Coordinated cadherin functions sculpt respiratory motor circuit connectivity
Figures
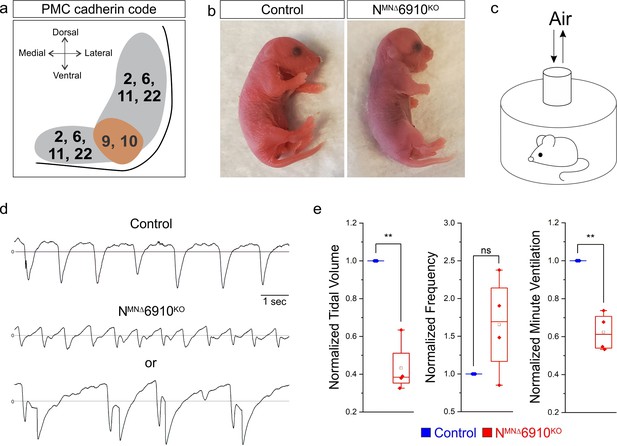
A combinatorial cadherin code establishes breathing and is required for life.
(a) A combinatorial cadherin code defines phrenic MNs during development. Reproduced from Figure 4c from Vagnozzi et al., 2020. The ventral lateral spinal cord at the level of the PMC (brown circle) is depicted (see also Figure 1—figure supplement 1a). (b) To determine the function of cadherins in respiratory motor circuits, we specifically inactivated a combination of type I and II cadherins in MNs- N-cadherin and Cadherins 6, 9, 10 (Cdh2flox/flox;Olig2Cre;Cdh6−/−;Cdh9−/−;Cdh10−/−, referred to as NMNΔ6910KO mice). NMNΔ6910KO mice are cyanotic, appear to gasp for breath, and die shortly after birth. (c) Experimental setup for whole body plethysmography experiments (see also Figure 1—figure supplement 2a). (d) Representative 10s traces in room air from control and NMNΔ6910KO mice at P0. NMNΔ6910KO mice either exhibit fast, shallow breathing (middle), or irregular gasping behavior (bottom). (e) NMNΔ6910KO mice display reduced tidal volume and increased variability in respiratory frequency, resulting in a 40% reduction in overall ventilation (n = 4 for each genotype). **p < 0.01, unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test.
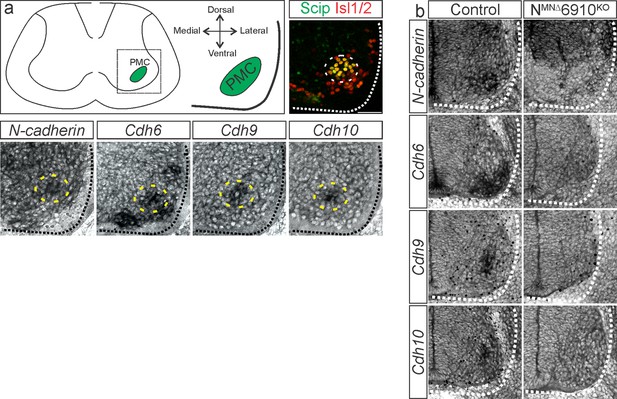
Validation of NMNΔ6910KO mice.
(a) N-cadherin, cdh6, 9, and 10 expression in phrenic motor neurons (MNs) at e13.5 (modified from Vagnozzi et al., 2020). The images shown are taken from the ventral lateral spinal cord at the level of the Phrenic Motor Column (PMC) (see schematic). Phrenic MNs are labeled by the co-expression of Scip and Isl1/2. (b) NMNΔ6910KO mice show loss of N-cadherin and cdh6, 9, and 10 expression in all MNs at e11.5. N-cadherin expression is maintained in non-MN populations. Scale bar = 50 µm.
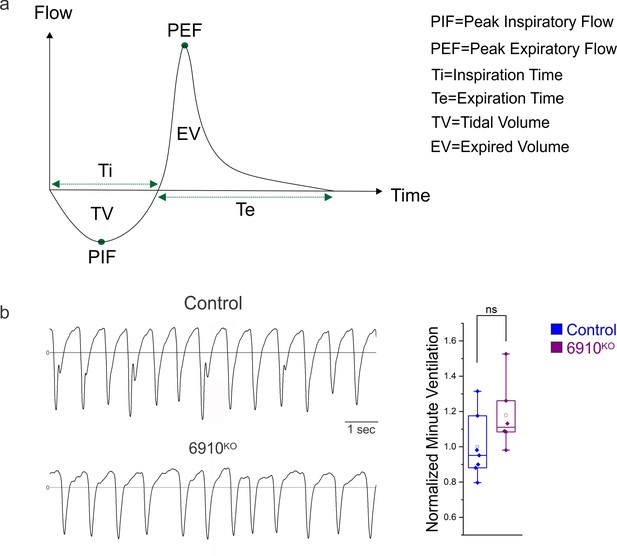
Normal breathing behaviors in 6910KO mice.
(a) Schematic of a representative breath and related respiratory parameters recorded by plethysmography (adapted from emka user manual). (b) 6910KO mice do not show changes in minute ventilation at P2 (n = 7 control, n = 6 6910KO mice).
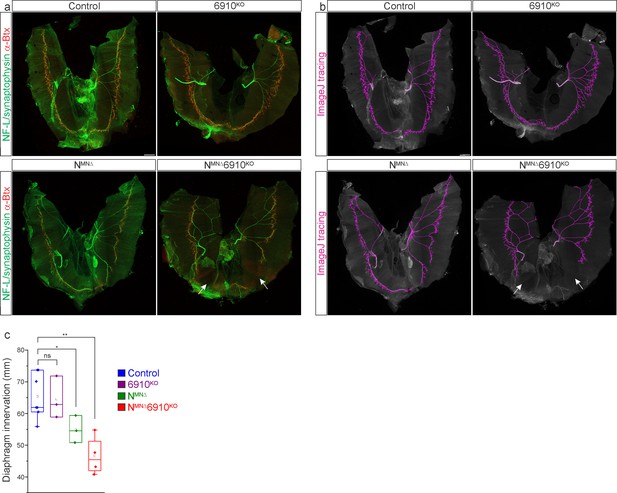
Cadherins N, 6, 9, and 10 control diaphragm innervation.
(a) Diaphragm innervation in control, 6910KO, NMNΔ, and NMNΔ6910KO mice. NMNΔ6910KO mice display a reduction in ventral diaphragm innervation (arrows) and arborization complexity at e18.5. Motor axons are labeled in green (combination of neurofilament light chain/synaptophysin) and neuromuscular junctions in red (α-bungarotoxin, btx). Scale bar = 500 µm. (b) Phrenic projections were traced and quantified in ImageJ. (c) Quantification of diaphragm innervation (n = 7 control, n = 3 6910KO, n = 3 NMNΔ, n = 4 NMNΔ6910KO mice). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test.
Respiratory insufficiency in NMNΔ6910KO mice.
NMNΔ6910KO mice appear cyanotic at birth and gasp for air before perishing shortly after birth.
Functional neuromuscular junctions (NMJs) in NMNΔ6910KO mice.
Stimulation of the phrenic nerve at e18.5/P0 in NMNΔ6910KO mice can elicit robust diaphragm contractions, demonstrating functional NMJs.
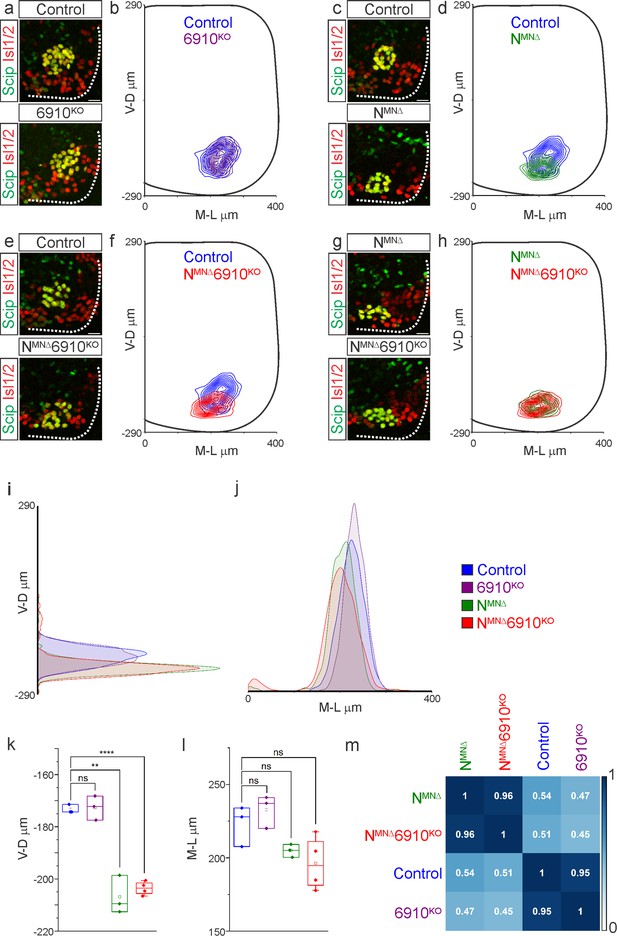
N-cadherin predominantly establishes phrenic motor neuron (MN) cell body position.
Analysis of cell body position reveals differential contributions of type I and II cadherins to phrenic motor topography. (a, c, e, g) Phrenic MN cell bodies (yellow, defined by the co-expression of the phrenic-specific TF Scip in green and the MN-specific TF Isl1/2 in red) are located at the same position in control and 6910KO mice, but show a similar ventral shift in both NMNΔ and NMNΔ6910KO mice at e13.5. Scale bar = 25 µm. (b, d, f, h) Contour density plot of cell body position in control, 6910KO, NMNΔ, and NMNΔ6910KO mice at e13.5. NMNΔ and NMNΔ6910KO mice display a similar ventral shift in phrenic MN position, suggesting that additional deletion of type II cadherins does not exacerbate positional changes caused by loss of N-cadherin. V-D µm: ventrodorsal position, M-L µm: mediolateral position. (0,0) represents the center of the spinal cord in both dimensions. Density plots of ventrodorsal (i) and mediolateral (j) cell body position in control, 6910KO, NMNΔ, and NMNΔ6910KO mice. Quantification of ventrodorsal (k) and mediolateral (l) position in control, 6910KO, NMNΔ and NMNΔ6910KO mice. Cell bodies in NMNΔ and NMNΔ6910KO mice display a statistically significant ventral shift. (m) Correlation analysis of phrenic MN positional coordinates in control, 6910KO, NMNΔ, and NMNΔ6910KO mice. 0 is no correlation, while 1 is a perfect correlation (n = 1442 control, n = 1422 6910KO, n = 1052 NMNΔ, and n = 1220 NMNΔ6910KO somas from n = 3 control, n = 3 6910KO, n = 3 NMNΔ, and n = 4 NMNΔ6910KO mice). **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001, unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test.
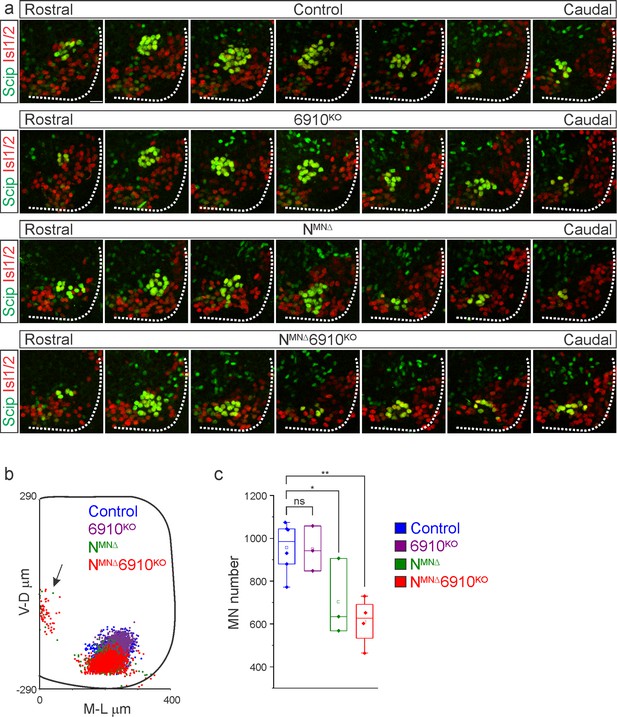
N-cadherin predominantly establishes phrenic motor neuron (MN) cell body position.
(a) Rostral to caudal distribution of e13.5 phrenic MN cell bodies (yellow, defined by the expression of Scip in green and Isl1/2 in red) in control, 6910KO, NMNΔ, and NMNΔ6910KO mice. While phrenic MN cell bodies in control and 6910KO mice gradually shift toward more ventral positions at caudal locations, they are located ventrally in NMNΔ and NMNΔ6910KO mice even at rostral levels. Scale bar = 25 µm. (b) Reconstructed distribution of cell bodies in control, 6910KO, NMNΔ, and NMNΔ6910KO mice. Occasional cell bodies in NMNΔ, and NMNΔ6910KO mice remain near the progenitor zone (arrow), while others seem to be dragged out of the spinal cord by their axon (n = 1442 control, n = 1422 6910KO, n = 1052 NMNΔ, and n = 1220 NMNΔ6910KO somas from n = 3 control, n = 3 6910KO, n = 3 NMNΔ, and n = 4 NMNΔ6910KO mice). (c) Quantification of phrenic MN number in control, 6910KO, NMNΔ, and NMNΔ6910KO mice. Both NMNΔ and NMNΔ6910KO mice show a reduction in MN number. Each point represents the sum of both left and right sides from the embryo (n = 6 control, n = 3 6910KO, n = 3 NMNΔ, and n = 4 NMNΔ6910KO mice). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test.
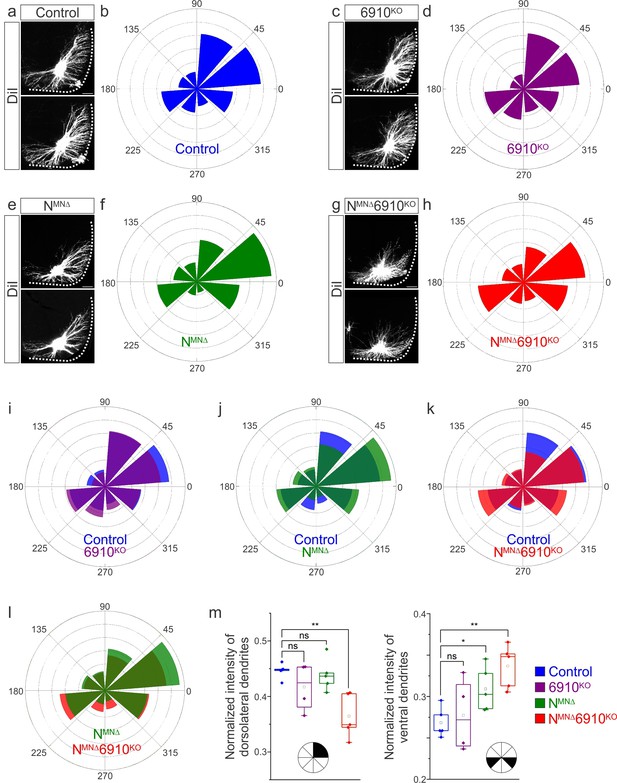
Cadherins N, 6, 9, and 10 dictate phrenic motor neuron (MN) dendritic orientation.
(a, c, e, g) DiI injections into the phrenic nerve in control, 6910KO, NMNΔ, and NMNΔ6910KO mice reveal phrenic MN dendrites, which extend in the dorsolateral and ventromedial directions in control mice. Phrenic MN dendrites do not change in 6910KO mice, but appear to not reach as far in the dorsolateral direction and to increase ventrally in NMNΔ mice. Strikingly, in NMNΔ6910KO mice, phrenic MN dendrites appear defasciculated, have reduced dorsolateral projections, and an increase in ventral projections. Scale bar = 100 µm. (b, d, f, h) Radial plot of the normalized fluorescent intensity in each octant in control, 6910KO, NMNΔ, and NMNΔ6910KO mice. Zero degrees represents a line through the center of the phrenic MN cell bodies that is perpendicular to the midline. Radial plot of the normalized fluorescent intensity in (i) control and 6910KO mice, (j) control and NMNΔ mice, (k) control and NMNΔ6910KO mice, and (l) NMNΔ and NMNΔ6910KO mice. (m) Quantification of the proportion of dendritic fluorescent intensity from 0 to 90 degrees (dorsolateral) and from 180 to 225 and 315 to 360 degrees (ventral, n = 5 control, n = 4 6910KO, n = 5 NMNΔ, and n = 5 NMNΔ6910KO mice). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test.
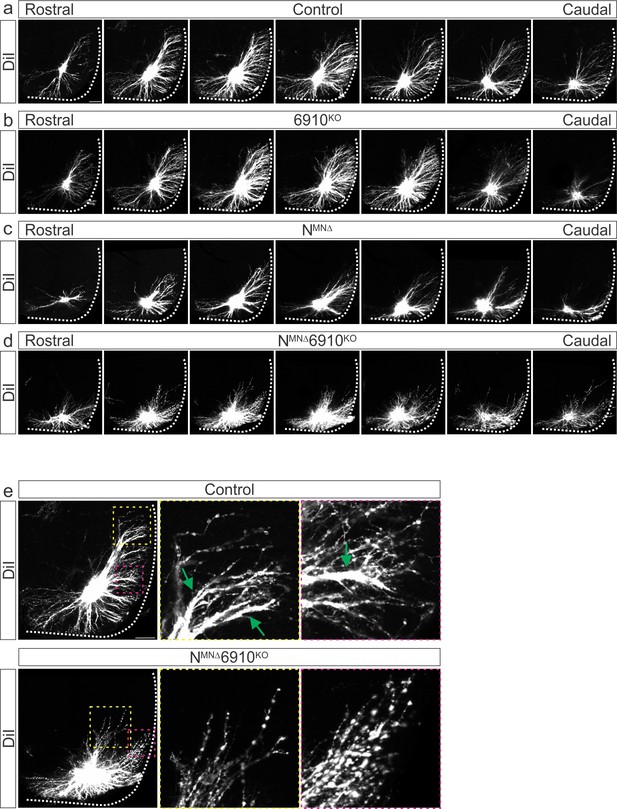
Phrenic motor neuron (MN) dendritic orientation requires cadherins N, 6, 9, and 10.
(a–d) Rostral to caudal extent of phrenic MN dendrites, as revealed by DiI injections into the phrenic nerve. In control and 6910KO mice, dendrites elaborate in dorsolateral to ventromedial directions, while NMNΔ dendrites show an increase in ventral projections. NMNΔ6910KO dendrites appear defasciculated, ventrally shifted, and with a severe reduction in dorsolateral projections. (e) Higher magnification images of dendrites show loss of dendritic fasciculation in NMNΔ6910KO mice. While control dendrites often bundle together (green arrows), NMNΔ6910KO dendrites do not. Scale bar = 100 µm.
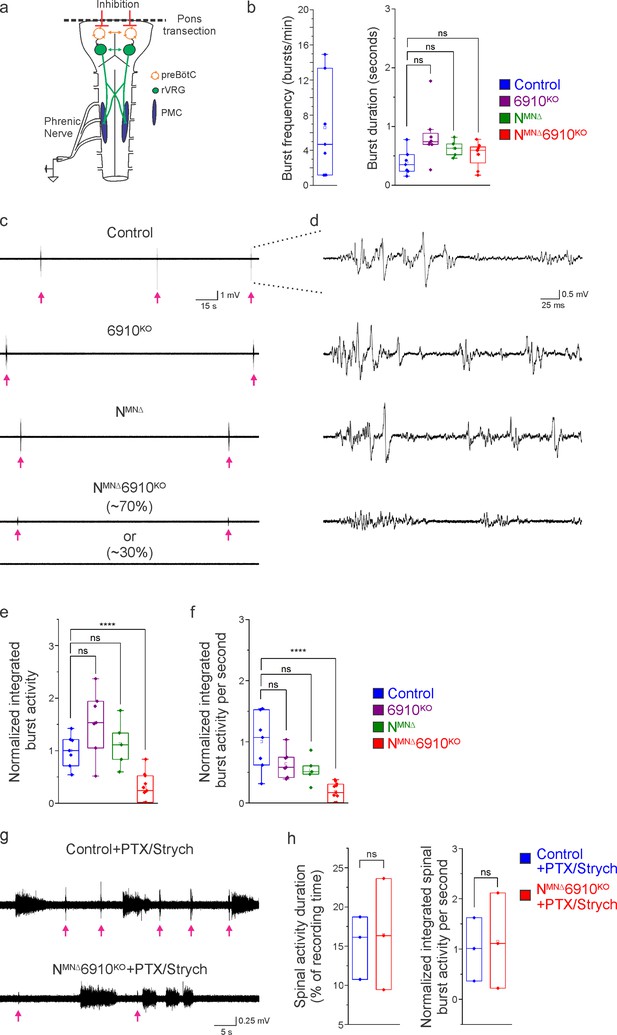
Coordinated type I and II cadherin signaling drives phrenic motor neuron (MN) activation.
(a) Schematic of brainstem–spinal cord preparation, which displays fictive inspiration after removal of the pons. Suction electrode recordings were taken from the phrenic nerve in the thoracic cavity at e18.5/P0. (b) Burst frequency is highly variable in control mice at e18.5/P0, as the respiratory rhythm has not yet stabilized, precluding meaningful analysis of respiratory frequency amongst different cadherin mutants. Burst duration is similar in all mice at e18.5/P0. (c) Three minute recordings from the phrenic nerve in control, 6910KO, NMNΔ, and NMNΔ6910KO mice. While 70% of NMNΔ6910KO mice display respiratory bursts, 30% show no bursts throughout the recording period. Respiratory bursts are indicated with magenta arrows. (d) Enlargement of single respiratory bursts reveals a reduction in burst amplitude and overall activity in NMNΔ6910KO mice. Partial (initial 350 ms) bursts are shown. (e, f) NMNΔ6910KO mice exhibit nearly 70% reduction in normalized integrated burst activity and normalized integrated burst activity over time; see Materials and methods for more information about quantification (n = 7 control, n = 7 6910KO, n = 5 NMNΔ, n = 11 NMNΔ6910KO mice). (g) Recordings from control and NMNΔ6910KO mice after disinhibition of the brainstem–spinal cord preparation with picrotoxin and strychnine at e18.5/P0. Disinhibition reveals the existence of latent spinal network activity, which is distinct from respiratory bursts (indicated with magenta arrows) and exhibits longer duration. (h) Control and NMNΔ6910KO mice display similar spinal network activity duration and normalized integrated activity over time, suggesting that phrenic MNs are normally integrated into propriospinal circuits and, despite the reduction in respiratory activity, can be robustly activated by other inputs in NMNΔ6910KO mice. ****p < 0.0001, unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test.
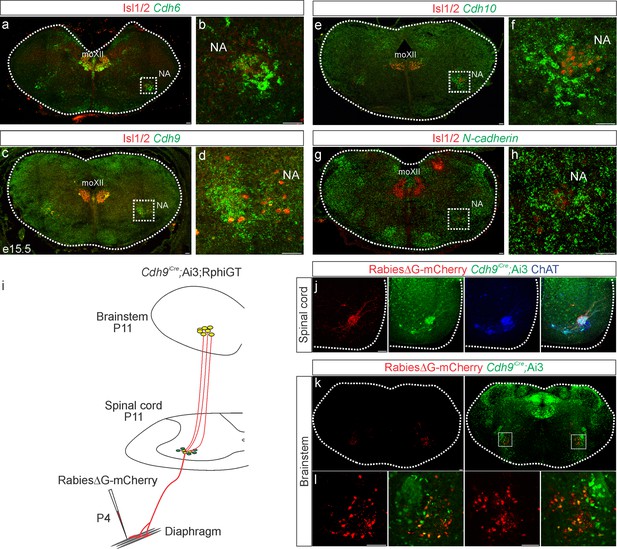
Cadherin expression defines the core motor respiratory circuit.
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) showing expression of Cdh6 (green, a, b), Cdh9 (green, c, d), Cdh10 (green, e, f), and N-cadherin (green, g, h) in the brainstem, at the putative location of the rostral Ventral Respiratory Group (rVRG), the main source of synaptic input to phrenic motor neurons (MNs). The location of the rVRG is inferred based on its relationship to motor nuclei at the same rostrocaudal level of the brainstem, the nucleus ambiguous (NA) and the hypoglossal motor nucleus (moXII), which are labeled by the MN-specific transcription factor (TF) Isl1/2 (red, a–h). b, d, f, and h are the enlarged regions outlined in the boxes in a, c, e, and g, respectively. Scale bar = 50 µm. (i) Strategy for tracing respiratory motor circuits in neonatal (P4) mice. RabiesΔG-mCherry is injected into the diaphragm of Cdh9iCre;Ai3;RphiGT mice. Ai3 labels Cdh9iCre expressing cells in green and RphiGT allows for Cre-dependent G protein expression and transsynaptic labeling. (j) Cdh9iCre-induced recombination in phrenic MNs, demonstrated by Cre-dependent YFP expression (green). All MNs are labeled by Choline Acetyltransferase (ChAT) expression (blue). RabiesΔG-mCherry injection into the diaphragm exclusively infects phrenic MNs (red). Scale bar = 100 µm. (k, l) RabiesΔG-mCherry injection into the diaphragm of Cdh9iCre;Ai3;RphiGT mice results in transsynaptic labeling of rVRG neurons (red). 80% of rVRG neurons are cdh9+ (green, n = 136/195 and 301/335 mCherry + neurons from two mice), demonstrating that a complementary cadherin code defines the core respiratory motor circuit. Scale bar = 100 µm.
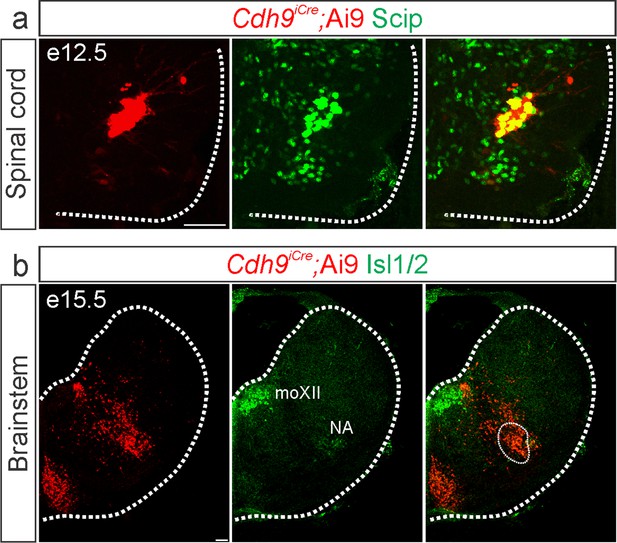
Validation of Cdh9iCre mice.
Cre-dependent fluorescent reporter expression (Ai9-Tdtomato, red) in Cdh9iCre mice labels phrenic motor neurons (MNs) at e12.5 (a, identified by Scip expression in green) and the putative rostral Ventral Respiratory Group (rVRG) at e15.5 (b, circled). The location of the rVRG is inferred based on its relationship to motor nuclei at the same rostrocaudal level of the brainstem, the nucleus ambiguous (NA) and the hypoglossal motor nucleus (moXII), which are labeled by the MN-specific transcription factor (TF) Isl1/2, green (b). Scale bar = 50 µm.
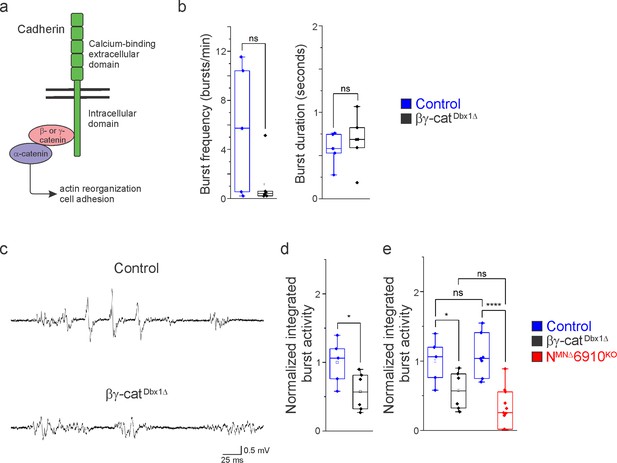
Cadherin signaling is required in Dbx1-derived neurons for robust respiratory output.
(a) B- and γ-catenin are obligate intracellular factors required for cadherin-mediated cell adhesive function. We utilized inactivation of β- and γ-catenin in Dbx1-derived interneurons (Ctnnb1flox/flox;Jupflox/flox;Dbx1Cre, referred to as βγ-catDbx1∆ mice) as a strategy to define the function of cadherins in premotor respiratory populations. (b) Bγ-catDbx1∆ mice do not show changes in burst frequency and duration. (c) Suction electrode recordings from the phrenic nerve at e18.5/P0 in control and βγ-catDbx1∆ mice. Enlargement of a single respiratory burst reveals a reduction in burst amplitude and overall activity in βγ-catDbx1∆ mice. (d) βγ-catDbx1∆ mice exhibit a 50% reduction in burst activity; see Materials and methods for more information about quantification. (e) NMNΔ6910KO mice and βγ-catDbx1∆ mice display a similar reduction in burst activity (n = 12 control, n = 6 βγ-catDbx1∆, n = 11 NMNΔ6910KO mice; data are normalized to the control for βγ-catDbx1∆ experiments), suggesting that cadherin function is required in both motor neurons (MNs) and Dbx1-derived interneurons for robust respiratory output. *p < 0.05, ****p < 0.0001, unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test.
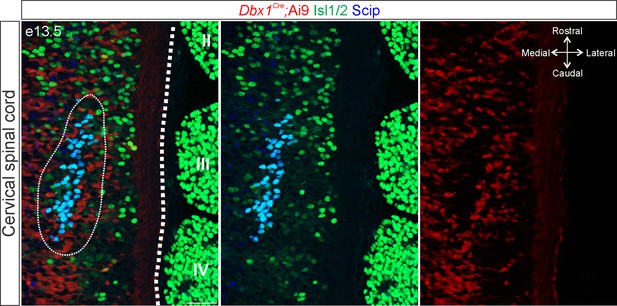
Dbx1-mediated recombination does not target phrenic motor neurons (MNs).
Cre-dependent fluorescent reporter expression (Ai9-Tdtomato, red) in Dbx1Cre mice does not label phrenic MNs (circled) at e13.5 (identified by Isl1/2 and Scip expression in green and blue, respectively). A longitudinal section of the spinal cord is shown, spanning the location of dorsal root ganglia (DRG) II–IV. Scale bar = 50 µm.
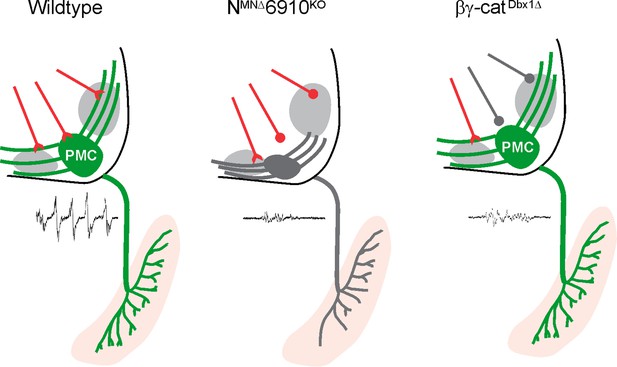
Coordinated cadherin functions dictate respiratory motor output.
In control animals, phrenic motor neurons (MNs) form a cluster in the cervical, ventral spinal cord and project their dendrites in a stereotypical ventromedial and dorsolateral orientation. This Phrenic Motor Column (PMC) topography is dictated by a combinatorial cadherin code during development. In the absence of cadherins N, 6, 9, and 10, phrenic MN topography is eroded, likely resulting in the selective loss of excitatory inputs and a reduction in respiratory motor output. Inactivation of cadherin signaling in Dbx1-derived neurons, which provide the major input to phrenic MNs, also results in a reduction of phrenic MN output, demonstrating that cadherins are required in both populations for robust activation of phrenic MNs.





