The ellipse of insignificance, a refined fragility index for ascertaining robustness of results in dichotomous outcome trials
Figures
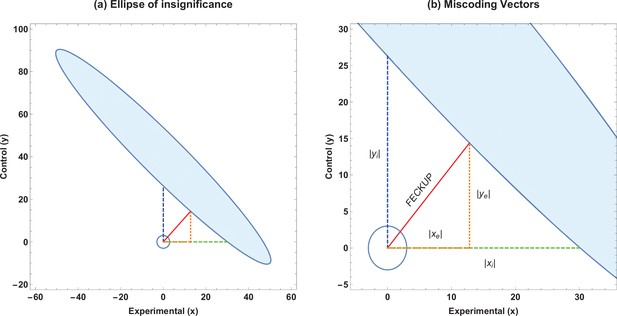
Ellipse of insignificance example.
(a) An example ellipse of insignificance for the , , , at a significance level of . All points bounded by the ellipse depict combinations which would not lead to the null being rejected. (b) Relevant vectors for ascertaining misconding thresholds. In this example, the Fewest Experimental/Control Knowingly Uncoded Participants (FECKUP) point is , , and . See text for details.
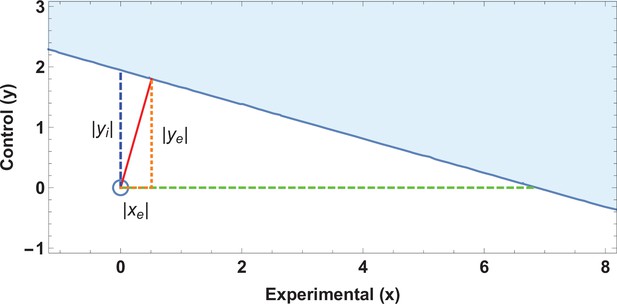
Application of ellipse of insignificance analysis to existent data.
(a) Ellipses of insignificance analysis for a published study (n = 913) for illustrative example 1 of published data. The shaded region denotes the ellipse of insignificance, the red line shows the Fewest Experimental/Control Knowingly Uncoded Participants (FECKUP) vector (the minimum vector from the origin to the ellipse).
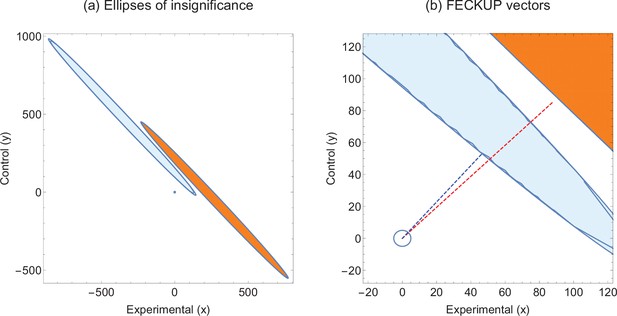
Illustrative example 2.
(a) Ellipses of insignificance analysis for two studies with same statistic. (b) Fewest Experimental/Control Knowingly Uncoded Participants (FECKUP) vectors for both studies. Experiment 1 is given by orange ellipse and red dotted line, Experiment 2 by the blue ellipse and dotted line.
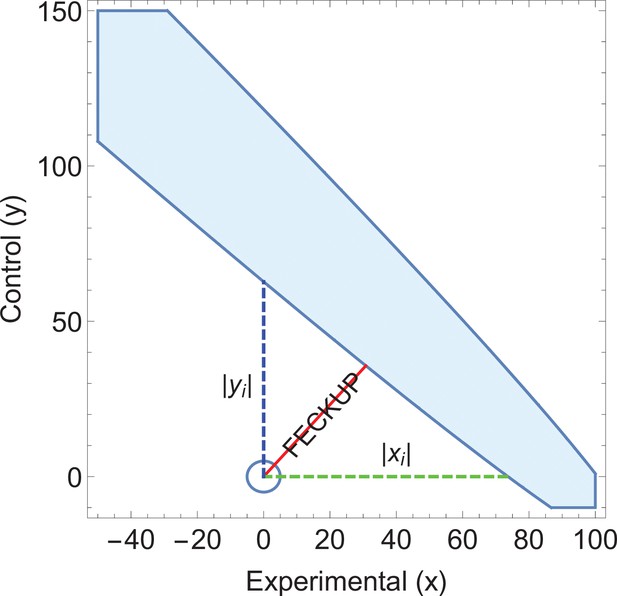
Illustrative example 3.
An ellipse of insignificance (EOI) analysis on the data supplied in the City A/City B screening comparison yields a Fewest Experimental/Control Knowingly Uncoded Participants (FECKUP) vector (in red) of 46.2 subjects, corresponding to a minimum tolerance of 66.5 total subjects after resolving the vector.
As (shown in green) with (shown in blue), but as the sensitivity and specificity of the tests used in City A are known, it can be shown that , exceeding the limits of xi, placing the point within the ellipse and rendering any seeming significance void. Note that only a part of the EOI (denoted by the blue solid shape) is shown for clarity.
Tables
Reported groups and related variables.
| Endpoint positive | Endpoint negative | |
|---|---|---|
| Experimental group | ||
| Control group |
Ellipse of insignificance (EOI) derived metrics for published data.
| EOI statistic () | Derived value |
|---|---|
| Experimental group tolerance xi | 6.9 subjects |
| Control group tolerance yi | 1.9 subjects |
| FECKUP vector length | 1.9 subjects |
| Tolerance threshold for error (experimental group) | 0.99% |
| Tolerance threshold for error (control group) | 0.89% |
| Absolute tolerance threshold for error (all subjects) | 0.22% |
Experimental metrics for similar test statistics.
| Significance level | Data | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment 1 | 17.7% | 18.2% | 8.9% | |
| Experiment 2 | 11% | 9.5% | 5.0% | |
| Experiment 1 | 16.3% | 17.0% | 8.3% | |
| Experiment 2 | 10.4% | 8.6% | 4.6% | |
| Experiment 1 | 14.8% | 15.5% | 7.5% | |
| Experiment 2 | 9.8% | 7.6% | 4.1% | |
| Experiment 1 | 13.5% | 14.3% | 6.9% | |
| Experiment 2 | 9.2% | 6.8% | 3.8% |
Results of different analysis.
| CIN2 + positive | No CIN2 + detected | Methodology | |
|---|---|---|---|
| City A (measured) | 113 | 887 | LBC only |
| City B (measured) | 24 | 976 | HPV screening/LBC reflex |
| True values (both cities) | 20 | 980 | N/A |
Additional files
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79573/elife-79573-mdarchecklist1-v2.pdf
-
Source code 1
Sample MATLAB/OCTAVE code for rapid implementation of EOI analysis method outlined.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79573/elife-79573-code1-v2.zip





