Differentiation signals from glia are fine-tuned to set neuronal numbers during development
Figures
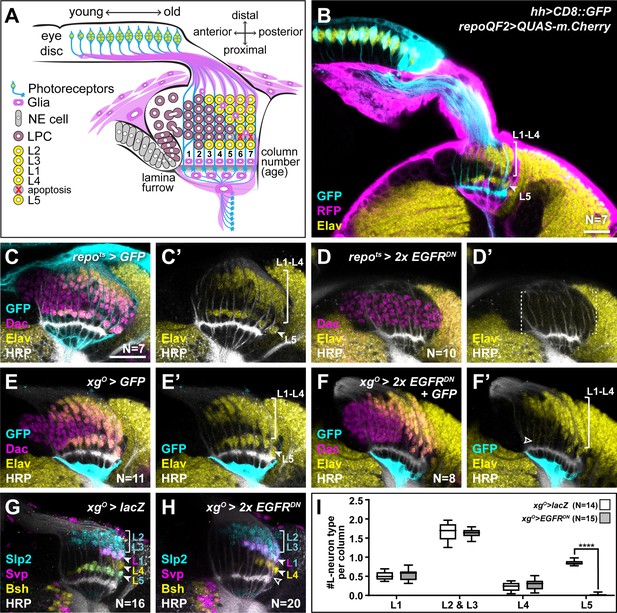
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) activity in the xgO is required for the differentiation of L5 neurons.
(A) Schematic of the developing lamina. Photoreceptors (blue) drive lamina precursor cell (LPC; purple) birth from neuroepithelial cells (NEs; grey) and their assembly into columns of ~6 LPCs, which differentiate into the L1-L5 neurons (yellow) following an invariant spatio-temporal pattern. The ‘extra’ LPC is cleared by apoptosis (red X). Several glial types (magenta) associate with the lamina. (B) A cross-sectional view of an early pupal (0–5 hr after puparium formation; APF) optic lobe where hh-Gal4 drives UAS-CD8::GFP expression in photoreceptors (cyan). The pan-glial driver repo-QF2 drives QUAS-m.Cherry (magenta) in all glia. Embryonic lethal abnormal vision (Elav) (yellow) marks all neurons. (C) A cross-sectional view of an optic lobe with pan-glial expression of CD8::GFP stained for GFP (cyan), Dachshund (Dac) (magenta), Elav (yellow), and Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP; axons; white). (D) Pan-glial expression of two copies of EGFRDN stained for Dac (magenta), Elav (yellow), and HRP (white). (E) xgO-specific expression of CD8::GFP stained for GFP (cyan), Dac (magenta), Elav (yellow), and HRP (white). (F) xgO-specific expression of two copies of EGFRDN and CD8::GFP stained for GFP (cyan), Dac (magenta), Elav (yellow), and HRP (white). The number of Elav+ cells in proximal row (L5s) decreased (empty arrowhead) relative to control (E). (G,H) HRP (white) and L-neuron-type-specific markers Sloppy paired 2 (Slp2) (cyan), Brain-specific homeobox (Bsh) (yellow), and Seven-up (Svp) (magenta) in (G) control xgO>lacZ optic lobe and (H) xgO>2xEGFRDN. L2s and L3s express Slp2; L1s express Slp2 and Svp; L4s express Bsh and L5s express Bsh and Slp2. (I) Quantification of the number of L-neuron types per column for control and xgO>2xEGFRDN. Only L5 neurons were decreased significantly (pL5<0.0001; Mann-Whitney U-test. Ns indicated in parentheses. Boxes indicate the lower and upper quartiles; the whiskers represent the minimum and maximum values; the line inside the box indicates the median). Scale bar = 20 μm.
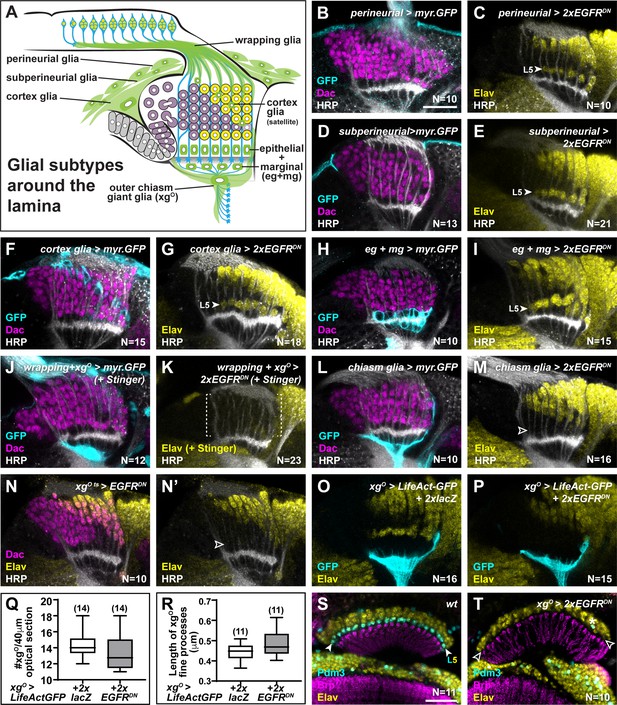
A Gal4 screen identifies xgO as the glial subtype that regulates L5 neuronal differentiation.
(A) Schematic of the developing lamina and associated glial types (green; labelled). (B) A perineurial glia-specific Gal4 drives expression of myr.GFP stained for GFP (cyan), Dachshund (Dac) (magenta), and Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) (white). (C) Perineurial glia-specific expression of EGFRDN stained for Embryonic lethal abnormal vision (Elav) (yellow) and HRP (white). L5 differentiation was not affected. (D) A subperineurial glia-specific Gal4 drives expression of myr.GFP stained for GFP (cyan), Dac (magenta), and HRP (white). (E) Suberineurial glia-specific expression of EGFRDN stained for Elav (yellow) and HRP (white). L5 differentiation was not affected. (F) A cortex glia-specific Gal4 drives expression of myr.GFP stained for GFP (cyan), Dac (magenta), and HRP (white). (G) Cortex glia-specific expression of EGFRDN stained for Elav (yellow) and HRP (white). L5 differentiation was not affected. (H) An epithelial and marginal glia (eg+mg) specific Gal4 drives expression of myr.GFP stained for GFP (cyan), Dac (magenta), and HRP (white). (I) Epithelial and marginal glia-specific expression of EGFRDN stained for Elav (yellow) and HRP (white). L5 differentiation was not affected. (J) A wrapping glia- and xgO-specific Gal4 drives expression of myr.GFP stained for GFP (cyan), Dac (magenta), and HRP (white). (K) Wrapping glia- and xgO-specific expression of EGFRDN stained for Elav (yellow) and HRP (white). L1-L4 and L5 differentiation were disrupted as observed by the lack of Elav+ cells in the lamina. (L) A chiasm glia (xgO and xginner) specific Gal4 drives expression of myr.GFP stained for GFP (cyan), Dac (magenta), and HRP (white). (M) Chiasm glia-specific expression of EGFRDN stained for Elav (yellow) and HRP (white). L1-L4 differentiation proceeded normally but L5 differentiation was disrupted as observed by the lack of Elav+ cells in the proximal lamina. (N) Gal80ts-restricted Gal4 expression in xgO, driving EGFRDN during lamina development (see Figure 3—source data 1) stained for Dac (magenta), Elav (yellow), and HRP (white). L5 neurons were dramatically reduced. (O,P) LifeAct-GFP expression driven in xgO in (O) controls and (P) when two copies of EGFRDN are co-expressed. In both conditions, the fine processes from the xgO are present. (Q) Quantification of xgO numbers in control xgO>LifeAct-GFP+2xlacZ and xgO>LifeAct GFP+2xEGFRDN. p>0.05; Mann-Whitney U-test. Ns indicated in parentheses. (R) Quantification of the length of xgO fine processes in control xgO>LifeAct-GFP+2xlacZ and xgO>LifeAct GFP+2xEGFRDN. p>0.05; Unpaired t-test. Ns indicated in parentheses. (S) Wild-type adult optic lobe stained for POU domain motif 3 (Pdm3) (L5 marker) (Tan et al., 2015), Bruchpilot (Brp; marks neuropils) and Elav (yellow). (T) xgO>2xEGFRDN adult optic lobe stained for Pdm3 (L5 marker) (Tan et al., 2015), Bruchpilot (Brp; marks neuropils) and Elav (yellow). Pdm3+ cells (L5s) are reduced dramatically. Scale bar = 20 μm. For all quantifications boxes indicate the lower and upper quartiles; the whiskers represent the minimum and maximum values; the line inside the box indicates the median.
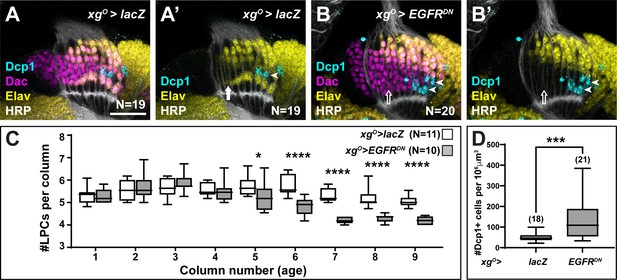
Lamina precursor cells (LPCs) that fail to differentiate into L5s undergo apoptosis.
(A) Control xgO>lacZ optic lobe stained for Death caspase-1 (Dcp-1) (cyan), Embryonic lethal abnormal vision (Elav) (yellow), and Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) (white). Dcp-1+ cells were always observed just distal to the most proximal row of cells (L5s). (B) xgO>EGFRDN stained for Dcp-1 (cyan), Dachshund (Dac) (magenta), Elav (yellow), and HRP (white). Dcp-1 positive cells were observed in the most proximal row of LPCs as well as the row just distal to these. (C) Quantification of the number of LPCs/column (i.e., Dac+ cells/column) for control and xgO>EGFRDN. *p<0.05, ****p<0.0002; Mann-Whitney U-test. Ns indicated in parentheses. (D) Quantification of the number of Dcp-1 positive cells in (A) compared to (B). ***p<0.0005, Mann-Whitney U-test. Ns indicated in parentheses. Boxes indicate the lower and upper quartiles; the whiskers represent the minimum and maximum values; the line inside the box indicates the median. Scale bar = 20 μm.
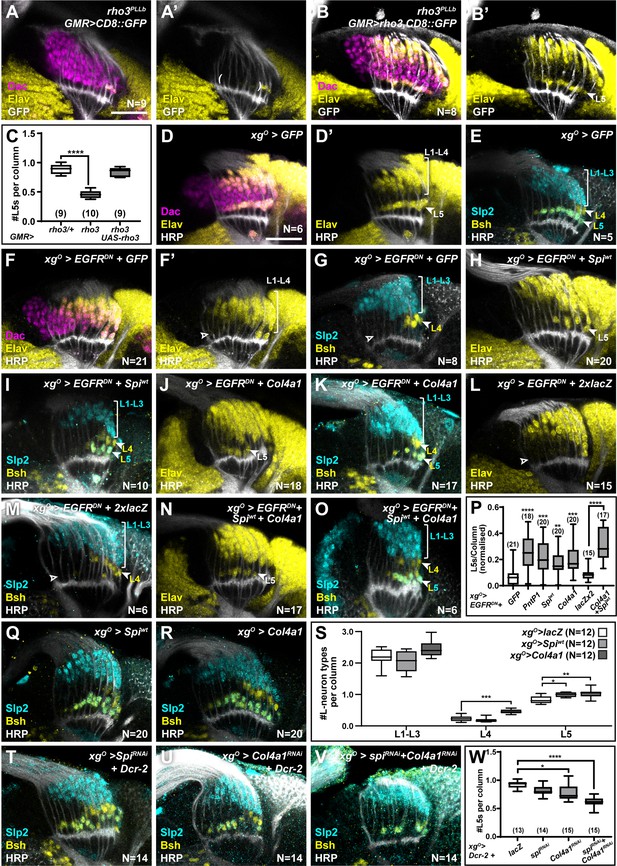
XgO secrete multiple ligands to induce L5 neuronal differentiation in response to epidermal growth factor (EGF) from photoreceptors.
(A) GMR-Gal4-driven CD8::GFP expression in photoreceptors in a rho3PLLb background stained for GFP (white), Dachshund (Dac) (magenta), Embryonic lethal abnormal vision (Elav) (yellow). Few proximal Elav+ cells (L5s) were recovered in older columns only as previously published (Fernandes et al., 2017). (B) GMR-Gal4-driven Rho3 and CD8::GFP in a rho3PLLb background stained for GFP (white), Dac (magenta), Elav (yellow) showed that L5 neuronal differentiation was rescued (Elav+ cells in the proximal lamina). (C) Quantifications for number of L5 neurons/column in (A) and (B) compared to rho3PLLb heterozygotes (rho3/+). ****p<0.0001, one-way ANOVA with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. Ns indicated in parentheses. (D,E) Control xgO>GFP optic lobes stained for (D) Dac (magenta), Elav (yellow), and Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) (white) or (E) HRP (white) and L-neuron-specific markers Sloppy paired 2 (Slp2) (cyan) and Brain-specific homeobox (Bsh) (yellow). (F,G) Gal4 titration control xgO>GFP + EGFRDN stained for (F) Dac (magenta), Elav (yellow), and HRP (white) or (G) HRP (white) and L-neuron-specific markers Slp2 (cyan) and Bsh (yellow). (H,I) Wild-type Spitz (Spi) (Spiwt) co-expression with EGFRDN specifically in xgO stained for (H) Elav (yellow) and HRP (white) or (I) HRP (white) and L-neuron-specific markers Slp2 (cyan) and Bsh (yellow). (J,K) Col4a1 co-expression with EGFRDN specifically in xgO stained for (J) Elav (yellow) and HRP (white) or (K) HRP (white) and L-neuron-specific markers Slp2 (cyan) and Bsh (yellow). (L,M) Gal4 titration control xgO>EGFRDN + 2xlacZ stained for (L) Elav (yellow) and HRP (white) or (M) HRP (white), Slp2 (cyan), and Bsh (yellow). (N,O) Wild-type Spiwt and Col4a1 co-expression with EGFRDN specifically in xgO. (N) stained for Elav (yellow) and HRP (white) or (O) HRP (white) and L-neuron-specific markers Slp2 (cyan) and Bsh (yellow). (P) Quantification of the number of L5s/column for the genotypes indicated compared to the appropriate titration control. For pntP1, spiwt, and Col4a1 co-expression with EGFRDN, the titration control is xgO>EGFRDN + GFP (**p<0.005, ***p<0.0005; ****p<0.0001; one-way ANOVA with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. Ns indicated in parentheses). For spiwt and Col4a1 simultaneous co-expression with EGFRDN, the titration control is xgO>EGFRDN + 2xLacZ (****p<0.0001, Mann-Whitney U-test. Ns indicated in parentheses). (Q,R) Optic lobes stained for Slp2 and Bsh when xgO overexpress (Q) spiwt or (R) Col4a1. (S) Quantification of the number of L-neuron types/column in (Q) and (R) compared to controls, xgO>lacZ. (*p<0.05; **p<0.005; ***p<0.001; one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons test). (T, U, V) Optic lobes stained for Slp2, Bsh, and HRP when xgO co-express Dcr-2 with (T) spiRNAi, (U) Col4a1RNAi, and (V) SpiRNAi and Col4a1RNAi simultaneously. (W) Quantifications of the number of L5s/column for genotypes indicated compared to the titration control xgO>Dcr-2+lacZ (*p<0.05, ****p<0.0001, one-way ANOVA with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. Scale bar = 20 µm. For all quantifications boxes indicate the lower and upper quartiles; the whiskers represent the minimum and maximum values; the line inside the box indicates the median).
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Excel file containing all the probe sequences used for in situ hybridisation chain reaction in this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/78092/elife-78092-fig3-data1-v2.zip
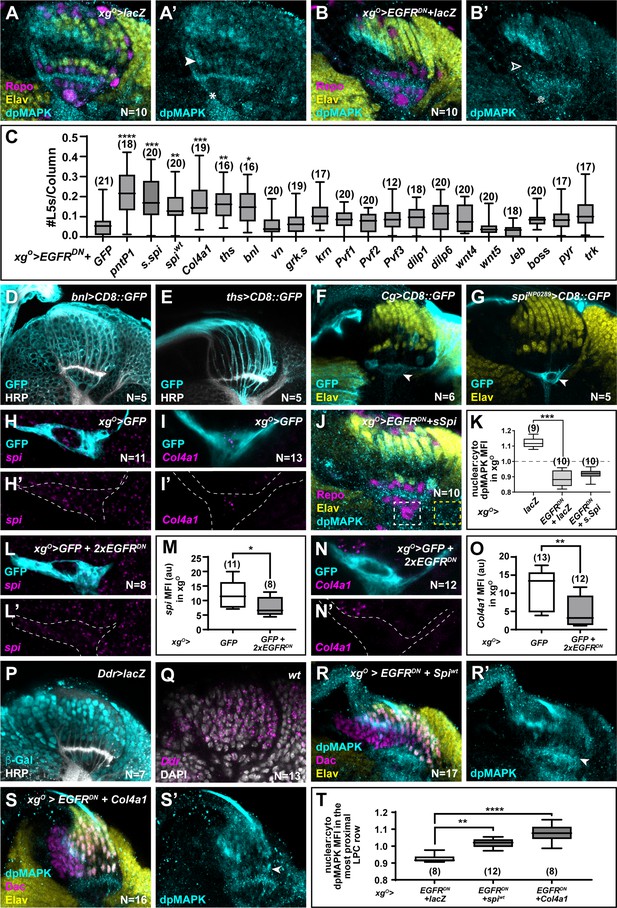
Multiple xgO secreted ligands activate mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signalling to drive L5 neuronal differentiation.
(A,B) Optic lobes stained for Embryonic lethal abnormal vision (Elav) (yellow), Repo (magenta), and double phosphorylated MAPK (dpMAPK) (cyan) in (A) xgO>lacZ controls and (B) with EGFRDN and lacZ expressed in xgO. dpMAPK levels decreased in the xgO (indicated by asterisk) and in cells in the proximal row of the lamina (indicated by arrowhead) when compared with xgO>lacZ controls. (C) Quantification of the number of L5s/column (based on Elav expression) when different ligands that can activate MAPK signalling were co-expressed with EGFRDN in the xgO (*p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.0005; ****p<0.0001; one-way ANOVA with Dunn’s multiple comparison test. Ns indicated in parentheses). (D) bnl>CD8::GFP showed GFP (cyan) expression in all cells in the optic lobe; Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) (white). (E) ths>CD8::GFP showed GFP (cyan) expression in photoreceptors; HRP (white). (F) Collagen>CD8::GFP drove GFP (cyan) expression in xgO (arrowhead); Elav (yellow). (G) spiNP0289>CD8::GFP drove GFP (cyan) expression in xgO (arrowhead); Elav (yellow). (H, I) xgO>GFP lobes stained for GFP (cyan) and (H) spi mRNA (magenta) and (I) Col4a1 mRNA (magenta) by in situ hybridisation chain reaction (HCR). (J) xgO>EGFRDN + s.spi lobes stained for Elav (yellow), Repo (magenta), and dpMAPK (cyan). Inset shows a magnified view of the xgO nucleus. (K) Quantifications of nuclear:cytoplasmic ratios of dpMAPK mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) in the xgO in indicated genotypes (p<0.0005, one-way ANOVA with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. Ns indicated in parentheses). (L) spi mRNA (magenta) detected by HCR in xgO>GFP + 2xEGFRDN lobes. (M) Quantification of spi MFI (arbitrary units) for (H and L). (p<0.05; Mann-Whitney U-test.). (N) Col4a1 mRNA (magenta) detected by HCR in xgO>GFP + 2xEGFRDN lobes. (O) Quantification of Col4a1 MFI (arbitrary units) for (I and N) (p<0.005; Mann-Whitney U-test). (P) Ddr>lacZ showed β-Galactosidase (β-Gal; cyan) expression in the lamina; HRP (white). (Q) Ddr mRNA (magenta) detected by HCR in wild-type lobes; DAPI (white). (R,S) Lobes stained for Dac (magenta), Elav (yellow), and dpMAPK (cyan) when (R) Spiwt is co-expressed with EGFRDN in xgO or (S) Col4a1 is co-expressed with EGFRDN in xgO. Arrowheads indicate Elav+ cells in the most proximal row. (T) Quantifications of nuclear:cytoplasmic ratios of dpMAPK MFI in the most proximal row of lamina precursor cells (LPCs) in indicated genotypes (**p<0.005, ****p<0.0001; one-way ANOVA with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test). Scale bar = 20 μm. For all quantifications boxes indicate the lower and upper quartiles; the whiskers represent the minimum and maximum values; the line inside the box indicates the median.
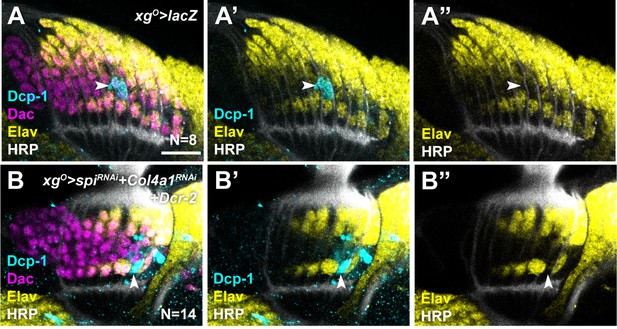
Spi and Col4a1 from xgO promote cell survival in proximal lamina precursor cells (LPCs).
(A) xgO>lacZ lobes stained for Death caspase-1 (Dcp-1) (cyan), Dachshund (Dac) (magenta), Embryonic lethal abnormal vision (Elav) (yellow), and Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) (white). Dcp-1 positive cells (indicated by arrowhead) were located between L4s and L5s and corresponds to ‘extra’ LPCs which undergo apoptosis. (B) xgO>SpiRNAi + Col4aRNAi + Dcr-2 lobes stained for Dcp-1 (cyan), Dac (magenta), Elav (yellow), and HRP (white). Dcp-1 positive cells were observed in the proximal row of L5s (indicated by arrowhead) which were never observed in controls.
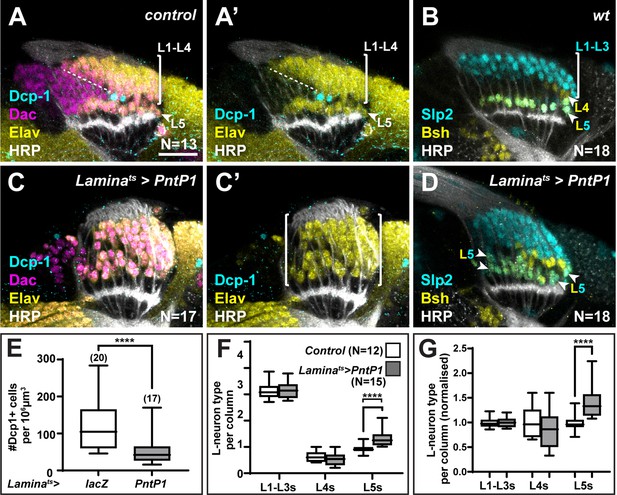
The ‘extra’ lamina precursor cells (LPCs) are specified as L5s.
(A) Wild-type optic lobes stained for Dachshund (Dac) (magenta), Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) (white), Embryonic lethal abnormal vision (Elav) (yellow), and cleaved Death caspase-1 (Dcp-1) (cyan). (B) Wild-type optic lobes stained for HRP (white) and L-neuron-type-specific markers sloppy paired 2 (Slp2) (cyan) and brain-specific homeobox (Bsh) (yellow). (C, D) Optic lobes with lamina-specific overexpression of PntP1 stained as in (A) and (B), respectively. (C) Fewer Dcp-1 positive cells were recovered compared with controls. (D) Roughly two rows of Slp2 and Bsh co-expressing cells (L5s) were recovered (arrowheads). (E) Quantification of the number of Dcp-1 positive cells in (B) compared with control Laminats>lacZ (Figure 4—figure supplement 1A) (p<0.0001; Mann-Whitney U-test). (F) Quantification of the number of L-neuron types per column based on Slp2 and Bsh expression from column 7 onwards shows an increase in the number of L5s/column in Laminats>PntP1 compared with controls; p<0.0001; Mann-Whitney U-test. (G) Same as (F) but normalised to the mean of the control. The number of L5s/column in Laminats>PntP1 increase ~1.2-fold relative to controls; p<0.0001; Mann-Whitney U-test. Ns indicated in parentheses. Scale bar = 20 µm. For all quantifications boxes indicate the lower and upper quartiles; the whiskers represent the minimum and maximum values; the line inside the box indicates the median.
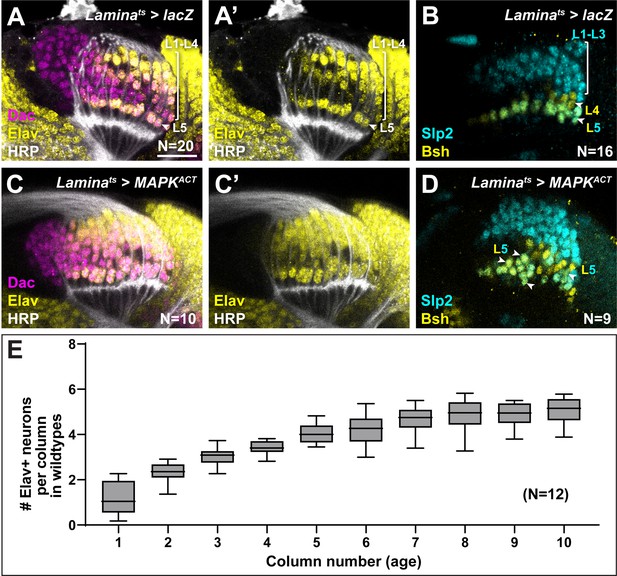
Hyperactivating Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in the lamina drives ectopic L5 differentiation.
(A,B) Control Laminats>lacZ optic lobes stained for (A) Dachshund (Dac) (magenta), Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) (white) and Embryonic lethal abnormal vision (Elav) (yellow), and (B) and L-neuron-type-specific markers Sloppy paired 2 (Slp2) (cyan) and Brain-specific homeobox (Bsh) (yellow). (C,D) Laminats>MAPKACT optic lobes stained for (C) Dac (magenta), HRP (white), and Elav (yellow), and (D) L-neuron-type-specific markers Slp2 (cyan) and Bsh (yellow). Ectopic Slp2 and Bsh co-expressing cells (L5s) were observed (arrowheads). (E) Quantification of the number of Elav+ cells per lamina column as a function of column number (age) in wild-type animals. Columns were fully differentiated (five Elav+ cells) by column 7. Boxes indicate the lower and upper quartiles; the whiskers represent the minimum and maximum values; the line inside the box indicates the median. Scale bar = 20 μm.
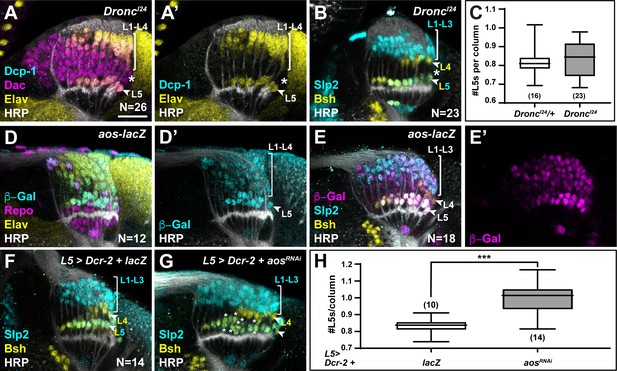
Newly induced L5 neurons secrete Aos to limit differentiation signals from xgO.
(A) DroncI24 optic lobes stained for Death caspase-1 (Dcp-1) (cyan), Dachshund (Dac) (magenta), Embryonic lethal abnormal vision (Elav) (yellow), and Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) (white). No Dcp-1 positive cells were recovered and Dac positive cells between L1-L4s and L5s persisted into the oldest columns (asterisk). (B) DroncI24 optic lobes stained for L-neuron-type-specific markers Sloppy paired 2 (Slp2) (cyan) and Brain-specific homeobox (Bsh) (yellow). A space (negative for both markers; asterisk) was present between L4s and L5s. (C) Quantifications for number of L5s/column in DroncI24 optic lobes compared to controls (DroncI24/+) (p>0.05, Mann-Whitney U-test. Ns indicated in parentheses). (D,E) aos-lacZ expression in the lamina with (D) β-Galactosidase (β-Gal) (cyan), Repo (magenta), Elav (yellow), HRP (white), and with (E) β-Gal (magenta) and L-neuron-type-specific markers Slp2 (cyan), Bsh (yellow), as well as HRP (white). (F) An L5-specific Gal4 was used to drive expression of Dcr-2 and lacZ in control lobes stained for Slp2 (cyan), Bsh (yellow), and HRP (white). (G) Optic lobes stained for HRP (white), Slp2 (cyan), and Bsh (yellow) when Dcr-2 and aosRNAi were expressed in developing L5 neurons specifically, which led to an increase in the number of Slp2 and Bsh co-expressing cells (L5s; asterisks). (H) Quantification of the number of L5s/column for (F) and (G). ***p<0.0005; Mann-Whitney U-test. Ns indicated in parentheses. For all quantifications boxes indicate the lower and upper quartiles; the whiskers represent the minimum and maximum values; the line inside the box indicates the median. Scale bar = 20 µm.
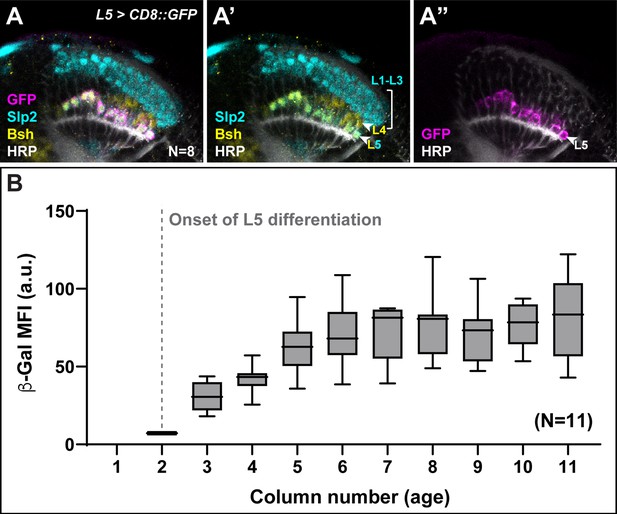
Aos expression is delayed in younger L5s.
(A) An L5-specific driver was used to drive the expression of GFP (magenta) in the lamina; Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) (white) and L-neuron-type-specific markers Sloppy paired 2 (Slp2) (cyan) and Brain-specific homeobox (Bsh) (yellow). (B) β-Galactosidase (β-Gal) mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) quantifications in the proximal row of L5s as a function of column number (age) in aos-lacZ lobes. β-Gal MFI is low in young columns and increases in older columns (from column 5). Boxes indicate the lower and upper quartiles; the whiskers represent the minimum and maximum values; the line inside the box indicates the median. Scale bar = 20 μm.
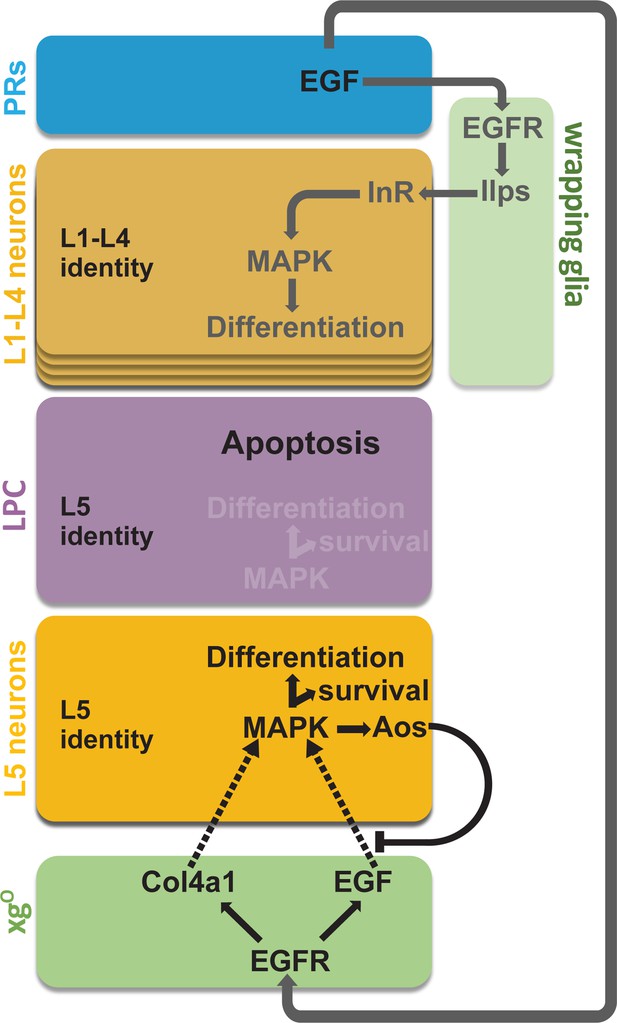
Summary schematic of neuronal differentiation in the lamina.
In our model of lamina neuronal differentiation, lamina precursor cells (LPCs) are prepatterned with unique identities based on their positions within a column, such that the two most proximal cells are specified with L5 identity. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) from photoreceptors activates EGF receptor (EGFR) signalling in wrapping glia, which induce L1-L4 differentiation, and in xgO, which induce L5 differentiation. Only a subset of the LPCs specified as L5s differentiate (i.e., those in the proximal row). We propose that this selective neuronal induction of L5s is due to tissue architecture and feedback from the newly born L5s, which limit available EGF (Spitz [Spi]) by secreting the antagonist Argos (Aos).
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | Canton S | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 64349 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | Bacc-GFP | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 36349 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | ey-Gal80 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 35822 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | Gal80ts | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 7108 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | DroncI24 | PMID:15800001 | Gift from M Amoyel | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R27G05-Gal4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 48073 | Lamina Gal4 |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R25A01-Gal4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 49102 | xgO Gal4 |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R64B07-Gal4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 71106 | Larval L5 Gal4 |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | hh-gal4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 67493 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | Repo-Gal4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 7415 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-CD8::GFP | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 32187 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-nls.lacZ | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 3956 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | GMR-Gal4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 9146 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | Repo-QF | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 66477 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | NP6293-Gal4 | Kyoto Stock Center | DGRC: 105188 | Perineural Glia |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | NP2276-Gal4 | Kyoto Stock Center | DGRC: 112853 | Subperineur-al Glia |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R54H02-Gal4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 45784 | Cortex Glia |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R10C12-Gal4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 47841 | Epithelial and marginal glia |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | Mz97-Gal4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 9488 | Wrapping glia and xgO |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R53H12-Gal4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 50456 | Chiasm glia |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | spiNP0289-Gal4 | Kyoto Stock Center | DGRC: 112828 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | Cg-Gal4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 7011 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | bnlNP2211-Gal4 | Kyoto Stock Center | DGRC: 112825 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | thsMI07139-Gal4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 77475 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | rho3PLLb, UAS-CD8::GFP | PMID:20957186 | Gift from B Shilo | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-rho3-3xHA | PMID:20957186 | Gift from B Shilo | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | aosw11 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 2513 | aos-lacZ |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | BaccGFP;10xQUAS-6xmCherry-HA | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 55270 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | 10xUAS-myrGFP | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 32197 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-LifeAct-GFP | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 35544 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-Dicer2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 24650 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | ;UAS-EGFRDN; UAS-EGFRDN | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 5364 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-rlSEM | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 59006 | rlSEM = MAPKACT |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-PntP1 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 869 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-jeb | PMID:21816278 | Gift from A Gould | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-Col4a1EY11094 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 20661 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-Cg25cRFP | PMID:26090908 | Gift from A Franz Cg25c=Col4a1 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-wnt5 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 64298 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-s.spi | PMID:7601354 | Gift from B Shilo | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-m.spi::GFP-myc (II) | PMID:11799065 | Gift from B Shilo m.spi=spiwt | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-m.spi::GFP-myc (III) | PMID:11799065 | Gift from B Shilo m.spi=spiwt | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-grk.sec | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 58417 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-vnEPgy | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 58498 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-krn-3xHA | FlyORF | F002754 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-bnl | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 64232 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-Ilp1 | PMID:12176357 | Gift from P Leopold | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-Ilp6 | PMID:20059956 | Gift from P Leopold | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-Pvf1XP | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 19632 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-Pvf2XP | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 19631 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-Wnt4EPgy2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 20162 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-boss-3xHA | FlyORF | F001365 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | SAM.dCas9.Trk | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 81322 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | SAM.dCas9.Pvf3 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 81346 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | SAM.dCas9.ths | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 81347 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | SAM.dCas9.pyr | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 81330 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | DdrCR01018-Gal4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 81157 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | spiRNAi | Vienna Drosophila Stock Center | GD3922 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | Col4a1RNAi | Vienna Drosophila Stock Center | GD28369 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | aosRNAi | Vienna Drosophila Stock Center | GD47181 | |
| Antibody | Anti-Dac2-3 (mouse monoclonal) | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | mAbdac2-3 | 1:20 |
| Antibody | Anti-Repo (mouse monoclonal) | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | 8D12 | 1:20 |
| Antibody | Anti-Elav (rat monoclonal) | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | 7E8A10 | 1:100 |
| Antibody | Anti-Elav (mouse monoclonal) | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | 9F8A9 | 1:20 |
| Antibody | Anti-Svp (mouse monoclonal) | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | 6F7 | 1:50 |
| Antibody | Anti-Slp2 (guinea pig polyclonal) | PMID:23783517 | C Desplan | 1:100 |
| Antibody | Anti-Bsh (Rabbit polyclonal) | PMID:33149298 | C Desplan | 1:500 |
| Antibody | Anti-Dcp-1 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling | 9578 | 1:100 |
| Antibody | Anti-Brp (guinea pig polyclonal) | C Desplan | 1:100 | |
| Antibody | Anti-phospho-p44/42-MAPK (Thr202/Tyr204) (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling | 9101 | 1:100 |
| Antibody | Anti-β-galactosidase (mouse monoclonal) | Promega | #Z3781 | 1:500 |
| Antibody | Anti-β-galactosidase (chicken polyclonal) | abcam | 9361 | 1:500 |
| Antibody | Anti-GFP (chicken polyclonal) | EMD Millipore | GFP-1010 | 1:400 |
| Antibody | Anti-Pdm3 (rat polyclonal) | PMID:22190420 | C Desplan | 1:20 |
| Antibody | Anti-RFP (chicken polyclonal) | Rockland | #600-901-379s | 1:500 |
| Antibody | Anti-GFP (rabbit polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | #A6455 | 1:500 |
| Antibody | AlexaFluor405-conjugated Goat Anti-HRP (goat polyclonal) | Jackson Immunolabs | 123-475-021 | 1:200 |
| Antibody | AlexaFluorCy3- conjugated Goat Anti-HRP (goat polyclonal) | Jackson Immunolabs | 11 23-165-021 | 1:200 |
| Antibody | AlexaFluor647- conjugated Goat Anti-HRP (goat polyclonal) | Jackson Immunolabs | 123-605-021 | 1:200 |
| Sequence-based reagent | Antisense probe pairs for in situ Hybridisation chain reaction | This study. ‘Prasad et al. HCR Probe Sequences.xls’ | DNA Oligos | Figure 3—source data 1 |
| Software, algorithm | RStudio | RStudio | R version 4.0.3 | |
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism 9 | GraphPad Prism 9 | GraphPad Prism version 9.4.1 | |
| Software, algorithm | Adobe Photoshop | Adobe Photoshop | Adobe Photoshop 2021 | |
| Software, algorithm | Adobe Illustrator | Adobe Illustrator | Adobe Illustrator 2021 | |
| Software, algorithm | Imaris | Imaris | Imaris ×64-9.5.1 | |
| Software, algorithm | FiJi, ImageJ | PMID:22743772 | ||
| Chemical compound, drug | HCR Amplification Buffer | Molecular Instruments | BAM02224 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | HCR Wash Buffer | Molecular Instruments | BPW02124 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | HCR Hybridisation Buffer | Molecular Instruments | BPH02224 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | HCR Amplifier B3-H1-546 | Molecular Instruments | S030724 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | HCR Amplifier B3-H2-546 | Molecular Instruments | S031024 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | HCR Amplifier B3-H1-647 | Molecular Instruments | S040124 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | HCR Amplifier B3-H2-647 | Molecular Instruments | S040224 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Para-formaldehyde | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 28908 | 4% solution |
| Chemical compound, drug | DAPI stain | Sigma | D9542-1MG | (1 µg/mL) |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Table summarising the results from the glial-Gal4 screen (Figure 1B and C, Figure 1—figure supplement 1B-N) to identify the glial type that regulates L5 development.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/78092/elife-78092-supp1-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Table listing all genotypes and experimental conditions used by figure panel.
(Note that only female genotypes are listed through both sexes were included in our analyses.)
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/78092/elife-78092-supp2-v2.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/78092/elife-78092-transrepform1-v2.docx





