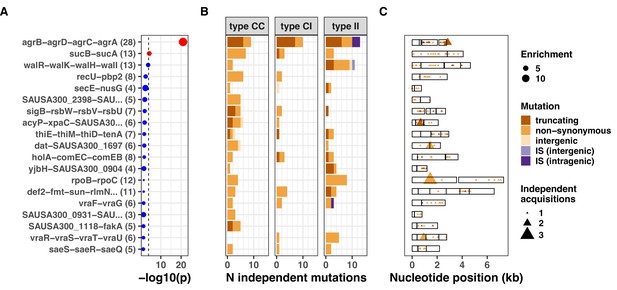
Top 20 operons with the most significant mutation enrichment across all dataset.
(A) Significance of the enrichment for protein-altering mutations. The dashed line depicts the Bonferroni-corrected significance threshold, and red circles and blue circles represent operons with p values below and above the Bonferroni threshold, respectively. (B) Bar plots of independent mutations separated in three panels according to the type of variant (type C>C: colonising-colonising; type C>I: colonising-invasive; type I>I: invasive-invasive) and coloured according to the class of mutation. Mutations were considered independent if they occurred in separate episodes of either colonisation or invasive infection. (C) Operon maps with positions of the mutations (relative to the start of the first gene of the operon). Operons are labelled with the names of the genes included, and longer labels were shorted for clarity (see Supplementary file 5 for details).
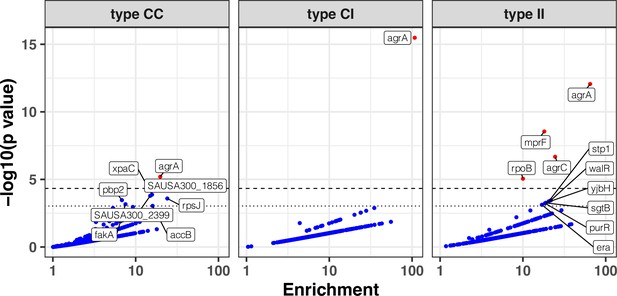
Modified volcano plot displaying enrichment (x-axis) and significance of enrichment (y-axis) within colonising-colonising (type C>C), colonising-invasive (type C>I), and invasive-invasive (type I>I) variants.
The horizontal dashed line depicts the Bonferroni-corrected significance threshold and dotted line shows the suggestive significance threshold. Labels indicate genes with significance of enrichment below the suggestive threshold. Genes are coloured in red if the p value is below the Bonferroni-corrected threshold and in blue otherwise.
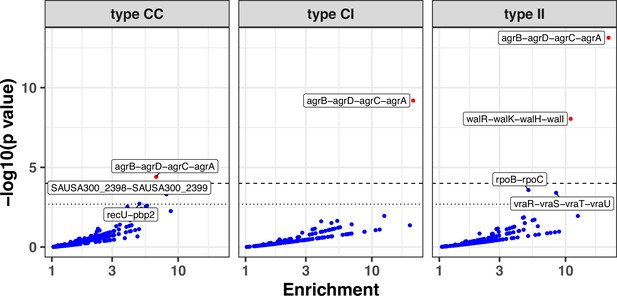
Modified volcano plot displaying enrichment (x-axis) and significance of enrichment (y-axis) for FPR3757 operons across the entire dataset, colonising-colonising (type CC), colonising-invasive (type CI), and invasive-invasive (type II) variants.
The horizontal line depicts the Bonferroni-corrected significance threshold. Genes are coloured in red if the p value is below the Bonferroni-corrected threshold and in blue otherwise. Operons are labelled if they were significantly enriched or reached near significance.
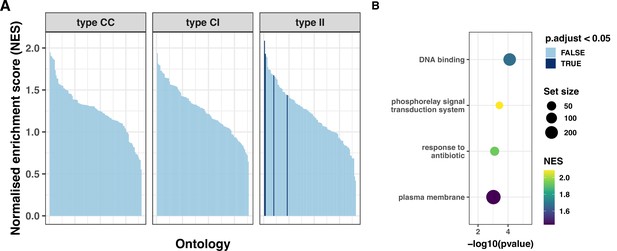
Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) for protein-modifying mutations in colonising-colonising (type CC), colonising-invasive (type CI), and invasive-invasive (type II) variants.
(A) Gene ontologies (minimum set size 10 for a total of 110 categories) ordered by normalised enrichment score (NES). Ontologies with negative enrichment were excluded. Dark blue bars indicate a significant p value after false discovery rate correction (B) Dot plot of nine significantly enriched ontologies among type II variants.
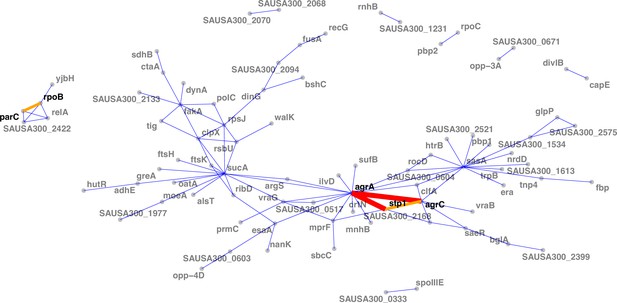
Network of mutations co-occurrence.
The width and colour of the edges represent the strength of the co-occurrence of mutated genes on the same strain (thin and blue, two independent co-occurrences; thick and orange, three independent co-occurrences).
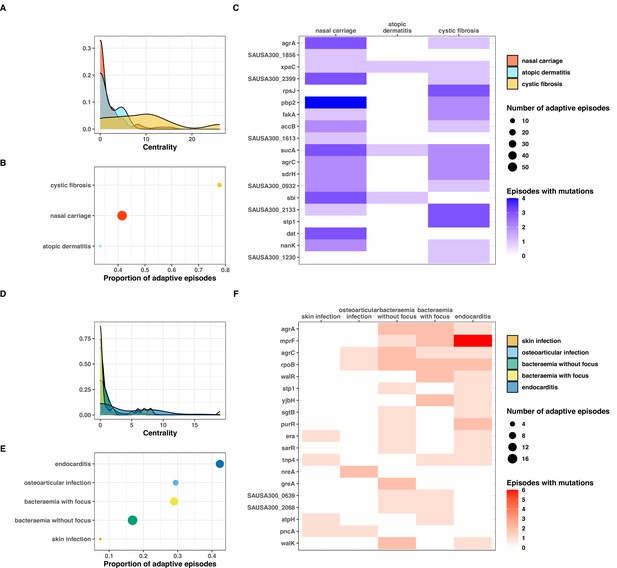
Clinical correlates of adaptive signatures within colonising (colonising-colonising [type C>C,] panels A–C) and invasive (invasive-invasive [type I>I], panels D–F) bacterial populations.
Adaptation was inferred by computing the Jaccard index of shared mutated genes between independent episodes, followed by network analysis of infection episodes pairs. The node centrality measure was used as an indicator of adaptation. To avoid overinflation of mutated genes, the calculation was limited to the 20 most significantly enriched genes within each group of mutations. (A, D) Density of centrality values across colonisation (panel A) and infection categories (panel D). (B, E) Number and proportion of adaptive episodes. An adaptive episode was defined by a centrality >0. (C, F) Distribution of mutations in the 20 most significantly enriched genes across categories of colonisation (panel C) and infection (panel F).
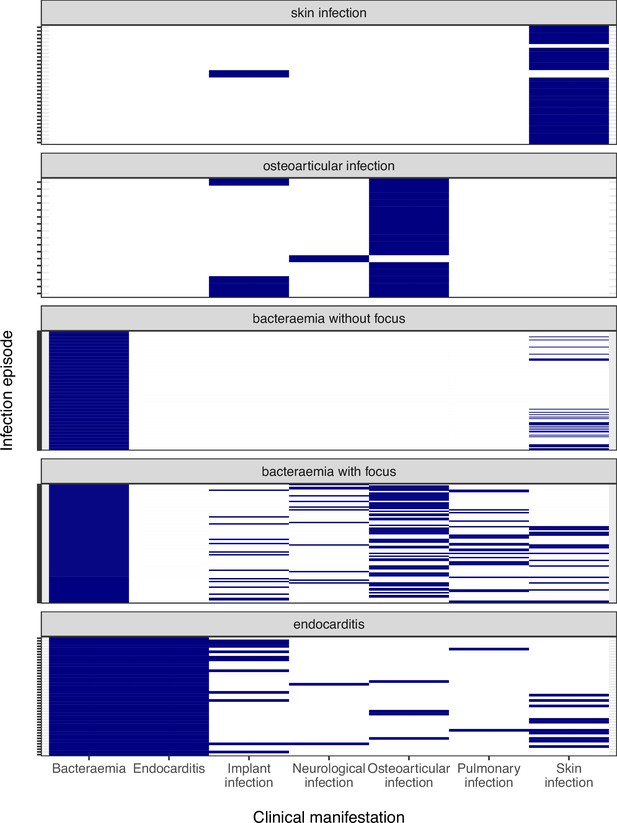
Clinical manifestations and infection sites of invasive episodes, grouped by the infection syndromes classification used for the adaptation analysis.
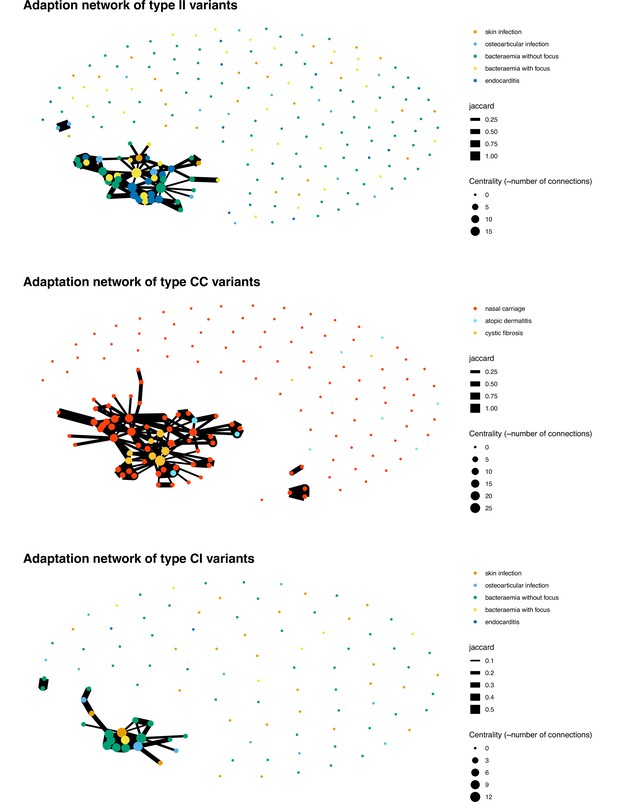
Network of colonisation/infection episodes for colonising-colonising (type CC) (panel A), colonising-invasive (type CI) (panel B), and invasive-invasive (type II) variants (panel C).
Nodes indicate independent episodes, coloured based on the clinical syndrome, edges show connections based on shared mutated genes (the width of the connection is proportional to the Jaccard index).
Tables
Microbiological and clinical characteristics of the colonisation and infection episodes included in the within-host evolution analysis.
| Strains(n=2590) | Episodes(n=396) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sequence type | ||
| 30 | 342 (13.2%) | 43 (10.9%) |
| 22 | 277 (10.7%) | 44 (11.1%) |
| 5 | 271 (10.5%) | 42 (10.6%) |
| 45 | 198 (7.6%) | 38 (9.6%) |
| 15 | 156 (6.0%) | 4 (3.5%) |
| 1 | 133 (5.1%) | 14 (3.5%) |
| 93 | 110 (4.2%) | 29 (7.3%) |
| 8 | 107 (4.1%) | 18 (4.5%) |
| 239 | 100 (3.9%) | 29 (7.3%) |
| Other | 896 (34.6%) | 125 (31.6%) |
| mecA positive | 1001 (38.6%) | 207 (52.3%) |
| Infection syndrome | ||
| Skin infection | 204 (7.9%) | 32 (8.1%) |
| Osteoarticular infection | 77 (3.0%) | 17 (4.3%) |
| Bacteraemia without focus | 588 (22.7%) | 152 (38.4%) |
| Bacteraemia with focus | 331 (12.8%) | 85 (21.5%) |
| Endocarditis | 197 (7.6%) | 44 (11.1%) |
| No invasive strains | 66 (16.7%) | |
| Colonisation syndrome | ||
| Nasal carriage | 974 (37.6%) | 166 (42%) |
| Cystic fibrosis | 57 (2.2%) | 9 (2%) |
| Atopic dermatitis | 162 (6.3%) | 9 (2%) |
| No colonising strains | 212 (54%) |
-
Table 1—source data 1
List of within-host studies included in the analysis.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/77195/elife-77195-table1-data1-v2.zip
Modified McDonald-Kreitman table displaying counts of variants (point mutations and structural variants) and the neutrality index for colonising-invasive (type C>I) and invasive-invasive (type I>I) variants (both compared to colonising-colonising [type C>C] variants).
| Classification of variant | Number of variants (Neutrality index) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Type C>C | Type C>I | Type I>I | |
| Synonymous | 381 | 130 | 155 |
| Non-synonymous | 978 | 300 (0.9) | 503 (1.3)* |
| Intergenic | 544 | 197 (1.1) | 549 (2.5)** |
| Truncating | 197 | 58 (0.9) | 190 (2.4)** |
| Insertion sequences insertion | 17 | 6 (1.0) | 137 (19.8)** |
| Large deletion | 76 | 17 (0.6)* | 122 (3.9)** |
-
Values are counts of independent mutations. The neutrality index is shown in brackets in italic.
-
Significance testing Fisher’s Exact Test: p<0.05; ** p<0.005.
Genome-wide significant gene signatures of within-host evolution.
The genes shown reached genome-wide significance in the entire dataset or in either colonising-colonising (type C>C), colonising-invasive (type C>I), or invasive-invasive (type I>I) variants.
| Gene | p value(whole dataset) | Description | N independent mutations | Significance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type C>C | Type C>I | Type I>I | ||||
| agrA* | 7.04 × 10–28 | Accessory gene regulator protein A | 5** | 9** | 8** | Part of the agr quorum sensing system, which is the master regulator of virulence factors expression in S. aureus. Recurrent mutations associated with invasive disease. |
| agrC** | 2.84 × 10–10 | Accessory gene regulator protein C | 4 | 2 | 6** | Histidine kinase, receptor for extracellular autoactivating peptide. Phosphorylates agrA. |
| stp1** | 1.13 × 10–7 | Protein phosphatase 2 C domain-containing protein | 3 | 2 | 3 | Associated with vancomycin resistance. |
| mprF** | 4.55 × 10–6 | Oxacillin resistance-related FmtC protein | 2 | 0 | 9** | Main determinant of daptomycin resistance. Association with persistence and immune evasion. |
| rpoB | 7.24 × 10–3 | DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta | 1 | 1 | 7** | Association with rifampicin resistance, but selection in the absence of rifampicin exposure can happen (R503H). Co-resistance to vancomycin, daptomycin, and oxacillin. Association with persistence. |
-
*
Significant enrichment (above the Bonferroni-corrected cut-off, see methods).
Gene signatures of within-host evolution with suggestive significant enrichment.
The genes shown reached the suggestive significance threshold in the entire dataset or in either type C>C, type C>I, or type I>I variants.
| Gene | p value(whole dataset) | Description | N independent mutations | Significance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type C>C | Type C>I | Type I>I | ||||
| sucA* | 6.82 × 10–5 | 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase E1 component | 6 | 2 | 2 | Encodes a subunit of the α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase of the tricarboxylic acid cycle. |
| saeR* | 1.83 × 10–4 | DNA-binding response regulator SaeR | 2 | 1 | 2 | Regulator component of the saeRS two-component system. Virulence regulation. |
| accB | 4.27 × 10–4 | Biotin carboxyl carrier protein of acetyl-CoA carboxylase | 3* | 1 | 0 | Part of the fatty acid synthesis pathway of S. aureus. |
| SAUSA300_1856 | 6.41 × 10–4 | Hypothetical protein | 4* | 0 | 0 | Intracellular cysteine peptidase. Putative chaperone in S. aureus. |
| xpaC | 1.38 × 10–3 | Hypothetical protein | 4* | 0 | 0 | Predicted 5-bromo-4-chloroindolyl phosphate hydrolysis protein, no data on S. aureus. |
| rpsJ | 1.58 × 10–3 | 30S ribosomal protein S10 | 3* | 0 | 0 | Mutations at residues 53–60 are associated with tigecycline resistance, at no apparent fitness cost. |
| SAUSA300_2399 | 1.68 × 10–3 | ABC transporter ATP-binding protein | 4* | 0 | 0 | Downregulated in the presence of fusidic acid |
| walR | 2.10 × 10–3 | DNA-binding response regulator | 1 | 0 | 3* | Part of walKR two-component response regulator. Associated with vancomycin resistance. |
| yjbH | 3.55 × 10–3 | Dsba-family protein | 1 | 0 | 3* | Negative regulator of spx (directs its ClpXP-dependent degradation). Association with antibiotic resistance, virulence regulation, and oxidative stress resistance. |
| purR | 3.86 × 10–3 | Pur operon repressor | 0 | 1 | 3* | purR mutants: increased biofilm formation and virulence in animal model; higher capacity to invave epithelial cells. |
| era | 5.34 × 10–3 | GTP-binding protein Era | 0 | 1 | 3* | Involved in ribosome assembly and stringent response. |
| pbp2 | 7.75 × 10–3 | Penicillin-binding protein 2 | 6* | 0 | 0 | Role in methicillin resistance (PBP2a synergism). Increased expression after oxacillin exposure. |
| fakA | 9.90 × 10–3 | Hypothetical protein | 5* | 0 | 0 | Fatty acid kinase. Deletion mutant displayed increased virulence in a murine model of skin infection. |
| sgtB | 2.65 × 10–2 | Glycosyltransferase | 0 | 0 | 3* | sgtB mutations in adaptive laboratory evolution experiments upon vancomycin exposure. |
-
*
suggestive significant enrichment (above the suggestive significance cut-off, adjusted for false-discovery, see methods).
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
List of colonisation/infection episodes included with publication data (first author, year, PubMed id), number of strains, sites of collection, clinical characterstics, classification of colonisation, and infection episodes.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/77195/elife-77195-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
List of strains included with site and date of collection, sequence type, presence of the mecA gene, information on whether the strain was designed as internal reference or baseline index strain, mash distance to the internal reference, number of variants called (as compared to the internal reference), and sequencing metrics.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/77195/elife-77195-supp2-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 3
List of variants identified annotated with gene, gene sequence, FPR3757 homologue, and FPR3757 operon.
Point mutations, insertion sequences insertions, large deletions, and copy number variants are presented separately.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/77195/elife-77195-supp3-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 4
Gene enrichment analysis for all mutated genes with a FPR3757 homologue with number of mutations, gene length, mutation enrichment, and p value based on a Poisson regression to model the number of variants per gene.
Results are presented separately for the complete dataset and for colonising-colonising (type C>C), colonising-invasive (type C>I), and invasive-invasive (type I>I) variants.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/77195/elife-77195-supp4-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 5
Operon enrichment analysis for all FPR3757 operons (i.e. mutated genes that could be assigned to a FPR3757 operon) with number of mutations, operon length, mutation enrichment, and p value based on a Poisson regression to model the number of variants per operon.
Results are presented separately for the complete dataset and for colonising-colonising (type C>C), colonising-invasive (type C>I), and invasive-invasive (type I>I) variants.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/77195/elife-77195-supp5-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 6
Gene set enrichment analysis for mutations in genes aggregated in gene ontologies (GO) categories with enrichment score, normalsied enrichment score (NES), and unadjusted and false-discovery rate (FDR) adjusted p value.
Results are presented separately for the complete dataset and for colonising-colonising (type C>C), colonising-invasive (type C>I), and invasive-invasive (type I>I) variants.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/77195/elife-77195-supp6-v2.xlsx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/77195/elife-77195-mdarchecklist1-v2.docx