Smoking, alcohol consumption, and 24 gastrointestinal diseases: Mendelian randomization analysis
Figures
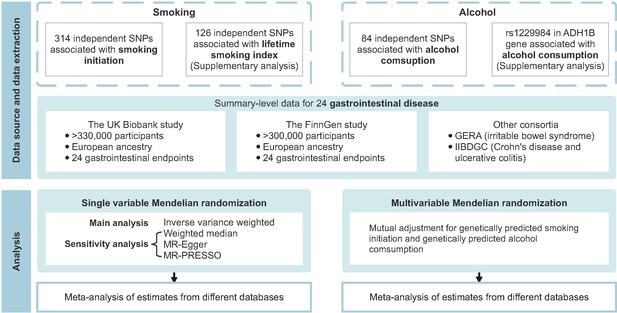
Overview of the present study design.
GERA, Genetic Epidemiology Research on Aging; IIBDGC, the International Inflammatory Bowel Disease Genetics Consortium; MR, Mendelian randomization; MR-PRESSO, Mendelian randomization pleiotropy residual sum and outlier; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism.
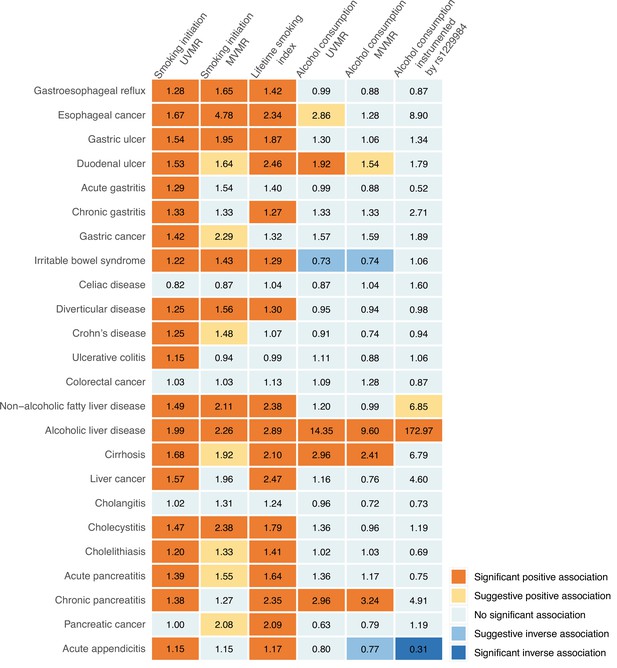
Summary of associations of genetically predicted smoking initiation, lifetime smoking, and alcohol consumption with 24 gastrointestinal diseases.
UVMR, univariable Mendelian randomization; MVMR, multivariable Mendelian randomization. The numbers in the box are the odds ratios for associations of exposure for gastrointestinal diseases. The association with a p-value <0.05 but Benjamini-Hochberg adjusted p-value >0.05 was regarded suggestive, and the association with a Benjamini-Hochberg adjusted p-value <0.05 was deemed significant.
Tables
Associations of genetic predisposition to smoking initiation with 24 gastrointestinal diseases in univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization analyses.
| Disease | Total cases | Total controls | UVMR | MVMR adjusted for alcohol consumption | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p Value | I2 (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | p Value | |||||
| Upper gastrointestinal diseases | Gastroesophageal reflux | 34,135 | 634,629 | 1.28 (1.20, 1.37) | 4.09 × 10-14* | 46.24 | 1.65 (1.35, 2.02) | 1.38 × 10-6* | |
| Esophageal cancer | 1130 | 702,116 | 1.67 (1.24, 2.25) | 6.84 × 10-4* | 22.68 | 4.78 (2.10, 10.90) | 1.97 × 10-4* | ||
| Gastric ulcer | 8651 | 666,879 | 1.54 (1.37, 1.72) | 3.83 × 10-14* | 44.96 | 1.95 (1.40, 2.71) | 7.31 × 10-5* | ||
| Duodenal ulcer | 5713 | 666,879 | 1.53 (1.34, 1.75) | 8.47 × 10-10* | 0.00 | 1.64 (1.07, 2.52) | 0.024 | ||
| Acute gastritis | 3048 | 643,478 | 1.29 (1.09, 1.53) | 0.003* | 0.00 | 1.54 (0.91, 2.62) | 0.106 | ||
| Chronic gastritis | 7975 | 643,478 | 1.33 (1.18, 1.49) | 1.55 × 10-6* | 77.04 | 1.33 (0.96, 1.86) | 0.091 | ||
| Gastric cancer | 1608 | 701,472 | 1.42 (1.13, 1.79) | 0.003* | 0.00 | 2.29 (1.14, 4.59) | 0.020 | ||
| Lower gastrointestinal diseases | Irritable bowel disease | 15,718 | 641,489 | 1.22 (1.12, 1.32) | 3.50 × 10-6* | 11.84 | 1.43 (1.10, 1.85) | 0.008* | |
| Celiac disease | 4808 | 631,700 | 0.82 (0.66, 1.02) | 0.071 | 0.00 | 0.87 (0.53, 1.43) | 0.590 | ||
| Diverticular disease | 50,065 | 587,969 | 1.25 (1.18, 1.33) | 5.23 × 10-14* | 67.29 | 1.56 (1.30, 1.87) | 1.41 × 10-6* | ||
| Crohn’s disease | 10,846 | 645,718 | 1.25 (1.11, 1.40) | 3.03 × 10-4* | 0.00 | 1.48 (1.01, 2.16) | 0.042 | ||
| Ulcerative colitis | 16,770 | 651,255 | 1.15 (1.04, 1.26) | 0.004* | 0.00 | 0.94 (0.71, 1.25) | 0.677 | ||
| Colorectal cancer | 9519 | 686,953 | 1.03 (0.92, 1.14) | 0.632 | 29.94 | 1.03 (0.76, 1.39) | 0.841 | ||
| Hepatobiliary and pancreatic diseases | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | 3242 | 707,631 | 1.49 (1.26, 1.76) | 3.82 × 10-6* | 0.00 | 2.11 (1.15, 3.88) | 0.016* | |
| Alcoholic liver disease | 2955 | 680,369 | 1.99 (1.65, 2.41) | 1.49 × 10-12* | 92.68 | 2.26 (1.26, 4.03) | 0.006 | ||
| Cirrhosis | 5904 | 706,200 | 1.68 (1.40, 2.02) | 3.39 × 10-8* | 0.00 | 1.92 (1.06, 3.47) | 0.032 | ||
| Liver cancer | 714 | 702,008 | 1.57 (1.13, 2.17) | 0.007* | 0.00 | 1.96 (0.73, 5.25) | 0.183 | ||
| Cholangitis | 1708 | 664,749 | 1.02 (0.80, 1.29) | 0.892 | 0.00 | 1.31 (0.61, 2.84) | 0.489 | ||
| Cholecystitis | 5893 | 664,749 | 1.47 (1.29, 1.68) | 4.71 × 10-9* | 84.72 | 2.38 (1.57, 3.60) | 4.14 × 10-5* | ||
| Cholelithiasis | 42,510 | 664,749 | 1.20 (1.13, 1.27) | 5.75 × 10-9* | 0.00 | 1.33 (1.02, 1.73) | 0.035 | ||
| Acute pancreatitis | 6634 | 679,713 | 1.39 (1.23, 1.56) | 6.71 × 10–8* | 79.71 | 1.55 (1.04, 2.31) | 0.031 | ||
| Chronic pancreatitis | 3173 | 679,713 | 1.38 (1.17, 1.64) | 1.79 × 10–4* | 0.00 | 1.27 (0.74, 2.16) | 0.384 | ||
| Pancreatic cancer | 1643 | 701,472 | 1.00 (0.79, 1.26) | 0.999 | 67.21 | 2.08 (1.06, 4.10) | 0.034 | ||
| Other | Acute appendicitis | 25,361 | 690,149 | 1.15 (1.08, 1.23) | 1.27 × 10–5* | 0.00 | 1.15 (0.92, 1.44) | 0.221 | |
-
*
Significant association after multiple testing.
-
UVMR, univariable Mendelian randomization; MVMR, multivariable Mendelian randomization; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval. *Significant association after multiple testing.
Associations of genetically predicted alcohol consumption with 24 gastrointestinal diseases in univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization analyses.
| Disease | Total cases | Total controls | UVMR | MVMR adjusted for smoking initiation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p Value | I2 (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | p Value | |||||
| Upper gastrointestinal diseases | Gastroesophageal reflux | 34,135 | 634,629 | 0.99 (0.81, 1.21) | 0.893 | 46.24 | 0.88 (0.72, 1.08) | 0.219 | |
| Esophageal cancer | 1130 | 702,116 | 2.86 (1.18, 6.91) | 0.020 | 22.68 | 1.28 (0.59, 2.82) | 0.533 | ||
| Gastric ulcer | 8651 | 666,879 | 1.30 (0.95, 1.77) | 0.098 | 44.96 | 1.06 (0.77, 1.47) | 0.721 | ||
| Duodenal ulcer | 5713 | 666,879 | 1.92 (1.23, 3.00) | 0.004* | 0.00 | 1.54 (1.01, 2.34) | 0.045 | ||
| Acute gastritis | 3048 | 643,478 | 0.99 (0.58, 1.69) | 0.960 | 0.00 | 0.88 (0.52, 1.48) | 0.621 | ||
| Chronic gastritis | 7975 | 643,478 | 1.33 (0.90, 1.95) | 0.147 | 77.04 | 1.33 (0.93, 1.89) | 0.115 | ||
| Gastric cancer | 1608 | 701,472 | 1.57 (0.75, 3.30) | 0.233 | 0.00 | 1.59 (0.79, 3.21) | 0.194 | ||
| Lower gastrointestinal diseases | Irritable bowel disease | 15,718 | 641,489 | 0.73 (0.57, 0.93) | 0.012 | 11.84 | 0.74 (0.57, 0.97) | 0.027 | |
| Celiac disease | 4808 | 631,700 | 0.69 (0.44, 1.07) | 0.097 | 0.00 | 1.04 (0.64, 1.68) | 0.887 | ||
| Diverticular disease | 50,065 | 587,969 | 0.95 (0.79, 1.13) | 0.553 | 67.29 | 0.94 (0.79, 1.13) | 0.527 | ||
| Crohn’s disease | 10,846 | 645,718 | 0.91 (0.62, 1.32) | 0.613 | 0.00 | 0.74 (0.53, 1.05) | 0.088 | ||
| Ulcerative colitis | 16,770 | 651,255 | 1.11 (0.82, 1.50) | 0.509 | 0.00 | 0.88 (0.67, 1.15) | 0.358 | ||
| Colorectal cancer | 9519 | 686,953 | 1.09 (0.76, 1.55) | 0.649 | 29.94 | 1.28 (0.95, 1.72) | 0.098 | ||
| Hepatobiliary and pancreatic diseases | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | 3242 | 707,631 | 1.20 (0.63, 2.28) | 0.574 | 0.00 | 0.99 (0.54, 1.79) | 0.962 | |
| Alcoholic liver disease | 2955 | 680,369 | 14.35 (7.69, 26.81) | 6.32 × 10-17* | 92.68 | 9.60 (5.28, 17.46) | 1.25 × 10-13* | ||
| Cirrhosis | 5904 | 706,200 | 2.96 (1.50, 5.85) | 0.002* | 0.00 | 2.41 (1.29, 4.52) | 0.006* | ||
| Liver cancer | 714 | 702,008 | 1.16 (0.43, 3.11) | 0.775 | 0.00 | 0.76 (0.29, 2.02) | 0.585 | ||
| Cholangitis | 1708 | 664,749 | 0.96 (0.44, 2.08) | 0.912 | 0.00 | 0.72 (0.33, 1.55) | 0.397 | ||
| Cholecystitis | 5893 | 664,749 | 1.36 (0.91, 2.03) | 0.132 | 84.72 | 0.96 (0.64, 1.45) | 0.862 | ||
| Cholelithiasis | 42,510 | 664,749 | 1.02 (0.75, 1.39) | 0.878 | 0.00 | 1.03 (0.79, 1.35) | 0.801 | ||
| Acute pancreatitis | 6634 | 679,713 | 1.36 (0.91, 2.03) | 0.128 | 79.71 | 1.17 (0.78, 1.75) | 0.456 | ||
| Chronic pancreatitis | 3173 | 679,713 | 2.96 (1.80, 4.89) | 2.13 × 10-5* | 0.00 | 3.24 (1.86, 5.64) | 3.18 × 10-5** | ||
| Pancreatic cancer | 1643 | 701,472 | 0.63 (0.32, 1.26) | 0.193 | 67.21 | 0.79 (0.40, 1.56) | 0.496 | ||
| Other | Acute appendicitis | 25,361 | 690,149 | 0.80 (0.63, 1.01) | 0.063 | 0.00 | 0.77 (0.61, 0.97) | 0.024 | |
-
*
Significant association after multiple testing.
-
UVMR, univariable Mendelian randomization; MVMR, multivariable Mendelian randomization; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
Additional files
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/84051/elife-84051-mdarchecklist1-v2.pdf
-
Supplementary file 1
Supplementary material.
(A) Information of included studies and consortia. (B) Definition of gastrointestinal diseases in UK Biobank and FinnGen. (C) Single nucleotide polymorphisms used as instrumental variables for smoking and alcohol consumption. (D) Power estimation of this Mendelian randomization analysis. (E) False discovery rate adjusted p values for all tested association. (F) Association of genetically-predicted smoke initiation with gastrointestinal disease in univaribale mendelian randomization. (G) Association of genetically-predicted smoking initiation (excluding 23andMe and UK Biobank), alcohol consumption (excluding 23andMe and UK Biobank) and lifetime smoking index with gastrointestinal disease in univariable mendelian randomization. (H) Association of genetically-predicted smoke initiation and alcohol consumption with gastrointestinal disease in multivaribale mendelian randomization. (I) Association of genetically-predicted alcohol consumption with gastrointestinal disease in univariable mendelian randomization. (J) Association of genetically-predicted alcohol consumption instrumented by rs1229984 in ADH1B with gastrointestinal diseases. (K) Evidence of causal association of smoking and drinking with 24 gastrointestinal diseases in the current study. (L) Association of genetically-predicted smoking initiation (excluding 23andMe and UK Biobank) with 24 gastrointestinal diseases. (M) Associations of genetically-predicted lifetime smoking with 24 gastrointestinal diseases. (N) Association of genetically-predicted alcohol consumption (excluding 23andMe and UK Biobank) with 24 gastrointestinal diseases.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/84051/elife-84051-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
Reporting standard 1
STROBE-MR checklist for current Mendelian randomization study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/84051/elife-84051-repstand1-v2.pdf





