Identification of epigenetic modulators as determinants of nuclear size and shape
Figures
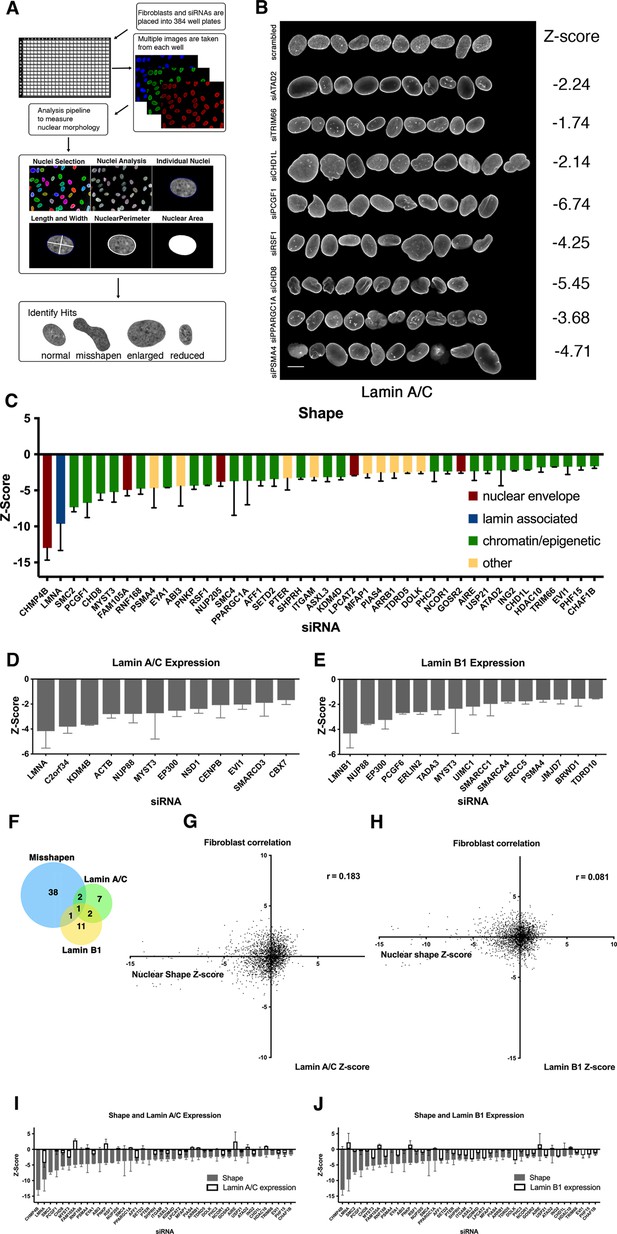
A high-throughput image-based screen for nuclear size and shape determinants.
(A) Schematic overview of the nuclear morphology screen to identify genes required for proper nuclear shape and size. Cells were cultured in the presence of siRNAs targeting specific genes in 384-well plates, fixed, and stained with specific antibodies to visualize lamin A/C, lamin B1, or DAPI. Cells were imaged using high-throughput microscopy and an image analysis pipeline was developed to segment individual nuclei, measure nuclear morphology, and lamin A/C and lamin B1 intensity. Datasets were analyzed to identify misshapen, enlarged, and shrunken nuclei. Nuclear morphology changes were measured as Z-scores. Typically, more than 250 nuclei were analyzed per sample. The fibroblast screen was performed in two biological replicates on different days. (B) Representation of normal nuclei and nuclear shape hits identified by high-throughput screening. Nuclear shape abnormalities are visualized by lamin A/C antibody staining. Scale bar: 10 μm. (C) Nuclear shape hits were calculated by scoring circularity (circularity = 4πArea/perimeter2). Z-scores were generated to compare hits across the screen. Nuclear shape hits were identified by a median Z-score of –1.5 or less. At least 250 nuclei were analyzed per sample. Error bars indicate the standard deviation. (D) Nuclear intensity of lamin A/C was assessed by calculating Z-scores of changes in lamin A/C expression on a per well basis. Lamin A/C hits were identified by median Z-scores of –1.5 or less. Error bars indicate the standard deviation. (E) Nuclear intensity of lamin B1 was assessed by calculating median Z-scores of changes in lamin B1 expression of –1.5 or less per well. Error bars indicate the standard deviation. (F) A comparison between lamin A/C and lamin B 1 expression hits and nuclear shape hits indicates lamin levels are not affected in most of nuclear shape hits. Error bars indicate the standard deviation. (G) Correlation between nuclear shape and lamin A/C expression of the Z-score of each parameter. Nuclear shape values relative to lamin A/C expression show little to no correlation. Spearman’s coefficient (r=0.183). (H) Scatterplot of nuclear shape values relative to lamin B1 expression shows little to no correlation in lamin B1 protein expression levels and nuclear shape scores in fibroblasts. Spearman’s coefficient (r=0.081). (I) Nuclear shape hits in panel C with gray bars indicating the Z-score for circularity. Lamin A/C Z-score values are overlayed with white bars indicating lamin A expression changes. Error bars indicate the standard deviation. (J) Nuclear shape hits in panel C displaying Z-score values. Lamin B1 Z-score values are overlayed with white bars to indicating levels of lamin B1. Error bars indicate the standard deviation.
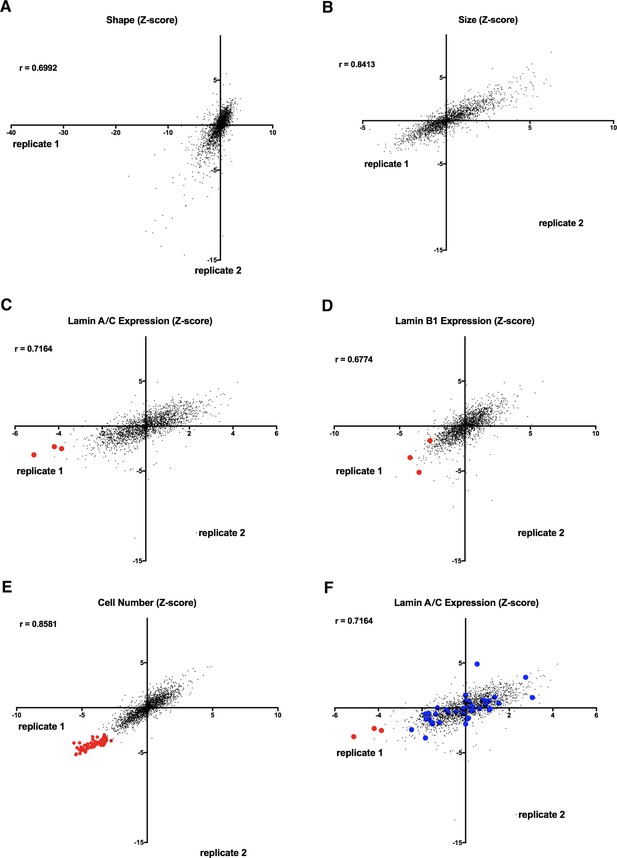
Reproducibility of nuclear morphology screen using human fibroblast cells.
(A) The initial screen was performed in two biological replicates on different days. Nuclear shape Z-scores of the two replicates (Replicate 1 and Replicate 2) of the nuclear shape screen. Spearman’s coefficient (r=0.6992). (B) Nuclear size Z-scores of the two replicates (Replicate 1 and Replicate 2) of the nuclear shape screen. Spearman’s coefficient (r=0.8413). (C) Lamin A/C expression Z-scores of the two replicates (Replicate 1 and Replicate 2) of the nuclear shape screen. Red dots indicate siRNAs targeting LMNA gene products. Spearman’s coefficient (r=0.7164). (D) Lamin B1 expression Z-scores of the two replicates (Replicate 1 and Replicate 2) of the nuclear shape screen. Red dots indicate siRNAs targeting LMNB1 gene products. Spearman’s coefficient (r=0.6774). (E) Correlation plot shows cell number Z-scores of the two replicates (Replicate 1 and Replicate 2) of the nuclear shape screen. Red dots indicate siRNAs designed to cause cell death as an indicator of transfection efficiency. Spearman’s coefficient (r=0.8581). (F) Correlation plot shows lamin A/C expression Z-scores of the two replicates (Replicate 1 and Replicate 2) of the nuclear shape screen. Data points labeled in red indicate siRNAS targeting LMNA gene products while shape hits are highlighted in blue. Spearman’s coefficient (r=0.7164).
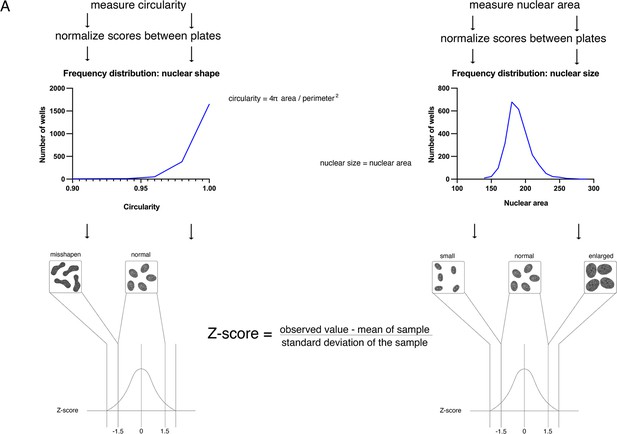
A schematic overview of nuclear shape and nuclear size image analysis pipeline and generation of Z-scores.
Independent Z-scores for nuclear size or nuclear shape were generated first by measuring nuclear circularity or area, respectively. Nuclear shape was measured by calculating circularity (circularity = 4πArea/perimeter2). Multiple plates were imaged for each screen. To account for differences between plates, measurement values were normalized by generating B-scores. siRNA screens were performed in dual replicates, and circularity was measured on a mean per well basis. Data points were converted into Z-scores (Z-score=observed value – mean of sample/standard deviation of the sample) and hits were identified as having a Z-score of at least –1.5. Nuclear size was measured as nuclear area derived from nuclear cross-sections. Raw values were then normalized across multiple plates by generating B-scores. Nuclear area measurements were generated on a mean per well basis and converted into Z-scores. Hits were identified as having a Z-score 1.5 or above (enlarged nuclei) or –1.5 (small nuclei) or below, depending on whether nuclei were enlarged or reduced in size.
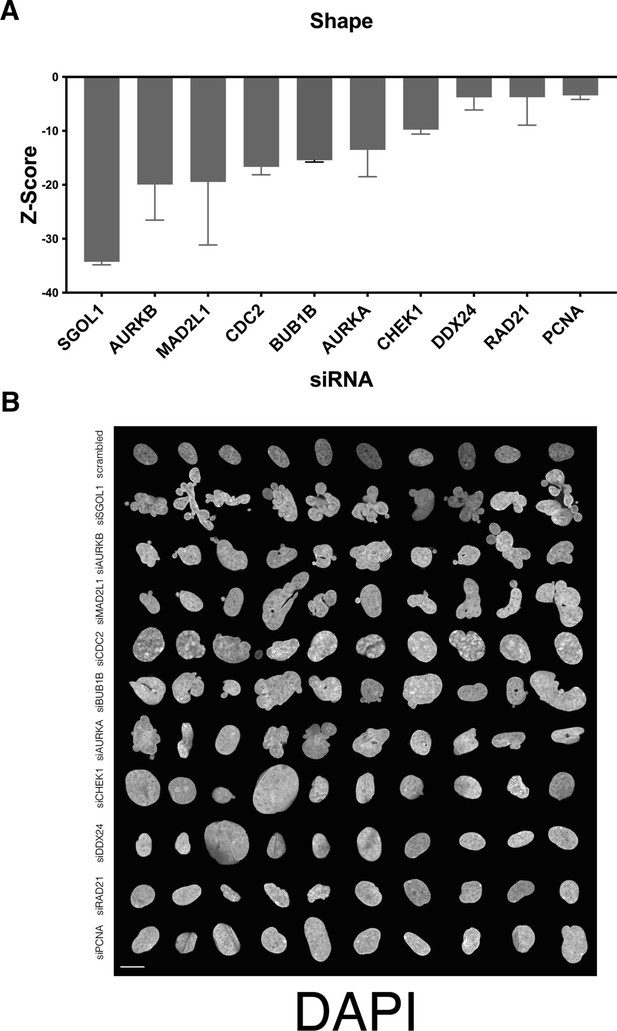
Nuclear shape hits that affected cell number.
(A) Z-scores of the top nuclear shape determinants which had low cell number. Error bars indicate the standard deviation. (B) Montage of nuclear shape determinants with low cell number revealed misshapen nuclei and mitotic defects. Signal represents DAPI staining. Scale bar = 10 μm.
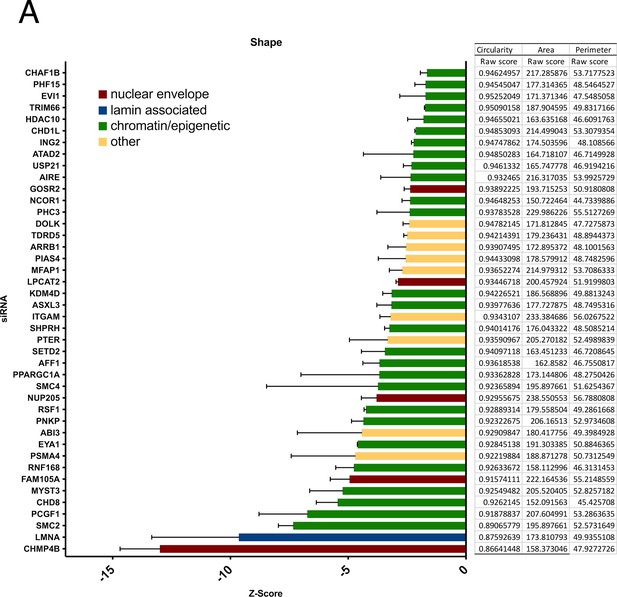
Nuclear shape Z-scores in comparison to nuclear shape, area, and perimeter raw scores of fibroblast hits.
(A) Nuclear shape hits were calculated by scoring circularity (circularity = 4πArea/perimeter2). Z-scores were generated to compare hits across the screen. Error bars indicate the standard deviation. Raw nuclear shape, perimeter, and area values are shown relative to nuclear shape Z-score values.
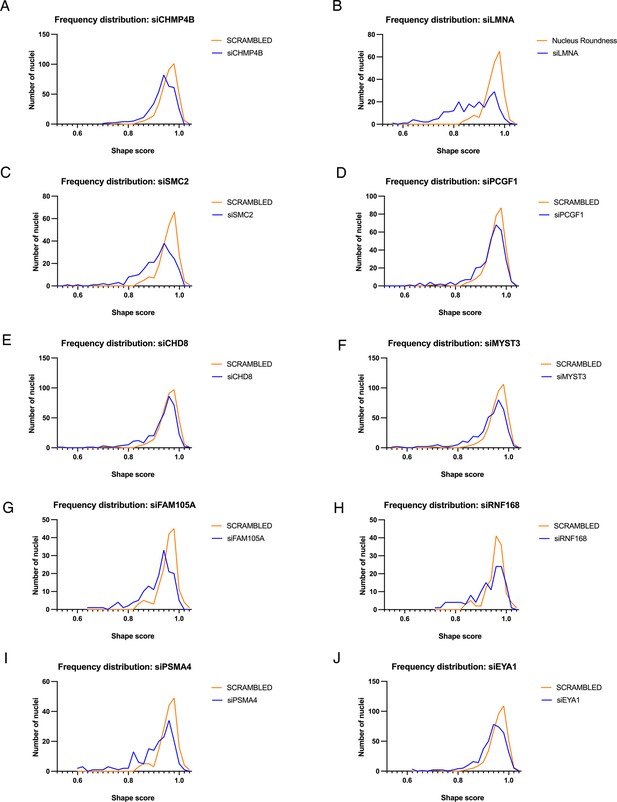
Single cell values of nuclear shape hits compared to control cells.
(A–J) Frequency distribution of nuclear shape in cells treated with scrambled control or indicated siRNA. siRNA-treated samples generally show a shift of the entire distribution rather than loss or gain of subpopulations. More than 250 nuclei were analyzed per sample. A p value of <0.0001 was obtained for all samples using a two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test.
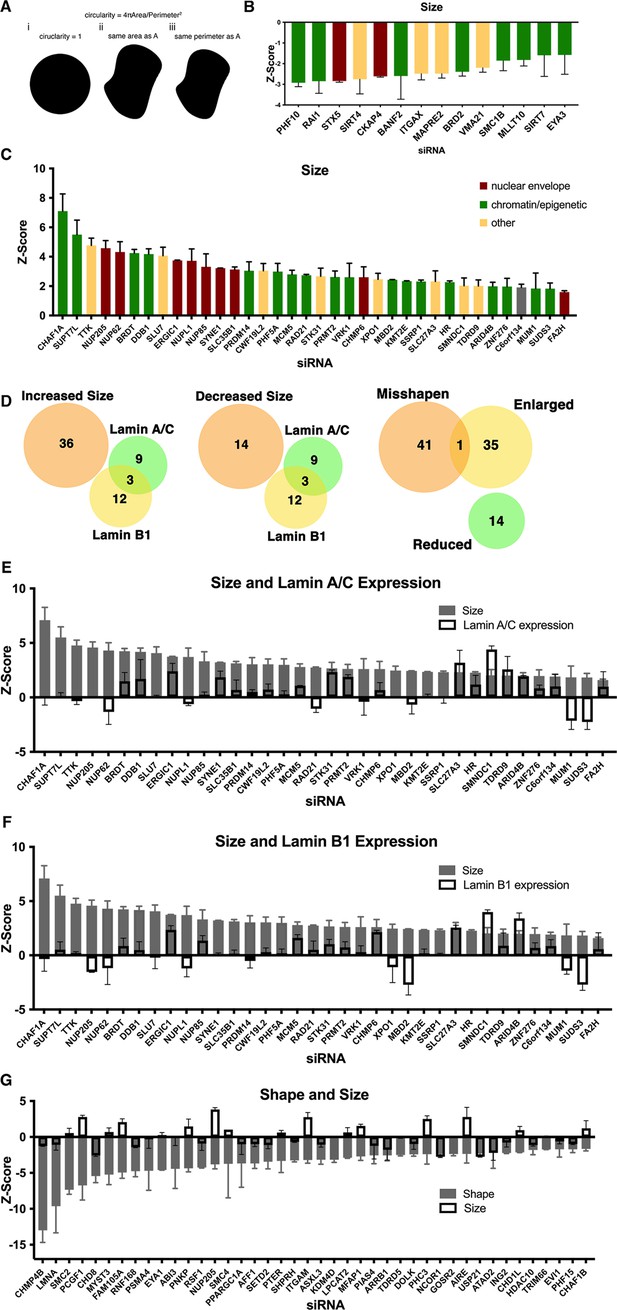
Identification of nuclear size determinants in human fibroblast cells.
(A) A diagram of the relationship between circularity used to calculate nuclear shape and nuclear perimeter and area revealing the possibility that nuclear size might affect nuclear shape. Nuclear size hits were calculated by (circularity = 4πArea/perimeter2). Panel i shows a perfect circle with a circularity score of 1. Panel ii shows the same area as in panel A but an increased perimeter. Panel iii shows the same perimeter as panel A but a decreased area. If perimeter is a cellular constant, shape hits would correlate with a decrease in nuclear size. (B) Z-scores of hits displaying a decrease in nuclear size. Nuclear size hits maintain a median Z-score of –1.5 or less. At least 250 nuclei were analyzed per sample. Error bars indicate the standard deviation. (C) Z-scores of hits displaying an increase in nuclear size. Nuclear size hits maintain a median Z-score of 1.5 or greater. At least 250 nuclei were analyzed per sample. Error bars indicate the standard deviation. (D) Relationship of nuclear size hits and lamin A/C and lamin B1 hits. Nuclear shape hits show little overlap with nuclear size hits. (E) Nuclear size hits in panel C with gray bars indicating the Z-score for hits displaying an increase in size. Lamin A/C Z-score values overlayed with white bars indicating lamin A/C level. Error bars indicate the standard deviation. (F) Bar graph of nuclear size hits displaying Z-score values. Lamin B1 Z-score values are overlayed with white bars indicating levels of lamin B1. Error bars indicate the standard deviation. (G) Z-score values of nuclear shape hits in gray. Nuclear size Z-score values are overlayed with white bars to show nuclear size varies among nuclear shape hits. Error bars indicate the standard deviation.
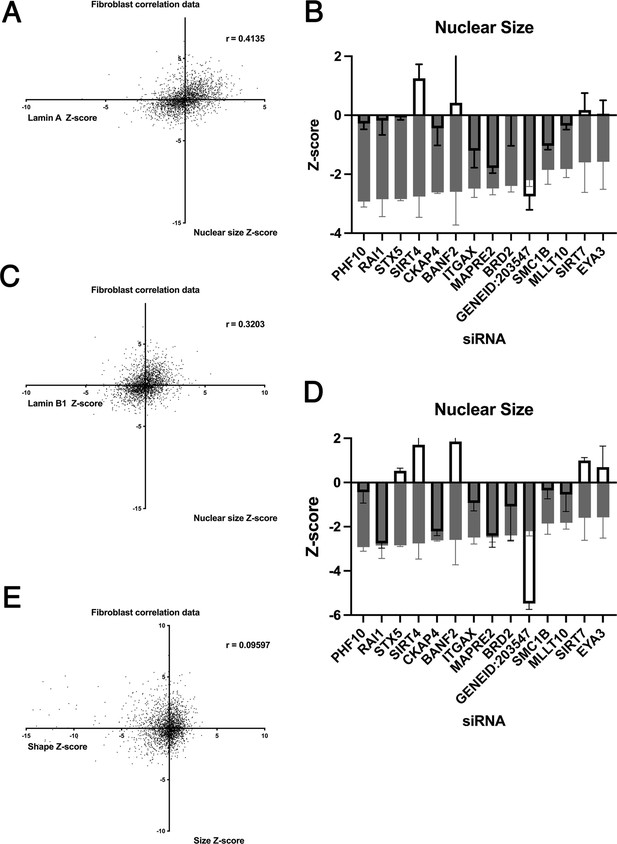
Nuclear morphology data using human fibroblast cells reveal lack of correlation between lamin expression and nuclear morphology features.
(A) The fibroblast screen was performed in two biological replicates on different days. Lamin A/C expression Z-scores compared to nuclear size Z-scores in human fibroblast cells. Spearman’s coefficient (r=0.4135). (B) Nuclear size Z-scores (gray bars) compared to lamin A/C expression (bars with black outline) reveals little correlation between lamin A/C expression and decreased nuclear size. (C) Correlation plot comparing lamin B1 expression Z-scores to nuclear size Z-scores in human fibroblast cells. Spearman’s coefficient (r=0.3203). (D) Nuclear size Z-scores (gray bars) compared to lamin B1 expression Z-scores (bars with black outline) reveals little correlation between lamin B1 expression and decreased nuclear size. (E) Nuclear shape Z-scores compared to nuclear size Z-scores in human fibroblast cells. Spearman’s coefficient (r=0.09597).
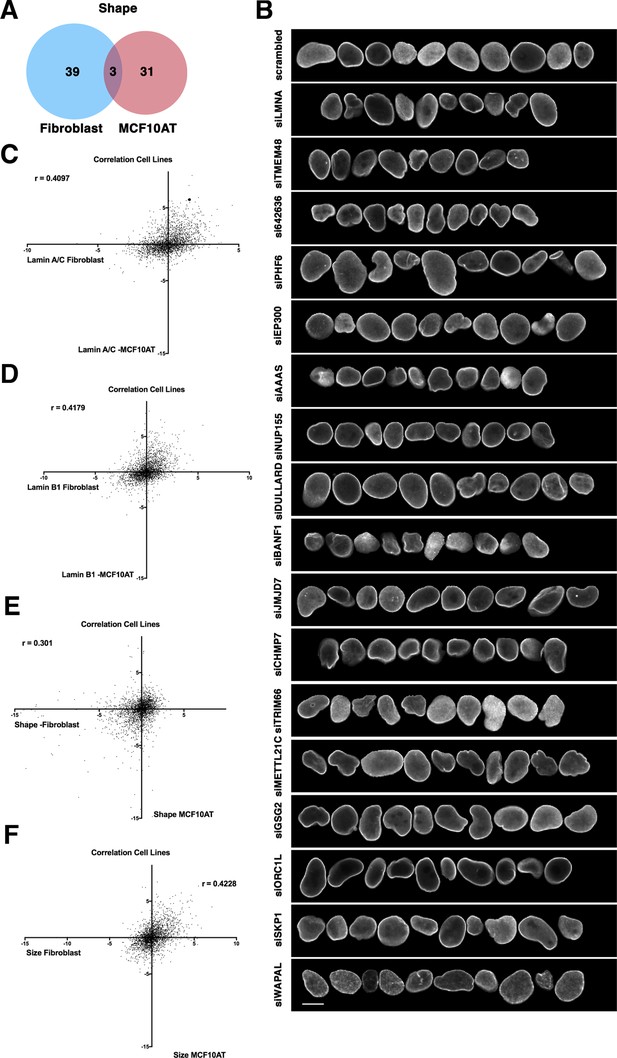
Cell-type specificity of effector hits.
(A) Little overlap of hits for nuclear shape changes in immortalized human fibroblast cells compared to nuclear shape hits for the breast epithelial cell line MCF10AT. The MCF10AT screen was performed in two biological replicates on different days. (B) Representative normal nuclei and nuclear shape hits of MCF10AT cells identified by high-throughput nuclear morphology screen and analysis. Nuclear shape abnormalities are visualized by lamin A/C antibody staining. Scale bar = 10 μm. (C) Lamin A/C Z-score values in fibroblasts compared with lamin A/C Z-score values in MCF10AT cells using the same siRNA target reveals little correlation between values. Spearman’s coefficient (r=0.4097). (D) Lamin B1 Z-score values in fibroblasts compared with lamin B1 Z-score values in MCF10AT cells using the same siRNA target reveals little correlation between values. Spearman’s coefficient (r=0.4179). (E) Nuclear shape Z-scores of fibroblast and MCF10AT cell lines reveal a lack of overlap between the same siRNA targets. Spearman’s coefficient (r=0.301). (F) Nuclear size Z-score values in fibroblast cells compared with nuclear size Z-score values in MCF10AT cells using the same siRNA target reveals little correlation between data points. Spearman’s coefficient (r=0.4228).
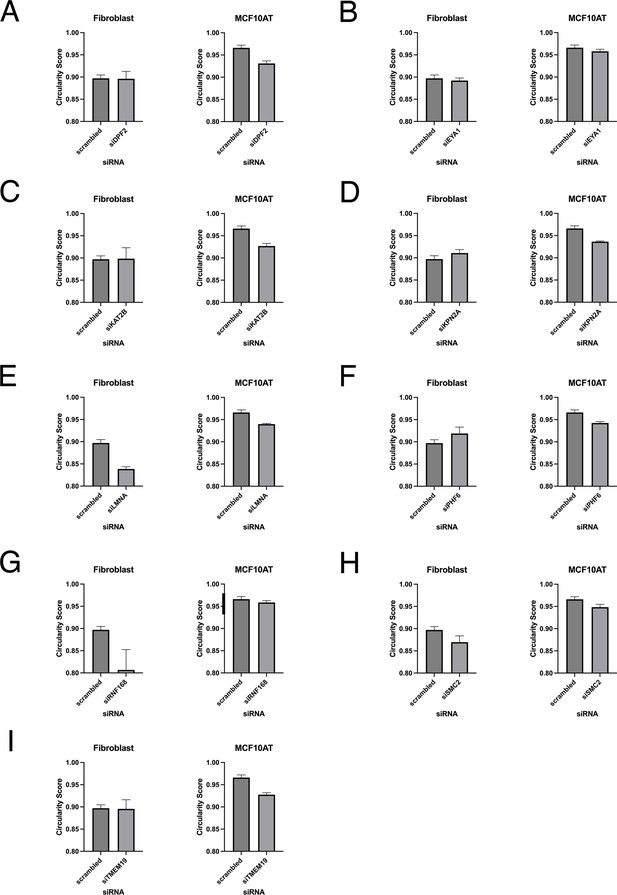
Validation of nuclear shape hits in fibroblast and MCF10AT cell lines.
Nuclear shape changes were measured by calculating mean circularity values on a per well basis. (A–J) Cells were treated with single siRNAs to the indicated target previously identified nuclear shape hits. Nuclear morphology changes were assessed in fibroblasts and MCF10AT cells. Error bars indicate the standard deviation.
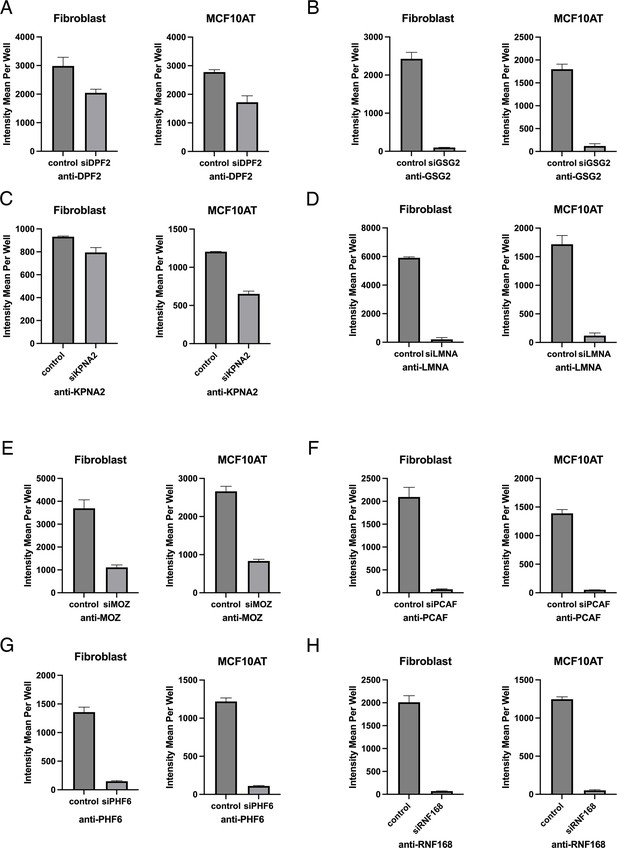
Validation of knockdown efficiency in both fibroblast and MCF10AT cell lines.
(A–H) Knockdown efficiency of indicated target gene in fibroblast and MCF10AT cells treated with a single siRNA. Error bars indicate standard deviation.
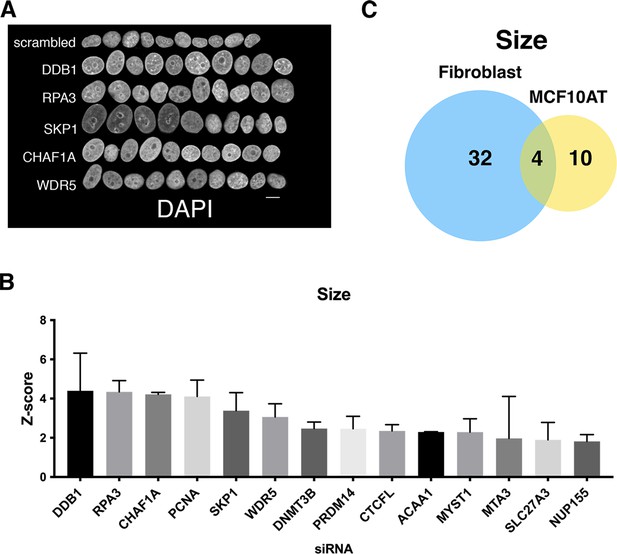
Identification of nuclear size determinants in MCF10AT cells.
(A) The MCF10AT screen was performed in two biological replicates on different days. Representation of normal nuclei and hits with enlarged nuclei identified by high-throughput screening in MCF10AT cells. Nuclear size abnormalities are visualized by DAPI staining. Scale bar = 10 μm. (B) Nuclear size hits were calculated by scoring nuclear area. Z-scores were generated to compare hits across the screen. Hits were identified as having a Z-score of 1.5 or more. At least 250 nuclei were analyzed per sample. (C) Little overlap of hits for nuclear size changes in immortalized human fibroblast cells compared to nuclear size hits for the breast epithelial cell line MCF10AT.
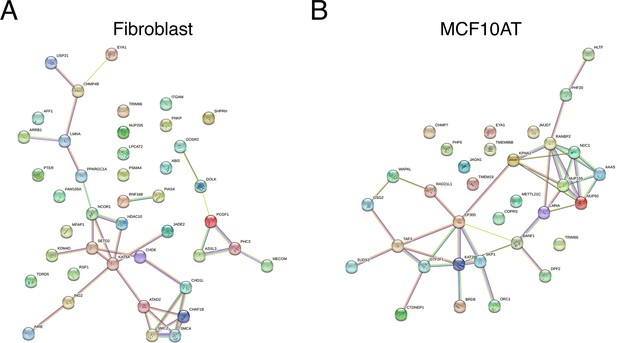
Functional protein association analysis using STRING for nuclear shape hits (A) in human fibroblast cells, (B) in MCF10AT cells.
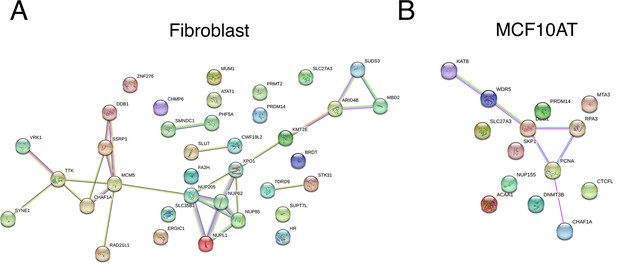
Functional protein association analysis using STRING for nuclear size hits (A) in human fibroblast cells, (B) in MCF10AT cells.
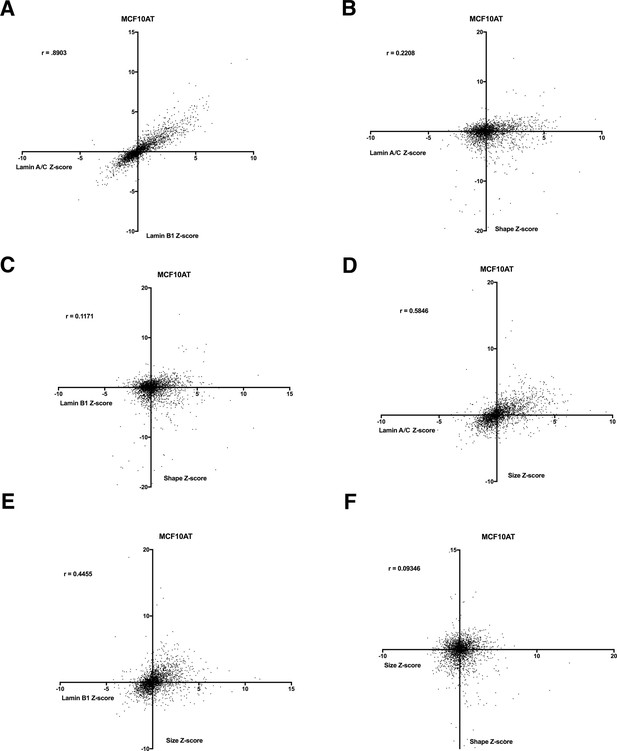
Correlation plots of nuclear morphology data using MCF10AT human breast epithelial cells.
(A) The MCF10AT screen was performed in two biological replicates on different days. Lamin A/C expression Z-scores compared to lamin B1 Z-scores in MCF10AT cells. Spearman’s coefficient (r=0.8903). (B) Lamin A/C expression Z-scores compared to nuclear roundness Z-scores in MCF10AT cells. Spearman’s coefficient (r=0.2208). (C) Correlation plot of lamin B1 expression Z-scores relative to nuclear shape Z-scores in MCF10AT cells. Spearman’s coefficient (r=0.1171). (D) Lamin A/C expression Z-scores compared to nuclear size Z-scores in MCF10AT cells. Spearman’s coefficient (r=0.5846). (E) Lamin B1 expression Z-scores compared to nuclear size Z-scores in MCF10AT cells. Spearman’s coefficient (r=0.4455). (F) Correlation plot of nuclear shape Z-scores compared to nuclear size Z-scores in MCF10AT cells. Spearman’s coefficient (r=0.9346).
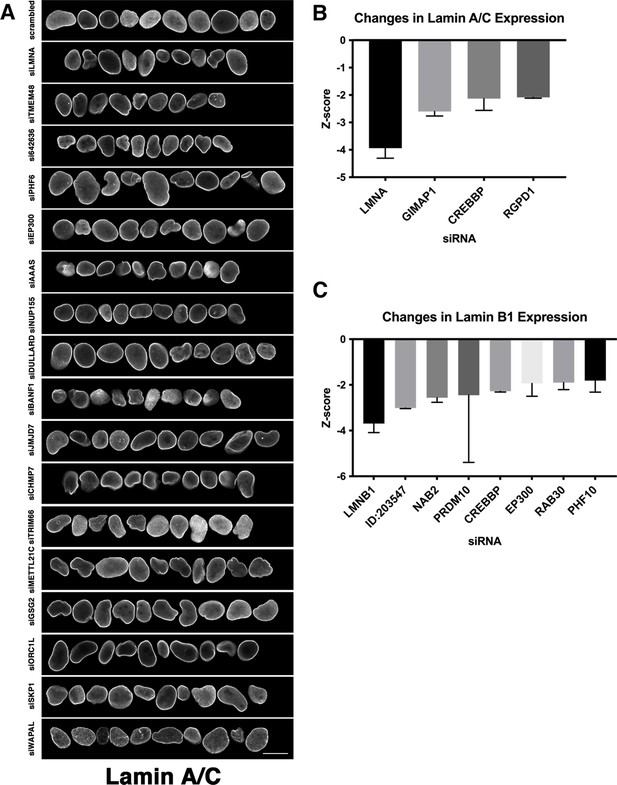
Identification of nuclear shape determinants in MCF10AT cells.
(A) The MCF10AT screen was performed in two biological replicates on different days. Representation of normal nuclei and nuclear shape hits identified by high-throughput screening in MCF10AT cells. Nuclear shape abnormalities are visualized by lamin A/C antibody staining. Scale bar = 10 μm. (B) Nuclear intensity of lamin A/C was assessed by calculating Z-scores of changes in lamin A/C expression on a per well basis. Lamin A/C hits were identified by Z-scores of –1.5 or less. At least 250 nuclei were analyzed per sample. (C) Nuclear intensity of lamin B1 was assessed by calculating Z-scores of changes in lamin B1 expression of –1.5 or less per well. At least 250 nuclei were analyzed per sample.
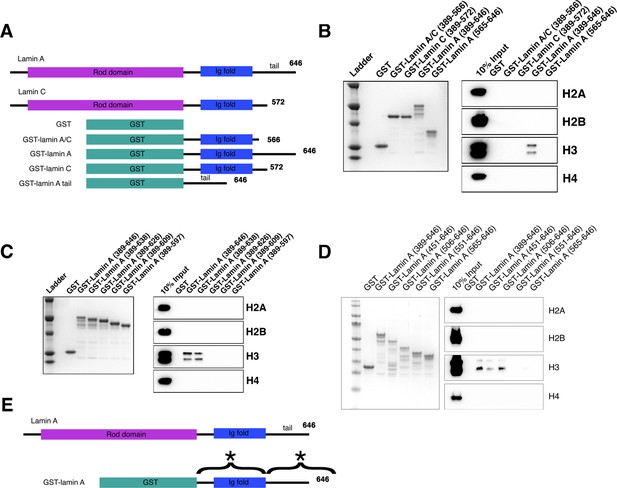
In vitro binding of lamin A to histone H3.
(A) A diagram of constructs used in binding assays. All histone pulldown assays were performed at least three times. (B) Colloidal staining of purified recombinant proteins and histone pulldown assays. GST-lamin A (389–646) directly binds to histone H3 but not histones H2A, H2B, and H4. The portion of lamin A and lamin C that is homologous (GST-lamin A/C [389–566], GST-lamin C [389–572], and the GST-lamin A truncation containing the C-terminal tail [GST-lamin A 565–646]) did not bind histones. (C) Colloidal staining of purified recombinant proteins and histone pulldown assay. The C-terminal portion of lamin A is required for binding histone H3. Full-length GST-lamin A (389–646) and the truncated GST-lamin A (389–638) bound histone H3 but not histones H2A, H2B, and H4. Further truncations to the lamin A tail (389–626), (389–609), and (389–597) did not interact with histones identifying the portion of the C-terminal tail essential for binding histone H3 as aa 638–646. (D) Colloidal staining of purified recombinant proteins and histone pulldown assay. The N-terminal portion of lamin A required for binding histone H3. Full-length GST-lamin A (389–646) and the truncated GST-lamin A (451–646) and GST-lamin A (506–646) bound histone H3 but not histones H2A, H2B, and H4. Further truncations to the GST-lamin A (551–646) and GST-lamin A (565–646) did not interact with histones identifying the portion of the N-terminus essential for binding histone H3 as aa 506–550. (E) A schematic summary of the two regions required for lamin A-H3 interactions marked with (*).
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Source data for Figure 4B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/80653/elife-80653-fig4-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 2
Source data for Figure 4C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/80653/elife-80653-fig4-data2-v2.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 3
Source data for Figure 4D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/80653/elife-80653-fig4-data3-v2.zip
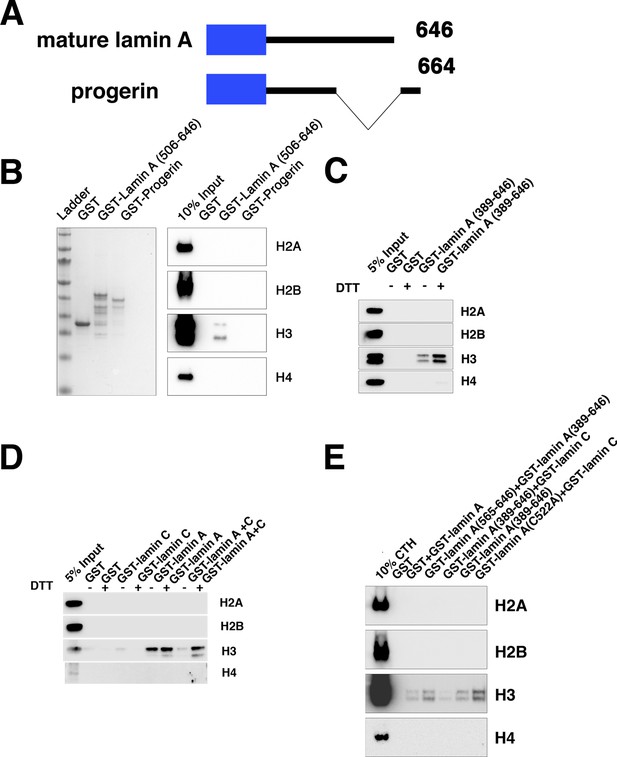
Lamin C inhibits lamin A-H3 interactions.
(A) Diagram of mature lamin A and progerin constructs used in the binding assays. All histone pulldown assays were performed at least three times. (B) GST pulldown assay with wild-type GST-lamin A and a mutated lamin A (GST-Progerin) encoding the disease-causing lamin A construct showed that the recombinant progerin peptide could not bind to histone H3. (C) GST pulldown assay identified that the addition of a reducing agent (DTT) which inhibits lamin A dimerization promotes lamin A-histone H3 interactions. (D) GST pulldown assay of lamin C and lamin A constructs in the presence of DTT identified that lamin A-H3 interactions are inhibited by the addition of lamin C and this can be alleviated by adding DTT. (E) GST pulldown assay of lamin A, lamin C, and mutant lamin A constructs. Lamin A-H3 interactions are inhibited by the addition of lamin C and inhibition is alleviated by mutation C522A in lamin A.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Source data for Figure 4—figure supplement 1B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/80653/elife-80653-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 2
Source data for Figure 4—figure supplement 1C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/80653/elife-80653-fig4-figsupp1-data2-v2.zip
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 3
Source data for Figure 4—figure supplement 1D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/80653/elife-80653-fig4-figsupp1-data3-v2.zip
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 4
Source data for Figure 4—figure supplement 1E.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/80653/elife-80653-fig4-figsupp1-data4-v2.zip
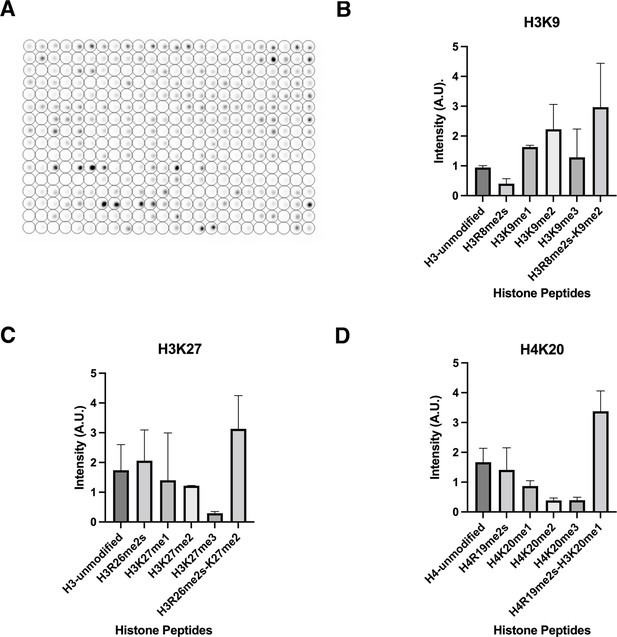
Specificity of lamin A binding histone modifications.
(A) In vitro peptide binding array assay using GST-lamin A (506–646). Intensity of signal indicates binding. The peptide binding assay was performed three times. (B) Peptide binding assays for select histone H3K8/9 modifications. H3R8me2/K9me2 maintained the most intense signal compared to single modifications alone. Error bars indicate the standard deviation. (C) Peptide binding assay for histone H3R26/K27 modifications. H3R26me2/K27me2 maintained the most intense signal compared to single modifications alone. Error bars indicate the standard deviation. (D) Peptide binding assay for histone H4R19/K20 modifications. H4R19me2/K20me1 maintained the most intense signal compared to single modifications alone. Values represent intensity. Error bars indicate the standard deviation.
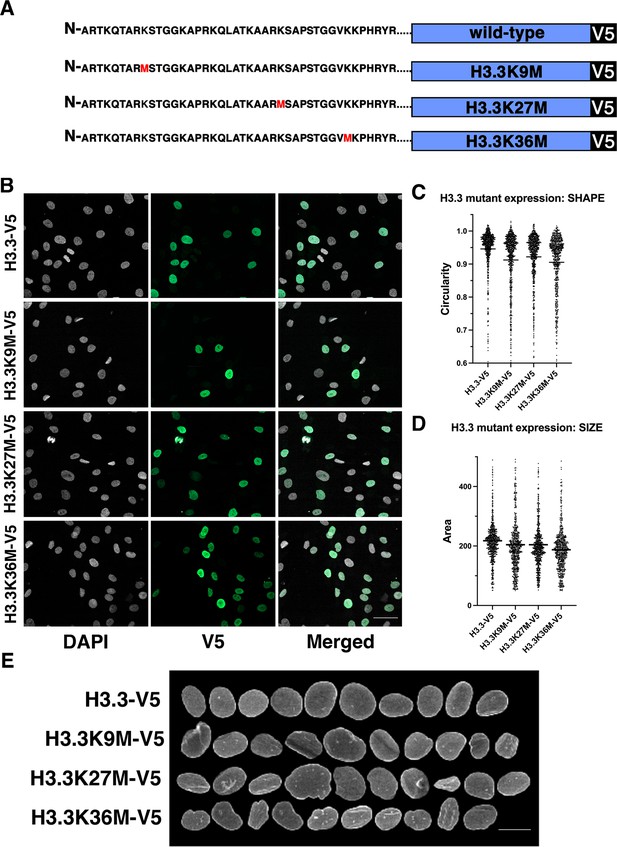
Expression of histone H3.3 mutants affect nuclear shape.
(A) Wild-type (WT) and mutant histone expression constructs . Mutant histone expression experiments were performed with three biological replicates. (B) Stable expression of indicated H3.3 mutants in fibroblast cells. Gray: DAPI to detect DNA, green: V5-tagged histone variant. Scale bar = 50 μm. (C) Cells expressing histone H3.3 constructs reveal that histone H3.3K9, H3.3K27M, or H3.3K36M mutants showed reduced nuclear shape scores compared to WT H3.3 expression. The mean is indicated by the horizontal line. (D) Cells expressing histone H3.3 constructs reveal histone H3.3K9, H3.3K27M, or H3.3K36M mutants showed reduced nuclear size scores compared to WT H3.3 expression. The mean is indicated by the horizontal line. (E) Representative nuclei of cells expressing the indicated H3.3 variants. Signal represents lamin A staining. Scale bar = 10 μm.
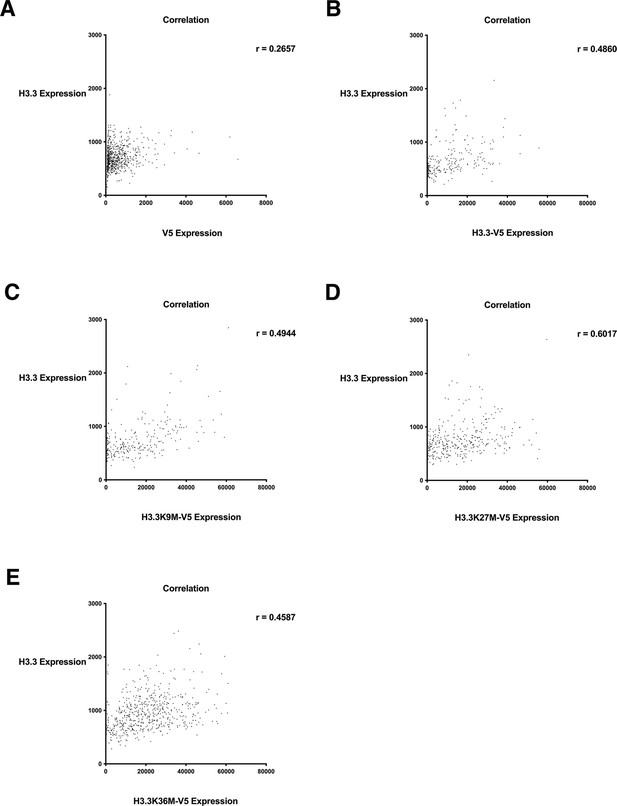
Histone H3.3 total expression relative to wild-type H3.3-V5 and H3.3-V5 mutant expression.
Correlation plot of total histone H3.3 expression relative to (A) V5 alone, (B) wild-type H3.3-V5, (C) H3.3K9M-V5 expression, (D) H3.3K27M-V5 expression, (E) H3.3K36M-V5 expression. Values determined by quantitative single cell imaging of total H3.3 stained with an antibody against H3.3 and histone H3.3 wild-type and mutant variants detected by antibody staining against V5. At least 500 cells were analyzed per sample.
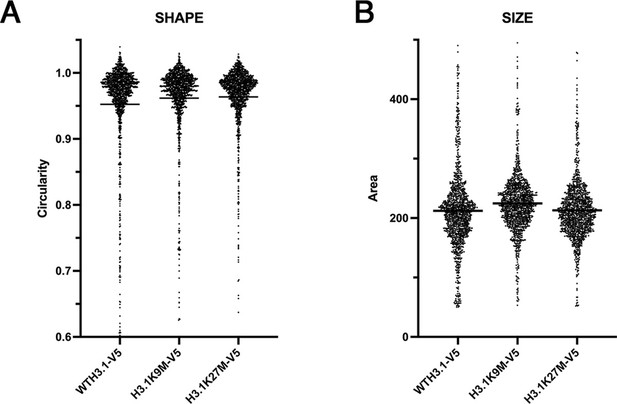
Histone H3.1 mutants display a lesser nuclear morphology phenotype compared to wild-type H3.1.
(A) Cells expressing wild-type histone H3.1, H3.1K9M, or H3.1K27M mutants showed little change in nuclear shape scores. The mean is indicated by the horizontal line. Mutant histone expression experiments were performed with three biological replicates. At least 500 nuclei were analyzed per sample. (B) Cells expressing wild-type histone H3.1, H3.1K9M, or H3.1K27M mutants showed some change in nuclear size scores. The mean is indicated by the horizontal line. At least 500 nuclei were analyzed per sample.
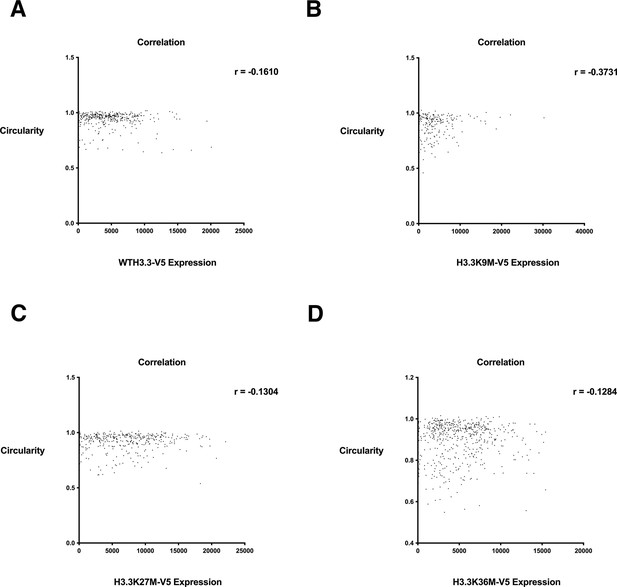
Nuclear shape score relative to wild-type H3.3-V5 and H3.3-V5 mutant expression.
Correlation plot of nuclear shape scores relative to (A) wild-type H3.3-V5 expression, (B) H3.3K9M-V5 expression, (C) H3.3K27M-V5 expression, (D) H3.3K36M-V5 expression. Values determined by quantitative single cell imaging of nuclear shape compared to histone variant expression detected by an antibody targeting V5. At least 500 cells were analyzed per sample.
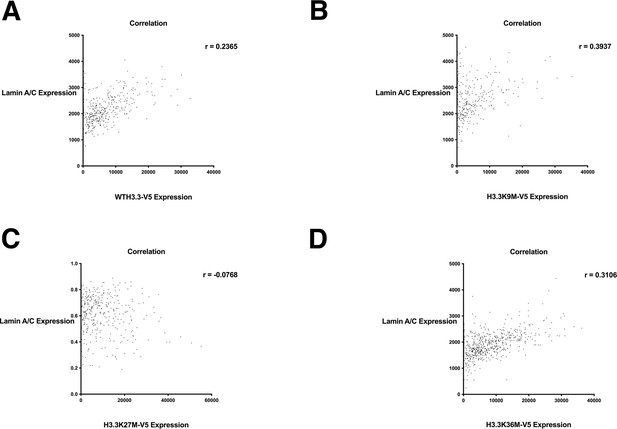
Lamin A/C expression relative to wild-type H3.3-V5 and H3.3-V5 mutant expression.
Correlation plot of lamin A/C expression relative to (A) wild-type H3.3-V5, (B) H3.3K9M-V5 expression, (C) H3.3K27M-V5 expression, (D) H3.3K36M-V5 expression. Values determined by quantitative single cell imaging of lamin A/C stained with an antibody against lamin A/C and histone variants detected by antibody staining against V5. At least 500 cells were analyzed per sample.
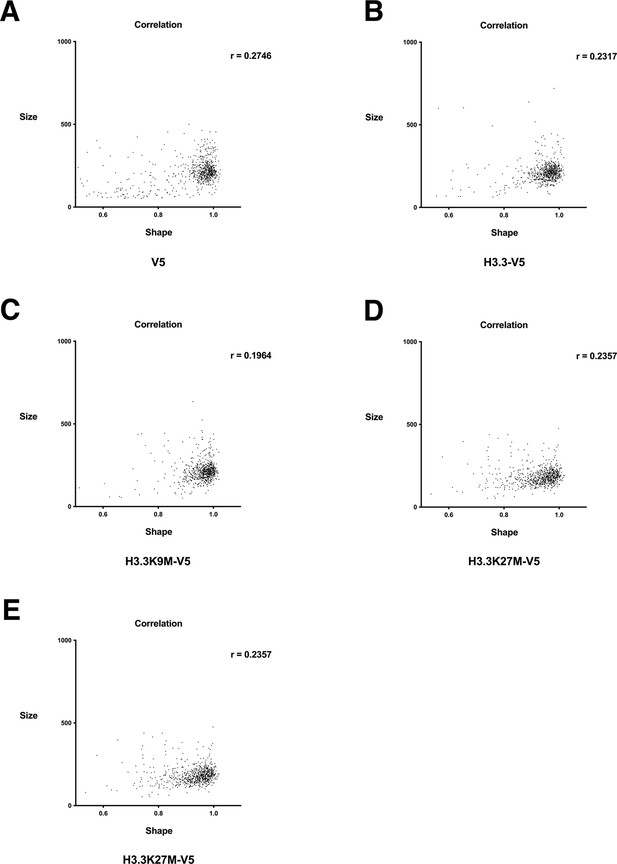
Single cell analysis of nuclear size and nuclear shape in cells expressing wild-type and mutant histone H3.3.
Correlation plot of nuclear size values relative to nuclear shape values in cells expressing (A) V5 alone, (B) wild-type H3.3-V5, (C) H3.3K9M-V5, (D) H3.3K27M-V5, (E) H3.3K36M-V5. Values determined by quantitative single cell imaging. At least 500 cells were analyzed per sample.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
High-throughput screening targets and hits.
(A) lists the genes targeted in the screen. (B) is a file describing the plasmids generated during this study. (C) lists the antibodies used in this study. (D) is a comparative list of nuclear shape Z-score, nuclear shape raw score, nuclear area, and nuclear perimeter measurements.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/80653/elife-80653-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
Nuclear shape hits.
(A) lists hits altering nuclear shape in fibroblast cells. (B) is a list of hits resulting in lower lamin A/C expression. (C) is a list of hits resulting in lowered lamin B1 expression.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/80653/elife-80653-supp2-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 3
Screen validation.
(A) lists validation results for the nuclear shape screen in fibroblast cells. (B) lists validation results for hits increasing nuclear size in fibroblast cells. (C) lists validation results for hits decreasing nuclear size in fibroblast cells. (D) identifies nuclear shape hits in MCF10AT cells. (E) lists lamin A interacting peptides.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/80653/elife-80653-supp3-v2.xlsx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/80653/elife-80653-mdarchecklist1-v2.pdf





