Redox regulation of KV7 channels through EF3 hand of calmodulin
Figures
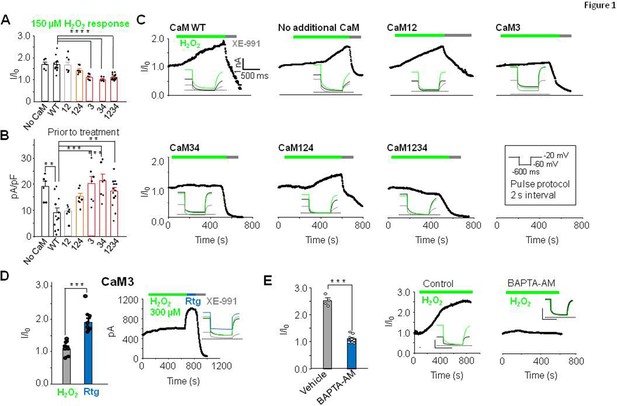
EF3 hand Ca2+ binding capacity of CaM is required for H2O2-mediated potentiation of KV7.4.
(A) Response of KV7.4 transfected HEK293 cells to 150 µM H2O2 (normalized steady-state current at –60 mV, I/I0) when transfected with wild-type CaM (CaMWT n=12), mutant CaMs lacking Ca2+ binding to one or more EF hands. The number in X-axis of panel B applies and pertains to the EF hand unable to bind Ca2+ (CaM12 n=7, CaM124 n=7, CaM3 n=7, CaM34 n=7, and CaM1234 n=13) or with no additional CaM transfected (No CaM, n=6). (B) Current density (pA/pF; –60 mV) of KV7.4 transfected cells prior to treatment with H2O2. (C) Representative currents at –60 mV in response to 150 µM H2O2 followed by 10 µM XE-991. Inset: representative current traces from each condition. (D) Comparative response of cells transfected with KV7.4 and CaM3 to 300 µM H2O2 and 10 µM retigabine (n=8). (E) Ca2+ dependence of H2O2 response in cells transfected with KV7.4 and CaMWT. Comparison of 300 µM H2O2 response in normal or low Ca2+ conditions induced by pre-incubation of cells in 10 µM BAPTA-AM for 30 min to chelate intracellular Ca2+. Control n=4, BAPTA-AM n=9. Data presented are mean ± SEM, statistical evaluation by independent measures ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, and ****p<0.0001 (A and B). A paired (D) or unpaired (E) two-tailed T test ***p<0.001 and ****p<0.0001.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
The current voltage relationship of cells transfected with mutant CaM does not differ significantly from CaMWT.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig1-data1-v2.xlsx
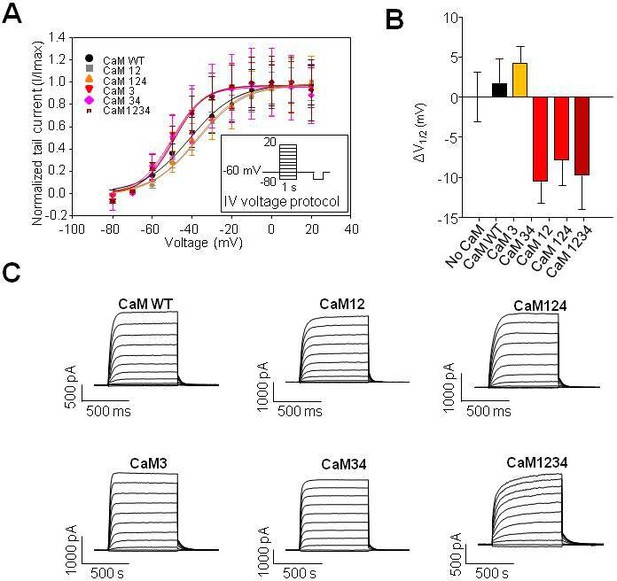
The current voltage relationship of cells transfected with mutant CaM does not differ significantly from CaMWT.
(A) Current voltage relationship of KV4 and CaM transfected cells prior to treatment with H2O2. IV calculated through measuring tail current normalized to the maximal current in each condition (I/Imax). (B) Change in voltage at which half maximal current is produced (ΔV1/2) compared to CaMWT. (C) Representative IV traces for each CaM condition. Data presented is mean ± SEM, statistical evaluation by independent measures ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc *p<0.05. CaMWT n=6, CaM12 n=9, CaM124 n=8, CaM3 n=9, CaM34 n=6, and CaM1234 n=6.
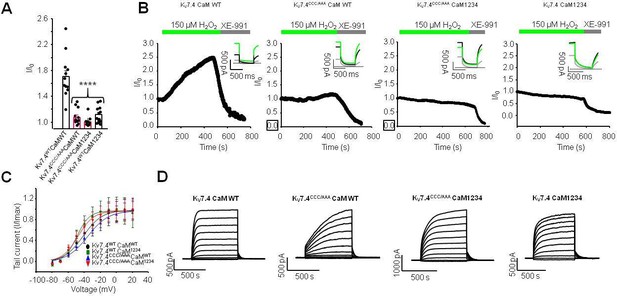
Further support for the link between H2O2, CaM, and the S2S3 linker in KV7 channels.
(A) Response of KV7.4 or KV7.4 triple cysteine to alanine mutant (KV7.4CCC/AAA) to 150 µM H2O2 when co-transfected with CaMWT or CaM1234. (B) Representative current trains at –60 mV in response to 150 µM H2O2 followed by 10 µM XE-991. Inset: representative current traces from each condition. (C) Current voltage relationship of KV7.4 or KV7.4CCC/AAA and CaMWT or CaM1234 transfected cells prior to treatment with H2O2. IV calculated through measuring tail current normalized to the maximal current in each condition (I/Imax). (D) Representative IV traces for each condition. Data presented are mean ± SEM, statistical evaluation by independent measures ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc ****p<0.0001.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Link between H2O2, CaM and the S2S3 linker in KV7 channels.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig1-figsupp2-data1-v2.xlsx
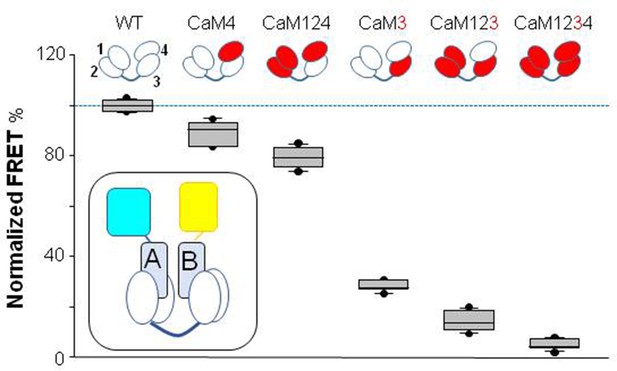
Influence of Ca2+-binding abolishing mutations in EF hands on Ca2+-dependent FRET changes.
Top: cartoon representation of CaM mutants. The EF-hands carrying a mutation that preclude Ca2+ binding are colored in red. Bottom: box-plot of the relative FRET index change produced by Ca2+ for the AB fork in complex with the indicated mutated CaM. Note that in the complex with CaM3 and CaM123, the changes prompted by 16 µM Ca2+ were almost obliterated, whereas in the complex with CaM124 the response was preserved. Each plot represents the average of six independent experiments. FRET index was defined as the ratio of the fluorescence peak between mcpVenus (yellow acceptor) and mTFP1 (blue donor). The index was normalized to the value obtained with WT CaM. Experiments were performed at 500 nM of hAB:CaM purified complex, in a 1:1 ratio. Inset: cartoon representing the FRET sensor in complex with CaM (mTFP1-hA-hB-Venus/CaM).
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Tabulated FRET values for each condition.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig2-data1-v2.xlsx
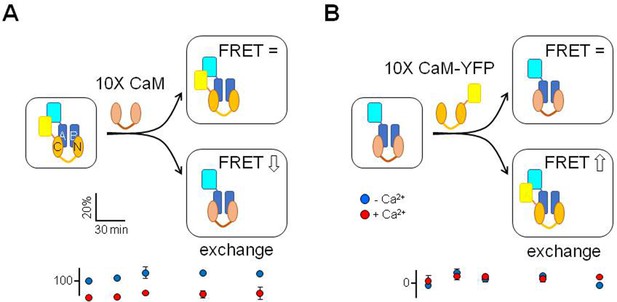
Residence of CaM in the calcium responsive domain (CRD) complex.
Top: cartoon representation of the assays. A blue fluorescent protein was attached to the AB fork. In one experiment (A), the tagged AB fork was complexed with CaM tagged with a yellow fluorescent protein. Subsequently, the complex was incubated with excess CaM, devoid of any tag (n=4). A reduction in FRET over time is expected if there was CaM exchange. In another experiment (B), the fork was complexed with CaM and mixed with excess CaM tagged with a yellow fluorescence protein (n=4). Increase in FRET is expected if CaM exchange takes place. Bottom: FRET values over time in the presence and absence of Ca2+.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Residence of CaM in the CRD complex.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig2-figsupp1-data1-v2.xlsx
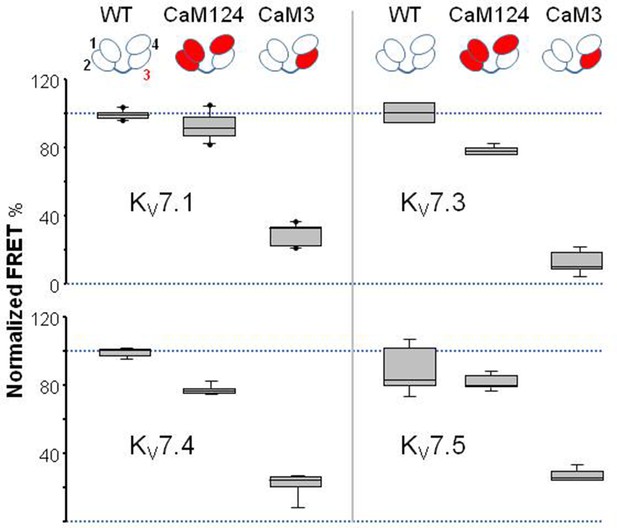
Box plot of the influence of Ca2+-binding abolishing mutations in EF hands on Ca2+-dependent FRET change on the indicated KV7 isoforms.
Each plot represents the average of at least six independent experiments.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Tabulated FRET values for each condition.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig2-figsupp2-data1-v2.xlsx
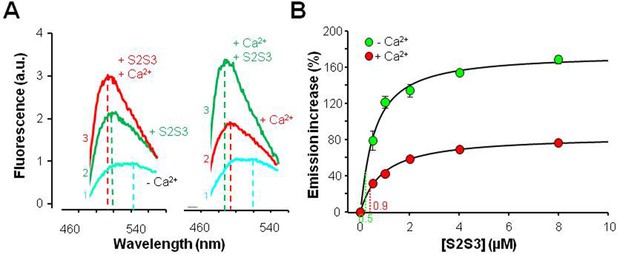
Effects of a 24 residues KV7 S2S3 peptide on fluorescence emission of dansylated calmodulin (D-CAM).
(A) Emission spectra of D-CaM (50 nM) in Ca2+-free conditions (cyan), and after subsequent sequential addition of the S2S3 peptide (16 µM, green), and Ca2+ (10 µM free concentration, red). The order of additions is indicated at the left of each trace. (B) Dose-dependent relative fluorescent emission increase as a function of S2S3 peptide concentration, in the absence (green) and the presence of Ca2+ (10 µM, red). For this purpose, the maximum fluorescence D-CaM emission was measured between 490 and 500 nm and normalized with respect to the reference value (D-CaM with no added Ca2+ [green] and D-CaM with 10 µM free Ca2+ [red]). A Hill equation was fitted to the data (continuous line) with EC50=0.88 ± 0.12 and 1.63±0.07 µM, in the absence and the presence of Ca2+, respectively. The KV7.1 S2S3 peptide sequence was Ac-RLWSAGCRSKYVGVWGRLRFARK-NH2.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Spectra data for the indicated conditions, and tabulated peak values.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx
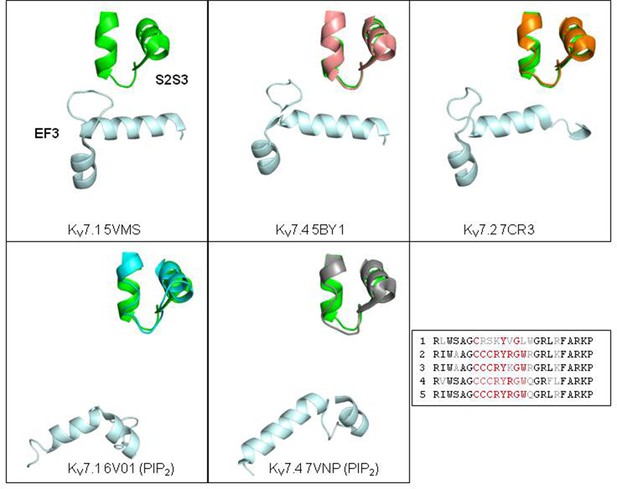
Relative disposition of calmodulin EF3 and S2S3 loop from different KV7 channel/CaM complexes solved by cryo-EM.
The PDB of each structure is indicated at the bottom of each panel. The 5VMS structure of KV7.1 suggests a potential interaction between the S2S3 loop and the EF3 hand, whereas this interaction is not apparent in cryo-EM images from other KV7 channels, or KV7.1 channels solved in the presence of PIP2 (PDB 6V01). The structure S2S3 of KV7.1 PDB 5VMS in green is superimposed in each figure. The main differences appear located at the distal region of the proximal helix of the S2S3 hairpin and the loop in the KV7.4 structure (PDB 7VNP), which was trapped in an open channel configuration thanks to the presence of PIP2, whereas it is remarkably similar in the structure of KV7.4 (PDB 5BY1) trapped in a close conformation. Inset: alignment of the S2S3 sequences.
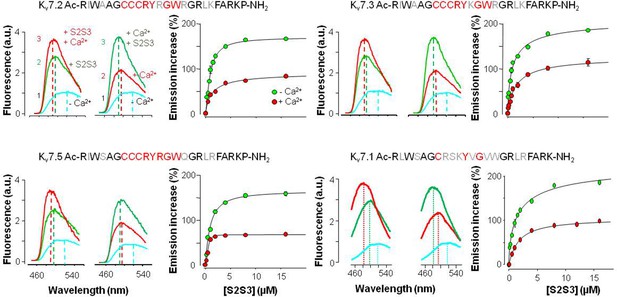
Effect of KV7 S2S3 peptides on fluorescence emission of dansylated calmodulin (D-CaM).
The residues forming the loop are highlighted in red in each peptide sequence. Emission spectra of D-CaM (50 nM) in Ca2+-free conditions (cyan), and after subsequent sequential addition of the S2S3 peptide (16 µM, green), and Ca2+ (10 µM free concentration, red). The order of additions is indicated at the left of each trace in the panel at the top left. A Hill equation was fitted to the emission increase data (continuous line) with EC50=0.89 ± 0.04 and 1.37±0.23 µM, (n=3) in the absence and presence of Ca2+, respectively for KV7.2 S2S3, 1.04±0.12 (n=3) and 1.78±0.34 µM for KV7.3 (n=3), 0.56±0.06 and 0.89±0.07 µM for KV7.4 (n=3), and 0.88±0.12 and 1.63±0.07 µM for KV7.1 (n=3).
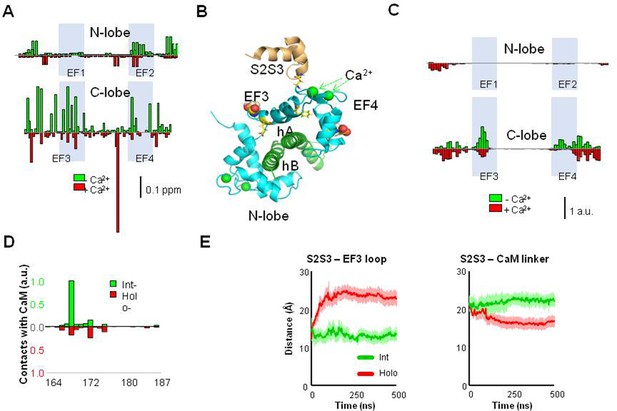
Interaction between the KV7 S2S3 peptide and CaM in complex with KV7.2 CDR.
(A) The chemical shift perturbation (CSP) analysis shows that the magnitude of local residue environmental alterations detected by NMR is larger in the C-lobe, both in the presence and in the absence of Ca2+. (B) Structural mapping of the main CSPs in the presence of Ca2+ over Ca2+-loaded KV7.2 CaM/CDR complex. The two resides with the larger displacements are represented as balls, whereas the remaining above three times the mean are represented as sticks. The structure of the S2S3 loop was derived from the Cryo-EM PDB 5VMS (Sun and MacKinnon, 2017) and placed according to structural alignment of the C-lobe of PDB 6FEH (Bernardo-Seisdedos et al., 2018). (C) Contact map derived from molecular dynamic (MD) simulations of the S2S3/CaM complex. Normalized CaM contacts with the S2S3 peptide residues (10 Å cut-off) for int- (green) and holo-systems (red; see Figure 5—figure supplement 1). Vertical calibration bar is in arbitrary units (a.u.). (D) S2S3 contact map with CaM residues (4 Å cut-off; see Figure 5—figure supplement 1). (E) Distance as a function of time between the mass centers of the EF3 loop (residues D93-G98) and (i) the S2S3 loop (residues R164-L173; left) or (ii) the linker connecting CaM lobes (residues R74-E84; right). Bars indicate SEM (n=6).
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Tabulated data values for NMR chemical shift perturbations.
Tabulated contact maps between calmodulin and Kv7.1 S2S3, and tabulated distance between S2S3 and EF3 mass centers.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig4-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 4—source data 2
NMR raw spectra of KV7.2/Calmodulin complex with and without calcium in presence of S2S3 peptide.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig4-data2-v2.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 3
Replica 1: Molecular dynamic trajectory of holo system, calcified calmodulin in presence of S2S3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig4-data3-v2.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 4
Replica 2: Molecular dynamic trajectory of holo system, calcified calmodulin in presence of S2S3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig4-data4-v2.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 5
Replica 3: Molecular dynamic trajectory of holo system, calcified calmodulin in presence of S2S3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig4-data5-v2.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 6
Replica 4: Molecular dynamic trajectory of holo system, calcified calmodulin in presence of S2S3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig4-data6-v2.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 7
Replica 5: Molecular dynamic trajectory of holo system, calcified calmodulin in presence of S2S3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig4-data7-v2.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 8
Replica 6: Molecular dynamic trajectory of holo system, calcified calmodulin in presence of S2S3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig4-data8-v2.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 9
Replica 6: Molecular dynamic trajectory of holo system, calcified calmodulin in presence of S2S3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig4-data9-v2.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 10
Replica 1: Molecular dynamic trajectory of int system, calcified N-lobe (no calcium C-lobe) of calmodulin in presence of S2S3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig4-data10-v2.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 11
Replica 2: Molecular dynamic trajectory of int system, calcified N-lobe (no calcium C-lobe) of calmodulin in presence of S2S3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig4-data11-v2.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 12
Replica 3: Molecular dynamic trajectory of int system, calcified N-lobe (no calcium C-lobe) of calmodulin in presence of S2S3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig4-data12-v2.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 13
Replica 4: Molecular dynamic trajectory of int system, calcified N-lobe (no calcium C-lobe) of calmodulin in presence of S2S3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig4-data13-v2.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 14
Replica 5: Molecular dynamic trajectory of int system, calcified N-lobe (no calcium C-lobe) of calmodulin in presence of S2S3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig4-data14-v2.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 15
Molecular dynamic trajectory of S2S3 peptide y solution.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig4-data15-v2.zip
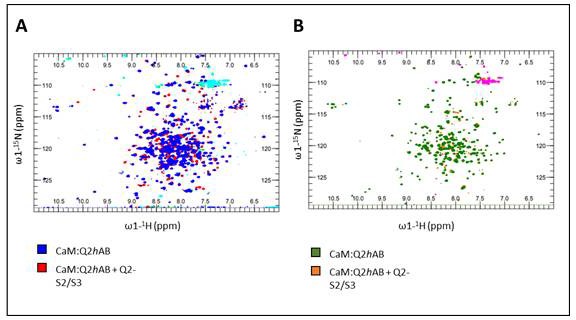
15N-HSQC of KV7.2 CDR:CaM titrated with unlabeled KV7.1-S2S3 in absence (left) and in presence of 1 mM Ca2+.
(A) 15N-HSQC of KV7.2 CDR:CaM complex at 75 µM (blue) and with KV7.1-S2S3 peptide at 1 mM (red). Signal overlap demonstrates that the structure of the complex was not altered in the presence of the peptide. (B) Green spectra corresponds to the complex KV7.2 CDR:CaM with 1 mM Ca2+, and orange to KV7.2 CDR:CaM 1 mM Ca2+ and 1 mM KV7.1-S2S3 peptide.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
HSQC of KV7.2 CDR:CaM titrated with unlabeled KV7.1-S2S3 in absence of 1 mM Ca2+.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v2.xlsx
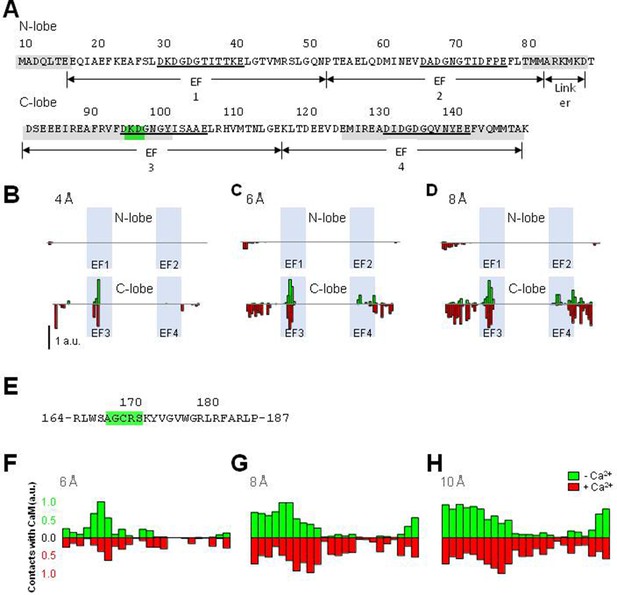
Contact maps derived from molecular dynamic (MD) simulations of the S2S3/CaM complex.
(A) CaM sequence highlighting the most relevant residues for the contacts with S2S3 peptide with a cut-off at 10 Å (in gray) and at 4 Å (in green). The EF loops are underlined. (B) Normalized CaM contacts between CaM and S2S3 peptide residues with cut-off at 4 Å, (C) 6 Å, and (D) 8 Å, for int- (green) and holo-systems (red). (E) S2S3 peptide sequence highlighting in green the most relevant residues for the contact with CaM with a cut-off at 4 Å. (F) Normalized S2S3 peptide contacts between CaM and S2S3 peptide residues with cut-off at 6 Å, (G) 8 Å, and (H) 10 Å.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 2—source data 1
HSQC of KV7.2 CDR:CaM titrated with unlabeled KV7.1-S2S3 in presence of 1 mM Ca2+.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig4-figsupp2-data1-v2.xlsx
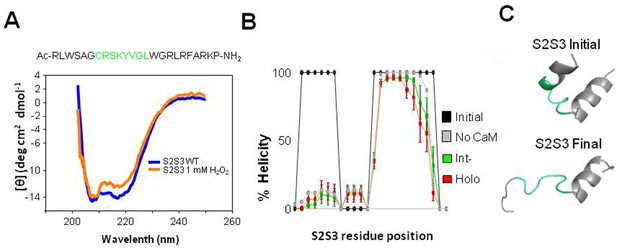
CD spectra of S2S3 peptide before and after treatment with H2O2.
(A) Circular Dichroism of the KV7.1 S2S3 peptide. The residues forming the loop are highlighted in green in the peptide sequence. CD (Circular Dichroism) spectra recorded at a fixed incubation time of the peptide (50 nM) in control (blue) and in presence of 1 m H2O2 (orange). Helicity (H) was 63.4%, S+T antiparallel β-sheet conformations was 16.2%, and U for disordered structures were estimated to be 21.1%. In the presence of 1 mM H2O2, H=63.6%, S+T = 15.3%, and U=21.8%. Spectrum is the average of 40 runs. (B). Percentage of the S2S3 helical character relative to the whole trajectory. Bars indicate SEM (n=6). Helical character of the initial S2S3 structure is shown in black. The peptide in solution (gray line) adopts a similar structure regardless of the presence or the absence of the CaM/KV7.2 complex. Both 310 and α-helices were combined to compute the degree of helicity. (C) Representative structures of the S2S3 peptide at initial (left) and final (right) times. Loop residues are shown in green.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 3—source data 1
Raw data for CD spectra of S2S3 peptide before and after treatment with H2O2, and tabulated values of percentage helicity vs position.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig4-figsupp3-data1-v2.xlsx
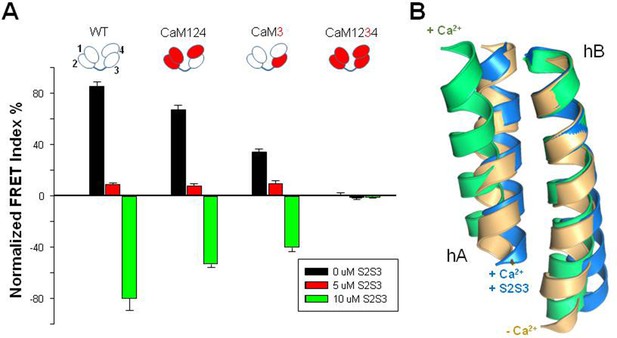
Relative FRET changes of the human KV7.2 in complex with mutant CaM.
(A) FRET change after Ca2+ addition (10 µM) in the presence of the indicated concentrations of the S2S3 peptide: control (black), 0 µM S2S3, 5 µM S2S3 (red), and 10 µM S2S3 (green) (n=4). (B) Superposition of helices A and B solved in the absence of Ca2+ (gold, PDB 6FEH, KV7.2), in the presence of Ca2+ (green, PDB 6FEG, KV7.2), and interacting with the S2S3 loop in the presence of Ca2+ (blue, PDB 5VMS, KV7.1).
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Tabulated FRET values for each condition.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig5-data1-v2.xlsx
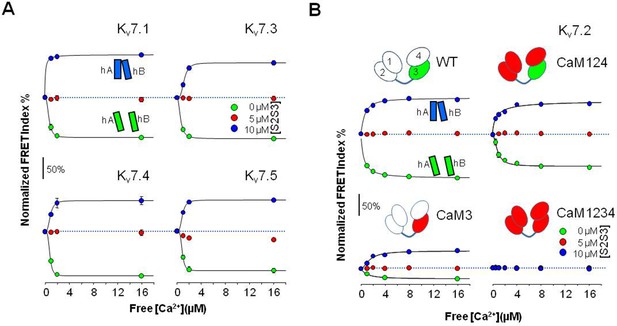
Relative FRET changes of KV7 CRD in complex with CaM.
(A) Relative FRET changes of KV7 calcium responsive domain (CRD) in complex with CaM. The concentration of peptide employed is indicated by the color of the symbol. Ca2+ dose-response in the presence of the indicated concentrations of the S2S3 peptide, normalized to the maximal response. FRET changes expanded from 100% reduction to 70% increase. Dotted lines mark no changes in FRET. The continuous lines are the result of the fit of a Hill equation, with EC50 values of 0.70±0.04 µM, 0.93±0.03 µM, 0.86±0.1, and 0.85±0.33 µM for KV7.1, KV7.3, KV7.4, and KV7.5, respectively, in the absence of S2S3. In the presence of 10 µM S2S3, the EC50 values were 1.06±0.2 µM, 1.17±0.6 µM, 0.94±0.6 µM, and 0.89±0.33 µM for KV7.1, KV7.3, KV7.4, and KV7.5, respectively. Each plot represents the average of four independent experiments. (B) Ca2+ dose-response in the presence of the indicated concentrations of S2S3 peptide, normalized to the maximal response. FRET changes expanded from 100% reduction to 70% increase. Dotted lines mark no changes in FRET. The CaM mutant forming part of each complex is indicated on top of the corresponding dose-response curve. The continuous lines are the result of the fit of a Hill equation, with EC50 values of 0.84±0.04 and 0.83±0.07 µM in the absence of S2S3 for WT and CaM124 (n=4), respectively. In the presence of 10 µM S2S3, the EC50 values were 0.62±0.91, 0.62±0.16, and 1.48±0.22 µM for WT, CaM124, and CaM3, respectively (n=4).
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Tabulated FRET values for each condition.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig5-figsupp1-data1-v2.xlsx
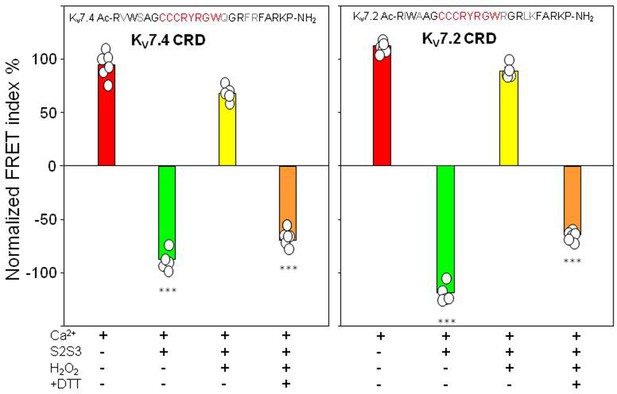
FRET efficiency changes prompted by oxidized and reduced S2S3 peptides.
Difference in FRET efficiency in the absence and the presence of Ca2+. Left, KV7.4-S2S3 peptide and KV7.4 CRD. Right, KV7.2-S2S3 peptide and KV7.2 CRD. Similar results were obtained with KV7.1-S2S3 peptide (Figure 6—figure supplement 2). Red, sensor alone. Green, in the presence of 10 µM peptide. Yellow, with 10 µM oxidized peptide. Orange, oxidized peptide treated with 1 mM DTT. Bars represent mean ± SEM FRET-efficiency. *p<0.05; ***p<0.001. Each plot represents the average of at least six independent experiments.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Tabulated FRET values for each condition.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig6-data1-v2.xlsx
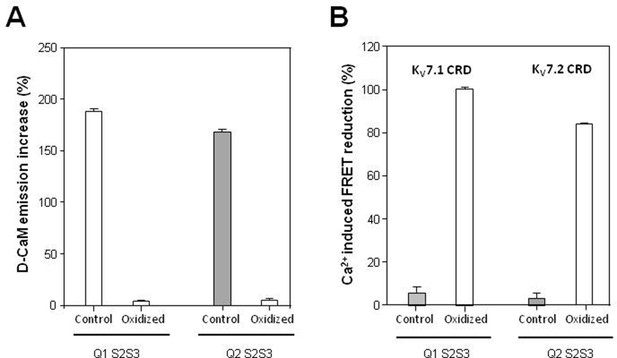
Fluorescent emission D-CaM enhancement caused by KV7.1 S2S3 and KV7.2 S2S3 peptides before and after oxidation.
(A) Fluorescent emission dansylated calmodulin (D-CaM) enhancement caused by KV7.1 S2S3 and KV7.2 S2S3 peptides before and after oxidation. (B). Normalized FRET changes produced by 8 µM Ca2+, in the presence of 5 µM KV7.1 S2S3 and KV7.2 S2S3 peptides in mTFP-Q1hAB-Venus/CaM and mTFP-Q2hAB-Venus complexes, respectively, before and after oxidation. Bars represent the means ± SEM from at least six independent experiments.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Tabulated fluoresce emission values for each condition.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig6-figsupp1-data1-v2.xlsx
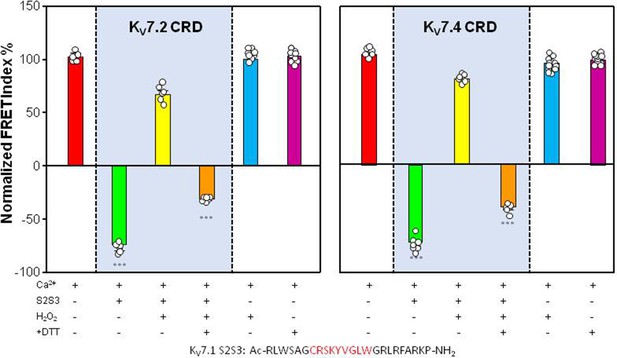
Percentage of FRET index changes prompted by oxidized and reduced S2S3 peptides.
(A) Percentage of FRET index changes prompted by oxidized and reduced S2S3 peptides. Difference in % FRET index in the absence and the presence of Ca2+ with sensors derived from the KV7.4 and KV7.2 CRD sequences. Red, sensor alone. Green, in the presence of 10 µM KV7.1-S2S3 peptide. Yellow, with 10 µM oxidized peptide. Orange, oxidized peptide treated with 1 mM DTT. Blue, KV7.x/CaM complex treated with 1 mM H2O2. Purple, KV7.x/CaM incubated with 1 mM DTT. Bars represent mean ± SEM FRET-efficiency. *p<0.05; ***p<0.001. Each plot represents the average of at least six independent experiments. Bottom: sequence of the KV7.1-peptide. The residues forming the loop are highlighted in red in the peptide sequence.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Tabulated FRET values for each condition.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-fig6-figsupp2-data1-v2.xlsx
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peptide, recombinant protein | KV7.1 S2S3 | Proteogenix | RLWSAGCRSKYVGVWGRLRFARKP | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | KV7.2 S2S3 | Proteogenix | RIWAAGCCCRYRGWRGRLKFARKP | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | KV7.3 S2S3 | Proteogenix | RIWAAGCCCRYRKGWRLFKFARKP | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | KV7.4 S2S3 | Proteogenix | RVWSAGCCCRYRGWQGRFRFARKP | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | KV7.5 S2S3 | Proteogenix | RIWSAGCCCRYRGWQGRLRFARKP | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | KV7.1 mtfp-hAB-Venus (residues I247-D456) in pPROEX HTc | This paper | NM_000218.2 | Plasmid, Fluorescence sensor |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | KV7.2 mtfp-hAB-Venus (residues I310-D549), in pPROEX HTc vector | This paper | NM_172107.3 | Plasmid, Fluorescence sensor |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | KV7.3 mtfp-hAB-Venus (residues I349-D556) in pPROEX HTc | This paper | NM_004519.3 | Plasmid, Fluorescence sensor |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | KV7.4 mtfp-hAB-Venus (residues I315-D539) in pPROEX HTc | This paper | NC_060925.1 | Plasmid, Fluorescence sensor |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | KV7.5 mtfp-hAB-Venus (residues I308-D527) in pPROEX HTc | This paper | NC_060930.1 | Plasmid, Fluorescence sensor |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | CaM in pOKD4 | Recombinant Human CALM2 in pOKD4 vector, GenScript | Genbank, NP_001292553.1 | Plasmid, Calmodulin, human CALM2 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | hKCNQ4-eYFPc | Gamper et al., 2006 | AF105202 | Plasmid,KCNQ4 bound to YFP |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | hKCNQ4CCC/AAA -eYFPc | Mutant AF105202; Gamper et al., 2006 | Plasmid, Mutant KCNQ4 bound to YFP | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | CaM 3 in pOKD4 | GenScript | Genbank, NP_001292553.2 | Plasmid, human CALM2, D93A mutation |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | CaM124 in pOKD4 | GenScript | Genbank, NP_001292553.3 | Plasmid, mutant human CALM2, D20A/D56A/D129A |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | CaM123 in pOKD4 | GenScript | Genbank, NP_001292553.4 | Plasmid, mutant human CALM2, D20A/D56A/D93A |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | CaM12 in pOKD4 | GenScript | Genbank, NP_001292553.5 | Plasmid, mutant human CALM2, D20A/D56A |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | CaM34 in pOKD4 | GenScript | Genbank, NP_001292553.6 | Plasmid, mutant human CALM2, D93A/D129A |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | CaM1234 in pOKD4 | GenScript | Genbank, NP_001292553.7 | Plasmid, mutant human CALM2, D20A/D56A/D93A/D129A |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | CaM WT in pCDNA3 | GenScript | Genbank, NP_001292553.8 | Plasmid, Calmodulin, human CALM2 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | CaM3 in pCDNA3 | GenScript | Genbank, NP_001292553.9 | Plasmid, human CALM2, D93A mutations |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | CaM34 in pCDNA3 | GenScript | Genbank, NP_001292553.10 | Plasmid, human CALM2, D93A/D129A mutations |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | CaM12 in pCDNA3 | GenScript | Genbank, NP_001292553.11 | Plasmid, human CALM2, D20A/D56A mutations |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | CaM124 in pCDNA3 | GenScript | Genbank, NP_001292553.12 | Plasmid, human CALM2, D20A/D56A/D129A mutations |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | CaM1234 in pCDNA3.1 | GenScript | Genbank, NP_001292553.13 | Plasmid, human CALM2, D20A/D56A/D93A/D129A mutations |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | KV7.4 in pCDNA3.1 | GenScript | Genbank, NP_001292553.14 | Plasmid, human KV7.4 channel |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | KV7.4CCC/AAA in pCDNA3.1 | Gamper et al., 2006 | Genbank, NP_001292553.15 | Plasmid, human KV7.4 channel, C156A, C157A, C158V |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | Kidney (normal epithelial, embryo) | ATCC | HEK293 | |
| Chemical compound and drug | 5-(Dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonyl chloride, DNSCl | SIGMA-ALDRICH | CAS Number: 605-65-2 | Dansyl chloride |
| Chemical compound and drug | Pierce DTT (ditiotreitol) | Thermo Scientific | CAT# 20290 | DTT |
| Chemical compound and drug | Hydrogen peroxide solution | SIGMA-ALDRICH | CAS Number = 7722-84-1 / Pubchem ID = 57654227 | H2O2 30% (w/w) in H2O, contains stabilizer |
| Chemical compound and drug | X2254 | SIGMA-ALDRICH | XE-991 | |
| Chemical compound and drug | ab145545 | Abcam | Retigabine | |
| Chemical compound and drug | E2311 | Promega | Fugene | |
| Software and algorithm | PyMOL | The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.3 Schrödinger, LLC. | Use for molecular dynamics and figure preparation | |
| Software and algorithm | Patchmaster V2 | HEKA Instruments | ||
| Software and algorithm | VMD | Humphrey et al., 1996 | Use for molecular dynamics and figure preparation | |
| Software and algorithm | NAMD | Phillips et al., 2020 | Use for molecular dynamics | |
Additional files
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-mdarchecklist1-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 1
S2S3 petides information.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-supp1-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Details of the molecular dynamics simulations.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81961/elife-81961-supp2-v2.docx






